Abstract
Five alkali-activated analcime (ANA) sorbents (ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, ANA 3, ANA-MK 4, and ANA-MK 5) were developed for ammonium (NH4+) ion removal. Acid treatment and calcination were used as pre-treatments for analcime, and metakaolin (MK) was used as a blending agent in three sorbents. Sorption experiments were performed to evaluate the effects of sorbent dosage (1–20 g L−1), initial NH4+ ion concentration (5–1000 g L−1), and contact time (1 min–24 h). ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, and ANA-MK 4 were the most efficient sorbents for NH4+ ion removal, with a maximum experimental sorption uptake of 29.79, 26.00, and 22.24 mg g−1, respectively. ANA 3 and ANA-MK 5 demonstrated lower sorption capacities at 7.18 and 12.65 mg g−1, respectively. The results for the sorption of NH4+ ions onto the alkali-activated analcime surfaces were modeled using several isotherms. The Langmuir, Freundlich, Sips, and Bi-Langmuir isotherms were the best isotherm models to represent the studied systems. The results of the kinetic studies showed the maximum NH4+ ion removal percentage of the sorbents was ~80%, except for ANA-MK 5, which had a ~70% removal. Moreover, the pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and Elovich models were applied to the experimental data. The results showed that the sorption process for ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, ANA 3, and ANA-MK 4 followed the Elovich model, whereas the pseudo-second-order model provided the best correlation for ANA-MK 5.
1. Introduction
Ammonium (NH4+) is an essential nutrient for plants, but its excessive amount in water streams may result in eutrophication in water reservoirs, such as lakes, rivers, and seas, causing undesirable effects on the environment, aquatic fauna, and humans. In protecting water resources, the effective removal of NH4+ from industrial wastewater prior to its discharge into natural water bodies is critical [1,2,3]. NH4+ pollution comes from agricultural, industrial, or municipal sources. Wastewater treatment plants also contribute to NH4+ pollution [4]. In response to this problem, many countries have established strict regulations concerning acceptable ammonia concentrations in surface waters [5]. For example, the EU urban wastewater directive has set the 15 mg/L (10,000–100,000 population equivalent) total-N limit in urban wastewater [6].
Various methods have been employed to remove nitrogen compounds from aqueous solutions. These methods include adsorption [7,8,9], air stripping [10,11], biological treatment (nitrification/denitrification process) [12,13], chemical co-precipitation [14,15], electrolysis [16,17], catalytic wet-air oxidation [18,19], ion-exchange [9,20,21] and membrane processes [22,23]. Many of these methods have several limitations, including high cost, low removal rate, high sensitivity to pH and temperature, and introduction of new pollutants. However, compared with other methods, ion exchange and adsorption techniques offer several advantages: high removal efficiency, low energy consumption, simplicity of application and operation, and environmental friendliness. These advantages render ion exchange and adsorption as competitive methods for large-scale NH4+ removal in commercial and water treatment plants [24].
Organic resins have been reported to be quite selective ion exchangers for NH4+ ion removal [25,26]. However, these materials are expensive; thus, efficient and low-cost side stream-derived sorbents must be developed. Numerous sorbents have been developed for NH4+ ion removal; these include carbon-based adsorbents [27,28,29], natural zeolites [3,30,31], clays [2,30,32], polymeric ion exchangers [21,33], hydrogels [34,35,36], industrial and agricultural wastes [37,38,39,40,41,42] and nanoparticles [43]. Among these materials, natural zeolites have been reported to be efficient sorbents for NH4+ ion removal. Removal of NH4+ ions is based on cation exchange or on adsorption in pores of aluminosilicate structures [26,31,33].
Natural zeolites are relatively cheap, easy to handle, and locally available [24]. These materials exhibit a three-dimensional framework and a cage-like structure, and they consist of SiO2 and Al2O4 (tetrahedral molecules) linked by shared oxygen atoms. Zeolites bear a negative charge because of the isomorphous replacement of Si4+ by Al3+. The magnitude of the charge depends on the number of Al atoms replaced by Si atoms and is balanced by alkali and alkaline-earth metal cations, such as Na+, K+, and Ca2+ [3]. These cations are exchangeable with certain cations in solutions, such as Zn2+, Ni2+, or NH4+.
Zeolites can be found in salt lakes, sediment layers, and volcanic environments (under hydrothermal conditions). The most common types of zeolites are clinoptilolite, analcime, mordenite, phillipsite, heulandite, and dachiardite. Each zeolite type exhibits a specific structural characteristic that affects the capacity of cation exchange to remove, for example, NH4+ ions from an aqueous solution. In addition, the nature of a cation (e.g., size and load), contact time, zeolite loading, initial anion concentration, pH, and temperature affect cation exchange. To improve the efficiency of NH4+ ion removal, zeolites can be modified with sole or combined treatments, such as heating and chemical treatments (acids, alkalis, and salts of alkaline metals) [44,45]. It has been reported that acid washing and calcination enhance NH4+ ion removal. This phenomenon may be attributed to the ability of acid washing to remove impurities and to the ability of high-temperature calcinations to remove water molecules and organics from the cavities and pores of zeolite [44,45,46]. In addition, acid washing progressively eliminates cations, such as Ca2+, Mg2+, and Na+, to change a zeolite into its H-form (proton exchange) and finally dealuminate the structure of a zeolite [45]. Zeolite can also be modified by using alkali (NaOH solution) or salts (e.g., sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, aluminum chloride, and ammonium chloride). Alkali enhances, resulting in the dissolution of the zeolite silicon, which decreases the ratio of silicon to aluminium (Si/Al) and forms mesoporous with relatively fine pore sizes. By treating the zeolite with a salt solution, water/inorganic impurities can be removed from the zeolite channel, and zeolite cations are exchanged with cations in the salt solution, which can increase the pore size [44].
Alkali activation is another possible modification method used to enhance sorption efficiency. This modification method is suitable for aluminosilicates containing raw materials, such as metakaolin, blast-furnace slag, fly ash, or zeolite. Alkali-activated materials can be prepared at ambient or slightly elevated temperatures via the hydrothermal conversion of a solid aluminosilicate material by using an alkali hydroxide and/or silicate solution. When alkali-activated materials are amorphous or partly crystalline in organic polymers consisting of three-dimensional, negatively charged framework structures, they can be called geopolymers [47].
In this study, analcime (ANA) was utilized for NH4+ ion removal. Analcime [Na16(Al16Si32O96)·16H2O]. is a by-product of the production of lithium carbonate from spodumene (LiAlSi2O6) through the sodium pressure leaching process [48]. Preliminary experiments have shown that raw analcime, without any modification, exhibits relatively low sorption capacity (<10 mg g−1) towards NH4+ ions [49]. This phenomenon has also been observed in other natural zeolites [24]. The target of this study was to render ANA a more efficient sorbent by subjecting it to different modification treatments. At first, the preliminary experiments were performed by modification analcime with different treatment methods. Based on these experiments, five alkali-activation methods were selected as modification methods for ANA. Namely, ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, ANA 3, ANA-MK 4, and ANA-MK 5 were prepared and compared in terms of their sorption efficiencies for NH4+ ion removal. Sorption kinetics, sorption isotherms, effects of pH, sorbent dosage, and NH4+ ion concentration were investigated. The prepared sorbents were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) to determine their mineralogical and physicochemical characteristics. The specific surface areas (SSAs), pore sizes, and pore volumes of the samples were also determined.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Analcime was obtained from a Finnish mining company. Metakaolin (MK) was obtained from a Finnish supplier and was used as a blending agent in some of the prepared sorbents. Technical grade sodium hydroxide (NaOH; VWR International, Radnor, PA, USA), sodium silicate (7.5–8.5% Na2O; 25.5–28.5% SiO2; VWR International), potassium silicate (K2SiO3; VWR International), and phosphoric acid (H3PO4, 85%, VWR International)) were used to synthesized alkali- or acid-activated analcime sorbents. A synthetic NH4+ ion stock solution was prepared from analytical grade ammonium chloride salt (NH4Cl, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and distilled water. The pH of the solution was adjusted by adding HCl and/or NaOH (FF-Chemicals, Haukipudas, Finland). All chemicals used in the experiments were of analytical grade.
2.2. Screening of Different Alkali- and Acid Activation Methods for Analcime
Analcime was pre-treated with acid washing, drying, and/or calcination prior to alkali and acid activation. The pre-treated analcime was alkali-activated using 10 M NaOH or with an alkaline solution containing 10 M NaOH and sodium silicate (7.5–8.5% Na2O; 25.5–28.5% SiO2) at a 1:1 weight ratio. Acid activation was performed using phosphoric acid (85%). Moreover, the effect of metakaolin as a blending agent was investigated. Three alkali-activation methods and one acid activation method were employed to prepare an effective analcime sorbent for NH4+ ion removal. The objective was to prepare a thoroughly consolidated mixture that would sufficiently harden and could be crushed and sieved to a certain particle size. The preparation methods are presented in Table 1. In addition, a schematic diagram of the preparation methods is shown in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Preparation conditions for the alkali- and acid activation of analcime. In one preparation method (F), metakaolin was used as a blending agent.
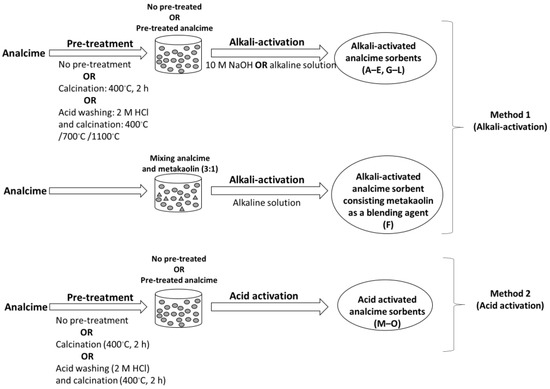
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the alkali- and acid-activated analcime sorbents.
2.2.1. Pre-Treatment of Analcime
Analcime was subjected to different pre-treatments prior to alkali or acid activation. These pre-treatments included acid washing with 2 M HCl at an L/S (liquid/solid) ratio of 100 for 24 h, drying at 105 °C overnight, and/or calcinating for 2 h at 400 °C or 700 °C. These pre-treatments are presented in Table 1 and Figure 1.
2.2.2. Alkali- and Acid Activation
Method 1: The pre-treated analcime was alkali-activated using 10 M NaOH or alkaline solution containing 10 M NaOH and sodium silicate (7.5–8.5% Na2O; 25.5–28.5% SiO2) at a 1:1 weight ratio. The alkaline solution was prepared a day before use. The analcime (dried at 105 °C) was mixed with the alkaline solution at a 1:1 weight ratio. In one sample, metakaolin was used as the blending agent. The mixture was mixed for 15 min, vibrated for 2 min, and allowed to consolidate for 3 days at room temperature. The resulting solid material was crushed to a particle size of 63–125 μm. The obtained materials were washed with deionized water, dried at 105 °C, and stored in a desiccator. The alkali-activation recipes are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1.
Method 2: The pre-treated analcime was mixed with phosphoric acid (85%) at a 1:1 weight ratio. A small amount of water was added as needed. The mixture was transferred into a mold, which was placed and sealed in a small plastic bag; the mixture was then allowed to consolidate at 60 °C for 24 h. The resulting solid material was crushed to a particle size of 63–125 μm. The obtained materials were washed with deionized water, dried at 105 °C, and stored in a desiccator. The acid activation recipes are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1.
2.3. Alkali-Activation
Alkali-activated analcime sorbents were prepared using five recipes (Table 2, Figure 2). The analcime was pre-treated as in the screening tests (Section 2.2.1). ANA 2 and ANA 3 were acid-washed, and ANA 3 was further calcinated at 400 °C prior to alkali activation. Metakaolin was used as a blending agent in the case of ANA-MK 1, ANA-MK 4, and ANA-MK 5. The alkali-activated analcime sorbents were prepared using the method described in Section 2.2.2. Sodium silicate was used as an alkaline chemical, but in the case of ANA-MK 4 and ANA-MK 5, potassium silicate was used.

Table 2.
Production conditions for the alkali-activated analcime sorbents.
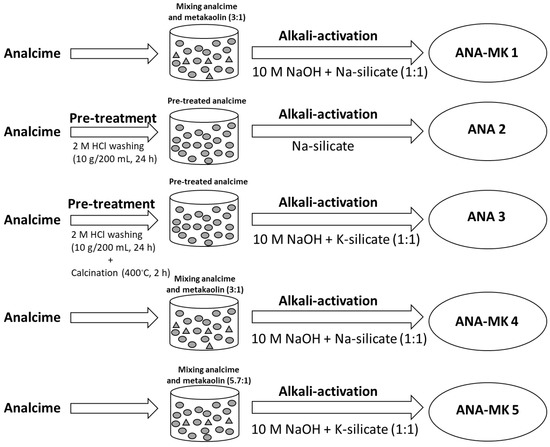
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the alkali-activated analcime sorbents.
2.4. Characterization Methods
The SSA and pore volumes of the samples were determined from nitrogen gas adsorption−desorption isotherms at the temperature of liquid nitrogen (−196 °C) using a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 instrument. The SSA was calculated based on the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) isotherm, and the pore size distributions were calculated from the desorption data using the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method. The XRD patterns were recorded by a PANalytical X’Pert Pro X-ray diffractometer (Malvern Panalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands) using monochromatic CuKα1 radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å) at 45 kV and 40 mA. Diffractograms were collected within the 2θ range of 10°–90° at 0.017° intervals at a scan step time of 100 s. The crystalline phases and structures of the adsorbents were analyzed using the HighScore Plus software (Version 4.0, PANalytical B. V., Almelo, The Netherlands). The peaks were identified according to the International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD) (PDF-4+ 2022 RDB). The phases were quantified through Rietveld analysis using HighScore. The XRF spectra were recorded by a PANalytical Axios mAX 4 kW wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (Malvern Panalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands), wherein samples were prepared as loose powders using a mylar film under a helium atmosphere at 4 kW. The FTIR spectra at the wavenumber range of 650–4000 cm−1 were collected using a PerkinElmer Spectrum One FT-IR spectrometer (PerkinElmer, Walthman, MA, USA) equipped with an attenuated total reflectance unit. The morphology and microstructure shown in the FESEM images were obtained using a Zeiss Sigma field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, Jena, Germany) at the Centre for Material Analysis in the University of Oulu operated at 5 kV.
2.5. Batch Sorption Experiments
The sorption properties of the alkali-activated analcime sorbents were characterized by batch experiments. Experiments that aimed to determine the effect of sorbent dose and initial NH4+ ion concentration were performed in 50 mL centrifuge tubes, which were placed in a shaker for 24 h. At the end of the sorption experiment, the sorbents were separated through centrifugation (3500 rpm, 2–5 min), and the supernatant was sampled with a pipette. NH4+-N concentration was analyzed using Hach HQ30d equipped with an NH4+ ion-selective electrode. Therefore, the concentration values presented are those of NH4+-N, although the phenomenon being studied (including trends and conclusions) is the removal of NH4+ ions. Given that NH4+ ions exist as ammonia in alkaline conditions, the pH was maintained below 9 during the batch experiments by adjusting the initial pH (0.1/1M HCl) to 2.5 [50,51].
Kinetic studies were performed in a 1 L reactor vessel equipped with a magnetic stirrer with an agitation speed of 800 rpm. Then, 30 mL of the sample was taken out from the vessel at different time intervals from 0 h to 24 h of sorption and then centrifuged prior to analysis. The detailed sorption conditions are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Target parameters used in the batch sorption experiments. All experiments were performed at room temperature (21 °C–23 °C). The initial pH of the synthetic NH4+ ion solution was adjusted to 2.5.
The removal efficiency (%) and sorption capacity for NH4+ ion were calculated using Equations (1) and (2), respectively:
C0 and Ce (mg L−1) are the initial and equilibrium liquid phase NH4+ ion concentrations, respectively, V (L) is the volume of the solution, and m (g) is the mass of the sorbent.
2.6. Sorption Isotherms
Several non-linear isotherm models (Langmuir, Freundlich, Sips, Bi-Langmuir, Toth, Temkin, and Dubin–Radushkevich) were applied to the experimental data. Four models provided accurate results. These models were the traditional Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms, the Sips model, which is suitable for heterogeneous sorption, and the Bi-Langmuir model, which is suitable when sorption occurs in two types of sorption sites. The other models did not provide any additional information about the sorption of NH4+. The isotherm parameters were obtained through non-linear regression using OriginPro 2018, and the equations used are as follows:
The non-linear form of Langmuir’s [52] equation is
where bL (L mg−1) represents the energy of sorption, qm (mg g−1) is the Langmuir constant, which is related to sorption capacity, and Ce (mg L−1) is the NH4+ ion concentration of the solution in equilibrium. The Freundlich model [53] can be written as
where Kf (L g−1) and nF are Freundlich constants, which are related to sorption capacity and intensity, respectively. The Sips isotherm [54] combines the properties of both the earlier mentioned models and is given as follows:
Analogous to the Langmuir model, in this equation, bS (L mg−1) is a constant related to sorption energy. The equation for the Bi-Langmuir model [55] is similar to that for the Langmuir model, except that it includes one term for both sorption sites:
To evaluate the fit of the isotherm equations to the experimental data, the residual root mean square error (RMSE) was determined. The smaller the error function value, the better the curve fitting. The calculated expression of the error function is as follows:
where n is the number of experimental data points, p is the number of parameters in the isotherm model, and qe(exp) (mg g−1) and qe(calc) (mg g−1) are the experimental and calculated values of the sorption capacity in equilibrium, respectively.
2.7. Reaction Kinetics of the Sorption Process
The kinetic parameters of the sorption experiments were solved using the non-linear forms of three models, namely, the traditionally used pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order models and the Elovich model, which could describe well slow sorption processes and which has gained more popularity in recent years.
The non-linear form of the pseudo-first-order equation [56] is
where qe (mg g−1) and qt (mg g−1) are the amounts of NH4+ ion sorbed at equilibrium and at time t (min), respectively; in addition, k1 (min−1) is the pseudo-first-order rate constant. The pseudo-second-order equation [57] can be written as
where k2 is the pseudo-second-order rate equilibrium constant (g mg−1 min−1). The non-linear form of the Elovich equation [58] is
where (mg g−1 min−1) is the initial sorption rate and β (g mg−1) is the desorption constant.
Intra-Particle Diffusion Model
To identify the diffusion mechanism, the intra-particle diffusion model based on the theory proposed by Weber and Morris [59] was used. The Weber–Morris equation can be written as follows:
where Kid (mg g−1 h−1/2) is the intra-particle diffusion rate constant, and C is the intercept.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Screening of the Preparation Methods
In this study, several sorption materials were prepared under different preparation conditions. The preparation methods for the materials used in the batch sorption experiments were developed based on the information obtained during the screening test. The results showed (Table 1) that either NaOH or phosphoric acid did not successfully consolidate the materials regardless of the pre-treatment employed. This can be because alkali and acid concentrations were too high, damaging the zeolite surface and internal pore structure [44]. By contrast, the treatment with an alkaline solution (10 M NaOH + SiO2:Na2O) resulted in consolidation when metakaolin was used as a blending agent, when analcime was acid washed, or when analcime was acid washed and calcinated (400 °C or 700 °C) before activation. Calcination without acid washing did not lead to consolidation. In other recipes (Section 2.3), analcime was pre-treated with acid washing and calcination. Calcination was performed only at 400 °C, as the objective was to prepare sorbents using the least amount of energy and chemicals. In addition, the preliminary sorption experiments (data not shown) indicated that sorption capacity was slightly lower during calcination at 700 °C than at 400 °C. Alkali activation using an alkaline solution (sodium silicate and NaOH) was performed to improve the sorption properties of analcime. Apart from sodium silicate, potassium silicate was also tested as an alkaline chemical.
3.2. Characterization of the Sorbents
The SSA, average pore size and volumes of the alkali-activated analcime sorbents are shown in Table 4. The results showed that ANA-MK 1 had the lowest SSA (4.182 m2/g) and the highest average pore diameter (31.281 nm). By contrast, ANA-MK 5 showed the highest SSA (46.712 m2/g) and the lowest average pore diameter (5.384 nm). The results showed that ANA-MK 5 has considerably higher SSA (46.712 m2/g) compared with ANA-MK 1 (4.182 m2/g) and ANA-MK 4 (7.784 m2/g). In all these sorbents, metakaolin was used as a blending agent. The ratio of analcime and metakaolin was 3:1 in the case of ANA-MK 1 and ANA-MK 4. For ANA-MK 5, the ratio was 5.4:1. Alkaline solution (10 M NaOH + Na-silicate) was used in the case of ANA-MK 1, and alkaline solution (10 M NaOH + K-silicate) in the case of ANA-MK 4 and ANA-MK 5. Based on the results, sorbent prepared using an alkaline solution consisting of potassium silicate in the alkaline solution and using a ratio of analcime and metakaolin 5.4:1 leads to the highest SSA value (ANA-MK 5: 46.712 m2/g) in this study. A mesopore structure was clearly dominant in each sorbent. Moreover, the surface areas of the alkali-activated analcime sorbents are higher than those of the non-modified sorbents (SSA: 3.01 m2/g) [60].

Table 4.
SSAs, pore sizes, and volumes of the prepared sorbents.
The chemical and mineral compositions of the alkali-activated analcime sorbents are presented in Table 5. The alkali-activated sorbents mainly consisted of silica and alumina with Si/Al mole ratios of 4.05, 2.31, 1.30, 1.36, and 1.44 for ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, ANA 3, ANA-MK 4, and ANA-MK 5, respectively. The mole ratio of raw analcime has previously been found to be 1.57 [49]. Raw analcime [47] and the alkali-activated analcime sorbents (Table 5) also contained exchangeable cations, such as Fe3+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and Mn2+. These cations play an important role in ion exchange with NH4+ ions [3]. In addition, the sorbents contained some impurities and volatile compounds (e.g., water).

Table 5.
Main chemical constituents (normalized values) of the adsorbents as determined by XRF.
The analcime used as raw material was characterized in our earlier studies. Previous results showed that all the main spikes in the XRD diffractogram are associated with analcime (Na8Al8Si16O48(H2O)8). In addition, analcime may contain silicon oxide (quartz, SiO2) and lithium aluminum silicate (spodumene, LiAlSi2O6) [49,60]. The obtained XRD patterns in the present study are shown in Figure 3. According to the software there are many candidates, and many peaks are overlapping. All of the alkali-activated sorbents contained silicon oxide (SiO2, ICDD 04-014-7568), iron oxide (Fe2O3, ICDD 04-010-3230), sodium aluminum silicate (hydrate) (NaAlSi3O8, ICDD 01-083-1609 or NaAl(Si2O6)(H2O), ICDD 01-074-2219), and lithium aluminum silicate (LiAlSi2O6, ICDD 04-020-3038). They may also contain magnesium silicate (Mg(SiO3), ICDD 01-076-6770), calcium aluminum silicate (CaAl2Si2O8, ICDD 00-041-1486), calcium magnesium iron oxide (CaMg2Fe16O27, ICDD 00-056-0629), and potassium sodium calcium aluminum silicate (K0.05Na0.94Ca0.01Al1.01Si2.99O8, ICDD 04-023-4722). The results showed that ANA-MK 1 considerably differed from the other alkali-activated analcime sorbents. Peak intensities were lower in ANA-MK 1; moreover, a high-intensity peak at position 27, which is associated with sodium aluminum silicate hydrate (NaAl(Si2O6)(H2O), ICDD 01-074-2219), was not observed in ANA-MK 1 compared with the other preparations. In the case of ANA-MK 1, SiO2 was crystallized very well, and the intensity peak at 2θ of 26.6° was very high.
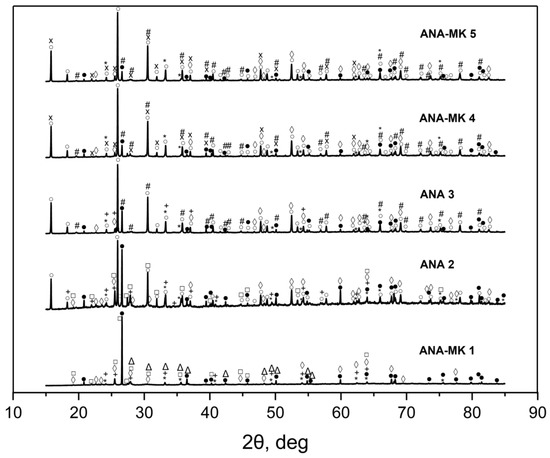
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of the alkali-activated analcime sorbents. * Fe2O3 (04-010-3230), ● SiO2 (04-014-7568), □ CaAl2Si2O8 (00-041-1486), Δ NaAlSi3O8 (01-083-1609), + CaMg2Fe16O27 (00-056-0629), ◊ LiAlSi2O6 (04-020-3038), ○ NaAl(Si2O6)(H2O) (01-074-2219), # Mg(SiO3) (01-076-6770), × K0.05Na0.94Ca0.01Al1.01Si2.99O8 (04-023-4722).
The FTIR spectra of the alkali-activated analcime sorbents are shown in Figure 4. The peaks between ~1621 and 1628 cm−1 can be attributed to the hydroxyl group with the stretching and bending vibrations of the adsorbed water [46,61]. The band between ~979 and 1031 cm−1 can be assigned to the internal stretching vibrations of Si–O(Si) and Si–O (Al) [46,62]. The bands between 697 and 880 cm−1 belong to the T–O (T=Al, Si) symmetric stretching vibrations [60,63,64,65,66]. These vibrations are typical for zeolite materials. The FTIR spectra of alkali-activated analcime sorbents exhibit similar vibrations to raw analcime and Ba-modified analcime [60].
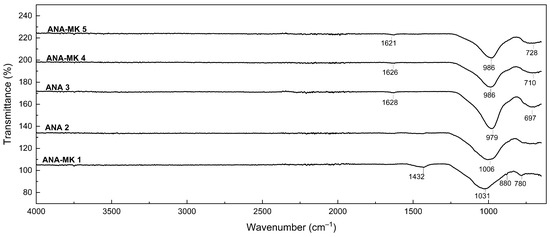
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra of the alkali-activated analcime sorbents.
Figure 5 shows the FESEM images of the raw materials analcime and metakaolin, as well as prepared sorbents ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, ANA 3, ANA-MK 4, and ANA-MK 5. It can be seen from Figure 5a–c that analcime consists of crystalline phases, which is typical for zeolite materials [67,68]. Figure 5d–f presents a FESEM image of metakaolin showing mainly flakes structure; on the flake surface, there are heterogeneous materials consisting of irregularly shaped particles [69,70]. After alkali activation, samples seem to have different morphological structures compared with raw materials analcime and metakaolin. This can be affected by different pre-treatments for analcime and alkali-activation processes. As can be seen from Figure 5, alkali-activated samples contain voids, unreacted particles, and cracks. In addition, it is possible to see a gel network characteristic of alkali-activated materials, which has also been reported in other studies [70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77].
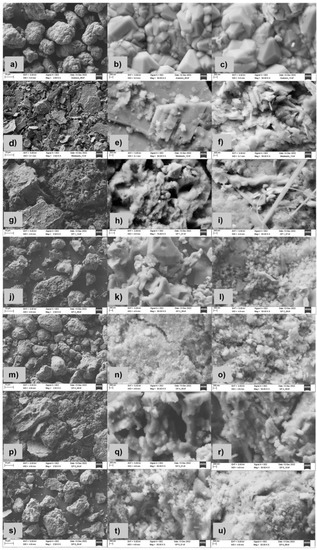
Figure 5.
FESEM images of the analcime (a–c), metakaolin (d–f), ANA-MK 1 (g–i), ANA 2 (j–l), ANA 3 (m–o), ANA-MK 4 (p–r) and ANA-MK 5 (s–u).
3.3. Effect of Sorbent Dosage
The sorbents used in this study are alkaline in nature, so they increase the pH during sorption experiments. The pH was maintained below 9 during the experiment by adjusting the initial pH to 2.5 after the addition of the sorbent to the solution. This was done because, as has been reported, NH4+ ions evaporate as ammonia at high pH values [2,50,51,78]. pH 2.5 was selected as the initial pH based on preliminary experiments (data not shown). However, a pH that is too low is not good because, under this condition, H+ ions start to compete with NH4+ ions [78].
The results (Figure 6) showed that the removal efficiency of NH4+ ions increased with increasing sorbent dosage. The same trend has been reported in several sorption studies. This observation can be explained by the fact that when sorbent content increases, the surface area and the number of available sorption sites increase [2,50,78]. On the contrary, the sorption capacities (qe) decreased when the sorbent dosage increased. This can be explained by the increase in the sorbent-to-adsorbate ratio. Moreover, these results showed that the removal percentage values were much higher when a lower NH4+ ion concentration was used. This same phenomenon has been observed in concentration optimization studies (Section 3.3).
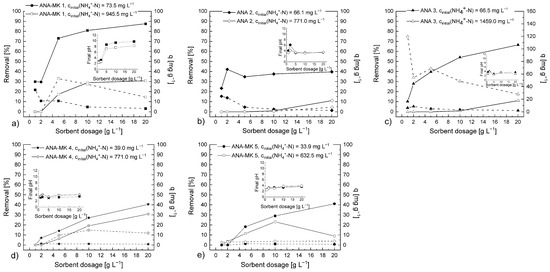
Figure 6.
Effect of sorbent dosage on the ability of (a) ANA-MK 1, (b) ANA 2, (c) ANA 3, (d) ANA-MK 4, and (e) ANA-MK 5 to remove NH4+ ions under two different initial NH4+ ion concentrations. The removal percentage of NH4+ ions is represented by a solid line, and the sorption capacities (qe) are represented by a dashed line. Experimental conditions: sorbent dosage: 1–20 g L−1; initial pH of the solution: 2.5 (pH was adjusted after the addition of sorbent to the solution); contact time: 24 h; and temperature: 22 °C–23 °C. Analysis was based on the concentrations of NH4+-N.
ANA-MK 1 was the most efficient among the prepared sorbents based on the removal percentage values. When a low NH4+ ion concentration was used, the removal efficiency was approximately 30% at sorbent dosages 1 and 2 g L−1. The removal percentage increased rapidly when the sorbent dosage was increased. The removal percentage was approximately 75–85% within the sorbent dosage range of 5–20 g L−1. The decreasing order of the removal percentages of the sorbents at a sorbent dosage of 5 g L−1 and at a low initial NH4+ ion concentration was as follows: ANA-MK 1 (75%) > ANA 3 (40%) > ANA 2 (35%) > ANA-MK 5 (20%) > ANA-MK 4 (15%). Although slightly higher removal percentages could be reached by using a higher sorbent dosage, 5 g L−1 was selected for the subsequent experiments, given the risk that pH will increase during the sorption experiment, driving the transformation of NH4+ ions into ammonia.
3.4. Effect of Initial NH4+ Ion Concentration
The effect of initial NH4+ ion concentration was investigated using model solutions within the concentration range of 5–1000 mg L−1. The results are presented in Figure 6. The concentrations used were selected for practical reasons, as sorbents should be suitable for use in a wide range of ion concentrations. The NH4+ ion concentration in wastewater from the mining industry is typically quite low (below 40 mg L−1), whereas that from agricultural sources may be as high as 900 mg L−1. It can be seen in Figure 7 that the removal percentage decreased with increasing initial NH4+ ion concentration. In the case of ANA-MK 1 and ANA 2, the NH4+ ion removal efficiencies increased rapidly at first. This can be explained by the fact that the driving force of the concentration gradient increases with increasing initial NH4+ ion concentration. When the initial NH4+ ion concentration was higher than 50 mg L−1 (NH4+-N: ~40 mg L−1), the removal efficiencies increased more slowly, reaching a plateau; subsequently, the uptake started to decrease. This phenomenon can be explained by the fact that at low initial concentrations, a sufficient number of available pores on the sorbent surface may adsorb most of the NH4+ ions, which in turn would occupy the available sites. As a result, the sorption efficiency increases to a certain level. Several investigations have shown that the removal efficiency of NH4+ ions is concentration dependent and that removal efficiency decreases with increasing initial ion concentration [2]. Based on these results, the optimum initial NH4+ ion concentration for the studied sorbents was 50 mg L−1. The decreasing order of removal percentages of the sorbents was as follows: ANA-MK 4 (~75%) > ANA-MK 1 (~55%) > ANA 2 (~50%) > ANA 3 (~40%) > ANA MK 5 (~40%).
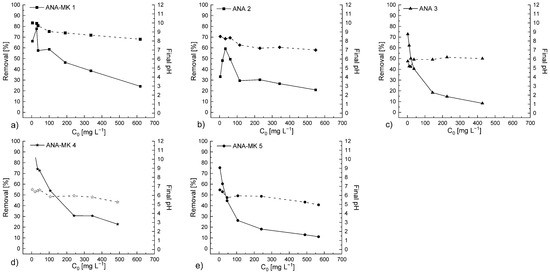
Figure 7.
Effect of initial concentration on NH4+ ion removal onto (a) ANA-MK 1, (b) ANA 2, (c) ANA 3, (d) ANA-MK 4, and (e) ANA-MK 5. The removal percentage for NH4+ ions is represented by a solid line, and the final pH values are represented by a dashed line. Experimental conditions: sorbent dosage: 5 g L−1; initial pH of the solution: 2.5; contact time: 24 h; and temperature: 22 °C–23 °C. Analysis was based on the concentrations of NH4+-N.
3.5. Sorption Isotherms
The functionality of the Langmuir, Freundlich, Sips, Bi-Langmuir, Toth, Temkin, and Dubin–Radushkevich models were tested for the sorption of NH4+ ions onto the alkali-activated analcime surfaces. However, only the results obtained using the first four models are presented. The experimental results and the modeled isotherms are illustrated in Figure 8. The isotherm parameters, correlation coefficients, and calculated errors given by the models are shown in Table 6.
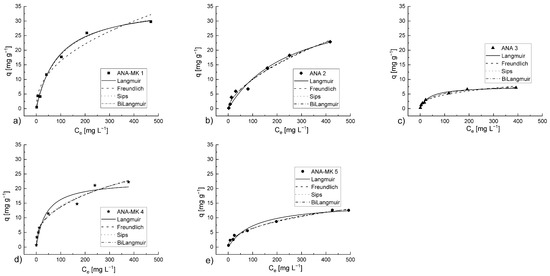
Figure 8.
Isotherms for the sorption of NH4+ ion onto (a) ANA-MK 1, (b) ANA 2, (c) ANA 3, (d) ANA-MK 4, and (e) ANA-MK 5. Experimental conditions: sorbent dosage: 5 g L−1; initial pH of the solution: 2.5; contact time: 24 h; and temperature: 22 °C–23 °C. Analysis was based on the concentrations of NH4+-N.

Table 6.
Parameters for the sorption isotherms.
On the basis of correlation coefficients (R2), all models represented quite well the studied systems. The Bi-Langmuir and Sips isotherm models showed the best fit for the sorption of NH4+ ions onto the sorbent surfaces. Nevertheless, the Langmuir and Bi-Langmuir models gave more realistic q-values than the Sips model. The shape of the curves produced by the Sips and Bi-Langmuir models were quite similar for all the studied sorbents, as can also be seen in the R2 values with the same order of magnitude. These findings support the conclusion that the surface of the adsorbent is heterogeneous; that is, it possesses two types of occupied sorption sites and exhibits different sorption energetics. Moreover, the RMSE values reinforced the conclusion that the RMSE values are smaller when the R2 values are higher.
In the case of ANA-MK 1, the nS value approached unity, which means that the R2 value of the Sips model approached that of the Langmuir model, leading to nearly identical R2 values for these models. Still, the Langmuir and Bi-Langmuir models showed a slightly better correlation than the Sips model, indicating that the process apparently followed the single monolayer sorption. In the case of ANA-MK 4 and ANA-MK 5, the Freundlich model provided quite similar correlations compared with the Sips and Bi-Langmuir models, whereas the Langmuir provided a weak correlation.
In terms of sorption capacities, the decreasing order of the effectiveness of the prepared sorbents was as follows: ANA-MK 1 (29.79 mg g−1) > ANA 2 (26.00 mg g−1) > ANA-MK 4 (22.24 mg g−1) > ANA-MK 5 (12.65 mg g−1) > ANA 3 (7.18 mg g−1). The only difference in the preparation of ANA-MK 1 and ANA-MK 4 was the activation with an alkali chemical (Table 2), demonstrating that Na-silicate with NaOH produced a slightly better adsorbent than the NaOH + K-silicate combination. In the case of ANA-MK 1, the final pH was higher than other sorbents (Figure 4). NH4+ starts to evaporate as ammonia at high pH values, and due to that, NH4+ removal can be based partly on evaporation as ammonia in the case of ANA-MK 1. Considering that the adsorption capacity of ANA-MK 4 was nearly twice that of ANA-MK 5, we can conclude that a higher metakaolin content of the prepared adsorbent leads to a more effective removal. In fact, metakaolin is apparently a requirement for the consolidation of materials treated with Na-silicate (Table 1). However, an effective adsorbent may be produced using only analcime as raw material (ANA 2) only if analcime is acid-washed prior to alkali activation. In the preparation step, it seemed that calcination also had a positive effect on consolidation; however, the sorption experiment showed that the calcinated ANA 3 had the worst q-value. The difference between the q-values of ANA 2 and ANA 3 may be due to the different alkali-activation treatments employed. The use of Na-silicate without NaOH also seems to produce effective adsorbents. Meanwhile, the SSA and average pore diameter of ANA-MK 5 differed from those of the other sorbents. This led to a slower sorption capacity (12.65 mg g−1) compared with that of the most effective adsorbents, namely, ANA-MK 1 (29.79 mg g−1), ANA 2 (26.00 mg g−1), and ANA-MK 4 (22.24 mg g−1).
The NH4+ removal mechanism of zeolites and alkali-activated is mostly based on ion exchange, which involves a reversible replacement of ions of the same charge [9,44,45,79,80,81,82]. The aluminosilicate structure is negatively charged, and the exchangeable cations are located in the voids [83,84]. High meso- and macro-pore volumes in alkali-activated sorbent enhance active contact sites for NH4+ sorption [84].
Several factors affect the ion-exchange behavior of zeolites and alkali-activated materials. These factors are the framework structure, ion size and shape, charge density of the anionic framework, ionic charge, and concentration of the external electrolyte solution [45,83]. For example, based on FESEM images (Figure 5), the porosity of the prepared alkali-activated sorbents has been increased compared to analcime. This can be one explanation for why these alkali-activated sorbents have higher q-values compared to raw analcime (<10 mg/g) [49].
3.6. Effect of Contact Time
Kinetic studies were performed for all the prepared sorbents at room temperature using the model solution with an NH4+ ion concentration of 50 mg L−1 (c(NH4+-N), 40 mg L−1). As can be seen in Figure 9, the removal percentage increased quite rapidly, reaching the maximum removal percentage and equilibrium. The availability of a larger number of sorption sites can explain this observation. The maximum NH4+ ion removal percentage of the sorbents was ~80%, except for ANA-MK 5, which had a ~70% removal.
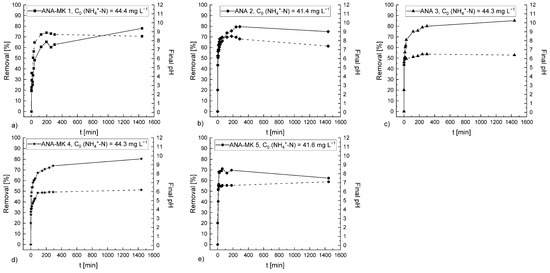
Figure 9.
Effect of contact time on NH4+ ion removal onto (a) ANA-MK 1, (b) ANA 2, (c) ANA 3, (d) ANA-MK 4, and (e) ANA-MK 5. The removal percentage of NH4+ ions is represented by a solid line, and the final pH values are represented by a dashed line. Experimental conditions: sorbent dosage: 5 g L−1; the volume of the solution: 0.975 L; C0 (NH4+-N): ~40 mg L−1; initial pH of the solution: 2.5; contact time: 24 h; and temperature: 22 °C–23 °C.
3.7. Kinetic Modeling
The pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and Elovich models were applied to the experimental data. The kinetic parameters and correlation coefficients are presented in Table 7, and the graphs are shown in Figure 10.

Table 7.
Pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and Elovich model parameters for the alkali-activated analcime sorbents used for NH4+ ion removal.
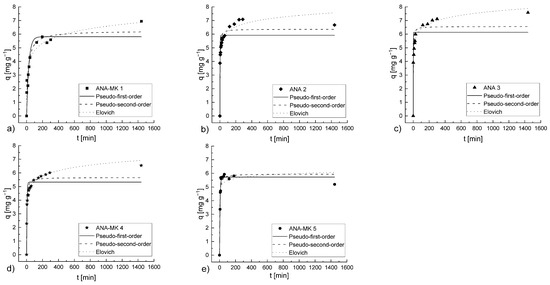
Figure 10.
Pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and Elovich model plots of NH4+ ion removal using (a) ANA-MK 1, (b) ANA 2, (c) ANA 3, (d) ANA-MK 4, and (e) ANA-MK 5. Experimental conditions: sorbent dosage: 5 g L−1; the volume of solution: 0.975 L; C0 (NH4+-N): ~40 mg L−1; initial pH of solution: 2.5; contact time: 24 h; and room temperature: 22 °C–23 °C.
Comparison of the correlation coefficients and RMSE values revealed that sorption of NH4+ ions onto the ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, ANA 3, and ANA-MK 4 surfaces were best represented by the Elovich model, indicating that sorption was relatively slow. However, sorption onto ANA-MK 5 differed from that observed in the other sorbents, as it showed a more angular curve. This pattern showed the best correlation obtained using the pseudo-first-order model. Although the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order models rarely showed a poor correlation, the correlation between the experimental and calculated q-values was reasonable. The differences in surface structures might be the reason behind having a different optimum kinetic model for ANA-MK 5 (pseudo-first-order) and for the other adsorbents (Elovich), an indication of differences in sorption behaviors.
3.8. Weber and Morris Intraparticle Diffusion Model
The plot qt versus t0.5 for the sorption of NH4+ ions onto the prepared sorbents is shown in Figure 11. The results showed that sorption proceeds in three or four stages. The first stage proceeds quite fast, wherein NH4+ ions diffuse through the solution to reach the external surface of the sorbent. This stage is called the external surface sorption or the macro-pore diffusion. Internal surface sorption or micro-pore diffusion occurs in the second and third steps. In the final step, small slopes indicate slow intraparticle diffusion onto the internal surface due to the extremely low solute concentrations in the bulk phase and boundary layer [3].
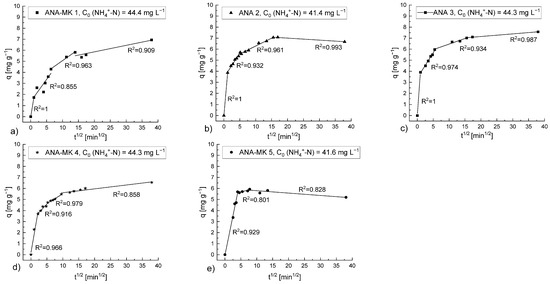
Figure 11.
Weber and Morris intraparticle diffusion model plot for the sorption of NH4+ ions onto the alkali-activated analcime sorbents, namely, (a) ANA-MK 1, (b) ANA 2, (c) ANA 3, (d) ANA-MK 4, and (e) ANA-MK 5. Experimental conditions: concentration of the model NH4+ ion solution, C0 (NH4+-N): ~40 mg L−1; initial pH: 2.5; sorbent dosage: 5 g L−1; contact time: 24 h; and room temperature: 22 °C–23 °C.
3.9. Comparison with the Other Adsorbents
The sorption capacities of the aluminosilicate-based materials during NH4+ ion removal are presented in Table 8. The materials exhibiting a high sorption capacity are obtained from virgin sources. The material developed in this study demonstrated a higher sorption capacity compared with other side stream-based materials, such as a zeolite synthesized from fly ash. Therefore, the sorption capacity obtained in this study indicated a very good functionality towards NH4+ ion of the sorbent produced using industrial side stream as raw material. However, comparing q values, it is good to consider operational conditions that are not exactly the same in all studies. For example, the initial pH is quite high (7–8) in some studies so ammonium can be partly evaporated during the adsorption experiment. In addition, the used adsorption temperature varies between 20–35 °C. Worth noting that 15 degrees may have a major impact on adsorption capacity. Initial concentration values and sorbent dosages vary between different studies even though values are mostly in the same scale compared to the values used in this study.

Table 8.
Comparison of the sorption capacity qm (mg g−1) of various sorbents for the removal of NH4+ ions from an aqueous phase.
The adsorbents studied in this study have an advantage from the local circular economy point of view. Analcime is formed as a side stream in lithium production, and the needed amount of lithium will increase in the future due to the green transition through electric vehicles. Therefore, the solutions to utilize local side streams need to be developed, and the adsorbents developed in this study are one answer.
4. Conclusions
A total of five alkali-activated analcime sorbents, namely, ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, ANA 3, ANA-MK 4, and ANA-MK 5, were prepared and studied for NH4+ ion removal. Analcime was pre-treated with acid washing and/or calcination at a high temperature. ANA 2 and ANA 3 were acid-washed, and ANA 3 was further calcinated at 400 °C prior to alkali activation. In the case of ANA-MK 1, ANA-MK 4, and ANA-MK 5, metakaolin was used as a blending agent. ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, and ANA 3 were alkali-activated using sodium silicate. In the case of ANA-MK 4 and ANA-MK 5, potassium silicate was used as the alkaline chemical for activation. The effects of sorbent dosage (1–20 g L−1), initial NH4+ ion concentration (5–1000 g L−1), and contact time (1 min–24 h) were studied. The results showed that ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, and ANA-MK 4 were the most efficient sorbents for NH4+ ion removal, with a maximum experimental sorption uptake of 29.79, 26.00, and 22.24 mg g−1, respectively. ANA 3 and ANA-MK 5 demonstrated lower sorption capacities at 7.18 and 12.65 mg g−1, respectively. The results of the kinetic studies showed the maximum NH4+ ion removal percentage of the sorbents was ~80%. The exception was ANA-MK 5, which had a ~70% removal. Different isotherm and kinetic models were applied to generate the experimental results for the prepared alkali-activated analcime sorbents. The equilibrium data were best represented by the Langmuir, Freundlich, Sips, and Bi-Langmuir isotherms. In the case of ANA-MK 1, ANA 2, ANA 3, and ANA-MK 4, the Elovich model provided the best correlation. ANA-MK 5 followed the pseudo-second-order model.
The results suggested that the alkali-activated analcime sorbents are feasible for NH4+ ion removal for wastewater treatment (e.g., municipal wastewater treatment). Pre-treatment involving acid washing prior to alkali activation or pre-treatment involving calcination enhanced the NH4+ ion removal efficiency. Moreover, the addition of metakaolin as a blending agent increased the NH4+ ion removal efficiency. The sorption capacities of the sorbents previously developed for NH4+ ion removal are similar to the results obtained in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.R., J.P., and S.T.; methodology, H.R., J.P., S.T., and T.K.; software, H.R., E.S., T.K., and T.H.; investigation, H.R., E.S., J.P., T.H., S.T., and T.K.; data curation, H.R., J.P., S.T., T.H., and T.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.R.; writing—review and editing, H.R., E.S., J.P., S.T., T.H., T.K., and U.L.; visualization, H.R., S.T., and T.K.; supervision, H.R., S.T., and U.L.; project administration, U.L.; funding acquisition, H.R., E.S., and U.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was conducted as part of WaterPro (ERDF Project No. A74635, funded by the Central Ostrobothnia Regional Council, the European Union, the European Regional Development Fund, and the Leverage from the EU) and was supported by Maaja vesitekniikan tukiry and K.H. Renlund Foundation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All processed data supporting the findings of this study are included in this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Enara Alday for her valuable help in the sorption experiments. The authors would also like to thank Jaakko Pulkkinen, Toni Varila, and Pekka Tynjälä for their assistance in the characterization of the samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Adam, M.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Puteh, M.H.; Ismail, A.F.; Mustafa, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J. Impact of Sintering Temperature and PH of Feed Solution on Adsorptive Removal of Ammonia from Wastewater Using Clinoptilolite Based Hollow Fibre Ceramic Membrane. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; He, H.; Zhu, J.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, R.; Ma, L.; Tao, Q. Adsorption of Ammonium by Different Natural Clay Minerals: Characterization, Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 159, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiastuti, N.; Wu, H.; Ang, H.M.; Zhang, D. Removal of Ammonium from Greywater Using Natural Zeolite. Desalination 2011, 277, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, S.; Börnick, H.; Stolte, S. Granular Natural Zeolites: Cost-Effective Adsorbents for the Removal of Ammonium from Drinking Water. Water 2022, 14, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU. Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption; EU: Maastricht, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Directive 91/271/EEC of the European Council Concerning Urban Waste-Water Treatment. Off. J. Eur. Union 1991, L135, 40–52. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:31991L0271&from=EN (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Vu, T.M.; Trinh, V.T.; Doan, D.P.; Van, H.T.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S.; Ngo, H.H. Removing Ammonium from Water Using Modified Corncob-Biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, G.; Yang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Cai, J.; Zheng, J. Enhanced Ammonium Removal on Biochar from a New Forestry Waste by Ultrasonic Activation: Characteristics, Mechanisms and Evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Butterly, C.; Zhang, W.; He, J.-z.; Chen, D. Adsorbent Materials for Ammonium and Ammonia Removal: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, J.Y.; Chang, C.Y. Ammonia Removal from Ammonia-Rich Wastewater by Air Stripping Using a Rotating Packed Bed. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh, A.; Sabzalipour, S.; Takdatsan, A.; Yengejeh, R.J.; Khafaie, M.A. Ammonia Removal Form Municipal Wastewater by Air Stripping Process: An Experimental Study. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 36, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, N.A.; Reusser, S.R.; Scarborough, M.J.; Grooms, A.L.; Seib, M.; Santo Domingo, J.; Noguera, D.R. Pilot Plant Demonstration of Stable and Efficient High Rate Biological Nutrient Removal with Low Dissolved Oxygen Conditions. Water Res. 2017, 121, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, F.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Q.; Tao, G. Removal of Ammonia Nitrogen from Wastewater Using an Aerobic Cathode Microbial Fuel Cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Yu, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous Recovery of Ammonium, Potassium and Magnesium from Produced Water by Struvite Precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Gao, F. Investigation on the Simultaneous Removal of Fluoride, Ammonia Nitrogen and Phosphate from Semiconductor Wastewater Using Chemical Precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo, M.; Viñas, M.; Bonmatí, A. Anaerobic Digestion and Electromethanogenic Microbial Electrolysis Cell Integrated System: Increased Stability and Recovery of Ammonia and Methane. Renew. Energy 2018, 120, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yao, J.; Fang, X.; Huang, Y.; Mu, Y. Electrolytic Ammonia Removal and Current Efficiency by a Vermiculite-Packed Electrochemical Reactor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, H.; Liu, X.; Feng, B.; Gai, C.; Huang, T.; Xiao, M.; Song, H. An Alternative Scheme of Biological Removal of Ammonia Nitrogen from Wastewater–Highly Dispersed Ru Cluster @mesoporous TiO2 for the Catalytic Wet Air Oxidation of Low-Concentration Ammonia. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousteau, C.; Besson, M.; Descorme, C. Catalytic Wet Air Oxidation of Ammonia over Supported Noble Metals. Catal. Today 2015, 241, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendel, Y.; Lahav, O. A Novel Approach for Ammonia Removal from Fresh-Water Recirculated Aquaculture Systems, Comprising Ion Exchange and Electrochemical Regeneration. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 52, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imchuen, N.; Lubphoo, Y.; Chyan, J.M.; Padungthon, S.; Liao, C.H. Using Cation Exchange Resin for Ammonium Removal as Part of Sequential Process for Nitrate Reduction by Nanoiron. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadiannamini, P.; Eswaranandam, S.; Wickramasinghe, R.; Qian, X. Mixed-Matrix Membranes for Efficient Ammonium Removal from Wastewaters. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 526, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradihamedani, P.; Abdullah, A.H. Ammonia Removal from Aquaculture Wastewater by High Flux and High Rejection Polysulfone/Cellulose Acetate Blend Membrane. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 2481–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kankanamge, N.R.; Chow, C.; Welsh, D.T.; Li, T.; Teasdale, P.R. Removing Ammonium from Water and Wastewater Using Cost-Effective Adsorbents: A Review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 63, 174–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malovanyy, A.; Sakalova, H.; Yatchyshyn, Y.; Plaza, E.; Malovanyy, M. Concentration of Ammonium from Municipal Wastewater Using Ion Exchange Process. Desalination 2013, 329, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, M.; Duta, A.; Teodosiu, C.; Draghici, C. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Study on Ammonium Removal from a Synthetic Water Solution Using Ion Exchange Resin. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismadji, S.; Tong, D.S.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ayucitra, A.; Yu, W.H.; Zhou, C.H. Bentonite Hydrochar Composite for Removal of Ammonium from Koi Fish Tank. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizito, S.; Wu, S.; Kipkemoi Kirui, W.; Lei, M.; Lu, Q.; Bah, H.; Dong, R. Evaluation of Slow Pyrolyzed Wood and Rice Husks Biochar for Adsorption of Ammonium Nitrogen from Piggery Manure Anaerobic Digestate Slurry. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Hanley, K.; Hestrin, R.; Enders, A. Adsorption and Desorption of Ammonium by Maple Wood Biochar as a Function of Oxidation and PH. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Assabri, A.M.; Lei, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, C. The Investigation into the Ammonium Removal Performance of Yemeni Natural Zeolite: Modification, Ion Exchange Mechanism, and Thermodynamics. Powder Technol. 2014, 258, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloomi, F.; Jalali, M. Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Natural Iranian Zeolite in the Presence of Organic Acids, Cations and Anions. J. Environ. Chem Eng. 2016, 4, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, N.S.M.; Lenggoro, I.W.; Naim, M.N.; Yoshida, N.; Man, H.C.; Bakar, N.F.A.; Puasa, S.W. Adsorptive Capacity of Spray-Dried PH-Treated Bentonite and Kaolin Powders for Ammonium Removal. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Chua, M.L.; Zhang, B. Effects of Competitive Ions, Humic Acid, and PH on Removal of Ammonium and Phosphorous from the Synthetic Industrial Effluent by Ion Exchange Resins. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, H.; Laycock, B.; Strounina, E.; Seviour, T.; Oehmen, A.; Pikaar, I. Modified Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Based Hydrogels for Enhanced Mainstream Removal of Ammonium from Domestic Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9573–9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, H.; Yap Gabon, M.; Salehin, S.; Seviour, T.; Laycock, B.; Pikaar, I. Magnetic Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Based Hydrogels for Rapid Ammonium Sorption and Efficient Sorbent Separation from Sewage. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2021, 6, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, D.; Han, L.; Niu, D.; Tian, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W. Removal of Ammonium from Aqueous Solutions Using Zeolite Synthesized from Fly Ash by a Fusion Method. Desalination 2011, 271, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Screening of Novel Low-Cost Adsorbents from Agricultural Residues to Remove Ammonia Nitrogen from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uurlu, M.; Karaolu, M.H. Adsorption of Ammonium from an Aqueous Solution by Fly Ash and Sepiolite: Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 139, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, A.M.; Keat, L.K.; Ibrahim, Z.; Majid, Z.A.; Nizam, N.A. Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies of the Removal of Ammonium Ions from Aqueous Solution by Rice Husk Ash-Synthesized Zeolite Y and Powdered and Granulated Forms of Mordenite. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 174, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Guo, W.; Tian, Y.L. Sorption Characteristics and Mechanisms of Ammonium by Coal By-Products: Slag, Honeycomb-Cinder and Coal Gangue. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Niu, Y.; Hu, X.; Xi, B.; Peng, X.; Liu, W.; Guan, W.; Wang, L. Removal of Ammonium Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Zeolite Synthesized from Red Mud. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 4720–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kolar, P.; Shah, S.B.; Cheng, J.J.; Lim, P.K. Avocado Seed-Derived Activated Carbon for Mitigation of Aqueous Ammonium. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 92, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh, H.; Shahryari-ghoshekandi, R.; Kazemi, M. Study in Synthesis and Characterization of Carbon Nanotubes Decorated by Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. Nano Lett. 2014, 4, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yang, Z.; Dai, H.; Lu, X.; Peng, L.; Tan, X.; Shi, L.; Fahim, R. Preparation and Application of Modified Zeolites as Adsorbents in Wastewater Treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 2017, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural Zeolites as Effective Adsorbents in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shen, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ding, T.; Xu, L.; Lee, S.S. Ammonium Removal Using a Calcined Natural Zeolite Modified with Sodium Nitrate. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 393, 122481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodehi, M.; Taghvaee, V.M. Alkali-Activated Materials and Geopolymer: A Review of Common Precursors and Activators Addressing Circular Economy. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2022, 2, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Q.; Chen, B.; Shi, X.; Liao, T. Preparation of Lithium Carbonate from Spodumene by a Sodium Carbonate Autoclave Process. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesonen, J.; Tuomikoski, S.; Näppä, J.; Prokkola, H.; Hu, T.; Lassi, U.; Runtti, H. Ammonium Uptake over Analcime and Its Soil Enhancer Potential. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Sustainable Solid Waste Management, Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–26 June 2021; Available online: www.thessaloniki2021.uest.gr (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Abukhadra, M.R.; Basyouny, M.G.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; El-Meligy, M.A. The Effect of Different Green Alkali Modification Processes on the Clinoptilolite Surface as Adsorbent for Ammonium Ions; Characterization and Application. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 300, 110145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xiao, X.; Yan, B.; Yang, L. Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Using Natural Chinese (Chende) Zeolite as Adsorbent. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 175, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Over the Adsorption in Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Sips, R. On the Structure of a Catalyst Surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D. The Characterization of Physical Adsorption Systems. I. The Equilibrium Function and Standard Free Energy of Adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. 1953, 57, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances, Zur Theorie Der Sogenannten Adsorption Gelöster Stoffe. Kungl. Sven. Vetensk. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.; McKay, G. Pseudo-Second-Order Model for Sorption Processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldowitsch, J. Über Den Mechanismus Der Katalytischen Oxydation von CO an MnO2 [About the Mechanism of Catalytic Oxidation of CO over MnO2]. Acta Physicochim. U.R.S.S. 1934, 1, 364–449. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.; Morris, J. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runtti, H.; Tynjälä, P.; Tuomikoski, S.; Kangas, T.; Hu, T.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Utilisation of Barium-Modified Analcime in Sulphate Removal: Isotherms, Kinetics and Thermodynamics Studies. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 16, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L. Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium and Phosphate by Alkaline-Activated and Lanthanum-Impregnated Zeolite. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgawa, W. The Relation between Structure and Vibrational Spectra of Natural Zeolites. J. Mol. Struct. 2001, 596, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczyk, K.; Mozgawa, W.; Król, M. Studies of Anions Sorption on Natural Zeolites. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 133, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadian, H.; Ghorbani, F.; Tayebi, H.A.; Asl, S.M.H. Study of the Adsorption of Cd (II) from Aqueous Solution Using Zeolite-Based Geopolymer, Synthesized from Coal Fly Ash; Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Studies. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, P. Synthesis and Characterization of Analcime Using Quartz Syenite Powder by Alkali-Hydrothermal Treatment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 201, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Tavakoli-Ghinani, S. Effect of a Nano-Sized Natural Clinoptilolite Modified by the Hexadecyltrimethyl Ammonium Surfactant on Cephalexin Drug Delivery. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novembre, D.; Gimeno, D. Synthesis and Characterization of Analcime (ANA) Zeolite Using a Kaolinitic Rock. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Cui, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, X.; Tong, H.; Ma, L. Occurrence, Composition, and Origin of Analcime in Sedimentary Rocks of Non-Marine Petroliferous Basins in China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 113, 104164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Bu, J.; Qiu, J. Effect and Mechanism of Metakaolin Powder (MP) on Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Cementitious Suspension. Materials 2022, 15, 5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Alouani, M.; Alehyen, S.; el Achouri, M.; Taibi, M. Preparation, Characterization, and Application of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4212901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianglor, K.; Sinthupinyo, S.; Piyaworapaiboon, M.; Chaipanich, A. Effect of Alkali-Activated Metakaolin Cement on Compressive Strength of Mortars. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 141, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Rahman, M.R.; Paswan, R.; Bhattacharyya, S.K. Effect of Activator Concentration on the Strength, ITZ and Drying Shrinkage of Fly Ash/Slag Geopolymer Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 118, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocullo, V.; Vitola, L.; Vaiciukyniene, D.; Kantautas, A.; Bajare, D. The Influence of the SiO2/Na2O Ratio on the Low Calcium Alkali Activated Binder Based on Fly Ash. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 258, 123846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrejkovičová, S.; Sudagar, A.; Rocha, J.; Patinha, C.; Hajjaji, W.; da Silva, E.F.; Velosa, A.; Rocha, F. The Effect of Natural Zeolite on Microstructure, Mechanical and Heavy Metals Adsorption Properties of Metakaolin Based Geopolymers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 126, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Rocha, T.; Dias, D.P.; França, F.C.C.; de Salles Guerra, R.R.; da Costa de Oliveira Marques, L.R. Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Mortars with Different Alkaline Activators (Na+ and K+). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvila, M.T.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Vieira, C.M.F. Reaction Mechanisms of Alkali-Activated Materials. Rev. IBRACON Estrut. E Mater. 2021, 14, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Tang, Q.; Fan, X.; Gan, M.; Chen, X.; Ji, Z.; Huang, X. Self-Compacting Alkali-Activated Materials: Progress and Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosanefi, S.; Alavi, N.; Eslami, A.; Saadani, M.; Ghavami, A. Ammonium Removal from Landfill Fresh Leachate Using Zeolite as Adsorbent. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaki, S.A.; Bingxue, Z.; Guarecuco, R.; Thomas, T.; Minghui, Y. Geopolymer for Use in Heavy Metals Adsorption, and Advanced Oxidative Processes: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Tolonen, E.-T.; Runtti, H.; Kemppainen, K.; Perämäki, P.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Optimization of the Metakaolin Geopolymer Preparation for Maximized Ammonium Adsorption Capacity. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 9363–9376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Metakaolin Geopolymer Characterization and Application for Ammonium Removal from Model Solutions and Landfill Leachate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinelli, D.; Foglia, A.; Fatone, F.; Papa, E.; Maggetti, C.; Bovina, S.; Frascari, D. Ammonium Recovery from Municipal Wastewater by Ion Exchange: Development and Application of a Procedure for Sorbent Selection. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rożek, P.; Król, M.; Mozgawa, W. Geopolymer-Zeolite Composites: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguanpak, S.; Wannagon, A.; Saengam, C.; Chiemchaisri, W.; Chiemchaisri, C. Porous Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Granules for Removal of Ammonium in Aqueous Solution and Anaerobically Pretreated Piggery Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angar, Y.; Djelali, N.-E.; Kebbouche-Gana, S. Investigation of Ammonium Adsorption on Algerian Natural Bentonite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11078–11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, Z. Adsorption Mechanism of High-Concentration Ammonium by Chinese Natural Zeolite with Experimental Optimization and Theoretical Computation. Water 2022, 14, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhu, Q.; Xing, Z. Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen in Low Temperature Domestic Wastewater by Modification Bentonite. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, W.; Ma, L.; Cao, D.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Simultaneous Removal of Ammonia and Phosphate Using Green Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Dispersed onto Zeolite. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu, M. Removal of Ammonium from Municipal Wastewater Using Natural Turkish (Dogantepe) Zeolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).