Abstract
Ternary choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents (TDESs) exhibit unique physicochemical properties, including lower viscosities, lower melting points, higher thermal stabilities, and enhanced solvations compared to binary deep eutectic solvents (BDESs). Although BDESs have been widely studied, the addition of a third component in TDESs offers opportunities to further optimize their performance. This review aims to evaluate the physicochemical properties of TDESs and highlight their potential applications in sustainable industrial processes compared to BDESs. A comprehensive analysis of the existing literature was conducted, focusing on TDES properties, such as phase behavior, density, viscosity, pH, conductivity, and the effect of water, along with their applications in various fields. TDESs demonstrated superior physicochemical characteristics compared to BDESs, including improved solvation and thermal stability. Their applications in biomass conversion, CO2 capture, heavy oil upgrading, refrigeration gases, and as solvents/catalysts in organic reactions show significant promise for enhancing process efficiency and sustainability. Despite their advantages, TDESs face challenges including limited predictive models, potential instability under certain conditions, and scalability hurdles. Overall, TDESs offer significant potential for advancing sustainable and efficient chemical processes for industrial applications.
1. Introduction
The chemical industry places significant importance on the development of solvents that are both cost effective and environmentally friendly. The need for solvents that are less harmful, biodegradable, derived from natural sources, and affordable has gradually stimulated the exploration of alternative solvents. Over the past decades, eco-friendly solvents such as supercritical fluids, bio-based solvents, ionic liquids (ILs), and, more recently, deep eutectic solvents (DESs) have emerged as safe alternatives [1]. DESs are novel eco-friendly solvents that exhibit many similarities with ILs. They exhibit properties comparable to those of ILs, such as low viscosity, low melting point, nonflammability, and low vapor pressure [2,3,4]. They can be synthesized using simple and economical techniques such as quenching and melt-quenching [5]. These methods involve mixing the components at a specific molar ratio and cooling the mixture to form DESs. Additionally, ultrasonic-assisted synthesis can be employed to enhance homogeneity and reduce reaction time [6]. In addition to their remarkable physicochemical properties, DESs are notable for their simple preparation using readily available and naturally derived compounds. This characteristic makes them promising and sustainable alternatives to conventional organic solvents; DESs appear to be promising alternatives to conventional organic solvents [7,8,9].
DESs are mixtures of two or more solid starting materials with high melting points that result in liquid eutectic mixtures at room temperature. This mixture has a significantly lower melting point than its individual pure components, owing to charge delocalization facilitated by hydrogen bonding (e.g., between a halide ion and a hydrogen-donor group). A eutectic reaction is an isothermal, reversible process in which a liquid transforms into multiple solid phases upon cooling [10]. The eutectic point represents the composition and the minimum melting temperature along the intersecting melting curve. Classical thermodynamics describes these melting curves using an equation that assumes a pure solid phase and negligible temperature influence on heat capacity [11].
where is the activity coefficient of compound at a given liquid mole fraction, T is the absolute temperature, is the melting temperature of component , is the melting enthalpy of the pure compound, R is the universal gas constant, and is the difference between the molar heat capacities of the liquid and the solid phases. The change in the heat capacity upon melting is negligible [10]. Hence, Equation (1) reduces to:
DESs are commonly binary or ternary mixtures that primarily interact via hydrogen bonding to form a eutectic mixture at a specific molar ratio [12]. A phase diagram (Figure 1) illustrates the transition between solid and liquid states in a binary mixture, showing the DES at a specific composition and temperature.
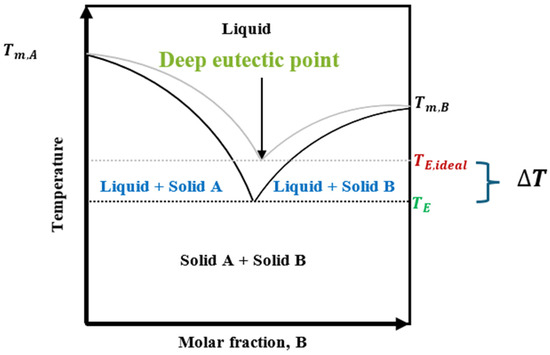
Figure 1.
A general solid–liquid equilibrium (SLE) of a simple ideal eutectic mixture and a deep eutectic mixture. and represent the melting temperatures of compound A and B, stands for the freezing point depression [13].
This characteristic supports the tunability and flexibility in designing DESs with varying properties, emphasizing deviations from ideality and the characteristic temperature depression of the DES systems. Thus, DESs can encompass a range of compositions within the liquid state at specific temperatures and molar ratios, promoting versatile solvent design beyond rigid stoichiometric proportions [10]. The eutectic composition indicated by the lowest melting temperature is unique in Figure 1. DESs exhibit lower melting points due to component interactions, which are significantly lower than those of their individual components. “Deep” in a DES context signifies deviation from ideal behavior due to strong, complex hydrogen bond networks between components, particularly between halide salt anions (HBAs) and hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) [12,14,15,16]. These hydrogen bonds affect the phase transition temperature, stability, and unique physicochemical and thermodynamic properties of the solvent [16,17]. Understanding the eutectic point is crucial for modifying DES properties for different applications, enabling adjustments in the melting temperature, density, viscosity, conductivity, and other key physicochemical properties.
1.1. Hydrogen Bond Acceptors and Donors
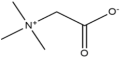
HBAs and HBDs are the two components of DESs. Numerous combinations of HBAs and HBDs or complexing agents have been reported to successfully produce DESs since research on DESs first appeared in the literature [18]. Examples of HBAs include Choline Chloride (ChCl) [19], methyl triphenyl phosphonium bromide [20,21,22], tetrabutylammonium bromide, and tetrabutyl phosphonium bromide [21].
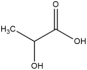
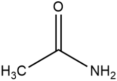
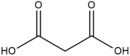
Many examples of HBDs and complexing agents have been reported, including urea (U), thiourea, oxalic acid, malonic acid, 1,1-dimethyl urea, acetamide, benzamide [19], ethylene glycol (EG), glycerol (GL), 2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide [22], and d-fructose [23]. Table 1 summarizes the commonly used hydrogen bond acceptors and donors along with their respective melting temperatures, as reported in the literature.

Table 1.
Some of the hydrogen bond acceptors and donors, with their corresponding individual melting temperatures, used in the formation of DESs.
1.2. Classification of Deep Eutectic Solvents
DES classification was based on the following formula [14]:
where denotes ammonium, phosphonium, or sulfonium and X is a Lewis base, typically a halide anion. The square brackets indicate the formation of complex anionic species with Lewis or Brønsted acid Y. Variable z represents the number of Y molecules interacting with the anion [14,30]. Common cations in DESs include quaternary ammonium and imidazolium salts, with choline chloride (ChCl) being emphasized for practical use. The DES classification depends on the nature of the complexing agent based on HBAs and HBDs, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
General formula for classification of deep eutectic solvents [14,30,31,32,33].
Most of the studied DESs fit into different categories. Type I includes quaternary ammonium salts, such as ChCl as HBA, with metal chlorides, such as zinc chloride (ZnCl2). Type II features a metal chloride hydrate, such as cobalt (II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2 · 6H2O), as the HBD, combined with ChCl as the HBA. Type III involves HBDs, such as urea, alcohol, carboxylic acids, amines, or sugars, with ChCl as the HBA. These DESs can solvate various transition metal species including chlorides [19] and oxides [34]. Type IV includes metal chloride hydrates, such as zinc chloride hydrate (ZnCl2 · H2O), as HBAs with organic molecules such as urea, acetamide, and EG [35].
A new class, Type V nonionic DESs, was introduced by Abranches and Coutinho [36,37]. This type consists solely of the molecular substances that form hydrogen bonds. A thymol-menthol system, using menthol (C10H20O) as the HBD and thymol (C10H14O) as the HBA, showed strong interactions owing to the acidity difference between the phenolic and hydroxyl groups. Their analysis of solid–liquid equilibrium phase diagrams revealed eutectic temperatures that were significantly lower than those expected from thermodynamic ideal behavior. However, most studies on Type V DESs have focused on determining the melting temperatures of specific mixtures without thoroughly investigating their phase behavior [38,39,40].
Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (HDESs) have recently gained attention for their use in hydrophobic compounds such as tetrabutylammonium bromide, menthol, thymol, and fatty acids as hydrogen bond acceptors (HBAs), while long alkyl chain alcohols and carboxylic acids serve as hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) [15,41]. These solvents can form stable two-phase systems with water, making them effective green alternatives to conventional solvents, particularly for extracting nonpolar organic and inorganic molecules from aqueous environments [32]. Their viscosities can be tailored by selecting appropriate components and adjusting their molar ratios, thereby enhancing their performance in various applications [42].
Specialized categories of DESs include therapeutic DESs (THEDESs), which incorporate active pharmaceutical ingredients such as ibuprofen, lidocaine, and phenylacetic acid for biomedical uses [43,44], and natural DESs (NADESs), which are derived from natural compounds such as organic acids and sugars and offer properties similar to those of synthetic DESs [44,45,46].
Recent advancements include supramolecular deep eutectic solvents (SUPRADESs) and organic solvents designed for diverse extraction techniques [47]. SUPRADESs form noncovalent interactions with analytes and exhibit inclusion capabilities. Their physical properties depend on the type of cyclodextrin used, other organic components, and stoichiometry, which significantly affects their physicochemical properties and extraction efficiency [48]. Cyclodextrins, which are key to SUPRADESs, have hydrophilic outer surfaces and hydrophobic cavities that form inclusion complexes through noncovalent host–guest interactions. The decomposition temperature of SUPRADESs determines their suitability for high-temperature processes, particularly for those that require solvent regeneration. Their melting points and glass transition temperatures are critical for effective extraction, ideally below the room temperature. However, the high melting points of cyclodextrins limit the number of suitable SUPRADESs, thereby challenging broader applications. Despite these limitations, SUPRADESs offer significant potential for sustainable and efficient extraction.
This review focuses on type III deep eutectic solvents (DESs) with choline chloride (ChCl) as a hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA). ChCl, one of the first salts used for DES synthesis, is popular because of its cost-effectiveness, biodegradability, nontoxicity, and ease of preparation [18,49,50]. They can be derived from biomass or fossil reserves. The adaptability of type III DESs is increased by a variety of hydrogen bond donors (HBDs), enabling the customization of their physical properties for specific uses [12,19]. In contrast, other DES types (e.g., Type I, II, IV, and V) are less emphasized due to limitations such as higher costs (e.g., metal chlorides in Type I and II), less explored phase behavior (Type V), or specific application constraints (e.g., hydrophobic DESs or SUPRADESs). Type III DESs based on ChCl and various HBDs are versatile and have been widely studied for applications, such as biofuel production from lignocellulosic biomass, acid gas removal, and enhanced oil recovery [51,52,53]. The selection of suitable HBDs allows the physical properties of the DESs to be tailored for diverse technological applications.
1.3. Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents
Choline, also known as the cholinium cation, is a non-toxic and affordable compound that is widely used as an animal feed supplement and is classified as a provitamin in Europe. It is produced via a one-step gas-phase reaction involving hydrochloric acid, ethylene oxide, and trimethylamine, which generates minimal waste [14]. ChCl-based DESs are promising candidates for creating eco-friendly, cost-effective, and advanced solvents [30,37,54]. They offer advantages over conventional ionic liquids (Table 3), such as 100% atom economy, no purification requirements, and suitability for large-scale applications [55,56]. ChCl-based DESs have a wide liquid range, water compatibility, low vapor pressure, non-flammability, biocompatibility, and biodegradability [12,57,58,59]. The natural DESs derived from ChCl include sugars, amino acids, and organic acids [45,60]. The combination of different starting materials allows control over the physical properties of DESs. ChCl-based DESs exhibit properties similar to those of imidazolium-based ILs, making them capable of replacing or enhancing ILs for various applications [56]. Unlike conventional organic solvents, ChCl-based DESs are nonflammable and nonvolatile, facilitating easy storage [12,61].
Several studies have explored diverse applications of ChCl-based DESs, such as catalysis [50,62], nanotechnology [63], organic synthesis [64], separation technology [65], heavy oil upgrading [53,66], gas separation [67], and biomass conversion [68,69,70]. A wide range of compounds has been used to develop ChCl-based deep eutectic solvents for these applications. Figure 2 summarizes the distribution of publications on ChCl-based DESs in various fields.

Table 3.
Advantages and disadvantages of DESs over ILs [12,57,58,59,61,71,72,73,74,75,76,77].
Table 3.
Advantages and disadvantages of DESs over ILs [12,57,58,59,61,71,72,73,74,75,76,77].
| Advantages |
| Availability: The majority of DESs are readily available in large quantities, as they are primarily composed of easily accessible raw materials such as urea and common halide salt. |
| Synthesis: The synthesis of DESs is a straightforward and energy-efficient process, with the synthetic reaction demonstrating high atom efficiency. |
| Economic and Environmentally Friendly: DESs can be composed of inexpensive and biodegradable components (mixture of ChCl and U), making them more cost-effective and environmentally friendly compared to some ionic liquids. |
| Recyclability: DES solvents can be fully recycled in the extraction process without any contamination or loss. |
| Performance: In terms of their application, such as extraction capacity, most DESs demonstrate comparable or even superior performance when compared to conventional solvents and ILs. |
| Toxicity: The majority of DESs exhibit minimal toxicity, thereby reducing potential harm to both individuals and wildlife. |
| Disadvantages |
| Limited Stability: Some DESs may have lower thermal and chemical stability compared to ionic liquids, limiting their use in certain high-temperature or harsh chemical environments. |
| Viscosity: DESs may have higher viscosity compared to ionic liquids, which limit their mass transfer and diffusion properties, as well as their applicability in some processes that require low-viscosity solvents. |
| Limited Solubility: The solubility of certain compounds in DESs may be lower than in ionic liquids, limiting their effectiveness in certain applications. |
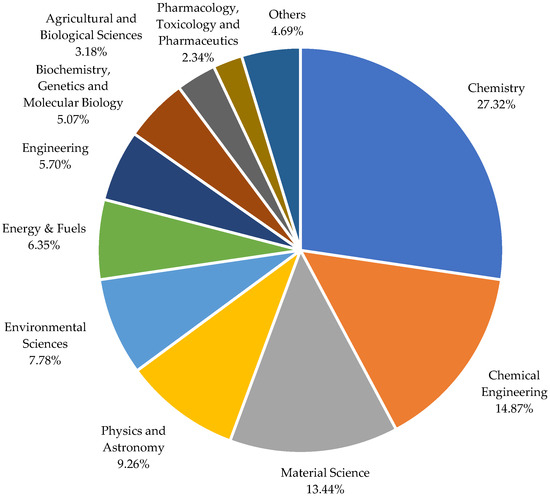
Figure 2.
Distribution of publications on choline chloride-based DESs in the various field of applications [78]. Keywords: (Choline AND Chloride-based AND deep AND eutectic AND solvents).
1.4. Binary Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents
Binary choline chloride-based DESs (BDESs) are formed by mixing two solid components with high melting points, resulting in liquids with significantly lower melting points. This approach, first introduced by [19], aims to provide cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternatives to ionic liquids (ILs). Researchers have demonstrated that a 1:2 molar mixture of ChCl and zinc chloride produces a DES with a melting point of 296–298 K [30]. This advancement has addressed the key limitations of ILs, including their volatility, flammability, toxicity, instability, and high production costs [79,80,81,82,83,84].
Further studies revealed that DESs can achieve tunable melting points and enhanced solubilization capabilities through specific hydrogen-bond interactions. For example, a 1:2 molar ratio of ChCl and U reduced the melting point to 285 K, which was significantly lower than that of the individual components ChCl (576 K) and U (407 K) [14]. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy confirmed that hydrogen bonding between U and chloride ions was responsible for this reduction [19].
Crespo et al. [85] investigated the phase behavior of ChCl-based DES systems and found that mixtures of fatty alcohols and fatty acids exhibited quasi-ideal behavior. However, deviations from ideality have been observed for mixtures of sugar alcohols and polycarboxylic acids [10]. These findings underscore the influence of specific hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA) and donor (HBD) components on the thermodynamic properties of DESs.
Martins et al. [10] estimated the fusion properties of ChCl because direct measurements are hindered by decomposition. The solubility curve data yielded a melting temperature of 579 ± 7 K and a melting enthalpy of 4300 ± 600 J/mol. Using these parameters, the phase diagram of the ChCl:U (1:2) system was modeled using the non-random two-liquid (NRTL) model, which accurately correlated with the experimental data (Figure 3). This study highlights the importance of considering the specific thermal properties when designing DES systems. Detailed on the method considered for the estimation of the NRTL parameters and deviations are reported in the Supplementary Information.
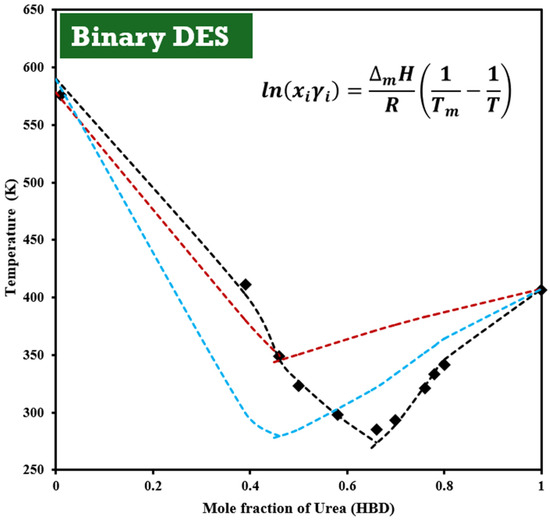
Figure 3.
Solid–liquid phase diagram of mixtures composed of ChCl + urea as a function of urea mole fraction. Experimental data [19] are represented by (■). Dashed lines indicate the phase equilibria calculated using Equation (2): red line for the ideal solution model, black line for the NRTL model with temperature-dependent parameters, and blue line for the NRTL model without temperature dependency. The ChCl:U (1:2) composition corresponds to the eutectic point of the deep eutectic solvent (DES) used in this study.
The preparation of ChCl-based DESs is both simple and efficient, typically involving heating and stirring the components into a homogeneous liquid form [7]. This solvent-free process eliminates the need for purification, making the DESs economically and environmentally advantageous. However, maintaining controlled temperatures between 323 and 373 K, as in esterification reactions, is essential for preventing degradation [86]. Alternative preparation methods, including mechanical mixing [87], freeze-drying, and solvent evaporation [45], offer flexibility based on the desired properties of the final product.
DESs exhibit unique physical and thermal properties. They are typically clear, viscous liquids with colors ranging from white to amber, and may become opaque solids at lower temperatures [7]. Thermal transitions, including glass transitions, are a notable feature, as demonstrated by the ChCl:U system, which undergoes glass transition during cooling at rates below 278 K/min.
Despite their advantages, BDESs have several limitations, including restricted solvent properties and reduced efficiency in certain applications. These challenges can be addressed by incorporating a third component into TDESs. By leveraging the synergistic interactions between these three components, TDESs offer enhanced solubility, extraction efficiency, and adaptability. They are also thermally and chemically stable, making them suitable for use under demanding conditions. Additionally, the use of sustainable materials in TDESs can further reduce their environmental impacts.
In summary, binary ChCl-based DESs represent a transformative step in solvent design, offering cost-effective and sustainable alternatives to conventional solvents and ILs. Their customizable properties and straightforward preparation methods make them versatile for a wide range of applications. However, the development of TDESs has addressed the inherent limitations of binary systems, unlocking their potential for robustness and broader applicability. The continuous exploration of DESs will further advance their role in innovative and green technologies.
2. Ternary Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents
Ternary deep eutectic solvents (TDESs) based on choline chloride (ChCl) have emerged as an advanced class of green solvents with remarkable tunability and enhanced performance compared to their binary counterparts. These solvents are synthesized by incorporating a third component, typically small organic molecules, such as alcohols, acids, or amino compounds, into a binary mixture of ChCl and HBD. The addition of this third component modifies the hydrogen-bonding network and the overall solvent environment, allowing fine-tuning of properties such as viscosity, polarity, thermal stability, and solvation power. The superior properties of TDESs over their binary counterparts can be attributed to the molecular-level structural and thermodynamic modifications induced by the third component [88]. Specifically, the introduction of an additional hydrogen bond donor disrupts the extensive hydrogen bonding network present in binary systems, thereby reducing the intermolecular cohesion and enhancing the molecular mobility. This leads to lower viscosity and improved fluidity [89]. Moreover, the third component often increases the free volume of the system and decreases the structural ordering, effectively suppressing the crystallinity and stabilizing the liquid phase at lower temperatures. From a thermodynamic perspective, the presence of a third species alters the entropy of mixing and Gibbs free energy profile, further facilitating the formation of a homogeneous eutectic liquid [90]. These effects collectively enhance the solvation capacity, improve conductivity, and widen the operational temperature range, offering better tunability and process compatibility in industrial applications. One of the defining advantages of TDESs is their ability to remain in the liquid state at room temperature, which is largely driven by strong intermolecular interactions that suppress crystallization and significantly lower the melting point of the mixture [5]. This feature is particularly important for applications requiring easy handling, pumping, and processing. In contrast, BDESs often produce solid or highly viscous mixtures even at eutectic compositions, which limits their practical use. By disrupting the crystalline packing and breaking the strong hydrogen bond networks in the binary system, the third component in TDES formulations enhances fluidity and facilitates better mass transfer and electrochemical behavior [89,91].
The physicochemical properties of TDESs can be precisely tailored by adjusting the molar ratio of the three components [92]. This composition-dependent behavior has enabled the rational design of TDESs for specific tasks, including extraction, catalysis, and electrochemical applications [5,93]. Reduced viscosity is one of the most frequently reported benefits of ternary mixtures, particularly when GL or EG is used as a third component. In some cases, thermal conductivity and conductivity were also improved, broadening the operational window for these solvents in the energy and separation processes. The preparation of TDESs typically involves mild heating and continuous stirring of the components until a homogeneous, transparent liquid is formed. This simplicity in synthesis, combined with the environmental benignity and biodegradability of the components, contributes to the green credentials of TDESs.
The first reported TDES was developed by Carriazo et al. [94] who synthesized a mixture of choline chloride, U, and resorcinol in a molar ratio of 1:2:3 at 333 K. The resulting TDES served as both a carbonaceous precursor and templating agent for the synthesis of hierarchical porous carbon monoliths. Their findings demonstrated that both choline chloride and urea actively participated in condensation reactions that yielded carbon materials with high surface areas, ranging from 455 to 612 m2/g, and favourable thermal transitions, including a low glass transition temperature and melting point of 341 K. This early work showcased the dual role of TDESs as both a solvent and functional material precursor, setting the stage for extensive investigations into their multifunctional properties. Subsequent studies have built on this foundation to explore various formulations and applications.
Kadhom et al. [95] synthesized two series of TDESs —choline chloride with urea and GL (ChCl:U:GL), and malonic acid and GL (ChCl:MA:GL)—and observed that changes in the molar ratio significantly influenced the density, viscosity, and thermal behavior of the mixtures. Their work highlighted how the choice and proportion of the third component can be leveraged to tune the balance between the fluidity and solvent strength. Similarly, Jablonsky et al. [96] examined TDESs composed of choline chloride, alcohol, and organic acids. They found that the inclusion of alcohols reduced both the viscosity and density, while organic acids tended to increase these parameters. This observation reflects the dual role of TDES components: not only do they contribute structurally to the eutectic behavior, but they also impart functional characteristics based on their chemical nature. Liu et al. [97] explored a ternary mixture of ChCl, GL, and L-arginine, which facilitated the conversion of D-glucosamine to deoxyfructosazine. Their study underlined the importance of complex hydrogen bonding interactions in stabilizing ternary mixtures and promoting specific chemical transformations.
A more recent study by Taysun et al. [5] introduced a TDES formulation comprising choline chloride, citric acid, and GL. The addition of GL significantly decreased the viscosity and improved the thermal conductivity, confirming that even small changes in the component identity and molar ratio can have profound effects on the solvent behavior. Collectively, these studies affirm the superior performance of TDESs over BDESs, particularly in enhancing processability, reaction efficiency, and selectivity. Their ability to dissolve a broader range of solutes, support catalytic cycles, and improve reaction kinetics make them attractive for numerous industrial and environmental applications.
TDESs demonstrate exceptional performance in high-impact applications, including CO2 capture, biomass delignification, heavy oil upgrading, and bioactive compound extraction, with quantitative data highlighting their advantages over BDESs. In carbon capture technologies, TDESs have demonstrated high CO2 absorption capacities, attributed to their enhanced polarity and ability to form transient chemical complexes with gas molecules. Sze et al. [98] reported that a ChCl:U:GL TDES (1:2:1) achieved a CO2 solubility of 0.25 mmol/g at 298 K and 101.3 kPa, a 20% improvement over the 0.15 mmol/g of a ChCl:U BDES (1:2), driven by reduced viscosity (200 mPa·s vs. 750 mPa·s at 298 K, [99]). Similarly, Ghazali et al. [100] noted a ChCl:U:Polyethyleneimine TDES captured 1.8 mmol/g of CO2, compared to 1.2 mmol/g for a ChCl:U BDES.
In the field of biomass processing, TDESs have been employed for efficient lignocellulosic fractionation, enabling the selective solubilization of lignin while preserving cellulose structures. This selectivity is crucial for the development of green biorefineries and sustainable materials. Ee et al. [101] achieved an 85% lignin removal yield from sugarcane bagasse in 6 h at 393 K using a ChCl:Guaiacol:Lactic Acid TDES (1:1:1), compared to 70% with a ChCl:U BDES, with Narayanan et al. [102] reporting 90% cellulose retention and 75% ethanol yield vs. 80% and 60% for a ChCl:Lactic Acid BDES.
In the petroleum industry, TDESs have shown potential in heavy oil upgrading by breaking down complex hydrocarbon matrices and improving flow properties. Their low interfacial tension and high thermal stability render them suitable for reservoir conditions. Mohsenzadeh et al. [103] found a ChCl:U:GL TDES increased oil recovery by 10%, yielding 65% of original oil in place at 423 K, compared to 55% for a ChCl:U BDES, due to lower interfacial tension. Additionally, TDESs have exhibited superior performance in extracting bioactive compounds from plant materials, often outperforming traditional organic solvents in terms of extraction efficiency, selectivity, and environmental safety [89,101,104,105,106]. This is particularly relevant in the pharmaceutical and food industries, where solvent toxicity and sustainability are critical considerations.
Despite these advantages, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize the potential of TDESs. One of the most pressing issues is the lack of predictive models capable of estimating TDES behavior based on molecular structure and composition. Unlike well-established solvent systems, TDES design remains largely empirical, with limited theoretical guidance. Furthermore, the stability over time and under varying operational conditions remains an area of concern. Phase separation, hydrolysis, and component degradation can occur, particularly in high-temperature or oxidative environments. Comprehensive toxicity and biodegradability assessments are also needed, particularly as new ternary components with less-established safety profiles are introduced. The scalability of TDES synthesis and recovery remains another hurdle for industrial adoption, necessitating the development of cost-effective, low-energy, recyclable processes.
TDESs represent a versatile and powerful class of green solvents with clear advantages over their binary counterparts. Through careful selection and tuning of a third component, a TDES can be designed with tailored properties to meet the demands of specific applications. Experimental studies have confirmed their superior performance in key areas, such as viscosity reduction, thermal and chemical stability, and solute compatibility. The scope of TDESs extends across carbon capture, biomass processing, oil recovery, green synthesis, and extraction technologies, underscoring their broad relevance to sustainable innovation. Nonetheless, future research should focus on developing predictive tools, understanding their long-term stability, and optimizing cost-effective production methods. As sustainability continues to drive innovation across scientific disciplines, TDESs are poised to play a central role in shaping the future of eco-friendly chemical processing and green solvent design.
Consequently, there has been a noticeable increase in the number of publications dedicated to TDESs and the reporting of relevant findings. Figure 4 provides a summarized overview of the existing literature on TDESs compared to their binary counterpart.
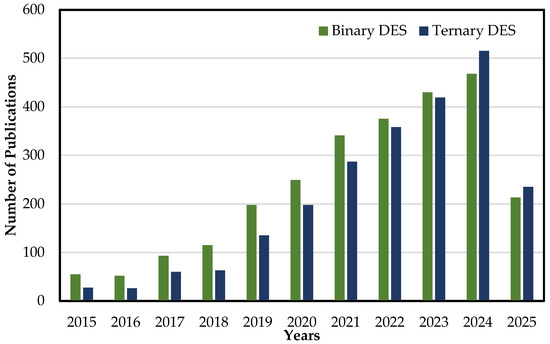
Figure 4.
Number of publications throughout 2015–2025 from Scopus database search for articles with topics of “Binary Choline Chloride-based deep eutectic solvents” and “Ternary Choline Chloride-based deep eutectic solvents” [78].
Looking at the period from 2015 to 2019, the number of studies available was limited to both DESs and TDESs. However, since 2020, interest in DESs has grown considerably, as indicated by the increase in publications on DESs. Despite the importance of this area of research, studies on the physicochemical properties of TDESs remain scarce compared to their binary counterparts. This specific aspect was examined in greater detail in this study.
3. The Role of DESs and TDESs in Modern Eco-Friendly Technologies
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their advanced variants, such as TDESs, have gained significant attention as sustainable alternatives to traditional solvents in various industrial and environmental applications. Typically formed by combining hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) and hydrogen bond acceptors (HBAs), DESs exhibit melting points lower than those of their individual components. This eutectic behavior imparts unique physicochemical properties, such as non-volatility, biodegradability, low toxicity, and cost-effectiveness, making them highly attractive for eco-friendly technologies [107,108].
DESs have been widely applied across numerous sectors, including rust and sulfur removal, biocatalysis, gasoline purification, alloy electrodeposition, gas separation, drug synthesis, stainless steel electropolishing, nanomaterial production, isomer and aromatic separation, sustainable bio-membrane fabrication, and enhanced oil recovery [53,62,63,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123]. These applications underscore the broad utility and flexibility of DESs in green technology.
The initial groundwork by Abbott et al. [19,35] demonstrated the industrial relevance of DESs. Current research continues to explore their potential with a particular focus on binary systems. However, the transition to ternary systems allows for further optimization. Key properties such as density, viscosity, thermal stability, pH, conductivity, refractive index, and interactions with water can be tailored by adjusting the types and ratios of HBDs and HBAs used [96]. The physicochemical behavior of DESs is also sensitive to environmental factors such as temperature and water content [17,68].
The synthesis and application of TDESs represents an important evolution in this field. Studies have shown that introducing a third component can enhance performance and functionality. For instance, Liu et al. [93] investigated TDESs based on imidazole ionic liquids, zinc halides, and amides, and observed instability at higher amide contents. Li and Row [123] developed six TDES formulations using HCl, choline chloride (ChCl), and formic acid, with potential applications in drug purification and clinical diagnostics. Despite these promising developments, a systematic framework for designing and optimizing TDESs remains underdeveloped [96].
TDESs offer an opportunity to overcome the limitations of BDESs by enabling the targeted modification of solvent properties. Comparative studies have demonstrated that TDESs can outperform BDESs in various applications. Their enhanced properties make them suitable for complex processes such as biomass conversion, CO2 capture, and heavy oil upgrading.
In materials science, DESs and TDESs play pivotal roles in the synthesis of polymers, nanomaterials, and metal deposits. They allow precise control over material characteristics, while supporting environmentally benign production processes [107,108]. In nanotechnology, DESs are used to synthesize metal and metal oxide nanoparticles, carbon-based materials, and functionalized adsorbents. These materials are integral to water treatment, pollutant removal, and other remediation technologies, owing to their low toxicity and high efficacy [108,124].
DESs have also been integrated into renewable-energy systems. As electrolytes in dye-sensitized solar cells and thermal energy storage devices, DESs enhance efficiency, thermal stability, and environmental performance [125,126]. Moreover, DES-based electrolytes in lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries exhibit superior ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability, contributing to the development of durable and sustainable energy-storage systems [127].
In industrial processing, DESs enable the eco-friendly electrodeposition of metals and semiconductors, offering improved nanostructure control and reduced toxicity [128]. In pharmaceuticals, DESs have emerged as green solvents for drug formulation and synthesis, promoting sustainable practices and reducing harmful emissions [129]. Additionally, DES-based materials are increasingly being used in environmental applications, such as wastewater treatment, where they enhance the adsorption and degradation of pollutants, such as dyes, pharmaceuticals, and heavy metals [124].
DESs have recently emerged as highly promising green absorbents for the separation and recovery of refrigeration gases, particularly fluorinated gases (F-gases) used in commercial refrigerant blends. For instance, DESs have been effectively employed to recover pentafluoroethane (R-125) and difluoromethane (R-32) from R-410A refrigerant mixtures, achieving high purity and significant recovery rates suitable for reuse. Unlike traditional methods such as distillation, which is energy-intensive and less effective for near-azeotropic blends, or adsorption, which may face limitations in selectivity and material costs, DES-based absorption offers tunable selectivity and lower energy requirements. This approach supports circular economy strategies by enabling efficient refrigerant recycling and reduces environmental impacts by 92–99% compared to conventional incineration or new production methods. As such, DES-based processes represent a sustainable and innovative solution for waste refrigerant management, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations [130,131,132].
The growing body of research on DESs and TDESs underscores their transformative potential in supporting environmentally conscious innovation across science and industry. Their tunable properties, low environmental impact, and economic viability render them ideal candidates for future technological applications. As sustainability becomes a global imperative, DESs and TDESs are poised to play a central role in the development of cleaner, safer, and more efficient industrial processes.
4. Physicochemical Properties of Binary and Ternary Choline Chloride-Based DESs
In this section, the main physicochemical properties of ternary ChCl-based deep eutectic solvents are presented and compared with their binary counterparts, including phase behavior, density, viscosity, pH, conductivity, and melting point.
A TDES typically consists of ChCl as the HBA, combined with two HBDs, which may include alcohols, acids, amides, or polyols. The composition of TDESs plays a critical role in determining their physicochemical behavior. For example, the inclusion of polyols such as GL or EG tends to reduce the viscosity and improve conductivity owing to the disruption of hydrogen bonding networks. Carboxylic acids (e.g., malonic or citric acid) generally lower the pH and increase acidity, whereas amides such as urea promote strong hydrogen bonding, which contributes to phase stability. The third component in TDES formulations often acts as a structural modulator, influencing the melting point depression, fluidity, and molecular packing. These structure–property relationships are outlined in Table 4 and further elaborated in the following subsections.

Table 4.
Comparison of physicochemical properties of BDES and TDES systems, highlighting tunability effects.
4.1. Phase Behaviour
The eutectic point of DESs represents the lowest melting point, which is influenced by the interaction between HBAs and HBDs in the binary mixture (Figure 3). This melting point deviated from that of the ideal theoretical mixture. TDESs exhibit a lower melting point than their binary forms, making it essential to understand the phase behavior and melting properties of each component. Factors such as the HBD choice, nature of the organic salts and anions, and molar concentration affect the melting point of the mixture.
Smith et al. [134] demonstrated that HBDs significantly affect melting-point depression by adding water to a ChCl:U (1:2) BDES to form a TDES, achieving the lowest melting point of 225 K at a water fraction of 0.67, beyond which the melting point increased (Figure 5). This mixture approached the limit for infinitely diluted urea and choline chloride in water. The binary ChCl:U (1:2) DES melted at 285 K [19].
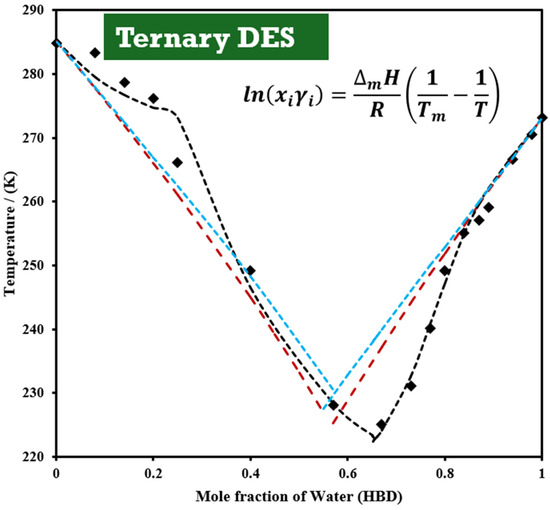
Figure 5.
Solid–liquid phase diagram of a TDES system composed of DES (ChCl:U at 1:2 molar ratio) and water, as a function of water mole fraction. Experimental data [134] are represented by (■). Dashed lines indicate the phase equilibria calculated using Equation (2): red line for the ideal solution model, black line for the NRTL model with temperature-dependent parameters, and blue line for the NRTL model without temperature dependency.
Figure 5 presents the SLE diagram for the ChCl:U:W system, considering the binary ChCl:U (1:2) system ( = 285.15 K, = 7.38 kJ/mol) and water ( = 273.15 K, = 6.01 kJ/mol) using Equation (2). Nonrandom two-liquid (NRTL) models, with and without temperature parameter dependency, accurately described the experimental data, with the temperature-dependent NRTL model being the most accurate.
Taysun et al. [5] studied a ChCl and citric acid BDES with melting points of 576 K and 429 K, respectively, achieving the lowest melting point of 303 K. However, this high melting point limits its application in biocatalysis because of enzyme denaturation at high temperatures. The introduction of GL lowered the melting point to 241 K by disrupting the hydrogen interactions, thereby enhancing the functionality of the TDES for its intended use.
The melting point of TDESs is significantly lower than that of their binary counterpart, as shown in Table 4, making TDESs more suitable for low-temperature processes such as biocatalysis and electroplating, which benefit from lower temperatures. The addition of a third component to the BDES forms a liquid eutectic mixture at room temperature, reducing intermolecular interactions and increasing DES fluidity. The lowest melting point among the TDES was 225 K, achieved by ChCl:U:W (1:2:6) [134] and ChCl:Gl:W (1:0.85:0.76) [99], with water acting as a hydrogen bond breaker, disrupting the ionic network, and significantly lowering the melting point.
4.2. Density
The density of DESs, correlated with temperature and pressure, is crucial for studying liquid–liquid equilibrium systems, process equipment design, mass transfer phenomena, equation of state development, and predictive models, influencing other thermodynamic parameters such as the thermal expansion coefficient, isothermal compressibility coefficient, speed of sound, and free volume [140,145]. Most DESs have higher densities than water at 298 K, with metal-salt-based DESs ranging from 1.3 to 1.6 g/cm3 [30]. Density is affected by molecular weight, intermolecular forces, molar ratio, choice of HBDs, and temperature [30,87,90,146,147,148]. The high density of DESs is attributed to the hydrogen bonds between the components, resulting in a more compact structure than that of water [30,149]. The precise mechanism is under investigation but is influenced by the packing and molecular arrangement. The density decreases at higher temperatures owing to the increased kinetic energy and molecular movement, which increases the molar volume [150,151]. Temperature-dependent density parameters are often determined using linear functions and accepted models, as shown in Equation [151,152]:
where a and b are fitting parameter coefficients. Some studies have used the following second-order polynomial equation for empirical density data:
Similar to ionic liquids, DESs contain voids and empty spaces that affect their density [35,140]. The density can be related to the amount of free space within the liquid, expressed as [%] [153]
where represents the molar volume [cm3 mol−1] and is the actual volume calculated from the molecular volume of the individual components.
Hydrophobic DESs have lower densities than water [15], which are influenced by the HBA-to-HBD molar ratio. Abbott et al. [154] found that the addition of choline chloride to GL reduced DES density owing to the increased free volume. Higher temperatures also decrease the DES density by enhancing the ionic mobility and free volume. According to hole theory, thermal-energy-driven local density fluctuations create extra space within a liquid DES system [14,109,154,155].
Table 4 summarizes the experimental density data of the TDES compared with their binary counterparts, showing the density variations with the composition. For example, ChCl:GL maintains a consistent density of 1.16–1.18 g/cm3 in both the binary and ternary forms. However, ChCl:MAL’s density decreases from 1.25 g/cm3 in the binary form to 1.18 g/cm3 in the ternary form with propanediol (PRP) addition. The lowest TDES density is 1.11 g/cm3 in ChCl:MAL:BTD, which includes butanediol, a bulky and flexible component.
The density difference between the BDES (ChCl:CA) and TDES (ChCl:CA:GL) was due to the higher molecular weight and density of GL than citric acid, increasing the TDES density to 1.25 g/cm3 from 1.22 g/cm3. Glycerol disrupts the hydrogen-bonding network, altering the molecular interactions and resulting in a denser system.
A comparison of the binary and TDES compositions shows that the third component affects the overall density by altering the molecular packing and intermolecular forces. Factors influencing DES density changes include component molar ratios, molecular interactions, and environmental conditions such as temperature and pressure. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting and controlling DES properties, highlighting the versatility of ternary systems for adjusting density and other properties for specific applications.
4.3. Viscosity
The use of DESs as solvents is a key advancement and offers suitable media for various physical and chemical processes. The efficacy of DESs is largely contingent on their viscosity, which significantly influences equipment design, activation energy, and mass transfer [140]. DESs generally exhibit higher viscosities at room temperature than molecular solvents because of their ion size relative to liquid voids, which affects the free volume and void size for solvent molecule movement [156].
Viscosity, such as density, depends on temperature; increasing the temperature reduces DES viscosity by weakening the molecular interactions and lowering the internal resistance [157]. The temperature effect on DES viscosity is typically modeled using nonlinear models, such as the Arrhenius model [151,158]:
where En is the activation energy and is the pre-exponential factor. Alternative models include the Vogel–Fulcher–Tammann (VFT) model, Williams–Landel–Ferry (WLF) model, and the Litovitz Equation [159].
where A, B, and To are fitting parameters. The Arrhenius equation is important because it relates viscosity to the reciprocal value of temperature, thereby determining the activation energy, En.
Ionic fluids, composed of positively charged metal ions and negatively charged non-metal ions, have viscosities that are affected by ion size and electrostatic force. Molten salts, a type of ionic fluid, have lower viscosities at high temperatures because of the smaller ion-filling spaces between larger ions. Conversely, at low temperatures, the increased ion size and reduced space increase viscosity, complicating industrial processes. Molten salts exhibit extremely high viscosities, exceeding those of water and honey. Researchers are currently investigating viscosity reduction methods for molten salts, such as the addition of other liquids or the use of electromagnetic fields.
Increasing the temperature can reduce DES viscosity during use [8,96], enhance fluidity, and lower flow resistance. This temperature-dependent viscosity decrease aligns with the Hole Theory [138], which posits that higher temperatures provide more energy, speed up molecular movement, and create larger gaps, thus reducing the viscosity [140,147,156]. Understanding this relationship is vital for optimizing DESs as solvents in practical applications. Figure 6 shows the effect of temperature on the viscosity of TDESs and their binary counterparts.
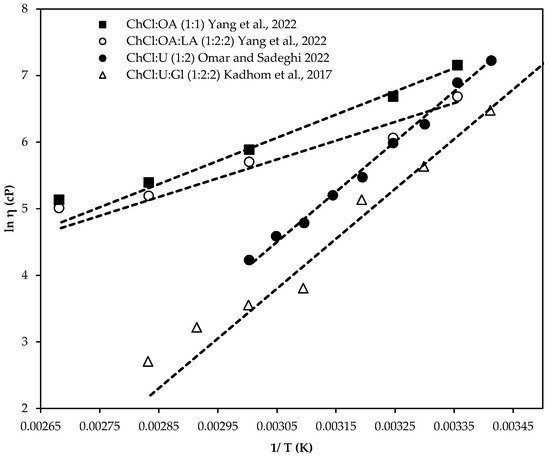
Figure 6.
Effect of temperature on the viscosity of ternary ChCl-based DESs with their corresponding binary counterpart: Symbol represent experimental data (ChCl:U (1:2) [109], ChCl:U:GL (1:2:2) [95], ChCl:OA (1:1) [51], ChCl:OA:LA (1:2:2) [51]) Dash lines represent the theoretical model calculated with Equation (6).
Figure 6 indicates that TDESs have lower viscosity than their binary counterparts due to complex molecular interactions and more efficient molecular packing, which reduces the flow resistance. The third component disrupted the hydrogen-bonding network in the BDESs, further decreasing its viscosity.
Table 4 presents the viscosity values of some ternary ChCl-based DESs compared with their binary counterparts from the literature, showing that TDESs have significantly lower viscosity, enhancing solvating qualities and mass transfer rates.
Jangir et al. [136] found that a TDES composed of ChCl:MAL:BTD (1:1:1) had a viscosity of 215.32 cP, compared to 510.55 cP for binary ChCl:MAL (1:1), which was attributed to the decrease in hydrogen bond interactions. Jablonsky et al. [96] reported a viscosity of 138.9 cP for ChCl:U:LA (1:2:3) at 303 K, while the binary ChCl:LA (1:2) had 220.96 cP, as noted by Alcalde et al. [139]. Dai et al. [160] observed a viscosity of 280.8 cP for the ChCl:FRU:W (5:2:5) system at 313 K, whereas Hayyan et al. [23] reported a viscosity of 11312 cP for the binary ChCl:FRU (2:1) system. The addition of water as a third component reduced viscosity by disrupting the dense hydrogen-bonding network and forming new hydrogen bonds with choline chloride and fructose. TDESs exhibit much lower viscosity than their binary counterparts, influenced by hydrogen bond interactions, van der Waals forces, and electrostatic interactions.
4.4. Potential of Hydrogen (pH)
The pH, which indicates the acidity of the solution, is of utmost importance in the development of DESs. DESs can be broadly classified as systems formed by a combination of Lewis or Brønsted acids and bases, highlighting the relevance of the pH in these systems. This is determined by the relative acidity of the mixed anionic and cationic species. The pH of a solution influences the selection of piping materials, owing to concerns regarding the kinetics of chemical reactions and corrosion. Therefore, it is important to carefully consider pH when developing DESs for industrial applications [7,109].
To investigate the pH dependence of DES compositions, Hayyan et al. [23] conducted a study focusing on mixtures of ChCl (HBA) and fructose (HBD), using varying molar ratios. Their results revealed a clear correlation between the decrease in HBA content and reduction in pH value. Jablonsky et al. [96] further investigated this by preparing a series of TDESs based on ChCl as HBA, accompanied by an acid as HBD. ChCl:MA:PRP (molar ratio 1:1:3, pH 2.21), ChCl:EG:LA (molar ratio 1:2:1, pH 2.22), ChCl:U:LA (molar ratio 1:2:3, pH 2.25), and ChCl:ACE:LA (molar ratio 1:2:3, pH 2.32) exhibited decreases in pH values associated with their specific compositions.
The pH of DESs can be adjusted by changing the temperature, particularly in ChCl-based DESs. Skulcova et al. [142] investigated the effect of temperature on the pH of the DESs. They discovered that the pH decrease, which is influenced by temperature-dependent HBDs, such as DES-based alcohols, gradually increased with increasing temperature. In contrast, DES-based carboxylic acids exhibit a more abrupt change in pH with increasing temperature [109].
Overall, these findings highlight the significance of understanding the acidity and basicity of DESs for optimizing their performance in various industrial applications. The ability to adjust pH by manipulating the temperature is particularly useful for controlling and fine-tuning the properties of DESs for specific purposes.
Table 4 summarizes the pH values of the TDESs in comparison with those of their corresponding BDESs. It can be observed that the pH of some TDESs is lower than that of their binary counterparts because of the strong interactions between HBAs and HBDs. However, some TDES systems may exhibit a higher pH than that of binary systems. Skulcova et al. [142] explained that EG and GL contain acidic hydrogen in their structures, resulting in pH values below 7. Additionally, an increase in temperature can affect the pH of the alcohol-based DESs. The pH of TDESs makes them suitable for certain applications, such as solvent extraction, chemical processes, and biological processes that do not involve an acidic medium.
4.5. Conductivity
Conductivity is crucial in various industries including petroleum and semiconductors. Most DESs have poor conductivity owing to their high viscosity, indicating an inverse relationship between the conductivity and viscosity [140]. Viscous fluids hinder ionic movement and negatively impact conductivity. Solvent consistency affects ionic motion, and a higher salt ratio in the DES improves conductivity. However, ion mobility is limited by ion availability. Factors such as the molar ratio of HBDs to HBAs, cation alkyl chain length, viscosity, and temperature influence DES conductivity [109]. Low ion mobility, caused by a large ion size or ion pairs, results in low conductivity [12]. Increased temperatures reduce viscosity and enhance conductivity by disrupting hydrogen-bond networks and increasing ionic mobility [109]. Table 4 displays the conductivities of TDESs compared with their binary counterparts. The third component affects the ionic conductivity owing to hydrogen bond interactions. The low viscosity of TDESs allows for free ionic movement, resulting in high conductivity. However, some TDESs have lower conductivity than binary counterparts, such as ChCl:MAL:BTD 1:1:1, with 1.40 mS/cm conductivity, due to longer diol molecules causing slower solvent dynamics.
Table 4 provides a summary of the key physicochemical properties of the binary and TDES systems, highlighting the trends and improvements observed in the ternary systems.
4.6. Effect of Water on the Physicochemical Properties of TDESs
Certain DESs and their constituents are hygroscopic and absorb water because of their prevalence [87,161,162]. Water, often seen as a contaminant, has been added in studies to adjust the solvent properties for specific uses and to enhance performance. However, water affects the physicochemical properties and stability of DESs, leading to inconsistencies in the literature owing to the varying preparation conditions [163]. Therefore, it is crucial to examine the effects of water on eutectic systems.
This section explores the effects of water on the physicochemical properties of TDESs (melting point, density, viscosity, and conductivity), based on previous studies. Some researchers researched low natural water content in DESs, while others examined a full range. For example, ChCl:U DESs absorbed up to 20 wt.% water after three weeks of atmospheric exposure [164]. Smith et al. [134] observed a linear decrease in the melting point from 285 K for binary ChCl:U (1:2) to 225 K for ChCl:U:W (1:2:6) owing to water. Rashid et al. [99] observed a similar decrease in temperature, from 290 K for binary ChCl:Gl (1:2) [133] to 240 K for ChCl:Gl:W (1:1.7:1.52). Water-induced melting point reduction is significant for DES applications.
Studies agree that viscosity and conductivity are highly sensitive to water in DESs, unlike density. Dai et al. [45] noted a slight density decrease in ChCl:FRU:W (5:2:5) to 1.21 g/cm3 compared to binary ChCl:FRU (2:1) at 1.28 g/cm3, due to water increasing free volume in DESs. Du et al. [162] showed that viscosity decreased 13-fold and conductivity increased 10-fold in 6 wt.% water in binary ChCl:U (1:2). Dai et al. [45] also found that water addition significantly reduced viscosity in ChCl:MA:W (1:1:2) to 445.9 cP and ChCl:FRU:W (5:2:5) to 280.8 cP, compared to their binary counterparts ChCl:MA (1:1) at 1100 cP [165] and ChCl:FRU (2:1) at 11312 cP [23]. In natural DESs, the presence of water significantly decreases viscosity and linearly reduces density, while conductivity initially increases with water content, peaking at 60–80 wt.% water, and then decreasing [160]. This initial conductivity increase was due to ionic dissociation, followed by a decrease as the electrolytes were diluted at higher water content. Choline chloride-based DESs with different glycols as hydrogen bond donors exhibited significantly reduced viscosity and increased conductivity as the water content increased, peaking at 60 wt.% water before declining [30].
4.7. Tunability and Design Flexibility of TDESs
One of the most compelling advantages of TDESs over binary systems is their enhanced tunability. By introducing a third component typically an organic acid, alcohol, polyol, amino compound, or even water, researchers can finely adjust multiple physicochemical properties simultaneously. This flexibility enables the formulation of task-specific solvents that are tailored to diverse industrial needs.
The inclusion of the third component directly impacts molecular interactions, particularly hydrogen bonding, free volume, and viscosity, allowing for a broad range of composition–property optimizations. For example, the addition of glycerol to a ChCl:CA binary system reduces the melting point from 303 to 241 K, thereby improving fluidity and expanding the temperature range for biocatalytic applications [5]. Similarly, incorporating butanediol into ChCl:MAL:BTD (1:1:1) results in a dramatic viscosity reduction from 510.55 cP to 215.32 cP—an improvement of over 57% [136].
The capacity to modulate the pH is also notable in TDES systems. For instance, formulations such as ChCl:MA:PRP (1:1:3) and ChCl:U:LA (1:2:3) achieve mildly acidic pH values in the range of 2.2 to 2.3, which are beneficial for catalysis and biomass solubilization [96]. Conductivity can likewise be enhanced through the inclusion of small polar molecules or water, simultaneously facilitating ionic mobility and reducing viscosity, as observed in the ChCl:FRU:W (5:2:5) system [45]. Table 4 shows a comparative summary of the key physicochemical properties of BDESs and TDESs, highlighting the tunability effects achieved through the introduction of a third component. The data illustrate how ternary formulations allow targeted manipulation of the melting point, density, viscosity, pH, and conductivity, enabling solvent systems to be optimized for specific process conditions and applications. The observed improvements were based on the values reported in the literature for representative systems.
Moreover, TDESs enable multi-objective optimization, where trade-offs between properties, such as reducing viscosity while maintaining thermal stability, can be balanced through careful compositional design. This characteristic contrasts with binary DESs, where the available tuning window is relatively limited.
Application-driven design is another significant implication of TDES tunability. In CO2 capture, acidic third components can enhance the sorption affinity, whereas polyols promote fluidity and mass transfer. In biomass processing, systems with selective solubilization power (e.g., ChCl:U:LA) are tailored for lignin extraction without degrading cellulose. The ability to align molecular design with functional requirements underscores the versatility of TDESs as next-generation green solvents.
As empirical data continue to accumulate, these composition property relationships form the basis for developing predictive tools such as QSPR models or machine-learning algorithms that could guide rational TDES formulation in the future.
5. Application of Ternary Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents
Ternary ChCl-based deep eutectic solvents have recently been the subject of much research interest owing to their unique physical and chemical characteristics. The following section presents some of the potential and promising applications of TDESs that have been recently investigated.
5.1. Biomass
Ternary ChCl-based deep eutectic solvents (TDESs) have been explored for biomass conversion as a renewable resource for producing valuable chemicals and fuels. Traditional methods require harsh conditions and generate considerable waste, whereas TDESs are promising alternatives owing to their unique properties. TDESs are complex hydrophobic hydrocarbon polymers that are insoluble in most solvents and have been widely applied in lignin extraction [166]. DESs have gained attention for their ability to selectively dissolve lignin while preserving the cellulose fibers. TDESs can effectively break down and extract lignin from biomass. Jablonsky et al. [96] prepared novel DESs, tested their delignification efficiency on unbleached pulp, and found that the addition of a third component to classical DESs improved their efficiency. Majovà et al. [167] also used TDESs to delignify unbleached pulp and achieved a lignin removal efficiency of 28.06% owing to the improved solvent penetration. Chourasia et al. [168] demonstrated that the use of water as a co-solvent in the microwave-assisted delignification of sugarcane bagasse with TDESs improved the efficiency, achieving 84% delignification and 99% enzyme digestibility in 30 min at 373 K. Yang et al. [51] found that TDES pretreatment of bagasse at low temperatures effectively disrupted cellulose and lignin structures, enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis, and potentially improved biofuel production efficiency. Duan et al. [169] studied TDES pretreatment of Eucommia ulmoides seed shells, achieving hemicellulose and lignin removal rates of 79.7% and 65.6%, respectively, and efficiently separating high-quality gutta-percha, value-added lignin, and monosaccharides.
TDESs have various applications in biomass conversion, including phenolic compound extraction. Duan et al. [170] optimized the extraction of four phenolic acids from Artemisia argyi leaves using a TDES of ChCl:MAL:U at a 2:1:2 ratio, yielding 22.80 mg/g, which was slightly higher than that of conventional solvents (22.41 mg/g). The hydroxyl groups of TDESs enhance the stability through more hydrogen bonds. Rashid et al. [99] explored the use of TDESs (ChCl:GL:W at a ratio of 1:3.4:3) for enzymatic hydrolysis, which significantly activated porcine pancreatic lipase. TDESs also improve biomass pretreatment and enhance conversion efficiency and yield. Table 5 summarizes TDES biomass conversion applications.

Table 5.
Applications of ternary choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents (TDESs).
The application of TDESs has also been extended to biomass deconstruction. Systems such as ChCl/EG/p-toluenesulfonic acid have been developed for rapid and efficient pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. These TDESs enable high removal rates of xylan and lignin, even at high solids loadings and low enzyme dosages, facilitating the production of concentrated sugar hydrolysates for biofuel and biochemical production. The effectiveness of these systems is attributed to their ability to disrupt the complex structure of the biomass, making cellulose more accessible for enzymatic hydrolysis [177].
Despite their potential to dissolve lignocellulosic materials, TDESs have certain limitations. High viscosity hampers mass transfer and increases the mixing energy, especially in large-scale processes. TDESs may have reduced thermal stability compared with binary systems because of component interactions at high temperatures. Recyclability is challenging because selective component loss or degradation reduces solvent effectiveness [102,178,179]. Their hygroscopic nature can alter viscosity and solvation, affecting biomass fractionation performance.
Additional limitations include selective solubility, potentially leading to incomplete biomass deconstruction, and environmental and health concerns, as some hydrogen bond donors may be toxic. Economic feasibility is an issue because of the cost of specialized components, which limits scalability. Design flexibility is constrained by the complexity of balancing the solvent strength, selectivity, and stability for specific applications. Further advancements in the solvent design, process optimization, and recovery strategies are required to address these challenges.
5.2. CO2 Capture
Carbon Capture, Usage, and Storage (CCUS) is a state-of-the-art technology for capturing and utilizing significant volumes of CO2 from various industrial processes, which makes CO2-focused research essential for climate change studies. TDESs have shown great potential for CO2 capture because of their high CO2 solubility [180]. However, their high viscosities hinder their practical application. Studies have indicated that mixing DESs with conventional solvents, such as water or PEG200, reduces viscosity [180]. Researchers have further enhanced CO2 capture by developing TDESs based on choline chloride and incorporating components, such as carboxylic acids, alcohols, and amides. These TDESs exhibit lower viscosities and higher CO2 capture capacities than those of BDESs, with CO2 capture involving hydrogen bond formation between the CO2 and DES components [67,181,182]. The optimization of TDESs for CO2 capture remains an active research area.
Abbott et al. [146] demonstrated that the addition of GL to choline chloride (ChCl) DESs significantly decreases their viscosity, facilitating their use. Maugeri and Pablo [183] found that adding GL to a ChCl-sugar based polyol DES resulted in a low-viscosity, low-melting point solution, exemplified by the viscosity reduction in ChCl:glucose:GL (1:0.5:0.5) at 323.15 K to 0.93 Pa s from 34.4 Pa s in ChCl:glucose (1:1). Sze et al. [98] explored a TDES for CO2 capture using choline chloride, GL, and superbases (DBU, DBN, and TBD). The ChCl:Gly:DBN system with a 1:2:6 molar ratio showed the best performance, capturing 103 mg of CO2 per gram of sorbent and being easily regenerable, simple to prepare, stable, and exhibiting high CO2 capture capacity. Excessive non-Newtonian viscosities were observed, potentially limiting the mass transfer rates. Hsu et al. [52] examined the CO2 solubility in a binary aqueous solution of a line (50, 60, and 70 wt.%) and its ternary solutions with monoethanolamine (MEA) and found that MEA increased the CO2 absorption capacity. Chemat et al. [171] modified deep eutectic solvents (DESs) by adding L-arginine to a choline chloride:GL DES to improve CO2 solubility. The Henry constant for ChCl:GL (1:2) decreased from 1.1835 to 0.4435 MPa with L-arginine (1:2:0.2), indicating enhanced CO2 solubility. Ghazali et al. [100] created a solid composite adsorbent with mesoporous silica gel and TDESs (choline chloride, urea, and polyethyleneimine) in a 1:2:1 molar ratio via wet impregnation. The 25% ChCl:U:PEI-loaded adsorbent showed a 60% higher CO2 adsorption capacity than the initial SG200 sample, suggesting its efficacy for CO2 capture. Ishaq et al. [184] studied the effects of superbases on DES-based membrane systems by synthesizing binary and ternary ChCl-based DESs. The TDES demonstrated significant permeability and selectivity for CO2, CH4, and N2, which was attributed to the basicity and rapid reaction kinetics of superbase/DBU. TDESs have the potential for CO2 capture because of their high CO2 affinity; however, they face limitations, such as high viscosity, which affects mass transfer rates and thermal stability. Ongoing research is seeking to address these issues and enhance the viability of DESs for CO2 capture applications.
5.3. Heavy Oil Upgrade
Heavy oil has lower mobility than conventional oil because of its higher specific gravity, density, and viscosity, with viscosity starting at 100 cP and API gravity below 20° [185]. This type of petroleum, which is rich in sulfur, results from the natural removal of light fractions [186]. Heavy oil inherently includes heavy fractions, such as asphaltenes, heavy metals, sulfur, and nitrogen. Upgrading heavy oil is necessary to enhance its quality and reduce its environmental impact. TDESs are a promising, low-cost, and environmentally friendly method for selective extraction and upgrading.
Sulfur compounds, which are harmful to the environment and human health, are produced during the combustion of fossil fuels, leading to sulfur oxides that cause acid rain, agricultural damage, and health issues such as cancer and respiratory diseases. These compounds present technical challenges in petroleum refining [187]. Desulfurization, traditionally achieved through hydrodesulfurization (HDS), involves high-cost catalysts, reduces gasoline octane grade, and emits toxic H2S gas [188,189]. TDESs can selectively remove organosulfur compounds for deep desulfurization [14,190].
Wei et al. [111] studied a TDES for heavy oil desulfurization and found that a boric acid-based TDES, specifically ChCl/BA/PEG, achieved a 99.2% desulfurization efficiency at 333 K in 2 h with a solvent-to-oil molar ratio of 6. PEG enhances the efficiency through improved extraction capability and hydrogen bonding, whereas t-butyl acetate (TBAC) improves the adsorption of longer carbon chains [187]. ChCl/BA increased sulfur removal from 3.2% (EDS) to 34.0% (ODS) and from 23.2% (EDS) to 27.4% (ODS). The catalytic action of BA enhanced sulfur removal, whereas an increase in PEG content reduced it. DESs with a long carbon-chain HBA had high EDS efficacy but insufficient catalytic activity. The acidity of the DESs is positively correlated with the sulfur compound extraction efficacy of the ODS method. ChCl/PEG/BA with a molar ratio of 1:1:1.5 demonstrated 96.4% efficiency.
In heavy-oil technology, DESs are also used for enhanced oil recovery, with most studies focusing on BDESs. Shuwa et al. [53] reported that a Choline Chloride/EG DES system improved the oil recovery by up to 68% with increasing reservoir temperature. Another study by Shuwa et al. [191] used a molybdenum oxide catalyst dissolved in a choline chloride-based DES for heavy crude oil upgrading, showing a 43% reduction in oil viscosity, a 2.5° increase in API gravity, and a 32 wt.% reduction in sulfur.
Mohsenzadeh et al. [66] used a ChCl-based DES to increase the interfacial tension between oil and brine, resulting in 14–30% recovery of residual heavy oil. Mohsenzadeh et al. [103] found that DESs followed by steam injection improved pure steam recovery by 12%. Sanati et al. [192] compared ionic liquids and DESs in core flooding experiments, with recoveries of 63.1% and 54.7%, respectively. BDESs have proven effective for heavy oil upgrading, dissolving and extracting asphaltenes, and high-molecular-weight components, thus improving the oil quality by reducing the viscosity, improving the pour point, and increasing the H/C ratio. However, further research is needed to address challenges, such as stability and compatibility with specific heavy oils.
TDESs are projected to be effective for heavy oil upgrading because of their unique properties such as reduced heavy oil viscosity and high solubility in asphaltenes. However, only a few studies have been conducted, indicating a gap that requires further investigation. Beyond heavy oil upgrading, TDESs have demonstrated versatility across numerous other applications, as summarized in Table 5. This highlights their potential to address diverse industrial and environmental challenges.
5.4. Refrigeration Gas Separation
TDESs, formed by combining a ChCl as HBA with two HBDs like EG, GL, or p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA), have emerged as promising green solvents for the separation of refrigeration gases [132]. These include fluorinated gases (F-gases) found in commercial blends like R-410A, as well as other refrigerants such as ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2). TDESs are attractive alternatives to conventional methods like distillation and adsorption due to their tunable selectivity, low toxicity, biodegradability, and reduced energy requirements [193].
The key to TDES performance lies in their ability to form extensive hydrogen-bonding networks, enabling selective absorption of target gases. For instance, ChCl:EG:PTSA (1:3:1) demonstrates high selectivity for R-32 over R-125 in R-410A mixtures, achieving recovery rates above 90% with high purity, as shown in Aspen Plus simulations [175]. Similarly, systems like 4-amino-4H-1,2,4-triazole:resorcinol:GL (1:5:4) exhibit excellent ammonia uptake (0.193 g NH3/g TDES at 313.15 K and 0.1 MPa), outperforming binary DESs due to enhanced molecular interactions [131,194].
Compared to traditional separation processes, TDES-based absorption offers notable advantages. Distillation, especially for near-azeotropic blends like R-410A (R-32: −51.7 °C; R-125: −48.1 °C), is highly energy-intensive (1–2 MJ/kg), while adsorption using materials like zeolites or MOFs often struggles with selectivity and incurs high costs [195,196]. In contrast, TDES absorption can operate at ambient conditions, reducing energy consumption by 50–70% [197]. Additionally, TDESs are cost-effective (e.g., ChCl ~$1–2/kg) and biodegradable, providing up to 99% lower environmental impact compared to incineration or fresh F-gas production [175]. Hybrid systems combining TDESs with distillation can further enhance efficiency by using TDESs for pre-separation, thereby reducing the thermal load on distillation columns [198].
In extractive distillation and liquid–liquid extraction, TDESs have proven effective in breaking azeotropic mixtures, such as methanol/dimethyl carbonate, analogous to separating hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) blends like R-410A [199,200]. Furthermore, TDESs immobilized in supported liquid membranes (SLMs) have shown promise in continuous gas separation processes (e.g., CO2/N2), with systems like ChCl:1,2-propanediol:water offering improved permeability due to reduced viscosity [176].
Despite their advantages, several challenges must be addressed for industrial application. High viscosity in some TDES formulations (e.g., ChCl:levulinic acid) can hinder mass transfer, although this can be mitigated by adding water or optimizing component ratios. Moreover, limited experimental data on high-pressure solubility and selectivity for gases like R-134a and R-410A hampers comprehensive performance evaluation. Stability issues, such as potential esterification in carboxylic acid-based DESs, may also affect long-term reusability. While molecular simulations (e.g., COSMO-RS, COSMO-SAC) support the design of DESs for specific gases, further refinement is needed to align predictions with experimental results [201].
TDESs represent a sustainable, low-cost, and efficient alternative for refrigeration gas separation, supporting circular economy goals through enhanced refrigerant recovery. Their tunable physicochemical properties, environmental compatibility, and potential for regeneration make them strong candidates to replace traditional solvents and ionic liquids. Future research should focus on experimental validation under industrial conditions, high-pressure behavior, viscosity reduction strategies, and the development of bio-based formulations to ensure scalability and long-term viability.
5.5. Solvent/Catalyst in Organic Reactions
TDESs are gaining significant attention as green, efficient alternatives to traditional organic solvents and catalysts in organic reactions. These solvents are typically formed by mixing ChCl with two hydrogen bond donors, resulting in a liquid with unique physicochemical properties such as strong hydrogen bonding, tunable viscosity, and high thermal stability. The ability to adjust the composition of these solvents allows the optimization of their properties for specific reactions, making them highly versatile [134,202].
One of the most notable applications of TDESs is in the field of organic synthesis, where they serve both as solvents and as catalysts. For example, in quaternization reactions such as the Menshutkin reaction [203], these TDESs have replaced volatile organic solvents such as acetone and dichloromethane. When ChCl is combined with hydrogen bond donors, such as GL, oxalic acid, or levulinic acid, the resulting TDES provides a safer and more sustainable reaction environment. These systems have demonstrated high efficiency, particularly under microwave-assisted conditions, where yields can approach quantitative levels. The simplicity of preparation, low cost, and reusability of these DESs further enhance their appeal for large-scale industrial applications, aligning with the principles of green chemistry [204].
TDESs also exhibited remarkable catalytic activity and selectivity in dehydration reactions. For instance, a TDES composed of ChCl, GL, and boric acid was shown to promote the selective dehydration of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine, yielding different nitrogen-containing furan derivatives depending on the TDES composition. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) studies have revealed that strong interactions between the TDES components and the substrate facilitate the activation and transformation of the reactant, leading to high selectivity and yield. The supramolecular structure of these solvents, as evidenced by NMR spectroscopy, is believed to be responsible for their unique catalytic behavior [172,205].
In addition to their role in organic synthesis, TDESs have proven to be highly effective for the extraction of bioactive compounds and the processing of biomass. For example, a TDES made from ChCl, guaiacol, and lactic acid has been used to extract polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum with high efficiency and stability. The extraction process benefits from the strong hydrogen bonding and high binding energy between TDESs and glucose, resulting in a maximal extraction yield and excellent cyclic stability. This highlights the potential of TDESs in natural product extraction and biorefinery applications, where traditional solvents may be less effective or environmentally harmful [173]. ChCl-based DESs also serve as dual-solvent-catalyst systems in one-pot and multicomponent organic syntheses. For example, a DES based on ChCl and malonic acid has been used as both the reaction medium and the catalyst for the synthesis of functionalized pyrroles via a four-component reaction. This approach not only simplifies the reaction setup but also allows for recycling and reuse of the DES without loss of efficiency, further enhancing the sustainability of the process [174].
The unique properties of TDESs are largely due to their supramolecular structures and strong hydrogen-bonding networks. These features enhance substrate solubility, stabilize the reaction intermediates, and promote catalytic activity. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and computational studies have shown that water and other hydrogen bond donors are integrated into the TDES structure, which can modulate the reactivity and selectivity of the system. The addition of components such as l-arginine can further increase the thermal stability, molar heat capacity, and glass transition temperature of TDESs, while also affecting their density, viscosity, and refractive index [171,205].
Moreover, TDESs have been explored for oxidative desulfurization processes, where they demonstrate high activity and stability at room temperature. For example, a TDES composed of ChCl, benzene sulfonic acid, and EG achieved the complete desulfurization of various sulfides within two hours, demonstrating their potential for environmental applications [206].
In summary, TDESs offer a sustainable, efficient, and versatile platform for a wide range of organic reactions and extraction processes. Their tunable properties, catalytic activities, and environmental benefits make them promising alternatives to conventional solvents and catalysts. Continued research into their structure-property relationships and mechanistic behavior is expected to further expand their applications in green chemistry and industrial processes.
6. Limitation and Practical Challenges of TDESs
TDESs are valued for their low volatility, high thermal stability, and tunable solvation properties, making them promising alternatives to conventional solvents in applications such as extraction and catalysis [90,134]. However, several practical challenges have limited widespread industrial adoption. A primary concern is the complexity of recycling TDESs compared with BDESs or traditional solvents. The presence of three components, typically ChCl combined with two HBDs, increases the risk of unequal volatilization, selective degradation, or component loss during recovery processes, such as distillation, membrane separation, or back-extraction [207]. Such disruptions can alter the original molar ratio, which is critical for maintaining the eutectic behavior and performance of the TDESs in subsequent cycles. Even minor deviations in composition can significantly affect viscosity and solubility, compromising solvent efficacy [208].
Impurity accumulation further complicates application of TDESs. During use, reaction by-products, dissolved solutes, or partial hydrolysis can accumulate, disproportionately affecting physicochemical properties, such as pH, viscosity, and solubility, compared to BDESs [209,210]. The multicomponent interactions in the TDESs amplify these effects, potentially disrupting the delicate eutectic balance. For instance, hydrolysis in the presence of water can produce acidic by-products, altering the solvent performance [194,211]. Water, whether introduced intentionally as a co-solvent or inadvertently through environmental exposure, poses additional challenges [212]. Uncontrolled water content can shift the hydrogen-bonding network, leading to phase changes, partial crystallization, or reduced solvation capacity [213]. Although water can reduce viscosity in some TDES formulations, its uncontrolled presence during recycling necessitates additional purification steps, further complicating the process [214].
From a process design perspective, scaling up TDESs’ production and their regeneration is challenging. Maintaining molar ratio consistency and purity across large-scale operations requires robust process controls, which are currently underdeveloped [215]. The multicomponent nature of TDESs makes them more susceptible to variations during synthesis and recycling, increasing the complexity of process optimization [90]. Energy-intensive purification methods, such as vacuum distillation or advanced membrane processes, are often required to restore the composition, potentially offsetting the environmental benefits of TDESs [216]. Additionally, the lack of standardized protocols for TDESs regeneration hinders cross-application comparability and techno-economic benchmarking, thereby limiting industrial adoption [217]. Comprehensive data on production costs, energy requirements, and lifecycle impacts for TDESs are sparse compared to those for BDESs, underscoring the need for standardized evaluation frameworks [218].
Operational limitations, such as mass transfer, heat transfer, and flow characteristics, further constrain the practical application of TDESs in industrial settings. Although TDESs generally exhibit lower viscosity than BDESs, their viscosity remains higher than that of conventional solvents, which impacts mass transfer efficiency [219]. This intermediate viscosity can still hinder solute diffusion compared to conventional solvents, potentially reducing the efficiency of processes like extraction, gas absorption, or catalysis, where rapid mass transfer is critical [12]. For example, in liquid–liquid extraction, the higher viscosity of TDESs compared to conventional solvents can lead to slower phase separation and reduced extraction yields [95]. In catalytic applications, the viscosity may limit reactant transport to active sites, though TDESs offer improvements over BDESs in this regard [191]. Heat transfer is another concern, as the relatively low thermal conductivity of TDESs, combined with their higher viscosity compared to conventional solvents, can impede heat dissipation in exothermic reactions or high-temperature processes [220]. This can result in localized hotspots, potentially affecting reaction control and accelerating degradation of TDES components [221]. Flow characteristics also pose challenges, particularly in continuous flow systems. While TDESs flow more readily than BDESs due to their lower viscosity, their flow properties are less favorable than those of conventional solvents, leading to higher pumping energy requirements and potential issues with uniform mixing or flow distribution [222]. These flow challenges may necessitate specialized reactor designs or equipment modifications, increasing operational complexity and costs [90]. To mitigate these limitations, strategies such as incorporating co-solvents (e.g., water or alcohols) to further reduce viscosity or designing reactors with enhanced mixing and heat transfer capabilities can be explored, though these must be balanced to preserve the eutectic properties of TDESs [223,224].
The long-term stability of TDESs under industrial conditions, such as elevated temperatures, oxidative environments, or mechanical shear, remains underexplored [225]. Degradation pathways, including thermal decomposition or chemical breakdown of hydrogen bond donors, can compromise performance over time [226]. Unlike conventional solvents with well-characterized degradation mechanisms, TDESs require further research to elucidate these pathways and develop mitigation strategies, such as stabilizers or optimized formulations [227]. To address these challenges, future research should focus on developing efficient recycling methods tailored to TDESs, such as selective separation techniques that preserve molar ratios. Standardized protocols for regeneration and techno-economic assessments are essential for facilitating industrial adoption. Additionally, investigating stabilizers or additives to mitigate impurity effects and to enhance stability could extend the lifespan of TDESs in continuous or batch operations. Comprehensive studies on the degradation under various conditions will provide critical insights into improving the durability of these green solvents.
In conclusion, although TDESs offer significant advantages as a sustainable solvent, its industrial implementation is constrained by recycling complexities, impurity sensitivity, scalability issues, and stability concerns. Targeted research and process optimization are crucial for overcoming these barriers and unlocking the full potential of TDESs in industrial applications.
7. Conclusions and Future Prospects
This review examines the physicochemical properties of ternary choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents (TDESs) and compares them with their binary counterparts. The incorporation of a third component has been shown to significantly improve critical solvent properties, such as reducing the viscosity, melting point, and density, while enhancing the conductivity, solvation ability, and overall performance. These enhancements expand the applicability of TDESs across various domains, including biomass conversion, CO2 capture, heavy oil upgrading, and use as solvents or catalysts in organic reactions.
TDESs offer a versatile and tunable platform for industrial and environmental applications with clear advantages over conventional solvents and ionic liquids in terms of cost, biodegradability, toxicity, and raw material availability.
Despite their promise, the full potential of tailored TDESs remains largely underexplored. Key research challenges include optimizing the composition and molar ratios for targeted applications, deep understanding of molecular-level interactions and mechanisms that govern their physicochemical behavior and developing accurate predictive models and thermodynamic frameworks. Moreover, long-term stability under industrial conditions, comprehensive toxicity assessments, and cost-effective synthetic routes must be addressed to facilitate large-scale adoption.
Future research should prioritize the design of functionalized TDESs tailored to specific needs, enhancing solubility, selectivity, catalytic activity, and conductivity while establishing reliable measurement protocols and predictive tools for property estimation. Interdisciplinary collaboration and pilot-scale studies are essential to bridge the gap between laboratory success and industrial implementation.
TDESs represent a promising class of green solvents that address the many limitations of traditional solvents and ionic liquids. Their adaptability and performance position them as key enablers of sustainable innovation and integral components in the transition toward a circular and bio-based economy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemengineering9040084/s1, Table S1: Results of the SLE calculations; Table S2: NRTL parameters for the DES system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.I. and C.C.; formal analysis, A.I., C.C., F.E. and M.M.T.; investigation, A.I., C.C., F.E. and M.M.T.; data curation, A.I., C.C., F.E. and M.M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, A.I.; writing—review and editing, A.I., C.C., F.E. and M.M.T.; supervision, C.C. and F.E.; project administration, C.C., F.E. and M.M.T.; funding acquisition, A.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was fully funded by Petroleum Technology Development Fund (PTDF), Nigeria (PTDF/ED/OSS/PhD/AGI/1721/20).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the RAPSODEE Research Centre, IMT Mines Albi, France and the Mangosuthu University of Technology, for providing the enabling environment to carry out this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DES | Deep eutectic solvent |
| TDES | Ternary choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents |
| ILs | Ionic liquids |
| ChCl | Choline chloride |
| HBAs | Hydrogen bond acceptors |
| HBDs | Hydrogen bond donors |
| NRTL | Non-random two liquid |
| CCS | Carbon capture and storage |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| U | Urea |
| W | Water |
| GL | Glycerol |
| EG | Ethylene glycol |
| LA | Lactic acid |
| OA | Oxalic acid |
| CA | Citric acid |
| PG | Propylene glycol |
| RES | Resorcinol |
| MA | Malic acid |
| MAL | Malonic acid |
| BTD | Butanediol |
| FRU | Fructose |
| VFT | Vogel–Fulcher–Tammann model |
| SUPRADES | Supramolecular deep eutectic solvents |
| THEDES | Therapeutic DES |
| ACE | Acetamide |
| BA | Boric acid |
| WLF | Williams–Landel–Ferry model |
| NADES | Natural DES |
| Cat+ | Ammonium, phosphonium, or sulfonium cation |
| PEI | Polyethyleneimine |
| PEG | Polyethylene |
| PRP | Propanediol |
| NI | NiCl2∙6H2O |
| GC | Guaiacol |
| PTSA | p-toluenesulfonic acid |
References
- Afonso, J.; Mezzetta, A.; Marrucho, I.M.; Guazzelli, L. History Repeats Itself Again: Will the Mistakes of the Past for ILs Be Repeated for DESs? From Being Considered Ionic Liquids to Becoming Their Alternative: The Unbalanced Turn of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 59–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, R.M.; van Rantwijk, F.; Seddon, K.R.; Sheldon, R.A. Lipase-Catalyzed Reactions in Ionic Liquids. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 4189–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, M.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. A Novel Technique for Separating Glycerine from Palm Oil-Based Biodiesel Using Ionic Liquids. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Fauzi, A.H.; Amin, N.A.S. An Overview of Ionic Liquids as Solvents in Biodiesel Synthesis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 5770–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taysun, M.B.; Sert, E.; Atalay, F.S. Synthesis, Characterization and Acid-Catalyzed Application of Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent: Effect of Glycerol Addition. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.N.; Do, H.D.; Trinh, K.T.; Lee, N.Y. Design Strategy and Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Green Synthesis of Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandelwal, S.; Tailor, Y.K.; Kumar, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) as Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Solvent/Catalyst Systems in Organic Transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 345–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leila, M.; Tarek, M.; Michel, F.; Hervé, B.; Sébastien, T.; Eric, M.; Margarida, F.C.G.; David, L.; Sophie, F. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Absorbents of Volatile Organic Pollutants. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, J.M.; Lichtenthaler, R.N.; de Azevedo, E.G. Molecular Thermodynamics of Fluid-Phase Equilibria; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-13-244050-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Syntheses, Properties and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielly, M. Modeling Solvent Selection for Biorefinery Application. Ph.D. Thesis, Mines Paris—PSL, Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florindo, C.; Lima, F.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Marrucho, I.M. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Overcoming 21st Century Challenges. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 18, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, I.I.I.; Bahamon, D.; Llovell, F.; Abu-Zahra, M.R.M.; Vega, L.F. Perspectives and Guidelines on Thermodynamic Modelling of Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 298, 112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. Low-Transition-Temperature Mixtures (LTTMs): A New Generation of Designer Solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3074–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljadri, M.A.K. Novel Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Application in the Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Aromatic Compounds. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel Solvent Properties of Choline Chloride/Urea Mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 39, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, M.A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids Analogues and Their Physical Properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4632–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, M.A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K.O.; Bagh, F.S.G.; Alnashef, I.M. Phase Equilibria of Toluene/Heptane with Tetrabutylphosphonium Bromide Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Potential Use in the Separation of Aromatics from Naphtha. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2012, 333, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, K.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Methyl Triphenyl Phosphunium Bromide for the Removal of Glycerol from Palm-Oil-Based Biodiesel. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2671–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, A.; Mjalli, F.S.; AlNashef, I.M.; Al-Wahaibi, T.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.M.; Hashim, M.A. Fruit Sugar-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Physical Properties. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 541, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, W.A.; Yager, T.D.; Korte, J.; Von Hippel, P.H. Betaine Can Eliminate the Base Pair Composition Dependence of DNA Melting. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnicki, S.D. Synthetic Organic Chemicals. In Handbook of Industrial Chemistry and Biotechnology; Kent, J.A., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 307–389. ISBN 978-1-4614-4259-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chary, M.V.; Keerthysri, N.C.; Vupallapati, S.V.N.; Lingaiah, N.; Kantevari, S. Tetrabutylammonium Bromide (TBAB) in Isopropanol: An Efficient, Novel, Neutral and Recyclable Catalytic System for the Synthesis of 2,4,5-Trisubstituted Imidazoles. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 2013–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlbusch, K.; Hammerschmidt, F.; Panten, J.; Pickenhagen, W.; Schatkowski, D.; Bauer, K.; Garbe, D.; Surburg, H. Flavors and Fragrances. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Vichy, France, 2003; ISBN 978-3-527-30385-4. [Google Scholar]
- Eccles, R. Menthol and Related Cooling Compounds. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.C.; Schmidt, M.W.; Gordon, M.S.; Ruedenberg, K. A Comprehensive Analysis in Terms of Molecule-Intrinsic, Quasi-Atomic Orbitals. III. The Covalent Bonding Structure of Urea. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 10368–10375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Gutiérrez, S.; Pérez, E.; Olmos-Greco, R.J.; Cabañas, A. Thermodynamic and Spectroscopic Study of Solutions of Therapeutic Deep Eutectic Solvents (THEDES) in Supercritical CO2. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 423, 127027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwamena, A.K. Recent Advances in Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Extraction. Separations 2019, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, K.A.; Ioannou, G.D.; Christou, A.; Schmid, M.G.; Stavrou, I.J.; Kapnissi-Christodoulou, C.P. Novel Supramolecular Deep Eutectic Solvent (SUPRADES) as a Sole Chiral Selector in Capillary Electrophoresis for the Enantiomeric Separation of Fluorine-Substituted Amphetamine Analogs. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1715, 464628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; McKenzie, K.J.; Obi, S.U. Solubility of Metal Oxides in Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Ryder, K.S.; Wilson, D. Eutectic-Based Ionic Liquids with Metal-Containing Anions and Cations. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Type V Deep Eutectic Solvents: Design and Applications. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 35, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Martins, M.A.R.; Silva, L.P.; Schaeffer, N.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Phenolic Hydrogen Bond Donors in the Formation of Non-Ionic Deep Eutectic Solvents: The Quest for Type V DES. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10253–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajar, A.T.N.; Hanada, T.; Hartono, A.D.; Goto, M. Estimating the Phase Diagrams of Deep Eutectic Solvents within an Extensive Chemical Space. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, G.; Abranches, D.O.; Ferreira, O.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Estimating the Melting Temperatures of Type V Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 14638–14647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, I.C.M.; Lobo Ferreira, A.I.M.C.; Silva, G.M.C.; Morgado, P.; Abranches, D.O.; Bastos, M.; Santos, L.M.N.B.F.; Filipe, E.J.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. The Path towards Type V Deep Eutectic Solvents: Inductive Effects and Steric Hindrance in the System Tert-Butanol + Perfluoro Tert-Butanol. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 11227–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Zubeir, L.F.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as Water-Immiscible Extractants. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadid, A.; Mokrushina, L.; Minceva, M. Influence of the Molecular Structure of Constituents and Liquid Phase Non-Ideality on the Viscosity of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2021, 26, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.R.C.; Ferreira, A.S.D.; Barreiros, S.; Cabrita, E.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A. A Comparison between Pure Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Therapeutic Deep Eutectic Solvents: Solubility and Permeability Studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 114, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents—Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Jaap, S.; Geert-Jan, W.; Robert, V.; Young, H.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as New Potential Media for Green Technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications, and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś-Chełstowska, P.; Słupek, E.; Fourmentin, S.; Gębicki, J. Supramolecular Deep Eutectic Solvents in Extraction Processes: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 23, 41–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Moufawad, T.; Ruellan, S.; Landy, D.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Cyclodextrins: From Solute to Solvent. Chem Commun Camb 2020, 56, 3385–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, H.G.; Sun, C.C.; Neervannan, S. Characterization of Thermal Behavior of Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Potential as Drug Solubilization Vehicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 378, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.S.; Lobo, H.R.; Shankarling, G.S. Choline Chloride Based Eutectic Solvents: Magical Catalytic System for Carbon–Carbon Bond Formation in the Rapid Synthesis of β-Hydroxy Functionalized Derivatives. Catal. Commun. 2012, 24, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ren, J.; He, B. Effect of Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents on Bagasse Cellulose and Lignin Structure in Low-Temperature Pretreatment. Processes 2022, 10, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-H.; Leron, R.B.; Li, M.-H. Solubility of Carbon Dioxide in Aqueous Mixtures of (Reline + Monoethanolamine) at T = (3132 to 3532) K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 72, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuwa, S.M.; Jibril, B.Y.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.M.; Al-Hajri, R.S. Heavy-Oil-Recovery Enhancement With Choline Chloride/Ethylene Glycol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. SPE J. 2015, 20, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, K.; Fatemi, M.H.; Estellé, P. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs): A Short Overview of the Thermophysical Properties and Current Use as Base Fluid for Heat Transfer Nanofluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Lobo, H.; Shankarling, G. Selective N-Alkylation of Aromatic Primary Amines Catalyzed by Bio-Catalyst or Deep Eutectic Solvent. Catal. Lett. 2011, 141, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.; Aparicio, S.; Ullah, R.; Atilhan, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Physicochemical Properties and Gas Separation Applications. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2616–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemeh Saadat, G.B. Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Potential Use in Production of Sodium. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wagle, D.V.; Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Sustainable Media for Nanoscale and Functional Materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Row, K.H. Recent Developments in Deep Eutectic Solvents in Chemical Sciences. Monatshefte Für Chem.—Chem. Mon. 2013, 144, 1427–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verberne, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R. Are Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents the Missing Link in Understanding Cellular Metabolism and Physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents for Biodiesel Synthesis: A Review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pätzold, M.; Siebenhaller, S.; Kara, S.; Liese, A.; Syldatk, C.; Holtmann, D. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Efficient Solvents in Biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 943–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Hamad, A.; Hayyan, M.; AlSaadi, M.A.; Hashim, M.A. Potential Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Nanotechnology. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanab, K.; Neudorfer, C.; Schirmer, E.; Spreitzer, H. Green Solvents in Organic Synthesis: An Overview. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahere, K.; Mehrorang, G.; Sonia, B.; Ali, D.; Mustafa, S. Deep Eutectic Solvent in Separation and Preconcentration of Organic and Inorganic Species. In New Generation Green Solvents for Separation and Preconcentration of Organic and Inorganic Species; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 381–423. ISBN 978-0-12-818570-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsenzadeh, A.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.; Jibril, A.; Al-Hajri, R.; Shuwa, S. The Novel Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Enhancing Heavy Oil Recovery. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 130, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Yu, D.; Guo, W.; Mu, T. Capture of Toxic Gases by Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5410–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loow, Y.-L.; New, E.K.; Yang, G.H.; Ang, L.Y.; Foo, L.Y.W.; Wu, T.Y. Potential Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents to Facilitate Lignocellulosic Biomass Utilization and Conversion. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3591–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Muhammad, G.; Khan, M.N.; Mofijur, M.; Lv, Y.; Xiong, W.; Xu, J. Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Extractants for the Isolation of Phenolic Compounds from Biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhor, P.; Ghandi, K. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Catalysts for Upgrading Biomass. Catalysts 2021, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.K.; Kumar, N.; Paul, N.; Banerjee, T. Deep Eutectic Solvents in Liquid–Liquid Extraction: Correlation and Molecular Dynamics Simulation, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-1-003-23115-8. [Google Scholar]
- Cichowska-Kopczyńska, I.; Nowosielski, B.; Warmińska, D. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties and Applications in CO2 Separation. Molecules 2023, 28, 5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P. Comparison of Deep Eutectic Solvents and Ionic Liquids. In Deep Eutectic Solvents for Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass; Bajpai, P., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 81–87. ISBN 978-981-16-4013-1. [Google Scholar]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; de la Guardia, M.; Andruch, V.; Vilková, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents vs. Ionic Liquids: Similarities and Differences. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.M.; Lee, M.S.; Nam, M.W.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Lee, D.-K.; Kwon, S.W.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, J. Tailoring and Recycling of Deep Eutectic Solvents as Sustainable and Efficient Extraction Media. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1424, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juneidi, I.; Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A. Evaluation of Toxicity and Biodegradability for Cholinium-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 83636–83647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Mellado, N.; Larriba, M.; Navarro, P.; Rigual, V.; Ayuso, M.; García, J.; Rodríguez, F. Thermal Stability of Choline Chloride Deep Eutectic Solvents by TGA/FTIR-ATR Analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsevier Scopus. Scopus Database. Available online: https://www.scopus.com (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Biczak, R.; Pawłowska, B.; Bałczewski, P.; Rychter, P. The Role of the Anion in the Toxicity of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Mac Dowell, N.; Welton, T.; Shah, N.; Hallett, J.P. Inexpensive Ionic Liquids: [HSO4]−-Based Solvent Production at Bulk Scale. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3098–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.M.; Gilman, J.W.; Morgan, A.B.; Shields, J.R.; Maupin, P.H.; Lyon, R.E.; Long, H.C.D.; Trulove, P.C. Flammability and Thermal Analysis Characterization of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 47, 6327–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maton, C.; De Vos, N.; Stevens, C.V. Ionic Liquid Thermal Stabilities: Decomposition Mechanisms and Analysis Tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meine, N.; Benedito, F.; Rinaldi, R. Thermal Stability of Ionic Liquids Assessed by Potentiometric Titration. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiglak, M.; Reichert, W.M.; Holbrey, J.D.; Wilkes, J.S.; Sun, L.; Thrasher, J.S.; Kirichenko, K.; Singh, S.; Katritzky, A.R.; Rogers, R.D. Combustible Ionic Liquids by Design: Is Laboratory Safety Another Ionic Liquid Myth? Chem. Commun. 2006, 24, 2554–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, E.A.; Silva, L.P.; Martins, M.A.R.; Fernandez, L.; Ortega, J.; Ferreira, O.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Characterization and Modeling of the Liquid Phase of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Fatty Acids/Alcohols and Choline Chloride. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12192–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.R.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kollau, L.J.B.M.; Kroon, M.C.; Binnemans, K. Degradation of Deep-Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11521–11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Fernandes, A.M.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the Synthesis and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Cholinium Chloride and Carboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Chavda, V.; Hirpara, D.; Sharma, V.S.; Shrivastav, P.S.; Kumar, S. Exploring the Potential of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Pharmaceuticals: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sato, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kansha, Y. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents: Evaluations Based on How Their Physical Properties Affect Energy Consumption during Post-Combustion CO2 Capture. Energy 2023, 270, 126901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.A.; Malik, T.; Naeem, A.; Khan, A.S.; Din, I.U.; Shaharun, M.S. Exploring the Dynamic World of Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents: Synthesis, Characterization, and Key Properties Unveiled. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Sun, P.; Ma, Q.; Su, H.; Leung, P.; Yang, W.; Xu, Q. Rationally Designed Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent Enabling Higher Performance for Non-Aqueous Redox Flow Batteries. Processes 2022, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhou, C.; Mo, H.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zang, L. New Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents for Effective Wheat Straw Deconstruction into Its High-Value Utilization under near-Neutral Conditions. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8713–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-A.; Xing, Y.-J. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriazo, D.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Ferrer, M.L.; del Monte, F. Resorcinol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Both Carbonaceous Precursors and Templating Agents in the Synthesis of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Monoliths. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6146–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhom, M.A.; Abdullah, G.H.; Al-Bayati, N. Studying Two Series of Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents (Choline Chloride–Urea–Glycerol) and (Choline Chloride–Malic Acid–Glycerol), Synthesis and Characterizations. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonsky, M.; Majova, V.; Ondrigova, K.; Sima, J. Preparation and Characterization of Physicochemical Properties and Application of Novel Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3031–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Pedersen, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, X.; Wang, Y. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents Catalyzed D-Glucosamine Self-Condensation to Deoxyfructosazine: NMR Study. Green Energy Environ. 2021, 6, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, L.L.; Pandey, S.; Ravula, S.; Pandey, S.; Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A.; Baker, S.N. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents Tasked for Carbon Dioxide Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2117–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.N.; Hayyan, A.; Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A.; Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Sani, F.S.; Basirun, W.J.; Lee, V.S.; Alias, Y.; Mohammed, A.K.; et al. Ternary Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Physicochemical Properties and Enzymatic Activity. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 169, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, Z.; Suhaili, N.; Tahari, M.N.A.; Yarmo, M.A.; Hassan, N.H.; Othaman, R. Impregnating Deep Eutectic Solvent Choline Chloride:Urea:Polyethyleneimine onto Mesoporous Silica Gel for Carbon Dioxide Capture. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3249–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ee, L.Y.; Tan, Y.K.; Miao, J.; Chu, H.T.; Li, S.F.Y. High-Purity Lignin from Selective Biomass Fractionation with Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 3137–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.; Venkatachalam, P.; Panakkal, E.J.; Tantayotai, P.; Tandhanskul, A.; Selvasembian, R.; Chuetor, S.; Sriariyanun, M. Exploring Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreatment in a One-Pot Process with Napier Grass for Bioethanol Production. BioEnergy Res. 2024, 17, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenzadeh, A.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.; Al-Hajri, R.; Jibril, B.; Mosavat, N. Sequential Deep Eutectic Solvent and Steam Injection for Enhanced Heavy Oil Recovery and In-Situ Upgrading. Fuel 2017, 187, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Bao, M.; Yu, X. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents for Esterification of 2-Methylpropenoic Acid with Alcohols. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 7951–7955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.; He, X.; Shen, F.; Xu, Z.; Yang, B.; Kong, L.; Dai, L. Emerging Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Preparation and Functionalization of Biomass-Derived Carbonaceous Materials: Challenges and Prospects. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 8123–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Sun, H.; Williams, P.T.; Wu, C. Recent Advances in Integrated CO2 Capture and Utilization: A Review. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 4546–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.I.N.; Baião, V.; da Silva, W.; Brett, C.M.A. Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Production and Application of New Materials. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 10, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiarto, S.; Aloka Weerasinghe, U.; Kinyanjui Muiruri, J.; Yu Qing Chai, A.; Chee Chuan Yeo, J.; Wang, G.; Zhu, Q.; Jun Loh, X.; Li, Z.; Kai, D. Nanomaterial Synthesis in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Physicochemical Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Novel Diglycolic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Applications as a Rust Remover. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Hao, J.; Hongping, L.; Linhua, Z.; Runming, T.; Wenshuai, Z.; Huaming, L.; Sheng, D. Boric Acid-Based Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent for Extraction and Oxidative Desulfurization of Diesel Fuel. Green Chem. 2019, 18, 1839–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manurung, R.; Syahputra, A.; Alhamdi, M.A. Purification of Palm Biodiesel Using Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Based Choline Chloride (ChCl) and 1,2-Propanediol (C3H8O2). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1028, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larriba, M.; Ayuso, M.; Navarro, P.; Delgado-Mellado, N.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M.; García, J.; Rodríguez, F. Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Dearomatization of Gasolines. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosoiu, S.P. Electrodeposition of Nickel and Tin Based Alloys from Deep Eutectic Solvents for Electronic Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University Politehnica of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Haq, I.U.; Lal, B.; Zaini, D. Deep Eutectic Solvents Feasibility in Oil and Gas Processing Field for Contaminated CO2 Control. preprints.org 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourmentin, S.; Costa Gomes, M.; Lichtfouse, E. (Eds.) Deep Eutectic Solvents for Medicine, Gas Solubilization and Extraction of Natural Substances; Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 56, ISBN 978-3-030-53068-6. [Google Scholar]
- Elise, E.A.; Coquelet, C. Physicochemical Properties of Gas. In Gases in Agro-Food Processes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 13–41. ISBN 978-0-12-812465-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L. Investigation of Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Derivatives for Pharmaceutical Applications. Master’s Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Abad-Gil, L.; Procopio, J.R.; Brett, C.M.A. Binary and Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent Mixtures: Influence on Methylene Blue Electropolymerisation. Electrochem. Commun. 2021, 124, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Versatile Media for the Synthesis of Noble Metal Nanomaterials. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGaughy, K.; Reza, M.T. Liquid-Liquid Equilibrium of Deep Eutectic Solvent-Aromatic-Aliphatic Ternary Systems: Experimental Study with COSMO Model Predictions. Processes 2021, 9, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Msahel, A.; Galiano, F.; Serocki, M.; Ryl, J.; Hamouda, S.B.; Hafiane, A.; Boczkaj, G.; Figoli, A. Towards Azeotropic MeOH-MTBE Separation Using Pervaporation Chitosan-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent Membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Row, K.H. Application of Novel Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Functional Monomer in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Purification of Levofloxacin. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1068, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Chavda, V.; Hirpara, D.; Pokar, R.; Kumar, S.; Shrivastav, P.S. Advances in Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Synthesis of Nanomaterials for Environmental Remediation. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 416, 126482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farsi, R.; Hayyan, M. Paving the Way for Advancement of Renewable Energy Technologies Using Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 184, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, C.L.; Quivelli, A.F.; Manfredi, N.; Capriati, V.; Abbotto, A. Deep Eutectic Solvents in Solar Energy Technologies. Molecules 2022, 27, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, M.R. The Roles of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Batteries for Sustainable Energy Storage. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kityk, A.; Pavlik, V.; Hnatko, M. Breaking Barriers in Electrodeposition: Novel Eco-Friendly Approach Based on Utilization of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 334, 103310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, L.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Jesus, A.R. How Can Deep Eutectic Systems Promote Greener Processes in Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery? Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codera, V.; Clijnk, D.; Pou, J.O.; Fernandez-Garcia, J.; Llovell, F.; Gonzalez-Olmos, R. Process Design for the Recovery of Waste Refrigerants Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clijnk, D.; Codera, V.; Pou, J.O.; Fernandez-Garcia, J.; Gonzalez-Olmos, R. Enhancing Circular Economy of Waste Refrigerants Management Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 41, e01062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Cao, M.; Mu, W.; Jovein, I.B.; Held, C.; Chen, B.; Yu, G. Selective Absorption of Fluorinated Gases by Deep Eutectic Solvents: Thermodynamics and Molecular Insights. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 364, 132342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlOmar, M.K.; Hayyan, M.; Alsaadi, M.A.; Akib, S.; Hayyan, A.; Hashim, M.A. Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Physical Properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Arroyo, C.B.; Lopez Hernandez, F.; Goeltz, J.C. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent Behavior of Water and Urea–Choline Chloride Mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 5302–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Flammia, V.; Carvalho, T.; Viciosa, M.T.; Dionísio, M.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Paiva, A. Properties and Thermal Behavior of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangir, A.K.; Patel, D.; More, R.; Parmar, A.; Kuperkar, K. New Insight into Experimental and Computational Studies of Choline Chloride-Based ‘Green’ Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent (TDES). J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1181, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.A.; Fagoroye, O.K.; Ajayi, T.O.; Kehinde, A.J. Ternary Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Data for n-Hexane-Benzene-DES (Choline Chloride/Ethylene Glycol, Choline Chloride/Glycerol, Choline Chloride/Urea) at 303 K and 101.3 kPa. Appl. Petrochem. Res. 2020, 10, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P. Application of Hole Theory to the Viscosity of Ionic and Molecular Liquids. ChemPhysChem 2004, 5, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalde, R.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. On the Properties of (Choline Chloride + lactic Acid) Deep Eutectic Solvent with Methanol Mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Database of Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Physical Properties: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 384, 121899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjalli, F.S.; Ahmed, O.U. Characteristics and Intermolecular Interaction of Eutectic Binary Mixtures: Reline and Glyceline. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulcova, A.; Russ, A.; Jablonsky, M.; Sima, J. The pH Behavior of Seventeen Deep Eutectic Solvents. BioResources 2018, 13, 5042–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wahaibi, I.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.; Al-Hajri, R.; Jibril, B.; Shuwa, S. The Novel Use of Malonic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for Enhancing Heavy Oil Recovery. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol. 2019, 20, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.M.; Squire, H.; Dean, W.; Gurkan, B.E. From Salt in Solution to Solely Ions: Solvation of Methyl Viologen in Deep Eutectic Solvents and Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 6348–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Row, K.H. Development of Deep Eutectic Solvents Applied in Extraction and Separation. J. Sep. Science 2016, 39, 3505–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Harris, R.C.; Ryder, K.S.; D’Agostino, C.; Gladden, L.F.; Mantle, M.D. Glycerol Eutectics as Sustainable Solvent Systems. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Harris, R.C.; Ryder, K.S. Application of Hole Theory to Define Ionic Liquids by Their Transport Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4910–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Li, C.; Yin, J.; Li, S.; Jia, Y.; Bao, M. Design, Synthesis and Properties of Acidic Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Understanding the Basics and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents. In Deep Eutectic Solvents for Medicine, Gas Solubilization and Extraction of Natural Substances; Fourmentin, S., Costa Gomes, M., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–40. ISBN 978-3-030-53069-3. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, A.P.R.; Mora-Vargas, J.A.; Guimarães, T.G.S.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Sustainable Synthesis of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES) by Different Methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeow, A.T.H.; Hayyan, A.; Hayyan, M.; Usman Mohd Junaidi, M.; Saleh, J.; Jefrey Basirun, W.; Roslan Mohd Nor, M.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Zulhaziman, M.; Salleh, M.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on the Physicochemical Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, H.; Liang, B. Insights into the Relationships between Physicochemical Properties, Solvent Performance, and Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 35537–35563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, C.; Harris, R.C.; Abbott, A.P.; Gladden, L.F.; Mantle, M.D. Molecular Motion and Ion Diffusion in Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents Studied by 1H Pulsed Field Gradient NMR Spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 21383–21391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Gray, S. Design of Improved Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Hole Theory. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Pandey, S. Densities and Viscosities of (Choline Chloride + Urea) Deep Eutectic Solvent and Its Aqueous Mixtures in the Temperature Range 293.15 K to 363.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.K.; Hayyan, M.; AlSaadi, M.A.; Ibrahim, S.; Hayyan, A.; Hashim, M.A. Physical Properties of Ethylene Glycol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Tang, S.; Wu, K.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, H.; Liang, B. Structure–Properties Relationships of Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Experimental and Computational Study. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1273, 134283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dawsari, J.N.; Bessadok-Jemai, A.; Wazeer, I.; Mokraoui, S.; AlMansour, M.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. Fitting of Experimental Viscosity to Temperature Data for Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouarab, A.F.; Harvey, J.-P.; Robelin, C. Viscosity Models for Ionic Liquids and Their Mixtures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Tailoring Properties of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents with Water to Facilitate Their Applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Mjalli, F.S. Effect of Water on the Thermo-Physical Properties of Reline: An Experimental and Molecular Simulation Based Approach. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 23900–23907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zhao, B.; Chen, X.-B.; Birbilis, N.; Yang, H. Effect of Water Presence on Choline Chloride-2urea Ionic Liquid and Coating Platings from the Hydrated Ionic Liquid. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Fourmentin, S.; Greige-Gerges, H. Deep Eutectic Solvents: An Overview on Their Interactions with Water and Biochemical Compounds. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 111028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Ballerat-Busserolles, K.; Husson, P.; Andanson, J.-M. Impact of Water on the Melting Temperature of Urea + Choline Chloride Deep Eutectic Solvent. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 4492–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzinjy, A.; Zankana, M. A Novel Application of the Quartz Crystal Microbalance for Determining the Rheological Properties of the Highly Viscous Liquids. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2016, 130, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Flores, F.G. Lignin: A Renewable Raw Material. In Encyclopedia of Renewable and Sustainable Materials; Hashmi, S., Choudhury, I.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 102–118. ISBN 978-0-12-813196-1. [Google Scholar]
- Majová, V.; Jablonský, M.; Lelovský, M. Delignification of Unbleached Pulp by Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourasia, V.R.; Bisht, M.; Pant, K.K.; Henry, R.J. Unveiling the Potential of Water as a Co-Solvent in Microwave-Assisted Delignification of Sugarcane Bagasse Using Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.-J.; Han, X.; Chang, Y.-H.; Xu, J.; Yue, G.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.-J. A Novel Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreatment for the Efficient Separation and Conversion of High-Quality Gutta-Percha, Value-Added Lignin and Monosaccharide from Eucommia Ulmoides Seed Shells. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Xue, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, L. Green Extraction of Phenolic Acids from Artemisia Argyi Leaves by Tailor-Made Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2019, 24, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Anjum, H.; Shariff, A.M.; Kumar, P.; Murugesan, T. Thermal and Physical Properties of (Choline Chloride + Urea +l-Arginine) Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 218, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Pedersen, C.M.; Chang, H.; Hou, X.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Switchable Product Selectivity in Dehydration of N-Acetyl-d-Glucosamine Promoted by Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. iScience 2023, 26, 106980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shi, G.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y. Polysaccharides Extraction from Ganoderma Lucidum Using a Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents of Choline Chloride/Guaiacol/Lactic Acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Li, B.-L.; Cui, Z.-S.; Zhang, Z.-H. Deep Eutectic Solvent Based on Choline Chloride and Malonic Acid as an Efficient and Reusable Catalytic System for One-Pot Synthesis of Functionalized Pyrroles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 7720–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.J.; Redondo, A.E.; Sosa, J.E.; Zakrzewska, M.E.; Nunes, A.V.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Absorption of Fluorinated Greenhouse Gases in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 13246–13259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowosielski, B.; Warmińska, D.; Cichowska-Kopczyńska, I. CO2 Separation Using Supported Deep Eutectic Liquid Membranes Based on 1,2-Propanediol. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 4093–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jacoby, W.A.; Wan, C. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents for Effective Biomass Deconstruction at High Solids and Low Enzyme Loadings. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amesho, K.T.T.; Lin, Y.-C.; Mohan, S.V.; Halder, S.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Jhang, S.-R. Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Transformation of Biomass into Biofuels and Fine Chemicals: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 183–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Liu, S. Choline Chloride–Based Deep Eutectic Solvents (Ch-DESs) as Promising Green Solvents for Phenolic Compounds Extraction from Bioresources: State-of-the-Art, Prospects, and Challenges. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 2949–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmad, S.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Ji, X. Carbon Dioxide Capture with Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents: A New Generation of Sorbents. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 324–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X. CO2 Capture/Separation Using Choline Chloride-Based Ionic Liquids. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Properties and Phase Equilibria for Process and Product Design, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–30 May 2013; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hou, M.; Han, B.; Wang, X.; Zou, L. Solubility of CO2 in a Choline Chloride + Urea Eutectic Mixture. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, Z.; Pablo, D.d.M. Novel Choline-Chloride-Based Deep-Eutectic-Solvents with Renewable Hydrogen Bond Donors: Levulinic Acid and Sugar-Based Polyols. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Gilani, M.A.; Arshad, I.; Bilad, M.R.; Ahmad, F.; Khan, A.L. Synergy of High Permeability and Selectivity of Superbase/Choline Chloride/Urea Solution Impregnated Membranes for CO2 Capture. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.A.A. Enhanced Oil Recovery of Heavy Oil by Using Thermal and Non-Thermal Methods. Master’s thesis, Dalhousie University Halifax, Halifax, NS, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, R.F.; Attanasi, E.D. Heavy Oil and Natural Bitumen—Strategic Petroleum Resources; U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 70-03; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tahir, S.; Qazi, U.Y.; Naseem, Z.; Tahir, N.; Zahid, M.; Javaid, R.; Shahid, I. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Alternative Green Solvents for the Efficient Desulfurization of Liquid Fuel: A Comprehensive Review. Fuel 2021, 305, 121502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fihri, A.; Mahfouz, R.; Shahrani, A.; Taie, I.; Alabedi, G. Pervaporative Desulfurization of Gasoline: A Review. Chem. Eng. Process.—Process Intensif. 2016, 107, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Du, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Development of Microwave Induced Hydrodesulfurization of Petroleum Streams: A Review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almashjary, K.H.; Khalid, M.; Dharaskar, S.; Jagadish, P.R.; Walvekar, R.; Gupta, T.C.S.M. Optimisation of Extractive Desulfurization Using Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Fuel 2018, 234, 1388–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuwa, S.M.; Al-Hajri, R.S.; Jibril, B.Y.; Al-Waheibi, Y.M. Novel Deep Eutectic Solvent-Dissolved Molybdenum Oxide Catalyst for the Upgrading of Heavy Crude Oil. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3589–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, A.; Rahmani, S.; Nikoo, A.H.; Malayeri, M.R.; Busse, O.; Weigand, J.J. Comparative Study of an Acidic Deep Eutectic Solvent and an Ionic Liquid as Chemical Agents for Enhanced Oil Recovery. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbek, M.G.; Rodriguez Reartes, S.B.; Llovell, F. Thermodynamic Analysis of the Absorption of Common Refrigerants in Fluorinated Deep Eutectic Solvents. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2024, 581, 114077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wei, L.; Wei, L.; Zhai, S.; Xiao, Z.; An, Q.; Hao, J. Constructing Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvents with Multiple Sites for Ammonia Storage. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 34102–34111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finberg, E.A.; May, T.L.; Shiflett, M.B. Multicomponent Refrigerant Separation Using Extractive Distillation with Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 9795–9812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finberg, E.A.; Cordry, M.; May, T.L.; Baca, K.R.; Shiflett, M.B. Ionic Liquid Selection for the Separation of Refrigerant Mixtures Using Extractive Distillation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 16070–16080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Yin, Z.; Huang, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Technologies and Perspectives for Achieving Carbon Neutrality. Innovation 2021, 2, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shao, H.; Feng, L.; Lu, Y.; Meng, H.; Li, C. Absorptive Separation of HCl Gas by Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 341, 116928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chu, S.; Cui, C.; Jia, K.; Li, J. Study on Separation of Methanol and Dimethyl Carbonate Azeotropic System with Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Gao, N. Extractive Distillation Using Salt-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent as Entrainer for Separating Acetonitrile-Water Mixture. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 414, 126120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, R.; Shen, Y.; Flake, J.C.; Hung, F.R. Deep Eutectic Solvents Mixed with Fluorinated Refrigerants for Absorption Refrigeration: A Molecular Simulation Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 4536–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, B.; Li, X. Can Deep Eutectic Solvents Be the Best Alternatives to Ionic Liquids and Organic Solvents: A Perspective in Enzyme Catalytic Reactions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bušić, V.; and Gašo-Sokač, D. Menshutkin Reaction in Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2023, 55, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bušić, V.; Molnar, M.; Tomičić, V.; Božanović, D.; Jerković, I.; Gašo-Sokač, D. Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Effective Medium for Quaternization Reactions. Molecules 2022, 27, 7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delso, I.; Lafuente, C.; Muñoz-Embid, J.; Artal, M. NMR Study of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Yang, B.; Yu, S.; Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Chi, W.; Yin, M.; Wu, H.; Guo, J. Ternary Choline Chloride/Benzene Sulfonic Acid/Ethylene Glycol Deep Eutectic Solvents for Oxidative Desulfurization at Room temperature. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 25888–25894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, X.; Deng, R.; Guo, M.; Gao, M.; Ru, J.; Xu, C.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, Q. Metal Separation and Recovery Employing Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Diverse Functions of Water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 364, 132341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połomski, D.; Garbacz, P.; Czerwinski, K.; Chotkowski, M. Synthesis and Physicochemical Properties of the Mixtures Based on Choline Acetate or Choline Chloride. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 327, 114820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijardar, S.P.; Singh, V.; Gardas, R.L. Revisiting the Physicochemical Properties and Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2022, 27, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailau, Z.; Almas, N.; Aldongarov, A.; Toshtay, K. Studying the Formation of Choline Chloride- and Glucose-Based Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent at the Molecular Level. J. Mol. Model. 2022, 28, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelä, H.; Salomäki, M.; Vainikka, P.; Mäkilä, E.; Poletti, F.; Ruggeri, S.; Terzi, F.; Lukkari, J. Effect of Water on a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Raynie, D.E. Thermal Behavior, Solvatochromic Parameters, and Metal Halide Solvation of the Novel Water-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 324, 114779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajkacz, S.; Adamek, J. Development of a Method Based on Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Extraction of Flavonoids from Food Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1330–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, A.F.; Caicedo, G.A.; Martínez, J.J.; Romanelli, G.P. Utilization of Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Production of High-Value Compounds from Biomass. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2024, 18, 1821–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba, N.; Sahu, P.; Das, N.; Sen, P. Rational Design, Preparation and Characterization of a Ternary Non-Ionic Room-Temperature Deep Eutectic Solvent Derived from Urea, Acetamide, and Sorbitol. J. Chem. Sci. 2021, 133, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Gawande, M.B. Editorial: Advances in the Development and Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1258718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Meng, X.; Li, W.; Yu, J.; Kemefa, C.O.; Dai, S.Y.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Yuan, J.S. Computational Modeling-Guided Design of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Tailoring Lignin Chemistry during Lignocellulose Pretreatment. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 6260–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, R.; Zurob, E.; Gomez, B.; Merlet, G.; Plaza, A.; Araya-Lopez, C.; Romero, J.; Olea, F.; Quijada-Maldonado, E.; Pino-Soto, L.; et al. Challenges and Possibilities of Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 17397–17422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gygli, G.; Xu, X.; Pleiss, J. Meta-Analysis of Viscosity of Aqueous Deep Eutectic Solvents and Their Components. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Rao, Z. Properties and Heat Transfer Mechanistic Study of Glycerol/Choline Chloride Deep Eutectic Solvents Based Nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 138, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehury, P.; Mahanta, U.; Singh, R.; Banerjee, T. Potential of Deep Eutectic Solvent Based Nanofluids as a New Generation Heat Transfer Media. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 379, 121700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehury, P.; Singh, J.; Banerjee, T. Thermophysical and Forced Convection Studies on (Alumina + Menthol)-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for Their Use as a Heat Transfer Fluid. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 18016–18027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Gao, D.; Song, F. Experimental Study on Thermophysical Property of Deep Eutectic Solvents as Heat Transfer Fluid. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 50, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Coquelet, C.; Valtz, A.; Espitalier, F. Thermophysical Properties: Viscosity, Density, and Excess Properties of 2-Propanol and n-Decane Mixtures from 283.15 K to 343.15 K under Atmospheric Conditions. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2025, 589, 114254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchel, M.; Cieśliński, H.; Boczkaj, G. Thermal Instability of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents and Its Influence on Their Toxicity—Important Limitations of DESs as Sustainable Materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 11288–11300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafpour, A.A.; Feyzi, F.; Rezaee, M. An Environmentally Friendly Deep Eutectic Solvent for CO2 Capture. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyoun, F.; Toncheva, A.; Henríquez, L.C.; Grougnet, R.; Laoutid, F.; Mignet, N.; Alhareth, K.; Corvis, Y. Deep Eutectic Solvents: An Eco-Friendly Design for Drug Engineering. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202300669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).