Feasibility Study on Using Calcium Lignosulfonate-Modified Loess for Landfill Leachate Filtration and Seepage Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Loess
2.2. Landfill Leachate Preparation
2.3. Calcium Lignosulfonate
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. Permeability Test and Experimental Design
2.6. Sample Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Degree of Compaction on Permeability of Loess Samples
3.2. Effect of Concentration of Landfill Leachate on Permeability Coefficient of Loess Samples
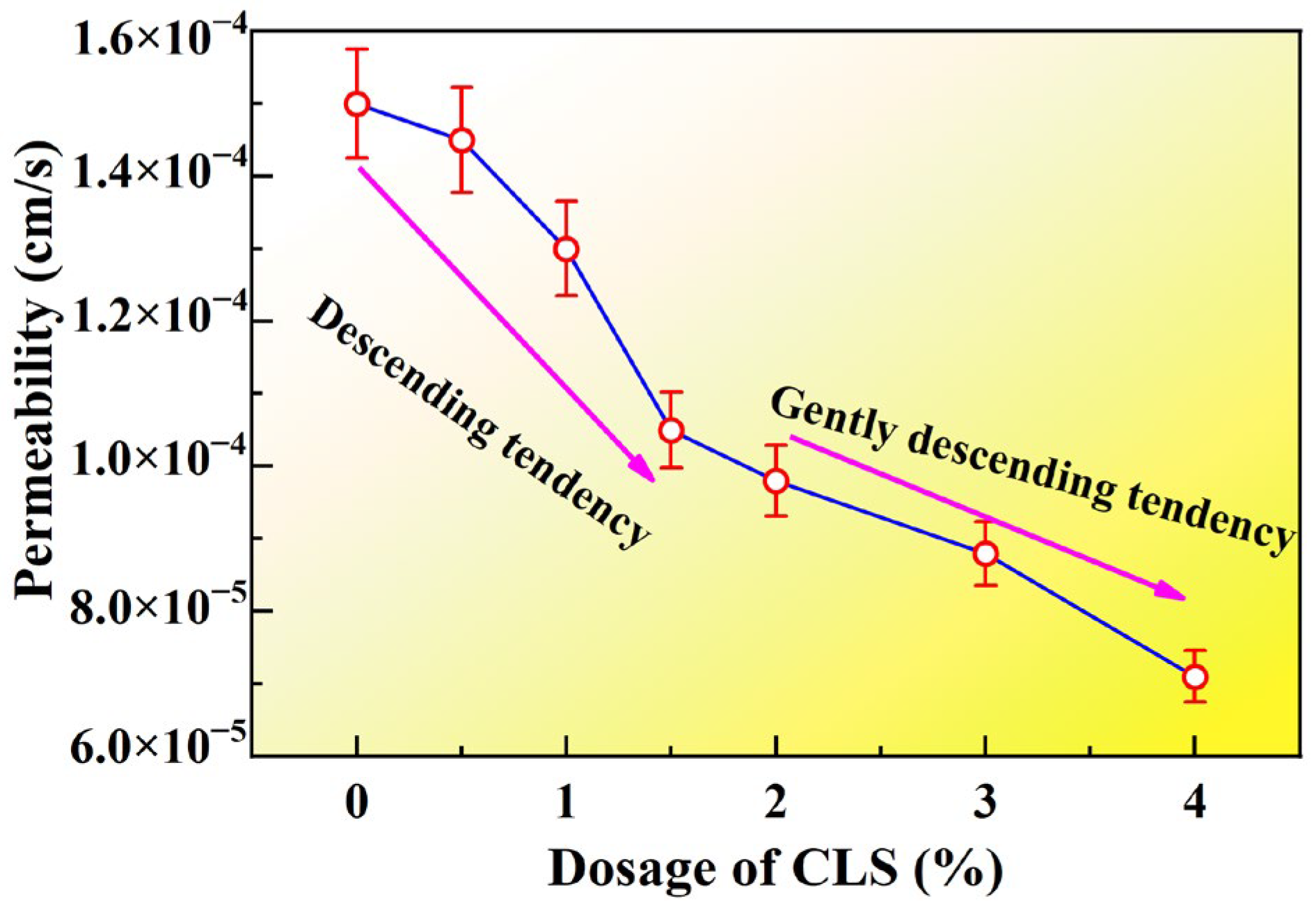
3.3. Effect of Dosage of CLS on Permeability Coefficient of Loess Samples
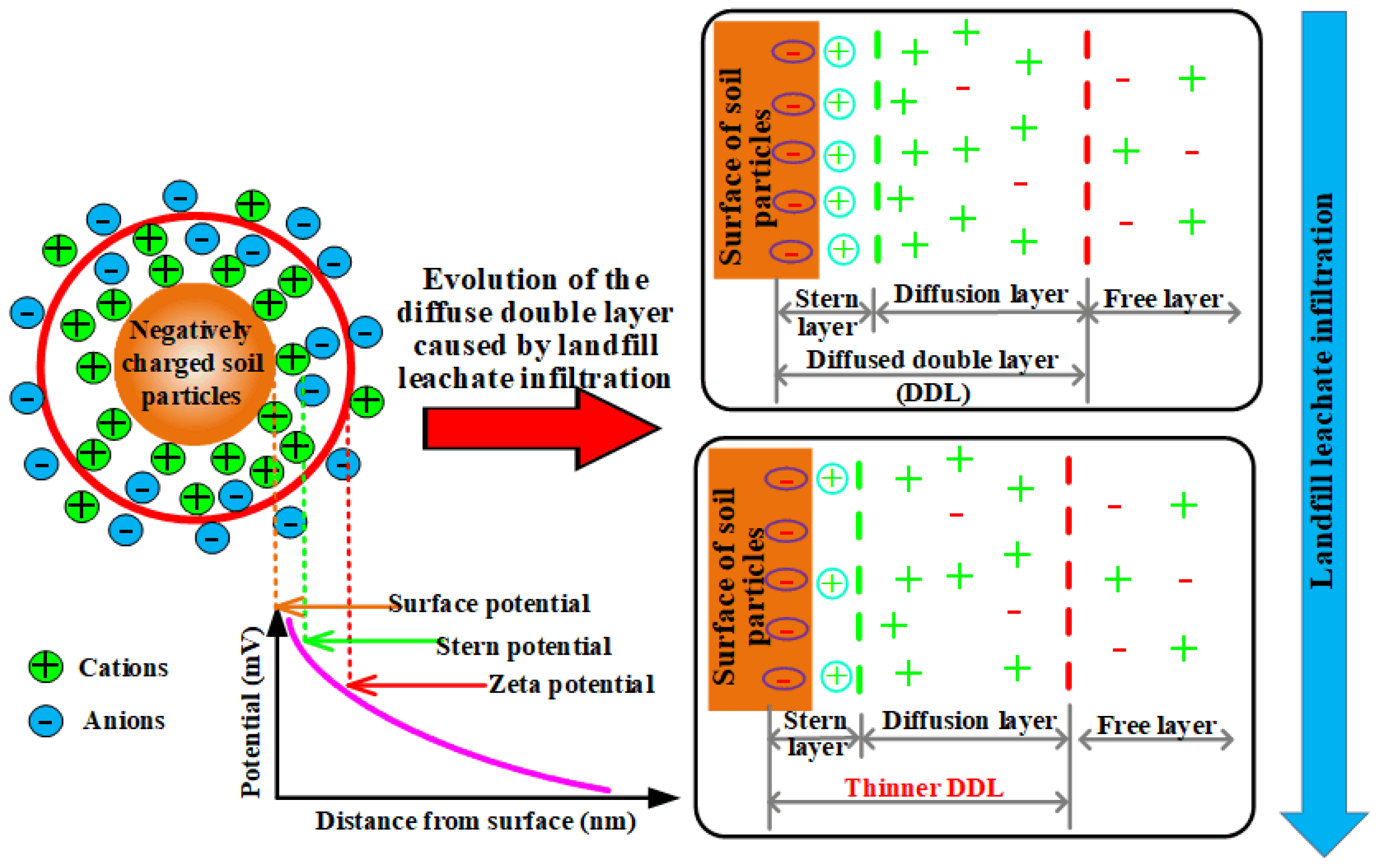
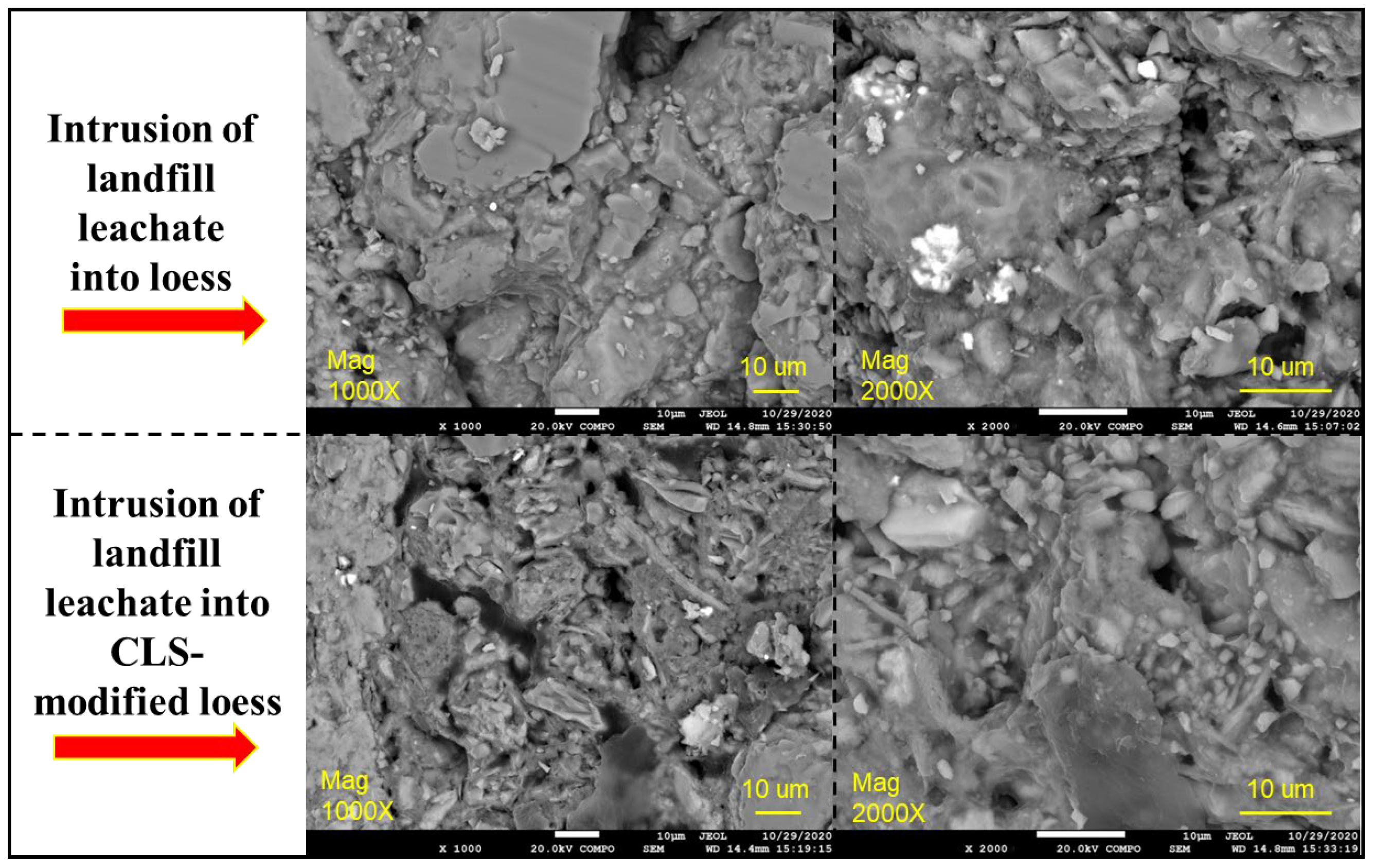
3.4. XRF, Zeta Potential and SEM Test Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- This study demonstrates that the permeability coefficient of remolded loess decreases with increasing compaction. Beyond a threshold compaction degree of 0.85, the rate of reduction diminishes, indicating that the pore network approaches a densely packed and structurally stable configuration. While initial compaction markedly enhances impermeability, further densification yields only marginal gains. Under landfill leachate infiltration, multivalent cations such as Ca2+ and Mg2+ penetrate the electrical double layer of loess particles, reducing the absolute Zeta potential. The resulting decrease in electrostatic repulsion promotes particle flocculation, enlarges pore pathways, and increases the permeability coefficient.
- (2)
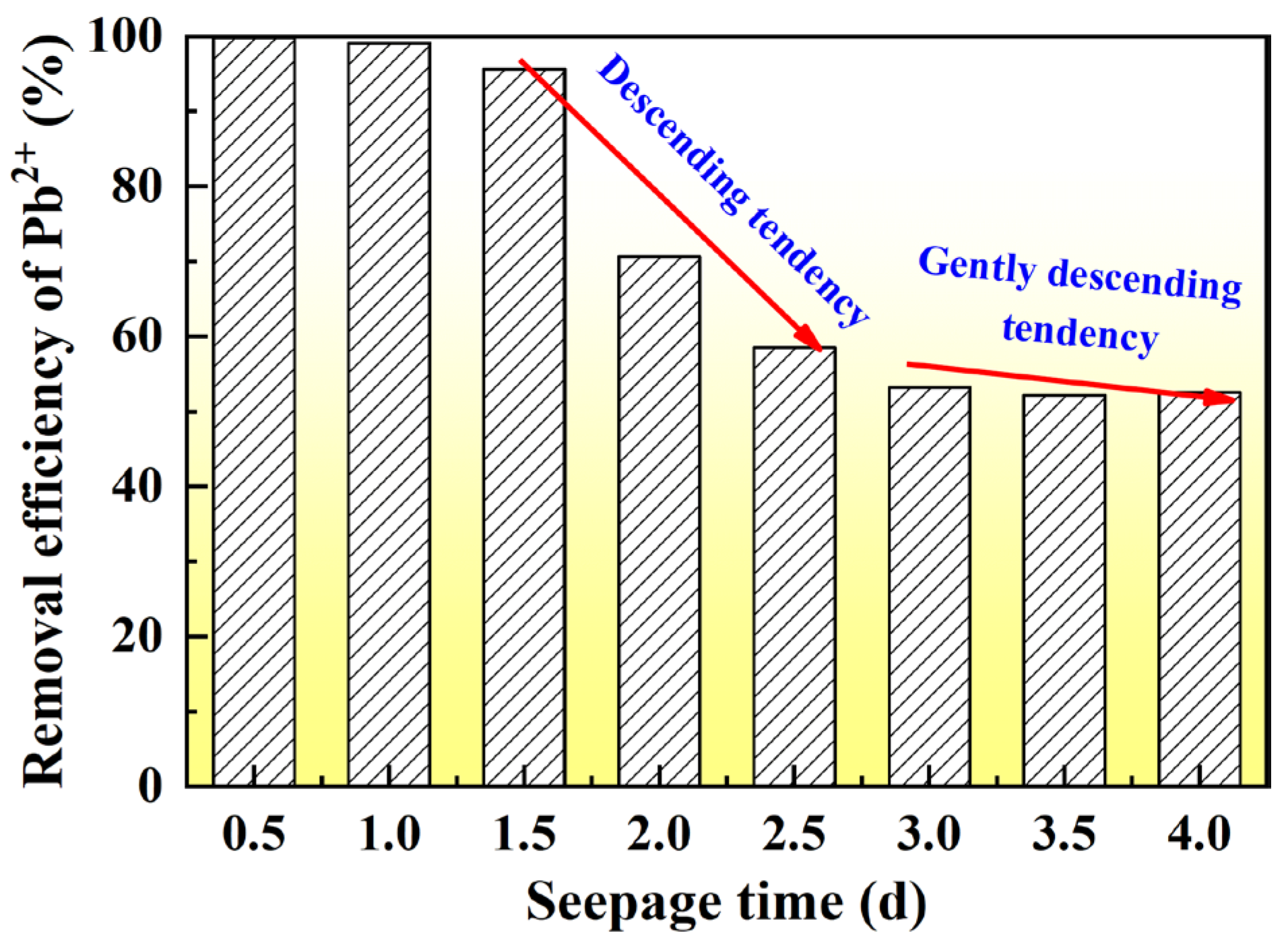
- The moisture and chemical constituents of landfill leachate act corrosively on the loess matrix, dissolving binding minerals, weakening structural integrity, and increasing permeability. This effect intensifies with leachate concentration, leading to pronounced structural degradation. At full-strength leachate, Pb2+ removal efficiency declines steadily during curing, indicating that prolonged exposure diminishes adsorption capacity and accelerates mineral destabilization.
- (3)
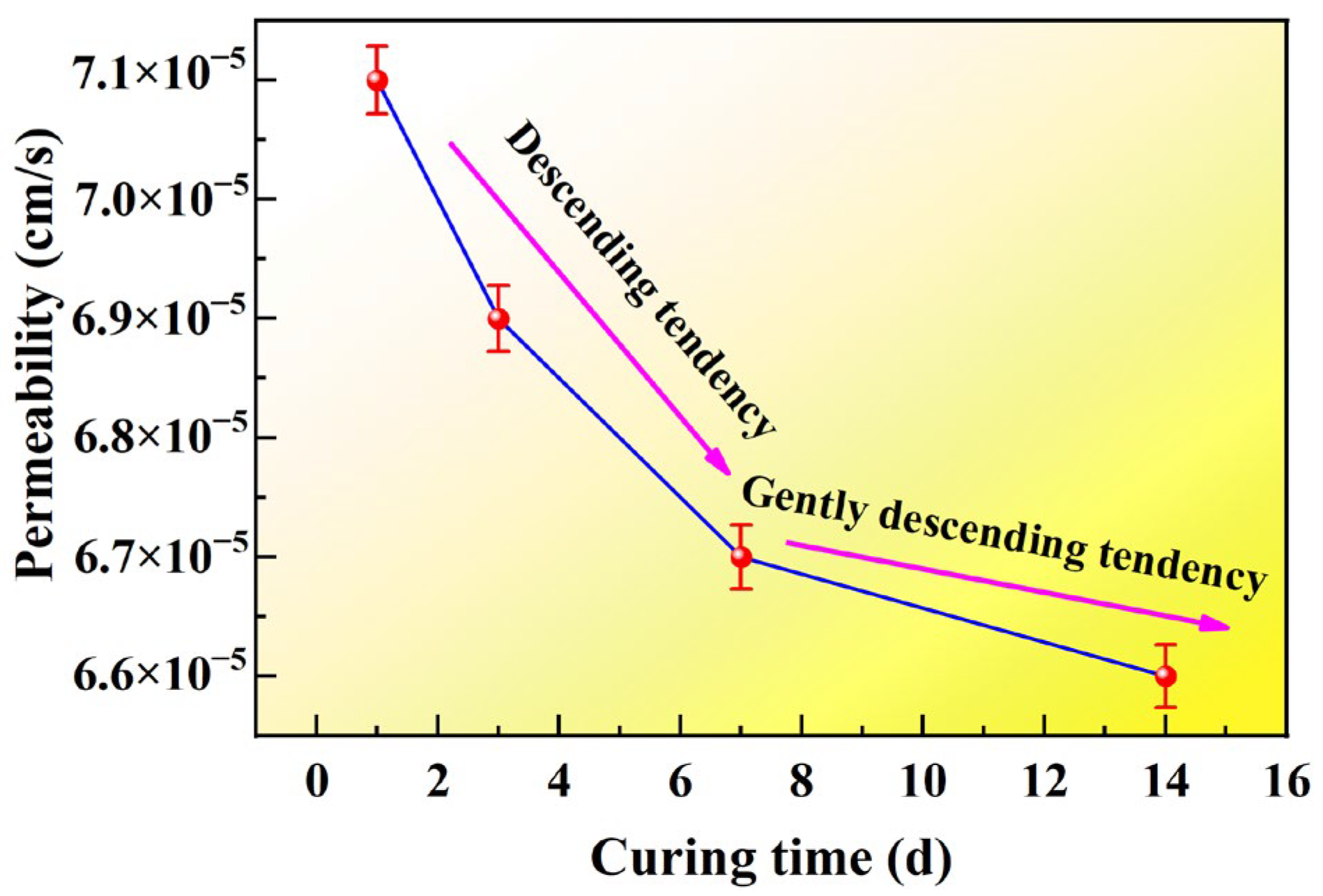
- The incorporation of CLS lowers the Zeta potential and facilitates particle flocculation, yet its strong Pb2+ binding affinity and pore-filling capacity dominate the overall response. An optimal dosage of 4% was identified. During curing, CLS forms stable cementitious linkages between particles, reduces porosity, and reinforces the soil fabric. Under seepage conditions, CLS-modified loess maintains structural integrity and demonstrates superior barrier performance, effectively immobilizing heavy metals while preserving low permeability.
- (4)
- Future research should focus on evaluating the long-term performance and environmental durability of CLS-modified loess under diverse field conditions, including seasonal wetting–drying and freeze–thaw cycles. Additionally, further investigation is required to assess the feasibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of applying this modification technique in real-world landfill barrier systems, ensuring its practical viability in engineering applications.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Y.; Gu, K.; Zhang, Y.P.; Shen, Z.T.; Tang, C.S.; Shi, B.; Zhou, Q.Y. Biochar implications for the engineering properties of soils: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, E.; Anggraini, V.; Raghunandan, M.E.; Asadi, A. Utilization of marine clay as a bottom liner material in engineered landfills. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodary, S.M.; Fath, H.; Negm, A.; Tawfik, A. Measuring the engineering properties of landfill leachate-contaminated soil in Egypt. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2021, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.P.; Nauerth, I.M.R.; Kasemodel, M.C.; Rodrigues, V.G.S. Systematic review of alternative materials that improve retention of potentially toxic metals in soil/clay liners in waste disposal areas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, G.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yuan, Y.; Xi, B.D.; Tan, W.B. Assessing the impacts and contamination potentials of landfill leachate on adjacent groundwater systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, S.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Zheng, Q.T.; Cao, B.Y. Fully coupled hydromechanical study of tunnel excavation considering leachate leakage from a high water-level landfill. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 175, 106696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.R.; Matlan, S.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Pishro, A.A.; Pishro, M.A.; Gao, X.; Taha, N.A.; Zhou, Y.X. Enhancing attapulgite and cement-modified loess for effective landfill lining: A study on seepage prevention and Cu/Pb ion adsorption. Open Geosci. 2024, 16, 20220617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daramola, S.O.; Demlie, M.; Hingston, E.D.C. Mineralogical and sorption characterization of lateritic soils from Southwestern Nigeria for use as landfill liners. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, B.; Dou, T.T.; Ge, B.Z.; Wang, L. Hydraulic performance of GCL under wet-dry cycling concurrent with municipal solid waste leachate permeation. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 701–707. [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam, H.M.; Fahimifar, A.; Ebadi, T.; Keramati, M.; Siddiqua, S. Assessment of leachate-contaminated clays using experimental and artificial methods. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 17, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.L.; Cheng, W.C.; Wen, S.J.; Rahman, M.M. Effects of chemical contamination on microscale structural characteristics of intact loess and resultant macroscale mechanical properties. Catena 2021, 203, 105361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, L.Z.; Zhang, W.P.; Wang, H.H.; Gao, Z.Y. Mechanism of calcium lignosulfonate in apatite and dolomite flotation system. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2022, 29, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, W.M.A.N.W.; Tan, N.P.; Low, L.Y.; Loh, J.Y.; Wee, C.Y.; Taib, A.Z.M.; Ong-Abdullah, J.; Lai, K.S. Calcium lignosulfonate improves proliferation of recalcitrant indica rice callus via modulation of auxin biosynthesis and enhancement of nutrient absorption. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Y.; Hou, X.; Mu, Y.H.; Ma, W.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, Y.C. Engineering properties of loess stabilized by a type of eco-material, calcium lignosulfonate. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.G.; Wang, B.Z.; Yang, X.J.; Fan, H.H. Experimental study of dispersive clay modified by calcium lignosulfonate. Rock Soil Mech. 2021, 42, 2405–2415. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, Y.; Zhong, J.R. Effect of sodium lignosulfonate/nano calcium carbonate composite filler on properties of isotactic polypropylene. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 3103–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Lin, G.C.; Wen, L.; Wang, Q. Microscopic mechanism affecting shear strength in lignin-treated loess samples. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.T.; Orlandi, S.; Codevilla, M.; Piqué, T.M.; Manzanal, D. Performance of calcium lignosulfonate as a stabiliser of highly expansive clay. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 27, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, K.Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Zeng, Y.F.; Sun, H.T.; Peng, H. Analysis of environmental impact of disposal of uranium waste in surface landfill facilities. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 50, 6655–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnmr, A.; Ray, R.; Alzawi, M.O. Comparative analysis of foundation systems in expansive soil: A three-dimensional model approach to moisture diffusion and volume changes. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2024, 42, 7935–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutrisno, H.; Trihadiningrum, Y.; Ekaputri, J.J.; Meilasari, F.; Yuniarto, A. Characteristics and potential use of residual waste from bauxite ore processing industry in West Kalimantan, Indonesia. J. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 26, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lu, H.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, G.H.; Zang, M. Experimental study on transport of Cd(II) and Cu(II) in landfill improved clay liners building material containing municipal sludge-activated carbon. Buildings 2024, 14, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Feng, Q.M.; Shi, Q. Effect of depressants in the selective flotation of smithsonite and calcite using potassium lauryl phosphate as collector. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.J.; She, W.; Wei, L.S.; Zuo, W.; Hu, X.; Hong, J.; Miao, C. Stabilization mechanism of calcium lignosulphonate used in expansion sensitive soil. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Mater. Sci.) 2020, 35, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50123-2019; Standard for Geotechnical Test Methods. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- He, P.L.; Guo, J.J.; Zhang, S.X. Feasibility of Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation to Enhance the Internal Stability of Loess under Zn-Contaminated Seepage Conditions. Buildings 2024, 14, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, N.C.; Faria, A.U.; Oloveira, V.J.A.; Govone, J.S.; Angelis, D.D. Biodegradation and toxicity of byproducts from the treatment of landfill leachate with hydrotalcite. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 118, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabba, F.; Kassar, C.; Zeng, T.; Mallick, S.P.; Downing, L.; Mcnamara, P. PFAS in landfill leachate: Practical considerations for treatment and characterization. J. Hazarous Mater. 2025, 481, 136685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodh, A.; Shafi, M.; Goel, S. Microplastics in municipal solid waste landfill leachate and their removal in treatment units: A perspective of controlled and uncontrolled landfills. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 369, 125853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirakawa, S.; Koga, T.; Shimizu, N.; Fujikawa, K.; Tobiishi, K.; Toba, M. Exploring landfill conditions: Analyzing relationships among waste composition, leachate water quality, and microbial community structure in inert-waste landfill sites. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2025, 27, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhu, J.R.; Wang, D.X.; Zhou, H.Y.; Bi, J.J. Experimental and mechanical characteristics of xanthan gum and calcium lignosulfonate-cured gravel soil. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wu, Q.; Ma, Q.W.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J. Study on Strengthening and Waterproofing Mechanism of Calcium Lignosulfonate in Silty Soil Sites. Coatings 2023, 13, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Li, H.X.; Zhang, H.Z.; Duan, D.Y.; Ding, Q.; Ding, L.; Liu, Y.J. Experimental Study on Mechanical Characteristics of Stabilized Soil with Rice Husk Carbon and Calcium Lignosulfonate. Materials 2024, 17, 5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, Q.L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, W.Z. Influence mechanisms of the calcium lignosulfonate on the pore structure of cement in coalbed methane well cementing. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2025, 246, 213660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Hong, C.S.; Li, S.; Xin, J.Y.; Huang, D. Experimental study on the efficiency of calcium lignosulfonate-modified red clay for radon mitigation. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2025, 334, 2861–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, W.C.; Han, H.J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.N. One-step depolymerization of calcium lignosulfonate to produce phenolics with the action of solid base oxides. Mater. Res. Express 2025, 12, 035505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruzelak, J.; Dzuganová, M.; Kvasnicáková, A.; Preto, J.; Hronkovic, J.; Hudec, I. Influence of plasticizers on cross-linking process, morphology, and properties of lignosulfonate-filled rubber compounds. Polymers 2025, 17, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudliar, R.; Rajesh, S. Mitigation of the swelling behavior of expansive soils using hydrophobic lignosulfonate: Adsorption mechanism. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2025, 37, 04024486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.L.; Guo, J.J.; Zhang, S.X. Investigating the Potential of Microbially Induced Carbonate Precipitation Combined with Modified Biochar for Remediation of Lead-Contaminated Loess. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosneaga, A.; Georgescu, L.; Ene, A. Evaluation Of Soils Pollution With Heavy Metals Using XRF Technique. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2024, 12, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Devarangadi, M.; Vuppala, S.; Shankar, M.U.; Raghunanda, M.E. Effect of collated fly ash, GGBS and silica fume on index and engineering properties of expansive clays as a sustainable landfill liner. Clean. Mater. 2024, 11, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Qian, H.; Li, W.; Ren, W.; Yang, F.; Wang, L. New insights into the seepage behavior of heavy metal-contaminated loess and its underlying geochemical mechanism. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.S.A.; Safingi, S.; Sidek, N.; Arshad, M.F. Landfill liners properties using pressmud and modified marine clay. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2025, 16, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Aswathy, C.M.; Sunil, B.M. Effect of ammonia on the hydraulic conductivity and adsorption characteristics of lithomargic clay-bentonite barrier in landfills. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspanathan, T.K.; Jayawardane, V.S.; Paul, S.C.; Ying, K.S.; Shukla, S.K.; Anggraini, V. Effect of biochar on desiccation of marine soils under constant and cyclic temperatures. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 5441–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyo, E.; Abbey, S.; Oti, J.; Ngambi, S.; Ganjian, E.; Coakley, E. Microstructure and physical-mechanical characteristics of treated kaolin-bentonite mixture for application in compacted liner systems. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.J.; Xu, S.C.; Li, D.G.; Li, J. An experimental study of mineral and microstructure for undisturbed loess polluted by landfill leachate. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 4891–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Li, D.; Zhao, D.; Lu, W.; Liu, J. Experimental research on collapsibility of Xi’an loess improved by calcium lignosulfonate. Coatings 2023, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbakht, M.; Sarand, F.B.; Dabiri, R.; Hajialilue Bonab, M. Investigation of leachate effect on permeability and geotechnical characteristics of fine-grained soil modified using nanoclay-nanofiber composites. Water 2023, 15, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizamir, M.; Kazemi, Z.; Kazami, Z.; Kermani, M.; Kim, S.; Heddam, S.; Kisi, O.; Chuang, I.M. Investigating landfill leachate and groundwater quality prediction using a robust integrate artificial intelligence model: Grey wolf metaheuristic optimization algorithm and extreme learning mechine. Water 2023, 15, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, P.; Fei, W.B.; Wang, J.D. Influence of biochar on the soil-water retention behavior of compacted loess in man-made earth structures in loess regions. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 1103–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gu, K.; Zhang, Y.P.; Shen, Z.T.; Tang, C.S.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Shi, B. Biochar-water-soil interactions: Implications for soil desiccation cracking behavior in subtropical regions. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 17, 1876–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, C.M.; Sunil, B.M. Improving landfill liner performance with bentonite-slag blend permeated with ammonia for a Municipal solid waste landfill. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 122013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.B.; Chen, Z.F.; Qi, L. Evaluating the potential of multi-walled carbon nanotube-modified clay as a landfill liner material. Materials 2023, 16, 7705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, R.L.; Tingle, J.S.; Webster, S.L. Stabilization of silty sand with nontraditional additives. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2002, 1787, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingle, J.S.; Santoni, R.L. Stabilization of clay soils with nontraditional additives. Transp. Res. Board J. Transp. Res. Board 2003, 1819, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50869-2013; Technical Code for Sanitary Landfill of Municipal Solid Waste. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
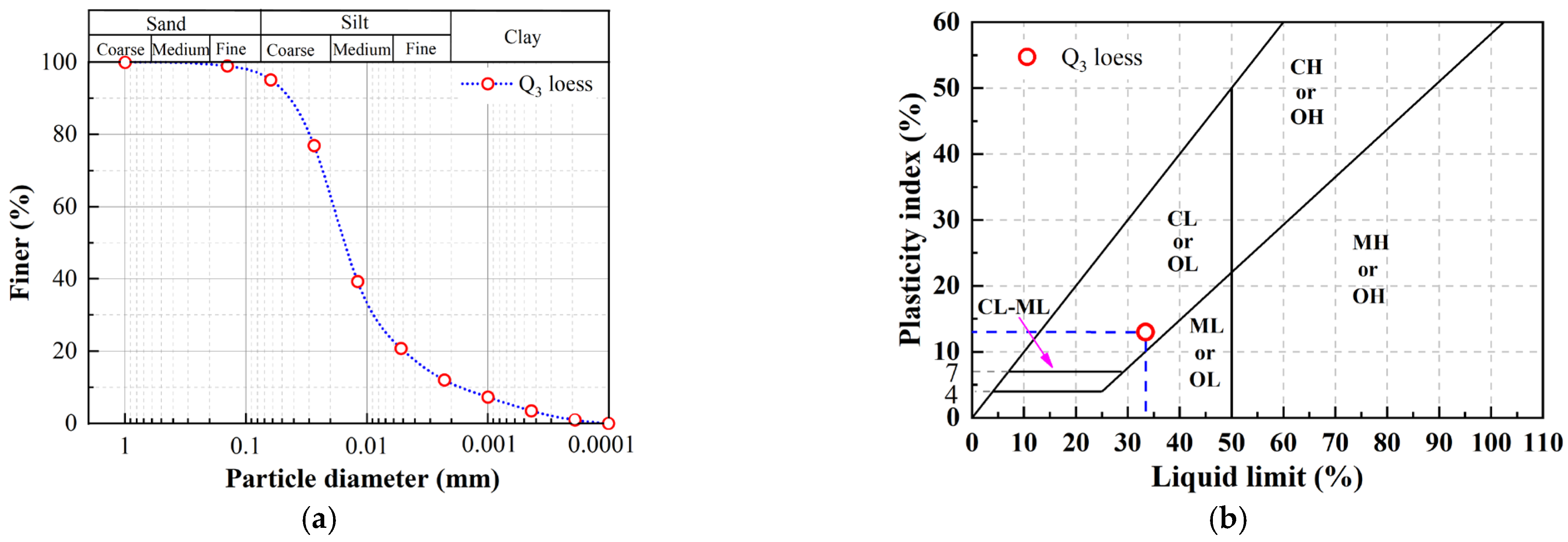






| Physical Index | Data |
|---|---|
| Fines (%) | 91.18 |
| Sand (%) | 8.82 |
| Gravel (%) | 0 |
| Specific gravity, Gs | 2.72 |
| Void ratio, e | 0.88 |
| Dry density, ρdmax/(g/cm3) | 1.78 |
| Initial water content, wn/% | 16.4 |
| The Atterberg limit | |
| Liquid limit, wL/% | 33.42 |
| Plastic limit, wP/% | 20.43 |
| Soil classification | CL |
| Chemical Element | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Silicon (Si) | 73.66 |
| Aluminum (Al) | 15.5 |
| Iron (Fe) | 7.93 |
| Potassium (K) | 1.09 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 0.95 |
| Sodium (Na) | 0.54 |
| Calcium (Ca) | 0.33 |
| Test | Degree of Compaction | Concentration of Landfill Leachate (%) | Concentration of CLS (%) | Curing Time (d) | Seepage Time | Quantity of Specimens |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp-01 | 0.75, 0.80, 0.85, 0.90 | / | / | 1 | 0–4 | 4 |
| Exp-02 | 0.75 | 10, 30, 50, 100 | / | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Exp-03 | 0.75 | 100 | 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 | 1–14 | 4 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, S. Feasibility Study on Using Calcium Lignosulfonate-Modified Loess for Landfill Leachate Filtration and Seepage Control. ChemEngineering 2025, 9, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9050096
Guo J, Hu W, Zhang S. Feasibility Study on Using Calcium Lignosulfonate-Modified Loess for Landfill Leachate Filtration and Seepage Control. ChemEngineering. 2025; 9(5):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9050096
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jinjun, Wenle Hu, and Shixu Zhang. 2025. "Feasibility Study on Using Calcium Lignosulfonate-Modified Loess for Landfill Leachate Filtration and Seepage Control" ChemEngineering 9, no. 5: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9050096
APA StyleGuo, J., Hu, W., & Zhang, S. (2025). Feasibility Study on Using Calcium Lignosulfonate-Modified Loess for Landfill Leachate Filtration and Seepage Control. ChemEngineering, 9(5), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9050096







