Abstract
In this paper, by using GNSS technologies, some features of the distribution and some morphometric parameters of dams and ponds created by the Eurasian beaver (Castor fiber L.) along ten rivers of the Volga-Kama region of European Russia were identified. Detected features depend on the geomorphological, lithological, and landscape features of these rivers and their basins. The significant role of river slopes, as well as landscape zoning, in the distribution of beaver dams and ponds along small rivers in the study region is shown. In the rivers under study, almost all beaver constructions are located on riverbed slopes of less than 3% (most often, less than 2%). In the south of the forest zone (the southern taiga of the Vyatka River basin), the majority of dams and ponds (about 90%) are located on slopes of less than 1%, while, within the uplands of the forest-steppe zone, this location varies depending on the length of the rivers. In general, the greater the average slope of the river (the greater the average elevation of the river basin), the lower, other things being equal, the degree of beaver transformation of such rivers. This feature is better expressed in the rivers of the forest landscape zone and less expressed in the rivers flowing in the forest-steppe zone. Analysis of the morphometric parameters of beaver dams shows statistically significant trends towards an increase in their average height, as the channel slopes increase. Statistically significant trends were also identified towards a decrease in the length of dams and the length of associated ponds, with an increase in channel slopes. It is noteworthy that the critical values of the slope for a statistically significant and relatively sharp change in these parameters are 1.45%, 1.07 (or 0.54)%, and 0.65 (or 0.47)%, respectively. The greatest average heights of beaver dams are confined to those rivers where their basins are composed of loamy rocks/soils (especially those that are poorly plowed), compared with “sandy” river basins. This may be due to the peculiarities of the ratio of surface and underground water runoff in these basins and, as a consequence, different intensities of snowmelt- and rainfall-induced flood flow. We assume that the above-mentioned features reflect the early stages of beaver expansion (population growth) in the studied rivers.
1. Introduction
Beavers are mammals that have the unique ability to transform the bottoms of river valleys through the construction of dams and associated ponds. They most intensively develop streams, small rivers, or small branches of larger rivers [1,2,3,4]. The construction of dams and ponds affects the hydrological and biochemical regime of small rivers, as well as the geomorphic processes in floodplain–channel complexes; therefore, the beaver is also called an “ecosystem engineer” [5,6]. The appearance of beaver ponds, on the one hand, results in changes in existing (transformed by anthropogenic activity) floodplain–channel complexes, which undoubtedly creates a conflict with humans [7]. On the other hand, their presence also results in some improvements in small rivers, especially in intensively agriculturally developed regions [8,9]. The settlement of beavers in new areas of channels and floodplains of small rivers can also cause significant changes in the structural and functional organization of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems [10]. Beaver ponds can also be used to restore small rivers [11,12,13].
At the beginning of the last century, in the vast territory of the former Russian Empire, the beaver (the Eurasian beaver, Castor fiber L.), as a species, was on the verge of extinction, due to hunting. In Russia, small populations (10–15 families each) survived in the Voronezh Oblast (European Russia) and Western Siberia, as well as in Belarus (the total number of the species was less than 1000 animals). Beaver reserves were created in the following places: Voronezhsky (1923), Berezinsky (1925), and Kondo-Sosvinsky (1927) (https://zapovednik-vrn.ru/o-zapovednike1/history/istoriya-bobrovogo-pitomnika/; accessed on 25 March 2024). As a result of their reintroduction, by the early 1960s, the beaver population had reached commercial levels. Currently, half of the beavers living in Russia originate from the Voronezhsky State Nature Biosphere Reserve (Voronezh Oblast’, southwest European Russia). The beaver population in European Russia has increased annually in recent decades and, by the end of 2022, the number of these animals amounted to over 650 thousand individuals, including the Canadian beaver (Castor canadensis Kuhl), which was introduced mainly in northwestern European Russia [14]. The distribution area of the beaver includes vast areas not only within forest zones, but also within forest-steppe and steppe zones of the temperate zone. The construction of dams and associated ponds also leads to a change in the longitudinal profile of the river channel, in increased (in areas near the dam) lateral erosion and the accumulation of sediment and organic matter at the bottom of ponds and, often, on low floodplains, which, as a result, leads to noticeable changes in the landscapes of floodplain–channel complexes [2,15,16,17]. A large number of studies examining the impact of beaver dams and ponds in small rivers have been carried out in North [1,15,16,17,18,19] and South [20] America, as well as in Europe [21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. However, in European Russia, such studies are rare [28,29,30,31].
First of all, among the factors influencing the construction activity of beavers, the slope of the river stands [32]. In lowland landscapes, riverbed slopes are usually low (<1.5%) [33]. Curtis and Jensen [34] showed that beavers use clay and silt as components to build their dams. In their study, the presence of clay and silt was highly correlated with river slope. Another factor influencing the distribution of beaver dams is the presence of vegetation [35]. Since the beaver prefers herbaceous vegetation [35], factors associated with the availability of food are often less important than factors associated with the morphological and morphometric characteristics of the riverbed and floodplain. In addition, the location of dams is influenced by the species composition of vegetation growing along the rivers [36], as well as the presence of anthropogenic hydraulic structures [37,38,39]. At the same time, there is no consensus regarding the identification of the main factors influencing the location of beavers, at the river scale [34].
Understanding these factors is necessary to predict beaver numbers and to calculate the habitat areas of other species that use beaver ponds, as well as other factors important to beaver management. This knowledge in human economic activity (assessment of the balance of water resources, water consumption projections, etc.) is no less important. Recognizing the growing global interest in studying the impact of beaver activity on small streams and the factors that control it [40,41,42,43,44,45], we also decided to make a feasible contribution to solving this problem, at the level of the selected region, which is one of the most susceptible to this activity, but, at the same time, is poorly studied—the Eastern European Plain, or rather in one of its central parts—the Volga-Kama region. In this regard, the following tasks are solved: In the Materials and Methods section, the characteristics of the rivers studied and the research methods used are given. The Results section presents the following: (1) the features of distribution of beaver constructions (dams and ponds) along the studied rivers, considering the morphometric characteristics of the latter, based on the landscape zoning of the study area; (2) the influence of these features on changes in the longitudinal structure of water flow in the rivers; and (3) the main regional features of the changes in the height and length of beaver dams and the length of associated ponds along the rivers, with changes in the main factors of their distribution (river slope, annual water flow, lithological structure, and the degree of plowing of soils in the basins of the studied rivers). In the Discussion section, the nature of the above-mentioned relationships and some aspects of the influence of the identified features on small rivers and the geomorphological, hydrological, and other processes occurring in them are discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Rivers
The field survey was carried out in August–October 2022–2023. The ten selected rivers, flowing in the forest (southern part) and forest-steppe zones of the east of the East European Plain (the basins of the Volga and Kama rivers (Figure 1)), differ in the length, slope, basin lithology, and the degree of anthropogenic transformation of the natural landscapes of their basins. The choice of these rivers was determined by their geomorphic representativeness in each subregion studied. The length of the rivers varies from 2.7 km to 16.6 km; the area of the basins varies from 3.1 to 86.9 km2. The feeding of the rivers under study is mixed, with a large predominance of snow. In this regard, the predominant value (more than 2/3) of the annual water flow of the studied rivers occurs during the spring flood (March and/or April).
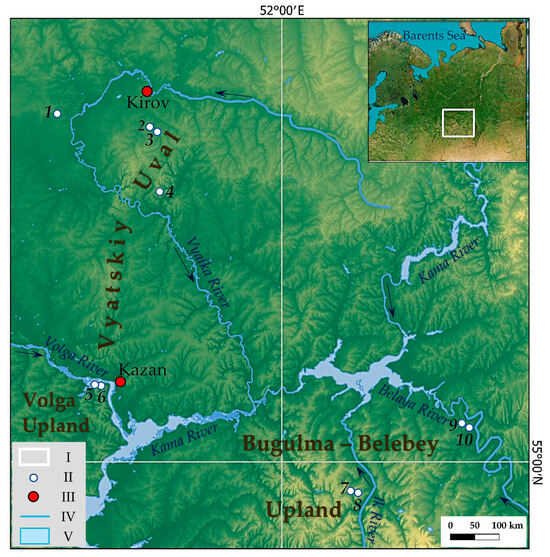
Figure 1.
The location of the study region and studied small rivers. I—the location of the study region in the East European Plain; II—the location of the studied small rivers in the study region, 1—Atsvezh River, 2—Peschanka River, 3—Brodovka River, 4—Kuser River, 5—Morkvashka River, 6—Morkvashinka River, 7—Karakashly River, 8—Zaumyat River, 9—Salayaz River, and 10—Aigildinka River; III—some administrative centers; IV—rivers; and V—reservoirs and lakes. NB: For geodetic coordinates of the mouths of the studied rivers, see Table A1 in Appendix A.
The steep right slopes of the valleys of the studied rivers are composed of bedrock in the lower part, mainly limestones and sandstones of the Upper Permian epoch, which are overlain by either brown deluvial loams with an abundance of broken stone (Morkvashinka, Morkvashka, Karakashly, Zaumyat, Salayaz, and Aigildinka rivers), or fluvioglacial (Peschanka, Brodovka, and Kuser rivers) and Triassic sands (Atsvezh River). In the valleys of the rivers studied, low (up to 0.5–0.7 m) and high (up to ≈1.5 m) floodplains are morphologically expressed in small fragments; the low (Early Holocene) river terrace (up to 4–5 m) is morphologically expressed in larger fragments (for example, in the Morkvashinka River). Natural vegetation is represented by spruce–fir–pine forests (south of the forest zone); linden–oak forests, with an admixture of maple, beech, and elm (forest-steppe zone); and forb–grass pasture meadows (the south of the forest-steppe zone) [46,47]. Due to the low efficiency of agriculture, most of the arable land, especially in the forest zone, has been abandoned over the last three to four decades. Low plowing is currently observed in some river basins in the northern forest-steppe zone, but most of these lands are used to expand the area of human settlements. Another part of these river basins is intensively used in agriculture (mainly in the forest-steppe zone). The studied rivers flow in the following administrative regions of Russia: The Republic of Tatarstan (Morkvashinka, Morkvashka, Karakashly, and Zaumyat rivers), the Republic of Bashkortostan (Salayaz and Aigildinka rivers), and the Kirov Oblast (Atsvezh, Peschanka, Brodovka, and Kuser rivers).
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Field Work
The survey of the bottom of river valleys was carried out using the satellite positioning method (GNSS receiver). The new generation Trimble R12i receiver was chosen for use as the equipment in this type of survey, which is well adapted to conditions of high dense vegetation and rugged terrain. The survey of riverbeds was carried out in the Radio RTK mode, the main feature of which is the use of two receivers, one of which—Trimble R10—is a base station and the second (Trimble R12) is a rover (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Field study of beaver dams and ponds, using GNSS technologies, along the Salayaz River (October 2023; photos by A.V. Gusarov and A.G. Sharifullin).
The base station was used as a stationary device during the survey to continuously provide the mobile rover with measurement and correction information for post-processing and high-precision real-time positioning. When working in radio mode at a distance from the base station of no more than 2 km, the standard deviation of the obtained coordinates averaged up to 15 mm in plan and up to 20 mm in height. The GNSS receiver determined the planned and elevation marks of the following elements of the riverbeds and beaver ponds: the position and height of the riverbed and water edge at river bends, the height of the lower and upper reaches (pounds) of beaver dams, and their width and length. The height and length of the beaver dams were determined using a surveying rod (see Figure 2) and measuring tape. The height was measured from the foot of the lower side of the dam in its central part (in the thalweg of the channel) to the level of the maximum height of the dam. The length of the dam was measured along its crest. The above-mentioned methods have been tested and used by various researchers [48,49,50,51].
2.2.2. Field Data Processing
In office conditions, field data obtained during topographic survey (horizontal and elevation marks) using GNSS equipment were loaded into Trimble Business Center software (version 5.70), where they were processed (editing and leveling). In this case, the average adjustment error was 2 cm in plan and 3 cm in elevation, which is quite acceptable when working at a basin scale. In the QGIS 3.28.2 program, for each mark of the channel or water edge and the position of the dams, as well as the lower and upper reaches (pounds) of the dams marked in the field, the distance from the mouth of the rivers under study was determined. When constructing curves of longitudinal river profiles, elevation values of the channel thalweg (for flooded and drained sections of the river) and the water level in beaver ponds were used. In addition, separate icons on the profile indicate the position of beaver dams and the mouths of tributaries (permanent and temporary watercourses).
Considering that in lowland rivers, most of the beaver dams and ponds are located, as mentioned above, on river slopes of less than 1.5% [32], and the fact that almost all beaver dams and ponds identified by us were located on river slopes of no more than 3%, along the longitudinal profiles of rivers, we identified and categorized areas with slopes into the following four groups: <1%, 1–2%, 2–3%, and >3%. This approach made it possible to compare the studied rivers from a single perspective. For each of these groups, the length, the so-called “fall” (the difference between the maximum and minimum absolute elevation in the section), the average slope (the ratio of the fall to the length of the section), the length of sectors within the section subjected to beaver activity, the number of dams, the density of dams (the ratio of the number of dams to the length of the section), the length of the pond as the distance from the dam to the point where the surface of the pond wedges out along the shortest broken (or straight, depending on the morphology of the pond) line, and the length of the river inside beaver colonies were determined [51]. The following elements (or sectors; that is, sections of a river (channel) distinguished by the presence or absence of beaver activity) were identified in the longitudinal structure of the water flow: drained fragments of the riverbed previously occupied by beaver ponds (without operating dams); drained fragments of the riverbed previously occupied by beaver ponds (with operating dams); drained fragments of the riverbed without ponds; flooded channel sectors with ponds; and flooded channel sectors without ponds.
In total, this work analyzed 256 beaver dams and associated ponds. All of them were considered when assessing their spatial distribution along the rivers. However, when assessing their morphometric parameters, only 212 dams and ponds were used, since the conditions for morphometric measurements in the dams and ponds were difficult (high levels of swampiness at the bottoms of small river valleys, first of all) in some cases.
In addition to the above-mentioned characteristics, the following quantitative parameters related to the studied rivers and their basins were determined (Table 1): L is the length of the river from the source (including a small dry valley in its upper reaches) to the mouth, which was determined based on the results of field surveys; S is the watershed area, determined from topographic maps at a scale of 1:50,000 [52] by identifying watershed lines in the QGIS program; Ě is the average elevation of the river basin, which was determined according to SRTM data (JPL Shuttle Radar Topography Mission 2009 Technical Fact Sheet; http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/srtm/index.html; accessed on 20 December 2023) in the QGIS program; A is the difference between the maximum and minimum absolute elevation of the riverbed obtained in the field; G is the river slope, calculated as the ratio of A to the length (L) of the river; R is average annual water runoff depth in the basin of a given river (according to the River basins Geoportal, https://bassepr.kpfu.ru/; accessed on 22 December 2023); Lith is the predominant lithology in the river basin, obtained from the geological map of pre-Quaternary and Quaternary deposits [53] (Sd—sands, Cl—clays, Lm—loams, BS—broken stone, Lim—limestone); and Ant is the share of the area of cultivated land (excluding abandoned land) in the total area of the river basin.

Table 1.
Some characteristics of small rivers and their basins involved in the study.
The studied river basins represent two natural (landscape) zones (or terrestrial ecosystems) of the East European Plain—forest (southern taiga) and forest-steppe. Their differences in basic environmental characteristics are presented in Table 1.
2.2.3. Statistics
A standard set of descriptive statistics was used. Student’s t-test was used to identify differences in the obtained means in the studied relationship series with their preliminary testing for normal distribution (the Shapiro–Wilk test). To identify trends and their statistical significance in the series, the Mann–Kendall test was applied. These series were previously tested for homogeneity (Pettitt’s test and Buishand’s test) and heteroscedasticity (White’s test). All the above tests were carried out using XLSTAT (version 2016.02.28451)/Statistical Software for Excel.
3. Results
The geodetic work carried out made it possible to identify the location of beaver dams and ponds depending on the characteristics of the longitudinal profiles of the rivers, which are presented in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5. As can be seen from these figures, almost all identified dams and associated ponds are located in river sections with prevailing slopes of less than 3% (Figure 6). It can be assumed that a slope of 3% is a critical value for the location of beaver constructions along the studied rivers. Moreover, the location of beaver dams and ponds in the uppermost reaches is also limited by the lack of permanent runoff, as shown in Figure 7.
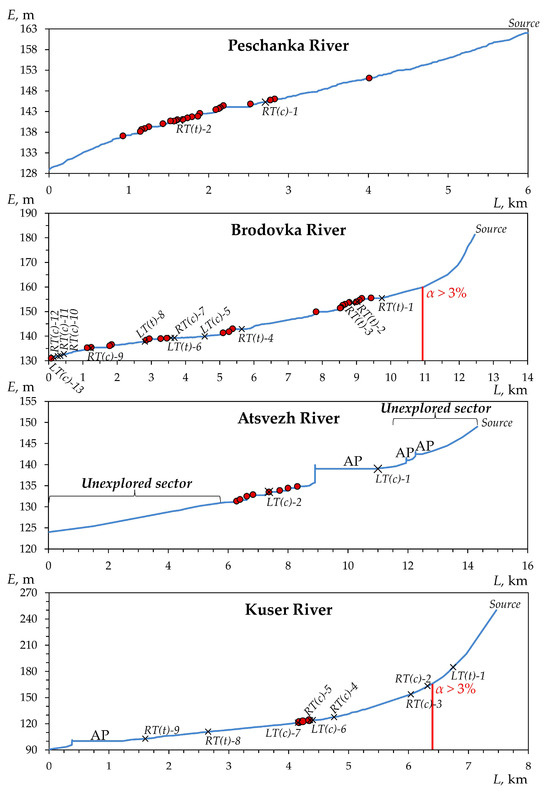
Figure 3.
Longitudinal profiles of the four studied rivers in the south of the forest zone of the Volga-Kama region (the Vyatka River basin) (see Figure 1) and the distribution of beaver dams (shown in red circles) along them. L—horizontal distance; E—absolute elevation; RT and LT—right and left tributaries, respectively (t is temporary, c is constant (permanent)); α is the average slope of the riverbed above the red line; and AP is anthropogenic pond.
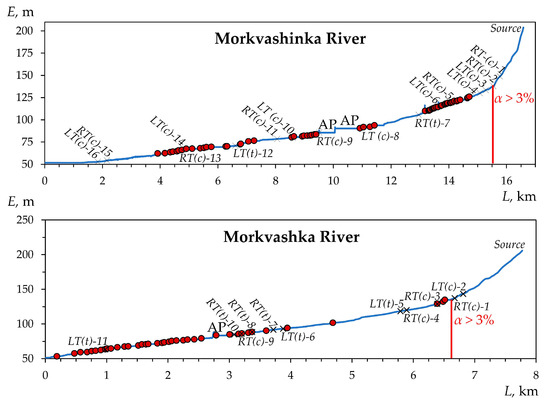
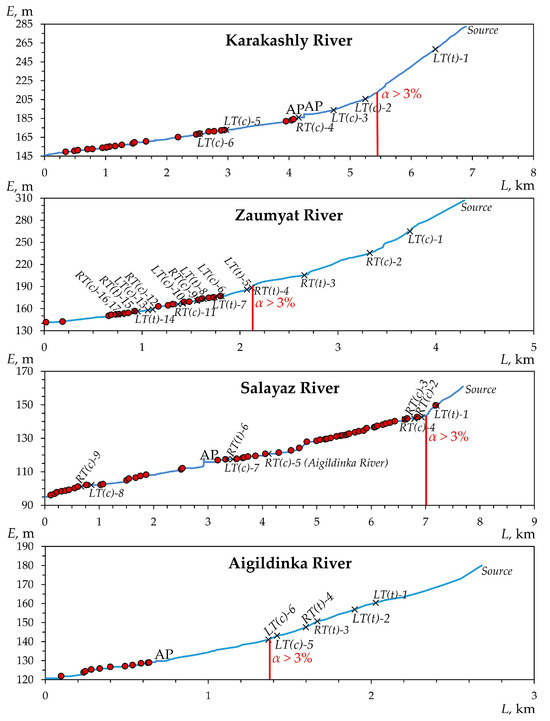

Figure 6.
Examples of channel and channel–floodplain beaver dams and ponds in the studied rivers with slopes of less than 3% (photos by A.G. Sharifullin).

Figure 7.
The upper seasonally dry reaches of the Zaumyat River, free from beaver dams and ponds, with channel slope over 3% (October 2023; photos by A.V. Gusarov).
We have identified (our own classification) four types of distribution of beaver dams and ponds along the rivers under study. Type I—central single colonial—in which dams and ponds are concentrated in the central part of the longitudinal profile of the river at some distance from the mouth (up to 4–6 km), in the form of a single colony. For example, this is typical for the Atsvezh (presumably, because it has not been fully studied) and Kuser rivers (Figure 3, A1). Type II—near-estuarine single colonial—is characterized by the location of dams and ponds in the lower, most flat part of the river profile (<1 km from the mouth). This type of distribution is found, for example, in the Aigildinka River, with a length of <3 km (Figure 5).
Type III—scattered colonial—is the most common, which involves the arrangement of dams and associated ponds in separate groups (colonies) located at some distance (from the first hundred meters to 1–1.5 km) from each other. The most typical rivers of this type are the Peschanka, Morkvashinka, Karakashly, Brodovka, and Salayaz (to a lesser extent) rivers. Type IV is transitional between the near-estuarine single colonial and scattered colonial types, which assumes the greatest concentration and number of dams and ponds in the near-estuarine part with their gradual spread along the colonial type upstream. Examples of such rivers are the Morkvashka and Zaumyat rivers.
The above-described is also reflected in the number of dams and ponds and their density within the river sections most developed by beavers (with slopes up to 3%). Within each slope subcategory (less than 1%, 1–2%, and 2–3%; see Section 2.2.2), we calculated the number and density of beaver constructions. Analysis of Figure 8 shows that in the south of the forest zone, the largest number of all identified dams and ponds is confined to slopes of less than 1%. At the same time, the density of beaver constructions does not always clearly correlate with their number. Thus, in the Brodovka River, located in the south of the forest zone, the largest number of beaver dams and ponds, as well as their highest density, occur on slopes of less than 1% and, in the shortest rivers (the Kuser and Peschanka rivers), the highest density falls on the second subcategory of slopes (1–2%), while the largest number of dams and ponds falls in the first subcategory (less than 1%). In more southern regions (the uplands of the forest-steppe zone of the Volga-Kama region), the above-mentioned pattern in the number of dams and ponds is preserved only in the longest rivers studied (the Morkvashinka and Salayaz rivers). However, the highest density of beaver dams and ponds in these rivers is confined to the second subcategory of slopes (1–2%). For shorter rivers in these conditions, the largest number of dams and ponds, as well as their highest density, are confined to the second (1–2%) or even the third (2–3%) subcategories of slopes; for example, in the Zaumyat River, which has the highest average absolute elevation.
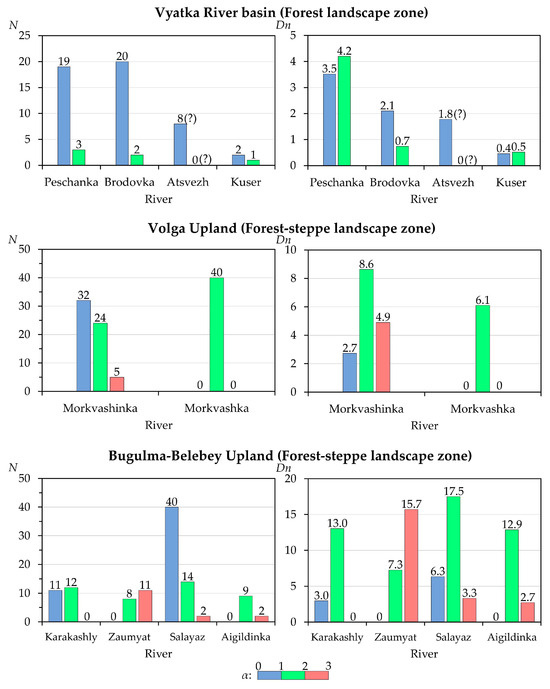
Figure 8.
The ratio between the number (N, un.) and density (Dn, un./km) of beaver dams along the studied small rivers depending on the slope (α, %) of their channels. The symbol (?) means the supposed (minimum) quantity.
The longitudinal structure of the water flow was also analyzed depending on the ratio of the lengths of the river channels occupied by the water flow, in connection with the activity of the beaver (Figure 9). For the selected elements of the longitudinal structure of the water flow, see Section 2.2.2.
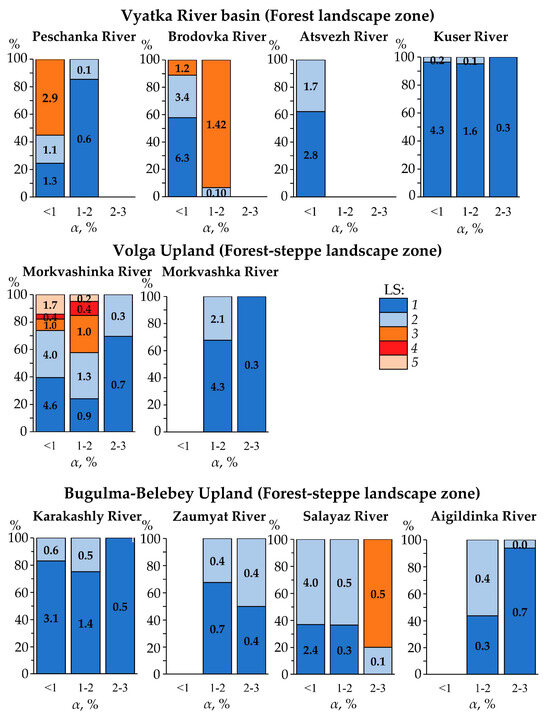
Figure 9.
The longitudinal structure (LS) of the water flow of the studied small rivers depending on the activity of the beaver at different average slopes (α) of their channels. LS: 1—flooded channel sectors without ponds; 2—flooded channel sectors with ponds; 3—drained fragments of the riverbed without ponds; 4—drained fragments of the riverbed previously occupied by beaver ponds (with operating dams); and 5—drained fragments of the riverbed previously occupied by beaver ponds (without operating dams).
It was revealed that in both the south of the forest zone and in the forest-steppe zone, one of the main limiting factors in the location of river sectors occupied by beaver ponds is the slope of the riverbed. Within the southern forest zone, the least amount of transformation of the rivers by beavers is observed in the Kuser River, characterized by the highest average slopes (2.13%), and the greatest amount of transformation is observed in the rivers with the lowest average slopes—the Peschanka (0.55%) and Brodovka (0.41%) rivers (Figure 9). Moreover, the latter rivers have the largest proportion of channel sectors with a lack of constant flow, which is partly due to the peculiarities of the geological structure of their basins. In more arid areas, in the forest-steppe zone, the average channel slopes are also an important factor, although to a lesser extent than in the south of the forest zone. An excellent example of this is the Zaumyat (3.91%), Aigildinka (2.21%), Karakashly (1.98%), and Morkvashinka (0.92%) rivers, where the proportion of sectors subject to beaver activity is still noticeably higher than in the Kuser River, characterized by a similar (close) average slope. Moreover, the variation of such sectors within the above-mentioned forest-steppe rivers is largely explained by their length. After all, the longer the river, the more diverse its longitudinal water flow structure. An excellent example of this is the longest and gently sloping river of the forest-steppe zone that we studied—the Morkvashinka River (0.92%).
As for the features of the changes in the height (h) and length (D) of the dams, as well as the length of their associated ponds (L), these are as follows: Across all the rivers studied, there is a tendency for the average height of beaver dams to increase as the channel slopes (α) increase (Figure 10). The critical value of the channel slope at which a statistically significant change in the height of beaver dams occurs is 1.45%, according to Pettitt’s test (p = 0.019) and Buishand’s test (p = 0.012). This feature is, perhaps, based on hydrological predetermination, the disclosure of which requires further research.
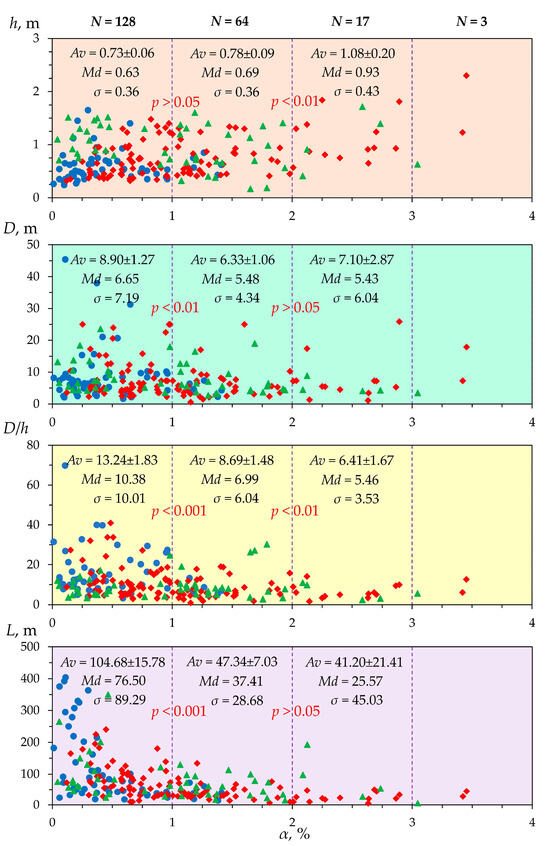
Figure 10.
Changes in the height (h) and length (D) of beaver dams and their ratio (D/h), as well as the length of beaver ponds (L), in the studied small rivers, due to changes in channel slopes (α). N is the total number of dams or ponds in the corresponding subcategory of channel slope; Av is the average value; Md is the median; σ is the standard deviation; and p is the statistical probability (t-test) of changes in the average values in adjacent subcategories of channel slope. The diagrams show rivers with figures of different colors, as follows: The Vyatka River basin in blue; the northern extremity of the Volga Upland in green; and the Bugulma-Belebey Upland in red. NB: According to the Mann–Kendall test, statistical significance of linear trends in the following relationships is α/h—a statistically significant positive trend (p = 0.002; Kendall’s τ = 0.144); α/D—a statistically significant negative trend (p = 0.021; Kendall’s τ = −0.107); α/(D/h)—a statistically significant negative trend (p = 0.0001; Kendall’s τ = −0.202); and α/L—a statistically significant negative trend (p = 0.00001; Kendall’s τ = −0.383). All four series are heterogeneous (according to Pettitt’s test and Buishand’s test) and heteroscedastic (according to White’s test).
There is also a reduction in the average length of the dams (D), as the slopes increase. The critical value of the channel slope at which a statistically significant change in the length of the beaver dams occurs is 1.07% (according to Pettitt’s test; p = 0.025) or 0.54% (according to Buishand’s test; p = 0.044). A further increase in the slope has little effect on the statistically significant change in the average length of the beaver dams (Figure 10). The overall decrease in the D/h index, which characterizes the ratio between the length and height of a beaver dam, can also be traced as the slopes increase. The critical value of the channel slope at which a statistically significant change in the average D/h index is 0.98%, according to Pettitt’s test (p = 0.000) and Buishand’s test (p = 0.000).
There is a clear and statistically significant trend for beaver pond lengths (L) to decrease as the channel slopes increase (Figure 10). The critical value of the channel slope at which a statistically significant change in the average length of beaver ponds occurs is 0.65% (according to Pettitt’s test; p < 0.0001) or 0.47% (according to Buishand’s test; p < 0.0001).
The distribution of the above-mentioned quantitative parameters of beaver dams and ponds reveals some regional features. We examined this issue using the example of river sections with slopes of less than 1%. The greatest average height of beaver dams is confined to the rivers of the northern extremity of the Volga Upland and it is statistically significantly different from the studied rivers of other subregions of the study region (Table 2). We calculated the longest average length of beaver dams for the studied rivers of the Vyatka River basin, characterized by the lowest average slopes. However, in this case, the difference between this length and the average lengths of beaver dams in the rivers in other subregions is statistically insignificant (Table 2). As for the length of beaver ponds, its maximum also occurs in the studied rivers of the Vyatka River basin. This maximum has a statistically significant difference (by 2.8 times) only from the average length of beaver ponds in the studied rivers flowing in the west of the Bugulma-Belebey Upland (the Karakashly and Zaumyat rivers) (Table 2) that are characterized by the greatest average slopes.

Table 2.
Changes in some morphometric parameters of beaver dams and ponds in the studied small rivers by subregions of the study region. Only river sections with slopes of less than 1% were analyzed.
It is also important to note the influence of the geological (lithological) features of river basins on the height and length of beaver dams. Thus, the greatest average height of dams is confined to the river basins composed of surface loamy deposits (with loamy soils) (see Table 1). It differs (on average by 44%), in a statistically significant manner, from the average height of beaver dams in the river basins, which are composed of predominantly sandy deposits (sandy soils) on the surface (Figure 11). As for the length of the dams, we did not identify such a feature of influence of the lithological structure of the studied river basins.
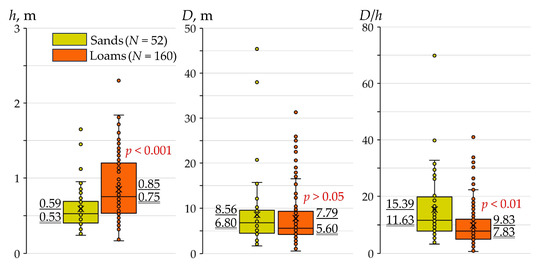
Figure 11.
Box plots showing changes in the height (h) and length (D) of beaver dams, as well as their ratio (D/h), in all the studied small rivers with basins composed of predominantly sandy or loamy rocks (soils) on the surface. Values underlined are average values; values underlined twice are median values; p is the statistical probability (t-test) of changes in average values; N is the number of the studied beaver dams.
In the “loamy” river basins (see Table 1), we also revealed the indirect influence of human activity within their watershed area on the morphometric parameters of beaver dams, which is expressed through the intensity of transformation of natural landscapes (primarily, the percentage of plowed soils in the watershed area; see Table 1) (Figure 12). In those river basins where soil plowing is less than 30%, the height of the beaver dams is statistically significantly higher (on average by 28%) than in the river basins with soil plowing of more than 30%. When comparing the average lengths of beaver dams, no statistically significant differences were revealed, although slightly greater dam lengths are also typical for the river basins with soil plowing of less than 30% (see Figure 12).
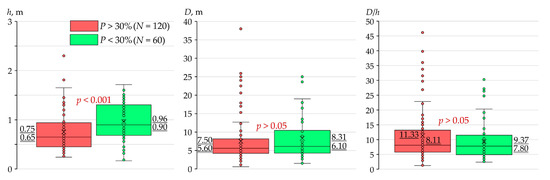
Figure 12.
Box plots showing changes in the height (h) and length (D) of beaver dams, as well as their ratio (D/h), in the studied small rivers with basins with a predominance of loamy rocks (soils) on the surface with different soil plowing (P). For symbols, see Figure 11.
An attempt was also made to identify features of changes in the morphometric parameters of beaver dams and their associated ponds with changes in the average long-term annual river water flow (W). Since there are no hydrometric observations in all the studied rivers, we derived the indicated hydrological parameter from the average long-term annual water runoff depth in the studied river basins (see Table 1), considering the known area (in km2) occupied by each river basin. The resulting patterns are depicted in Figure 13.
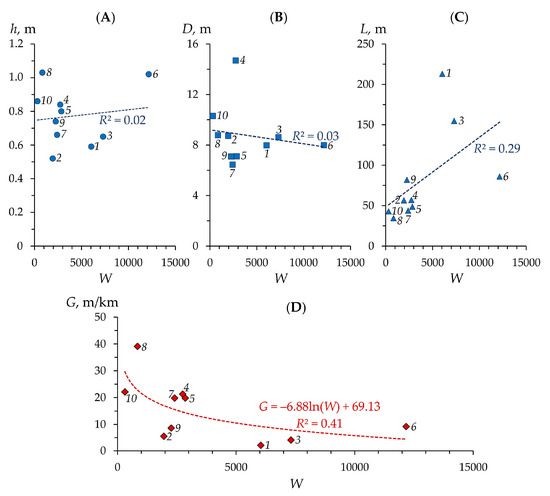
Figure 13.
Changes in the average height (h) (A) and length (D) (B) of beaver dams, as well as the length (L) of associated ponds (C), as the average long-term annual flow of water (W, ×103 m3 per year) in the studied small rivers changes. NB: According to the Mann–Kendall test, a statistically significant linear trend is only observed in the relationship W/L (p = 0.029; Kendall’s τ = 0.556). According to Figure 1, 1, 2, 3 … are the numbering of the rivers studied. (D) is the relationship between W and the average slopes of the rivers (G) (see Table 1).
According to Figure 13, only the direct relationship between annual water flow and beaver pond length is statistically significant. The longest ponds, on average, are characteristic of rivers with the highest water flow—the Morkvashinka, Brodovka, and Atsvezh rivers. Most likely, this relationship is not direct in its essence, but indirect, since these rivers have the smallest average slopes; the greater the annual water flow, the more gentle the average slopes develop in rivers during their long evolution (all other things being equal) (Figure 13) and the longer the beaver ponds they currently have (see also Table 2).
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion of Findings
The results presented above show the significant role of the morphometric characteristics of the studied rivers, primarily of the slopes, in the distribution of beaver dams and their associated ponds. This is primarily reflected both in their total number and in the density and type of distribution of these objects along the rivers. All other things being equal, the longer the river, the flatter its longitudinal profile and the more complex the distribution of beaver dams and ponds along it. In the rivers studied, we encountered only isolated cases of beaver constructions located on average slopes of more than 3% and almost all of these objects were located on slopes of less than 3% (mainly less than 2%). In the south of the forest zone, the majority of dams and ponds are located on slopes of less than 1%, while, within the uplands of the more arid forest-steppe zone, this distribution varies depending on the length of the rivers, whereby in longer rivers, the “northern” type (i.e., forest (taiga) zone type) of location is preserved; for shorter rivers, a “southern” type (i.e., forest-steppe zone type) is observed, which is characterized by a wide range of dam location depending on the slope (Figure 8). Moreover, the highest density of dams and ponds in the “southern” type generally occurs on slopes of 1–3%, while in the “northern” type, the highest density of dams and ponds occurs on slopes of less than 1%. In general, the higher the average slope of the river (the higher the average absolute elevation of the drainage basin), the lower the degree of beaver transformation of such rivers (other things being equal). This feature is better expressed for the rivers in the forest landscape zone (with a predominance of lowlands) and comparatively less expressed in the rivers flowing among forest-steppe landscapes (with a predominance of uplands) (Figure 9).
The above features largely determine the above-mentioned types of beaver distribution. The longer the river and the flatter its profile, the more the location of dams and ponds corresponds to the type of beaver distribution, which emphasizes a developed and ecologically sustainable structure, namely the dispersed colonial type of distribution along the river, in which separate clusters (beaver colonies) are identified [54].
The changes noted above in some morphometric parameters of beaver dams and ponds depending on slopes are quite expected. In river sections with large channel slopes, when forming a sufficiently large pond suitable for the life of a beaver family, it is necessary to build a higher dam, which is generally confirmed by a tendency to increase the average height of dams with increasing slopes. The greater height of beaver dams in the middle and upper reaches of the river is also due to the greater seasonal variability of the river water level than is usually observed in the lower reaches. This is partly due to the narrower and shallower river channels upriver.
In the lower reaches of rivers with the smallest slopes, where the water flow rates and the width of watercourses are greatest, the longest dams are required for the construction of ponds (often with pond water spilling onto the river floodplain). This conclusion is confirmed by a statistically significant increase in the average length of dams in small rivers with slopes of less than 1% (Figure 10). Upstream, as the channel slopes increase, the length of dams generally decreases, which follows a narrowing of the channel itself, due to its deeper vertical incision into bedrock (especially in the middle reaches of rivers).
The increase in the length of beaver ponds with decreasing slopes (especially with slopes less than 0.5–0.7%) also has a physical basis. With the same average height of beaver dams, at lower slopes, a pond water surface is formed that is larger in area and length than at higher slopes, according to the law of trigonometry. If there are exceptions, then they are local in nature and have their justification for a set of local reasons.
The influence of the lithological structure of the surface of the drainage basin on the morphometric characteristics of beaver dams is explained in the peculiarities of the distribution of snowmelt and rainfall water, forming surface and underground runoff. The more loamy the composition of the soils that make up the surface of a river basin, the higher, other things being equal, the seasonal variability of river water flow [55,56] and, therefore, there is a greater need for beavers to build higher dams than in rivers with basins composed of sandy deposits that better filter surface water runoff. Relatively weak anthropogenic transformation in the river basins with sandy soils (see Table 1) additionally reduces the seasonal variability of river water flow and, consequently, the average height of beaver dams. The influence of the lithological factor on the length of beaver dams does not have a reliable statistical significance (Figure 11). Some statistically insignificant excesses in the length of dams in the studied “sandy” river basins compared with the “loamy” basins are most likely associated with the peculiarities of erosive horizontal deformations of river floodplains, whereby, other things being equal, sandy deposits of floodplains (like looser deposits) are eroded more intensely than loamy deposits of floodplains [57] and, therefore, there is a greater need for the construction of longer beaver dams. This hypothesis needs to be tested using more data, since, in addition to the above-described, the location of beaver dams within the channel and its elements (relatively straight channel, meandering channel, and its elements) is also important to consider.
As for the greater average height of beaver dams in the “loamy” river basins with poorly plowed soils (see Figure 12), we assume that one of the reasons for this is the somewhat greater depth of incision of the channels of such rivers with their relatively weak siltation. The latter may be associated with a smaller mass of sediments entering the rivers with a relatively smaller area of eroded land (mainly cropland). The influence of soil plowing on the seasonal variability of river water flow and the intensity of water erosion in their basins is discussed in more detail in [55,56,57].
4.2. Beaver Activity and Rivers/Channels
The construction activity of the beaver results, first of all, in a change in hydrological characteristics, which is manifested in a reduction in the speed of water flow [58], a local increase in the water level in the riverbed, and an increase in the water reserves through the creation of beaver ponds [59]. This is especially true for small rivers of semi-arid regions, the flow of which has decreased significantly in recent decades due to climate change and increased human consumption of water resources [60]. An important geomorphological aspect of beaver activity is the creation of riverbank burrows and canals, as well as the accumulation of sediment in the beds and floodplains of small rivers. Beavers often build several burrows in one pond [61]. For example, along two temporarily drained beaver ponds with a total length of about 200 m in the Morkvashinka River and in the upper reaches of the Morkvashka River (Figure 14), we discovered several dozen such burrows of varying internal volumes.

Figure 14.
Beaver burrows created on the banks of the uppermost pond in the upper reaches of the Morkvashka River. These photos were taken by A.V. Gusarov in April 2023.
When creating such burrows, a significant amount of sediment enters the riverbed (pond bottom) [62,63]. In addition, riverbank burrows can be destroyed during snow melting or rain floods, as well as under the influence of other external factors [64], thereby transforming the topography of both the riverbed and the floodplain/terrace. The creation by beavers of relatively high and long dams, which also occupy a low floodplain, sometimes results in the appearance of multi-branch channels on them [61]. Such areas are identified in most of the rivers we studied, except for the Kuser, Zaumyat, and Aigildinka rivers. Sometimes, beavers build dams in places where anthropogenic dams have broken or on the bottoms of drained anthropogenic ponds, creating a complex topography and forming a complex sequence of accumulation of anthropogenic and beaver (castorogenic) sediments. We encountered similar phenomena in the Morkvashinka, Morkvashka, Peschanka, and Atsvezh rivers.
The revealed features of distribution of beaver dams and ponds can be traced, to one degree or another, not only in the small rivers of the east of the East European Plain, but also in the forest zone of the Upper Volga Plain [54], as well as in the plains of Western [61] and North America [65,66,67]. Thus, according to [65], the distribution densities of beaver dams in the studied rivers of Quebec (Canada) are close to those obtained from the rivers we studied, despite the fact that these rivers are longer, but are well comparable in the average slope. As in our study, almost the same river slopes of the greatest distribution of beaver constructions—0–2% and 1–4%—were found in [66,67], respectively.
A large amount of mineral and organic materials is deposited in beaver ponds, depending on both the morphometric characteristics of the ponds and the environmental features in their watersheds [1,2,13,68]. Butler and Malanson [68,69] estimated sediment accumulation rates of 2 to 39 cm per annum in some ponds in Montana (USA). In Oregon (USA), in the first years of the existence of ponds in this state, the sedimentation rate was up to 47 cm per annum, but, after six years, it decreased to 0.075 cm per annum [16]. In Germany, the average sedimentation rate in beaver ponds was 6 cm per annum [70]. According to Butler and Malanson [2], the rate of sedimentation can vary 10 times even within the same river basin and depends on the geological, geomorphological, and environmental features of the given territory. In the upper reaches of the studied Salayaz and Aigildinka rivers, along the shoreline of their ponds, areas with accumulations of bottom sediments were found, which indicates the periodic removal of material from the bottoms of the intra-channel ponds by beavers (including during the procedure for straightening the riverbed) (Figure 15), probably accumulated as a result of the soil erosion of agricultural fields in the river’s watershed area. Beaver-induced sediment management is strongly recommended as a beneficial practice that could contribute to the conservation and restoration of small rivers [11,12,13,71].

Figure 15.
Examples of some channel beaver ponds, cleared of bottom sediments and straightened by beavers, in the Salayaz (left) and Aigildinka (right) rivers (October 2023; photos by A.G. Sharifullin).
The above-mentioned and many other facts show the importance of studying the activities of the beaver as an environment-(trans)forming, ecological, and, sometimes, even social factor in the valleys of small rivers as one of the most environmentally vulnerable elements of the river network, as a whole. This research is becoming increasingly important and needed given the progressive changes in climate [72,73], hydrological processes [74], and land use [75] in the study region.
4.3. Study Limitations
In this work, only ten small rivers were studied. This somewhat reduces the representativeness of the results obtained, considering the relatively large area of the study region. However, at the same time, increasing the number of rivers is a difficult task, given the limited time for expeditionary field work. Also, this paper does not consider the location of beaver dams and associated ponds within the steppe zone, where, due to relatively higher aridity, their distribution conditions may differ somewhat and also depend on the feeding conditions for the beaver. Some sections of the channels of the small rivers studied are heavily swamped (especially in the forest zone), so the morphometric parameters of the dams, primarily the length of the dams, were determined with an error. In addition, for the Morkvashinka and Morkvashka rivers, these parameters were determined only for part of the dams and ponds and in the Atsvezh River, only the middle course of the river was examined in detail due to the high swampiness of the floodplain–channel complex of its valley in the upper and lower reaches. Due to the high swampiness of a number of river sections, it was not always possible to accurately determine the true length of the watercourse in these sections. This could lead to some distortion of their longitudinal profiles. Most of the studied rivers are located within uplands. This circumstance does not allow a statistically significant determination of the distribution of beaver dams and ponds along lowland rivers.
This study did not analyze changes in water flow along the rivers. This would help to detail the identified features, considering the variability of this hydrological factor.
In our study, we also did not analyze the characteristics of the beaver population (their numbers and densities; the stage of development of the beaver population (growth, stability, or decline)). It is known that as beavers reach maximum productivity and move into the so-called “climax” population, they willingly populate pessimal habitats, including rivers with channel slopes of up to 8%, which is confirmed by numerous observations in Canada and the southwest of the USA [76,77,78,79,80].
Beaver settlements began to occur again after a long absence in the studied rivers of the study region (at least in the forest-steppe zone) since the 2000s. According to oral information (personal communication) from one of the local beekeepers, beavers settled in the middle reaches of the Kuser River (the southern taiga) no more than 5 years ago. From the above-mentioned, it can be assumed that they have not yet reached the “climax” stage of population size in these rivers, despite the fact that the rivers of this region began to gradually be populated by beavers since the 1950s and especially intensively since the 2000s in the forest-steppe zone (Figure 16). Thus, we assume that all of the above-mentioned features reflect the early stages (population growth) of beaver settlement in the studied rivers.
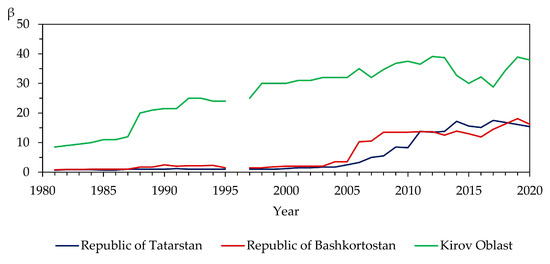
Figure 16.
Changes in the number of Castor fiber L. (β, in thousands of heads) in the administrative regions of the Russian Federation, in which the studied rivers flow, during 1981–2020 (based on data from [81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89]). NB: The administrative regions are located primarily in the following natural (landscape) zones (or terrestrial ecosystems): the Republic of Tatarstan in the forest-steppe zone, the Republic of Bashkortostan in the forest-steppe and steppe zones, the Kirov Oblast in the forest zone (mainly in the south taiga subzone).
4.4. Significance of the Results
The results obtained have both scientific and applied significance in the study and economic use of small rivers in the study region. From a scientific point of view, these results will help to better understand the main trends in the distribution of beavers in small rivers in the region, which began comparatively recently and did not cover all of the small rivers in this region. In addition, the beaver is a regulator of the hydrological regime of small rivers and, therefore, its role in hydrological calculations and in calculations of the load of sediment and dissolved substances should not be underestimated. This applies to both small rivers covered by stationary hydrological studies and those without them. The findings also contribute to a better understanding of the main trends in the stage-by-stage transformations and changes in the biodiversity of regional plant communities of floodplain–terrace complexes along small rivers that arise in connection with the distribution of beavers, as we previously identified in the example of a number of small rivers of the Volga-Kama State Biosphere Reserve [36]. As for the applied significance of the findings, it lies primarily in helping to calculate the reserves of surface water resources in the region. It is especially important for semi-arid forest-steppe landscapes in the east of European Russia. The shortage of these resources has become especially acute in recent decades due to climate change. We see an equally important applied aspect of applying the obtained results in their involvement in the analysis of underflooding zones along rivers and the dynamics of the redistribution of pollutants in small river basins as protective buffer zones on the way to the largest rivers of Eastern Europe—the Volga and Kama rivers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.V.G.; methodology, A.V.G. and A.G.S.; software, A.G.S.; validation, A.G.S. and A.V.G.; formal analysis, A.V.G. and A.G.S.; investigation, A.G.S. and A.V.G.; resources, A.G.S. and A.V.G.; data curation, A.G.S. and A.V.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.V.G. and A.G.S.; writing—review and editing, A.V.G., A.A.B., and F.N.L.; visualization, A.V.G. and A.G.S.; supervision, A.V.G.; project administration, A.G.S. and A.V.G.; funding acquisition, A.G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This investigation was carried out at the expense of the grant of the Russian Science Foundation No. 22-77-10087, https://rscf.ru/project/22-77-10087/, accessed on 25 December 2023 (field work; data processing; primary analysis). The work was also carried out in accordance with the Strategic Academic Leadership Program “Priority 2030” of the Kazan Federal University of the Government of the Russian Federation (spatial data analysis).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy reasons.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank G. Sharifullin, T. Mansurov and K. Khrnyak for their assistance in field work. The authors are also grateful to M.Y. Karavanov and R.V. Zagretdinov for providing geodetic equipment and consultations during topographic surveys using GNSS equipment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Geodetic coordinates of the mouths of the studied rivers (see Figure 1).
Table A1.
Geodetic coordinates of the mouths of the studied rivers (see Figure 1).
| River | Geodetic Coordinate | |
|---|---|---|
| X | Y | |
| Atsvezh | 48.02137093 | 58.27730517 |
| Peschanka | 49.88532696 | 58.25902658 |
| Brodovka | 49.93813719 | 58.24867556 |
| Kuser | 49.85481140 | 57.54595759 |
| Morkvashka | 48.79267707 | 55.78247276 |
| Morkvashinka | 48.85258569 | 55.77880625 |
| Karakashly | 53.23720905 | 54.67547755 |
| Zaumyat | 53.24304844 | 54.65804955 |
| Salayaz | 55.15120169 | 55.37277285 |
| Aigildinka | 55.19192755 | 55.37082866 |

Figure A1.
The largest beaver pond in the Kuser River (the Vyatka River basin, European Russia). (20 August 2023; photos by A.V. Gusarov).
References
- Gurnell, A.M. The Hydrogeomorphological Effects of Beaver Dam-Building Activity. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1998, 22, 167–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.R.; Malanson, G.P. The Geomorphic Influences of Beaver Dams and Failures of Beaver Dams. Geomorphology 2005, 71, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laland, K.N.; Boogert, N.J. Niche Construction, Co-Evolution and Biodiversity. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, C.J.; Cooper, D.J.; Butler, D.R. Beaver Hydrology and Geomorphology.Treatise on Geomorphology; Shroder, J.F., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 12, pp. 293–306. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as Ecosystem Engineers. Oikos 1994, 69, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.P.; Jones, C.G.; Flecker, A.S. An Ecosystem Engineer, the Beaver, Increases Species Richness at the Landscape Scale. Oecologia 2002, 132, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coz, D.M.; Young, J.C. Conflicts over wildlife conservation: Learning from the reintroduction of beavers in Scotland. People Nat. 2020, 2, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, M.M.; Beechie, T.J.; Wheaton, J.M.; Jordan, C.E.; Bouwes, N.; Weber, N.; Volk, C. Using Beaver Dams to Restore Incised Stream Ecosystems. Bioscience 2014, 64, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polvi, L.E.; Wohl, E. Biotic Drivers of Stream Planform: Implications for Understanding the Past and Restoring the Future. Bioscience 2013, 63, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, F.; Bozser, O.; Collen, P.; Parker, H. Ecological impact of beavers (Castor fiber and Castor canadensis) and their ability to modify ecosystems. Mamm. Rev. 2005, 35, 248–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.; Gaywood, M.J.; Jones, K.C.; Ramsay, P.; Willby, N.J. Using ecosystem engineers as tools in habitat restoration and rewilding: Beaver and wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willby, N.J.; Law, A.; Levanoni, O.; Foster, G.; Ecke, F. Rewilding wetlands: Beaver as agents of within-habitat heterogeneity and the responses of contrasting biota. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylak, A.; Kukuła, K. Impact of Fine-Grained Sediment on Mountain Stream Macroinvertebrate Communities: Forestry Activities and Beaver-Induced Sediment Management. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Report on the State and Protection of the Environment of the Russian Federation. The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment of the Russian Federation. Available online: https://www.mnr.gov.ru/docs/gosudarstvennye_doklady/gosudarstvennyy_doklad_o_sostoyanii_i_ob_okhrane_okruzhayushchey_sredy_rossiyskoy_federatsii_v_2022_/?ysclid=lq409eixqr763011706 (accessed on 23 December 2023).
- McCullough, M.C.; Harper, J.L.; Eisenhauer, D.E.; Dosskey, M.G. Channel Aggradation by Beaver Dams on a Small Agricultural Stream in Eastern Nebraska. In Proceedings of the Self-Sustaining Solutions for Streams, Wetlands, and Watersheds, St. Paul, MN, USA, 12–15 September 2004; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, M.M.; Beechie, T.J.; Jordan, C.E. Geomorphic Changes Upstream of Beaver Dams in Bridge Creek, an Incised Stream Channel in the Interior Columbia River Basin, Eastern Oregon. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, C.J.; Cooper, D.J.; Baker, B.W. Beaver Assisted River Valley Formation. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malison, R.L.; Kuzishchin, K.V.; Stanford, J.A. Do beaver dams reduce habitat connectivity and salmon productivity in expansive river floodplains? PeerJ 2016, 4, e2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meentemeyer, R.K.; Vogler, J.B.; Hill, C.; Butler, D.R. The Geomorphic Influences of Burrowing Beavers on Streambanks, Bolin Creek, North Carolina. Z. Geomorphol. 1998, 42, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.; González Garraza, G.; Garcia, V.; Granitto, M.; Escobar, J. Beaver dam effect on phytoplankton and periphyton composition and hydrology in streams from Tierra Del Fuego (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1461–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.R. The Failure of Beaver Dams and Resulting Outburst Flooding: A Geomorphic Hazard of the Southeastern Piedmont. Geogr. Bull. 1989, 31, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- John, S.; Klein, A. Hydrogeomorphic Effects of Beaver Dams on Floodplain Morphology: Avulsion Processes and Sediment Fluxes in Upland Valley Floors (Spessart, Germany). Quaternaire 2004, 15, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelec, M.; Białek, K.; Spyra, A. Activity of Beavers as an Ecological Factor That Affects the Benthos of Small Rivers-a Case Study in the Żylica River (Poland). Biologia 2018, 73, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyra, A.; Cieplok, A.; Krodkiewska, M. Beavers Ecosystem Altering: Influence of Beaver Dams on Aquatic Invertebrates in Newly Created Beavers Ponds and Small Mountain River. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.; McLean, F.; Willby, N.J. Habitat Engineering by Beaver Benefits Aquatic Biodiversity and Ecosystem Processes in Agricultural Streams. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virbickas, T.; Stakėnas, S.; Steponėnas, A. Impact of Beaver Dams on Abundance and Distribution of Anadromous Salmonids in Two Lowland Streams in Lithuania. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Visscher, M.; Nyssen, J.; Pontzeele, J.; Billi, P.; Frankl, A. Spatio-Temporal Sedimentation Patterns in Beaver Ponds along the Chevral River, Ardennes, Belgium. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1602–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinitsyn, M.G.; Rusanov, A.V. European Beaver Impact on Small Rivers Valley and Channel Relief in the Vetluga-Unzha Woodlands. Geomorfologiya 1990, 1, 85–91. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sinitsyn, M.G.; Rusanov, A.V. Effect of River Beaver on Phytocenosises and Soils of the Small River Valleys of Vetluzhsko-Unzhenskoe Woodland. Byull. Mosk. O-Va Ispyt. Prir. Otd. Biol. 1989, 94, 30–40. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Katsman, E.A.; Suzdaleva, A.L.; Osipov, V.V.; Bashinskiy, I.V. Concentrations of Biogenic Compounds in Forest-Steppe Water Bodies and Streams Inhabited by Beavers (Castor fiber L.). Russ. J. Biol. Invasions 2020, 11, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkov, D. Is It Possible to Use Beaver Building Activity to Reduce Lake Sedimentation? Lutra 2003, 46, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, A.W. Habitat Suitability Index Models: Beaver; Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- St-Pierre, M.L.; Labbé, J.; Darveau, M.; Imbeau, L.; Mazerolle, M.J. Factors Affecting Abundance of Beaver Dams in Forested Landscapes. Wetlands 2017, 37, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.D.; Jensen, P.G. Habitat Features Affecting Beaver Occupancy along Roadsides in New York State. J. Wildl. Manag. 2004, 68, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.H. A Size-Distance Relation in Food Selection by Beavers. Ecology 1980, 61, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, N.G.; Prokhorov, V.E.; Sharifullin, A.G.; Gusarov, A.V.; Lisetskii, F.N. The Influence of Eurasian Beaver (Castor fiber L.) Activity on the Transformation and Functioning of Riparian Phytocoenoses in the Southern Boreal Zone (European Russia). Earth 2023, 4, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.G.; Curtis, P.D.; Lehnert, M.E.; Hamelin, D.L. Habitat and Structural Factors Influencing Beaver Interference with Highway Culverts. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2001, 29, 654–664. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, N.J. Spatial Associations of Beaver Ponds and Culverts in Boreal Head Water Streams. Master’s Thesis, Department of Renewable Resources, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2006; p. 108. [Google Scholar]
- Jakes, A.F.; Snodgrass, J.W.; Burger, J. Castor canadensis (Beaver) Impoundment Associated with Geomorphology of Southeastern Streams. Southeast. Nat. 2007, 6, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halley, D.; Rosell, F.; Saveljev, A. Population and Distribution of Eurasian Beaver (Castor fiber). Balt. For. 2012, 18, 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, B. Eager: The Surprising, Secret Life of Beavers and Why They Matter; Chelsea Green Publishing: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Boon, S. Nature’s Riverkeepers. Science 2018, 361, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.; Hoyos-Santillan, J.; Lara, A.; Mentler, R.; Huertas-Herrera, A.; Toro-Manríquez, M.D.R.; Sepulveda-Jauregui, A. Equivalent Impacts of Logging and Beaver Activities on Aboveground Carbon Stock Loss in the Southernmost Forest on Earth. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halley, D.J.; Saveljev, A.P.; Rosell, F. Population and Distribution of Beavers Castor fiber and Castor canadensis in Eurasia. Mamm. Rev. 2021, 51, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Rogers, K.H. Large Animals and System-Level Characteristics in River Corridors. Bioscience 1997, 47, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrov, D.D. (Ed.) Atlas of the Kirov Oblast; Roscartography: Moscow, Russia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ermolaev, O.P.; Igonin, M.E.; Bubnov, A.Y.; Pavlova, S.V. Landscapes of the Republic of Tatarstan. Regional Landscape-Ecological Analysis; Slovo: Kazan, Russian, 2007; 411p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Graham, H.A.; Puttock, A.; Chant, J.; Elliott, M.; Campbell-Palmer, R.; Anderson, K.; Brazier, R.E. Monitoring, Modelling and Managing Beaver (Castor fiber) Populations in the River Otter Catchment, Great Britain. Ecol. Solut. Evid. 2022, 3, e12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, G.; Puttock, A.; Coxon, G.; Clarke, S.; Brazier, R.E. Testing a Novel Sonar-Based Approach for Measuring Water Depth and Monitoring Sediment Storage in Beaver Ponds. River Res. Appl. 2023, 39, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, R.; Ilçi, V.; Ozulu, I.M.; Saka, M.H. A Comparative Study for Accuracy Assessment of PPP Technique Using GPS and GLONASS in Urban Areas. Measurement 2015, 69, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifullin, A.G.; Gusarov, A.V.; Lavrova, O.A.; Beylich, A.A. Channel Gradient as a Factor in the Distribution of Beaver Dams and Ponds on Small Rivers: A Case Study in the Northern Extremity of the Volga Upland, the East European Plain. Water 2023, 15, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topomapper. Topographic Map. Available online: http://www.atlogis.de (accessed on 23 December 2023).
- Russian Geological Research Institute. Available online: https://webmapget.vsegei.ru/?ysclid=lq57uwqvj7713899222 (accessed on 23 December 2023).
- Zavyalov, N.A. Beavers (Castor fiber and Castor canadensis), the Founders of Habitats and Phytophages. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2014, 4, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedkov, A.P.; Mozzherin, V.I. Erosion and Suspended Sediment on the Earth; Kazan University: Kazan, Russia, 1984. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Golosov, V.N. Erosion and Deposition Processes in River Basins of Cultivated Plains; GEOS: Moscow, Russia, 2006. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chalov, R.S. Drivers and Conditions of River Channel Character and Chande. In Fluvial Processes: Theory and Applications; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; 569p. [Google Scholar]
- Stout, T.L.; Majerova, M.; Neilson, B.T. Impacts of Beaver Dams on Channel Hydraulics and Substrate Characteristics in a Mountain Stream. Ecohydrology 2017, 10, e1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.P.; Olden, J.D. Ecology, Management, and Conservation Implications of North American Beaver (Castor canadensis) in Dryland Streams. Aquat. Conserv. 2014, 24, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.; Larsen, J.R.; Lane, S.N. Dam Builders and Their Works: Beaver Influences on the Structure and Function of River Corridor Hydrology, Geomorphology, Biogeochemistry and Ecosystems. Earth Sci. Rev. 2021, 218, 103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, R.E.; Puttock, A.; Graham, H.A.; Auster, R.E.; Davies, K.H.; Brown, C.M.L. Beaver: Nature’s Ecosystem Engineers. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2021, 8, e1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsodis, R.; Ulevičius, A. Geomorphological Effects of Beaver Activities in Lowland Drainage Ditches. Z. Geomorphol. 2012, 56, 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, G.L.; Henshaw, A.J.; Brasington, J.; England, J. Burrowing Invasive Species: An Unquantified Erosion Risk at the Aquatic-Terrestrial Interface. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 1018–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, G.; Törnlöv, S. Influence of Watercourse Depth and Width on Dam-Building Behaviour by Eurasian Beaver (Castor fiber). J. Zool. 2006, 268, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Melillo, J.M.; Hobbie, J.E. Ecosystem Alteration of Boreal Forest Streams by Beaver (Castor canadensis). Ecology 1986, 67, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, P.; Barrett, R.H. Beaver Habitat Use and Impact in Truckee River Basin, California. J. Wildl. Manag. 1987, 51, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, I.D. Habitat Needs of Furbearers in Relation to Logging in Boreal Ontario. For. Chron. 1988, 64, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.R.; Malanson, G.P. Beaver Landforms. Can. Geogr. 1994, 38, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.R.; Malanson, G.P. Sedimentation Rates and Patterns in Beaver Ponds in a Mountain Environment. Geomorphology 1995, 13, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Klein, A. Beaver Pond Development and Its Hydrogeomorphic and Sedimentary Impact on the Jossa Floodplain in Germany. Lutra 2003, 46, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Katsman, E.A. Floristic Diversity of Watercourses and Temporary Reservoirs of the Ostrovtsovsky Cluster of the Volga Regional Forest-Steppe State Natural Biospheric Reserve Impacted by the European Beaver’s Expansion. Povolžskij Èkologičeskij Žurnal 2018, 4, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevedentsev, Y.; Gusarov, A.; Mirsaeva, N.; Sherstyukov, B.; Shantalinsky, K.; Guryanov, V.; Aukhadeev, T. Contemporary Climate Change and Its Hydrological Consequence in the Volga Federal District, European Russia. Climate 2022, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevedentsev, Y.P.; Shantalinsky, K.M.; Gusarov, A.V.; Mirsaeva, N.A.; Aukhadeev, T.R.; Nikolaev, A.A. Air Temperature Change at the End of the Late Holocene and in the Anthropocene in the Middle Volga Region, European Russia. Quaternary 2023, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusarov, A.V. The response of water flow, suspended sediment yield and erosion intensity to contemporary long-term changes in climate and land use/cover in river basins of the Middle Volga Region, European Russia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 134770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusarov, A.V. Land-Use/-Cover Changes and Their Effect on Soil Erosion and River Suspended Sediment Load in Different Landscape Zones of European Russia during 1970–2017. Water 2021, 13, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.L.; Jasinski, B.L.; Kendall, A.D.; Dahl, T.A.; Hyndman, D.W. Quantifying Beaver Dam Dynamics and Sediment Retention Using Aerial Imagery, Habitat Characteristics, and Economic Drivers. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccomb, W.C.; Sedell, J.R.; Buchholz, T.D. Dam-Site Selection by Beavers in an Eastern Oregon Basin. Great Basin Nat. 1990, 50, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane, W.W.; Wheaton, J.M.; Bouwes, N.; Jensen, M.L.; Gilbert, J.T.; Hough-Snee, N.; Shivik, J.A. Modeling the Capacity of Riverscapes to Support Beaver Dams. Geomorphology 2017, 277, 72–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, L.; Meyer, G. Natural and Historical Variability in Fluvial Processes, Beaver Activity, and Climate in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 728–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, K.A.; Johnson, B.G. The Effect of Sub-Alpine Landslides on Headwater Stream Gradient and Beaver Habitat. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 37, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Committee of the Republic of Tatarstan for Biological Resources in 2011–2020. Available online: https://ojm.tatarstan.ru/gosohotreestr.htm?page=1 (accessed on 27 March 2024). (In Russian).
- State Report on the State of Natural Resources and Environment of the Republic of Bashkortostan in 2011–2020. Available online: https://ecology.bashkortostan.ru/presscenter/lectures/ (accessed on 27 March 2024). (In Russian).
- Regional Reports on the State of the Environment of the Kirov Oblast in 2011–2020. Available online: https://kirovreg.ru/econom/ecology/doklad.php (accessed on 27 March 2024). (In Russian).
- Fund of Hunting Grounds and the Number of Main Species of Wild Animals in the RSFSR. Reference Materials; Novikova, B.V., Ed.; Central Scientific Research Laboratory of the Main Directorate of Hunting and Reserves under the Council of Ministers of the Rrussian Federation: Moscow, Russia, 1992. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lomanov, I.K.; Borisov, B.P.; Volodina, O.A.; Gubar, Y.P.; Lomanova, N.P.; Mirutenko, V.S.; Molochayev, A.V.; Mosheva, T.S.; Naumova, A.A.; Novikov, G.B.; et al. Resources of the Main Species of Game Animals and Hunting Grounds of Russia (1991–1995); Reference Materials; Lomanov, I.K., Ed.; Central Scientific Research Laboratory of the Hunting Department of the Ministry of Agriculture and Food of Russia: Moscow, Russia, 1996. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lomanov, I.K. (Ed.) State of Game Animal Resources in the Russian Federation. Information and Analytical Materials. In Game Animals of Russia (Biology, Protection, Study of Resources, and Rational Use); Tsentrokhotkontrol: Moscow, Russia, 2000. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lomanov, I.K. (Ed.) State of Game Animal Resources in the Russian Federation in 2000–2003. Information and Analytical Materials. In Game Animals of Russia (Biology, Protection, Study of Resources, and Rational Use); Tsentrokhotkontrol: Moscow, Russia, 2004. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gubar, Y.P. (Ed.) State of Game Animal Resources in the Russian Federation in 2003–2007. Information and Analytical Materials. In Game Animals of Russia (Biology, Protection, Study of Resources, and Rational Use); Tsentrokhotkontrol: Moscow, Russia, 2007. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lomanov, I.K. (Ed.) State of Game Animal Resources in the Russian Federation in 2008–2010. Information and Analytical Materials. In Game Animals of Russia (Biology, Protection, Study of Resources, and Rational Use); Tsentrokhotkontrol: Moscow, Russia, 2011. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).