Anthropogenic Activity in the Topo-Climatic Interaction of the Tapajós River Basin, in the Brazilian Amazon
Abstract
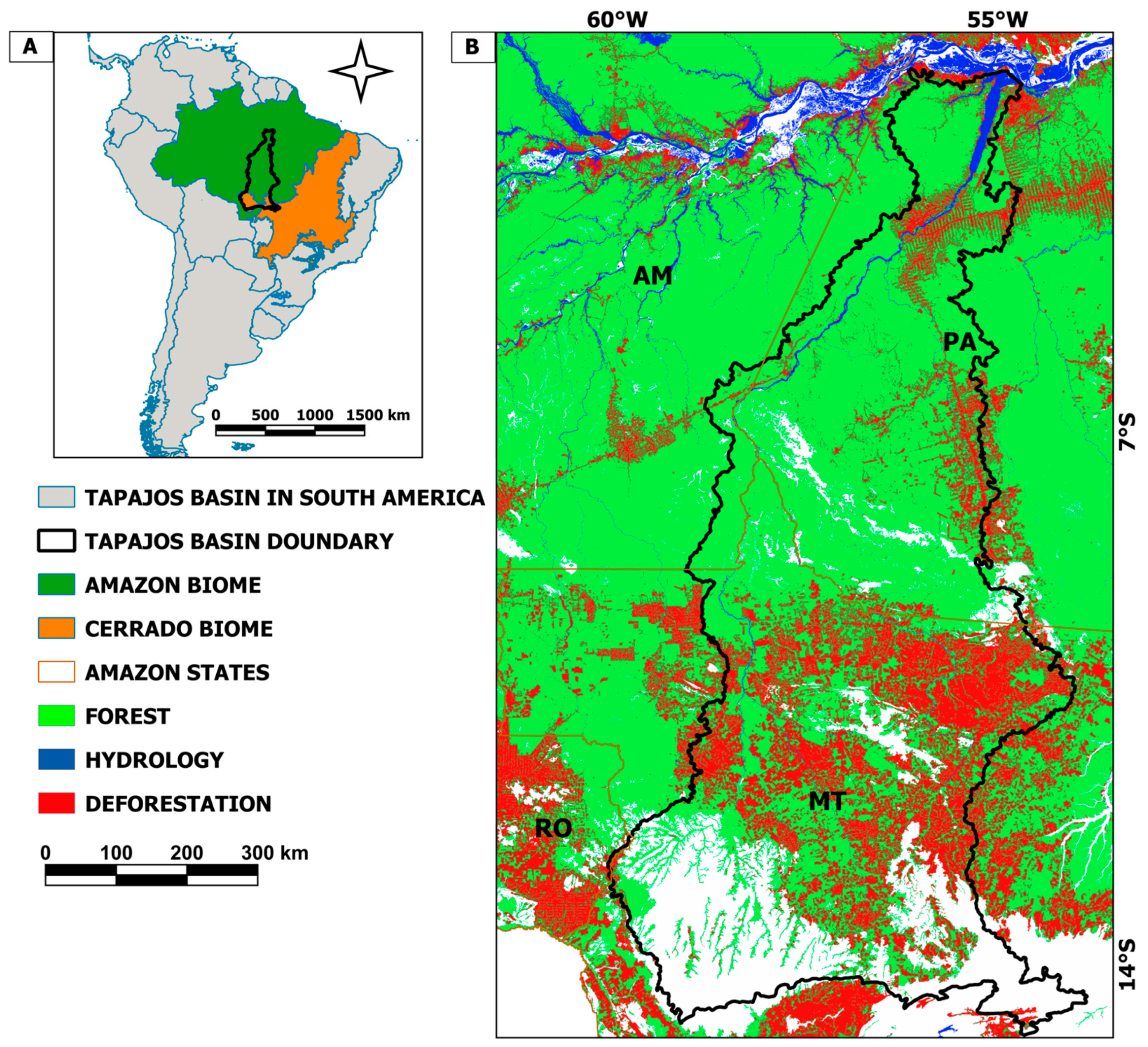
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- (1)
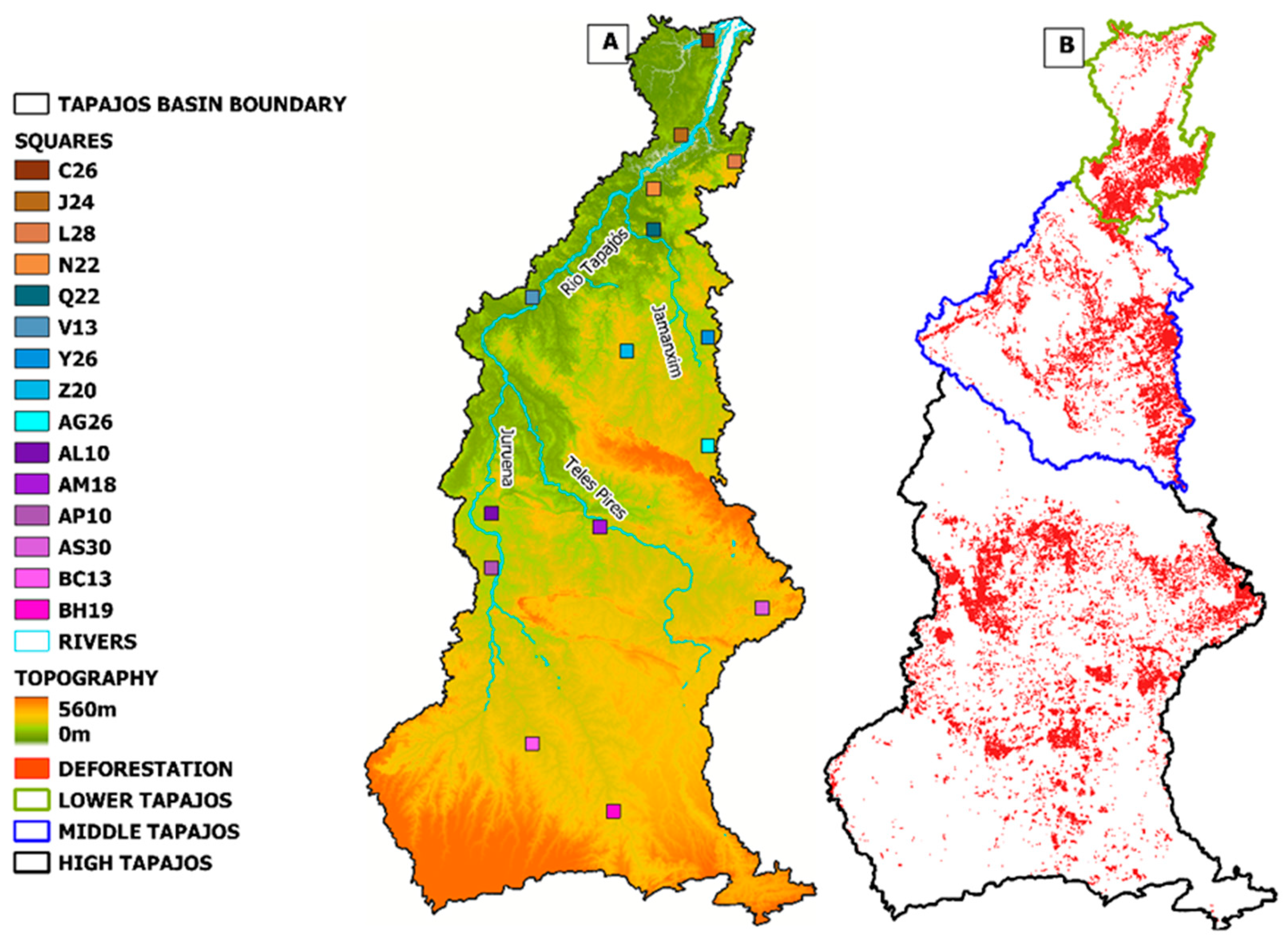
- From this grid, time series of data were extracted pointwise at each grid cell, thus allowing for the creation of tables and the performance of statistical calculations. The sampling aimed for the greatest uniformity of the internal landscape of each grid cell, allowing the relationship to have a more direct correspondence with the dominant land cover (deforested area).
- (2)
- After selection, the total DFT value, accumulated PREC and average TMAX and TMIN for the CHU+ and CHU− stations were calculated for each grid cell from 2008 to 2018 (11 years). Microsoft Excel was used along with Pearson’s correlation r tests (the quotient between covariance and the product of their standard deviations), Equation (4) and the coefficient of determination—R² (a measure (in percentage) of the amount of variation in one variable explained by the other; this is the square of Pearson’s correlation coefficient) were applied to the tabulated data, which were then applied to the values of these variables [30,35]:where COV represents covariance; X, Y represent the variables in question; and , the standard deviation of the variable.
3. Results
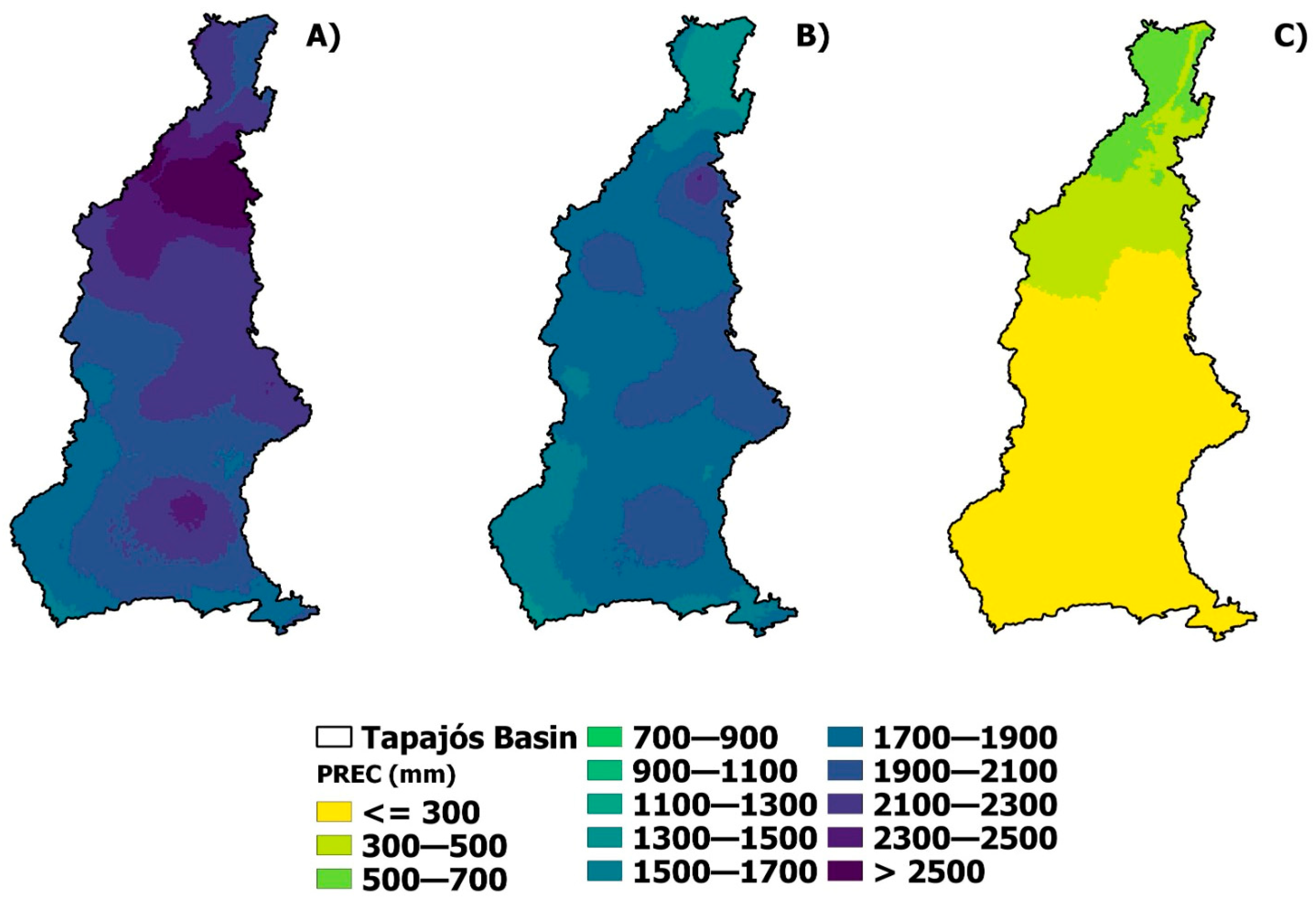
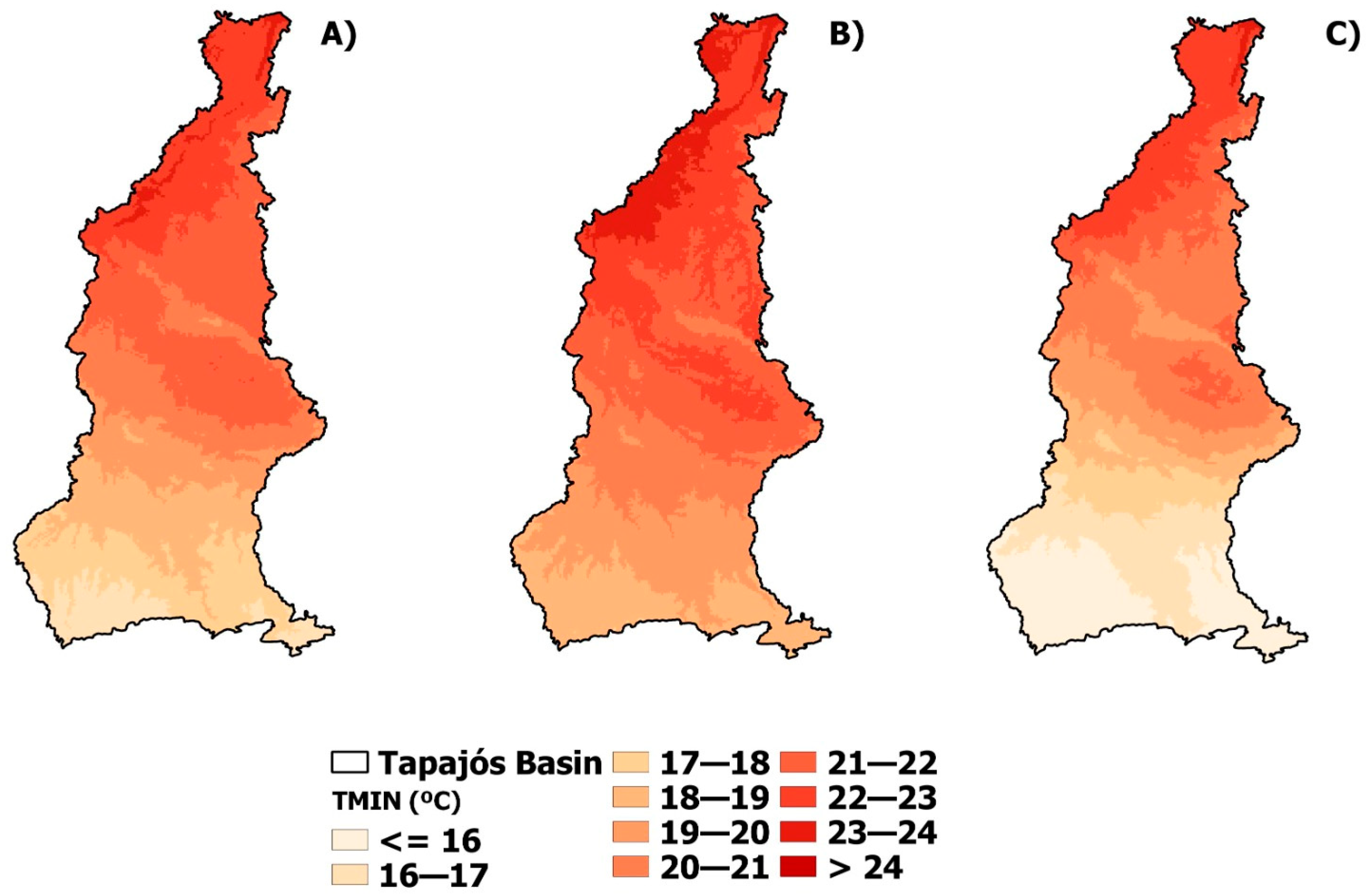
3.1. Climatological Normal and Precipitation and Temperature Anomaly
3.2. Integrated Analysis between Deforestation and Meteorological Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wajim, J. Impacts of deforestation on socio-economic development and environment in Nigeria. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Invent. 2020, 7, 5852–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologna, M.; Aquino, G. Deforestation and world population sustainability: A quantitative analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, D.; Vandecar, K.; Radel, C.; Schmook, B.; Schneider, L.; Rogan, J.; Geoghegan, J. When the Forest is Cut Down, Does it Matter How It is Cut? Biophysical and Socioeconomic Feedbacks of Selective Logging. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2022, 5, e756115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazel-Rastgar, F. The Evidence of Recent Canadian Arctic Climate Change. A Case Study, the Baffin Island. Int. J. Glob. Warm. 2020, 20, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves de Oliveira, B.F.; Bottino, M.J.; Nobre, P.; Nobre, C.A. Deforestation and climate change are projected to increase heat stress risk in the Brazilian Amazon. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulizia, C.N.; Raggio, G.A.; Camilloni, I.A.; Saurral, R.I. Changes in mean and extreme climate in southern South America under global warming of 1.5 °C, 2 °C, and 3 °C. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 150, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, P.A.; Rivera, J.A.; Sörensson, A.A.; Zachariah, M.; Barnes, C.; Philip, S. Interplay between climate change and climate variability: The 2022 drought in Central South America. Clim. Chang. 2023, 177, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapola, D.M.; Pinho, P.; Barlow, J.; Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Berenguer, E.; Carmenta, R.; Liddy, H.M.; Seixas, H.; Silva, C.V.J.; Walker, W.S. The drivers and impacts of Amazon forest degradation. Science 2023, 379, eabp8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matricardi, E.A.T.; Skole, D.L.; Costa, O.B.; Pedlowski, M.A.; Samek, J.H.; Miguel, E.P. Long-term forest degradation surpasses deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. Science 2020, 369, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, O.; Chaudhari, S.N.; Pokhrel, Y. H030-0019 Hydrological Thresholds for Sustainable Land Use and Land Cover Change in Amazon River Basin. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, Online, 1–17 December 2020; Volume 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.F.B.; Rodrigues, L.N.; Sena, A.; Santos, M.A.; Torres, G.G.; Santos, M.A.S. A Modeling Approach for Analyzing the Hydrological Impacts of the Agribusiness Land-Use Scenarios in an Amazon Basin. Land 2023, 12, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitani, C.; Angelini, R.; Keppele, F.W.; Hallwass, G.; Silvano, R.A.M. Food web modeling indicates the potential impacts of increasing deforestation and fishing pressure in the Tapajós River, Brazilian Amazon. Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, J.B.; Freitas, P.B.; Fontgalland, I.L.; Macri, L.M.S.R.; Estrela, T.F. Payments for Environmental Services (PES): A study on brazilian legislation and the structuring of agreements. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e38791211306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, T.W. Policy, drought and fires combine to affect biodiversity in the Amazon basin. Nature 2021, 597, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Vásquez, M.; Arias, P.A.; Martínez, J.A.; Espinoza, J.C. Effects of Amazon basin deforestation on regional atmospheric circulation and water vapor transport towards tropical South America. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 4169–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R. One River and 40+ Dams: The China Factor in the Amazonian Tapajós Waterway. In The Political Economy of Hydropower in Southwest China and Beyond; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Swizerland, 2021; pp. 275–293. [Google Scholar]
- Théry, H. A expansão da produção de grãos e a infraestrutura de circulação no Brasil. Rev. Política E Planej. Reg. 2019, 2019, 284–305. [Google Scholar]
- Bieri, M.L.; Picanço, V.M.P.A. Considerations of mining in Tapajos basin and impacts on Munduruku land. Int. J. Dev. Res. 2019, 9, 28622–28631. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, R.; Castro, E. Desenvolvimento e conflitos na Amazônia: Um olhar sobre a colonialidade dos processos em curso na BR- 163. Rev. Nera 2018, 42, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite-Filho, A.T.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Davis, J.L.; Abrahão, G.M.; Börner, J. Deforestation reduces rainfall and agricultural revenues in the Brazilian Amazon. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, e259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Tourneau, F.M. Is Brazil now in control of deforestation in the Amazon? Cybergeo Eur. J. Geogr. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, M.; De Alencastro Graça, P.M.L.; Yanai, A.M.; Ramos, C.J.P.; Fearnside, P.M. Forest fires and deforestation in the central Amazon: Effects of landscape and climate on spatial and temporal dynamics. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, e112310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.V.F.; Petri, C.A.; Broggio, I.S.; Chagas, G.O.; Macul, M.S.; Leite, C.C.S.; Ferrari, E.M.M.; Amim, C.G.V.; Freitas, A.L.R.; Motta, A.Z.V.; et al. Drivers of Fire Anomalies in the Brazilian Amazon: Lessons Learned from the 2019 Fire Crisis. Land 2020, 9, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, D.M.; Kolden, C.A.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Johnston, F.H.; Van der Werf, G.R.; Flannigan, M. Vegetation fires in the Anthropocene. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latrubesse, E.M. Quaternary megafans, large rivers and other avulsive fluvial systems: A potential “who is who” in the geological record. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 146, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearnside, P.M. Desmatamento na Amazônia: Dinâmica, impactos e controle. Acta Amaz. 2006, 36, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, T.O.; Nogueira, R.J.B. A geopolítica rodoviária na Amazônia: BR-163/Santarém-Cuiabá. Rev. De Geopolít. 2016, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, T.O. As rodovias na Amazônia: Uma discussão geopolítica. Rev. Fr.-Bras. De Geogr. 2019, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.; Aguiar, A.; Toledo, P.; Araújo, R.; Do Canto, O.; Folhes, R.; Adami, M. Rural landscapes and agrarian spaces under soybean expansion dynamics: A case study of the Santarém region, Brazilian Amazonia. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2021, 21, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debortoli, N.S.; Dubreuil, V.; Hirota, M.; Rodrigues Filho, S.; Lindoso, D.P.; Nabucet, J. Detecting deforestation impacts in Southern Amazonia rainfall using rain gauges. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.C.; Blanco, C.; Oliveira Júnior, J.F. Distribution of rainfall probability in the Tapajos River Basin, Amazonia, Brazil. Rev. Ambiente Água 2019, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, D.F.; Millikan, B.; Torres, M. Ocekadi: Hidrelétricas, Conflitos Socioambientais e Resistência na Bacia do Tapajós, 2nd ed.; International Rivers Brasil: Brasília, DF, Brasil, 2016; 531p. [Google Scholar]
- Nery, J.T.; Stivari, S.M.S.; Martins, M.L.O.F.; Silva, E.S.; Sousa, P. Estudo da precipitação do estado do Paraná e sua associação à temperatura da superfície do Oceano Pacífico. Rev. Bras. De Agrometeorol. 2005, 13, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Ai, T. The visualization and analysis of urban facility pois using network kernel density estimation constrained by multi-factors. Bol. De Ciênc. Geod. 2014, 20, 902–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite Filho, A.T.; De Sousa Pontes, V.Y.; Costa, M.H. Effects of deforestation on the onset of the rainy season and the duration of dry spells in southern Amazonia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 5268–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral Júnior, J.B.; Lucena, R.L. Análises das precipitações pelos testes não paramétricos de Mann-Kendall e Kruskal-Wallis. Mercator 2020, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.P.; Marengo, J.A.; Alvala, R.C.; Deusdara-Leal, K.R.; Cuartas, L.A.; Seluchi, M.; Zeri, M.; Ribeiro-Neto, G.; Brodel, E.; Cunningham, C.; et al. Secas e Seus Impactos No Brasil 2018, 1st ed.; São Jose dos Campos, SP, Brasil, 2019; 19p. Available online: http://www2.cemaden.gov.br/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Boletim_Anual_SECAS_f.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Nobre, C.A.; Sellers, P.J.; Shukl, A.J. Amazonian deforestation and regional climate change. J. Clim. 1991, 4, 957–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werth, D.E.; Avissar, R. The local and global effects of Amazon deforestation. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, D20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voldoire, A.; Royer, E.J.F. Tropical deforestation and climate variability. Clim. Dyn. 2004, 22, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, G.; Nobre, C.; Costa, M.H.; Satyamurty, P.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Cardoso, M. Regional climate change over eastern Amazonia caused by pasture and soybean cropland expansion. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L17709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloor, M.; Barichivich, J.; Ziv, G.; Brienen, R.; Schöngart, J.; Peylin, P.; Barcante Ladvocat Cintra, B.; Feld Pausch, T.; Phillips, O.; Baker, J. Recent Amazon climate as background for possible ongoing and future changes of Amazon humid forests. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2015, 29, 1384–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.; Spracklen, D. Climate benefits of intact Amazon forests and the biophysical consequences of disturbance. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2019, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; de Lucia Lobo, F.; Barbosa Lopes Cavalcante, R.; Mota, J.A.; da Rocha Nascimento, W., Jr.; Santos, D.C.; Siqueira, J.O. Land-use intensity of official mineral extraction in the Amazon region: Linking economic and spatial data. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvério, D.V.; Brando, P.M.; Macedo, M.N.; Beck, P.S.; Bustamante, M.; Coe, M.T. Agricultural expansion dominates climate changes in southeastern Amazonia: The overlooked non-GHG forcing. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 104015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdougall, A.H.; Beltrami, H. Impact of deforestation on subsurface temperature profiles: Implications for the borehole paleoclimate record. Environmental. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 074014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Araújo, I.B.; Wanzeler, R.T.S.; Serrão, E.A.O.; Farias, M.H.C.S.; Lima, A.M.M. Regionalização hidroclimatológica da bacia hidrográfica do Rio Tapajós. Rev. Geogr. Acad. 2015, 9, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPTEC/INPE. Centro de Previsão de Tempo e Estudos Climáticos. Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais. Available online: https://tempo.cptec.inpe.br/boletimtecnico/pt (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Cavalcanti, I.F.A. Tempo e clima no Brasil, 2nd ed.; Oficina de Textos: São Paulo, SP, Brasil, 2016; 464p. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, F.F.; Dos Santos, F.A.; Dos Santos, J.M. Índice de anomalia de chuva (IAC) aplicado ao estudo das precipitações no município de caridade, Ceará, Brasil. Rev. Bras. De Climatol. 2020, 27, 426–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.M.V.; Jones, C.; Liebmann, B. The South Atlantic convergence zone: Intensity, form, persistence, and relationships with intraseasonal to interannual activity and extreme rainfall. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 88–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spera, S.A.; Galford, G.L.; Coe, M.T.; Macedo, M.N.; Mustard, J.F. Land-use change affects water recycling in Brazil’s last agricultural frontier. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3405–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathiany, S.; Claussen, M.; Brovkin, V.; Raddatz, T.; Gayler, V. Combined biogeophysical and biogeochemical effects of large-scale forest cover changes in the MPI Earth system model. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1383–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, R.; Garcia, A.S.; Vilela, V.M.D.F.; Ballester, M.V.R.; Neill, C.; Victoria, D.C.; Coe, M.T. Land use changes in Southeastern Amazon and trends in rainfall and water yield of the Xingu River during 1976–2015. Clim. Chang. 2020, 162, 1419–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdum, R.; Gamboa, C.; Bebbington, A.J. Assessment and Scoping of Extractive Industries and Infrastructure in Relation to Deforestation: Amazonia, 1st ed.; Derecho, Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (DAR): Lima, Peru, 2019; 81p. [Google Scholar]
- Fearnside, P.M. Brazil’s Cuiabá-Santarém (BR-163) Highway: The environmental cost of paving a soybean corridor through the Amazon. Environ. Manag. 2007, 39, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.M.; Rocha, M.P.; Farias, V.; Tavares, H. Optimization of soybean outflow routes from Mato Grosso, Brazil. Int. J. Innov. Educ. Res. 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, I.; Rodrigues, C.; Dallacort, R.; Marimon Junior, B.H.; Carvalho, M.A.C. Rainfall and deforestation in the municipality of Colíder, southern Amazon. Rev. Bras. De Meteorol. 2014, 29, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spracklen, D.V.; Garcia-Carreras, L. The impact of Amazonian deforestation on Amazon basin rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 9546–9552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

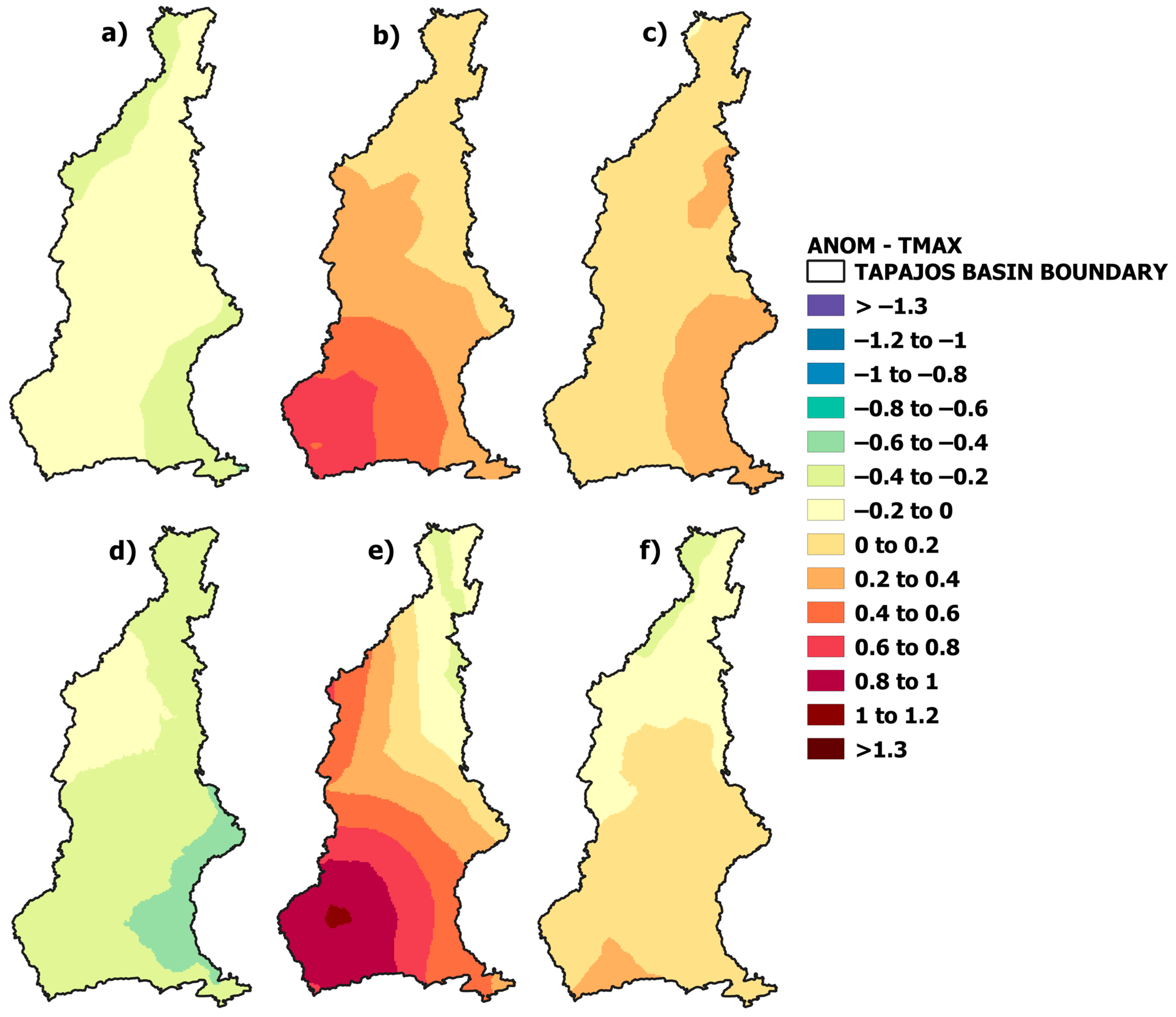
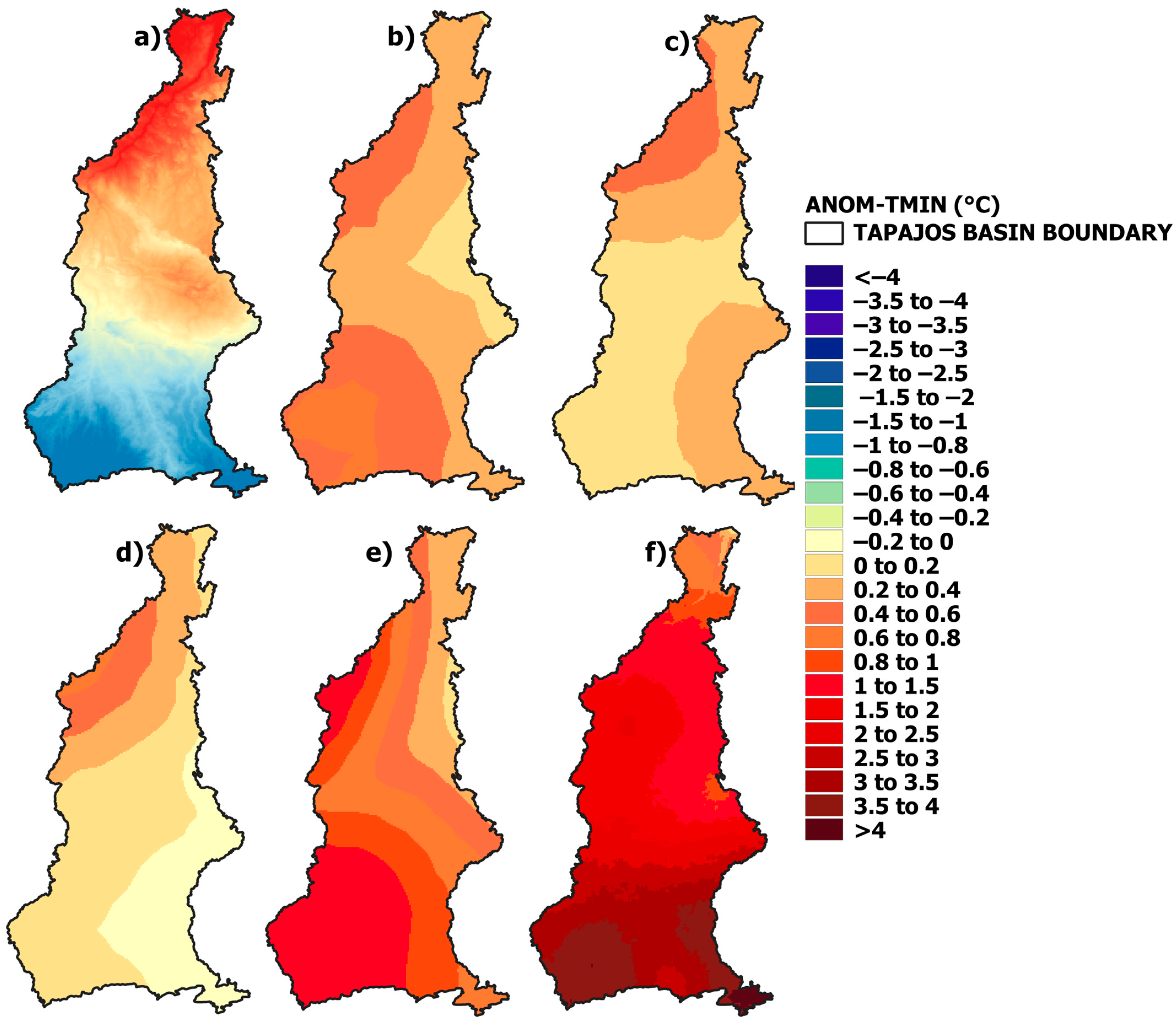
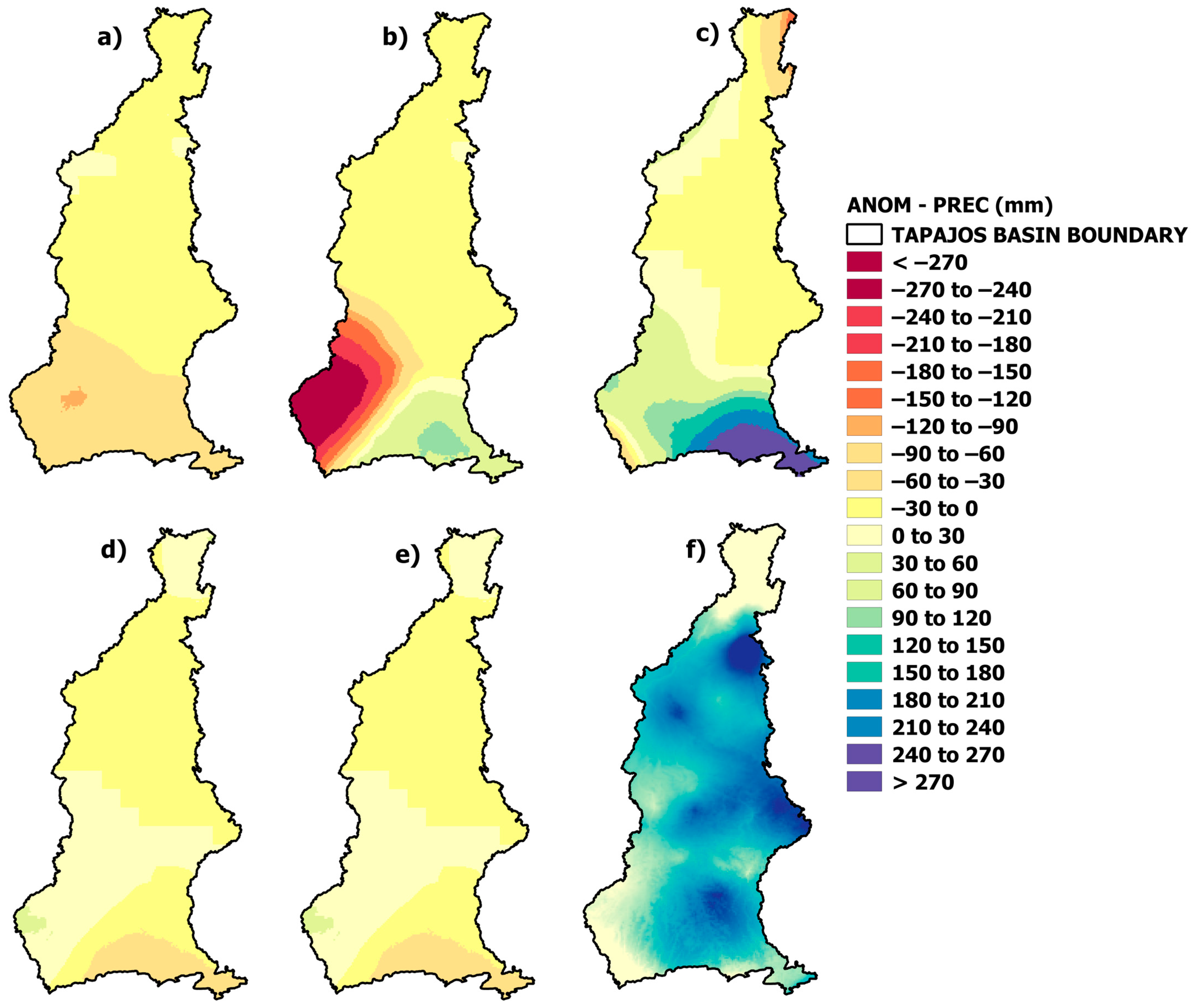
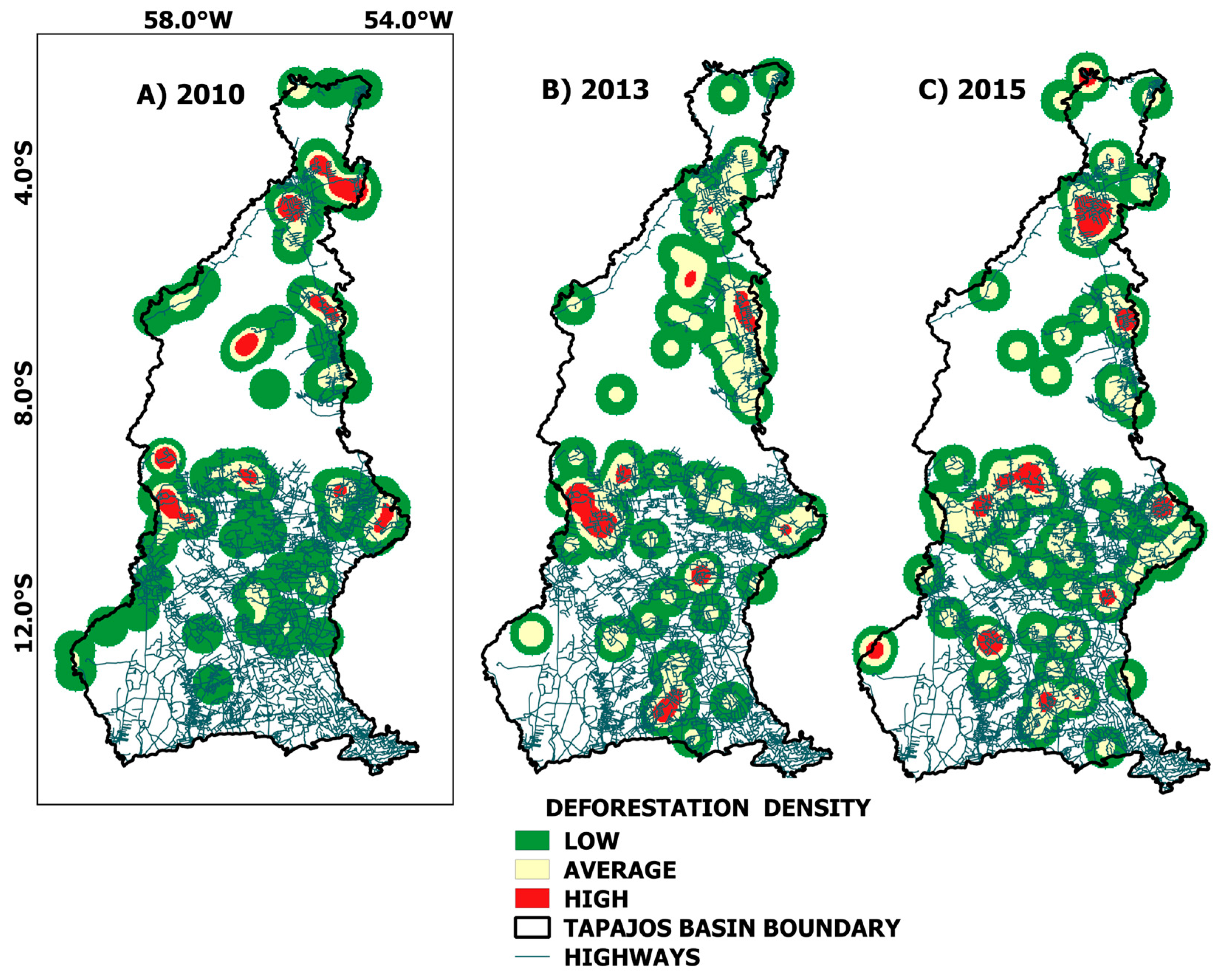
| PREC | TMAX | TMIN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHU+ | CHU− | CHU+ | CHU− | CHU+ | CHU− | |
| Year | 2011–2012 (CHU+)/2012 (CHU−) | |||||
| Average | 1835.6 | 242.9 | 30.8 | 33.2 | 20.9 | 19.0 |
| Standard deviation | 131.3 | 111.7 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 2.4 |
| Year | 2014–2015 (CHU+)/2015 (CHU−) | |||||
| Average | 1816.8 | 237.8 | 31.3 | 33.9 | 21.3 | 19.7 |
| Standard deviation | 206.7 | 116.8 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 2.0 |
| Year | 2016–2017 (CHU+)/2017 (CHU−) | |||||
| Average | 1897.6 | 246.2 | 31.1 | 33.5 | 21.2 | 21.2 |
| Standard deviation | 126.2 | 111.3 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| Sub-Basins | Squares | TMAXCHU+ | TMAXCHU− | TMINCHU+ | TMINCHU− | PRECCHU+ | PRECCHU− | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | R² | r | R² | r | R² | r | R² | r | R² | r | R² | ||
| Low | C26 | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.00 | −0.21 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.39 | 0.15 |
| J24 | −0.30 | 0.09 | −0.28 | 0.08 | −0.58 | 0.34 | −0.51 | 0.26 | 0.34 | 0.11 | −0.02 | 0.00 | |
| L28 | −0.34 | 0.11 | −0.66 | 0.43 | −0.43 | 0.19 | −0.70 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.04 | −0.22 | 0.05 | |
| N22 | −0.28 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 0.14 | −0.19 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 0.17 | |
| Average | Q22 | −0.14 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.03 | −0.08 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.01 | −0.60 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 0.19 |
| V13 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 0.56 | 0.40 | 0.16 | 0.47 | 0.22 | −0.19 | 0.04 | −0.17 | 0.03 | |
| Z20 | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.03 | −0.10 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Y26 | −0.62 | 0.39 | −0.63 | 0.40 | −0.63 | 0.40 | −0.61 | 0.37 | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.32 | 0.10 | |
| AG26 | −0.45 | 0.20 | −0.14 | 0.02 | −0.45 | 0.20 | −0.14 | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.24 | 0.06 | |
| High | AL10 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.20 | 0.04 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.2 | 0.04 | −0.03 | 0.00 | −0.11 | 0.01 |
| AM18 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.25 | 0.06 | −0.19 | 0.04 | −0.16 | 0.03 | |
| AP10 | −0.49 | 0.24 | −0.24 | 0.06 | −0.48 | 0.23 | −0.24 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | |
| AS30 | −0.43 | 0.19 | −0.06 | 0.00 | −0.43 | 0.19 | −0.06 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.03 | |
| BH19 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 0.31 | −0.16 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.01 | |
| Mann Kendall Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Statistic S | Var (S) | Tau | p-Value | Alpha |
| PRECCHU+ | 4320 | 2,896,013 | 0.099 | 0.01115 | 0.05 |
| PRECCHU− | −4670 | 2,925,206 | −0.106 | 0.00634 | 0.05 |
| DFT | 2600 | 268,666 | 0.333 | 0.1272 | 0.05 |
| TMAXCHU+ | 4597 | 1,639,297 | 0.167 | 0.0003 | 0.05 |
| TMAXCHU− | 2615 | 2,590,038 | 0.072 | 0.1043 | 0.05 |
| TMINCHU+ | 8049 | 2,706,214 | 0.211 | 0.0000 | 0.05 |
| TMINCHU− | 17,580 | 2,797,603 | 0.441 | 0.0000 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco, V.d.S.; Lima, A.M.M.d.; Oliveira, R.R.S.d.; Souza, E.B.d.; Sodré, G.R.C.; Santos, D.C.; Adami, M.; Serrão, E.A.d.O.; Dias, T.S.d.S. Anthropogenic Activity in the Topo-Climatic Interaction of the Tapajós River Basin, in the Brazilian Amazon. Hydrology 2024, 11, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11060082
Franco VdS, Lima AMMd, Oliveira RRSd, Souza EBd, Sodré GRC, Santos DC, Adami M, Serrão EAdO, Dias TSdS. Anthropogenic Activity in the Topo-Climatic Interaction of the Tapajós River Basin, in the Brazilian Amazon. Hydrology. 2024; 11(6):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11060082
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco, Vânia dos Santos, Aline Maria Meiguins de Lima, Rodrigo Rafael Souza de Oliveira, Everaldo Barreiros de Souza, Giordani Rafael Conceição Sodré, Diogo Correa Santos, Marcos Adami, Edivaldo Afonso de Oliveira Serrão, and Thaiane Soeiro da Silva Dias. 2024. "Anthropogenic Activity in the Topo-Climatic Interaction of the Tapajós River Basin, in the Brazilian Amazon" Hydrology 11, no. 6: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11060082
APA StyleFranco, V. d. S., Lima, A. M. M. d., Oliveira, R. R. S. d., Souza, E. B. d., Sodré, G. R. C., Santos, D. C., Adami, M., Serrão, E. A. d. O., & Dias, T. S. d. S. (2024). Anthropogenic Activity in the Topo-Climatic Interaction of the Tapajós River Basin, in the Brazilian Amazon. Hydrology, 11(6), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11060082









