Abstract
Groundwater is the main source of water for both domestic and agricultural use in arid regions. This study assessed the hydrogeochemical characteristics and suitability of groundwater for drinking and irrigation in Kenya’s Ewaso Ng’iro–Lagh Dera Basin. A total of 129 borehole groundwater samples were collected and analyzed for pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total hardness, and major ions. The groundwater was found to be mostly neutral to slightly alkaline and ranged from marginal to brackish in salinity. The dominant water type is Na-HCO3, with the ionic order Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+ and HCO3− > Cl− > SO42− > NO3−. Mineral saturation indices indicate that the water is undersaturated with gypsum and anhydrite but is saturated with calcite, dolomite, and aragonite. Groundwater chemistry is primarily influenced by ion exchange, the mixing of fresh and paleo-saline water, and rock weathering processes. The water quality index (WQI) reveals that 80.5% of groundwater is suitable for drinking. The rest have high levels of sodium, EC, and bicarbonate. Thus, they are not suitable. The irrigation water quality index (IWQI) places most samples in the moderate-to-severe restriction category due to high salinity and sodicity. These findings highlight the importance of properly treating groundwater before use.
1. Introduction
Water is one of the vital resources for human survival in this world. Approximately 97.5% of the global water is saline/saltwater, while the remaining 2.5% comprises freshwater, of which 30% of these global freshwater resources are groundwater [1]. In arid regions, groundwater is the main water source for domestic, agricultural, and industrial purposes.
Numerous global studies highlight the critical role of understanding hydrogeochemistry in assessing groundwater quality [2,3,4,5,6]. The chemistry of groundwater is generally diverse [7]. However, groundwater quality has been observed to range from brackish to saline in most arid areas [2,8]. Therefore, assessing hydrogeochemistry to understand the suitability of groundwater in arid regions is very important [9,10].
Generally, as groundwater flows from recharge to discharge areas, it chemically evolves as it interacts with aquifer materials or mixes with different groundwater bodies along the flow path [11]. This chemical evolution is driven by processes such as dissolution, ion exchange, evaporation, and saline water intrusion [6,11,12]. Additionally, the type of groundwater flow—whether local, intermediate, or regional—can influence the hydrogeochemical signature by affecting the reaction kinetics during water–rock interactions. The concentration and distribution of major ions may serve as indicators of flow regimes and can aid in understanding aquifer dynamics [13,14]. The interaction of rocks with groundwater leads to the saturation of various mineral species at equilibrium conditions. Changes in the saturation states are helpful in the identification of the different geochemical reactions that control the groundwater and decipher the various stages of the hydrochemical evolution of the groundwater [3,5]. The calculation of the saturation index (SI) assesses the chemical equilibrium between groundwater and a specific mineral.
Major ion chemistry determinations, combined with the application of statistical methods, have been used in groundwater studies to provide insight into the hydrogeochemical processes affecting the groundwater chemistry in an aquifer [7,15,16]. These statistical methods include bivariate regression analysis, correlation, the calculation of the ion ratio [12,15,17,18,19], and multivariate statistical methods.
Multivariate statistical techniques have become essential in hydrogeochemical studies for analyzing large and complex datasets [20]. Methods such as principal component analysis (PCA), cluster analysis, and factor analysis help to decipher patterns in groundwater chemistry by identifying the relationships between variables and grouping samples with similar characteristics [4,21,22,23]. These approaches are particularly useful in distinguishing between processes, such as mineral dissolution, ion exchange, or evaporation, and the anthropogenic influences that have affected hydrogeochemistry. By simplifying the data interpretation, multivariate analysis enhances our understanding of the key factors influencing groundwater quality. PCA analysis is instrumental in helping to simplify diverse and complex relationships among various observed variables [24,25,26,27]. It is also helpful in identifying relationships and patterns in each dataset while highlighting similarities and differences [28,29,30]. Statistical methods complement the classical standard graphical methods, such as Piper and Scholler diagrams, used to classify water facies and identify factors affecting groundwater quality in an aquifer [17,31].
The suitability of groundwater for drinking and agricultural purposes can be determined by applying the water quality indices (WQI). The WQI is a single, dimensionless numeric score that reports the water quality as a single score [32]. This numeric score was first used by Horton [33]. The calculation and the mode of deriving the WQI have been updated and applied successfully in various hydrogeological contexts and for many different purposes [34,35,36,37]. The water quality data is often extensive and has many parameters to consider, such as electrical conductivity (EC), TDS, and the concentration of various analyzed ions. The WQI is an essential and effective tool that helps minimize the data into a single numeric value that is easy to understand, evaluate, and monitor [37].
The suitability of water for irrigation purposes is commonly assessed using the irrigation water quality index (IWQI) [38,39,40,41]. This tool combines various physical and chemical water quality variables into a single value representing the water quality level [38,39]. The commonly used parameters in calculating the IWQI are those that measure salinity, sodicity, and toxicity, e.g., EC, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), and the concentration of ions [42,43].
International and national standards typically guide the assessment of groundwater quality for domestic and agricultural uses to ensure public health and environmental safety. The World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines [44] provide globally accepted thresholds for drinking water quality. This offers a comprehensive framework for evaluating the potential health risks associated with chemical and microbiological contaminants that have been applied globally [45,46]. Complementing these, the Water Services Regulatory Board (WASREB) of Kenya has established localized standards that account for regional water use patterns, environmental conditions, and infrastructural capacities [47]. Integrating both WHO and WASREB standards in water quality assessments enables a more context-specific evaluation, ensuring that water resources meet both international safety benchmarks and the practical needs of local populations. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) also provides guidelines for various agricultural applications [42,43,48].
Ewaso Ng’iro–Lagh Dera basin, on which this study is based, is a water-stressed, arid region of Kenya where groundwater is the primary water source. The demand for groundwater is high due to the dry climatic conditions and limited surface water. This demand is expected to persist, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa, where the projected population is anticipated to increase drastically [49]. Specifically, in Kenya, the population is expected to increase from approximately 48.8 million in 2020 to about 70.2 million by 2045, representing approximately a 43.85% increase [50]. The combined effects of climate change, pollution, population increase, and land use changes are causing an alarming decline in groundwater level and quality [51,52,53].
Agriculture plays a significant role in Kenya’s economic growth [54]. The agricultural sector is largely carried out by small-to-medium-scale farmers who rely on the rainfall seasons [55]. Unfortunately, the study area lies in an arid region with low and unpredictable rainfall [56]. This leads to farmers concentrating their activities along riverbanks [57]. It has been proposed that precision irrigated farming is needed to expand farming activities and food production sustainably [58]. Given that the rivers in the region are ephemeral, groundwater serves as a viable alternative to support agricultural activities.
The study area is a key region for animal husbandry in Kenya, where pastoralism is the primary livelihood activity [57]. Since the area experiences unreliable rainfall, livestock production relies heavily on groundwater resources. Studies show that residents of the arid regions of Northern Kenya, in areas such as Ewaso Ngi’ro basin, rely heavily on groundwater for domestic and farming purposes, especially in the dry season [59,60]. Therefore, groundwater is a critical resource in the region, necessitating sustainable utilization and management. One of the critical steps in the management and sustainable utilization involves understanding the hydrogeochemical and hydrogeological properties of the aquifer [61].
Several studies have been conducted on groundwater resources within the Ewaso Ngi’iro–Lagh Dera basin [62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72]. These studies have assessed the extent of the aquifers, established the spatial and temporal variation of various geochemical and geophysical parameters, modeled the groundwater flow, and investigated the groundwater recharge and discharge dynamics. The overextraction of groundwater resources and the possibility of a decline in water quality through up-coning have been expounded by Leudeling et al. [71]. Recharge in the study area has been noted to occur during the sporadic and episodic rainfall within inundation along the ephemeral rivers and the swamp [67,69]. The possibility of recent episodic recharge has been established using tritium and carbon isotope analysis carried out by [64,73,74,75]. However, these studies have not provided a detailed analysis of the ion chemistry necessary to interpret and identify the various hydrogeochemical processes affecting groundwater quality. Identifying these processes can substantially contribute to ensuring the sustainable management of groundwater resources. Therefore, this study’s main objective was to identify and characterize the hydrogeochemical processes that control groundwater chemistry and assess the groundwater’s suitability for human and livestock consumption and irrigation purposes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Area
The Ewaso Ng’iro–Lagh Dera basin is located in the northeastern part of Kenya. It is bounded by longitudes 38°10″ E to 40°60″ E and latitudes 0°05″ S to 1°45″ N (Figure 1), covering an approximate area of 42,997 km2. The study area is part of the large Ewaso Ng’iro basin (Figure 1) that covers parts of Kenya, Ethiopia, and Somalia. In Kenya, the Ewaso Ng’iro River, which drains the basin, originates from the central parts of the country as a perennial river. The river flows into the northeastern part of the country as the ephemeral Lagh Dera river, which extends into Somalia and drains into the Indian Ocean. Climatically, the study area is an arid region, with temperatures ranging between 22 °C and 33.4 °C and an average rainfall of about 250 mm per year. The rainy seasons occur biannually, one from March to May and another from October to December, with the latter being more significant [56]. Shrubs and grassland largely cover the study area. Thus, nomadic pastoralism is the main land use activity [71]. Farming activities are carried out along the Lagh Dera river. The towns are mainly low-density urban centers, apart from Hagadera, which has a moderately high population density. Hagadera hosts Dadaab refugee camp, the largest in East and Central Africa. Topographically, the area is mainly flat, with a few elevated grounds. The altitude ranges from 45 m to 1543 m above the mean sea level.
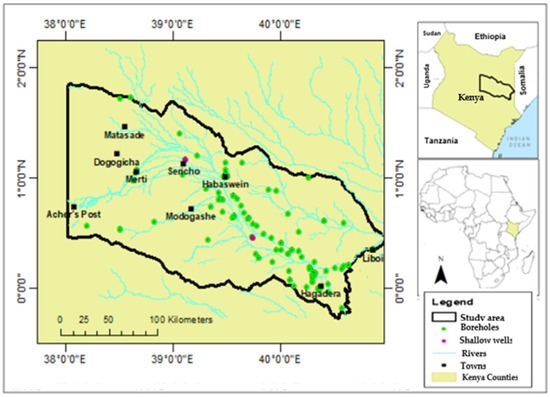
Figure 1.
The study area map.
2.2. Geological and Structural Setting
The Ewaso Ng’iro–Lagh Dera basin is located mainly within the Anza Basin, Kenya. The Anza basin is an inactive continental rift system formed in the Mesozoic Era. The basin stretches inland from the coast of Kenya with a northwest–southeast trend [76,77,78]. The Anza basin is filled with very deep (>3 Km) sediments. In the Mesozoic era, the basin experienced a period of marine incursion followed by a long period of uplift and erosion, which was later followed by the paleo-Tethyan transgression of the Trans-Eritrean trough. Later in the Cenozoic era, extensive continental erosion led to leveling in most parts of the study area, followed by periods of deposition in the Miocene and continued deposition and peneplanation in the Pliocene [79].
The exposed lithologies of the Anza basin are Pliocene sediments consisting of sandstone, conglomerates, limestone, siltstone, sand, grits, gravel, and clays. The Holocene colluvium consists of gravel, silts, and sands, whereas the Holocene alluvium consists of clays, sand, and silts. The cross-section in Figure 2 indicates that deeper formations include the Miocene limestone, Miocene sand and clay, and further below, at 500 m below the surface, are the Miocene marine shales [69,80]. The metamorphic rocks consist of metamorphosed components of calcareous rocks, semi-pelitic sedimentary rocks, intrusive rocks, and psammitic sediments [80]. Lithologies that do not belong to the Anza basin are the Precambrian metamorphic and the Quaternary volcanic rocks occurring in the western and southwestern part of the study area, respectively. The Quaternary volcanic rock prevalent in the study area is the olivine basalt of the Pleistocene Epoch (Figure 2).
Deep-seated faults are the main structural features, since the study area occurs within the Anza basin trough [79]. Most of these faults are deep structures (>0.8 Km below ground level) and are therefore concealed by various superficial unconsolidated sediments and volcanic rocks of the Quaternary age [77,81]. However, the overlying formation mimics the deep structures, forming thick layers as the sediment accumulates in the depressions. It has, therefore, been hypothesized that they impact the occurrence and flow of groundwater in the area. In addition, there is a postulation that these structures influence the recharge and discharge of the freshwater lens of the aquifers in the study area [72].
2.3. Hydrogeology
Hydrogeologically, the principal aquifer in the study area is the Merti aquifer. The aquifer is comprised of fresh water along the Lagh Dera river axis. Salinity increases away from the river axis [66]. This is especially evident at the fresh lens of the Merti aquifer stretches from Habaswein to Liboi [71] (on the Kenya–Somalia border), with an aerial geographical extent of approximately 20,000 square kilometers. The Merti aquifer is multilayered [65,71], with a shallow unconfined aquifer occurring at an average depth of 20 m, constituted mainly of alluvial and colluvial deposits. A deeper aquifer is largely confined and occurs at depths greater than 80 m below ground level, primarily comprising weathered sandstone, gravel, sand, clay, dolomite, and limestones [67]. The transmissivity is high in the alluvium and colluvium and low in the sandstone and metamorphic zones [62,69,72].
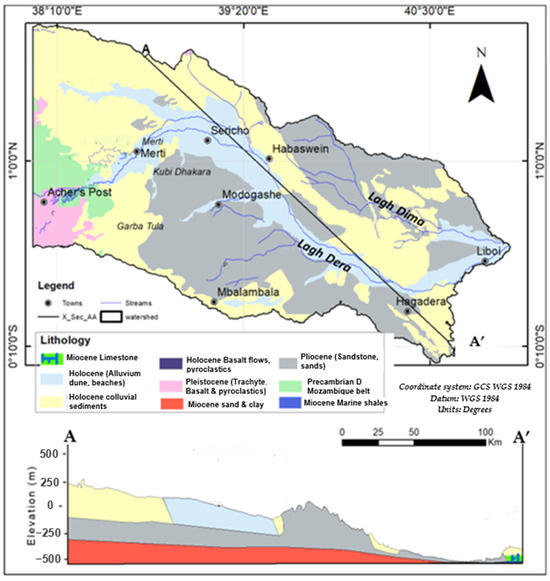
Figure 2.
The geology of the study area was adopted from the Geological Map, Geostructural, and Bouguer gravity map of Kenya (National Oil Corporation Kenya (NOCK) [82]). Geological cross-section A–A’ representing the subsurface formation adopted from [69,79].
2.4. Sampling and Analysis
One hundred and twenty-nine water samples were collected from the aquifer in the study area to analyze the major ion chemistry in December 2021. Two groundwater samples were collected from the shallow wells (Figure 1) at depths less than 20 m, whereas the rest of the samples were collected from boreholes at depths greater than or equal to 80 m below ground level. The groundwater samples were taken from the boreholes using already installed pumps. Standard sampling procedures were followed according to the local authority (WASREB) [47] guidelines and the APHA [83] guidelines. After pre-rinsing the bottles with the water sample, 500 mL polyethylene bottles were used to collect the final water samples.
The water samples were collected in duplicates. One sample was used to analyze major anions, while the other was treated with nitric acid (HNO3) to a pH of less than 2 for analysis of major cations. The cations analyzed were Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ while the anions were HCO3−, SO42−, NO3−, and Cl−. The pH and electrical conductivity (EC) were measured in the field using a portable conductivity, salinity, and pH meter, and the location of the sample was recorded using a Garmin GPS. To ensure quality sampling, the collected samples were stored and transported in cooler boxes at 4 °C and then taken to the laboratory for analysis. The major cations were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) methods using the Thermo Scientific Model—iCAP 6000 Series (ISO 11885:2007) [84]. The Cl− concentration was determined colorimetrically by forming a red/brown iron(III) thiocyanate complex, with its intensity measured at 480 nm using spectrophotometry (EPA Method 325.1). SO42− was analyzed colorimetrically using the barium chloride–glycerol method. The HCO3− was determined using the titration method with hydrochloric acid to a pH endpoint (around 4.5), where the volume of acid required reflects the bicarbonate concentration.
For quality assurance and control, all the laboratory analyses were performed in duplicate. To ensure accuracy, the charge balance error (CBE) was calculated as indicated in Equation (1), and the dataset used in this study had a charge balance error range of ±10%, which is an acceptable standard limit [18,85,86]. The error was computed based on the analyzed ions expressed in milliequivalent per liter (meq/L).
The analyzed ions in the groundwater were plotted on a Piper diagram [87] to characterize the groundwater into the different water types. Interpretations of the potential interactions between the groundwater and host rocks were conducted and illustrated using geochemical plots. The saturation index (SI) was calculated using PHREEQC (Version 3) geochemical modeling software. The saturation index (SI) indicates the status of a mineral phase reaction, whether it is dissolving or precipitating [7]. It is, therefore, used to determine the equilibrium state of the groundwater with respect to the mineral phase using Equation (2).
where the ion activity product (IAP) is the product of the dissociated chemical species in solution, and Ksp(T) is the equilibrium constant at sample temperature T [88].
SI = log (IAP/Ksp(T))
The saturation index quantitatively indicates the sampled water’s deviation from the equilibrium [89]. If the groundwater is at equilibrium, SI = 0. If the groundwater is under saturated, SI < 0, and if SI > 0, then the water is supersaturated with respect to the mineral facies and may represent the precipitation phase [90].
Statistical techniques such as bivariate analysis were used to understand the relationship between the parameters. Bivariate analysis reveals the existence of an association, strength, or the presence of differences between the two variables [91,92]. This study used bivariate regression and correlation using EXCEL and XLSTAT 2016 to carry out the analysis. A correlation matrix was used to examine the statistical relationships between the hydrogeochemical parameters, and this helped to identify the common sources or geochemical processes influencing groundwater composition [93,94]. By revealing strong positive or negative correlations, it can point to processes such as mineral dissolution, ion exchange, or anthropogenic inputs. Correlation analysis, therefore, supports the interpretation of groundwater chemistry and further helps in parameter selection for further multivariate techniques like PCA, as well as helps distinguish between natural and human-induced influences on water quality.
PCA, a multivariate statistical method, was applied to identify the most influential variables and underlying geochemical processes [24]. The dataset was first standardized and converted into a correlation matrix with normally distributed variables. Eigenvalues and eigenvectors were then extracted, and only components with eigenvalues greater than one, indicating significant contributions to total variance, were retained [22]. To better interpret the influence of each variable, a varimax rotation was applied to the factor loadings, aligning them closer to +1, 0, or −1 to indicate strong positive, negligible, or strong negative contributions, respectively. These results were used to compute factor scores, revealing dominant variables and associated geochemical processes. The PCA analysis was carried out using XLSTAT 2016 software.
The suitability of the groundwater for human consumption was assessed by comparing the sample-measured parameter with the World Health Organization (WHO) 2017 guideline values [44] and the Water Services Regulatory Board of Kenya (WASREB) [47]. The drinking suitability for livestock was compared with the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) 2016 guidelines [48].
Drinking water suitability was also analyzed using the water quality index (WQI) obtained using the parameters assessed in this study. The tool used in this analysis was a weighted arithmetic water quality index whose procedure involved four main steps.
- Selection of the parameters. In this study, all the analysed parameters were used; these are EC, TDS, pH, TH, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, HCO3−, Cl−, SO42−, and NO3−;
- Assigning weights to the parameters (Wi). The assigning of the weight took into consideration the influence of the parameter on water quality and the weight rating of the studies carried out in similar settings [95,96]. The weighting ranged from 2 to 5. The highest weight of 5 was awarded TDS, and NO3−. EC, pH, and SO42− were awarded a weight of 4. HCO3− and Cl− were awarded a weight of 3, whereas Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, and TH were awarded a weight of 2. Relative weights (wi) for the ith parameter and n number of parameters were then calculated using the formulae (Equation (3)).
- 3.
- Calculate the quality rating (Qi) of each of the parameters using the formulae (Equation (4)).
- 4.
- Calculate the overall water quality index using Equation (5).
The calculated WQI values range from 0 to values greater than 300. These values are then categorized into five rating classes, with values close to zero having excellent water quality and values greater than 300 being the unsuitable water quality [97].
The irrigation water quality index (IWQI) was used to determine the suitability of the groundwater for irrigation. The procedure for calculating the IWQI is similar to that used in WQI. Here, the parameters influencing salinity, sodium hazard, and toxicity were considered: EC, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), and ion (Na+, Cl−, and HCO3−) concentration.
The EC helps evaluate the salinity, while the Cl− and HCO3− ion concentrations help evaluate the toxicity. The concentration of Na+ and SAR measures the hazard of sodium. SAR can be determined using Equation (7).
where Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ are expressed in meq/L
After identifying the parameters to consider, relative weights, wi, were assigned to each depending on the parameter’s impact on irrigation. The weights assigned to the parameters were according to [42] (Table 1).

Table 1.
Weights for the IWQI parameters according to [42].
The next step was calculating the quality rating (Qi) for each parameter according to [43]. (Table 2) by applying Equation (8).
where is an upper limit of the last class of each parameter, is the observed value of chemical parameters, is the minimal limit of the class to which each parameter belongs, is the class amplitude, and is an upper limit of the last class of each parameter.

Table 2.
Limiting values of qi calculations [43,98].
The irrigation water quality index is calculated using Equation (9).
where represents the parameter’s quality measurement, ith is the number between 1 and 100 representing the concentration of the parameter, and wi is the normalized weight of the ith parameter. The results of IWQI are values ranging from 0–100 and are categorized into five categories.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Geochemistry
The pH level of the water samples analyzed ranged between 7.1 and 8.9, indicating that the groundwater is neutral to slightly alkaline. The electrical conductivity (EC) of the groundwater ranges from 419.8 to 18,000.0 μS/cm (Table 3). The average EC of the collected samples in the study area is 1937.0 μS/cm. Based on the EC values, the groundwater system can be classified into three groups: freshwater (<1500 μS/cm), brackish water (1500–3000 μS/cm), and saline water (>3000 μS/cm) [99]. Of 129 samples analyzed, 62.0% are freshwater, 25.6% are brackish water, and 12.4% are saline water. Therefore, the groundwater in the study area is primarily fresh and brackish. The fresh groundwater with relatively lower EC occurs in the zone adjoining and close to the Lagh Dera River (downstream from Habaswein) (Figure 3), and the salinity increases with increasing distance from the river [69]. A higher EC is evident in the northeastern part of the study area along the Lagh Dima River. The low-transmissive sandstone dominates this zone. Further, high EC values occur in the central part of the study, around Modagashe, and this zone is dominated by thick clay formation in areas close to Lagh Dera, surrounded by the Pliocene sandstone. The total dissolved solids (TDS) range from 314 to 8366 mg/L, with an average of 1423 mg/L (Table 3).

Table 3.
Summary statistics of the measured parameters in the study area.
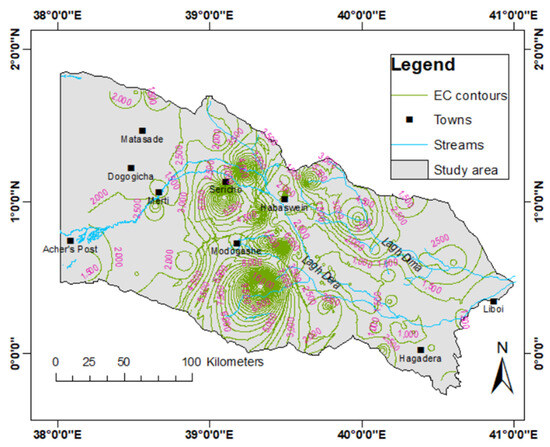
Figure 3.
Contour map showing the distribution of EC in the study area.
Na+ is the most abundant cation in the groundwater, and the sequence of the relative abundance of the cations is Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+. The most abundant anion is HCO3−, and the sequence of the relative abundance of the anions in the basin is HCO3− > Cl− > SO42− > NO3−. The Na+ concentration ranges between 10.4 and 3410.0 mg/L, with a median of 221.0 mg/L. The concentration of Ca2+ in the groundwater varies from 2.8 to 233.0 mg/L, with a median of 20.0 mg/L. The Mg2+ concentrations ranged from 1.0 to 151.0 mg/L, with a median concentration of 11.1 mg/L. The K+ concentration in the groundwater ranges from 2.0 to 83.0 mg/L, with a median of 11.0 mg/L. The concentration of HCO3− ranges from 109.2 to 4779.2 mg/L, with a median of 560.5 mg/L. The Cl− ion concentration ranges from 2.0 to 4300.0 mg/L, with a median of 60.0 mg/L. The SO42− concentration varies from 3.0 to 1230.0 mg/L, with a median of 35.3 mg/L. The NO3− concentration in the study area ranges from 0.0 to 129.9 mg/L, with a median of 1.1 mg/L (Table 3).
The major ions were illustrated graphically using the Piper diagram [87] (Figure 4). The diagram shows that the alkaline earth elements dominate, i.e., Na+ + K+ > Ca2+ + Mg2+, and weak acidic anions exceed strong acidic anions, i.e., HCO3− > Cl− + SO42−. Most of the groundwater samples are Na+ + K+ and bicarbonate types. Therefore, the dominant water facies are Na-HCO3, which accounts for 45.74% of the collected samples. Other facies present are Na-HCO3-Cl, Na-Mg-HCO3, Na-Ca-HCO3, Na-Cl-HCO3, Na-Cl, Na-HCO3-SO4, Na-Mg-Cl-HCO3, Na-Ca-Mg-HCO3-Cl, Na-Ca-HCO3-Cl, and Na-Mg-HCO3-Cl, with percentage abundances of 17.83%, 11.63%, 3.88%, 3.88%, 2.33%, 2.33%, 2.33%, 1.55%, 1.55%, and 1.55%, respectively. Ca-Na-HCO3-NO3, Na-Ca-Cl-HCO3, Ca-Na-HCO3, Ca-K-HCO3, Na-Ca-Mg-HCO3, Mg-Na-Ca-HCO3-Cl, and Mg-Na-HCO3 were all represented by 0.78%. The Ca2+ and Mg2+-dominated facies were from the shallow wells, and areas dominated by bicarbonates.
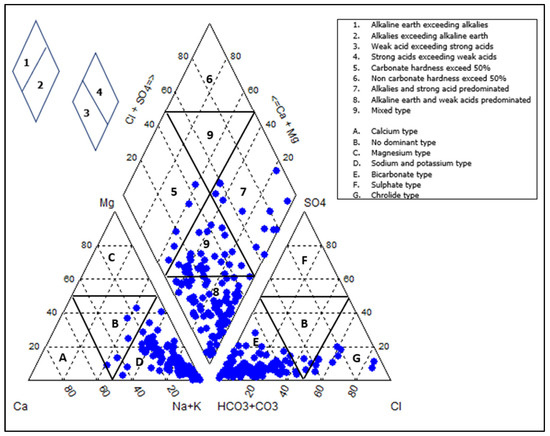
Figure 4.
A Piper diagram illustrating the geochemical classification of the groundwater in the study area, indicating dominance of NaHCO3 water type; the blue dots represents the position of the sampled water, 1 represents alkaline earths exceeding alkalies, 2 represents alkalies exceeding alkaline earths, 3 represents weak acids exceeding strong acids, and 4 represents strong acid exceeding weak acids [87].
3.2. Processes Controlling the Groundwater Chemistry
Chemical changes occur to groundwater as it moves within/through the aquifers. These changes occur because of various processes, such as rock interactions, groundwater residence time in the aquifer, mixing of various groundwater bodies, and ion exchange processes. The processes usually lead to solute acquisition by the groundwater, which generally reflects an increase in the TDS and EC. A p × p correlation matrix of the 11 analyzed parameters was carried out (Table 4) to decipher and identify the various processes. The good correlation between TDS with sodium (r = 0.93), sulphate (r = 0.83), bicarbonate (r = 0.77), and chloride (r = 0.66) indicates that these ions contribute to groundwater chemical enrichment. The low correlation between TDS with potassium r = 0.14), calcium (r = −0.08), magnesium (r = −0.06), and nitrate (r = −0.06) indicates that the ions do not have a very high impact on groundwater TDS.

Table 4.
Correlation matrix between analyzed parameters in groundwater.
The high correlation between Cl− and SO42− (r = 0.80), Na+ and Cl− (r = 0.86), SO42− and HCO3− (r = 0.51), and Na+ and SO42− (r = 0.9) suggests increased salinization of the groundwater through processes such as cation exchange and mixing of groundwater with old saline connate water. The moderately good correlation between K+ and Mg2+ (r = 0.61) suggests silicate weathering. The correlation between Ca2+ and Mg2+ indicates that the ions may have originated from carbonate dissolution. The moderately good correlation between Ca2+ and NO3− suggests groundwater anthropogenic contamination from agricultural activities.
3.2.1. Ion Exchange
The ion exchange between the aquifer rocks and the groundwater is one of the processes that controls the relative concentration of ions in the groundwater [89]. If Na+ + K+ replaces Ca2+ + Mg2+, the ion exchange process is referred to as a cation exchange, and if Ca2+ + Mg2+ replaces Na+ + K+, the process is referred to as a reverse ion exchange [100].
A major indicator of ion exchange is the Chloralkaline indices, as described by Schoeller [101]. The Chloralkaline indices 1 and 2 (CAI 1 and 2) help to understand the ion exchange process between the groundwater and the host environment. These indices are calculated using equations 10 and 11, and the results are as in Table 3:
(These indices are expressed or calculated in meq/L.) The CAI1 and CAI2 are negative when cation exchange occurs. In such cases, the Ca2+/Mg2+ in the water is exchanged with Na+/K+ in the host environment, creating a chloro-alkaline disequilibrium [89]. Conversely, a positive index indicates a reverse ion exchange between Na+ or K+ with Mg2+ or Ca2+ in the groundwater [4,27,88,102]. All the samples have negative CAI 1 and CAI 2 indices (Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively), implying that cation exchange is the dominant process. These results show that Na+ and K+ are being added into the groundwater, whereas Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions are removed through adsorption processes. CAI 1 indices had a very large data range, from −306.7 to −0.01, with a median of −4.9, and thus, due to the scale factor, most samples plot close to the zero line (Figure 5). Values very close to zero indicate slight ion exchange processes and vice versa. CAI 2 ranges from −1.7 to −0.06, with a median of −0.7, corroborating the results of CAI 1, that sodium enrichment of groundwater is due to the cation exchange process.
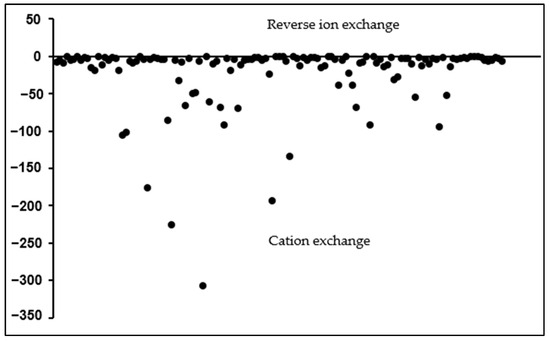
Figure 5.
Chloro-alkaline indices (CAI 1) for the analyzed groundwater samples.
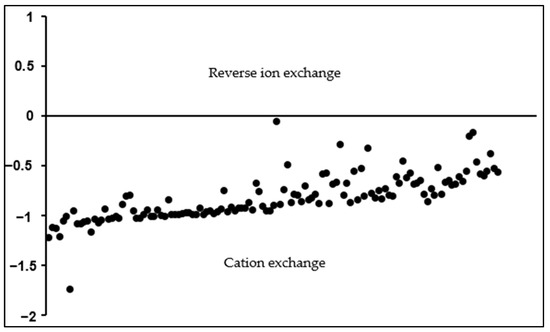
Figure 6.
Chloro-alkaline indices (CAI 2) for the analyzed groundwater samples.
The bivariate plot of (Ca2+ + Mg2+) − (HCO3− + SO42−) as a function of (Na+ + K+ − Cl−) provides evidence of the cation exchange (Figure 7). Data would be plotted at the origin if the ion exchange were not a significant process in the aquifer system. In cases where the cation exchange is a major controlling process, the two parameters plot linearly, with a slope of −1 [27,88]. Figure 7 shows that the analyzed samples have a linear relationship, with a slope of −0.94. Therefore, an increase in Na+ + K+ is related to a decrease in Ca2+ + Mg2+ or an increase in HCO3− + SO42− [103]. Therefore, the cation exchange process is a possible cause of increasing Na+ concentration and reduction of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the groundwater in the study area.
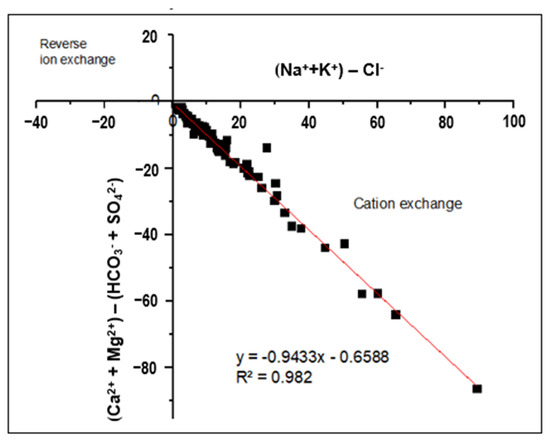
Figure 7.
Bivariate plots indicate the dominance of the cation exchange process. The red line represents the linear regression line with a slope of −0.94 and R2 = 0.982.
3.2.2. Silicate Weathering
Silicate weathering is also a probable cause of the abundance of sodium (Na+) in the study area. The higher concentrations of sodium support this conclusion compared to chloride ions in the groundwater (Table 3). A good indicator of the silicate weathering process is the Na+/Cl− ion ratio [18,19]. A ratio greater than one suggests that sodium in the groundwater originates from silicate minerals.
The analyzed groundwater samples exhibited Na+/Cl− ratios ranging from 1.0 to 306.6, with an average of 22.7 (Table 3). Notably, all samples had a ratio exceeding one, indicating silicate weathering as an important process. The reaction of feldspar minerals with carbonic acid in the presence of water releases bicarbonate (HCO3−) [12,104], thus contributing to the concentration of HCO3− in the groundwater. While halite dissolution could also introduce Na+ and Cl− ions, no halite deposits have been identified in the study area, making this an unlikely source. The significant enrichment of Cl− in the study area is probably because Cl− is readily transported within the soil. Further Cl− ions could result from a prolonged interaction of groundwater with the host rocks due to the long residence time of groundwater in the aquifers, and also paleo-marine brine connate water.
3.2.3. Carbonate Precipitation and Dissolution
Carbonate rocks such as limestone and dolomite are abundant in the study area [62,64]. Therefore, carbonate mineral dissolution is expected to contribute to the concentrations of HCO3−, Ca2+, and Mg2+ in the groundwater. However, only a few samples plot along the carbonate dissolution line (Figure 8). Furthermore, the weak correlations among Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− (Table 4) suggest that these ions are being removed from the solution. The reduced concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ may be attributed to two main processes: (1) cation exchange reactions and (2) precipitation of carbonate minerals under supersaturated conditions.
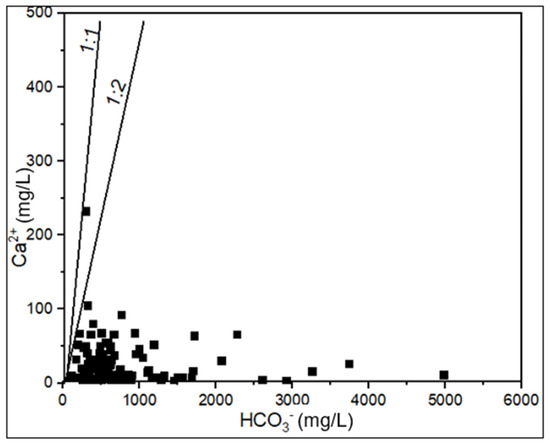
Figure 8.
Bivariate plots of Ca2+ versus HCO3− ions.
Positive saturation indices of calcite, dolomite, and aragonite mineral phases in most samples (Figure 9) indicate supersaturation, suggesting that excess carbonates are likely precipitating. This further indicates that the groundwater has significantly interacted with the carbonates and reached geochemical equilibrium with respect to the calcite, dolomite, and aragonite mineral phases. The widespread occurrence of calcrete in the study area [62] supports the hypothesis that carbonate precipitation processes play a role in the evolution of groundwater chemistry.
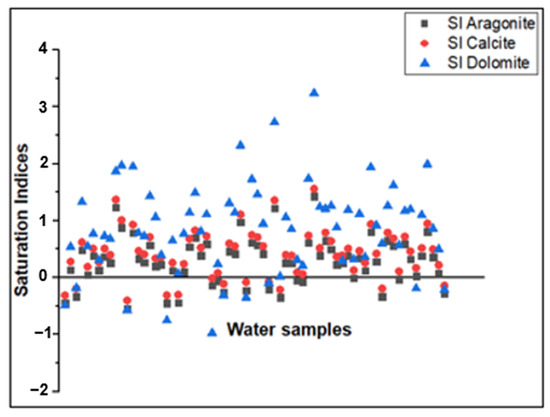
Figure 9.
Plots of saturation index (SI) of aragonite, calcite, and dolomite.
Carbonate dissolution is only evidenced in a few samples that fall on the carbonate dissolution trend line (Figure 8) and in several groundwater samples that exhibited negative saturation indices (Figure 9). The negative SI does imply that, in some aquifer sections, there is an insufficient concentration of the dissolved ions required to form the carbonate mineral phase, and thus, the system is undersaturated and has the chemical potential for dissolution. These samples are mainly the Ca-HCO3 and Mg-HCO3 water types from the shallow wells and from the zones dominated by carbonate rocks. The dissolution of carbonate minerals, such as calcite, dolomite, and aragonite, occurs when rainwater comes into contact with carbonate rocks, releasing Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− ions in the groundwater. The chemical reactions shown in Equations (12) and (13) can describe these processes.
Calcite dissolution: −CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 → Ca2+ + 2HCO3−
Dolomite dissolution: −CaMg(CO3)2 + 2H2O + 2CO2 → Ca2+ + Mg2+ + 4HCO3−
3.2.4. Fresh–Saline Water Mixing
The principal aquifer in the study area is the fresh–brackish Merti aquifer, bounded laterally and vertically by saline water aquifers [62]. The movement and interaction of the groundwater in the Merti aquifer is facilitated by stratigraphic heterogeneity and possible structural controls, such as buried faults or paleo-depositional features [105]. At greater depths, the Paleo saline aquifer, characterized by Na-Cl water facies, may result from prolonged residence time within the aquifer [64,67]. Laterally, the observed increase in salinity is primarily due to the low transmissivity of the fine-grained geological formations, which slows groundwater movement and promotes prolonged water–rock interaction. This leads to a gradual enrichment of anions—particularly Cl− and SO42+—as groundwater migrates slowly from the recharge zone along the Lagh Dera River, which is consistent with the geochemical evolution described by the Chebotarev sequence (Equation (14)) [7,106].
Travel along the flow path:
HCO3− → HCO3− + SO42− → SO42− + HCO3− → SO42− + C1− → C1− + SO42− → C1−
Increasing age.
Luedeling et al. [71] postulated that groundwaters in the study area continually become saline through fresh–saline water mixing. This study evaluated the extent of salinization using the Cl−/HCO3− ratio. The ratio classifies the water into five classes: good quality (<0.5), slightly contaminated (0.5–1.3), moderately contaminated (1.3–2.8), highly contaminated (2.8–6.6), and extremely contaminated (6.6–15.5) [107,108]. This ratio was considered because the chloride ion is stable and a good proxy for TDS [109]. The results show that 81.4% of the groundwater is of good quality, with a ratio of less than 0.5. 11.6%, 5.4%, 0.7%, and 0.9% representing slightly, moderately, highly, and extremely contaminated groundwater, respectively (Table 5). The extremely contaminated reflect the Na-Cl and Na-HCO3-SO4 facies located in the saline zones, which are located in low transmissivity formations, such as clays and Pliocene sandstone.

Table 5.
Classification of groundwater using Cl−/HCO3− ion ratio.
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
In analyzing the groundwater of a large basin, one is faced with the complexity associated with many measured variables. Therefore, in this study, PCA was used to recognize the pattern that explains the variance in the intercorrelated variables. PCA helps to show an association between variables, thus reducing the dimensionality of the dataset. This analysis, therefore, reduced the measured parameters into four factors. Among these factors, three factors with eigenvalues > 1 were extracted. These three factors accounted for 78.08% of the total variance of the dataset. Factor F1 accounted for 44.06%, F2, 24.38%, and F3 accounted for 9.63% of the total variance in the original dataset (Table 6).

Table 6.
Factor loading of principal component analysis.
The results indicate that Factor 1 (F1) is highly influenced by electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), and the concentrations of Na+, Cl−, and SO42−, and is moderately influenced by the concentration of HCO3−, suggesting a strong interrelationship among these variables. Therefore, F1 is primarily governed by geogenic processes that contribute to the salinization of the groundwater. That is, the processes that cause the abundance of Na+, HCO3−, SO42−, and Cl−, which correlate highly with EC and the TDS. These processes are cation exchange, silicate weathering, and mixing between the saline and fresh groundwater. Additionally, the prolonged residence time of groundwater within the aquifer contributes to the elevated ion concentrations.
Factor 2 (F2) is primarily influenced by the concentration of Ca2+ and Mg2+ (Table 6). Therefore, this factor represents the precipitation process of the carbonate mineral facies. Factor 3 is moderately influenced by K+ and NO3−, which indicates contamination of the aquifer through agricultural practices, though it is not prevalent in the study area.
3.4. Drinking Water Quality
The suitability of the groundwater for drinking was evaluated by comparing it with the drinking water guidelines provided by the World Health Organization (WHO) [44] and the Water Services Regulatory Board of Kenya (WASREB KENYA 2016) [47] (Table 3). The maximum recommended limit in the WASREB recommendations is less than or equal to that of the WHO recommendations, apart from the concentrations Cl−, Mg2+, and NO3−. This study, therefore, applied the WHO standard to assess the limits of the parameters because it is universally acceptable. Only the HCO3− and Na parameters had a high percentage of samples exceeding the WHO maximum allowable limit, with 85.5% and 49.3%, respectively.
- Water Quality Index (WQI)
Since assessing drinking water suitability involves many parameters, the drinking water quality index (WQI) was used to simplify the evaluation. According to the results in Table 7, only 20.31% of the samples are of excellent quality, 60.16% are of good quality, and are suitable for drinking, and 13.27% of the samples have a poor rating, with 6.26% being poor and unsuitable for drinking.

Table 7.
Drinking water index rating class and percent sample representation.
Excellent-to-good drinking water quality is primarily found downstream along the Lagh Dera River (Figure 10), where alluvial and colluvial deposits dominate the aquifer. In the western part of the study area, good water quality is also observed within volcanic formations, particularly west of Garba Tula. Poor-to-very poor water quality is prevalent primarily in the northeastern region, where the aquifer is composed predominantly of Pliocene sandstone. Unsuitable water quality is found in the central part of the study area, which is characterized by thick clay formations with low transmissivity.
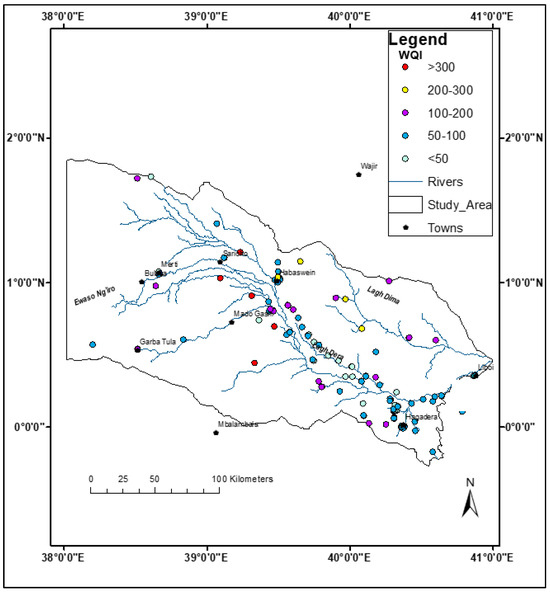
Figure 10.
The distribution of the drinking WQI categories in the study area.
The economic activity practiced by the residents in the study area is mainly pastoralism [56]. Therefore, it is vital to assess the suitability of the water for livestock consumption to prevent poisoning from toxic solutes, salt imbalances, and even diseases [110]. Unlike human drinking water standards, livestock water quality standards allow for higher salinity levels and total dissolved solids (TDS) [111]. TDS is the main parameter considered when assessing the suitability of water for livestock farming. Based on the FAO livestock drinking water standard, values less than 4000 mg/L and between 4000 and 5000 mg/L are very satisfactory and satisfactory for most livestock, apart from poultry, in which values greater than 3000 mg/L are unfit [48]. The analyzed TDS values in the study area ranged from 313.8 mg/L to 8366.0 mg/L, and 93.7% of the analyzed water had values less than 4000 within the permissible range for most livestock. Only 7.8% of the analyzed samples had a TDS value greater than 3000 mg/L. Therefore, they were unfit for poultry consumption. Overall, groundwater in the study area is largely suitable for livestock consumption.
3.5. Irrigation Water Quality
Groundwater is the primary source of irrigation water in arid areas. Therefore, careful assessment of the water’s suitability for irrigation projects is critical as it influences the mineral availability to the soils and plants, soil structure, and permeability of the soils [63] suitability of groundwater for agriculture is evaluated using the sodium adsorption ratio (SAR).
The calculated SAR values in the study area are as displayed in the standard SAR value table according to Richards [112] (Table 8). From the analysis, only 39.54% and 17.83% of the analyzed groundwater samples can be used for irrigation as they fall into the excellent and good categories, respectively. The excellent and the good groundwater samples plot within the low (S1) and medium (S2) sodium hazard sections in the Wilcox diagram [113] (Figure 11). However, 9.33% and 33.33% of the sampled groundwater cannot be applied for irrigation, as this water is categorized as doubtful and unsuitable, respectively (Table 8). These samples are plotted in high (S3) to very high (S4) sodium (alkali hazard section, Figure 11). However, approximately more than 80% of the analyzed samples plotted in the C3 and C4 indicated a high salinity (EC) hazard.

Table 8.
Showing the classification of groundwater in the study area using irrigation parameters.
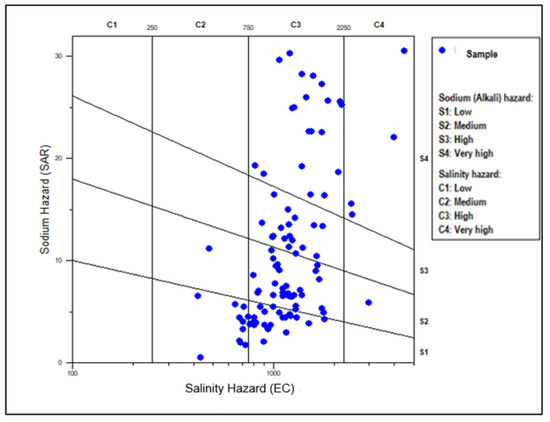
Figure 11.
Classification of the groundwater in the study area using the Wilcox salinity diagram.
- Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI)
The irrigation water index was used to assess the suitability of groundwater in the study area for irrigation purposes. The results indicate that most of the groundwater in the study area is largely not suitable for irrigation, with only 12.4% having moderate restrictions (Table 9). The rest of the groundwater has high-to-severe restrictions, with 45.7% and 41.9%, respectively. Most of the groundwater with a severe restriction for irrigation is in the north–northeastern part of the study area (Figure 12), whereas those with moderate and high restrictions occur along the Lagh Dera River. Water classified as having a moderate irrigation water quality index (IWQI) can be used on soils with high permeability and moderate salt leaching [43,98]. Similarly, water with a high restriction rating is suitable for highly permeable soils without compact layers. Under normal soil conditions, high restriction water should be avoided [42]

Table 9.
Irrigation water index rating class and percent sample representation [42].
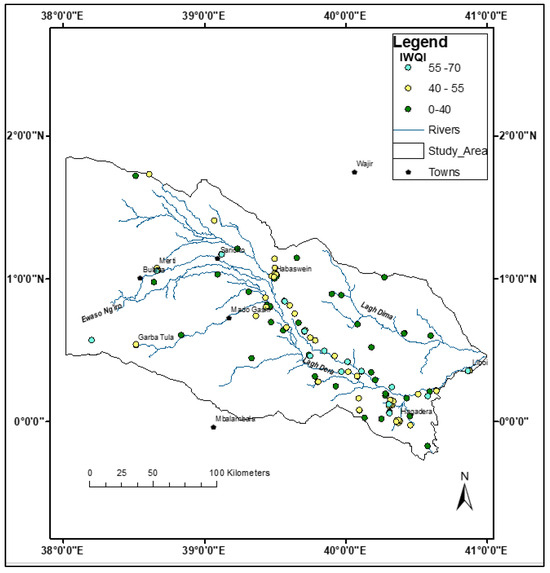
Figure 12.
The distribution of the IWQI categories in the study area. Only three out of the five classes are plotted, representing moderate restriction, high restriction, and severe restriction classes. None of the samples were in the no-restriction and low-restriction categories.
4. Discussion
The principal aquifer in the study area, known as the Merti Aquifer, exhibits unique groundwater chemistry influenced by geological and hydrological processes. Groundwater in this aquifer predominantly has a neutral-to-alkaline pH, which is consistent with findings from prior studies [64,67,69,114]. Elevated electrical conductivity (EC) and total dissolved solids (TDS) levels suggest significant mineralization, classifying the groundwater as fresh to brackish. The aquifer’s multilayered lithology includes weathered sandstone, limestone, sand, silt, gravel, and clay-rich materials, contributing to its diverse water chemistry [63,69].
The study area’s groundwater chemistry is significantly influenced by rock weathering. The silicate weathering provides Na+ and Mg2+ ions. Carbonate weathering occurring in the shallow aquifer and in zones dominated by carbonate rocks further adds Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− ions. Shallow wells in the southwestern study area and the downstream sections of the Lagh Dera River also display Ca/Mg-HCO3 water facies, which is indicative of young, fresh recharge water [64,67]. In addition, positive saturation indices for calcite, dolomite, and aragonite mineral phases indicate supersaturation, supporting the role of precipitation in regulating Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− abundance [100].
Cation exchange also plays a critical role, as evidenced by the abundance of Na+ and HCO3− ions and the dominance of Na-HCO3 water facies in the aquifer. This process occurs when fresh recharge water interacts with paleo-sodium-rich brine, replacing Ca2+ and Mg2+ with Na+ [115]. It was also noted that the pH was relatively stable in the range between 7.1 and 8.9 in all the samples. Since the study area’s aquifer largely contains clay and carbonates, the carbonate equilibrium and cation exchange processes provide adequate buffering capacity for pH. Additionally, the incongruent weathering of silicate minerals can further contribute to pH buffering, leading to an increase in sodium (Na+) and bicarbonate (HCO3−) ions in the groundwater [116]. Moreover, the observed Na+ and HCO3− concentrations are relatively high and strongly correlate with electrical conductivity (EC) and total dissolved solids (TDS). In contrast, magnesium (Mg2+) and calcium (Ca2+) exhibit a weaker correlation with EC and TDS, suggesting that precipitation and ion exchange processes are actively influencing the groundwater system.
Overexploitation of the aquifer can lead to the upconing or intrusion of deep-seated, naturally occurring saline water, as observed by Luedeling et al. [71]. Still, this phenomenon remains minimal, with only 18.6% of groundwater samples indicating saline contamination (Table 5).
The underlying geology strongly influences the water quality. Excellent-to-good groundwater quality is found along the Lagh Dera River downstream of Habaswein, likely due to its proximity to a recharge zone via alluvial deposits [72] and highly transmissive aquifer materials [69]. Transmissivity is highest along the Lagh Dera River and decreases laterally away from it [64,67,69], which may explain the decline in water quality in those areas. Clay material with low transmissivity dominates the central part of the study area along Lagh Dera. These clay formations slow down the groundwater flow, causing clogging and swampy conditions in the section. This causes surface water to evaporate, leading to the accumulation of salt that slowly recharges the deeper aquifer. In this zone, the groundwater is typically older [64] and saline, leading to poorer drinking water quality. Given that groundwater is the main source of potable water in the region, appropriate treatment methods such as desalination are essential to protect public health.
The dwellers in the study area are nomadic pastoralists, and most groundwater is suitable for livestock consumption according to FAO (2016) standards. Concerning irrigation, most of the groundwater had high salinity and alkalinity, as exemplified by the high SAR indices, and therefore, was unsuitable for irrigation purposes. Moreover, with regard to the irrigation water quality index, most of the groundwaters were classified into the high and severe restriction categories. The severity pattern is similar to that of the drinking water quality index, with good-to-moderate quality groundwater occurring along the Lagh Dera. This poor quality was interpreted to be a result of long groundwater residence time, poor transmissivity of the aquifer materials, and increasing distances to zones of groundwater recharge [64,69,72]. Prolonged application of saline water for irrigation can cause poor soil permeability. Furthermore, saline water may affect osmotic activities, inhibiting crop germination and growth [45,46]. Hence, water treatment, such as desalination, and soil treatment, such as the addition of gypsum, are essential if irrigation is carried out. Adding gypsum may help prevent sodium from displacing the adsorbed calcium and magnesium in the soil, which causes damage to the soil structure [117,118].
5. Conclusions
This study successfully achieved its objectives by identifying the primary geochemical processes influencing groundwater in the Ewaso Ngi’iro–Lagh Dera basin. The groundwater is predominantly fresh to brackish, with Na-HCO3 as the dominant water type. Sodium (Na+) is the most abundant cation, while bicarbonate (HCO3−) is the most abundant anion. The groundwater chemistry in the study area is shaped by natural processes, such as ion exchange, mixing fresh and paleo-saline water, silicate weathering, and calcite and dolomite precipitation and dissolution.
The findings of this study enhance our understanding of how hydrogeochemistry affects groundwater quality in the basin. An assessment of drinking water quality based on WHO (2017) standards indicates that the average levels of TDS, Cl−, SO42−, Ca2+, Mg2+, and total hardness (TH) are within permissible limits. Thus, most groundwater samples have good WQI. However, elevated EC, HCO3−, and Na+ values render some groundwater to have a poor-to-unsuitable drinking water quality index (WQI) rating.
Irrigation suitability, assessed using SAR, reveals moderate-to-high salinity and alkalinity hazards in the groundwater. The IWQI rating of the groundwater, calculated using the EC, SAR, Cl−, HCO3−, and Na+ concentration, showed that groundwater is mostly in the mostly in the moderate—severe restrictions categories. Consequently, most groundwater samples are not suitable for irrigation without proper management. This study recommends that (1) careful management and treatment are necessary to utilize groundwater for domestic and agricultural purposes safely. (2) Farming practices should focus on crops that tolerate high salinity levels. (3) Regular groundwater quality monitoring is essential to understand spatial and temporal variations, enabling sustainable groundwater management in the basin. We also recommend further studies investigating groundwater salinization processes in the aquifer using advanced geochemical and isotopic techniques. This will provide deeper insights into salinization mechanisms and support long-term groundwater sustainability in the region.
Author Contributions
G.T.W.: Conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, data curation, and writing of the original draft paper. D.E.W.: Visualization, supervision, writing, review, and editing. K.Z.N.: Visualization, methodology, supervision, writing, review, and editing. O.D.O.: Visualization, supervision, validating, writing, review, and editing. G.C.M.: Investigation, data curation, writing, review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The Authors of this research manuscript acknowledge the Department of Earth and Climate Science, University of Nairobi, for the provision of facilities used in this research. We also acknowledge Earthwater Limited for providing the resources used in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Gicheruh Chrysanthus Muchori was employed by the company Earth Water Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| TDS | Total Dissolved Solids |
| WQI | Water Quality Index |
| IWQI | Irrigation Water Quality Index |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WASREB | Water Services Regulatory Board |
| NOCK | National Oil Corporation Kenya |
References
- Shiklomanov, I. World fresh water resources. In Water in Crisis: A Guide to the World’s Fresh Water Resources; Gleick, P.H., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Edmunds, W.M. Hydrogeochemical processes in arid and semi-arid regions—Focus on North Africa. In Understanding Water in a Dry Environment; CRC Press: London, UK, 2003; pp. 267–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetsiers, M.; Walraevens, K. Chemical characterization of the Neogene Aquifer, Belgium. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumari, K.; Singh, U.K.; Ramanathan, A.L. Hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Muktsar, Punjab: Conventional graphical and multivariate statistical approach. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenini, I.; Farhat, B.; Ben Mammou, A. Identification of major sources controlling groundwater chemistry from a multilayered aquifer system. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2010, 22, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, R.; Brindha, K.; Murugan, R.; Elango, L. Influence of hydrogeochemical processes on temporal changes in groundwater quality in a part of Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Etikala, B.; Adimalla, N.; Madhav, S.; Somagouni, S.G.; Keshava Kiran Kumar, P.L. Salinity problems in groundwater and management strategies in arid and semi-arid regions. In Groundwater Geochemistry: Pollution and Remediation Methods; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, H.; Haftu, S. Hydrogeochemical studies of groundwater in semi-arid areas of northern Ethiopia using geospatial methods and multivariate statistical analysis techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghrib, F.; Bahaj, T.; El Kasmi, S.; Hilali, M.; Kacimi, I.; Nouayti, N.; Dakak, H.; Bouzekraoui, M.; El Fatni, O.; Hammani, O. Hydrogeochemical study of groundwater in arid and semi-arid regions of the Infracenomanian aquifers (Cretaceous Errachidia basin, Southeastern Morocco). Using hydrochemical modeling and multivariate statistical analysis. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2024, 209, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, J. The role of regional gravity flow in the chemical and thermal evolution of ground water. In Proceedings of the First Canadian/American Conference on Hydrogeology, Practical Applications of Ground Water Geochemistry, Worthington, OH, USA, 22–26 June 1984; pp. 3–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmanan, E.; Kannan, R.; Kumar, M.S. Major ion chemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes of ground water in a part of Kancheepuram district, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Geosci. 2003, 10, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, B.; Peterson, E.W.; Honings, J.; Oberhelman, A.; Oware, P.; Rusthoven, I.; Watson, A. Differentiation of Surface Water and Groundwater in a Karst System Using Anthropogenic Signatures. Geosciences 2019, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippi, F.M.; Iacurto, S.; Grelle, G.; Sappa, G. Magnesium as Environmental Tracer for Karst Spring Baseflow/Overflow Assessment—A Case Study of the Pertuso Karst Spring (Latium Region, Italy). Water 2021, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizro, A.T.; Voudouris, K.S. Groundwater quality in the semi-arid region of the Chahardouly basin, West Iran. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3066–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenini, I.; Mammou, A.B.; Turki, M.M. Groundwater resources of a multilayered aquiferous system in arid area: Data analysis and water budgeting. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 5, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, M.V.; Chidambaram, S.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. Statistical analysis of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in hard and sedimentary aquifers system of Gadilam river basin, South India. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2010, 22, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, F.K.; Nazzal, Y.; Jafri, M.K.; Naeem, M.; Ahmed, I. Reverse ion exchange as a major process controlling the groundwater chemistry in an arid environment: A case study from northwestern Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajil Kumar, P.J.; James, E.J. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes in the Coimbatore district, Tamil Nadu, India. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamma, B.; Alodah, A.; Bouaicha, F.; Bekkouche, M.F.; Barkat, A.; Hussein, E.E. Hydrochemical assessment of groundwater using multivariate statistical methods and water quality indices (WQIs). Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kura, N.U.; Ramli, M.F.; Sulaiman, W.N.A.; Ibrahim, S.; Aris, A.Z.; Mustapha, A. Evaluation of factors influencing the groundwater chemistry in a small tropical island of Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 10, 1861–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R.K. Principal component analysis and hydrochemical facies characterization to evaluate groundwater quality in Varahi river basin, Karnataka state, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Zou, J.; Zhen, P. Multivariate statistical analysis of chemical and stable isotopic data as indicative of groundwater evolution with reduced exploitation. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenning, R.J.; Erickson, G.A. Interpretation and analysis of complex environmental data using chemometric methods. Trends Anal. Chem. 1994, 13, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helena, B.; Pardo, R.; Vega, M.; Barrado, E.; Fernandez, J.M.; Fernandez, L. Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res. 2000, 34, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassane, A.; Trabelsi, R.; Dovonon, L.F.; Odeloui, D.J.; Boukari, M.; Zouari, K.; Mama, D. Chemical evolution of the continental terminal shallow aquifer in the south of coastal sedimentary basin of Benin (West-Africa) using multivariate factor analysis. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2015, 7, 496–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okiongbo, K.S.; Douglas, R.K. Evaluation of major factors influencing the geochemistry of groundwater using graphical and multivariate statistical methods in Yenagoa city, Southern Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.E. A User’s User’s Guide to Principal Components; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Meglen, R.R. Examining large databases: A chemometric approach using principal component analysis. Mar. Chem. 1992, 39, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M. Application of Multivariate analysis to study water chemistry of groundwater in a semi-arid aquifer, Malayer, Western Iran. Desalination Water Treat. 2010, 19, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarrah, N.; Walraevens, K. Groundwater Overexploitation and Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Areas of Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Water 2018, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Gupta, R.; Singh, A.N.; Shrinivas, A. Assessment and monitoring of groundwater quality in semi–arid region. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.K. An index number system for rating water quality. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1965, 37, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A water quality index-do we dare. Water Sew. Work. 1970, 117, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ott, W.R. Water Quality Indices: A Survey of Indices Used in the United States; Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Office of Monitoring and Technical Support: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Boah, D.K.; Twum, S.B.; Pelig-Ba, K.B. Mathematical computation of water quality index of Vea dam in upper east region of Ghana. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P.; Venkatayogi, S. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes and Integrated Interpretation with Water Quality Index Studies. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batarseh, M.; Imreizeeq, E.; Tilev, S.; Al Alaween, M.; Suleiman, W.; Al Remeithi, A.M.; Al Tamimi, M.K.; Al Alawneh, M. Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation in the arid regions using irrigation water quality index (IWQI) and GIS-Zoning maps: Case study from Abu Dhabi Emirate, UAE. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 14, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’nassri, S.; El Amri, A.; Nasri, N.; Majdoub, R. Estimation of irrigation water quality index in a semi-arid environment using data-driven approach. Water Supply 2022, 22, 5161–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Saleh, A.H.; Hussein, H.; Elsayed, S.; Farouk, M. Water quality evaluation and prediction using irrigation indices, artificial neural networks, and partial least square regression models for the Nile River, Egypt. Water 2023, 15, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyango, G.W.; Bhowmick, G.D.; Bhattacharya, N.S. A Critical Review of Irrigation Water Quality Index and Water Quality Management Practices in Micro-Irrigation for Efficient Policy Making. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 318, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, A.C.M.; Andrade, E.M.D.; Chaves, L.C.G.; Frischkorn, H.; Crisostomo, L.A. A new proposal of the classification of irrigation water. Rev. Cienc. Agron. 2010, 41, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation: Rome, Italy, 1985; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Cotruvo, J.A. WHO guidelines for drinking water quality: First addendum to the fourth edition. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2017, 109, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaraja, C.; Chidambaram, S.; Anandhan, P.; Thivya, C.; Thilagavathi, R.; Sarathidasan, J. Hydrochemistry of groundwater in a coastal region and its repercussion on quality, a case study—Thoothukudi district, Tamil Nadu, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, J.; Menggui, J.; Shah, M.H.; Shahab, A.; Rehman, F.; Rasool, U. Integrated approach to hydrogeochemical appraisal and quality assessment of groundwater from Sargodha District, Pakistan. Geofluids 2020, 1, 6621038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Services Regulatory Board. Drinking Water Quality and Effluent Monitoring Guideline; Water Services Regulatory Board: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016; Available online: https://wasreb.go.ke/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Drinking-Water-Guidelines-gwqem_Edited.pdf (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- Drechsel, P.; Marjani Zadeh, S.; Pedrero, F. Water Quality in Agriculture: Risks and Risk Mitigation; FAO & IWMI: Italy, Rome, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olago, D.O. Constraints and solutions for groundwater development, supply and governance in urban areas in Kenya. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1031–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenya National Bureau of Statistics. 2019 Kenya Population and Housing Census: Analytical Report on Population Projections (Volume XVI); National Bureau of Statistics: Nairobi, Kenya, 2022. Available online: https://www.knbs.or.ke/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/2019-Kenya-population-and-Housing-Census-Analytical-Report-on-Population-Projections.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Osman, A.D. Groundwater Quality in Wajir (Kenya) Shallow Aquifer: An Examination of the Association Between Water Quality and Water-Borne Diseases in Children. Ph. D. Thesis, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Australia, 2012. Available online: https://opal.latrobe.edu.au/articles/thesis/Groundwater_quality_in_Wajir_Kenya_shallow_aquifer_an_examination_of_the_association_between_water_quality_and_water-borne_diseases_in_children/21845703?file=38768880 (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Okello, C.; Tomasello, B.; Greggio, N.; Wambiji, N.; Antonellini, M. Impact of Population Growth and Climate Change on the Freshwater Resources of Lamu Island, Kenya. Water 2015, 7, 1264–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H. Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: A case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyoro, J.K. Agriculture and Rural Growth in Kenya; Tegemeo Institute: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandro, S.; Caballero, J.; Simpkin, S.; Lichte, J. Kenya Agricultural Risk Assessment; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; Available online: https://bit.ly/2RnCyhP (accessed on 4 March 2024).
- Ericksen, P.J.; Said, M.Y.; Leeuw, J.D.; Silvestri, S.; Zaibet, L.; Kifugo, S.C.; Sijmons, K.; Kinoti, J.; Ng’ang’a, L.; Landsberg, F.; et al. Mapping and Valuing Ecosystem Services in the EWASO Ng’iro Ng’iro Watershed; ILRI: Nairobi, Kenya, 2011; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/12483 (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Rakotoarisoa, M.; Massawe, S.C.; Mude, A.G.; Ouma, R.; Freeman, H.A.; Bahiigwa, G.; Karugia, J.T. Investment Opportunities for Livestock in the North Eastern Province of Kenya: A Synthesis of Existing Knowledge; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10568/187 (accessed on 4 March 2024).
- Muya, E.M.; Obanyi, S.; Ngutu, M.; Sijali, I.V.; Okoti, M.; Maingi, P.M.; Bulle, H. The Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Soils of Northern Kenya Aridlands: Opportunity for Sustainable Agricultural Production. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2011, 2, 1–8. Available online: http://www.academicjournals.org/JSSEM (accessed on 4 March 2024).
- Turman-Bryant, N.; Nagel, C.; Stover, L.; Muragijimana, C.; Thomas, E.A. Improved Drought Resilience Through Continuous Water Service Monitoring and Specialized Institutions—A Longitudinal Analysis of Water Service Delivery Across Motorized Boreholes in Northern Kenya. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.A.; Needoba, J.; Kaberia, D.; Butterworth, J.; Adams, E.C.; Oduor, P.; Macharia, D.; Mitheu, F.; Mugo, R.; Nagel, C. Quantifying increased groundwater demand from prolonged drought in the East African Rift Valley. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazadeh, N.; Chitsazan, M.; Golestan, Y. Hydrochemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in the Ardabil area, Iran. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3599–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarzenski, W.V.; Mundorff, M.J. Geohydrology of North Eastern Province, Kenya; USGS Water Supply Paper, 1757-N; USGS Publications Warehouse: Reston, VA, USA, 1977; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Mwango, F.K.; Muhangú, B.C.; Juma, C.O.; Githae, I.T. Groundwater resources in Kenya. In Managing Shared Aquifer Resources in Africa; ISARM-AFRICA: Tripoli, Libya, 2002; pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- GIBB (Eastern Africa) Ltd. Study of the Merti Aquifer; Technical Report Issue 2.0; UNICEF Kenya Country Office: Nairobi, Kenya, 2004; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Mumma, A.; Lane, M.; Kairu, E.; Tuinhof, A.; Hirji, R. Kenya Groundwater Governance; Case Study Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kuria, D.N.; Kamunge, H.N. Merti Aquifer Recharge Zones Determination Using Geospatial Technologies; Dedan Kimathi University of Technology: Nyeri, Kenya, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Earth Water Ltd. Phase 1—Aquifer Monitoring. Merti Aquifer Study; EarthWater Ltd.: Nairobi, Kenya, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- IGAD Design and Development of a Data System for the Application of Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) in the Merti Aquifer. Technical Report Inland Water Resources Management Programme. 2015. Available online: https://www.un-igrac.org/special-project/igad-mar (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Blandenier, L. Recharge Quantification and Continental Freshwater Lens Dynamics in Arid Regions: Application to the Merti aquifer (Eastern Kenya). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Neuchâtel, Neuchâtel, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Krhoda, G.; Amimo, M.O. Groundwater quality prediction using logistic regression model for Garissa county. Afr. J. Phys. Sci. 2019, 3, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Luedeling, E.; Arjen, L.O.; Boniface, K.; Sarah, O.; Maimbo, M.; Keith, D.S. Fresh groundwater for Wajir—Ex-ante assessment of uncertain benefits for multiple stakeholders in a water supply project in Northern Kenya. Front. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githinji, T.W.; Dindi, E.W.; Kuria, Z.N.; Olago, D.O. Application of analytical hierarchy process and integrated fuzzy-analytical hierarchy process for mapping potential groundwater recharge zone using GIS in the arid areas of Ewaso Ng’iro–Lagh Dera Basin, Kenya. HydroResearch 2022, 5, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklash, M.G.; Mwangi, M.P. An Isotopic Study of Groundwater Supplies in the Eastern Province of Kenya. J. Hydrol. 1991, 128, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, I.M. A Preliminary Assessment of the Hydrogeology and Hydrochemistry of the Merti Aquifer (North Eastern Province, Kenya: And Lower Juba. Somalia. Unpublished Thesis, University College London, London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gachanja, A.; Tole, M. Management of Ground Water Resources of The MertiAquifer Preliminary Report; Ministry of Environment and Natural resources, Department of Water: Nairobi, Kenya, 2002.
- Reeves, C.V.; Karanja, F.M.; MacLeod, I.N. Geophysical evidence for a failed Jurassic rift and triple junction in Kenya. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1987, 81, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, L.C.; Richards, D.R.; Johnson, R.A. Crustal structure and tectonic evolution of the Anza rift, northern Kenya. Tectonophysics 1991, 197, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W. Mesozoic and early tertiary rift tectonics in East Africa. Seismology and relate sciences in East Africa. Tectonophysics 1992, 209, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W.; Morley, C.K. Structural and stratigraphic evolution of the Anza rift, Kenya. Tectonophysics 1994, 236, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, F.J. Geology of the Garbatula Area, (Degree Sheet 37, NE); Geological Survey of Kenya: Nairobi, Kenya, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Dindi, E.W. Crustal structure of the Anza graben from gravity and magnetic investigations. Tectonophysics 1994, 236, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Oil Corporation Kenya (NOCK). Geological Map of Kenya with Bouguer Gravity Contours; Ministry of Energy and Regional Development: Nairobi, Kenya, 1987.
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11885:2007; Water Quality–Determination of Selected Elements by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES), 2nd ed. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; p. 28.
- Roy, A.; Keesari, T.; Mohokar, H.; Pant, D.; Sinha, U.K.; Mendhekar, G.N. Geochemical evolution of groundwater in hard-rock aquifers of South India using statistical and modelling techniques. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 951–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Baba, M.; Kayastha, P.; Huysmans, M.; De Smedt, F. Evaluation of the Groundwater Quality Using the Water Quality Index and Geostatistical Analysis in the Dier al-Balah Governorate, Gaza Strip, Palestine. Water 2020, 12, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, H.J.; Farhat, B.; Ben Mammou, A.; Oueslati, N. Characterization of recharge mechanisms and sources of groundwater salinization in Ras Jbel coastal aquifer (Northeast Tunisia) using hydrogeochemical tools, environmental isotopes, GIS, and statistics. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 8610894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, A.K. Hydrogeochemical investigation and groundwater quality assessment of Pratapgarh district, Uttar Pradesh. J. Geol. Soc. India 2014, 83, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater & Pollution; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sandilands, D. Bivariate Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research; Michalos, A.C., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauth, M.H. Bivariate Statistics. In MATLAB® Recipes for Earth Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelshafy, M.; Saber, M.; Abdelhaleem, A.; Abdelrazek, S.M.; Seleem, E.M. Hydrogeochemical processes and evaluation of groundwater aquifer at Sohag city, Egypt. Sci. Afr. 2019, 6, e00196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, N.; Senthilkumar, M.; Alqarawy, A.M. Hydrogeochemistry and its relationship with land use pattern and monsoon in hard rock aquifer. Appl. Water Sci. 2025, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdessamed, D.; Jodar-Abellan, A.; Ghoneim, S.S.M.; Almaliki, A.; Hussein, E.E.; Pardo, M.Á. Groundwater quality assessment for sustainable human consumption in arid areas based on GIS and water quality index in the watershed of Ain Sefra (SW of Algeria). Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.H.; Megahed, H.A.; Sayed, A.G.; Abdalla, O.; Scopa, A.; Hassan, S.H.A. Hydro-Geochemistry and Water Quality Index Assessment in the Dakhla Oasis, Egypt. Hydrology 2024, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, A.K.; Pandey, H.K.; Tiwari, S.K.; Prakash, R.; Pandey, P.; Ram, A. Groundwater quality assessment using Water Quality Index (WQI) in parts of Varanasi District, Uttar Pradesh, India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejashvini, A.; Subbarayappa, C.T.; Mudalagiriyappa; Chowdappa, H.D.; Ramamurthy, V. Assessment of irrigation water quality for groundwater in Semi-Arid Region, Bangalore, Karnataka. Water Sci. 2024, 38, 548–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, N.C.; Singh, V.S.; Rangarajan, R. Aquifer characteristics and its modeling around an industrial complex, Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu, India: A case study. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 118, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; Balkema publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2005; p. 683. [Google Scholar]
- Schoeller, H. Geochemistry of groundwater. In Groundwaterstudies—An International Guide for Research and Practice; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1977; Chapter 15; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Schoeller, H. Hydrodynamique Lans Lekarst (Ecoulemented Emmagusinement); Actes Colloques Doubronik, I, AIHS et UNESCO: Paris, France, 1965; pp. 3–20. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usf.edu/kip_articles/8272 (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- García, G.M.; Hidalgo, M.d.V.; Blesa, M.A. Geochemistry of groundwater in the alluvial plain of Tucuman province, Argentina. Hydrogeol. J. 2001, 9, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.J. Geochemical comparison of groundwater in areas of New England, New York, and Pennsylvania. Groundwater 1989, 27, 690–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oord, A.; Collenteur, R.; Tolk, L. Hydrogeological Assessment of the Merti Aquifer, Kenya. Technical Report. Acacia Water 2014. Available online: https://www.worldagroforestry.org/sites/default/files/TR1%20ARIGA-%20Hydrological%20Assessment%20of%20the%20Merti%20Aquifer%20Kenya.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Chebotarev, I.I. Metamorphism of natural waters in the crust of weathering—2. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 1955, 8, 137–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moujabber, M.E.; Samra, B.B.; Darwish, T.; Atallah, T. Comparison of different indicators for groundwater contamination by seawater intrusion on the Lebanese coast. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudaryanto and Wilda Naily. Ratio of Major Ions in Groundwater to Determine Saltwater Intrusion in Coastal Areas. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 118, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, S.; Sarathidasan, J.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Thivya, C.; Thilagavathi, R.; Prasanna, M.V.; Singaraja, C.; Nepolian, M. Assessment of hydrogeochemical status of groundwater in a coastal region of Southeast coast of India. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Reza, A.H.M.S.; Roy, M.K. Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater quality of the Tista floodplain, Rangpur, Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Singh, D.S. Surface and groundwater quality characterization of Deoria district, Ganga plain, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; US Government Printing Office: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1954; Volume 78.
- Wilcox, L.V. Classification and Use of Irrigation Water (Circular 969); USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; Available online: https://dn720401.ca.archive.org/0/items/classificationus969wilc/classificationus969wilc.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Krhoda, G.O. Groundwater Assessment in Sedimentary Basins of Eastern Kenya, Africa. In Regional Characterization of Water Quality, Proceedings of the a Symposium During the Third Scientific Assembly of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–18 May 1989; International Association of Hydrological Sciences: Wallingford, UK, 1989; pp. 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Sidibe, A.M.; Lin, X.; Koné, S. Assessing groundwater mineralization process, quality, and isotopic recharge origin in the Sahel Region in Africa. Water 2019, 11, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, S.; Atteia, O.; Ursula Salmon, S.; Siade, A.; Douglas, G.; Prommer, H. Identification and quantification of redox and pH buffering processes in a heterogeneous, low carbonate aquifer during managed aquifer recharge. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 4003–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, N.J. Hydrogeochemical parameters for assessment of groundwater quality in the upper Gunjanaeru River basin, Cuddapah District, Andhra Pradesh, South India. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed-Aslam, M.A.; Rizvi, S.S. Hydrogeochemical characterisation and appraisal of groundwater suitability for domestic and irrigational purposes in a semi-arid region, Karnataka state, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).