Preparation and Characterization of Unactivated, Activated, and γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticle-Functionalized Biochar from Rice Husk via Pyrolysis for Dyes Removal in Aqueous Samples: Comparison, Performance, and Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
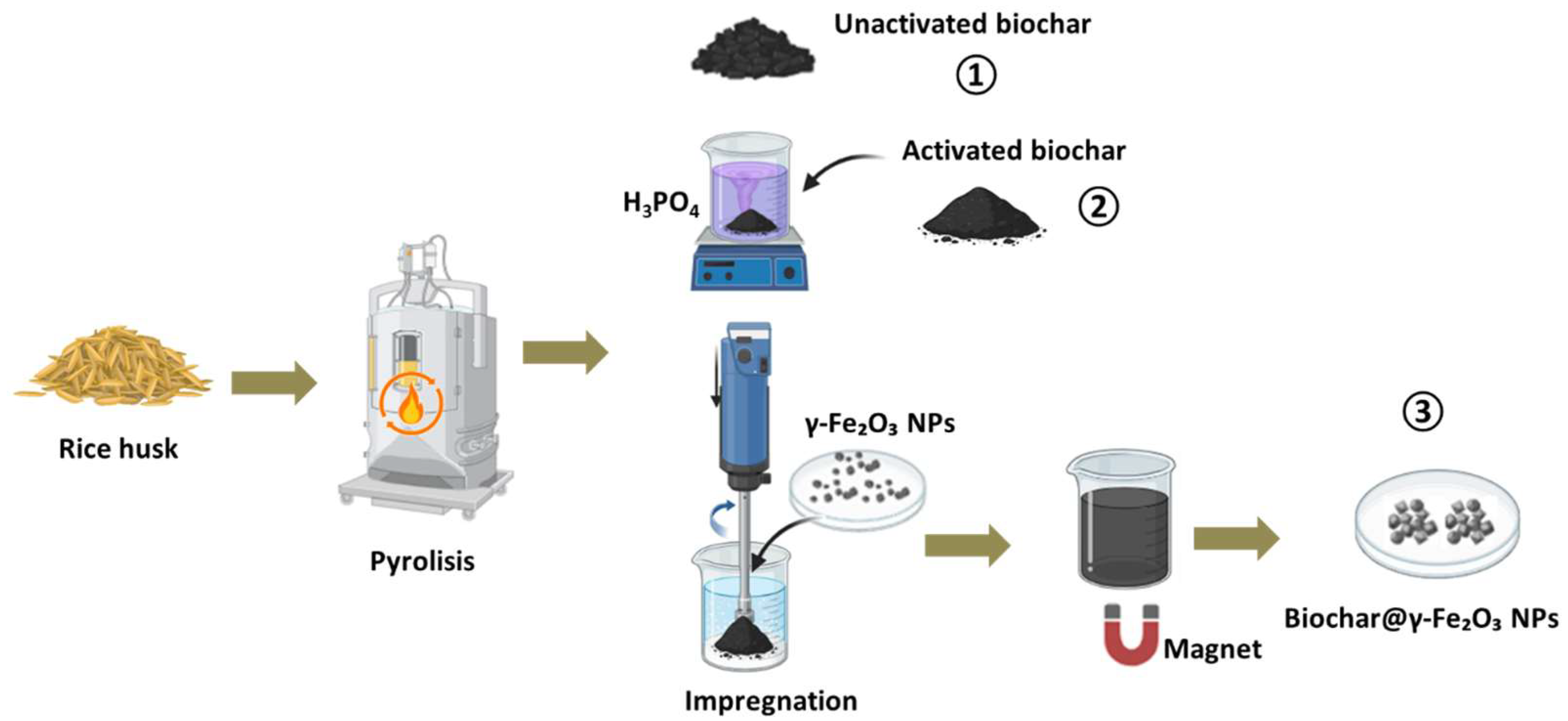
2.1. Production of Biochar from Rice Husk
2.2. Preparation of Activated Biochar from Rice Husk
2.3. Obtaining Biochar@γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles
2.4. Characterization of the Prepared Biochars
2.5. Batch Experiments
2.6. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm
3. Results
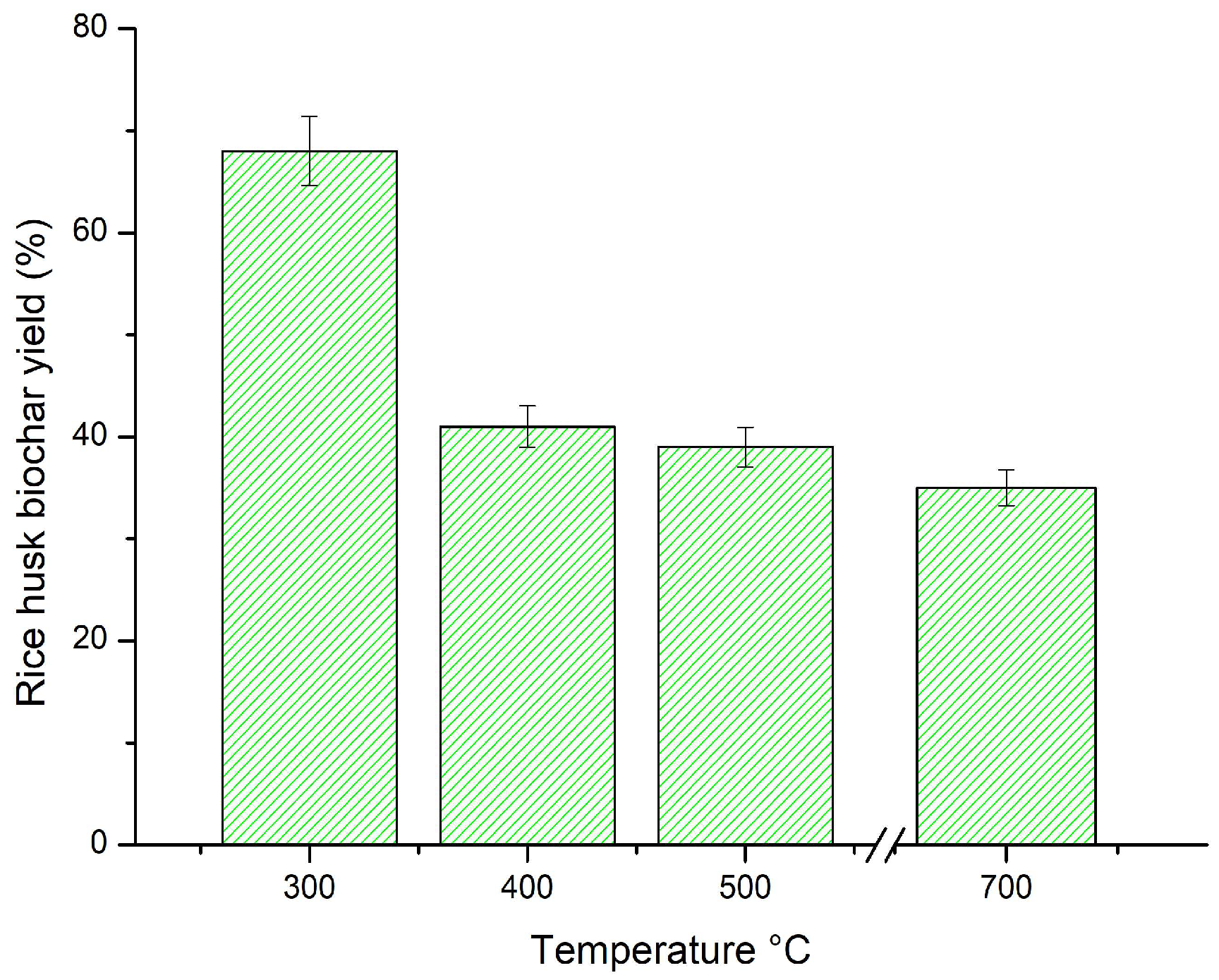
3.1. Biochar Yield (%)
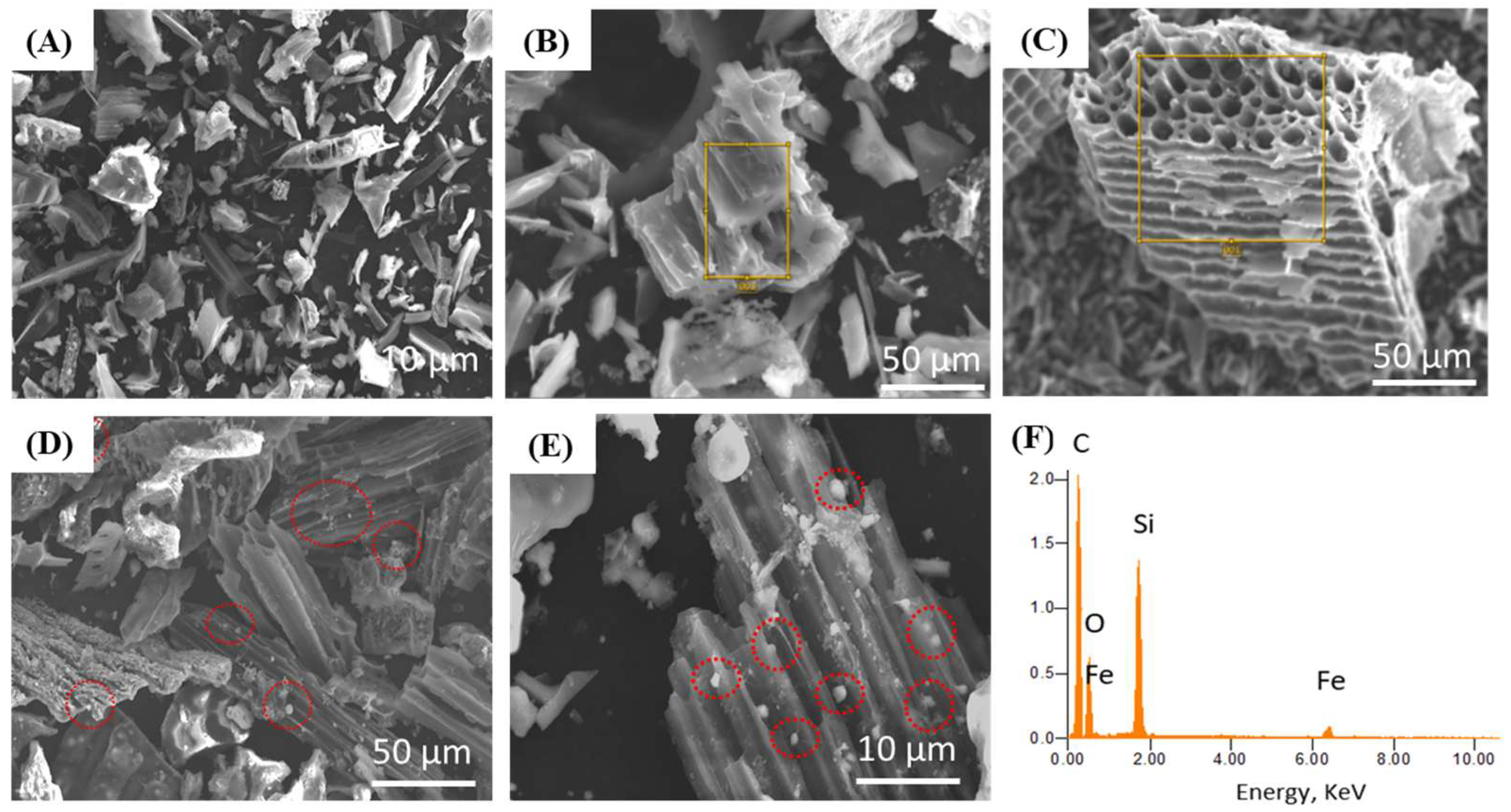
3.2. Characterization of Unactivated Biochar, Acid-Activated Biochar, and Biochar@γ-Fe2O3 NPs
3.3. Optimization of Extraction Parameters
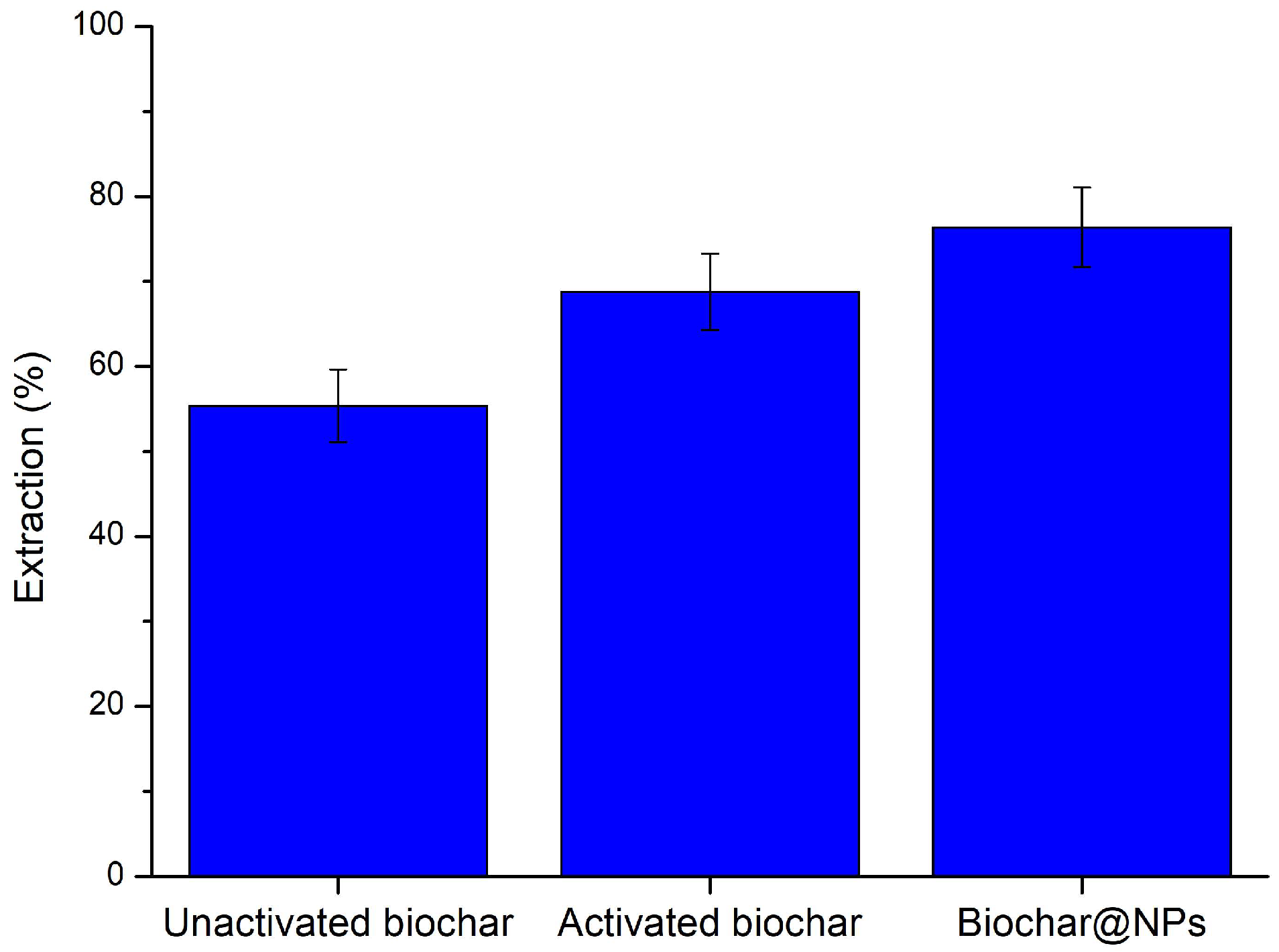
3.3.1. Selection of the Biochar for Removal Dyes
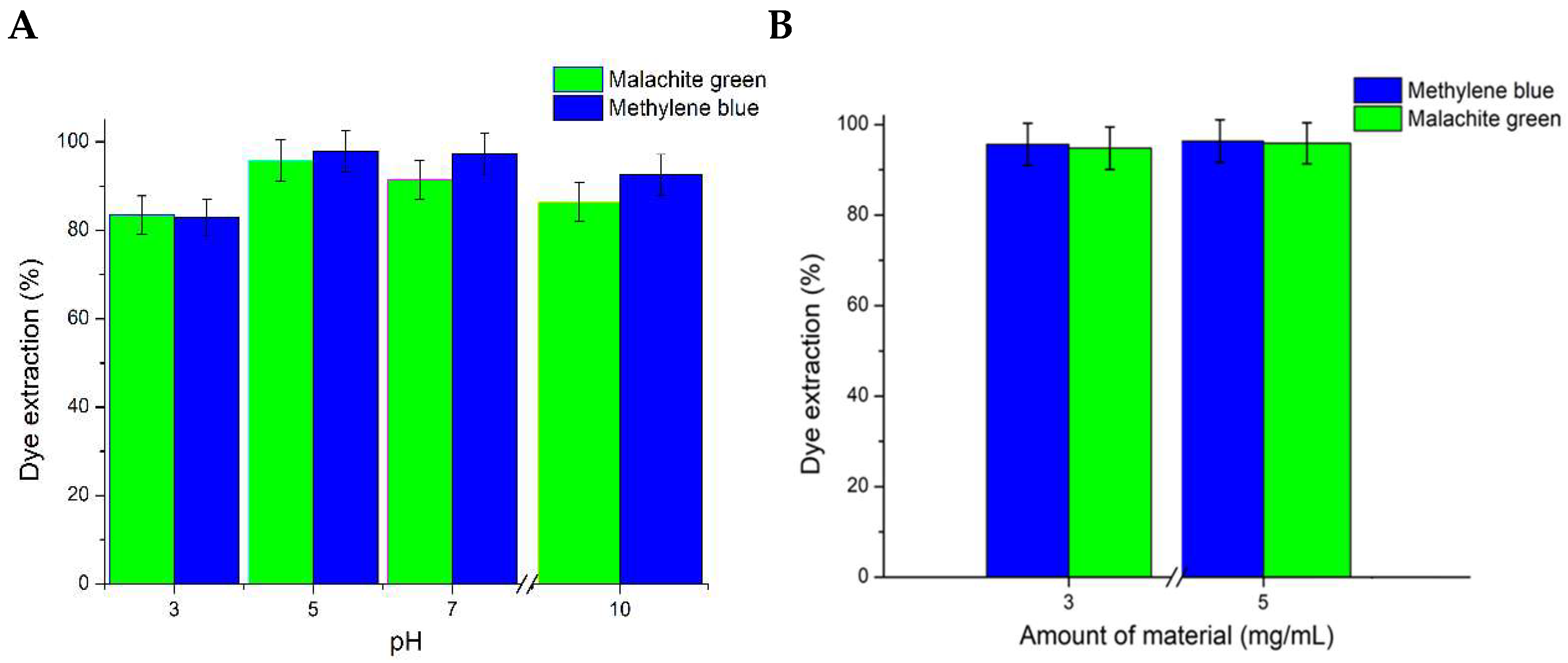
3.3.2. Effect of pH and Biochar@γ-Fe2O3 NPs’ Dosage on Dye Adsorption Capacity
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
3.5. Adsorption Isotherm Modeling
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism
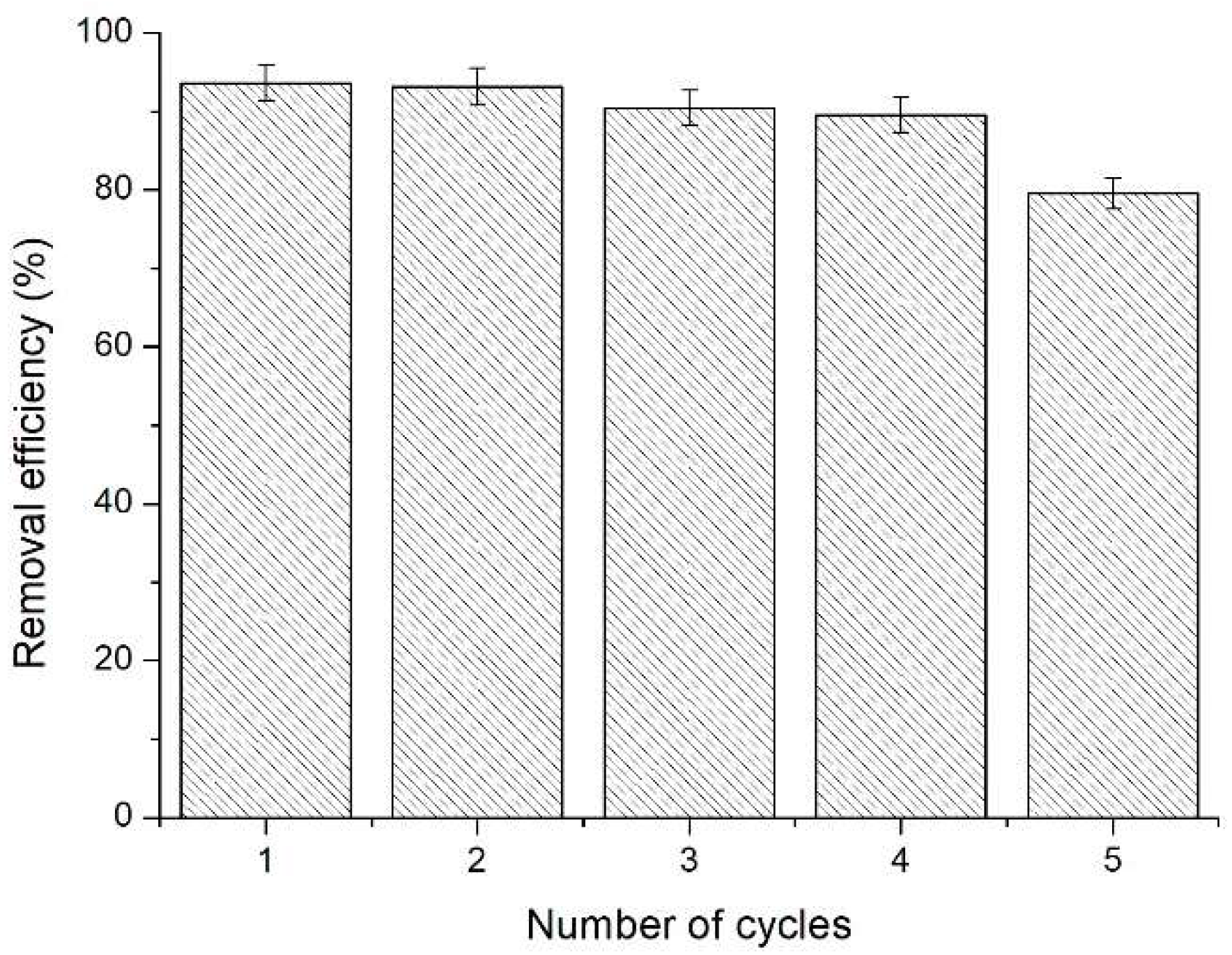
3.7. Reusability of the Adsorbent
3.8. Comparison with Other Metholodogies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashemi, E.; Norouzi, M.M.; Sadeghi-Kiakhani, M. Magnetic Biochar as a Revolutionizing Approach for Diverse Dye Pollutants Elimination: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rápó, E.; Tonk, S. Factors Affecting Synthetic Dye Adsorption; Desorption Studies: A Review of Results from the Last Five Years (2017–2021). Molecules 2021, 26, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karce, H.E.; Boumessaidia, S.; Bahloul, A.; Lal, B.; Saravanan, A.; Ouakouak, A.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Sridevi, C.; Prakash, C. Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue by a Biochar from Neem Tree Shell Wastes Using Adsorption Technology. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathy, A.; Krishnamoorthy, N.; Chang, S.X.; Paramasivan, B. Malachite Green Removal Using Algal Biochar and Its Composites with Kombucha SCOBY: An Integrated Biosorption and Phycoremediation Approach. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 30, 101880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Bagotia, N.; Yadav, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, S. Adsorptive Studies on the Removal of Dyes from Single and Binary Systems Using Saccharum Munja Plant-Based Novel Functionalized CNT Composites. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedher, M.; Mosaad, M.; El-Etriby, H. Treatment of Colored Wastewater from Textile Industry Using Electrocoagulation Process. Mansoura Eng. J. 2020, 42, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almhana, N.M.; Al-Najjar, S.Z.; Naser, Z.A.; Al-Sharify, Z.T.; Nail, T.H. Photocatalytic Degradation of Textile Dye from Wastewater by Using ZnS/TiO2 Nanocomposites Material. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Akinnawo, S.O.; Adebusuyi, T.A.; Ajala, O.A.; Adegoke, R.O.; Maxakato, N.W.; Bello, O.S. Modified Biomass Adsorbents for Removal of Organic Pollutants: A Review of Batch and Optimization Studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 11615–11644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, K. Efficient Removal of Both Heavy Metal Ion and Dyes from Wastewater Using Magnetic Response Adsorbent of Block Polymer Brush-Grafted N-Doped Biochar. Chemosphere 2023, 340, 139811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavali, M.; Libardi Junior, N.; de Sena, J.D.; Woiciechowski, A.L.; Soccol, C.R.; Belli Filho, P.; Bayard, R.; Benbelkacem, H.; de Castilhos Junior, A.B. A Review on Hydrothermal Carbonization of Potential Biomass Wastes, Characterization and Environmental Applications of Hydrochar, and Biorefinery Perspectives of the Process. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Karam, D.; Nagabovanalli, P.; Sundara Rajoo, K.; Fauziah Ishak, C.; Abdu, A.; Rosli, Z.; Melissa Muharam, F.; Zulperi, D. An Overview on the Preparation of Rice Husk Biochar, Factors Affecting Its Properties, and Its Agriculture Application. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2022, 21, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, J.; Samsuri, W.A.; Othman, R.; Hamdani, M.S.A. Evaluation of Adsorptive Characteristics of Cow Dung and Rice Husk Ash for Removal of Aqueous Glyphosate and Aminomethylphoshonic Acid. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, F.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Tan, X.; Duan, A. Lignocellulosic Biomass Carbonization for Biochar Production and Characterization of Biochar Reactivity. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mashad, H.M.; Edalati, A.; Zhang, R.; Jenkins, B.M. Production and Characterization of Biochar from Almond Shells. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, S.; Patil, P.; Jadhav, J. Recent Advances in Biochar Technology for Textile Dyes Wastewater Remediation: A Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, M.; Hamda, A.S.; Abo, L.D.; Daba, B.J.; Venkatesa Prabhu, S.; Rangaraju, M.; Jabesa, A.; Periyasamy, S.; Suresh, S.; Baskar, G. Comprehensive Review on Lignocellulosic Biomass Derived Biochar Production, Characterization, Utilization and Applications. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Feng, Q.; Lee, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, M. Biochar Supported Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron-Calcium Alginate Composite for Simultaneous Removal of Mn(II) and Cr(VI) from Wastewater: Sorption Performance and Mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semida, W.M.; Beheiry, H.R.; Sétamou, M.; Simpson, C.R.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Rady, M.M.; Nelson, S.D. Biochar Implications for Sustainable Agriculture and Environment: A Review. South Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 127, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güleç, F.; Williams, O.; Kostas, E.T.; Samson, A.; Stevens, L.A.; Lester, E. A Comprehensive Comparative Study on Methylene Blue Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Biochars Produced from Rapeseed, Whitewood, and Seaweed via Different Thermal Conversion Technologies. Fuel 2022, 330, 125428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekanye, T.; Dada, O.; Kolapo, J. Pyrolysis of Maize Cob at Different Temperatures for Biochar Production: Proximate, Ultimate and Spectroscopic Characterisation. Res. Agric. Eng. 2022, 68, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonappan, L.; Rouissi, T.; Das, R.K.; Brar, S.K.; Ramirez, A.A.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Valero, J.R. Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Biochar Microparticles Derived from Different Waste Materials. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, G.; Gangola, S.; Dhasmana, A.; Rajput, V.; Gupta, S.; Malik, S.; Slama, P. Nano-Biochar: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities for Sustainable Environmental Remediation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1214870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Tu, G.; Ying, G.; Fang, Z.; Tsang, E.P. Magnetic Biochar Derived from Rice Straw and Stainless Steel Pickling Waste Liquor for Highly Efficient Adsorption of Crystal Violet. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, A.I.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Mehta, N.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Al-Fatesh, A.S.; Rooney, D.W. Facile Synthesis and Life Cycle Assessment of Highly Active Magnetic Sorbent Composite Derived from Mixed Plastic and Biomass Waste for Water Remediation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 12433–12447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.F.; López, J.E.; Saldarriaga, J.F. Use of Activated Rice Husk Biochar for the Removal of Metals and Microorganisms from Treated Leachates from Landfills. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 3414–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, A.; Layne, C.A.; Perez, F.; Hassan, E.B.; Pittman, C.U.; Mlsna, T.E. KOH-Activated High Surface Area Douglas Fir Biochar for Adsorbing Aqueous Cr(VI), Pb(II) and Cd(II). Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Zhou, L.; Cai, D.; Ren, C. H3PO4 Activated Biochars Derived from Different Agricultural Biomasses for the Removal of Ciprofloxacin from Aqueous Solution. Particuology 2023, 75, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; H’ng, P.S.; Chin, K.L.; Paridah, M.T.; Rashid, U.; Go, W.Z. Characterization of Bioadsorbent Produced Using Incorporated Treatment of Chemical and Carbonization Procedures. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesh, N.; Sundaram, B. Adsorption of Pollutants from Wastewater by Biochar: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 9, 100226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Ghorbani, M.; Rezaei-Rashti, M.; Abrishamkesh, S.; Amirahmadi, E.; Chengrong, C.; Gorji, M. Application of Rice Husk Biochar for Achieving Sustainable Agriculture and Environment. Rice Sci. 2021, 28, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Xu, J.; Wei, X.; Shi, L.; Sumita; Li, C.; Lichtfouse, E. Performance and Mechanism of Fe3O4 Loaded Biochar Activating Persulfate to Degrade Acid Orange 7. Water 2023, 15, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Qin, J.; Wu, Y.; Feng, F. Tetracycline Adsorption on Magnetic Sludge Biochar: Size Effect of the Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 210805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, J.T.; Nunes, K.G.P.; Cardoso Estumano, D.; Féris, L.A. Applying the Bayesian Technique, Statistical Analysis, and the Maximum Adsorption Capacity in a Deterministic Way for Caffeine Removal by Adsorption: Kinetic and Isotherm Modeling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 1530–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, D.; Li, X.; Xiang, L.; Tu, S. Review on Rice Husk Biochar as an Adsorbent for Soil and Water Remediation. Plants 2023, 12, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, R. Effects of Pyrolysis Temperature and Heating Time on Biochar Obtained from the Pyrolysis of Straw and Lignosulfonate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 176, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidayat; Rahmat, A.; Nissa, R.C.; Sukamto; Nuraini, L.; Nurtanto, M.; Ramadhani, W.S. Analysis of Rice Husk Biochar Characteristics under Different Pyrolysis Temperature. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1201, 012095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severo, F.F.; da Silva, L.S.; Moscôso, J.S.C.; Sarfaraz, Q.; Rodrigues Júnior, L.F.; Lopes, A.F.; Marzari, L.B.; Molin, G.D. Chemical and Physical Characterization of Rice Husk Biochar and Ashes and Their Iron Adsorption Capacity. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Peng, C.; Ali, I.; Li, J.; Khan, Z.M.; Sultan, M.; Naz, I. Synthesis of Rice Husk-Derived Magnetic Biochar Through Liquefaction to Adsorb Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, N.; Nizamuddin, S.; Griffin, G.; Selvakannan, P.; Mubarak, N.M.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Synthesis and Characterization of Rice Husk Biochar via Hydrothermal Carbonization for Wastewater Treatment and Biofuel Production. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, J.; Wasag, H. Biochar: A Low-Cost Adsorbent of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1736, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palniandy, L.K.; Yoon, L.W.; Wong, W.Y.; Yong, S.T.; Pang, M.M. Application of Biochar Derived from Different Types of Biomass and Treatment Methods as a Fuel Source for Direct Carbon Fuel Cells. Energies 2019, 12, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.A.M.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Moustafa, H.M. Comparing Specific Capacitance in Rice Husk-Derived Activated Carbon through Phosphoric Acid and Potassium Hydroxide Activation Order Variations. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, R.; Zhao, J.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q. Characterization of H3PO4-Treated Rice Husk Adsorbent and Adsorption of Copper(II) from Aqueous Solution. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 496878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelkheir, S.S.; Ibrahim, H.A.H.; Beltagy, E.A. Functionalized Maghemite Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (γ-Fe2O3-SPIONs)-Amylase Enzyme Hybrid in Biofuel Production. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, H.; Mishra, S.B. Gum Ghatti and Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles Based Nanocomposites for the Effective Adsorption of Rhodamine B. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Kan, H.; Zheng, Y. Preparation of Acid- And Alkali-Modified Biochar for Removal of Methylene Blue Pigment. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30906–30922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Khan, N.; Giri, B.S.; Chowdhary, P.; Chaturvedi, P. Removal of Methylene Blue Dye Using Rice Husk, Cow Dung and Sludge Biochar: Characterization, Application, and Kinetic Studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.; Uzair, B.; Ali, M.I.; Anbreen, S.; Umber, F.; Khalid, M.; Aljabali, A.A.; Mishra, Y.; Mishra, V.; Serrano-Aroca, Á.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanobiochar from Rice Husk Biochar for the Removal of Safranin and Malachite Green from Water. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 116909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Josephraj, J.; Thillainayagam, B.P.; Ravindiran, G. Evaluation of the Adsorptive Removal of Cationic Dyes by Greening Biochar Derived from Agricultural Bio-Waste of Rice Husk. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 4047–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, W.; Sulistyaningsih, T.; Kusumastuti, E.; Thomas, G.Y.R.S.; Kusnadi, R.Y. Thermal Conversion of Pineapple Crown Leaf Waste to Magnetized Activated Carbon for Dye Removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 287, 121426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegan, J.; Praveen, S.; Bhagavathi Pushpa, T.; Gokulan, R. Sorption Kinetics and Isotherm Studies of Cationic Dyes Using Groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea) Shell Derived Biochar a Low-Cost Adsorbent. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 1925–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhan, L.; Sun, G.; Luo, L. On the Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanism of Methylene Blue by Ball Mill Modified Biochar. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeghioud, H.; Mouhamadou, S. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Dye Removal Characteristics of Magnetic Biochar Derived from Sewage Sludge: Isotherm, Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Mechanism. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Wang, Y.F.; You, S.J.; Chao, H.P. Insights into the Mechanism of Cationic Dye Adsorption on Activated Charcoal: The Importance of π–π Interactions. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 107, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Niu, Y.; Shen, T.; Dong, K.; Wang, D. Magnetic Biochar Prepared by a Dry Process for the Removal of Sulfonamides Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 400, 124576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabrpisheh, Z.; Lemraski, E.G.; Abbasi, Z.; Tahmasebi, Z. Methylene Blue Adsorption on Modified Biochar with Magnetic Nanoparticles and Humic Acid Coating. Phys. Chem. Res. 2024, 12, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, D.; Sharma, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Gupta, K.; Sengupta, S.; Shang, J. Study of Methylene Blue Dye Removal Using Biochar Derived from Leaf and Stem of Lantana camara L. Carbon Res. 2024, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohdee, K.; Semmad, S.; Jotisankasa, A.; Jongsomjit, B.; Somsiripan, T.; Asadullah. Sustainable Adsorption of Methylene Blue onto Biochar-Based Adsorbents Derived from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Branch: Performance and Reusability Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 25, 101755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Liu, H. Dyeing Sludge-Derived Biochar for Efficient Removal of Malachite Green from Dyeing Wastewater. Water Emerg. Contam. Nanoplastics 2024, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri, A.F.; Siregar, P.M.S.B.N.; Palapa, N.R.; Mohadi, R.; Mardiyanto, M.; Lesbani, A. Mg-Al/Biochar Composite with Stable Structure for Malachite Green Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2021, 16, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| pH | C (%) | N (%) | P (%) | S (%) | K2O (%) | CaO (%) | MgO (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.0 | 29.6 | 0.2 | 2.9 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 4.0 | 0.6 |
| Sample | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Size DBJH (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RHB300 | 17.54 | 0.012 | 4.31 |
| RHB500 | 88.21 | 0.029 | 5.04 |
| Activated RHB | 207. 44 | 0.047 | 6.84 |
| Parameter | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Intra-Particle Diffusion | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mg/g) | K1 | R2 | Qe (mg/g) | K2 | R2 | Kipd | C | R2 | |
| Biochar@γ-Fe2O3 NPs | 6.01 | 0.091 | 0.96 | 6.67 | 0.018 | 0.99 | 0.51 | 1.39 | 0.82 |
| Adsorption Isotherm | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir isotherm | R2 | 0.93 |
| KL | 4.00 | |
| Qm | 11.45 | |
| Freundlich isotherm | R2 | 0.40 |
| KF | 7.10 | |
| nF | 6.02 | |
| Temkin isotherm | R2 | 0.78 |
| B | 1.52 | |
| Kt | 139.06 | |
| Sips isotherm | R2 | 0.99 |
| Qs | 10.37 | |
| Ks | 19.62 | |
| n | 2.46 |
| Adsorbent | Pyrolysis Conditions 1 | Dye | Removal Efficiency (%) | Reusability | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar from oak forests infused with Fe2O3 NPs and humic acid | T = 300–600 °C, RT: 3 h | Methylene blue | 97 | — | [56] |
| Biochar from leaf and stem of Lantana camara L. | T = 600 °C | Methylene blue | 69.1 | — | [57] |
| Untreated biochar from palm oil empty fruit branches and biochar activated with KOH | T = 450 °C RT = 90 min | Methylene blue | <90 | 4 cycles | [58] |
| Nanobiochar from rice husk | T = 600 °C RT = 2 h | Malachite green | 87.5 | — | [48] |
| Sludge biochar modified with ZnCl2 | T = 700–900 °C, HR = 5 °C/min, RT: 1–2 h | Malachite green | 99.1 | 2 cycles | [59] |
| Mg-Al/biochar from rice husk | - | Malachite green | 66.7 | 1 cycle | [60] |
| Rice husk-derived biochar with γ-Fe2O3 NPs | T = 500 °C, HR = 10 °C/min. | Malachite green and methylene blue | 95–97 | 4 cycles | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barzallo, D.; Carrasquero, E.; Andrade, M.; Heredia Jara, D.A.; Palmay, P. Preparation and Characterization of Unactivated, Activated, and γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticle-Functionalized Biochar from Rice Husk via Pyrolysis for Dyes Removal in Aqueous Samples: Comparison, Performance, and Mechanism. ChemEngineering 2025, 9, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9020030
Barzallo D, Carrasquero E, Andrade M, Heredia Jara DA, Palmay P. Preparation and Characterization of Unactivated, Activated, and γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticle-Functionalized Biochar from Rice Husk via Pyrolysis for Dyes Removal in Aqueous Samples: Comparison, Performance, and Mechanism. ChemEngineering. 2025; 9(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarzallo, Diego, Edwuin Carrasquero, Mónica Andrade, Daniel Alejandro Heredia Jara, and Paúl Palmay. 2025. "Preparation and Characterization of Unactivated, Activated, and γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticle-Functionalized Biochar from Rice Husk via Pyrolysis for Dyes Removal in Aqueous Samples: Comparison, Performance, and Mechanism" ChemEngineering 9, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9020030
APA StyleBarzallo, D., Carrasquero, E., Andrade, M., Heredia Jara, D. A., & Palmay, P. (2025). Preparation and Characterization of Unactivated, Activated, and γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticle-Functionalized Biochar from Rice Husk via Pyrolysis for Dyes Removal in Aqueous Samples: Comparison, Performance, and Mechanism. ChemEngineering, 9(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9020030






