Abstract
The controlling hydrogeochemical processes of an intermontane aquifer in central Mexico were identified through multivariate statistical analysis. Hierarchical cluster (HCA) and k-means clustering analyses were applied to Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, F−, Cl−, SO42−, NO3−, HCO3−, As, pH and electrical conductivity in 40 groundwater samples collected from shallow and deep wells, where As and F− are contaminants of concern. The effectiveness of each hierarchical and k-means clustering method in explaining solute concentrations within the aquifer and the co-occurrence of arsenic and fluoride was tested by comparing two datasets containing samples from 40 and 36 wells, the former including ionic balance outliers (>10%). When tested without outliers, cluster quality improved by about 5.4% for k-means and 7.3% for HCA, suggesting that HCA is more sensitive to ionic balance outliers. Both algorithms yielded similar clustering solutions in the outlier-free dataset, aligning with the k-means solution for all 40 samples, indicating that k-means was the more robust of the two methods. k-means clustering resolved fluoride and arsenic concentrations into four clusters (K1 to K4) based on variations in Na+, Ca2+, As, and F−. Cluster K2 was a Na-HCO3 water type with high concentrations of As and F. Clusters K1, K3, and K4 exhibited a Ca-HCO3, Na-Ca-HCO3, and Ca-Na-HCO3 water types, respectively, with decreasing As and F concentrations following the order K2 > K3 > K1 > K4. The weathering of evaporites and silicates and Na-Ca ion exchange with clays were the main processes controlling groundwater geochemistry. The dissolution of felsic rocks present in the aquifer fill is a likely source of As and F−, with evaporation acting as an important concentration factor.
1. Introduction
Arsenic has been declared a carcinogenic agent, affecting almost all cellular processes and organs. Long-term arsenic effects on health include hyperkeratosis, skin, lungs, liver, kidneys, and bladder cancer. Other health issues have been associated, such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and reproductive and neurological effects [1,2]. Studies of arsenic in human blood, urine, and other biological indicators in Mexico have revealed constant exposure to arsenic in the population [3,4,5,6]. Fluoride is known to be a cause of dental and skeletal fluorosis, endocrine diseases like hyperparathyroidism, and cognitive and neurological disorders, as well as cardiovascular diseases like arteriosclerosis and arterial calcification, high blood pressure, reproductive and skin problems, and diabetes [7].
Natural As and F− contamination of groundwater is a worldwide problem. In oxic aquifers, their presence is commonly associated with volcanic rock and alluvial aquifers [8,9,10]. Mexico is not an exception: approximately 178 municipalities distributed in 23 states have aquifers with As and/or F− concentrations surpassing the WHO guidelines of 10 µg L−1 As and 1.5 mg L−1 F−. In Mexico, states located in the north-central part have been identified as the most affected [11]. Several studies have been conducted at the local or regional level on fluoride distribution and health risk assessment [12,13,14,15] and the co-occurrence of both As and F− has been reported in many of these studies, concluding that this pollution has geological origins, mainly associated with the dissolution of felsic rocks and desorption from secondary minerals [16,17,18].
Statistical multivariate techniques applied to water quality studies have successfully characterized a variety of natural and anthropogenic contaminants under a variety of scenarios [19,20]. Multivariate analysis studies have multiplied in the past few decades because of their ability to examine numerous parameters simultaneously and to detect the source and spread of contaminants in groundwater [20]. Commonly utilized multivariate techniques include principal component analysis (PCA), factor analysis (FA), hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), k-means clustering, self-organized maps (SOM), and fuzzy C-mean clustering (FCM) for grouping analyses [20,21,22,23,24]. We utilized these techniques in an aquifer naturally contaminated with arsenic (As) and fluoride (F−) located in north-central Mexico at the foot of the Sierra Madre Occidental.
Various studies have characterized water quality and hydrogeochemical mechanisms in north-central Mexico. Some of them include the water quality characterization of the Comarca Lagunera by Mora [19] and Mahlknecht [6], drinking water sources for the city of Monterrey [25,26], irrigation areas with salinization problems like Santo Domingo aquifer [27], and areas affected by wastewater from large urban centers: the Mezquital Valley [28] and Lake Cajatitlán [29]. All these have applied PCA and cluster analysis in combination with other approaches such as water quality index [28] or discriminant analysis [29]. In the above studies, contaminants of concern were salinity, heavy metals, wastewater irrigation, and municipal treated water. Despite the widespread and serious health risks posed by As and F−, multivariate techniques have not been applied to the characterization of As and F− in aquifers where As and F− concentrations represent a health hazard, such as in Durango, Mexico. In water quality studies supported by multivariate analysis like those mentioned above (using HCA, k-means or another technique), an ionic balance between major cations and anions is carried out to assess the reliability of the chemical analysis of the samples. An error in ionic balance of 10% is the maximum accepted value for general purposes, and for samples above that percentage, the data are discarded prior to hydrogeochemical analysis. Nevertheless, what happens when the number of sampled wells is small, some of them exceed the ionic balance error, and wells cannot be resampled? Can they still be part of the cluster analysis? A commonsense answer is “no”, but studies addressing outlier problems in clustering algorithms have proved that algorithms like HCA and k-means can withstand outliers and give reasonable clustering solutions, measuring this through cluster validation indices like Dunn or Davies–Bouldin indices [22,30].
In this study, multivariate data analyses were applied in conjunction with conventional hydrogeochemical studies to (1) identify the main processes governing water quality in an intermontane aquifer highly affected by arsenic and fluoride in the north-central part of Mexico (the Valle del Guadiana aquifer), and (2) compare the effectiveness of hierarchical cluster (HCA) and k-means clustering methods in explaining the groundwater composition of the aquifer under ionic balance outliers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Of Mexico’s 653 aquifers, 157 are overexploited [31]. Valle del Guadiana aquifer operates with a deficit of −20.82 hm3 y−1 and is the water source for about 700,000 people [32]. The Valle del Guadiana aquifer is bounded by parallels 23°27′ N and 24°29′ N and meridians 104°19′ W and 105°8′ W and has a surface area of 4817 km2. The aquifer is located in the central high plains of Mexico, surrounded by the Sierra Madre Oriental to the immediate west, and the Sierra Madre Oriental and the Mexican Transvolcanic belt to the northeast and to the south, respectively. The climate in this area is predominantly semiarid and temperate, with average annual temperatures of 31 °C (max.) and 1.7 °C (min.). The average yearly rainfall is approximately 500 mm during summer, mainly during July, August, and September. Agricultural, drinking, household, and industrial needs are the primary groundwater uses, in that order. Despite this being a water-scarce area, about 36% of the wells are used for agriculture and 12.6% are used for livestock. The study area is confined to the Valle del Guadiana, the productive zone of the Valle del Guadiana aquifer, which occupies the eastern half of its surface area. Groundwater from this aquifer is reportedly contaminated with As and F− [33].
2.2. Hydrogeology
The Valle del Guadiana aquifer is an unconfined, heterogeneous, and anisotropic aquifer. Alluvial, fluvial, lacustrine, and piedmont sediments constitute the upper part of the aquifer, with polymictic conglomerates in place. Some clay-rich sediments create localized semi-confinement conditions. A sequence of volcanic rocks (acid tuffs, rhyolites, ignimbrites, andesites, and basalts) constitute the lower part of the aquifer.
The aquifer is dominated by volcanic rocks and sedimentary material of the Guadiana Formation (fluvial sequence containing fossils of pre-Wisconsin Pleistocene Age) and Neogene alluvial fans. Rocks form the Lower Volcanic Complex that surrounds the valley–composed of lava flows and ignimbrites—which are superimposed by rhyolitic volcanic rocks, mainly as ash flows. The latter is superimposed with basalt from the Miocene in the northern part and gravel and basalt from the Quaternary in the lower parts of the valley [31]. The Sierra Madre Occidental is a geologically young mountain range that has tectonic and volcanic origins [34].
Due to clay sediments, there can be local semi-confinement conditions, which, in turn, leads to different piezometric levels between close wells. At greater depths, limestones constitute deep aquifer systems with secondary permeability caused by fracture and conditions of semi-confinement and confinement due to alternance between lutites and limolites [31].
The transmissivity values vary between 0.75 × 10−3 and 26.7 × 10−3 m2 s−1, with a mean value of 6.1 × 10−3 m2 s−1. Hydraulic conductivity ranges from 2.29 × 10−4 to 5.28 × 10−6 m s−1, with a mean value of 6.9 × 10−5 m s−1 associated with sediments of fine to medium granulometry. Piezometric levels range from 4 m to 75 m. Groundwater flow shows a preferential west-to-east and northeast-to-southeast direction [31].
2.3. Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
The sampling was conducted in May–June 2022 (dry season). Groundwater samples were collected from 40 wells distributed in the productive zone of the Valle del Guadiana aquifer, ranging in depths from 1.6 to 74 m. The sampling sites are shown in Figure 1. Polyethylene sampling bottles were properly washed and labelled, and water samples collected at least 10 min after the pumping process started to ensure well purging and representative groundwater chemical composition. Samples for metal and metalloid analysis were preserved according to the standard methodology (NOM-AA-051-SCFI-2016). Samples for ion chromatography were collected according to US EPA Method 300.0. No headspace clearances were allowed, and samples were kept at 4 °C in the dark during sampling and transport. Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42−, HCO3−, and CO32− were selected as variables because they are the main constituents of groundwater. As and F were selected because they are the main contaminants in this aquifer. Electrical conductivity is a good estimator of dissolved solids, and pH is related to pH-dependent reactions that explain some hydrogeochemical processes. Major cations (Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+) were quantified using flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry (GBC Scientific Equipment, Mexico City, Mexico, XplorAA Dual), and the total arsenic was measured using a graphite furnace (GBC Scientific Equipment, Mexico City, GF5000). Bicarbonate (HCO3−) was measured via titration according to the NMX-AA-036-SCFI-2001 method, and other major anions (F−, Cl−, SO42−, NO3−) were quantified using ion chromatography (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Guadalajara, Mexico, Dionex Integrion HPIC, AS11-HC column). Electrical conductivity (EC) and pH were measured in the field using a portable Thermo Fisher Scientific, Guadalajara, Mexico, Orion Star A329 field meter.
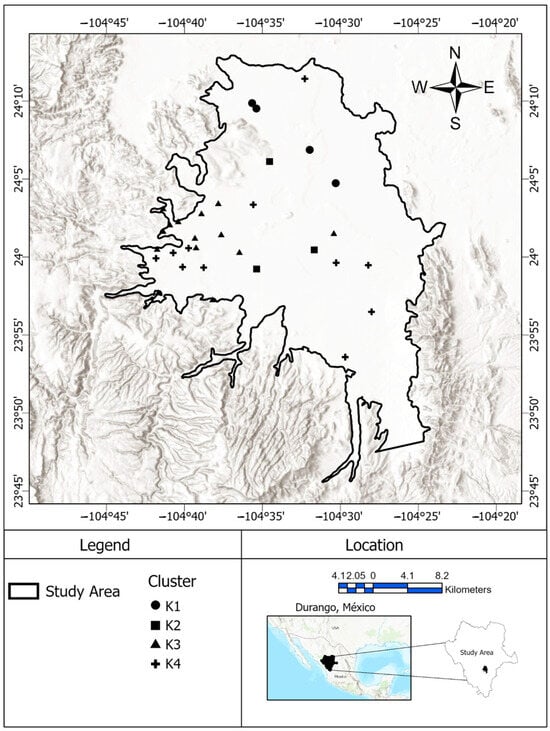
Figure 1.
Study area, the main exploitation zone, in the eastern part of the Valle del Guadiana aquifer.
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Multivariate Analysis and Hydrogeochemical Diagrams
Two criteria were used for the selection of the two clustering methods: (1) HCA and k-means are known algorithms that can withstand outliers giving reasonable clustering solutions and, (2) among other methods, HCA is widely used in hydrogeochemical studies [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53].
To compare the HCA and k-means clustering methods regarding their effectiveness in explaining the groundwater composition of the aquifer in terms of ionic balance outliers, the ionic balance was first calculated according to the following formula [54]:
where the concentrations of ions are expressed in milliequivalents per liter. Of the 40 sampled wells, 34 samples (about 15% of the dataset) had less than 10% error in ionic balance; the other 6 samples ranged between 10% and 28%.
To compare the effectiveness of the hierarchical HCA and non-hierarchical k-means algorithms, two analyses were performed, using Euclidean distance to measure the numerical distance between two objects: (1) a clustering analysis using HCA and k-means to identify wells with similar hydrogeochemical processes using the original dataset (40 wells including ionic balance outliers; referred through the manuscript as the “40 wells” dataset), and (2) the same analysis with the depurated dataset (34 wells, ionic balance < 10%; referred to as the “34 wells” dataset). For these clustering analyses, major cations, anions, total arsenic, fluoride, pH, and electrical conductivity were the variables utilized.
Statistical analysis was conducted using R 4.2.2 software. As descriptive statistical analysis showed non-normal distribution and skewness, Box–Cox transformation was applied to all variables to normalize the data prior to standardization. Saturation indices (SI) were calculated using Visual MINTEQ 3.1 software [55].
Grouping tendency was tested using Hopkins’ statistic () and principal component analysis (PCA). A threshold was selected to reject the null hypothesis that the dataset is uniformly distributed, i.e., no meaningful clusters are present in the dataset/weak clustering tendency; thus, means that the dataset contains defined clusters and close to 1.0 means a large clustering tendency [56]. Sampling site grouping was carried out via non-hierarchical k-means clustering with the kmeans function, establishing the optimal number of clusters from the data obtained via PCA and the fviz_nbclust function from the factoextra package. Hierarchical clustering (HCA) was performed with Euclidean distances and four agglomerative distance computations between pairs: average, single, complete, and Ward using the hclust function. To select the best HCA method, the agnes function from the cluster package was used to calculate the agglomerative coefficient of each method, which measures the number of clustering structures found.
Silhouette (Sil), Dunn, and Davies–Bouldin indices were calculated in the clusters formed with the original and depurated datasets according to the following formulas:
where
where is a set of objects represented as vectors in an -dimensional space , is the number of clusters, is an intercluster distance between cluster centroids and , and is an intracluster distance of any cluster ; is the average distance between the points within a cluster, and the same is true for and cluster . To assess clustering quality using the Silhouette index and Dunn index, the higher the value, the better. In the case of Davies–Bouldin, the lower, the better [30,57].
All diagrams were constructed in R 4.2.2 software. Piper and Stiff diagrams were constructed using smwrGraphs and smwrData packages from the U.S. Geological Survey. All plots (bivariate, boxplot, Na-normalized Ca2+ vs. HCO3−) were constructed using the ggplot2 package.
2.4.2. Geographical Information Systems (GIS)
Maps of the study area showing the sampling sites and the distribution of contaminants were constructed using ArcGIS version 10.8 with a WGS projection and UTM coordinates (Zone 13). Geologic data were obtained from the data bank (GeoInfoMex) of the Mexican Geologic Service. Aquifer geographical delimitation was obtained from the Water National Commission (CONAGUA) site [58].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Statistical Analysis and Piper Diagram
The nature of sampled sites is alkaline, with pH values ranging from 7.20 to 8.72. The chemical composition of major ions shows a dominance of Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+ for cations and HCO3− > SO42− > NO3− > Cl− > F− for anions. Descriptive statistics of major ions (mean, standard deviation, minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, maximum, and skewness) are listed in Table 1. The latter statistical analysis revealed that 72.5% of the sampled sites have concentrations of As and/or F− above 0.01 mg L−1 and 1.0 mg L−1, respectively, exceeding Mexican regulations for drinking water. A positively skewed distribution is observed in all parameters. This must be taken into account for multivariate analysis. The pH values indicated slightly alkaline groundwater. From the Piper diagram (Figure 2), the main hydrogeochemical facies identified are Ca-Na-HCO3, Na-Ca-HCO3, Na-HCO3, Na-Ca-HCO3-SO4, and Ca-HCO3.

Table 1.
Summarized descriptive statistics of groundwater chemical parameters.
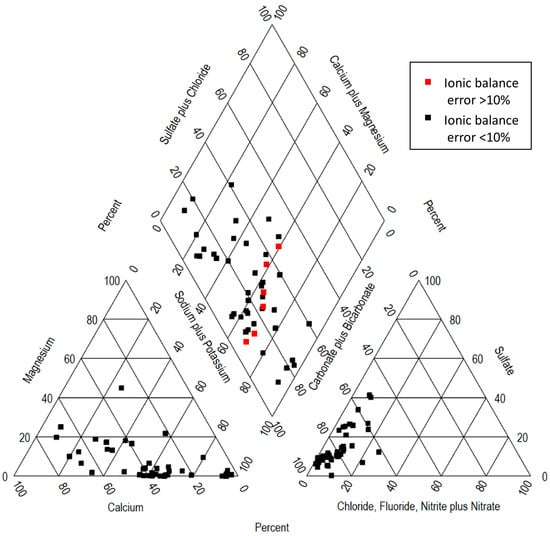
Figure 2.
Piper diagram of the 40 sampled sites. Red points were omitted in 30-sample subset.
3.2. Grouping Tendency
Hopkins’ statistic (H) of both datasets is close to 1.0 (H = 0.99), meaning that there are defined clusters in the dataset. PCA analysis shows three to four clusters in the complete dataset; note that Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3−, As and F− are the major contributors, in percentage, to the given principal components (Figure 3). The number of clusters resembles the main hydrogeochemical facies identified in Figure 2.
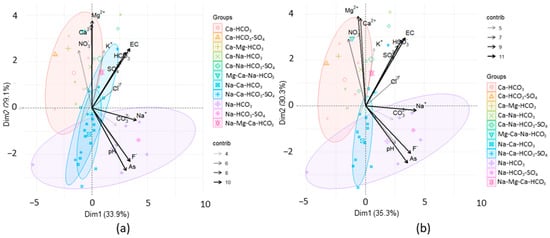
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis validation for grouping tendency: (a) four groups were identified in the original 40-well dataset; (b) three groups were identified in the depurated 34-well dataset.
Table 2 shows three principal components and the explained variance for both subsets in which eigenvalues were higher than one, according to Kaiser criterion, excluding the rest. In both cases, cumulative variance seems to be reasonable (>73%). Principal component 1 (Dim1) shows a strong loading of EC, Na+, As, F−, and HCO3−. Moderate As and F− loading to EC, Na+, and HCO3− suggests geological origin [59] and possible ion exchange processes, since the presence of Na+ and HCO3− is related to this mechanism. Principal component 2 (Dim2) is probably related to carbonate dissolution since there are Ca-HCO3 groundwater-type samples associated. Principal component 3 (Dim3) is lightly related to K-bearing mineral dissolution, with minor anthropogenic influence, such as K-rich fertilizers.

Table 2.
Principal component analysis of the two datasets.
3.2.1. Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm (40 Wells)
Agglomeration coefficients (from agnes function in R) of the average linkage, single linkage, complete linkage, and Ward’s minimum variance method are 0.68, 0.60, 0.78, and 0.88, respectively. Ward’s method generates more homogeneous clusters from these coefficients than the other linkage methods. The dendrogram obtained using Ward’s method shows similarities with the grouping found in PCA analysis (Figure 4).
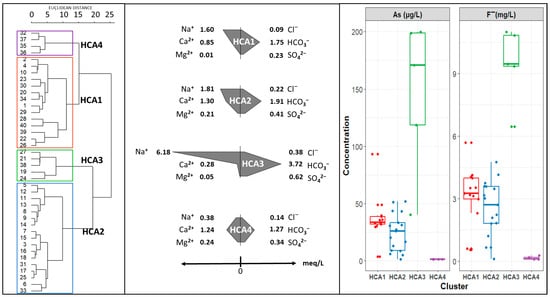
Figure 4.
Dendrogram of sampling sites constructed using Ward’s method and Euclidean distances.
Cluster HCA1 and cluster HCA2 are characterized by a Na-Ca-HCO3 composition but a more pronounced Ca concentration in the latter. Cluster HCA3 has a primarily Na-HCO3 composition, with the highest median concentration of arsenic and fluoride. Cluster HCA4 has a mainly Ca-HCO3 composition, with the lowest median concentration of arsenic and fluoride.
3.2.2. Dataset k-Means Algorithm (40-Well Original Dataset)
From the grouping tendencies, the non-hierarchical k-means clustering algorithm was evaluated with clusters. Figure 5 shows some differences for groups formed with HCA. In this case, cluster K1 represents mixed waters, where Ca-Na-HCO3. This group has a median concentration of arsenic and fluoride of 17 µg L−1 and 2.42 mg L−1, respectively. Cluster K2 has a Na-HCO3 composition and the highest median concentration of arsenic and fluoride. Cluster K3 has a Na-Ca-HCO3 composition, with lower arsenic and fluoride concentrations than group K1. Cluster K4 groups sampling sites with Ca-a HCO3 composition, with the lowest arsenic and fluoride median concentration.
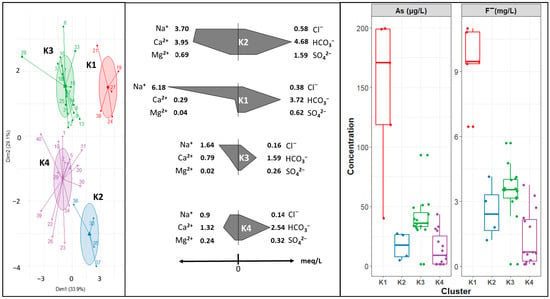
Figure 5.
Clusters of sampling sites constructed using the k-means clustering algorithm. Concentration is expressed as the median value of the group.
3.2.3. Comparison between Clustering Methods (40 Wells)
Figure 4 and Figure 5 suggest discrepancies in clusterization. Only sampling sites with the very marked characteristic of Na-HCO3 and high arsenic and fluoride concentrations remained in the same group. Spatial comparison shows an overlap between HCA1 and HCA2, while in the case of k-means clusterization, a more homogeneous stratification is observed (Figure 6). Regarding hydrogeochemical data, it seems that k-means clusters are grouped based mainly on the cation dominance by group Na+ > Na+ + Ca2+ mix > Ca2+ + Na+ mix > Ca2+ + Mg2+, and the HCO3− > HCO3−, SO42− + Cl− mix. This grouping trend agrees with PCA analysis, where Na+, F−, and As are the main variables for principal component 1 (explains 33.9% of the variance), and Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3−, and SO42− in principal component 2 (explains 29.1% of the variance). Because the presence of HCO3− and Na+ is related to the occurrence of As and F− via ion exchange, principal component 1 could be associated with that process. Principal component 2 could be associated with the dissolution of carbonates or silicates.
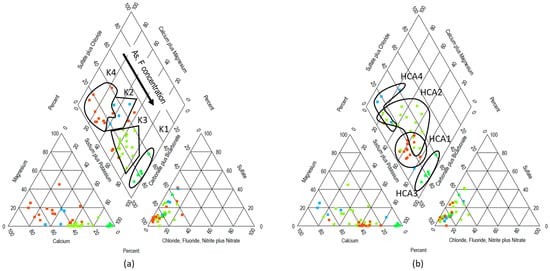
Figure 6.
Piper diagram color-coded by cluster. (left): clusters from k-means algorithm; (right): clusters from hierarchical clustering algorithm. (Note 1: Cluster boundaries are arbitrarily drawn to highlight the difference in the clusterization pattern. Note 2: Group colors in this figure were assigned for clusters visualization).
Figure 4 and Figure 5 show that arsenic and fluoride concentrations also contribute significantly to cluster formation. They are in the following order: K1 > K3 > K2 > K4. Cluster K1 key factors on group formation are high concentrations in As, F−, and Na+ and low concentrations (<0.3 meq L−1) of Ca2+ and Mg2+. Cluster K3 seems to have approximately the same contribution in terms of the variables used; therefore, the formation considered the lack of Mg2+, lower K+ concerning other groups, and the F− and Cl− concentrations. Cluster K4 group formation could be addressed to K+ and low Na+, As, and F− concentrations. Cluster K2’s main features seem to be high Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− concentrations when compared to the rest of the clusters, and its median concentration of arsenic and fluoride.
The homogeneity in groups in the case of the k-means algorithm is because it is iterative and randomly changes the distance assessment between clusters, allowing it to find a local minimal squared sum of errors (which does not imply an optimal cluster solution). This circumstance gives an advantage over the HCA method in defining subtle group differences.
3.2.4. Comparison between Clustering Methods (34 Wells)
When HCA and k-means algorithms were applied to data from the subset with <10% of error in ionic balance (34 wells), both clustering solutions yielded pretty similar results (Figure 7). Regarding clustering solutions from the complete dataset, only the k-means solution agrees with the latter results. From this, it seems that if few points with ≥10% error in ionic balance are also considered in the analysis (in this case, six points ranging from 10% to 28%, meaning the 15% of the dataset), k-means is still robust enough to yield useful grouping solutions. HCA, on the contrary, is more sensitive to deviations in ionic balance.
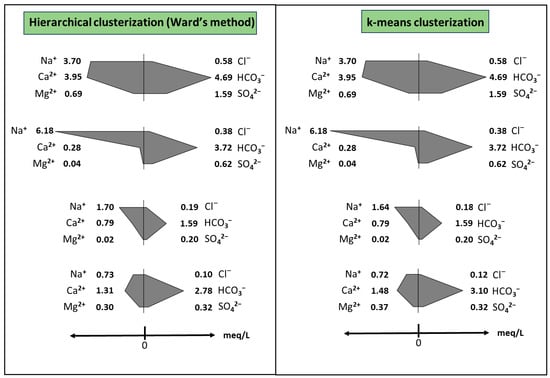
Figure 7.
Comparative Stiff diagrams of the groups formed by the two algorithms tested with the depurated 34 well dataset (error in ionic balance < 10%).
3.3. Clustering Quality Computation
Table 3 shows the computation of the Dunn and Davies–Bouldin indices before and after the removal of the six ionic balance outliers from the original dataset of 40 well samples for HCA and k-means clustering. For k-means, Dunn and Davies–Bouldin indices improved by about 18.3% and 5.4%, respectively, but the Silhouette index deteriorated by −9.6%. HCA shows a deterioration in the Dunn index and Silhouette index, about −2.8% and −9.8%, but the Davies–Bouldin index improved by about 7.3%.

Table 3.
Cluster quality computation for each clustering method before and after the removal of ionic balance outliers.
In this case, discrepancies in cluster validation indices are expected because each index evaluate different features of data clustering. The degradation of the Silhouette index can be explained since the index evaluates good clusters by assessing how similar a data point is with respect to the centroid of its own cluster in relation to its similarity to centroids of other clusters [60]. The apparently low value obtained possibly comes from small differences in the main cation concentrations between clusters, making it difficult for the index to differentiate small differences. The Dunn index is the ratio of the minimum distance between clusters to the maximum cluster diameter. It assesses the compactness of clusters and the distance between clusters (as far apart as possible). An improvement in the Dunn index means better clusters’ compaction [30]. In contrast, the Davies–Bouldin index considers good clusters to have low within-cluster variation and high between-cluster separation. This fact shows the proclivity of the Davies–Bouldin index to be sensitive to outliers in the dataset [60].
Regarding the Davies–Bouldin index as the adequate cluster validation index for outlier effect with the best performance [30,57], it can be seen that, after the removal of outliers, there is a general improvement in the quality of the formed clusters. Despite the slight improvement in each algorithm, HCA seems to be more sensitive to the presence of outliers in this case, while k-means seems to be more robust. As seen in Figure 8, HCA and k-means yield similar clustering solutions after the removal of outliers, giving more homogeneity to HCA clusters, while in the case of k-means, the clustering remained practically the same.
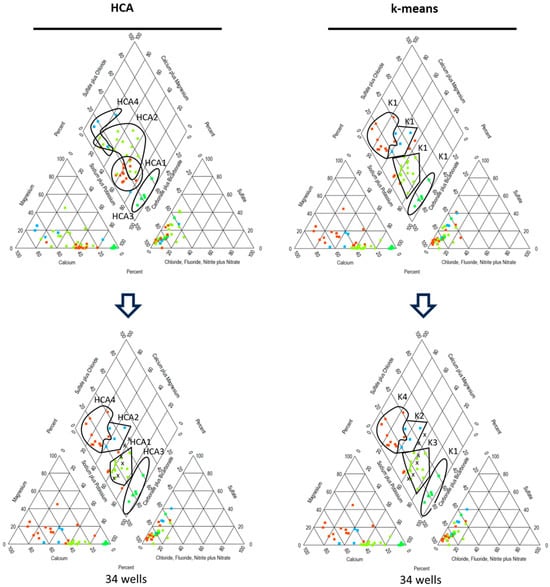
Figure 8.
Comparative Piper diagrams of the groups formed by k-means and HCA before and after the removal of ionic balance outliers (Note: Group colors in this figure were assigned for clusters visualization only).
More hydrogeochemical datasets need to be analyzed to support these conclusions, as k-means have been reported to be more sensitive to data outliers than HCA [30]. Nevertheless, this contradiction could be addressed to the fact that outliers in that kind of study were detected through algorithms like the Local Outlier Factor and Connectivity-based Outlier Factor; however, in this study, outliers were identified using the 10% error in ionic balance threshold, appealing to a chemical consideration more than a mere numeric one.
Various studies address the topic of ionic balance errors from the perspective of the quality in chemical analysis. However, there are no works comprising the effect of the outliers in clusterization of groundwater data for hydrogeochemical purposes. Since many studies rely on clusterization (frequently HCA) to identify processes or pollution sources, it is of great importance to take into account these outlier effects when datasets are not depurated (omitting data with ionic balance error > 10%), because the selected clusterization can lead to the misinterpretation of data and differences with the hydrogeochemical water classification when using a Piper diagram.
Thus, in terms of management, let us consider a sampling strategy to create a groundwater monitorization network in the aquifer. In this case, the purpose is to obtain representative groundwater data from the aquifer using the fewest wells possible. If outliers in ionic balance are not eliminated and a non-robust clusterization algorithm is used to establish monitoring zones, the selected sampling method may not be suitable, and consequently, the representativity of the results will be compromised.
3.4. Hydrogeochemical Analysis
Regarding the previous multivariate results, 40 well samples were used to identify the hydrogeochemical processes in the aquifer since previous analysis demonstrated that general conclusions are less affected by outliers if the k-means algorithm is used.
The dominant anion in the aquifer is HCO3−. A strong correlation of main cations with HCO3− (r = 0.885) was observed, indicating that silicate/carbonate weathering is a main process (Figure 9a). The Mg2+/(Mg2+ + Ca2+) ratio suggests calcite or dolomite weathering as the source of Ca2+ and HCO3− (Figure 9b). Ca2+/(Ca2+ + SO42−) suggests a source of calcium different from gypsum (Figure 9c), probably carbonates or silicates [21,61,62,63]. This evidence points to the main sources of HCO3− being carbonate or silicate weathering/dissolution. The weathering of silicates like feldspar (Equation (7)) or carbonates like calcite (Equation (8)), common minerals in Earth’s crust, is a source of HCO3− [64].
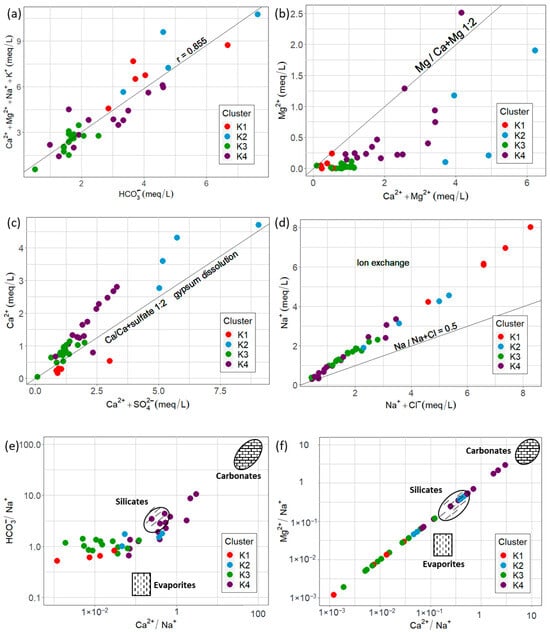
Figure 9.
Graphic hydrogeochemical process assessment: (a–d) bivariate plots; (e,f) Na+-normalized plot for HCO3−.
Feldspar:
Calcite:
Nevertheless, Na-normalized Ca2+ vs. HCO3− and Mg2+ vs. Ca2+ plots (after [65]) show that, for clusters K1, K2, and K3, Ca2+ and Mg2+ come from evaporites, and that for K4, silicate weathering is the main source. HCO3− mainly originates from silicate weathering.
In addition, ion exchange processes can occur, as indicated by the Na+/(Na+ + Cl−) > 0.5 ratio (Figure 9d). The Chloroalkaline indexes CA-I and CA-II in all samples plot in the negative quadrant (Figure 10), indicating a direct ion exchange process in which Ca2+ and Mg2+ in aquifer groundwater are exchanged by Na+ and K+ in clays of the aquifer matrix, as shown in Equation (9) [66]. This is feasible since the main exploitation zone is in the alluvial part of the aquifer.
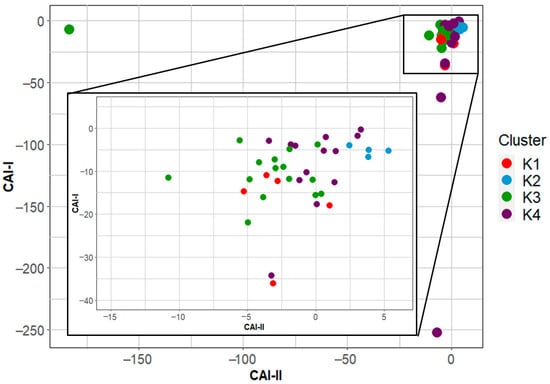
Figure 10.
Chloroalkaline indices of the 40 sampled wells.
Summarizing, hydrogeochemical processes involving As and F− were grouped into four clusters (K1 to K4) based on variations in Na+, Ca2+, As, and F−. Cluster K2 was a Na-HCO3 water type with high concentrations of As and F. Cluster K1, K3, and K4 exhibited Ca-HCO3, Na-Ca-HCO3, and Ca-Na-HCO3 water types, respectively, with decreasing As and F concentrations following the order K2 > K3 > K1 > K4. The groundwater of groups K2 and K3 are not suitable for drinking since they have greater ion exchange and felsic rock dissolution than the other two groups, exceeding the allowed limit of NOM-127-SSA-2021 for As and fluoride.
Hydrogeochemical processes of weathering of silicates and evaporites, and Na-Ca ion exchange with clays are likely the main processes controlling groundwater geochemistry in the Valle del Guadiana aquifer. The dissolution of felsic rocks present in the aquifer fill releases As and F−, with evaporation acting as an important concentration factor.
3.5. As and F Co-Occurrence in the Valle del Guadiana Aquifer
Taking into account the semiarid and volcanic nature of the Valle del Guadiana aquifer, several mineral sources of fluoride can be considered since it is present in the amorphous material of rhyolites in the Sierra Madre Occidental [18]. In the Valle del Guadiana aquifer, two hydrogeochemical processes affecting the fluoride concentration probably take place: calcite precipitation and ion exchange.
Figure 11a,b show that calcite precipitation can occur in 62.5% of the sampled sites. However, the magnitude of ion exchange processes could address the difference in fluoride concentration among groups. In cluster K1, a Na+/Ca2+ ratio of approximately 20 for the sampled sites (Figure 12) and undersaturation of calcite saturation indices of some of them suggests that fluoride pollution is caused by a scarcity of Ca2+ ions in groundwater due to an ion exchange process with clays, enhancing the dissolution of F-bearing minerals like apatite and micas. In clusters K2 and K4, calcite precipitation due to alkaline conditions (7 < pH < 9) and high HCO3− concentration is probable, with some contribution of ion exchange (K2 > K4), but low concentrations of fluoride in K4 can be assigned to fluoride adsorption onto precipitated calcium carbonates. Cluster K3 suggest a significant contribution to the ion exchange effect in the dissolution of F-bearing minerals due to low Ca2+ concentrations and higher Na+/Ca2+ with respect to K2 and K4 (Figure 12).
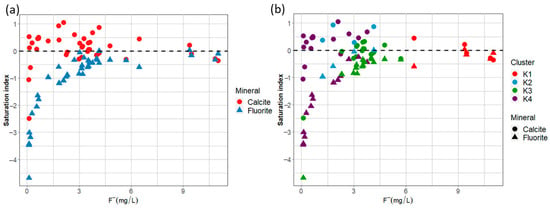
Figure 11.
(a) Saturation indices for calcite and fluorite as a function of fluoride concentration; (b) saturation indices for calcite and fluorite classified by cluster.
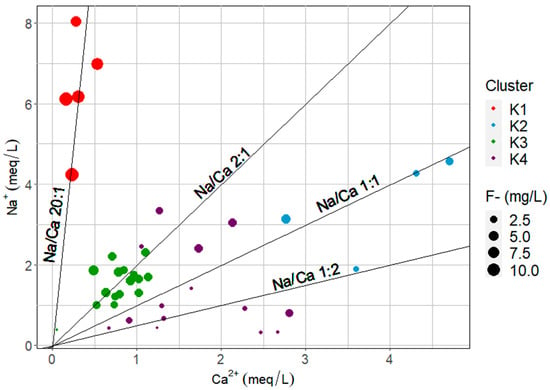
Figure 12.
Effect of Na+/Ca2+ ratio in fluoride concentration.
Regarding arsenic, potential sources are desorption from iron oxides (magnetite, hematite, and limonite), As-bearing minerals (arsenopyrite, pyrrhotite, and pyrite), and the weathering of As-containing volcanic glass, all of which are present in the zone [67]. Arsenic and fluoride exhibit a high correlation (r = 0.8381, t =14.026, p < 0.001), which suggests a common pathway to groundwater. Since pH > 8.0 and the concentration of HCO3− is >100 meq L−1 in most samples, arsenic leaching and desorption from aquifer sediments is feasible [68]. Additionally, there is a poor correlation between arsenic and sulfate (r = 0.022, t = 0.925, p = 0.361), which means that the oxidation of sulfur minerals is not a great source of arsenic [63]. Because no significant or barely significant correlation is observed between As and pH (r = 0.159, t = 0.925, p = 0.011), HCO3− (r = 0.007, t = 0.540, p = 0.592) and SO42−, arsenic and fluoride groundwater pollution probably comes mainly from the dissolution of felsic rocks and volcanic glass [69]. Figure 13 shows the arsenic and fluoride distributions of the sampled sites.
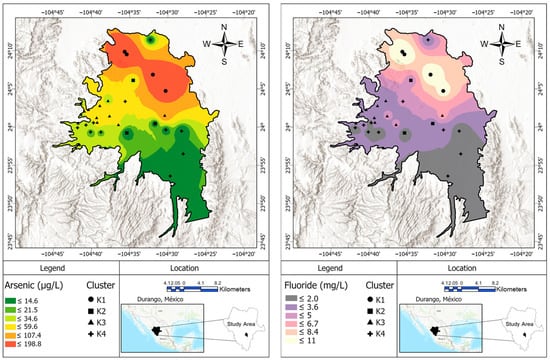
Figure 13.
Spatial distributions of arsenic (left) and fluoride (right) in Valle del Guadiana, May–June 2022.
According to an extensive review of the co-occurrence of As and F− in groundwater, focused on past and contemporary works from around the globe in the field [69], the mechanisms and sources proposed above are reasonable since the conditions of As-bearing minerals in the aquifer, oxidizing groundwater conditions, and evidence of ion exchange processes are present. In addition, according to the same review, this study is consistent with other works on semiarid regions in Latin America in which the co-occurrence points towards geological origins, sharing common aspects like being a sedimentary aquifer, felsic rocks being present in the zone, a Na-HCO3 groundwater type, aridity, and over-exploitation, amongst others.
3.6. Groundwater Management and Risk Mitigation in the Case of As and F Co-Occurrence
Groundwater management and risk mitigation strategies become crucial when faced with the co-occurrence of arsenic (As) and fluoride (F) in aquifers. Firstly, it is essential to delineate the spatial extent of contamination and identify hotspots where concentrations exceed regulatory limits. This information can guide targeted remediation efforts and prioritize areas for immediate intervention. Secondly, understanding the geochemical processes governing the mobilization of As and F is vital for developing effective treatment technologies. Techniques like adsorption, ion exchange, or membrane filtration may be employed, but their efficiency can be influenced by factors such as pH, redox conditions, and the presence of competing ions. The continuous monitoring of water quality parameters is necessary to ensure the long-term effectiveness of treatment systems. Additionally, raising public awareness about the health risks associated with As and F exposure is crucial for promoting safe water consumption practices and encouraging community participation in water management initiatives. Lastly, implementing sustainable groundwater management practices, such as controlled extraction, artificial recharge, and land-use regulations, can help mitigate further deterioration of water quality and protect this valuable resource for future generations.
4. Conclusions
The groundwater in the Valle del Guadiana aquifer exhibits alkaline conditions, with pH values ranging from 7.20 to 8.72. The chemical composition shows a dominance of Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+ for cations and HCO3− > SO42− > NO3− > Cl− > F− for anions. The main hydrogeochemical facies identified indicate a predominantly bicarbonate-type groundwater. Multivariate analysis and hydrogeochemical plots revealed that the k-means clustering algorithm was more robust in terms of ionic balance outliers (15% of the dataset) than hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA). Both algorithms yielded almost identical clustering solutions when the dataset was free of ionic balance outliers. These results suggest that using k-means with the original dataset does not compromise the identification of hydrogeochemical processes.
Four clusters (K1 to K4) were identified based on variations in Na+, Ca2+, As, and F−. Cluster K2 was a Na-HCO3 water type with high concentrations of As and F−, probably due to ion exchange. Cluster K1, K3, and K4 Ca-HCO3, Na-Ca-HCO3, and Ca-Na-HCO3 water types, respectively, had decreasing As and F concentrations following the order K2 > K3 > K1 > K4, showing a decrease in the ion exchange effect and felsic rock dissolution. The groundwater of groups K2 and K3 and some of the other clusters are not suitable for drinking purposes due to their As and F− contents.
The identified hydrogeochemical processes governing groundwater chemistry are weathering and ion exchange. The dominant anion, HCO3−, is primarily derived from silicate/carbonate weathering and the dissolution of minerals like feldspar and calcite. Ion exchange processes involve the exchange of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in groundwater with Na+ and K+ in the aquifer matrix clays, particularly in the alluvial part of the aquifer.
The release of fluoride into groundwater is likely due to the dissolution of F-bearing minerals, facilitated by the removal of Ca2+ through ion exchange and calcite precipitation. Potential sources of fluoride include amorphous materials in rhyolites and minerals like apatite and micas. The co-occurrence of arsenic shows a high correlation (r = 0.84) with fluoride but barely significant correlations with pH, HCO3−, and SO42−. This suggests that the primary sources of both arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater are the dissolution of felsic rocks in the aquifer. Potential sources of arsenic include iron oxides, As-bearing minerals like arsenopyrite and pyrite, and As-containing volcanic glass present in the area. In summary, the groundwater chemistry in the Valle del Guadiana aquifer is governed by weathering and ion exchange processes, leading to the release of fluoride and arsenic into the groundwater, primarily from the dissolution of felsic rocks and F-bearing minerals in the aquifer matrix.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation: J.R.I.-C.; Conceptualization: J.R.I.-C. and M.T.A.-H.; Methodology: J.R.I.-C., M.T.A.-H., and D.B.-B.; Data curation: J.R.I.-C.; Formal analysis and investigation: J.R.I.-C., L.A.T.-C., L.R.-C., and D.B.-B.; Funding acquisition: J.R.I.-C.; Resources: L.A.T.-C.; Software: J.R.I.-C. and D.B.-B.; Validation: D.B.-B. and M.G.; Visualization: J.R.I.-C.; Supervision: M.T.A.-H., D.B.-B., and M.G.; Project administration: J.R.I.-C. and M.T.A.-H.; Writing—review and editing: M.T.A.-H., M.G., and L.R.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Council of Science and Technology of the State of Durango (Grant: Promotion of Applied Research with Emphasis on Regional Development and Social, Environmental and Economic Relevance, 2021). Durango’s local office of the National Water Commission (CONAGUA) and Waters of the Municipality of Durango (AMD) personnel for all their help during this study. Additionally, to Joel García Pazos for the edition of all maps.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abdul, K.S.M.; Jayasinghe, S.S.; Chandana, E.P.S.; Jayasumana, C.; De Silva, P.M.C.S. Arsenic and Human Health Effects: A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 828–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Arsenic. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic#:~:text=Long%2Dterm%20exposure%20to%20arsenic,increased%20deaths%20in%20young%20adults (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- Hurtado-Jiménez, R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Arsenic in Drinking Water in the Los Altos de Jalisco Region of Mexico. Rev. Panam. Salud Pública 2006, 20, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.M.; Chakraborty, R.; Bundschuh, J.; Bhattacharya, P.; Parvez, F. Health Effects of Arsenic Exposure in Latin America: An Overview of the Past Eight Years of Research. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamboa-Loira, B.; Cebrián, M.E.; López-Carrillo, L. Arsenic Exposure in Northern Mexican Women. Salud Publica Mex. 2020, 62, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlknecht, J.; Aguilar-Barajas, I.; Farias, P.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Hoogesteger, J.; Lara, R.H.; Ramírez-Mendoza, R.A.; Mora, A. Hydrochemical Controls on Arsenic Contamination and Its Health Risks in the Comarca Lagunera Region (Mexico): Implications of the Scientific Evidence for Public Health Policy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solanki, Y.S.; Agarwal, M.; Gupta, A.B.; Gupta, S.; Shukla, P. Fluoride Occurrences, Health Problems, Detection, and Remediation Methods for Drinking Water: A Comprehensive Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, S.J.; Winkel, L.H.E.; Voegelin, A.; Berg, M.; Johnson, A.C. Arsenic and Other Geogenic Contaminants in Groundwater—A Global Challenge. Chimia 2020, 74, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, P.K.; Tripathi, P. Arsenic and Fluoride Contamination in Groundwater: A Review of Global Scenarios with Special Reference to India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 13, 100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, H.R.; Balogun, F.O.; Bowers, C.A.; Miller, C.T.; Obeidy, C.S.; Polizzotto, M.L.; Tashnia, S.U.; Vinson, D.S.; Duckworth, O.W. Towards Understanding Factors Affecting Arsenic, Chromium, and Vanadium Mobility in the Subsurface. Water 2022, 14, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz Pérez, M.D. Panorama de La Calidad de Agua de Consumo Humano En México. In Hacia el Cumplimiento del Derecho Humano al Agua. Arsénico y Fluoruro en Agua: Riesgos y Perspectivas Desde la Sociedad Civil y la Academia en México; Del Razo, L.M., Ledón, J.M., Velasco, M.N., Eds.; UNAM-Instituto de Geofísica: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2021; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, D.; Castro, L.; Turrubiates, F.; Milan, J.; Díaz-Barriga, F. Assessment of the Exposure to Fluoride from Drinking Water in Durango, Mexico, Using a Geographic Information System. Fluoride 1998, 31, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Vázquez, F.J.; González-Martell, A.D.; Fernández-Macias, J.C.; Rocha-Amador, D.O.; González-Palomo, A.K.; Ilizaliturri-Hernández, C.A.; González-Mille, D.J.; Cilia-Lopez, V.G. Health Risk Assessment in Children Living in an Urban Area with Hydrofluorosis: San Luis Potosí Mexico Case Study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 68, 126863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Gómez, V.M.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Gutiérrez, M.; López, D.N. Fluoride and Arsenic in an Alluvial Aquifer System in Chihuahua, Mexico: Contaminant Levels, Potential Sources, and Co-Occurrence. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Alegría, C.J.; Fuentes-Rivas, R.M.; García-Rivas, J.L.; Fonseca-Montes de Oca, R.M.G.; García-Gaitán, B. Presence and Distribution of Fluoride Ions in Groundwater for Human in a Semiconfined Volcanic Aquifer. Resources 2019, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armienta, M.A.; Segovia, N. Arsenic and Fluoride in the Groundwater of Mexico. Environ. Geochem. Health 2008, 30, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, O.; González, J.; Júnez-Ferreira, H.E.; Bautista, C.-F.; Cardona, A. Correlation of Arsenic and Fluoride in the Groundwater for Human Consumption in a Semiarid Region of Mexico. Procedia Eng. 2017, 186, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Gaytán-Alarcón, A.P. Arsenic and Fluorine in Groundwater in Northern Mexico: Spatial Distribution and Enrichment Factors. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, A.; Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Moreau, C.; Bertrand, G.; Mahlknecht, J. Mapping Salinization and Trace Element Abundance (Including as and Other Metalloids) in the Groundwater of North-Central Mexico Using a Double-Clustering Approach. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, D.H.F.; Oliveira-Filho, E.C. Multivariate Statistical Analysis for Water Quality Assessment: A Review of Research Published between 2001 and 2020. Hydrology 2023, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastianoni, A.; Guastaldi, E.; Barbagli, A.; Bernardinetti, S.; Zirulia, A.; Brancale, M.; Colonna, T. Multivariate Analysis Applied to Aquifer Hydrogeochemical Evaluation: A Case Study in the Coastal Significant Subterranean Water Body between “Cecina River and San Vincenzo”, Tuscany (Italy). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Liu, W.; Pan, Z.; Ling, K. Comparative Study of Hydrochemical Classification Based on Different Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, X.W.; Wan, L.; Han, G.; Guo, H. Hydrogeochemical Characterization of Groundwater Flow Systems in the Discharge Area of a River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, A.; Liesch, T.; Broda, S. Feature-Based Groundwater Hydrograph Clustering Using Unsupervised Self-Organizing Map-Ensembles. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Rosales-Lagarde, L.; Hernández-Antonio, A.; Mahlknecht, J. Hydrogeochemistry of Groundwater Supplied to the City of Monterrey, Mexico. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 17, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.; Bux, R.K.; Medina, D.I.; Barrios-Piña, H.; Mahlknecht, J. Spatial and Multivariate Statistical Analyses of Human Health Risk Associated with the Consumption of Heavy Metals in Groundwater of Monterrey Metropolitan Area, Mexico. Water 2023, 15, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Celestino, A.E.; Martínez-Cruz, D.A.; Otazo-Sánchez, E.M.; Gavi-Reyes, F.; Vásquez-Soto, D. Groundwater Quality Assessment: An Improved Approach to K-Means Clustering, Principal Component Analysis and Spatial Analysis: A Case Study. Water 2018, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín Celestino, A.E.; Ramos Leal, J.A.; Martínez Cruz, D.A.; Tuxpan Vargas, J.; De Lara Bashulto, J.; Morán Ramírez, J. Identification of the Hydrogeochemical Processes and Assessment of Groundwater Quality, Using Multivariate Statistical Approaches and Water Quality Index in a Wastewater Irrigated Region. Water 2019, 11, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradilla-Hernández, M.S.; de Anda, J.; Garcia-Gonzalez, A.; Meza-Rodríguez, D.; Yebra Montes, C.; Perfecto-Avalos, Y. Multivariate Water Quality Analysis of Lake Cajititlán, Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak-Brzezińska, A.; Gaibei, I. How the Outliers Influence the Quality of Clustering? Entropy 2022, 24, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CONAGUA. Actualización de La Disponibilidad Media Anual de Agua en el Acuífero Valle del Guadiana (1003), Estado de Durango. Ciudad de México, México. 2024. Available online: https://sigagis.conagua.gob.mx/gas1/Edos_Acuiferos_18/durango/DR_1003.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- INEGI En Durango Somos 1 832 650 Habitantes: Censo de Población y Vivienda 2020. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/saladeprensa/boletines/2021/EstSociodemo/ResultCenso2020_Dgo.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- CONAGUA. Acuerdo Por El Que Se Dan a Conocer Los Estudios Técnicos Del Acuífero 1003 Valle Del Guadiana, En El Estado de Durango. Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5150942&fecha=07/07/2010#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Ferrari, L.; Valencia-Moreno, M.; Bryan, S. Magmatismo y Tectónica En La Sierra Madre Occidental y Su Relación Con La Evolución de La Margen Occidental de Norteamérica. Boletín Soc. Geológica Mex. 2005, 57, 343–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.M.; Kusin, F.M.; Asha’ari, Z.H.; Aris, A.Z. Characterization of Water Quality Conditions in the Klang River Basin, Malaysia Using Self Organizing Map and K-Means Algorithm. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.; Bandela, N.; Kulkarni, J.; Sahoo, S.K.; Kumar, A. Hydrogeochemistry and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Groundwater Quality of Hard Rock Aquifers from Deccan Trap Basalt in Western India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, R.; Zouari, K. Coupled Geochemical Modeling and Multivariate Statistical Analysis Approach for the Assessment of Groundwater Quality in Irrigated Areas: A Study from North Eastern of Tunisia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woocay, A.; Walton, J. Multivariate Analyses of Water Chemistry: Surface and Ground Water Interactions. Ground Water 2008, 46, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatou, R.D.; Kabeyene, V.K.; Mboudou, G.E. Multivariate Statistical Analysis for the Assessment of Hydrogeochemistry of Groundwater in Upper Kambo Watershed (Douala-Cameroon). J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2017, 5, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.A.; Szabó, N.P.; Szűcs, P. Multivariate Statistical and Hydrochemical Approaches for Evaluation of Groundwater Quality in North Bahri City-Sudan. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, T.G.; Zaidi, F.K. Hydrochemical Classification and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Groundwater from Wadi Sahba Area in Central Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Xiao, C.; Li, M.; Liang, X. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Groundwater Quality Evaluation Based on Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Water 2020, 12, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjerezi, M.; Vogt, R.D.; Aagaard, P.; Saka, J.D.K. Hydro-Geochemical Processes in an Area with Saline Groundwater in Lower Shire River Valley, Malawi: An Integrated Application of Hierarchical Cluster and Principal Component Analyses. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Gurugnanam, B.; Vasudevan, S.; Rajeshkanna, B.; Dharanirajan, K.; Prabhakaran, N. Hydrogeochemical Studies by Multivariate Statistical Analysis in Upper Thirumanimuthar Sub-Basin, Cauvery River, Tamil Nadu, India. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2009, 8, 693–700. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Nag, S.K. Application of Multivariate Statistical Analysis Concepts for Assessment of Hydrogeochemistry of Groundwater—A Study in Suri I and II Blocks of Birbhum District, West Bengal, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G. Cluster Analysis. In Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery for Geoscientists; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 191–237. [Google Scholar]
- Abboud, I.A. Statistical Analysis of the Hydro-Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the Aquifers of the Yarmouk Basin, North Jordan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.H.; Eissa, M.; Mohamed, E.A.; Ramadan, H.S.; Czuppon, G.; Kovács, A.; Szűcs, P. Application of Stable Isotopes, Mixing Models, and K-Means Cluster Analysis to Detect Recharge and Salinity Origins in Siwa Oasis, Egypt. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, P.; Wolkersdorfer, C.; Wolkersdorfer, K. Application of Multivariate Statistical Analysis in Mine Water Hydrogeochemical Studies of the Outcropped Upper Carboniferous, Ruhr Area, Germany. In Proceedings of the IMWA 2020, Christchurch, New Zealand, 9–13 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Eskandari, E.; Mohammadzadeh, H.; Nassery, H.; Vadiati, M.; Zadeh, A.M.; Kisi, O. Delineation of Isotopic and Hydrochemical Evolution of Karstic Aquifers with Different Cluster-Based (HCA, KM, FCM and GKM) Methods. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaafi, M.; Abba, S.I.; Tawabini, B.; Abdulazeez, I.; Salhi, B.; Usman, J.; Aljundi, I.H. Integrated Clustering Analysis for Delineating Seawater Intrusion and Heavy Metals in Arabian Gulf Coastal Groundwater of Saudi Arabia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, C.R.; Das, S.; Panda, S. Groundwater Quality Monitoring by Correlation, Regression and Hierarchical Clustering Analyses Using WQI and PAST Tools. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 16, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, H.; Wu, B.; Ye, L. A Review of the Application of Machine Learning in Water Quality Evaluation. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Rice, E.W., Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Eds.; APHA Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, J.P. Visual MINTEQ (3.1). KTH. Royal Institute of Technology. 2013. Available online: https://vminteq.com/ (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Banerjee, A.; Dave, R.N. Validating Clusters Using the Hopkins Statistic. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37542), Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 July 2004; pp. 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Arbelaitz, O.; Gurrutxaga, I.; Muguerza, J.; Pérez, J.M.; Perona, I. An Extensive Comparative Study of Cluster Validity Indices. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAGUA. Sistema de Información Geográfica de Acuíferos y Cuencas SIGACUA. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conagua/acciones-y-programas/sistema-de-informacion-geografica-de-acuiferos-y-cuencas-sigacua-55161 (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Ali, S.; Verma, S.; Agarwal, M.B.; Islam, R.; Mehrotra, M.; Deolia, R.K.; Kumar, J.; Singh, S.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Raj, D.; et al. Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Water Quality Index and Principal Component Analysis in the Achnera Block, Agra District, Uttar Pradesh, Northern India. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekemeyong Awong, L.E.; Zielinska, T. Comparative Analysis of the Clustering Quality in Self-Organizing Maps for Human Posture Classification. Sensors 2023, 23, 7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounslow, A.W. Water Quality Data. Analysis and Interpretation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Ma, B. The Origin of Major Ions of Groundwater in a Loess Aquifer. Water 2019, 11, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.; Neog, N.; Bhagat, C.; Hdeib, R.; Mahlknecht, J.; Kumar, M. Arsenic in the Groundwater of the Upper Brahmaputra Floodplain: Variability, Health Risks and Potential Impacts. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar, R.; Asghari Moghaddam, A.; Tziritis, E. Hydrogeochemical Features of Groundwater Resources in Tabriz Plain, Northwest of Iran. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3997–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupre, B.; Louvat, P.; Allegre, C.J. Global Silicate Weathering and CO2 Consumption Rates Deduced from the Chemistry of Large Rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morici, S.; Gagliano Candela, E.; Favara, R.; La Pica, L.; Scaletta, C.; Pecoraino, G. Hydrogeochemical Characterization of the Alluvial Aquifer of Catania Plain, Sicily (South Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servicio Geológico Mexicano Descarga Las Cartas Impresas Editadas Por El Sgm.Gob.Mx. Available online: http://www.gob.mx/sgm/articulos/descarga-las-cartas-impresas-editadas-por-el-sgm-70622?idiom=es (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Kim, M.-J.; Nriagu, J.; Haack, S. Carbonate Ions and Arsenic Dissolution by Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Goswami, R.; Patel, A.K.; Srivastava, M.; Das, N. Scenario, Perspectives and Mechanism of Arsenic and Fluoride Co-Occurrence in the Groundwater: A Review. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).