Kinetic Study of Acid Hydrolysis of the Glucose Obtained from Banana Plant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
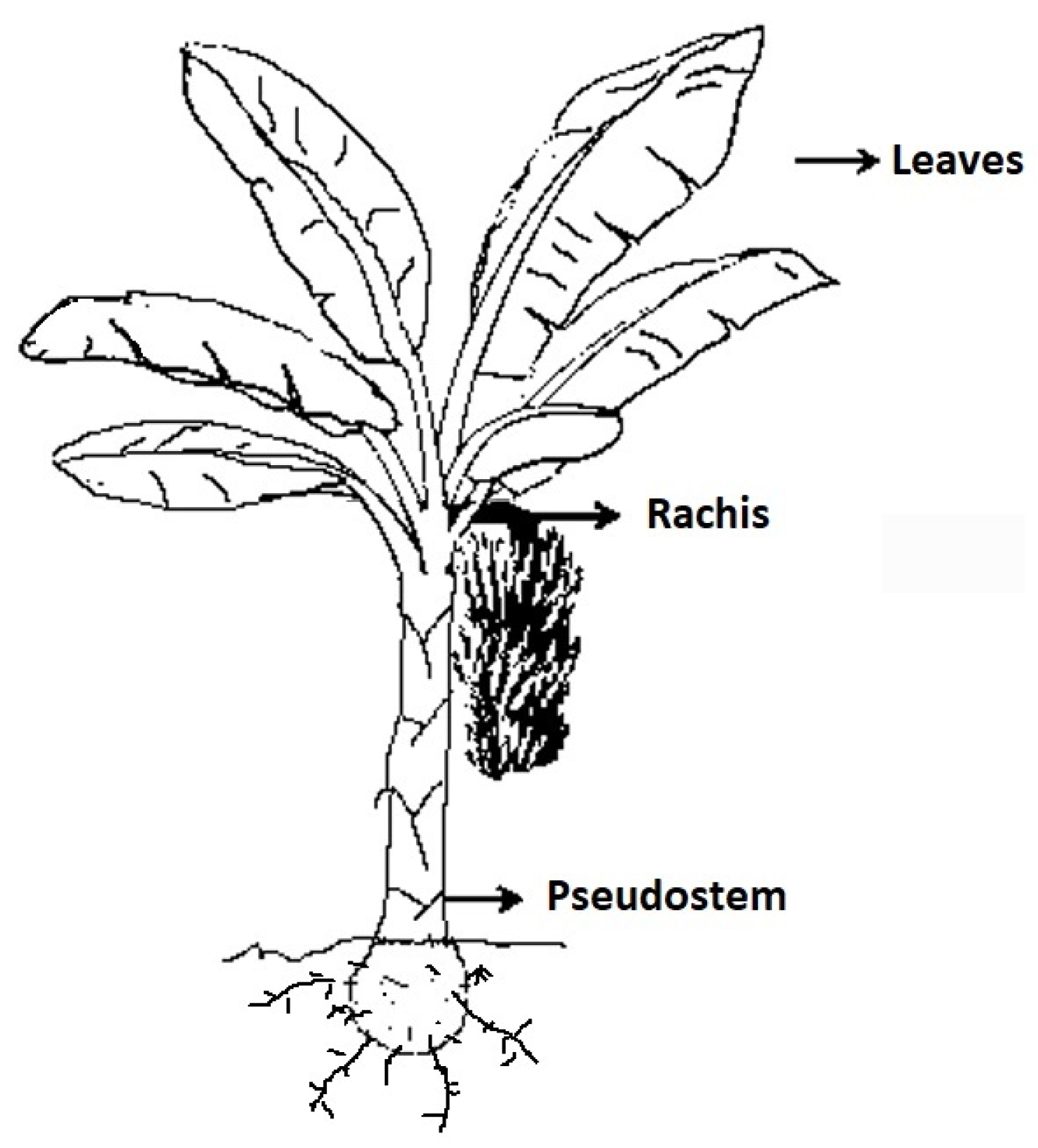
2.2. Collection and Preparation of Biomass
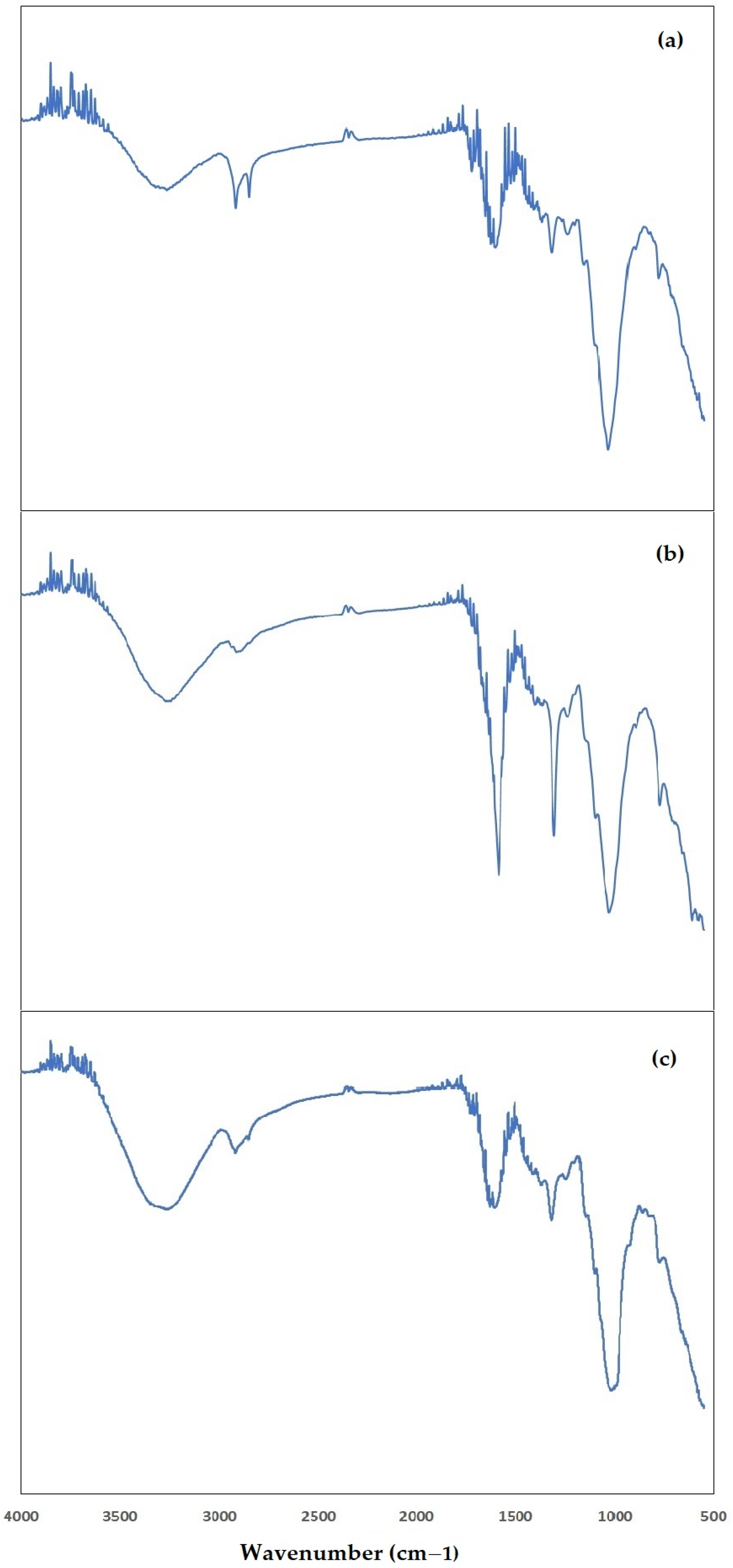
2.3. Structural Characterization
2.4. Acid Hydrolysis Process
2.5. Chromatographic Analysis
2.6. Kinetic Model Development
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biomass Characterization
3.2. Acid Hydrolysis
3.3. Reaction Kinetics
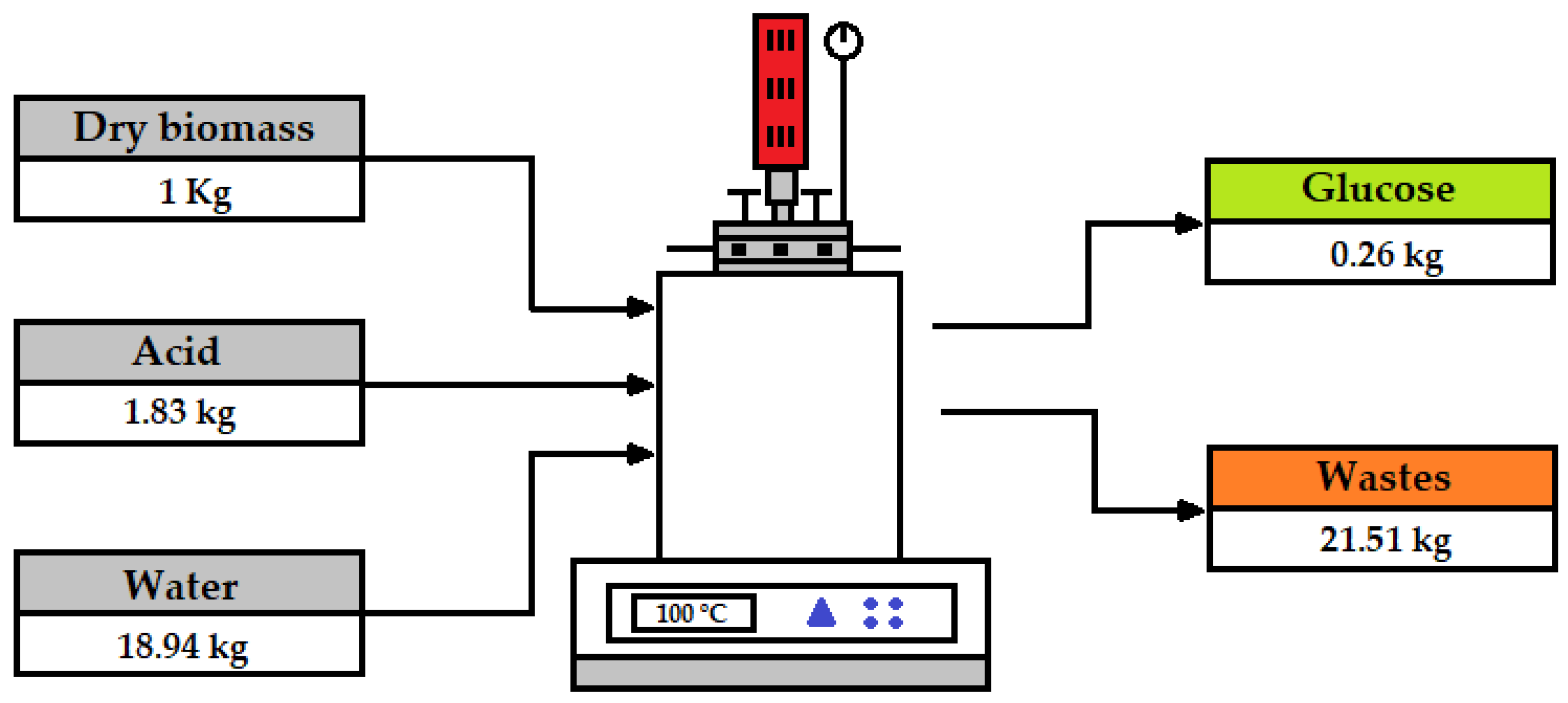
3.4. Material Balance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhushan, S.; Rana, M.S.; Mamta; Nandan, N.; Prajapati, S.K. Energy harnessing from banana plant wastes: A review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Ulloa, J.A.; Abril-González, M.F.; Pelaez-Samaniego, M.R.; Zalamea-Piedra, T.S. Biomass yield and carbon abatement potential of banana crops (Musa spp.) in Ecuador. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18741–18753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encuesta de Superficie y Producción Agropecuaria Continua-2020. Available online: https://www.ecuadorencifras.gob.ec/encuesta-de-superficie-y-produccion-agropecuaria-continua-2020/ (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- INEC-ESPAC. Estadísticas Agropecuarias, Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos. 2022. Available online: https://www.ecuadorencifras.gob.ec/estadisticas-agropecuarias-2/ (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Atlas Bioenergetico Del Ecuador. 2014. Available online: http://www.mediafire.com/file/17dz5lbnwloiea6/ATLAS_BIOENERGETICO_DEL_ECUADOR.zip/file (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- Kumar, K.A.; Subalakshmi, R.; Jayanthi, M.; Abirami, G.; Vijayan, D.; Prabhu, S.V.; Baskaran, L. Production and characterization of enriched vermicompost from banana leaf biomass waste activated by biochar integration. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, A.R. Aprovechamiento de la biomasa como fuente de energía alternativa a los combustibles fósiles. Cienc. Exact. Fís. Nat. 2010, 104, 331–345. [Google Scholar]
- Acevedo, S.A.; Carrillo, J.D.; Flórez-López, E.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. Recovery of Banana Waste-Loss from Production and Processing: A Contribution to a Circular Economy. Molecules 2021, 26, 5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondo-Gómez, C.; Quesada, M.R.; Astúa, S.V.; Zamora, J.P.M.; Lopretti, M.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R. Biorefinery of Biomass of Agro-Industrial Banana Waste to Obtain High-Value Biopolymers. Molecules 2020, 25, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.; Baranwal, M.; Saxena, S.; Reddy, M.S. Utilization of banana waste as a resource material for biofuels and other value-added products. Biomass-Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, H.L.; Wahab, R.A. Towards an eco-friendly deconstruction of agro-industrial biomass and preparation of renewable cellulose nanomaterials: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1414–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Iqbal, T.; Khan, M.J. Recent advances in the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and value-added products. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 20, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Lei, F.; Li, P.; Jiang, J. Lignocellulosic biomass to biofuels and biochemicals: A comprehensive review with a focus on ethanol organosolv pretreatment technology. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 115, 2683–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursi, A. A review on biomass: Importance, chemistry, classification, and conversion. Biofuel Res. J. 2019, 6, 962–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loow, Y.-L.; Wu, T.Y.; Jahim, J.M.; Mohammad, A.W.; Teoh, W.H. Typical conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into reducing sugars using dilute acid hydrolysis and alkaline pretreatment. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1491–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.; Ummalyma, S.B.; Okram, A.K.; Pandey, A.; Sankar, M.; Sukumaran, R.K. Effect of dilute acid pretreatment of wild rice grass (Zizania latifolia) from Loktak Lake for enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nizetic, S.; Ong, H.C.; Chong, C.T.; Atabani, A.; Pham, V.V. Acid-based lignocellulosic biomass biorefinery for bioenergy production: Advantages, application constraints, and perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, X.; Shen, G.; Chen, S.; Yu, J.; Zhai, R.; Xu, Z.; Jin, M. Densifying lignocellulosic biomass with sulfuric acid provides a durable feedstock with high digestibility and high fermentability for cellulosic ethanol production. Renew. Energy 2022, 182, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Bhat, N.S. Chemocatalytic value addition of glucose without carbon–carbon bond cleavage/formation reactions: An overview. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 4891–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Rahim, S.K.E.; Kasi, H.A.; Abdullah, N.S. Fermentable Sugar via Diluted Acid Hydrolysis of Sugarcane Bagasse. Key Eng. Mater. 2022, 908, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizazu, B.Z.; Moholkar, V.S. Kinetic and thermodynamic analysis of dilute acid hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, N.S.H.C.; Salimi, M.N. Glucose Production from Sugarcane Bagasse by Two Stages Chemical Pretreatment & Hydrolysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 743, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, N.; Razali, A.N.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Chowdhury, T.; Chowdhury, H.; Ong, H.C.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Silitonga, A.S. Experimental Investigation, Techno-Economic Analysis and Environmental Impact of Bioethanol Production from Banana Stem. Energies 2019, 12, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, A.B.; Ballesteros, I.; Ballesteros, M. The potential of agricultural banana waste for bioethanol production. Fuel 2018, 213, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Luke, A.; de Sonora, U.; Herrera-Urbina, J.; Martínez-Tellez, M.; Mártin-García, A. Acid hydrolysis of hemicellulose from Ipomoea arborescens: Kinetics of xylose production. Rev. Mex. De Ing. Química 2022, 21, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhao, X. Conversion of lignocellulose to biofuels and chemicals via sugar platform: An updated review on chemistry and mechanisms of acid hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeman, J.F. Kinetics of Wood Saccharification-Hydrolysis of Cellulose and Decomposition of Sugars in Dilute Acid at High Temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1945, 37, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, M.S. Biofuel Production: Recent Developments and Prospects; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Lu, M.; Guo, X.; Han, L. A novel diffusion–biphasic hydrolysis coupled kinetic model for dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómora-Hernández, J.; Carreño-De-León, M.D.C.; Flores-Alamo, N.; Hernández-Berriel, M.D.C.; Fernández-Valverde, S. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of corncob hydrolysis in phosphoric acid with a low yield of bacterial inhibitors. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 143, 105830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzoh, B.N.; Onyelucheya, O.E.; Obijiaku, J.C. Kinetic Study of Acid Hydrolysis of Corn Cob to Xylose. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 2539–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, M.; Asiedu, N.Y.; Neba, F.A.; Amaniampong, P.N.; Boakye, P.; Addo, A. Modeling, optimization and kinetic analysis of the hydrolysis process of waste cocoa pod husk to reducing sugars. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TAPPI: Technical Association of The Pulp and Paper Industry. Acid-insoluble lignin in wood and pulp (Reaffirmation of T 222 om-02). Available online: https://www.tappi.org/content/sarg/t222.pdf/ (accessed on 16 June 2006).
- ASTM D1107-21; Standard Test Method for Ethanol-Toluene Solubility of Wood. ASTM Philadelphia: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM D1104-56; Method of Test for Holocellulose in Wood. ASTM Philadelphia: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1956.
- TAPPI (Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry). TAPPI test methods, T 212 om-98, One Percent Sodium Hydroxide Solubility of Wood and Pulp; TAPPI Press: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Salto, A.M.V.; González, M.F.A.; Piedra, T.S.Z.; Vélez, V.P.P. Mini-Revisión: Aplicación de líquidos iónicos en hidrólisis ácida de material lignocelulósico para la obtención de azúcares. Cienc. EN Desarro. 2021, 12, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, N.; Sheridan, C.; Van Dyk, L.; Harding, K.G. Modelling of low temperature dilute sulfuric acid pre-treatment of South African grass. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2018, 4, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.G.; dos Santos, R.V.; Barreto, E.D.S.; Baffi, M.A.; Gurgel, L.V.A.; Baêta, B.E.L.; Pasquini, D. Pretreated Sugarcane Bagasse with Citric Acid Applied in Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Ind. Biotechnol. 2020, 16, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, M.M.; San, C.P.; Atan, N.A. Combustion Performance of Biomass Composite Briquette from Rice Husk and Banana Residue. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2019, 9, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, M.B.; Jumpah, H.; Boadi, N.O.; Awudza, J.A. Assessment of quantities and composition of corn stover in Ghana and their conversion into bioethanol. Sci. Afr. 2021, 12, e00731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.H.; Linh, V.N.; Dung, L.D.; Ha, V.T.T. Physico-chemical characterization of forest and agricultural residues for energy conversion processes. Vietnam. J. Chem. 2020, 58, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.F.; Mohamed, M.; Lu, N.A.L.M.I.; Sarman, N.S.P.; Samsudin, S.N.S. Computer-Assisted Analysis of Fourier Transform Infrared (Ftir) Spectra for Characterization of Various Treated and Untreated Agriculture Biomass. Bioresources 2012, 7, 5367–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Negi, Y.; Choudhary, V.; Bhardwaj, N. Characterization of Cellulose Nanocrystals Produced by Acid-Hydrolysis from Sugarcane Bagasse as Agro-Waste. J. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Wong, Y.C.; Veloo, K.V. Sugarcane bagasse powder as biosorbent for reactive red 120 removals from aqueous solution. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 140, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabanko, N.; Baryshnikov, S.V.; Kazachenko, A.S.; Miroshnikova, A.; Skripnikov, A.M.; Lavrenov, A.V.; Taran, O.P.; Kuznetsov, B.N. Hydrothermal hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose from birch wood catalyzed by Al2O3-B2O3 mixed oxides. Wood Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 437–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Jiang, K.; Liu, X.; Han, D.; Zhang, Q. Review on development of ionic liquids in lignocellulosic biomass refining. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 359, 119326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Biomass | Hydrolysis Process Conditions [Temperature, Time and H2SO4 Concentration] | Monosaccharide Performance, gL−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sugarcane bagasse | 90 °C, 3 h, 4% w/v | Fermentable sugars = 10.26 | [20] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | 130 °C, 0.25 h, 2% v/v | Xylose = 9.26 | [21] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | 90 °C, 1 h, 3% v/v | Fermentable sugars = 0.32–5 | [22] |
| Banana steam | 90 °C, 1.5 h, 0.5 M | Glucose = 5.61 | [23] |
| Banana pseudostem | 177 °C, 5 min, 2.2% | Glucose = 38.90 | [24] |
| Banana rachis | 198 °C, 5 min, 1.5% | Glucose = 3.40 | [24] |
| Biomass | Insoluble Lignin, % | Holocellulose, % | Alpha Cellulose % | Hemicellulose, % | Calorific Value, kJKg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | 19.84 ± 0.13 | 66.64 ± 0.18 | 36.98 ± 0.39 | 29.66 ± 0.20 | 17,369.0 ± 65.05 |
| Pseudostem | 14.12 ± 0.10 | 71.75 ± 0.06 | 39.25 ± 0.05 | 32.496 ± 0.01 | 12,457.5 ± 71.42 |
| Rachis | 7.67 ± 0.01 | 55.63 ± 0.29 | 31.40 ± 0.52 | 24.23 ± 0.52 | 12,212.5 ± 6.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abril-González, M.; Vele-Salto, A.; Pinos-Vélez, V. Kinetic Study of Acid Hydrolysis of the Glucose Obtained from Banana Plant. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7020039
Abril-González M, Vele-Salto A, Pinos-Vélez V. Kinetic Study of Acid Hydrolysis of the Glucose Obtained from Banana Plant. ChemEngineering. 2023; 7(2):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7020039
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbril-González, Mónica, Angélica Vele-Salto, and Verónica Pinos-Vélez. 2023. "Kinetic Study of Acid Hydrolysis of the Glucose Obtained from Banana Plant" ChemEngineering 7, no. 2: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7020039
APA StyleAbril-González, M., Vele-Salto, A., & Pinos-Vélez, V. (2023). Kinetic Study of Acid Hydrolysis of the Glucose Obtained from Banana Plant. ChemEngineering, 7(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7020039









