Mechanisms of Soil Aggregate Stability Influencing Slope Erosion in North China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
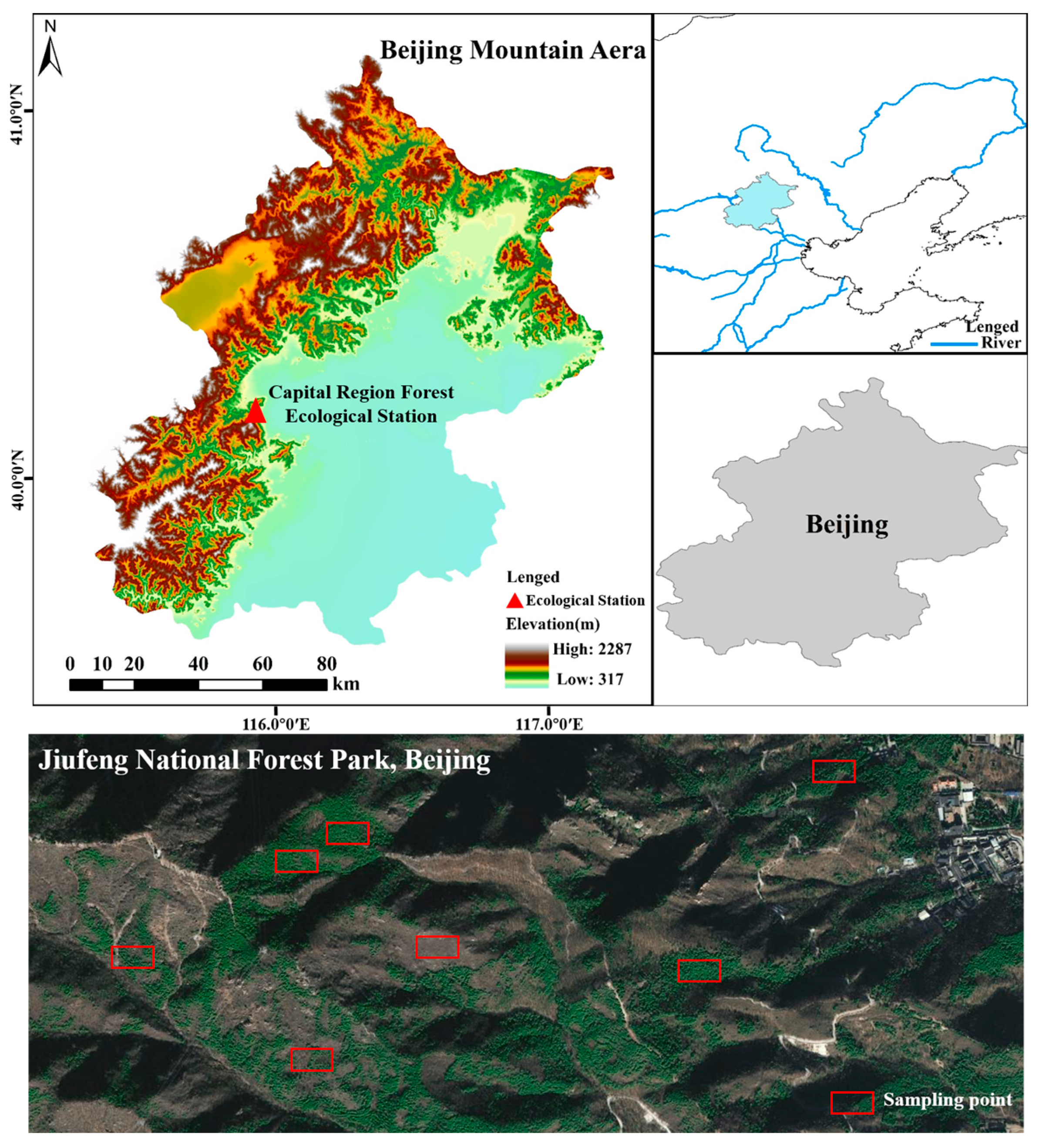
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Field-Based Simulated Rainfall Experiment
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.3.1. Soil Aggregate Stability
2.3.2. Physicochemical Properties
2.3.3. High-Throughput DNA Sequencing and Analysis
2.3.4. Vegetation Root Sampling
2.3.5. Soil Sampling for Microbial Communities
2.3.6. Root Length and Mycorrhizal Colonization
2.4. Soil Erodibility Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
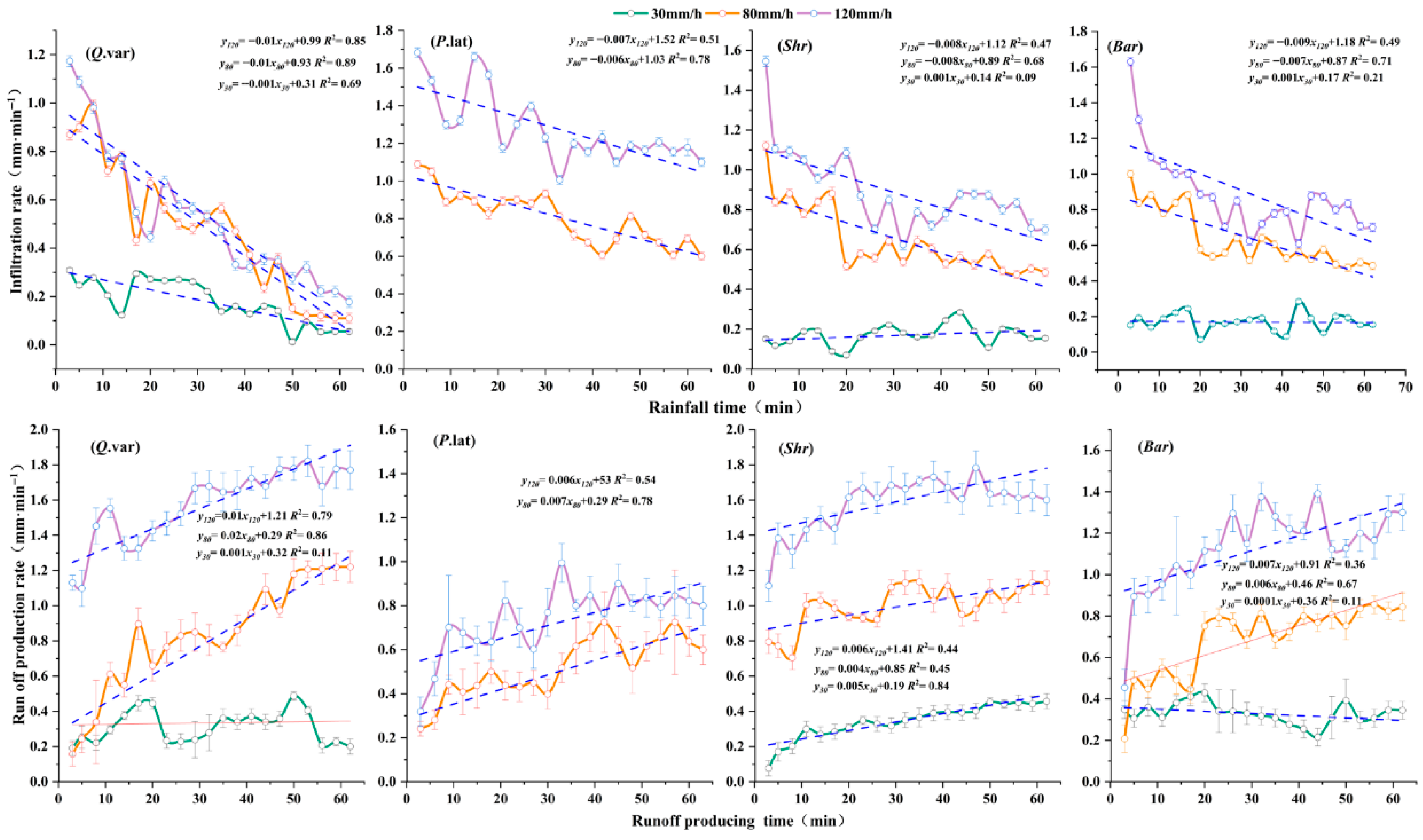
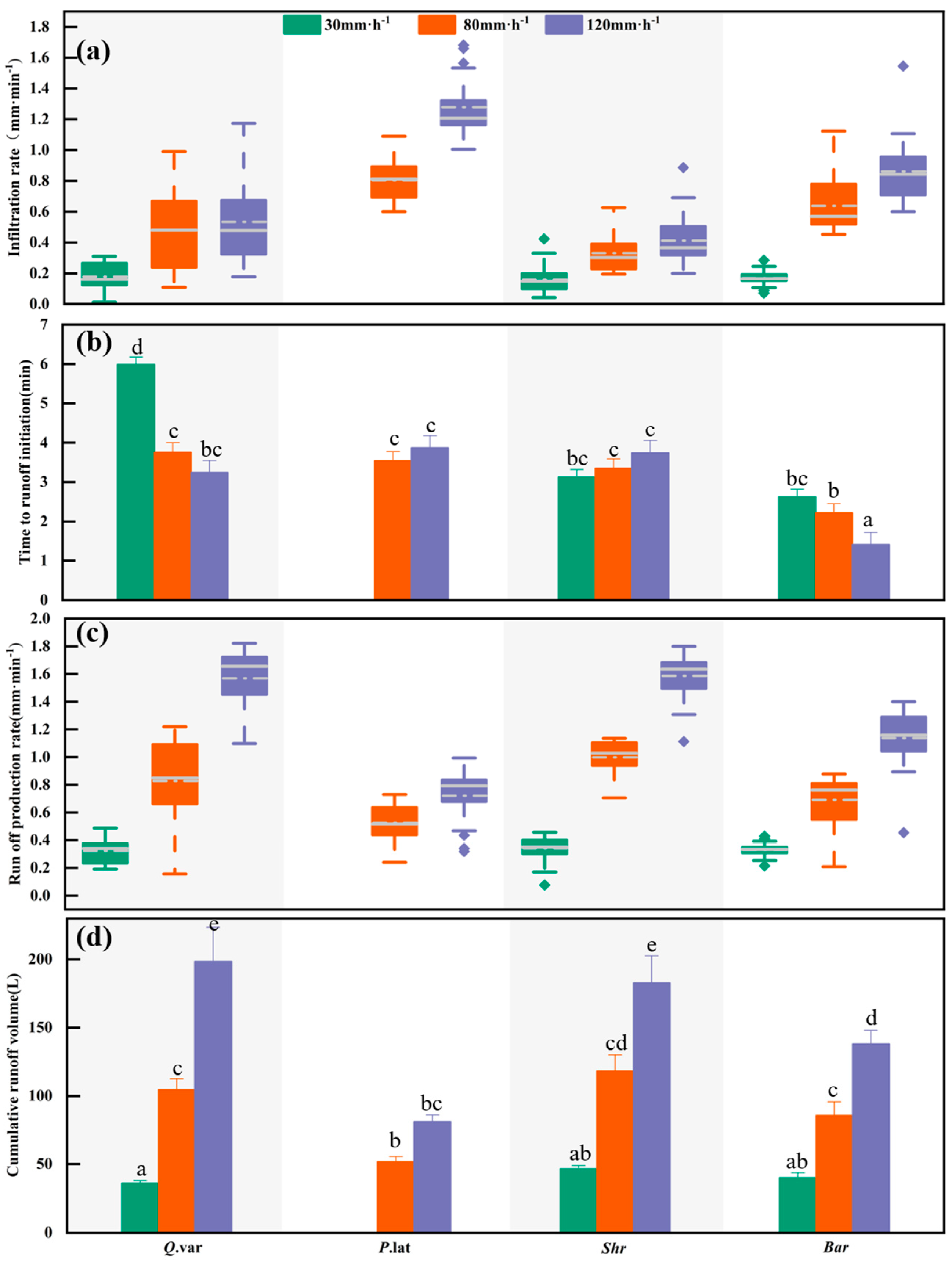
3.1. Variations in Infiltration and Runoff Generation Across Different Vegetation-Type Slopes
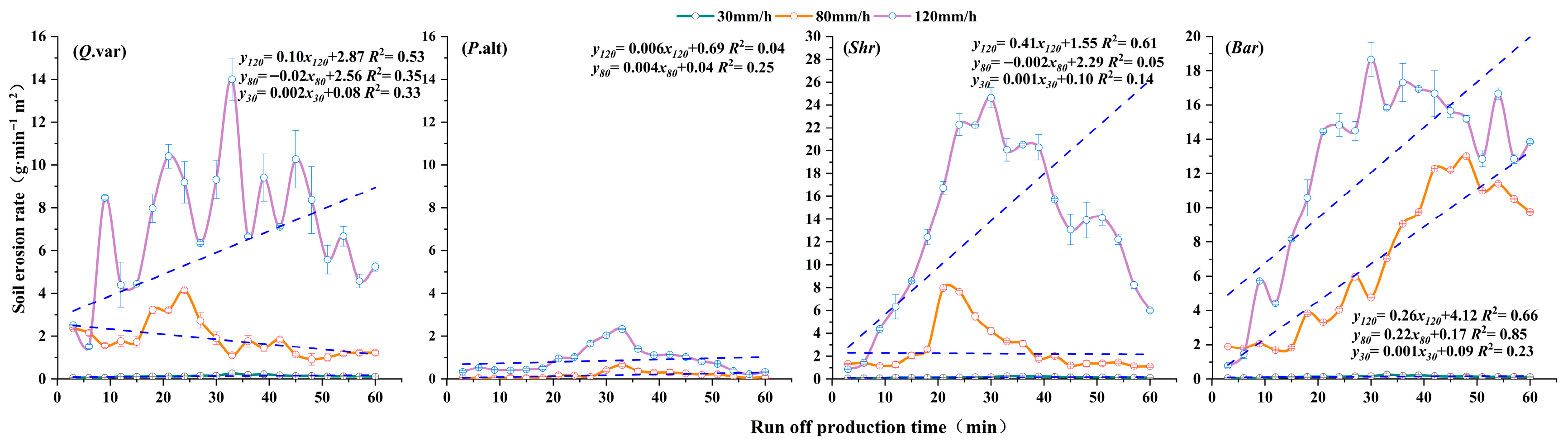
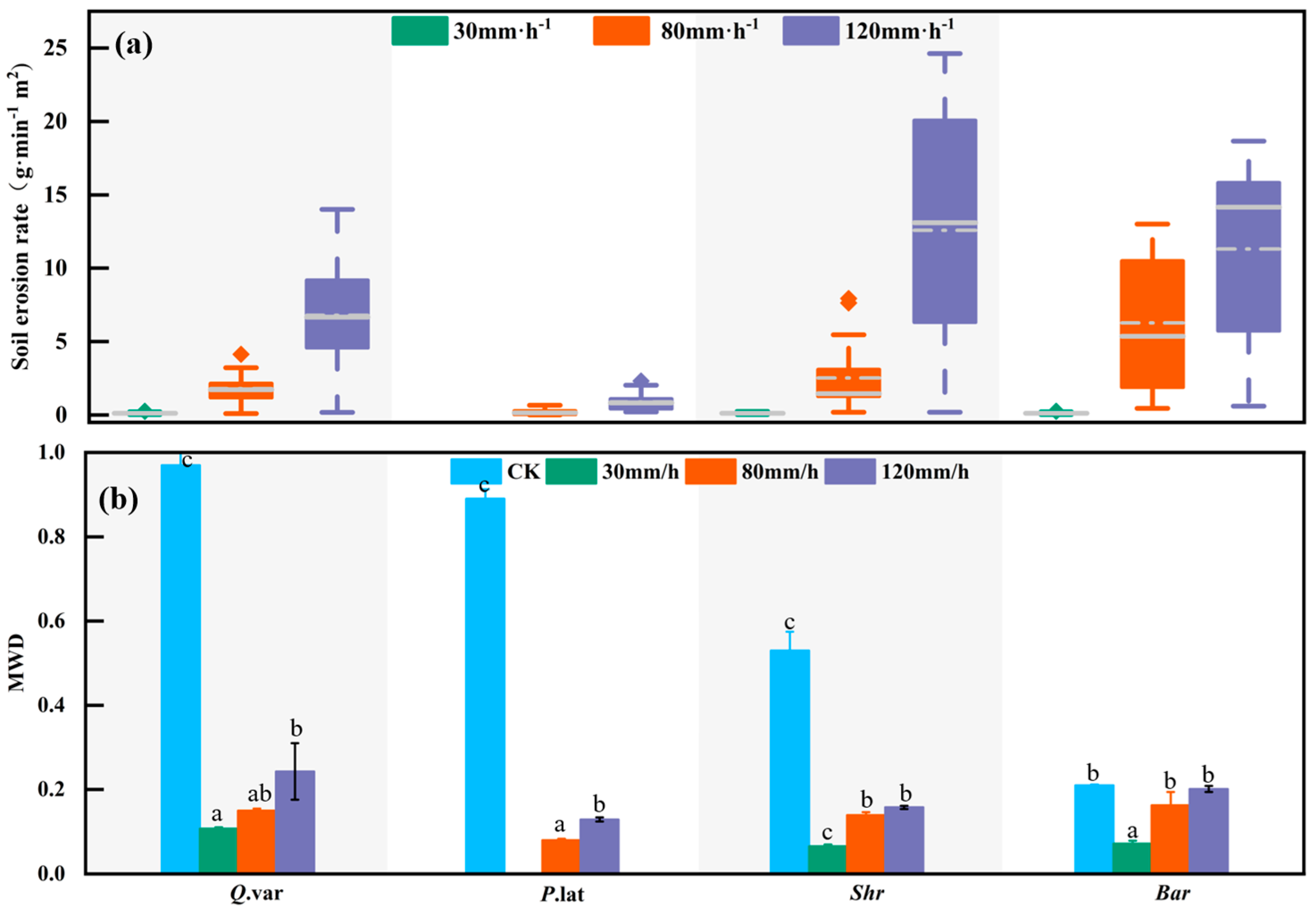
3.2. Slope Soil Loss Mechanisms Under Different Vegetation Types
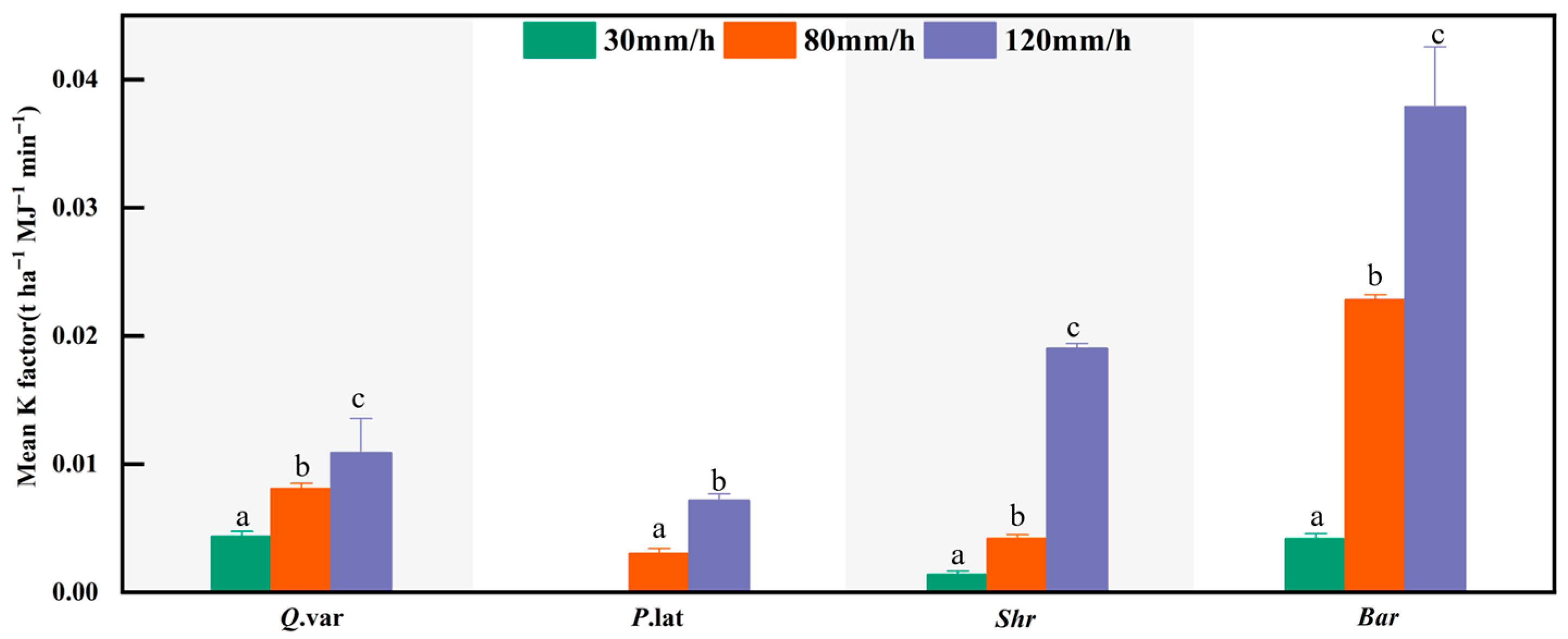
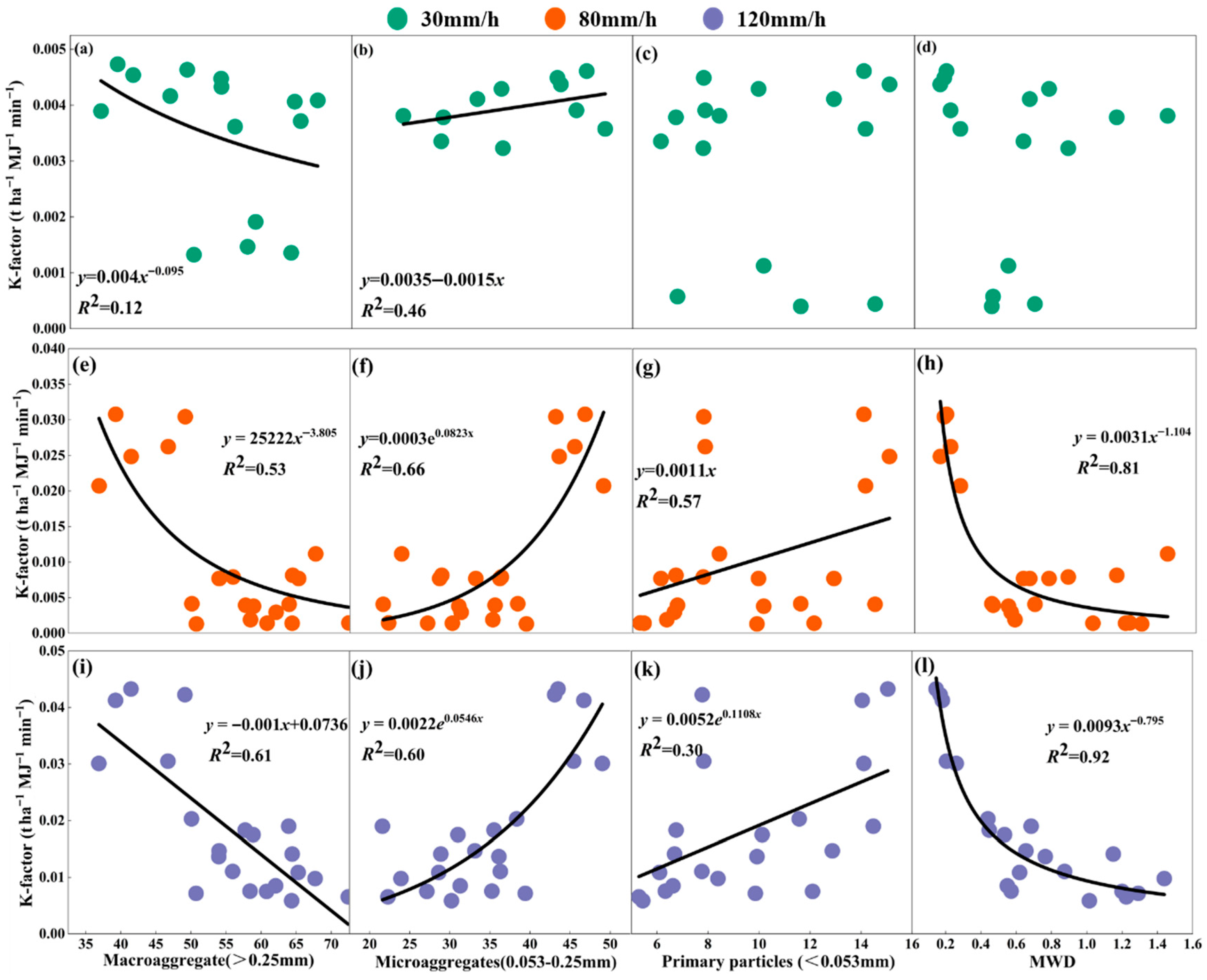
3.3. Impact of Aggregate Stability on Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
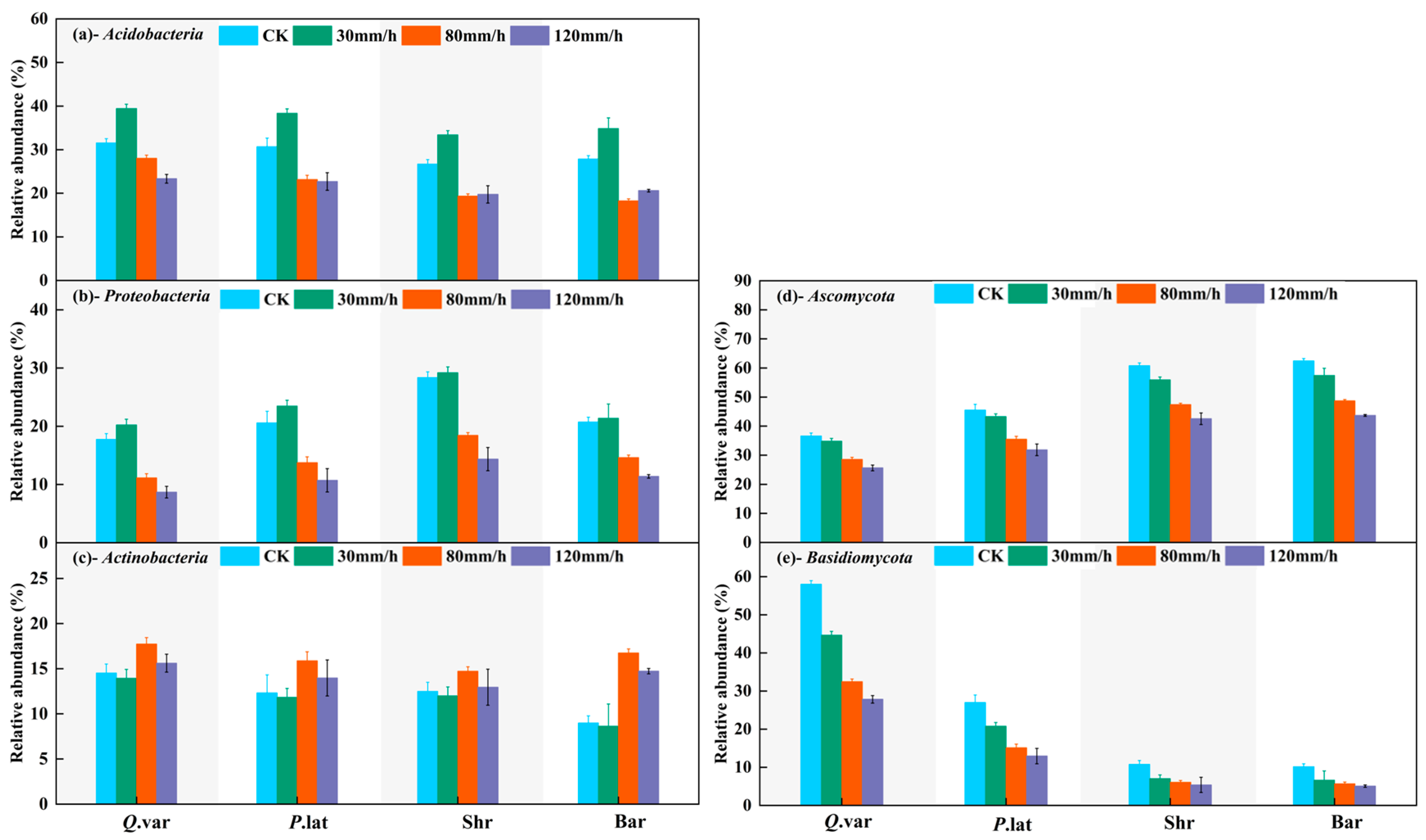
3.4. Key Microbial Community Characteristics After Rainfall Erosion
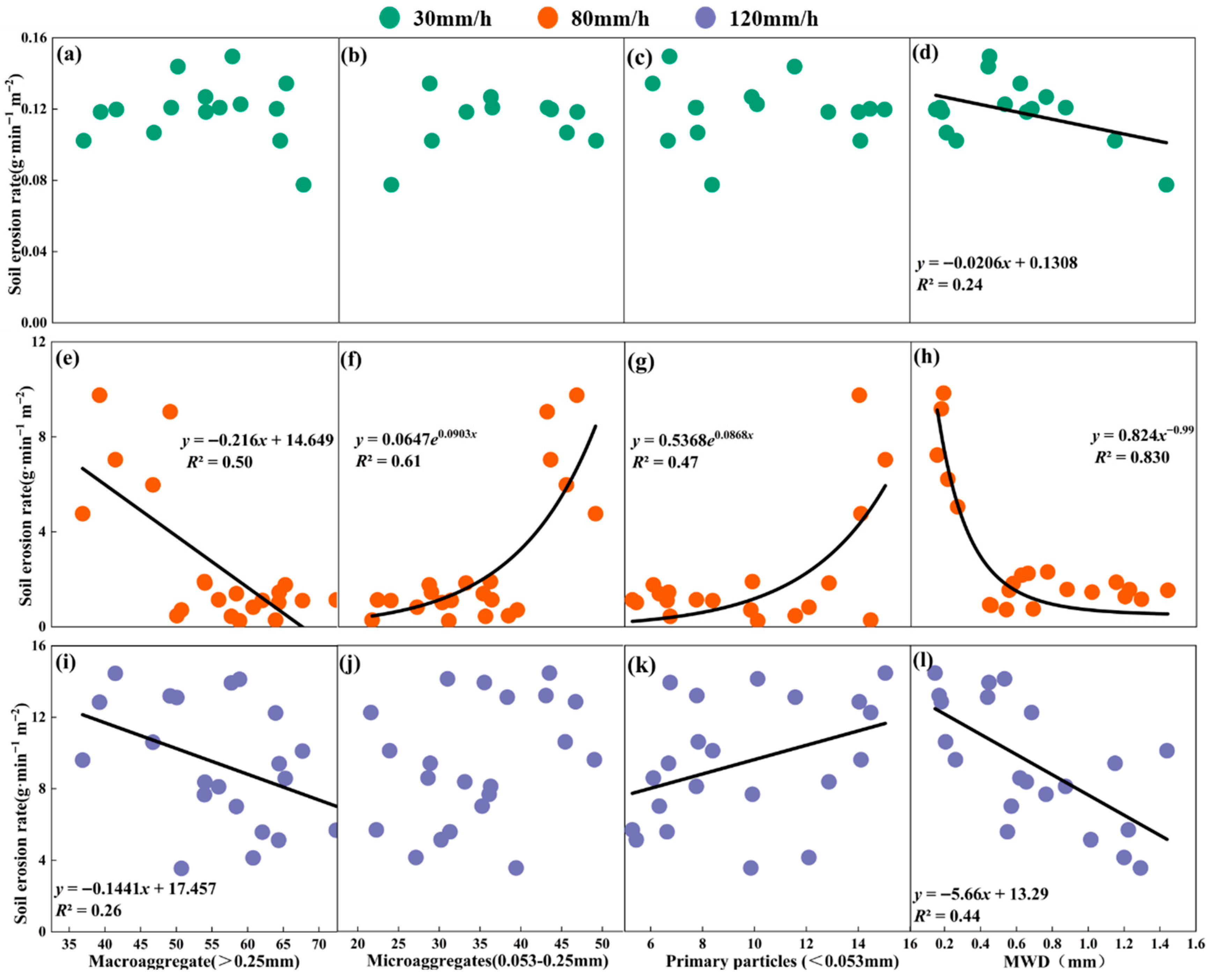
3.5. Analysis of Factors Influencing Slope Erosion Under Different Rainfall Intensities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahmoodabadi, M.; Sajjadi, S.A. Effects of Rain Intensity, Slope Gradient and Particle Size Distribution on the Relative Contributions of Splash and Wash Loads to Rain-Induced Erosion. Geomorphology 2016, 253, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Su, D.; Li, P.; He, Z. Experimental Study of the Impact of Rainfall Characteristics on Runoff Generation and Soil Erosion. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Steiner, J.; Zheng, F.; Gowda, P. Impact of Rainfall Pattern on Interrill Erosion Process. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 1833–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Moussavi, A.; Ghadiri, H.; Rose, C.W. Flow-Driven Soil Erosion Processes and the Size Selectivity of Sediment. J. Hydrol. 2011, 406, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Raindrop-Impact-Induced Erosion Processes and Prediction: A Review. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 2815–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, S.; Seeger, M.; Ries, J.B. Field Experiments for Understanding and Quantification of Rill Erosion Processes. CATENA 2012, 91, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirfam, H.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Darki, B.Z. Soil Conservation in an Abandoned Agricultural Rain-Fed Land through Inoculation of Cyanobacteria. Catena 2020, 187, 104341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet, E.J.; Dunne, T. Sediment Detachment by Rain Power. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, ESG 1-1–ESG 1-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.J.; Wang, Z.L. Interrill Soil Erosion Processes on Steep Slopes. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.B. Soil Erodibility and Processes of Water Erosion on Hillslope. Geomorphology 2000, 32, 385–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Nearing, M.A.; Stone, J.J.; Guertin, D.P.; Spaeth, K.E.; Pierson, F.B.; Nichols, M.H.; Moffet, C.A. A New Splash and Sheet Erosion Equation for Rangelands. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, F.; Li, R.; Yan, B.; Zhang, W.; Jing, J.; Xue, C.; Yi, Z. Rainfall Predominantly Governs Soil Organic Carbon Loss, Exceeding the Contribution of Vegetation Carbon Sequestration in Karst Watersheds. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, ldr.70085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Du, J.; Bahadur, A.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, T.; Chen, S. Soil Erosion and Risk Assessment on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Shang, W.; Luo, H. Effect of Rainfall Intensity and Gravel Content on Hydraulic Characteristics and Hydraulic Parameters on Soil Erosion of Spoil Heaps: Laboratory Experiments with Simulated Rainfall. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2025, 13, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, M.; Raclot, D.; Bahri, H.; Bailly, J.S.; Gomez, C.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Spatial Variability of Soil Aggregate Stability at the Scale of an Agricultural Region in Tunisia. CATENA 2017, 153, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, J.M.; Ferris, J.E.; Remley, P.A. Interrill Soil Erosion Processes: I. Effect of Surface Sealing on Infiltration, Runoff, and Soil Splash Detachment. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhou, J.L.; Cai, Q.; Liu, S.; Xiao, J. Comparing Surface Erosion Processes in Four Soils from the Loess Plateau under Extreme Rainfall Events. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Hansel, C.M.; Kaiser, C.; Kleber, M.; Maher, K.; Manzoni, S.; Nunan, N.; Reichstein, M.; Schimel, J.P.; Torn, M.S. Persistence of Soil Organic Carbon Caused by Functional Complexity. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y. Effects of Four Storm Patterns on Soil Loss from Five Soils under Natural Rainfall. CATENA 2016, 141, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L. Spatiotemporal Evolutionary Analysis of Rainfall Erosivity during 1901–2017 in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 2510–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, W.D.; Rosenau, R.C. Aggregate Stability and Size Distribution. In SSSA Book Series; Klute, A., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 425–442. ISBN 978-0-89118-864-3. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Reich, P.B.; Banerjee, S.; Van Der Heijden, M.G.A.; Sa-dowsky, M.J.; Ishii, S.; Jia, X.; Shao, M.; et al. Erosion Reduces Soil Microbial Diversity, Net-work Complexity and Multifunctionality. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2474–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, L.; Osman, O.A.; Bertilsson, S.; Eiler, A. Microbial Community Composition and Diversity via 16S rRNA Gene Amplicons: Evaluating the Illumina Platform. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, R.C.; Paula, F.S.; Mirza, B.S.; Rodrigues, J.L.M.; Nüsslein, K.; Bohannan, B.J.M. Links between Plant and Fungal Communities across a Deforestation Chronosequence in the Amazon Rainforest. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rillig, M.C.; Wright, S.F.; Allen, M.F.; Field, C.B. Rise in Carbon Dioxide Changes Soil Structure. Nature 1999, 400, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.; Yoder, D.; Weesies, G.; McCool, D.; McGregor, K.; Bingner, R. Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation Version 2; Draft Science Documentation; USDA-Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Runoff Dependent Erosivity and Slope Length Factors Suitable for Modelling Annual Erosion Using the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-16-048938-5. [Google Scholar]
- Vaezi, A.R.; Sadeghi, S.H.R.; Bahrami, H.A.; Mahdian, M.H. Modeling the USLE K-Factor for Calcareous Soils in Northwestern Iran. Geomorphology 2008, 97, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Deng, J.; Gu, C.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Gao, J. Effect of Shrub-Grass Vegetation Coverage and Slope Gradient on Runoff and Sediment Yield under Simulated Rainfall. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gao, J.; He, M.; Jing, J.; Xiong, L.; Chen, M.; Zhao, L. Effect of Rock Exposure on Runoff and Sediment on Karst Slopes under Erosive Rainfall Conditions. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Q.; Zhang, C.; Tong, J.; Wu, S.; Pang, T.; Wang, L. Experimental Study on the Mechanism of Artificial Runoff Generation on Typical Slopes in Farmland of North China. Hydrol. Process. 2025, 39, e70078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, W.J.; Cambardella, C.A.; Bailey, T.B. Root-Derived Carbon and the Formation and Stabilization of Aggregates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, C.O.; Garcia, V.J.; Cambardella, C.A.; Schultz, R.C.; Isenhart, T.M. Aggregate-Size Stability Distribution and Soil Stability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthès, B.; Roose, E. Aggregate Stability as an Indicator of Soil Susceptibility to Runoff and Erosion; Validation at Several Levels. CATENA 2002, 47, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erktan, A.; Cécillon, L.; Graf, F.; Roumet, C.; Legout, C.; Rey, F. Increase in Soil Aggregate Stability along a Mediterranean Successional Gradient in Severely Eroded Gully Bed Ecosystems: Combined Effects of Soil, Root Traits and Plant Community Characteristics. Plant Soil 2016, 398, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, N.; Zhang, B.; Yang, H. Variation in Soil Erodibility under Five Typical Land Uses in a Small Watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 2019, 174, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y. Aggregate Stability and Assessment of Soil Crustability and Erodibility: I. Theory and Methodology. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A History of Research on the Link between (Micro) Aggregates, Soil Biota, and Soil Organic Matter Dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Ben-Hur, M. Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Slope Gradient on the Dynamics of Interrill Erosion during Soil Surface Sealing. Catena 2006, 66, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Ashour, J.; Lee, H. Transport of Bacteria on Sloping Soil Surfaces by Runoff. Environ. Toxicol. 2000, 15, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, N.J.; Hoffmann, T.; Schwanghart, W.; Dotterweich, M. Agricultural Soil Erosion and Global Carbon Cycle: Controversy Over? Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Bliss, N.; Sundquist, E.; Huntington, T.G. Modeling Carbon Dynamics in Vegetation and Soil under the Impact of Soil Erosion and Deposition. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 2002GB002010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Driessen, J.P.; Haygarth, P.M.; Mckelvie, I.D. Potential Contribution of Lysed Bacterial Cells to Phosphorus Solubilisation in Two Rewetted Australian Pasture Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.; Haygarth, P.M.; Bardgett, R.D. Drying and Rewetting Effects on Soil Microbial Community Composition and Nutrient Leaching. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.J.; Van Der Gast, C.J.; McNamara, N.P.; Rowe, R.; Bending, G.D. Extreme Rainfall Affects Assembly of the Root-associated Fungal Community. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 1172–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet, E.J.; Dunne, T. A Stochastic Sediment Delivery Model for a Steep Mediterranean Landscape. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 2003WR002341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Mummey, D.L. Mycorrhizas and Soil Structure. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, M.; Houot, S.; Francou, C.; Poitrenaud, M.; Bissonnais, Y.L. Soil Aggregate Stability Improvement with Urban Composts of Different Maturities. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, A.; Rillig, M.C. Understanding Mechanisms of Soil Biota Involvement in Soil Aggregation: A Way Forward with Saprobic Fungi? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmile-Gordon, M.; Gregory, A.S.; White, R.P.; Watts, C.W. Soil Organic Carbon, Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS), and Soil Structural Stability as Affected by Previous and Current Land-Use. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirfam, H.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Zarei Darki, B.; Homaee, M. Controlling Rainfall-Induced Soil Loss from Small Experimental Plots through Inoculation of Bacteria and Cyanobacteria. CATENA 2017, 152, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, G.; Palmeri, V.; Settanni, L.; Gaglio, R.; Tolone, M.; Ferro, V. Ability of Soil Bacterial Composition as an Indicator of Levels of Soil Erosion in a Badland. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2022, 37, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchicela, J.; Sullivan, T.S.; Bontti, E.; Bever, J.D. Soil Aggregate Stability Increase Is Strongly Related to Fungal Community Succession along an Abandoned Agricultural Field Chronosequence in the B Olivian A Ltiplano. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Vegetation Types | Plot Area (m2) | Elevation (m) | Density (Tree·hm−2) | DBH (cm) | Tree Height (m) | Slope Gradient (°) | Aspect | Sand Content (%) | Silt Content (%) | Clay Content (%) | SOC (g·kg−1) | pH | Total N (g·kg−1) | Total P (g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q.var | 20 × 20 | 319.29 | 1983 | 17.21 | 10.9 | 20 | shaded slope | 42.3 ± 3.1 | 38.5 ± 2.7 | 19.2 ± 1.8 | 12.5 ± 1.3 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 1.12 ± 0.11 | 0.65 ± 0.08 |
| P.lat | 20 × 20 | 142.43 | 2050 | 12.77 | 9.42 | 15 | shaded slope | 45.6 ± 2.9 | 35.2 ± 2.4 | 19.2 ± 1.5 | 11.8 ± 1.1 | 6.9 ± 0.3 | 1.05 ± 0.09 | 0.62 ± 0.07 |
| Shr | 5 × 20 | 152.51 | 5900 | 2.23 | 0.98 | 15 | shaded slope | 51.2 ± 3.5 | 32.8 ± 2.6 | 16.0 ± 1.4 | 8.3 ± 0.9 | 7.2 ± 0.2 | 0.78 ± 0.08 | 0.45 ± 0.06 |
| Bar | 2 × 2 | 160.49 | - | - | 0.27 | 15 | shaded slope | 58.5 ± 4.2 | 28.3 ± 3.1 | 13.2 ± 1.6 | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 0.35 ± 0.05 | 0.28 ± 0.04 |
| Vegetation Types | Rainfall Intensity (mm·h−1) | Macroaggregates | Microaggregates | Primary Particles | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g | % | g | % | g | % | ||
| Q.var | 30 | 0.89 c | 22.41 | 0.54 c | 13.78 | 2.52 c | 63.81 |
| 80 | 89.04 b | 39.41 | 53.89 b | 23.85 | 83.00 b | 36.74 | |
| 120 | 345.49 a | 41.29 | 168.83 a | 20.18 | 322.33 a | 38.53 | |
| P.lat | 80 | 2.17 b | 9.71 | 1.09 b | 4.86 | 19.09 a | 85.44 |
| 120 | 7.68 a | 24.46 | 3.94 a | 12.55 | 19.77 a | 62.99 | |
| Shr | 30 | 3.53 c | 21.68 | 2.44 c | 14.98 | 10.33 b | 63.34 |
| 80 | 18.76 b | 41.38 | 19.25 b | 42.44 | 7.34 b | 16.18 | |
| 120 | 912.97 a | 48.96 | 273.93 a | 44.69 | 677.84 a | 16.35 | |
| Bar | 30 | 4.17 c | 41.52 | 3.26 c | 32.44 | 2.61 c | 26.04 |
| 80 | 504.09 b | 54.18 | 214.83 a | 23.09 | 211.50 b | 22.73 | |
| 120 | 873.12 a | 64.00 | 168.79 b | 12.37 | 322.33 a | 23.63 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, W.; Li, Z.; Deng, X.; Wang, L. Mechanisms of Soil Aggregate Stability Influencing Slope Erosion in North China. Hydrology 2025, 12, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12100267
Yang Y, Zhang S, Yuan W, Li Z, Deng X, Wang L. Mechanisms of Soil Aggregate Stability Influencing Slope Erosion in North China. Hydrology. 2025; 12(10):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12100267
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ying, Shuai Zhang, Weijie Yuan, Zedong Li, Xiuxiu Deng, and Lina Wang. 2025. "Mechanisms of Soil Aggregate Stability Influencing Slope Erosion in North China" Hydrology 12, no. 10: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12100267
APA StyleYang, Y., Zhang, S., Yuan, W., Li, Z., Deng, X., & Wang, L. (2025). Mechanisms of Soil Aggregate Stability Influencing Slope Erosion in North China. Hydrology, 12(10), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12100267





