Daily Simulation of the Rainfall–Runoff Relationship in the Sirba River Basin in West Africa: Insights from the HEC-HMS Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
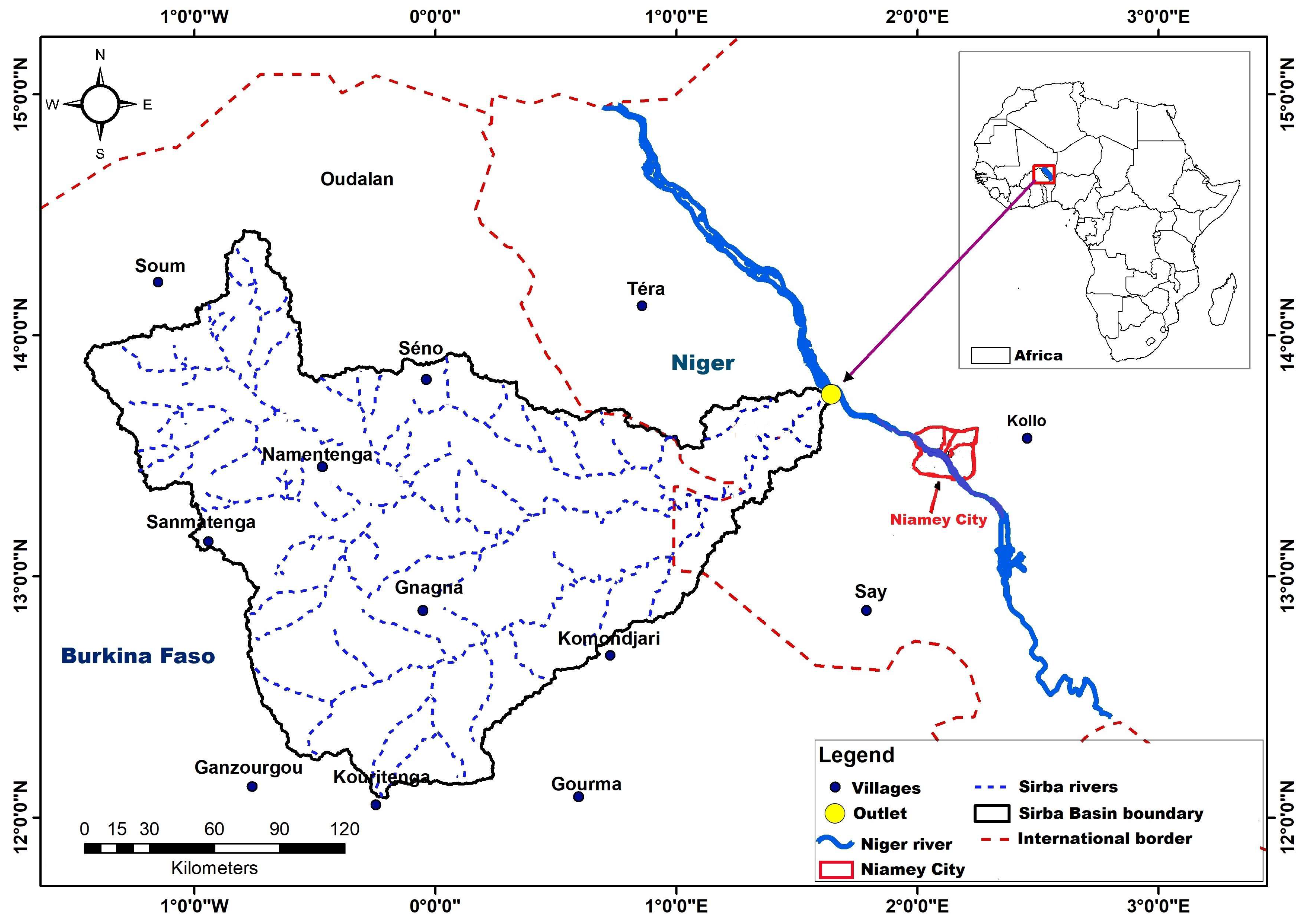
2.1. Study Area Description
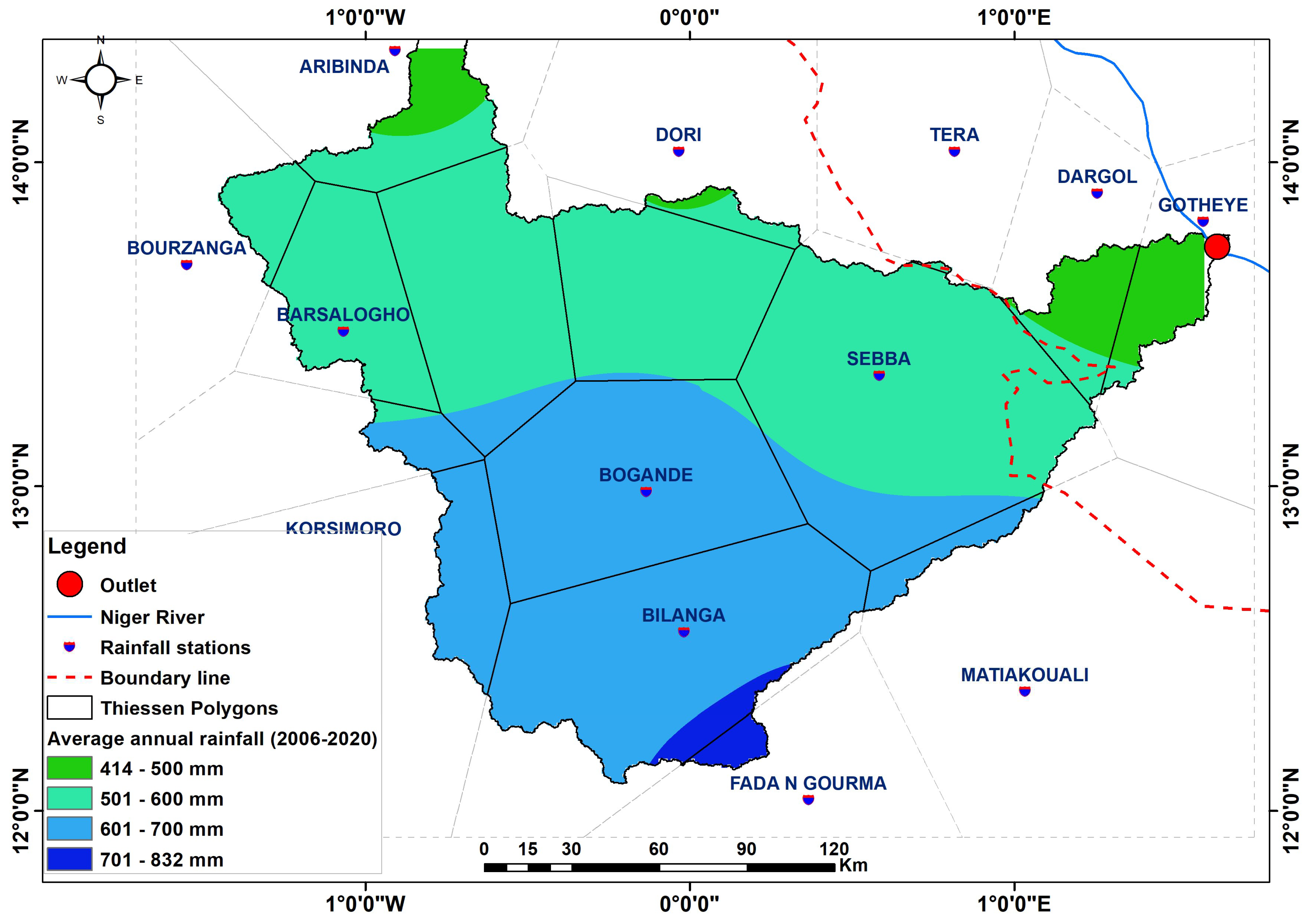
2.2. Data Used in This Study and Preprocessing Steps
2.3. Rainfall–Runoff Hydrological Modeling
2.3.1. HEC-HMS Model Presentation
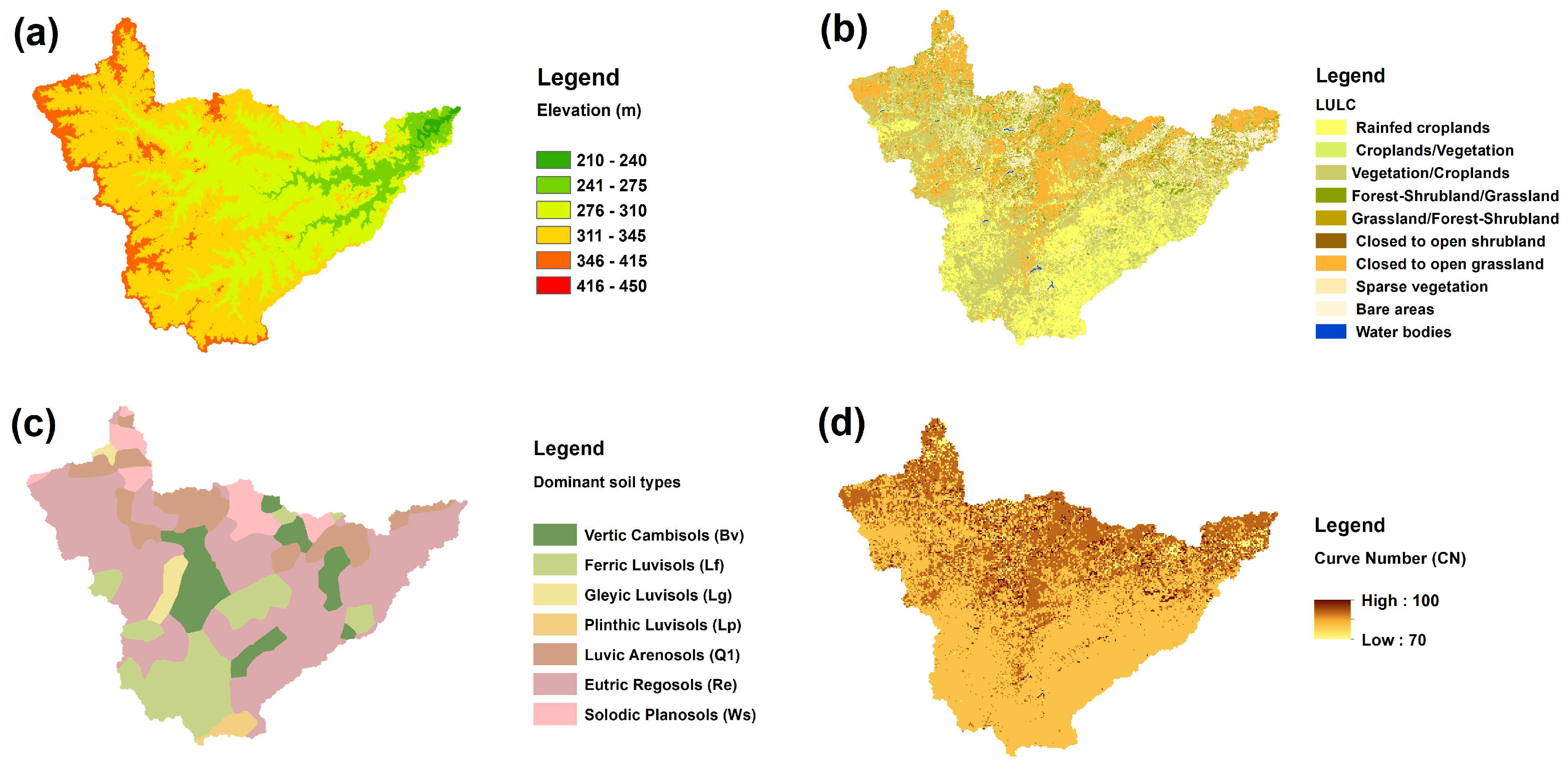
2.3.2. Catchment Delineation and Model Preparation
2.3.3. Loss Model
2.3.4. Transform Model
2.3.5. Routing Model
2.3.6. Modeling Scenarios, Calibration, Validation and Assessment of Model Performance
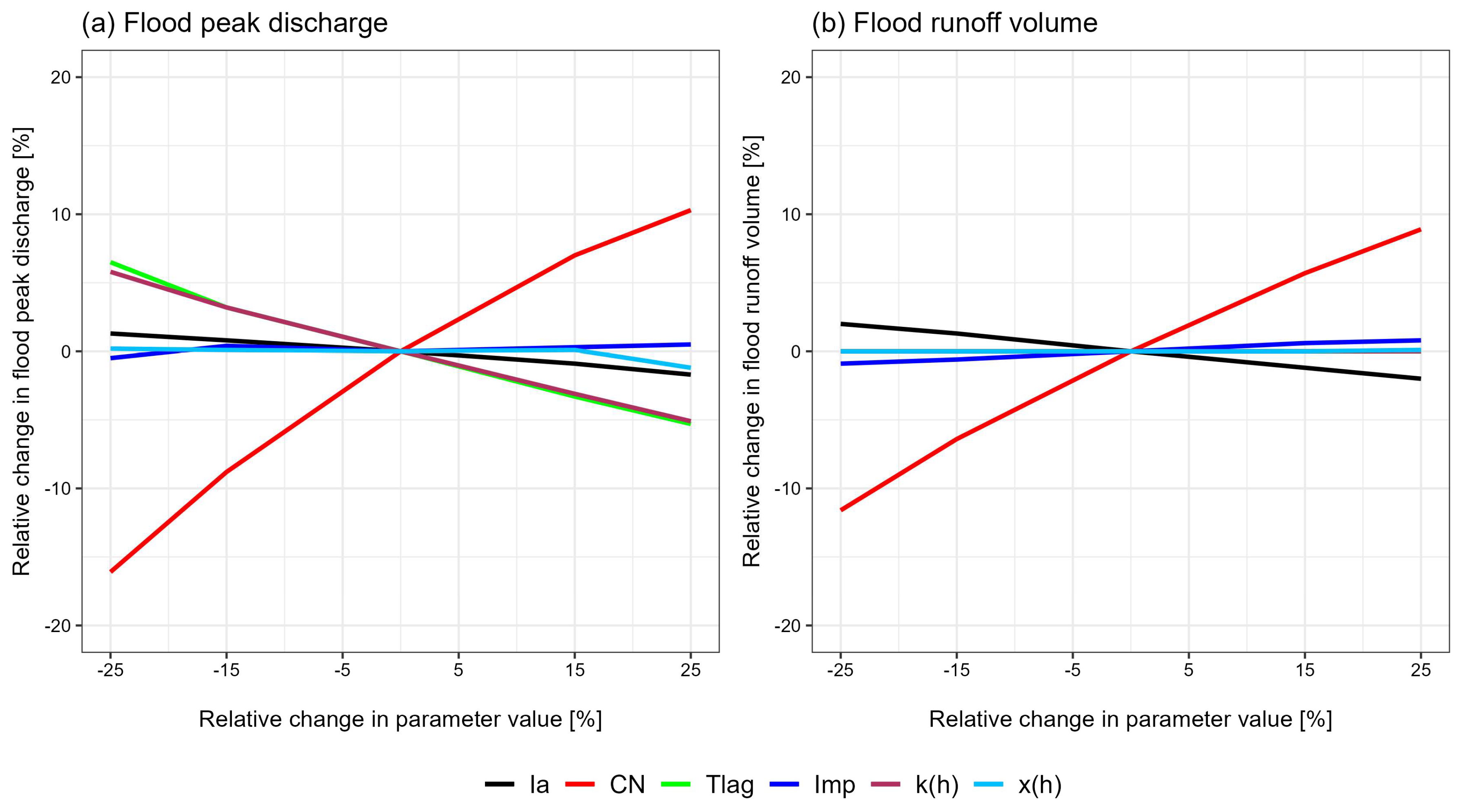
2.3.7. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Calibrated Model Parameters
3.2. Hydrological Model Performance
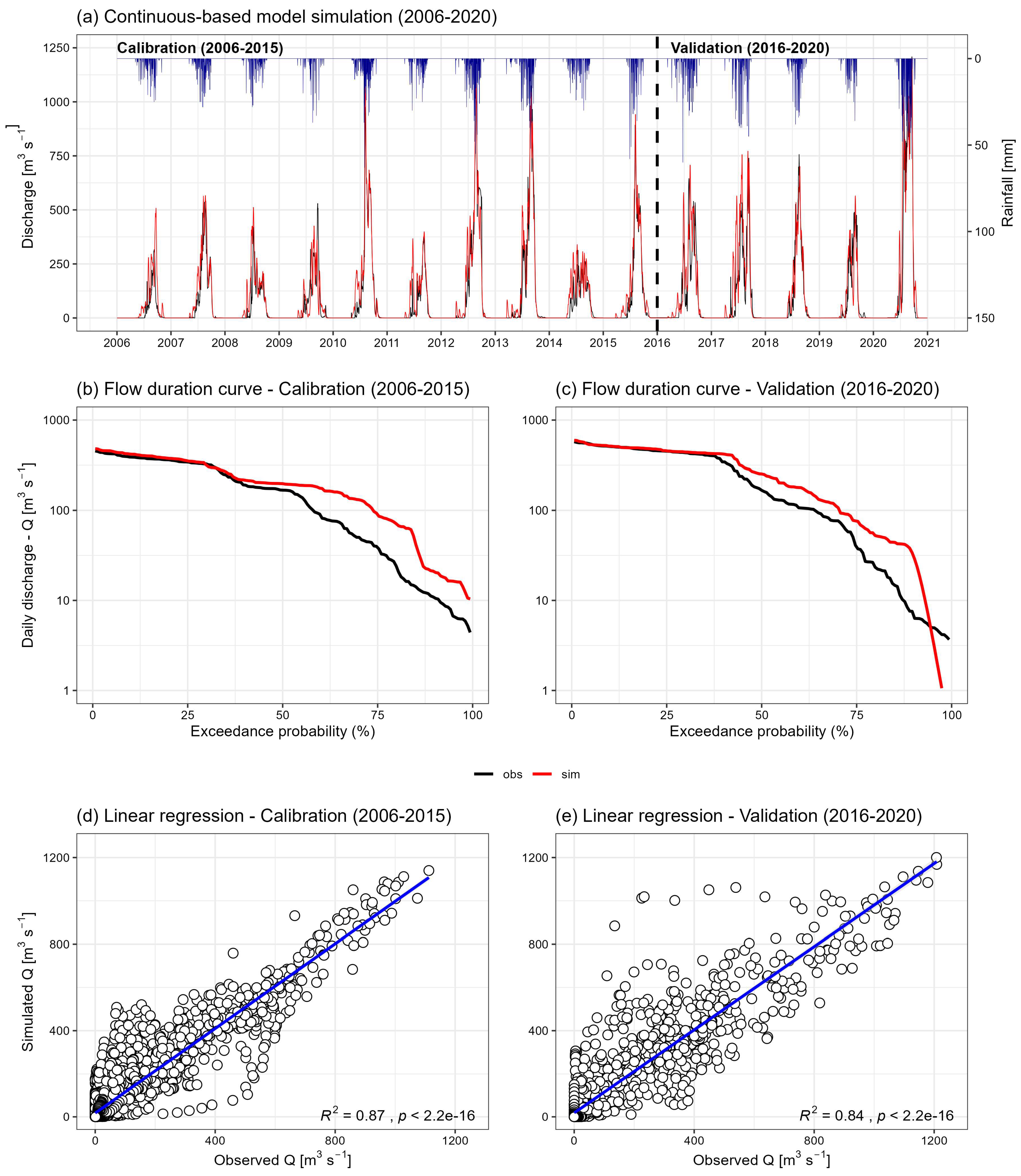
3.2.1. Continuous-Based (CS) Hydrological Simulation
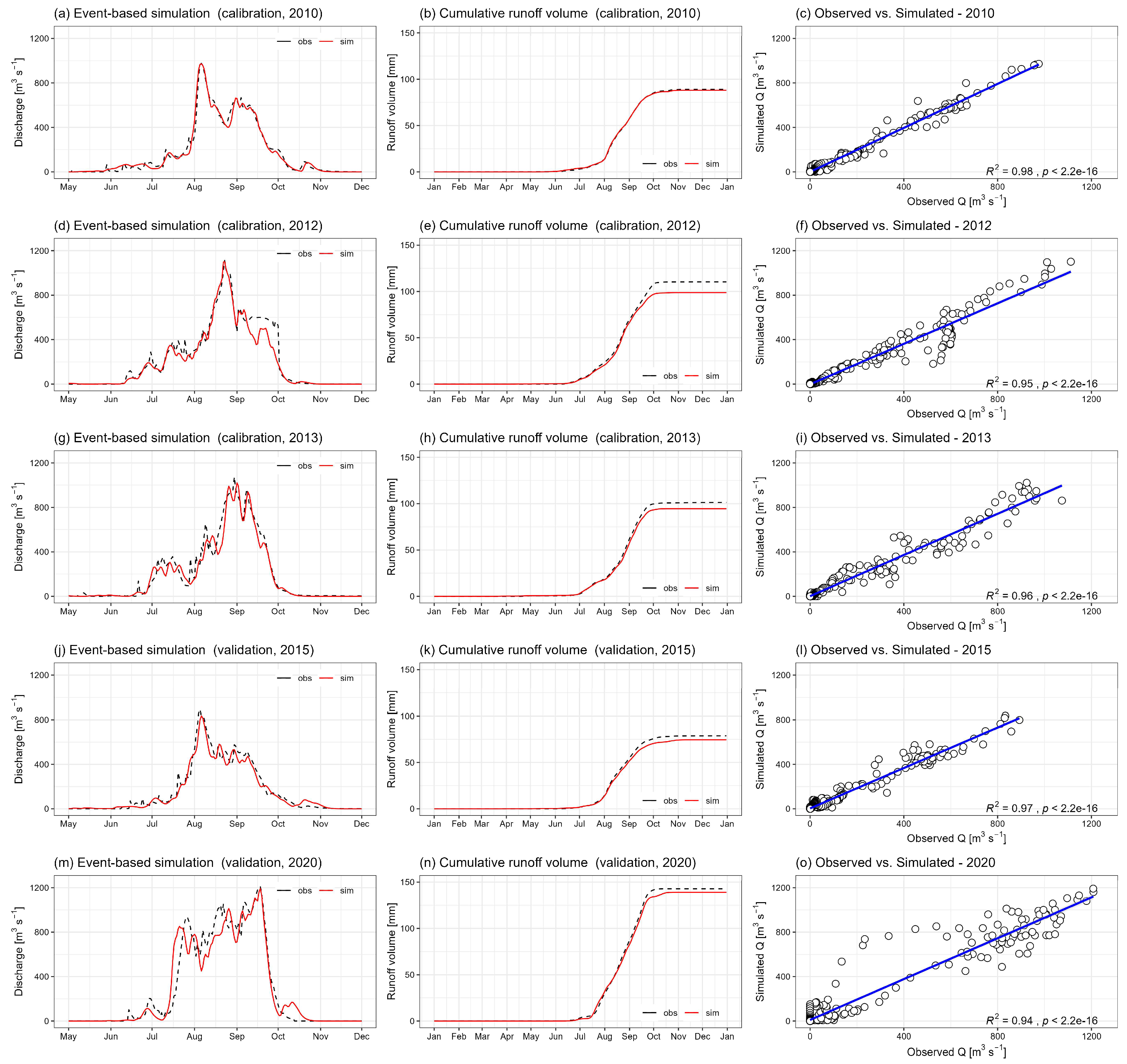
3.2.2. Event-Based (ES) Hydrological Simulation
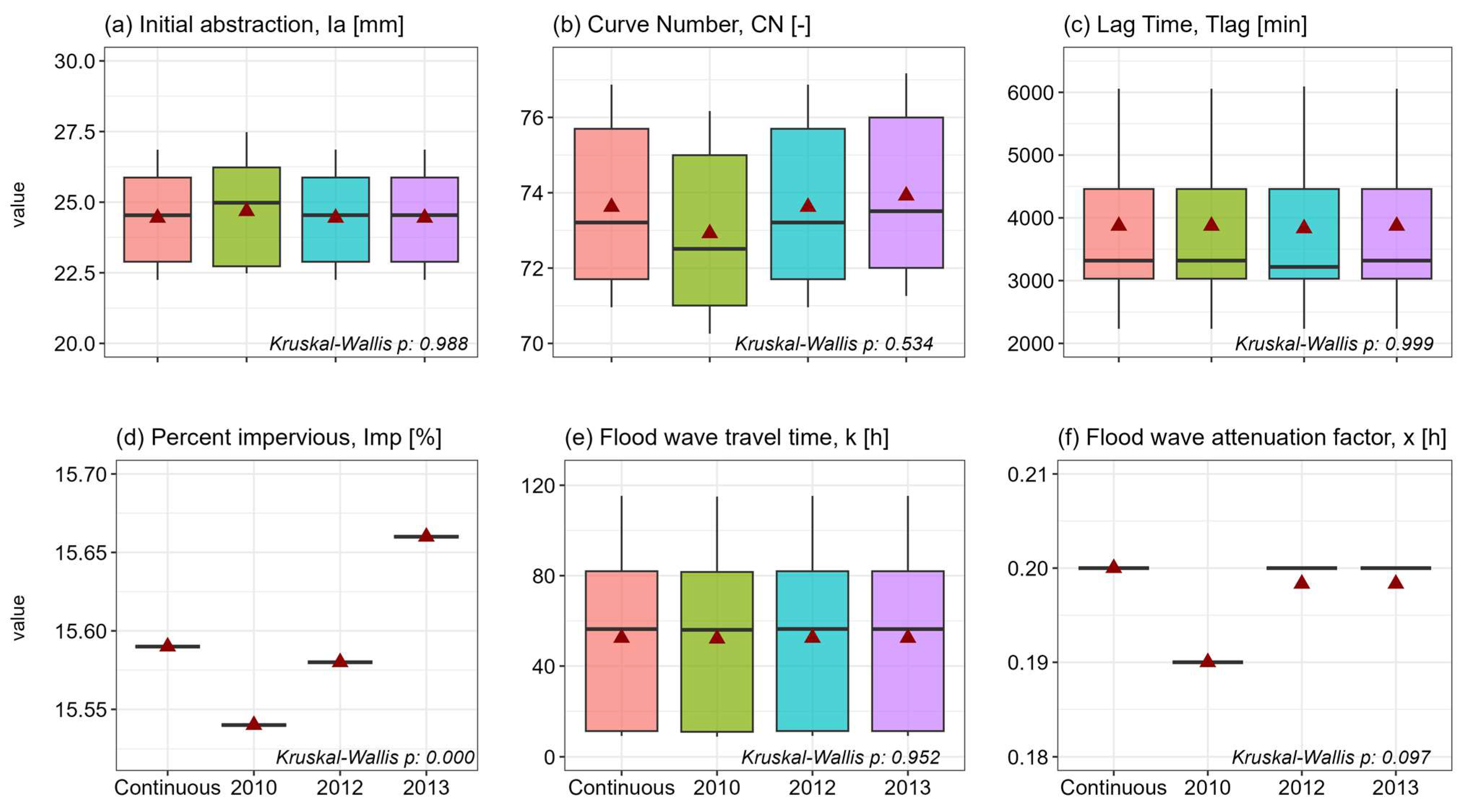
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yonaba, R. Spatio-Temporal Land Use and Land Cover Dynamics and Impact on Surface Runoff in a Sahelian Landscape: Case of Tougou Watershed (Northern Burkina Faso). Ph.D. Thesis, International Institute for Water and Environmental Engineering (2iE), Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Cockburn, C.; Lamouroux, N.; Pella, H.; Snelder, T.; Tockner, K.; Trautmann, T.; Watt, C.; Datry, T. Global Prevalence of Non-Perennial Rivers and Streams. Nature 2021, 594, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonaba, R.; Koïta, M.; Mounirou, L.A.; Tazen, F.; Queloz, P.; Biaou, A.C.; Niang, D.; Zouré, C.; Karambiri, H.; Yacouba, H. Spatial and Transient Modelling of Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) Dynamics in a Sahelian Landscape under Semi-Arid Climate in Northern Burkina Faso. Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowé, T.; Yonaba, R.; Mounirou, L.A.; Ouédraogo, E.; Ibrahim, B.; Niang, D.; Karambiri, H.; Yacouba, H. From Meteorological to Hydrological Drought: A Case Study Using Standardized Indices in the Nakanbe River Basin, Burkina Faso. Nat. Hazards 2023, 119, 1941–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowé, T.; Diarra, A.; Kabore, R.F.W.; Ibrahim, B.; Bologo/Traoré, M.; Traoré, K.; Karambiri, H. Trends in Flood Events and Their Relationship to Extreme Rainfall in an Urban Area of Sahelian West Africa: The Case Study of Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2019, 12, e12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; Villarini, G.; Zhang, W. Observed Changes in Flood Hazard in Africa. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1040b5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amogu, O.; Descroix, L.; Yéro, K.S.; Le Breton, E.; Mamadou, I.; Ali, A.; Vischel, T.; Bader, J.-C.; Moussa, I.B.; Gautier, E.; et al. Increasing River Flows in the Sahel? Water 2010, 2, 170–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amogu, O.; Esteves, M.; Vandervaere, J.-P.; Malam Abdou, M.; Panthou, G.; Rajot, J.-L.; Souley Yéro, K.; Boubkraoui, S.; Lapetite, J.-M.; Dessay, N.; et al. Runoff Evolution Due to Land-Use Change in a Small Sahelian Catchment. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, I.; Abdourahamane, Z.S. Extreme Rainfall Characterisation under Climate Change and Rapid Population Growth in the City of Niamey, Niger. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fofana, M.; Adounkpe, J.; Dotse, S.-Q.; Bokar, H.; Limantol, A.M.; Hounkpe, J.; Larbi, I.; Toure, A. Flood Forecasting and Warning System: A Survey of Models and Their Applications in West Africa. AJCC 2023, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahiri, E.-P.; Bamba, I.; Famien, A.M.; Koffi, A.K.; Ochou, A.D. Mesoscale Extreme Rainfall Events in West Africa: The Cases of Niamey (Niger) and the Upper Ouémé Valley (Benin). Weather Clim. Extrem. 2016, 13, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lèye, B.; Zouré, C.O.; Yonaba, R.; Karambiri, H. Water Resources in the Sahel and Adaptation of Agriculture to Climate Change: Burkina Faso. In Climate Change and Water Resources in Africa; Diop, S., Scheren, P., Niang, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 309–331. ISBN 978-3-030-61224-5. [Google Scholar]
- Boubacar Moussa, M.; Abdourhamane Touré, A.; Kergoat, L.; Lartiges, B.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Robert, E.; Gosset, M.; Alkali Tanimoun, B.; Grippa, M. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Middle Niger River Using in-Situ and Satellite Radiometric Measurements. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahé, G.; Lienou, G.; Bamba, F.; Paturel, J.; Adeaga, O.; Descroix, L.; Mariko, A.; Olivry, J.; Sangare, S.; Ogilvie, A.; et al. The Niger River and Climate Change over 100 Years. In Hydro-climatology: Variability and Change; Proceedings of symposium J-H02 held during IUGG2011 in Melbourne, 2011; pp. 131–137.
- Mahé, G.; Lienou, G.; Descroix, L.; Bamba, F.; Paturel, J.E.; Laraque, A.; Meddi, M.; Habaieb, H.; Adeaga, O.; Dieulin, C.; et al. The Rivers of Africa: Witness of Climate Change and Human Impact on the Environment: How Climate and Human Changes Impacted River Regimes in Africa. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonaba, R.; Biaou, A.C.; Koïta, M.; Tazen, F.; Mounirou, L.A.; Zouré, C.O.; Queloz, P.; Karambiri, H.; Yacouba, H. A Dynamic Land Use/Land Cover Input Helps in Picturing the Sahelian Paradox: Assessing Variability and Attribution of Changes in Surface Runoff in a Sahelian Watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouré, C.O.; Kiema, A.; Yonaba, R.; Minoungou, B. Unravelling the Impacts of Climate Variability on Surface Runoff in the Mouhoun River Catchment (West Africa). Land 2023, 12, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descroix, L.; Genthon, P.; Amogu, O.; Rajot, J.-L.; Sighomnou, D.; Vauclin, M. Change in Sahelian Rivers Hydrograph: The Case of Recent Red Floods of the Niger River in the Niamey Region. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 98–99, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casse, C.; Gosset, M.; Peugeot, C.; Pedinotti, V.; Boone, A.; Tanimoun, B.A.; Decharme, B. Potential of Satellite Rainfall Products to Predict Niger River Flood Events in Niamey. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, E.; Crisci, A.; Issa, H.; Maracchi, G.; Morabito, M.; Tarchiani, V. Recent Changes of Floods and Related Impacts in Niger Based on the ANADIA Niger Flood Database. Climate 2018, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djibo, A.; Seidou, O.; Saley, H.; Philippon, N.; Sittichok, K.; Karambiri, H.; Paturel, J. A Copula-Based Approach for Assessing Flood Protection Overtopping Associated with a Seasonal Flood Forecast in Niamey, West Africa. JGEESI 2018, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descroix, L.; Mahé, G.; Lebel, T.; Favreau, G.; Galle, S.; Gautier, E.; Olivry, J.-C.; Albergel, J.; Amogu, O.; Cappelaere, B.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Hydrological Regimes around the Boundaries between Sahelian and Sudanian Areas of West Africa: A Synthesis. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aich, V.; Liersch, S.; Vetter, T.; Andersson, J.; Müller, E.; Hattermann, F. Climate or Land Use?—Attribution of Changes in River Flooding in the Sahel Zone. Water 2015, 7, 2796–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descroix, L.; Guichard, F.; Grippa, M.; Lambert, L.; Panthou, G.; Mahé, G.; Gal, L.; Dardel, C.; Quantin, G.; Kergoat, L.; et al. Evolution of Surface Hydrology in the Sahelo-Sudanian Strip: An Updated Review. Water 2018, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putty, M.R.Y.; Prasad, R. Understanding Runoff Processes Using a Watershed Model—A Case Study in the Western Ghats in South India. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelelew, D.; Melesse, A. Applicability of a Spatially Semi-Distributed Hydrological Model for Watershed Scale Runoff Estimation in Northwest Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounirou, L.A.; Zouré, C.O.; Yonaba, R.; Paturel, J.-E.; Mahé, G.; Niang, D.; Yacouba, H.; Karambiri, H. Multi-Scale Analysis of Runoff from a Statistical Perspective in a Small Sahelian Catchment under Semi-Arid Climate. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounirou, L.A.; Yonaba, R.; Koïta, M.; Paturel, J.-E.; Mahé, G.; Yacouba, H.; Karambiri, H. Hydrologic Similarity: Dimensionless Runoff Indices across Scales in a Semi-Arid Catchment. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 193, 104590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonaba, R.; Mounirou, L.A.; Tazen, F.; Koïta, M.; Biaou, A.C.; Zouré, C.O.; Queloz, P.; Karambiri, H.; Yacouba, H. Future Climate or Land Use? Attribution of Changes in Surface Runoff in a Typical Sahelian Landscape. Comptes Rendus. Géosci. 2023, 355, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoungou, B.; Abdou, A. Land Surface Modeling for Food and Water Security in the Sirba River Basin. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, Online, 13–17 December 2021; Volume 2021, p. H54C-04. [Google Scholar]
- Sittichok, K.; Djibo, A.G.; Seidou, O.; Saley, H.M.; Karambiri, H.; Paturel, J. Statistical Seasonal Rainfall and Streamflow Forecasting for the Sirba Watershed, West Africa, Using Sea-Surface Temperatures. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittichok, K.; Seidou, O.; Gado Djibo, A.; Rakangthong, N.K. Estimation of the Added Value of Using Rainfall–Runoff Transformation and Statistical Models for Seasonal Streamflow Forecasting. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagnone, P.; Massazza, G.; Pezzoli, A.; Rosso, M. Hydrology of the Sirba River: Updating and Analysis of Discharge Time Series. Water 2019, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelina, A.; Gado Djibo, A.; Seidou, O.; Seidou Sanda, I.; Sittichok, K. Changes to Flow Regime on the Niger River at Koulikoro under a Changing Climate. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 1709–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.C.M.; Arheimer, B.; Traoré, F.; Gustafsson, D.; Ali, A. Process Refinements Improve a Hydrological Model Concept Applied to the Niger River Basin. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4540–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyerinde, G.T.; Fademi, I.O.; Denton, O.A. Modeling Runoff with Satellite-Based Rainfall Estimates in the Niger Basin. Cogent Food Agric. 2017, 3, 1363340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massazza, G.; Tarchiani, V.; Andersson, J.C.M.; Ali, A.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Pezzoli, A.; De Filippis, T.; Rocchi, L.; Minoungou, B.; Gustafsson, D.; et al. Downscaling Regional Hydrological Forecast for Operational Use in Local Early Warning: HYPE Models in the Sirba River. Water 2020, 12, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyerinde, G.T.; Lawin, A.E.; Anthony, T. Multiscale Assessments of Hydroclimatic Modelling Uncertainties under a Changing Climate. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2022, 13, 1534–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerotti, G.; Massazza, G.; Pezzoli, A.; Bigi, V.; Zsótér, E.; Rosso, M. Hydrological Model Application in the Sirba River: Early Warning System and GloFAS Improvements. Water 2020, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USACE HEC-HMS Hydrologic Modeling System User’s Manual; Version 4.2; United States Army Corps of Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Fanta, S.S.; Tadesse, S.T. Application of HEC–HMS for Runoff Simulation of Gojeb Watershed, Southwest Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 4687–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakarneh, M.O.A.; Khan, A.J.; Mahmood, Q.; Khan, R.; Shahzad, M.; Tahir, A.A. Modeling of Rainfall–Runoff Events Using HEC-HMS Model in Southern Catchments of Jerusalem Desert-Palestine. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdessamed, D.; Abderrazak, B. Coupling HEC-RAS and HEC-HMS in Rainfall–Runoff Modeling and Evaluating Floodplain Inundation Maps in Arid Environments: Case Study of Ain Sefra City, Ksour Mountain. SW of Algeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassew, B.G.; Belete, M.A.; Miegel, K. Application of HEC-HMS Model for Flow Simulation in the Lake Tana Basin: The Case of Gilgel Abay Catchment, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrology 2019, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, V.; Pezzoli, A.; Rosso, M. Past and Future Precipitation Trend Analysis for the City of Niamey (Niger): An Overview. Climate 2018, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aieb, A.; Madani, K.; Scarpa, M.; Bonaccorso, B.; Lefsih, K. A New Approach for Processing Climate Missing Databases Applied to Daily Rainfall Data in Soummam Watershed, Algeria. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, A.; Ghose, D.K. Imputation of Missing Precipitation Data Using KNN, SOM, RF, and FNN. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 5919–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, F.R. Simple, Practical Method for Determining Station Weights Using Thiessen Polygons and Isohyetal Maps. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2003, 8, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Alaska Satellite Facility Distributed Active Archive Center, PALSAR Radiometric Terrain Corrected High Res, 2014. Available online: https://asf.alaska.edu/data-sets/derived-data-sets/alos-palsar-rtc/alos-palsar-radiometric-terrain-correction/ (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- Arino, O.; Gross, D.; Ranera, F.; Leroy, M.; Bicheron, P.; Brockman, C.; Defourny, P.; Vancutsem, C.; Achard, F.; Durieux, L.; et al. GlobCover: ESA Service for Global Land Cover from MERIS. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 2412–2415. [Google Scholar]
- Bontemps, S.; Boettcher, M.; Brockmann, C.; Kirches, G.; Lamarche, C.; Radoux, J.; Santoro, M.; Vanbogaert, E.; Wegmüller, U.; Herold, M.; et al. Multi-Year Global Land Cover Mapping at 300 m and Characterization for Climate Modelling: Achievements of the Land Cover Component of the ESA Climate Change Initiative. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-7/W3, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/IIASA/ISRIC/ISSCAS/JRC Harmonized World Soil Database, Version 1.2; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy; International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis: Laxenburg, Austria, 2012.
- NRCS Natural Resources Conservation Service. Urban Hydrology for Small Watersheds; NRCS Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; TR-55.
- ESRI ArcGIS Desktop|ArcCatalog 2016. Version 10.3.1. Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI): Redlands, CA, USA, 2012.
- Soulis, K.X. Soil Conservation Service Curve Number (SCS-CN) Method: Current Applications, Remaining Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Water 2021, 13, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, J. The Application and Applicability of HEC-HMS Model in Flood Simulation under the Condition of River Basin Urbanization. Water 2023, 15, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.N.A.; Almuktar, S.; Scholz, M. Rainfall-Runoff Modeling Using the HEC-HMS Model for the Al-Adhaim River Catchment, Northern Iraq. Hydrology 2021, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.D. Hydrologic Modeling System HEC-HMS: Technical Reference Manual; US Army Corps of Engineers, Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Arc Hydro: GIS for Water Resources; Maidment, D.R., Ed.; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-1-58948-034-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jhs, B.; Alt, F.; Ad, L.; Lc, A. The Influence of Spatial Discretization on HEC-HMS Modelling: A Case Study. IJH 2019, 3, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughton, W. A Review of the USDA SCS Curve Number Method. Soil Res. 1989, 27, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbohoui, Y.P.; Paturel, J.-E.; Tazen, F.; Mounirou, L.A.; Yonaba, R.; Karambiri, H.; Yacouba, H. Impacts of Climate and Environmental Changes on Water Resources: A Multi-Scale Study Based on Nakanbé Nested Watersheds in West African Sahel. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 35, 100828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, E.T.; Nohegar, A.; Malekian, A.; Hoseini, M.; Holisaz, A. Estimating Time of Concentration in Large Watersheds. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Kong, F.; Zhu, Z. Application of Muskingum Routing Method with Variable Parameters in Ungauged Basin. Water Sci. Eng. 2011, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Radhakrishnan, N. Simulation of Rainfall–Runoff Process for an Ungauged Catchment Using an Event-Based Hydrologic Model: A Case Study of Koraiyar Basin in Tiruchirappalli City, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 130, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Liew, M.W.V.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and Water Quality Models: Performance Measures and Evaluation Criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCuen, R.H. The Role of Sensitivity Analysis in Hydrologic Modeling. J. Hydrol. 1973, 18, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, C.; Xuan, Y.; Ye, M.; Xu, C. Global Sensitivity Analysis in Hydrological Modeling: Review of Concepts, Methods, Theoretical Framework, and Applications. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ju, Q.; Jiang, P.; Huang, P.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Sensitivity Analysis of Hydrological Model Parameters Based on Improved Morris Method with the Double-Latin Hypercube Sampling. Hydrol. Res. 2023, 54, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Ahmad, S.; Dascalu, S.M.; Harris, F.C., Jr. MELPF Version 1: Modeling Error Learning Based Post-Processor Framework for Hydrologic Models Accuracy Improvement. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 4115–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chathuranika, I.M.; Gunathilake, M.B.; Baddewela, P.K.; Sachinthanie, E.; Babel, M.S.; Shrestha, S.; Jha, M.K.; Rathnayake, U.S. Comparison of Two Hydrological Models, HEC-HMS and SWAT in Runoff Estimation: Application to Huai Bang Sai Tropical Watershed, Thailand. Fluids 2022, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Radhakrishnan, N. Simulation of Extreme Event-Based Rainfall–Runoff Process of an Urban Catchment Area Using HEC-HMS. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 1867–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Liang, R.; Wang, Y.; Tumula, P. Flood-Runoff in Semi-Arid and Sub-Humid Regions, a Case Study: A Simulation of Jianghe Watershed in Northern China. Water 2015, 7, 5155–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messager, C.; Gallée, H.; Brasseur, O.; Cappelaere, B.; Peugeot, C.; Séguis, L.; Vauclin, M.; Ramel, R.; Grasseau, G.; Léger, L.; et al. Influence of Observed and RCM-Simulated Precipitation on the Water Discharge over the Sirba Basin, Burkina Faso/Niger. Clim. Dyn. 2006, 27, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodja, D.J.; Akognongbé, A.J.S.; Amoussou, E.; Mahé, G.; Vissin, E.W.; Paturel, J.-E.; Houndénou, C. Calibration of the Hydrological Model GR4J from Potential Evapotranspiration Estimates by the Penman-Monteith and Oudin Methods in the Ouémé Watershed (West Africa). Proc. Hydrol. Process. Water Secur. A Chang. World 2020, 383, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonaba, R.; Tazen, F.; Cissé, M.; Mounirou, L.A.; Belemtougri, A.; Ouedraogo, V.A.; Koïta, M.; Niang, D.; Karambiri, H.; Yacouba, H. Trends, Sensitivity and Estimation of Daily Reference Evapotranspiration ET0 Using Limited Climate Data: Regional Focus on Burkina Faso in the West African Sahel. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2023, 153, 947–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafando, M.B.; Koïta, M.; Le Coz, M.; Yonaba, O.R.; Fowe, T.; Zouré, C.O.; Faye, M.D.; Leye, B. Use of Multidisciplinary Approaches for Groundwater Recharge Mechanism Characterization in Basement Aquifers: Case of Sanon Experimental Catchment in Burkina Faso. Water 2021, 13, 3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafando, M.B.; Koïta, M.; Zouré, C.O.; Yonaba, R.; Niang, D. Quantification of Soil Deep Drainage and Aquifer Recharge Dynamics According to Land Use and Land Cover in the Basement Zone of Burkina Faso in West Africa. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiepolo, M.; Rosso, M.; Massazza, G.; Belcore, E.; Issa, S.; Braccio, S. Flood Assessment for Risk-Informed Planning along the Sirba River, Niger. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiepolo, M.; Belcore, E.; Braccio, S.; Issa, S.; Massazza, G.; Rosso, M.; Tarchiani, V. Method for Fluvial and Pluvial Flood Risk Assessment in Rural Settlements. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, A.E.; Hachett, S.; Uber, J.G.; Boccelli, D.L.; Shang, F. Real-Time Implementation of Contamination Source Identification Method for Water Distribution Systems. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress, American Society of Civil Engineers, Kansas City, MO, USA, 12 May 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tibangayuka, N.; Mulungu, D.M.M.; Izdori, F. Assessing the Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Streamflow in the Data-Scarce Upper Ruvu River Watershed, Tanzania. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2022, 13, 3496–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunderlik, J.M.; Simonovic, S.P. Calibration, Verification, and Senstivity Analysis of the HEC-HMS Hydrologic Model; University of Western Ontario, Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering: London, ON, Canada, 2004; ISBN 978-0-7714-2626-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rauf, A.; Ghumman, A. Impact Assessment of Rainfall-Runoff Simulations on the Flow Duration Curve of the Upper Indus River—A Comparison of Data-Driven and Hydrologic Models. Water 2018, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model Component | Parameter (Unit) | Initial Range/Values 1 | Maximum Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCS loss model | Initial abstraction (, mm) | 9.03–16.37 | 0–500 |
| Curve Number (, -) | 75.63–84.91 | 1–100 | |
| SCS-UH transform model | Lag time (, min) | 1163.81–3516.57 | 3.6–30,000 |
| Percent impervious (, %) | 10 | 0–100 | |
| Muskingum routing model | (, hours) | 4.91–62.26 | 0.1–150 |
| (, -) | 0.1 | 0–0.5 |
| Criteria | Calibration (2006–2015) | Validation (2016–2020) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.850 | 0.813 | |
| 0.780 | 0.820 | |
| 0.873 | 0.837 | |
| 0.400 | 0.400 | |
| (%) | 21.710% | 15.220% |
| (%) | 2.480% | −0.670% |
| Criteria | Calibration (2010 Event) | Calibration (2012 Event) | Calibration (2013 Event) | Validation (2015 Event) | Validation (2020 Event) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.94 | |
| 0.98 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.93 | |
| 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.94 | |
| 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.30 | |
| Observed peak discharge (m3/s) | 975.6 | 1112.3 | 1074.2 | 893 | 1208.6 |
| Simulated peak discharge (m3/s) | 972.2 | 1100.7 | 1021.3 | 835.7 | 1191.2 |
| (%) | −0.35% | −1.04% | −4.92% | −6.42% | −1.44% |
| Observed timing of peak 1 | 08/06 | 08/23 | 08/30 | 08/05 | 09/17 |
| Simulated timing of peak 1 | 08/06 | 08/23 | 09/01 | 08/06 | 09/18 |
| Observed volume (mm) | 89.81 | 111.24 | 102.08 | 79.48 | 143.85 |
| Simulated volume (mm) | 88.79 | 99.54 | 95.28 | 75.09 | 140.03 |
| (%) | −1.13% | −10.50% | −6.66% | −5.52% | −2.65% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souley Tangam, I.; Yonaba, R.; Niang, D.; Adamou, M.M.; Keïta, A.; Karambiri, H. Daily Simulation of the Rainfall–Runoff Relationship in the Sirba River Basin in West Africa: Insights from the HEC-HMS Model. Hydrology 2024, 11, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11030034
Souley Tangam I, Yonaba R, Niang D, Adamou MM, Keïta A, Karambiri H. Daily Simulation of the Rainfall–Runoff Relationship in the Sirba River Basin in West Africa: Insights from the HEC-HMS Model. Hydrology. 2024; 11(3):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouley Tangam, Idi, Roland Yonaba, Dial Niang, Mahaman Moustapha Adamou, Amadou Keïta, and Harouna Karambiri. 2024. "Daily Simulation of the Rainfall–Runoff Relationship in the Sirba River Basin in West Africa: Insights from the HEC-HMS Model" Hydrology 11, no. 3: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11030034
APA StyleSouley Tangam, I., Yonaba, R., Niang, D., Adamou, M. M., Keïta, A., & Karambiri, H. (2024). Daily Simulation of the Rainfall–Runoff Relationship in the Sirba River Basin in West Africa: Insights from the HEC-HMS Model. Hydrology, 11(3), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11030034







