Impact of Precipitation Uncertainty on Flood Hazard Assessment in the Oueme River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Datasets
2.1.1. Study Site
2.1.2. Datasets
2.2. Precipitation Estimation
2.3. Models
2.3.1. The HBV Model
2.3.2. The HEC–RAS Model
2.3.3. Model Evaluation Criteria
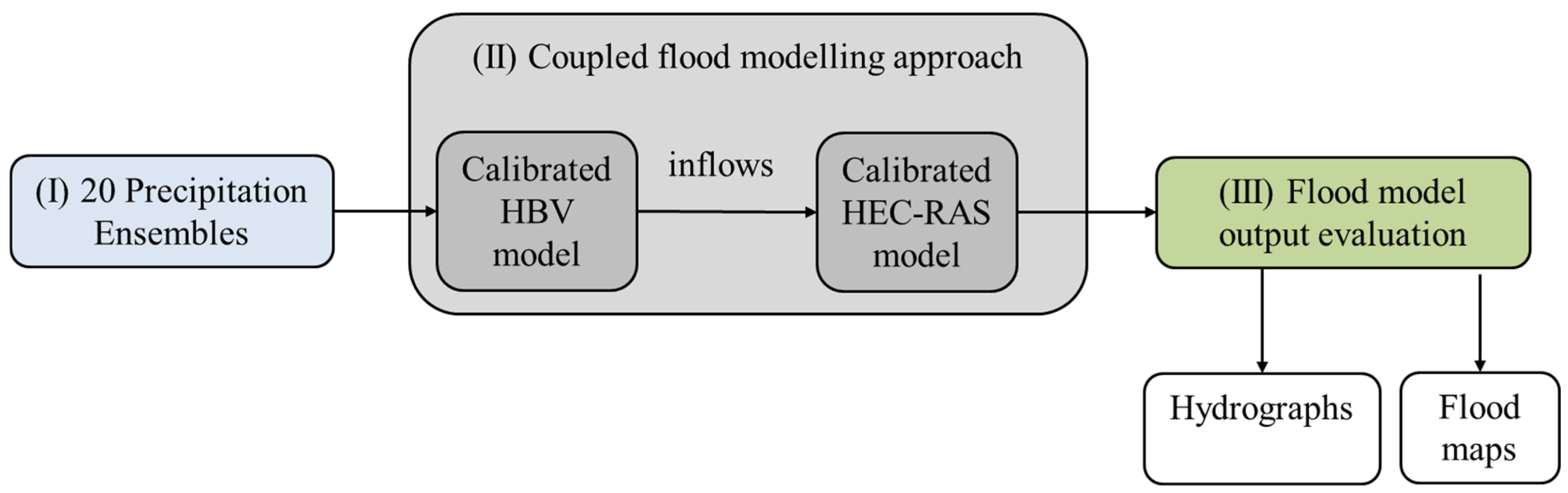
2.3.4. Coupling HBV–HEC–RAS
3. Results
3.1. Model Evaluation
3.1.1. Calibration and Validation of HBV Model
3.1.2. Performance Evaluation of the HEC–RAS Model
3.2. Implications of Precipitation Ensembles on Discharge and Flood Map Modeling
3.2.1. Discharge Comparison
3.2.2. Use of the Flow Rates Resulting from the Coupling of the Two Models
3.2.3. Use of Flood Maps for Uncertainty Estimation
Ensembles Maps
Uncertainty Analysis Through Statistic Descriptions
Flood Occurrence and Flood Probabilities Maps
4. Discussion
4.1. Modeling
4.2. Flood Hazard Maps and Uncertainty
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



Appendix B




References
- Baldassarre, G.D.; Montanari, A. Uncertainty in river discharge observations: A quantitative analysis. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndehedehe, C.E. The water resources of tropical West Africa: Problems, progress, and prospects. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 621–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazen, F.; Diarra, A.; Kabore, R.F.W.; Ibrahim, B.; Bologo/Traoré, M.; Traoré, K.; Karambiri, H. Trends in flood events and their relationship to extreme rainfall in an urban area of Sahelian West Africa: The case study of Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2019, 12, e12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; Villarini, G.; Zhang, W. Observed changes in flood hazard in Africa. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1040b5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounkpè, J.; Diekkrüger, B.; Badou, D.F.; Afouda, A.A. Non-stationary flood frequency analysis in the Ouémé River Basin, Benin Republic. Hydrology 2015, 2, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nka, B.N.; Oudin, L.; Karambiri, H.; Paturel, J.E.; Ribstein, P. Trends in floods in West Africa: Analysis based on 11 catchments in the region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4707–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounkpè, J.; Diekkrüger, B.; Badou, D.F.; Afouda, A.A. Change in heavy rainfall characteristics over the Ouémé River Basin, Benin Republic, West Africa. Climate 2016, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounguè, R. Climate Change Impacts on Hydrodynamic Functioning of Oueme Delta (Benin). Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/345798176 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Logah, F.Y.; Amisigo, A.B.; Obuobie, E.; Kankam-Yeboah, K. Floodplain hydrodynamic modelling of the Lower Volta River in Ghana. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, J.N.; Gyamfi, C.; Arthur, E. Impacts of retention basins on downstream flood peak attenuation in the Odaw river basin, Ghana. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 47, 101364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, S.; Seidou, O.; Konte, D.; Barmou Batoure, M.B. Evaluation of adaptation options to flood risk in a probabilistic framework. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoussou, E.; Amoussou, F.T.; Bossa, A.Y.; Kodja, D.J.; Totin Vodounon, H.S.; Houndenou, C.; Borrell Estupina, V.; Paturel, J.E.; Mahe, G.; Cudennec, C.; et al. Use of the HEC RAS model for the analysis of exceptional floods in the Oueme basin. In Proceedings of the International Association of Hydrological Sciences; Copernicus Publications: Göttingen, Germany, 2024; Volume 385, pp. 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, H.; Thieken, A.H.; Merz, B.; Blöschl, G. Flood risk assessment and associated uncertainty. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 4, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Solomatine, D. A framework for uncertainty analysis in flood risk management decisions. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2008, 6, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guse, B.; Pfannerstill, M.; Kiesel, J.; Strauch, M.; Volk, M.; Fohrer, N. Analysing spatio-temporal process and parameter dynamics in models to characterise contrasting catchments. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, H.L.; Pappenberger, F. Ensemble flood forecasting: A review. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Emerton, R.; Duan, Q.; Wood, A.W.; Wetterhall, F.; Robertson, D.E. Ensemble flood forecasting: Current status and future opportunities. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaba, C.; Alamou, E.; Afouda, A.; Diekkrüger, B. Improvement and comparative assessment of a hydrological modelling approach on 20 catchments of various sizes under different climate conditions. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 1499–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Seidou, O.; Mohammadian, A.; Djibo, A.G.; Liersch, S.; Fournet, S.; Karam, S.; Perera, E.D.P.; Kleynhans, M. Improving the Accuracy of Hydrodynamic Simulations in Data Scarce Environments Using Bayesian Model Averaging: A Case Study of the Inner Niger Delta, Mali, West Africa. Water 2019, 11, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, A.; Kilsby, C.; Birkinshaw, S.; Wang, N.; Anwar, F. Is Precipitation Responsible for the Most Hydrological Model Uncertainty? Front. Water 2022, 4, 836554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Clark, M.P.; Knoben, W.J.M.; Liu, H.; Gharari, S.; Arnal, L.; Beck, H.E.; Wood, A.W.; Newman, A.J.; Papalexiou, S.M. The Impact of Meteorological Forcing Uncertainty on Hydrological Modeling: A Global Analysis of Cryosphere Basins. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner-McGraw, A.P.; Ajami, H. Impact of Uncertainty in Precipitation Forcing Data Sets on the Hydrologic Budget of an Integrated Hydrologic Model in Mountainous Terrain. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, M.; Bernhofer, C.; Koide, S.; Volk, M.; Lorz, C.; Makeschin, F. Using precipitation data ensemble for uncertainty analysis in SWAT streamflow simulation. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhang, C.; Fu, G.; Sweetapple, C.; Zhou, H. Evaluation of global fine-resolution precipitation products and their uncertainty quantification in ensemble discharge simulations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biao, I.E.; Charlene, G.; Eric, A.A.; Abel, A. Influence of the Uncertainties Related to the Random Component of Rainfall Inflow in the Ouémé River Basin (Benin, West Africa). Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2015, 5, 1618–1629. Available online: http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Bergström, S. THE HBVMODEL-Its Structure and Applications. 1992. Available online: https://www.smhi.se/download/18.38e7941719209b36a1fb2c4/1728367395288/RH_4.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Lindström, G.; Johansson, B.; Persson, M.; Gardelin, M.; Bergström, S. Development and Test of the Distributed HBV-96 Hydrological Model. J. Hydrol. 1997, 201, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, G.W.; CEIWR-HEC. HEC-RAS River Analysis System User’s Manuel. Hydrologic Engineering Center. 2016. Available online: https://www.hec.usace.army.mil/software/hec-ras/documentation/HEC-RAS%205.0%20Users%20Manual.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Bossa, A.Y. Multi-Scale Modeling of Sediment and Nutrient Flow Dynamics in the Ouémé Catchment (Benin)—Towards an Assessment of Global Change Effects on Soil Degradation and Water Quality. 2012. Available online: https://docslib.org/doc/9679859/multi-scale-modeling-of-sediment-and-nutrient-flow-dynamics-in-the (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Deng, Z. Vegetation Dynamics in Oueme Basin, Benin, West Africa. 27 November 2007. Available online: https://cuvillier.de/de/shop/publications/1629 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Dègan, B.A.S.; Alamou, E.A.; N’Tcha M’Po, Y.; Afouda, A. Ouémé River Catchment SWAT Model at Bonou Outlet: Model Performance, Predictive Uncertainty and Multi-Site Validation. Hydrology 2018, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djossou, J.; Akpo, A.; Afféwé, J.; Donnou, V.; Liousse, C.; Léon, J.-F.; Nonfodji, F.; Awanou, C. Dynamics of the Inter Tropical Front and Rainy Season Onset in Benin. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, M.; Bliefernicht, J.; Maranan, M.; Fink, A.H.; Kunstmann, H. Geostatistical Simulation of Daily Rainfall Fields—Performance Assessment for Extremes in West Africa. J. Hydrometeorol. 2024, 25, 1425–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Climate Change Service. ERA5-Land Hourly Data from 1950 to Present; Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS): Reading, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, D.; Chilès, J.P.; Delfiner, P.J.-P.; Chilès, P. Delfiner: Geostatistics: Modeling Spatial Uncertainty. Math. Geosci. 2013, 45, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J.; Bergström, S. A retrospective on hydrological catchment modelling based on half a century with the HBV model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 1371–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehanzaib, M.; Ajmal, M.; Achite, M.; Kim, T.W. Comprehensive Review: Advancements in Rainfall-Runoff Modelling for Flood Mitigation. Climate 2022, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, L.; Gan, T.Y.; Scheepers, H.; Islam, M.S. Application of the hbv model for the future projections of water levels using dynamically downscaled global climate model data. J. Water Clim. Change 2021, 12, 2364–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounguè, N.R. Assessment of Mid-Century Climate Change Impacts on Mono River’s Downstream Inflows. 2018. Available online: https://wascal-togo.org/public/images/publication/Rholan_Houngue_thesis_140218-1.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Samani, Z.A. Reference Crop Evapotranspiration from Temperature. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1985, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, C.; Ferro, S.V. Estimation of Evapotranspiration by Hargreaves Formula and Remotely Sensed Data in Semi-arid Mediterranean Areas. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1997, 68, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J. Multi-criteria calibration of a conceptual runoff model using a genetic algorithm. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2000, 4, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J. HBV Light Manual. 2005. Available online: https://www.geo.uzh.ch/dam/jcr:c8afa73c-ac90-478e-a8c7-929eed7b1b62/HBV_manual_2005.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River Flow Forecasting Through Conceptual Models Part I—A Discussion of Principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, H.; Fuchs, M.; Paulin, M. Runoff conditions in the upper Danube basin under an ensemble of climate change scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; McCabe, G.J. Evaluating the use of “goodness-of-fit” Measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossa, A.Y.; Kpossou, M.A.O.; Hounkpè, J.; Badou, F.D. Multi-Model Approach for Assessing the Influence of Calibration Criteria on the Water Balance in Ouémé Basin. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2024, 16, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Liew, M.W.V.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeneghetti, A.; Castellarin, A.; Brath, A. Assessing rating-curve uncertainty and its effects on hydraulic model calibration. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, H.; Dance, S.L.; Mason, D.C.; Bevington, J.; Shelton, K. Spatial scale evaluation of forecast flood inundation maps. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounkpè, J.; Diekkrüger, B.; Afouda, A.A.; Sintondji, L.O.C. Land use change increases flood hazard: A multi-modelling approach to assess change in flood characteristics driven by socio-economic land use change scenarios. Nat. Hazards 2019, 98, 1021–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, M.I.; Slater, L.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Clark, M. Challenges in modeling and predicting floods and droughts: A review. WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gichamo, T.Z.; Tarboton, D.G. Ensemble Streamflow Forecasting Using an Energy Balance Snowmelt Model Coupled to a Distributed Hydrologic Model with Assimilation of Snow and Streamflow Observations. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 10813–10838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Wetterhall, F.; Haiden, T.; Richardson, D.; Salamon, P. Evaluation of ensemble streamflow predictions in Europe. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, A.D.; Viet Dung, N.; Schröter, K.; Vorogushyn, S.; Guse, B.; Kreibich, H.; Merz, B. The role of spatial dependence for large-scale flood risk estimation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enu, K.B.; Merk, F.; Su, H.; Rauch, M.; Zingraff-Hamed, A.; Broich, K.; Förster, K.; Pauleit, S.; Disse, M. A scenario-based analysis of wetlands as nature-based solutions for flood risk mitigation using the TELEMAC-2D model. Nat.-Based Solut. 2025, 7, 100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, M.; Brissette, F.; Leconte, R. Effectiveness of Multi-Site Weather Generator for Hydrological Modeling1: Effectiveness of Multi-site Weather Generator for Hydrological Modeling. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2011, 47, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Zhang, X.J. Hydrological Modeling Using a Multisite Stochastic Weather Generator. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 04015060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Data | Period | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Daily precipitation | 1994–2016 | CS-STBM [33] |
| Daily air temperature | 1994–2016 | Météo Bénin, ERA5 |
| Daily discharge | 1994–2016 | DGEau, Benin |
| Daily water level | 2011–2016 | DG Eau, Benin |
| Flood maps | October 2016 | SENTINEL-1 |
| DEM | - | Copernicus-GLO30 |
| Rating curve | 2011–2016 | DG Eau, Benin |
| Parameter | Explanation | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Snow routine | ||
| TT | Threshold temperature | °C |
| CFMAX | Degree-Δt factor | mm °C−1Δt −1 |
| SFCF | Snowfall correction factor | - |
| CWH | Water holding capacity of snow | - |
| CFR | Refreezing coefficient | - |
| SP | Seasonal variability in degree-Δt factor | - |
| Soil moisture routine | ||
| FC | Field capacity: Maximum soil moisture storage | mm |
| LP | Soil moisture value above which AET reaches PET | - |
| BETA | Shape coefficient | - |
| Response routine | ||
| K0 | Additional recession coefficient of upper groundwater store | Δt −1 |
| K1 | Recession coefficient of upper groundwater store | Δt −1 |
| K2 | Recession coefficient of lower groundwater store | Δt −1 |
| UZL | threshold parameter for K0 outflow | mm |
| PERC | Threshold parameter | mm Δt −1 |
| Routing routine | ||
| MAXBAS | Length of equilateral triangular weighting function | mm Δt −1 |
| Simulated Flooded | Simulated Not Flooded | |
|---|---|---|
| Observed flooded | A (correct flooding) | C (under-prediction) |
| Observed not flooded | B (over-prediction) | D (correct dry) |
| Eff. | Bétérou | Savè | Kaboua | Atchérigbé | Zangnanado | Bonou |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KGE | 0.83 | 0.73 | 0.80 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 0.91 |
| NSE | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.62 | 0.87 | 0.90 |
| NSE-SS | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.46 | 0.80 | 0.82 |
| R2 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.87 | 0.91 |
| Vol-Eff. | 0.93 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.95 |
| Eff. | Bétérou | Savè | Kaboua | Atchérigbé | Zangnanado | Bonou |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KGE | 0.77 | 0.61 | 0.82 | 0.60 | 0.90 | 0.64 |
| NSE | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.51 | 0.89 | 0.77 |
| NSE-SS | 0.73 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.42 | 0.83 | 0.63 |
| R2 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.54 | 0.89 | 0.90 |
| Vol-Eff. | 0.98 | 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 0.95 | 0.75 |
| Eff. | 2011 | 2012 | 2014 | 2016 | Mean of All Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KGE | 0.78 | 0.50 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 0.69 |
| NSE | 0.72 | −0.10 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.53 |
| R2 | 0.72 | 0.50 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afféwé, D.J.; Merk, F.; Bodjrènou, M.; Rauch, M.; Usman, M.N.; Hounkpè, J.; Bliefernicht, J.-G.; Akpo, A.B.; Disse, M.; Adounkpè, J. Impact of Precipitation Uncertainty on Flood Hazard Assessment in the Oueme River Basin. Hydrology 2025, 12, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060138
Afféwé DJ, Merk F, Bodjrènou M, Rauch M, Usman MN, Hounkpè J, Bliefernicht J-G, Akpo AB, Disse M, Adounkpè J. Impact of Precipitation Uncertainty on Flood Hazard Assessment in the Oueme River Basin. Hydrology. 2025; 12(6):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060138
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfféwé, Dognon Jules, Fabian Merk, Marleine Bodjrènou, Manuel Rauch, Muhammad Nabeel Usman, Jean Hounkpè, Jan-Geert Bliefernicht, Aristide B. Akpo, Markus Disse, and Julien Adounkpè. 2025. "Impact of Precipitation Uncertainty on Flood Hazard Assessment in the Oueme River Basin" Hydrology 12, no. 6: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060138
APA StyleAfféwé, D. J., Merk, F., Bodjrènou, M., Rauch, M., Usman, M. N., Hounkpè, J., Bliefernicht, J.-G., Akpo, A. B., Disse, M., & Adounkpè, J. (2025). Impact of Precipitation Uncertainty on Flood Hazard Assessment in the Oueme River Basin. Hydrology, 12(6), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060138








