Synthesis and Characterization of Fluorinated Phosphonium Ionic Liquids to Use as New Engineering Solvents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Thermal Properties
2.2.2. Viscosity and Density
2.2.3. Ionic Conductivity
2.2.4. Refractive Index
2.2.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Properties
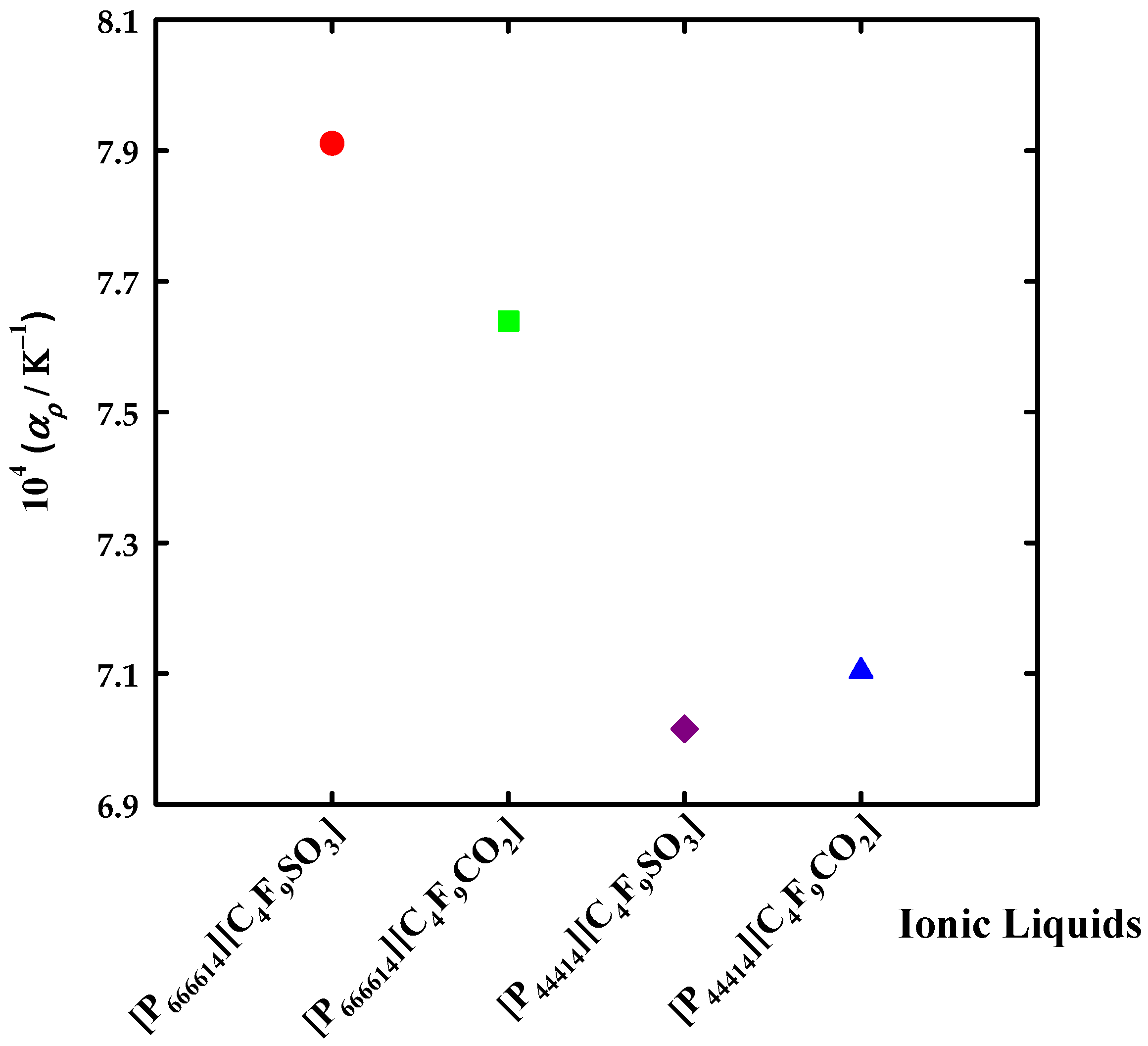
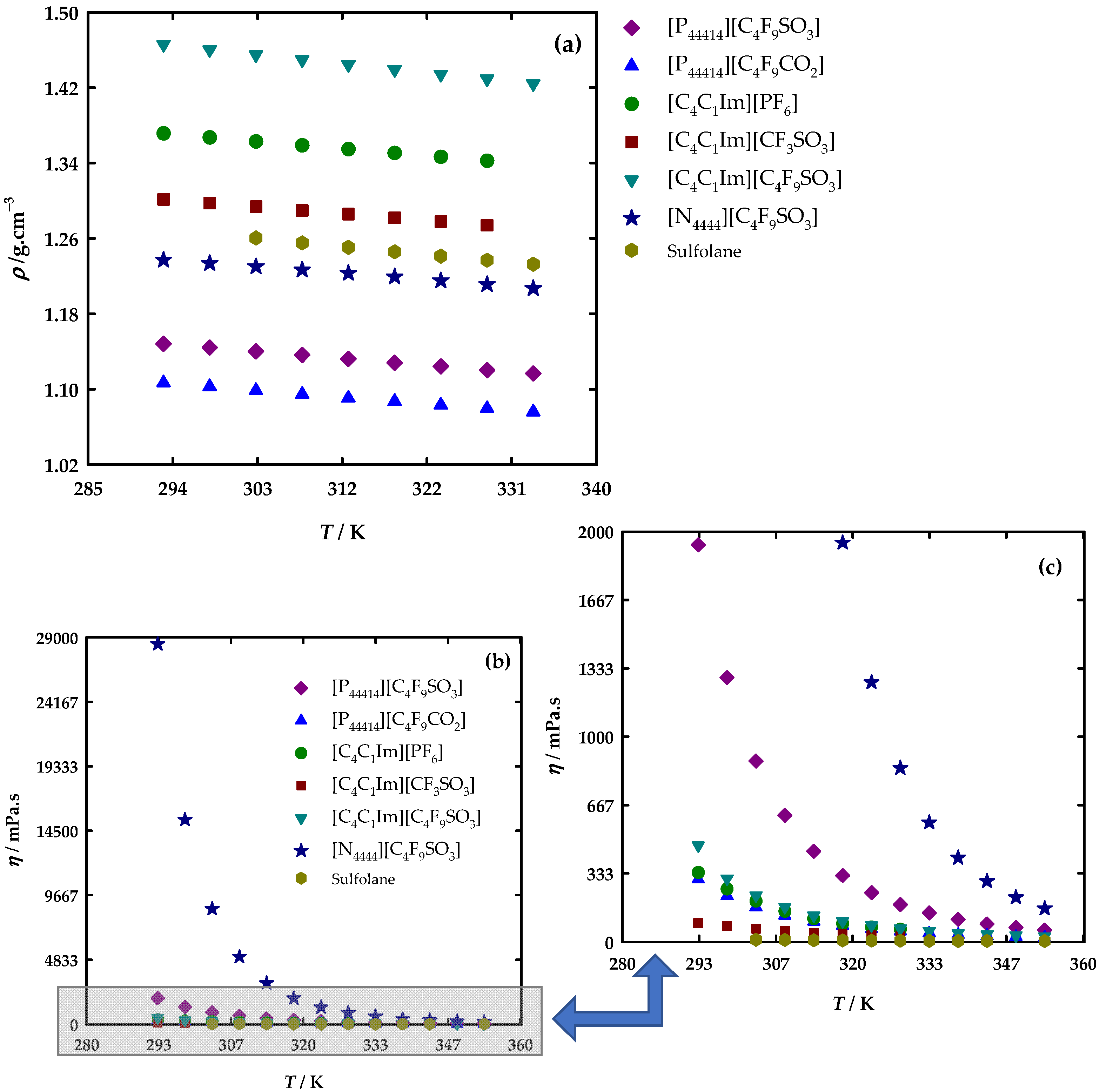
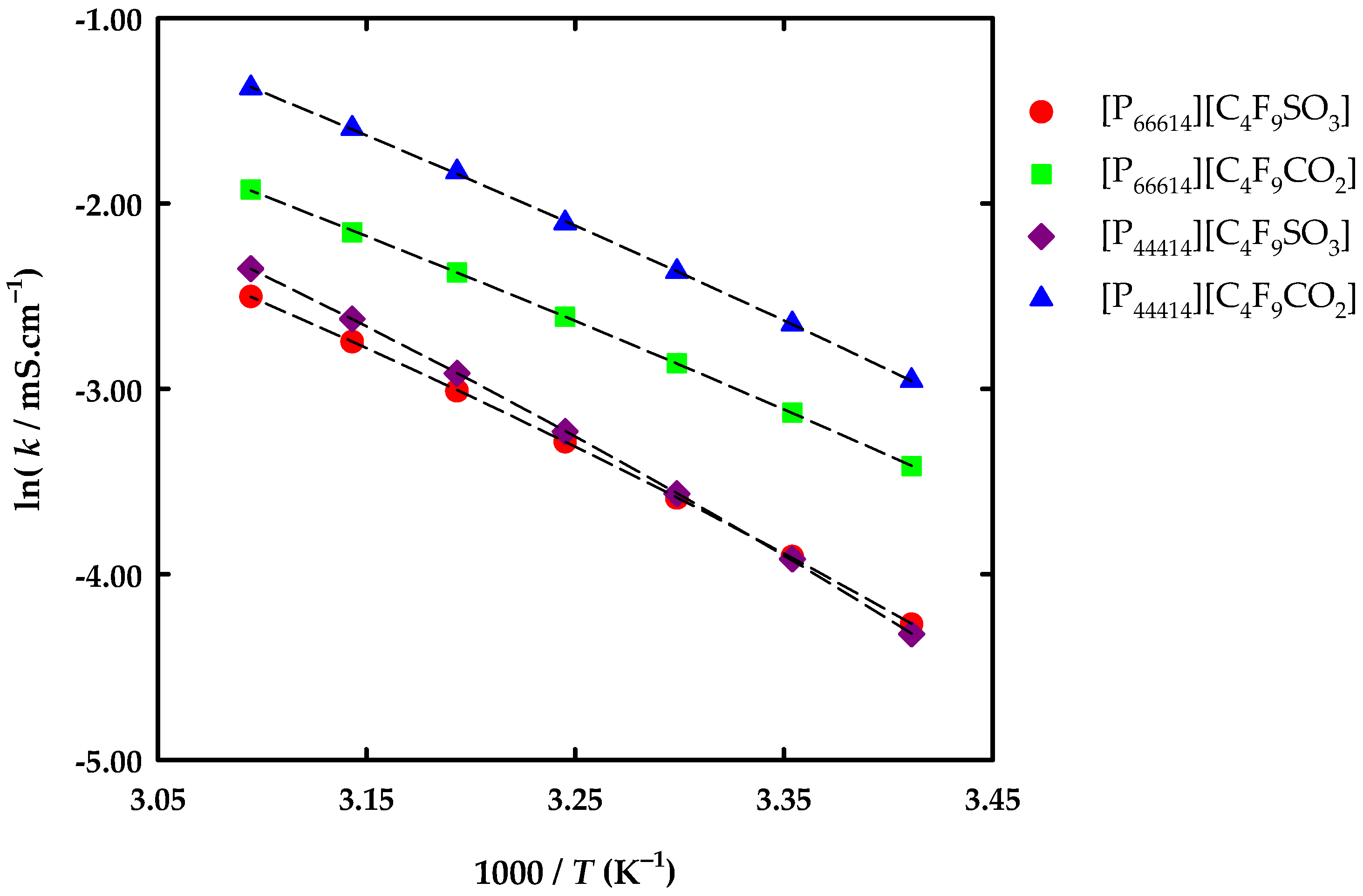
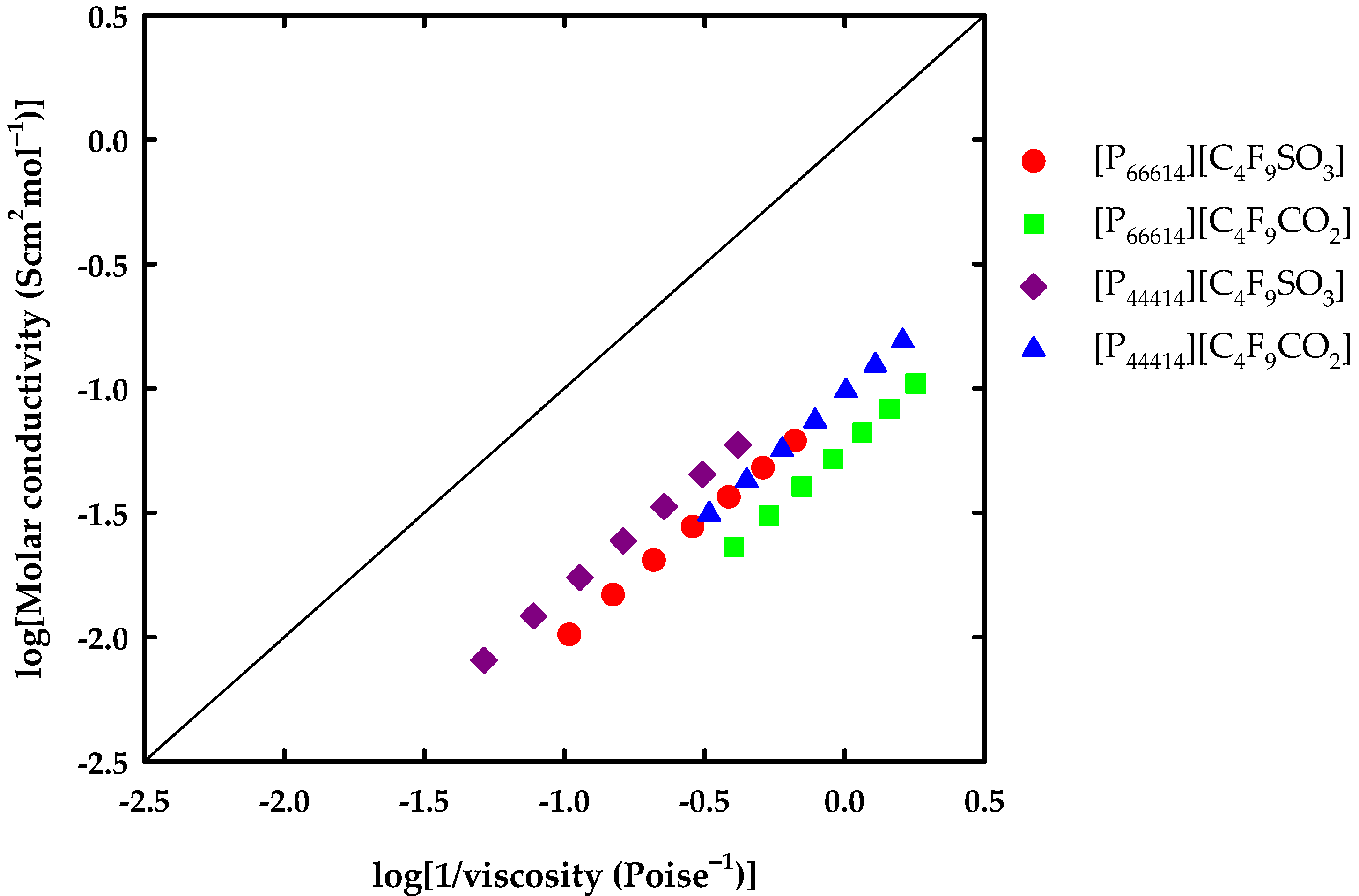
3.2. Thermophysical Properties
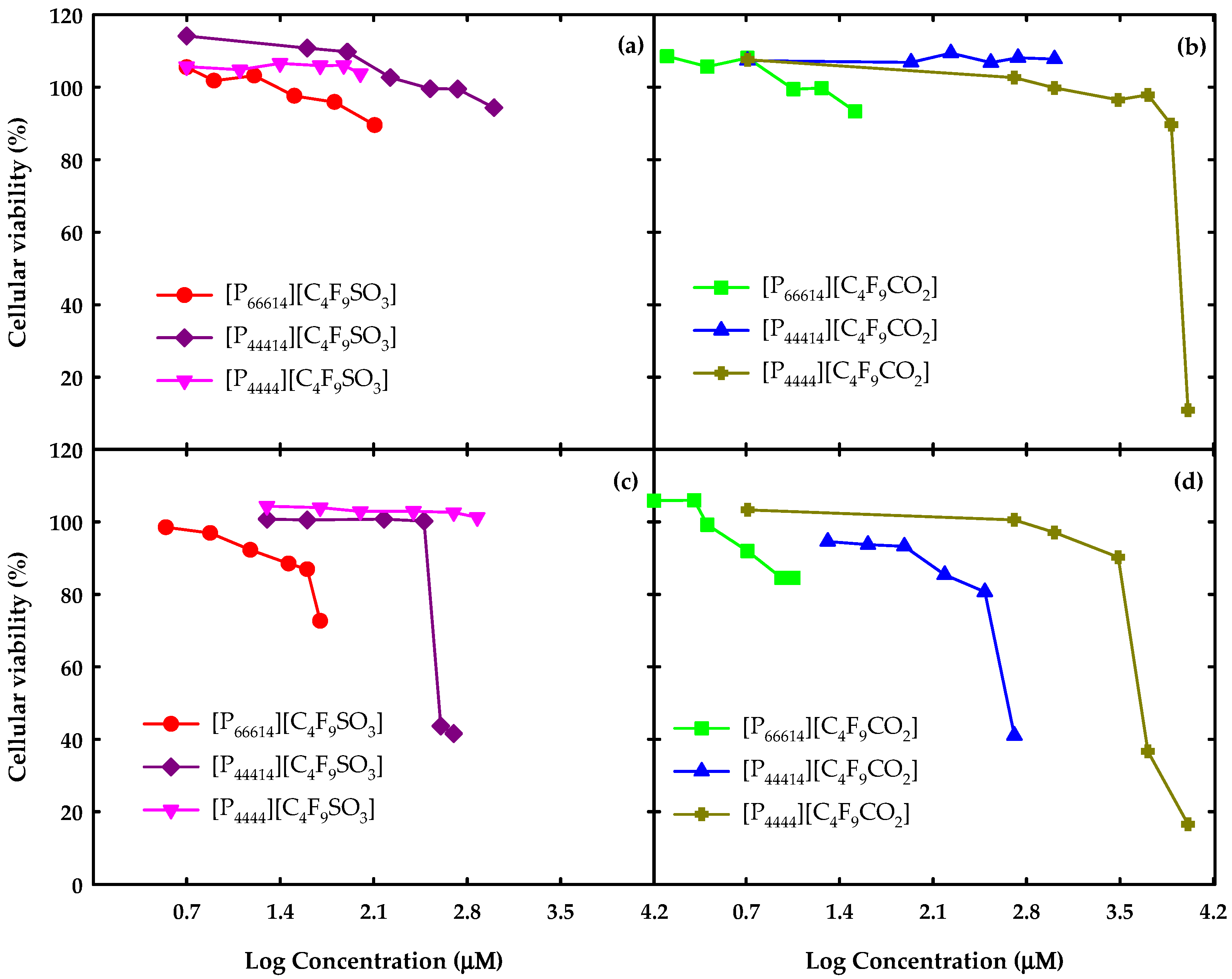
3.3. In Vitro Cell Viability Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilkes, J.S. A Short History of Ionic Liquids—From Molten Salts to Neoteric Solvents. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez de María, P.; Maugeri, Z. Ionic Liquids in Biotransformations: From Proof-of-Concept to Emerging Deep-Eutectic-Solvents. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorke, J.; Srienc, F.; Kazlauskas, R. Toward Advanced Ionic Liquids. Polar, Enzyme-Friendly Solvents for Biocatalysis. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2010, 15, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkiewicz, F.; Materna, K.; Kropacz, A.; Michalczyk, A.; Gwiazdowski, R.; Praczyk, T.; Pernak, J. Multifunctional Long-Alkyl-Chain Quaternary Ammonium Azolate Based Ionic Liquids. New J. Chem. 2010, 34, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Ionic Liquids in Surface Electrochemistry. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of Ionic Liquids in the Chemical Industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.D.; Zhang, C.; Hantao, L.W.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic Liquids in Analytical Chemistry: Fundamentals, Advances, and Perspectives. Anal. Chem. 2013, 86, 262–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological Activity of Ionic Liquids and Their Application in Pharmaceutics and Medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgers, C.; Uerdingen, M.; Wagner, M.; Wasserscheid, P.; Schlücker, E. Processing or Working Machine Comprising an Ionic Liquid as the Service Fluid, European Patent Office, EP1848789A1; Merck Patent GmbH, 2007.
- Maton, C.; De Vos, N.; Stevens, C.V. Ionic Liquid Thermal Stabilities: Decomposition Mechanisms and Analysis Tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, M.; Perosa, A.; Noé, M. Phosphonium Salts and P-Ylides. Organophosphorus Chem. 2016, 45, 132–169. [Google Scholar]
- Cieszynska, A.; Wisniewski, M. Selective Extraction of Palladium(II) from Hydrochloric Acid Solutions with Phosphonium Extractants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frackowiak, E.; Lota, G.; Pernak, J. Room-Temperature Phosphonium Ionic Liquids for Supercapacitor Application. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 164104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunashima, K.; Sugiya, M. Physical and Electrochemical Properties of Low-Viscosity Phosphonium Ionic Liquids as Potential Electrolytes. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 2353–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, R.R.; Soares, B.G. Sepiolite Modified with Phosphonium Ionic Liquids as Anticorrosive Pigment for Epoxy Coatings. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 200, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Malhotra, S.V. Study on the Potential Anti-Cancer Activity of Phosphonium and Ammonium-Based Ionic Liquids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4643–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruokonen, S.K.; Sanwald, C.; Sundvik, M.; Polnick, S.; Vyavaharkar, K.; Duša, F.; Holding, A.J.; King, A.W.T.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Lämmerhofer, M.; et al. Effect of Ionic Liquids on Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Viability, Behavior, and Histology; Correlation between Toxicity and Ionic Liquid Aggregation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7116–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Martinho, S.; Alves, F.; Nunes, S.; Matias, A.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Fluorinated Ionic Liquids: Properties and Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindale, J.J.; Na, C.; Jennings, M.C.; Ragogna, P.J. Synthesis and Characterization of Fluorinated Phosphonium Ionic Liquids. Can. J. Chem. 2011, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Ferreira, M.L.; Castro, P.J.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Fluorinated Ionic Liquids as Task-Specific Materials: An Overview of Current Research. In Ionic Liquids-Thermophysical Properties and Applications; Murshed, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Reis, P.M.; Shimizu, K.; Cortes, O.A.; Marrucho, I.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Pereiro, A.B.; Rebelo, L.P.N. A Thermophysical and Structural Characterization of Ionic Liquids with Alkyl and Perfluoroalkyl Side Chains. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65337–65350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Stolte, S.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Pereiro, A.B.; Markiewicz, M. Acute Aquatic Toxicity and Biodegradability of Fluorinated Ionic Liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Bastos, J.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Matias, A.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Human Cytotoxicity and Octanol/Water Partition Coefficients of Fluorinated Ionic Liquids. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Mohamed, H.M.; Kurowska-Susdorf, A.; Dewani, R.; Fares, M.Y.; Andruch, V. Green analytical chemistry as an integral part of sustainable education development. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 31, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centi, G.; Perathoner, S. Catalysis and sustainable (green) chemistry. Catal. Today. 2003, 77, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tundo, P.; Anastas, P.; Black, D. StC.; Breen, J.; Collins, T.J.; Memoli, S.; Miyamoto, J.; Polyakoff, M.; Tumas, W. Synthetic pathways and processes in green chemistry. Introductory overview. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1207–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukumoto, K.; Yoshizawa, M.; Ohno, H. Room Temperature Ionic Liquids from 20 Natural Amino Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2398–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Oliveira, F.S.; Bernardes, C.E.S.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Marrucho, I.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Inorganic salts in purely ionic liquid media: The development of high ionicity ionic liquids (HIILs). Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3656–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debenedetti, P.G.; Stillinger, F.H. Supercooled Liquids and the Glass Transition. Nature 2001, 410, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, D.M.; Moens, L.; Rudnicki, D.; Pilath, H. Lifetime of Imidazolium Salts at Elevated Temperatures. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2006, 128, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.F.; Simões, P.N.; Ferreira, A.G.M. Quaternary Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids: Thermal Stability and Heat Capacity of the Liquid Phase. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 45, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.S.M.; Zhang, X.; MacFarlane, D.R. Synthesis and Physicochemical Properties of Fluorinated Ionic Liquids with High Nitrogen Gas Solubility. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 24550–24558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Sesto, R.E.; Corley, C.; Robertson, A.; Wilkes, J.S. Tetraalkylphosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 2536–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A.; Wagle, D.V.; Ravula, S.; Zhang, Q. Tuning Task-Specific Ionic Liquids for the Extractive Desulfurization of Liquid Fuel. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4771–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, K.N.; Brennecke, J.F.; Chirico, R.D.; Frenkel, M.; Heintz, A.; Magee, J.W.; Peters, C.J.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Seddon, K.R. Thermodynamic and Thermophysical Properties of the Reference Ionic Liquid: 1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Bis[(Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl]Amide (Including Mixtures) Part 1. Experiment Al Methods and Results (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, R.D.; Diky, V.; Magee, J.W.; Frenkel, M.; Marsh, K.N. Thermodynamic and Thermophysical Properties of the Reference Ionic Liquid: 1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Bis[(Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl]Amide (Including Mixtures). Part 2. Critical Evaluation and Recommended Property Values (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 791–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Refractive Index. Edited by Adam Augustyn. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/refractive-index (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Tariq, M.; Forte, P.A.S.; Gomes, M.F.C.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Densities and Refractive Indices of Imidazolium- and Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids: Effect of Temperature, Alkyl Chain Length, and Anion. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2009, 41, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, A.R.H.; Marsh, K.N.; Wakeham, W.A. IUPAC Experimental Thermodynamics Vol. VI: Measurement of the Thermodynamic Properties of Single Phases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 435–451. [Google Scholar]
- Gardas, R.L.; Coutinho, J.A.P. A Group Contribution Method for Viscosity Estimation of Ionic Liquids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2008, 266, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Llovell, F.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Santos, A.S.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Vega, L.F. Thermophysical Characterization of Ionic Liquids Based on the Perfluorobutanesulfonate Anion: Experimental and Soft-SAFT Modeling Results. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 2012–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez, M.S.; Vega, Y.A.; Romero, C.M. Effect of temperature on the viscosities and the volumetric properties of the binary mixtures of the ionic liquids [bmim][PF6] and [bmim][CF3SO3]. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Águila-Hernández, J.; Trejo, A.; García-Flores, B.E.; Molnar, R. Viscometric and volumetric behaviour of binary mixtures of sulfolane and N-methylpyrrolidone with monoethanolamine and diethanolamine in the range 303–373K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2008, 267, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Marrucho, I.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Ionic liquids in separations of azeotropic systems—A review. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 46, 2–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M.; Izgorodina, E.I.; Abbott, A.P.; Annat, G.; Fraser, K. On the Concept of Ionicity in Ionic Liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 4962–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, K.; Tokuda, H.; Watanabe, M. Ionicity in Ionic Liquids: Correlation with Ionic Structure and Physicochemical Properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.R. Relations between the Fractional Stokes−Einstein and Nernst−Einstein Equations and Velocity Correlation Coefficients in Ionic Liquids and Molten Salts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 9572–9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, A.B.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Oliveira, F.S.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Marrucho, I.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Solubility of Inorganic Salts in Pure Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 55, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miran, M.S.; Kinoshita, H.; Yasuda, T.; Susan, M.A.B.H.; Watanabe, M. Physicochemical Properties Determined by ΔpKa for Protic Ionic Liquids Based on an Organic Super-Strong Base with Various Brønsted Acids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 5178–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cooper, E.I.; Austen, A.C. Ionic Liquids: Ion Mobilities, Glass Temperatures, and Fragilities. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 6170–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, M.J.; Goetz, G.S.; Alpers, D.H. Caco-2 Cells Express a Combination of Colonocyte and Enterocyte Phenotypes. J. Cell. Phys. 1998, 174, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lorenzo, A.; Tojo, E.; Tojo, J.; Teijeira, M.; Rodríguez-Berrocal, F.J.; González, M.P.; Martínez-Zorzano, V.S. Cytotoxicity of Selected Imidazolium-Derived Ionic Liquids in the Human Caco-2 Cell Line. Sub-Structural Toxicological Interpretation through a QSAR Study. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambuy, Y.; De Angelis, I.; Ranaldi, G.; Scarino, M.L.; Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. The Caco-2 Cell Line as a Model of the Intestinal Barrier: Influence of Cell and Culture-Related Factors on Caco-2 Cell Functional Characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005 211 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, A.; Nunes, S.L.; Poejo, J.; Mecha, E.; Serra, A.T.; Madeira, P.J.A.; Bronze, M.R.; Duarte, C.M.M. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of a Flavonoid-Rich Concentrate Recovered from Opuntia Ficus-Indica Juice. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 3269–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, T. Caco-2 Cell Line. In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkening, S.; Stahl, F.; Bader, A. Comparison of Primary Human Hepatocytes and Hepatoma Cell Line Hepg2 with Regard to Their Biotransformation Properties. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, M.T.; Tolosa, L.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J. Culture and Functional Characterization of Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells. Protoc. Vitr. Hepatocyte Res. 2015, 1250, 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Frade, R.F.M.; Matias, A.; Branco, L.C.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Duarte, C.M.M. Effect of Ionic Liquids on Human Colon Carcinoma HT-29 and CaCo-2 Cell Lines. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, S.K.; Robciuc, A.; Lokajová, J.; Holding, A.J.; Lämmerhofer, M.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Holopainen, J.M.; King, A.W.T.; Wiedmer, S.K. Impact of Amphiphilic Biomass-Dissolving Ionic Liquids on Biological Cells and Liposomes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zeng, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, F.; Tan, Z. Assessment of the Cytotoxicity of Ionic Liquids on Spodoptera Frugiperda 9 (Sf-9) Cell Lines via in Vitro Assays. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 348, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name and Acronym | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|
| Trihexyltetradecylphosphonium perfluorobutanesulfonate [P66614][C4F9SO3] |  |
| Trihexyltetradecylphosphonium perfluoropentanoate [P66614][C4F9CO2] |  |
| Tributyltetradecylphosphonium perfluorobutanesulfonate [P44414][C4F9SO3] | 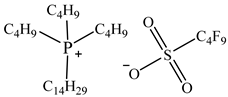 |
| Tributyltetradecylphosphonium perfluoropentanoate [P44414][C4F9CO2] | 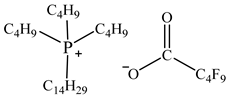 |
| Tetrabutylphosphonium perfluorobutanesulfonate [P4444][C4F9SO3] | 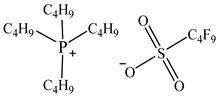 |
| Tetrabutylphosphonium perfluoropentanoate [P4444][C4F9CO2] | 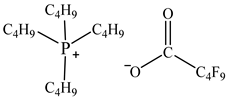 |
| Ionic Liquid | Tg [K] | Ts-s [K] |
|---|---|---|
| [P66614][C4F9SO3] | 201 | - |
| [P66614][C4F9CO2] | 196 | - |
| [P44414][C4F9SO3] | 211 | - |
| [P44414][C4F9CO2] | 205 | - |
| [P4444][C4F9SO3] | 221 | 247 |
| [P4444][C4F9CO2] | - | 253 |
| Ionic Liquid | Tstart 1[K] | Tonset 1[K] | Tdec 1[K] |
|---|---|---|---|
| [P66614][C4F9SO3] | 499 | 673 | 670 |
| [P66614][C4F9CO2] | 378 | 421 | 413 |
| [P44414][C4F9SO3] | 484 | 669 | 676 |
| [P44414][C4F9CO2] | 374 | 420 | 413 |
| [P4444][C4F9SO3] | 492 | 669 | 664 |
| [P4444][C4F9CO2] | 494 | 669 | 665 |
| Tstart 2[K] | Tonset 2[K] | Tdec 2[K] | |
| [P66614][C4F9CO2] | 435 | 529 | 514 |
| [P44414][C4F9CO2] | 440 | 473 | 499 |
| Tstart 3[K] | Tonset 3[K] | Tdec 3[K] | |
| [P66614][C4F9CO2] | 552 | 608 | 609 |
| [P44414][C4F9CO2] | 586 | 704 | 691 |
| EC50 (µM) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ionic Liquid | Caco-2 | HepG2 |
| [P66614][C4F9SO3] | >128 | >50 |
| [P66614][C4F9CO2] | >32 | >11 |
| [P44414][C4F9SO3] | >1000 | 389 |
| [P44414][C4F9CO2] | >1000 | 447 |
| [P4444][C4F9SO3] | >100 | >750 |
| [P4444][C4F9CO2] | 8710 | 7244 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naranjo, M.C.; Redondo, A.E.; Acuña, J.C.; Vieira, N.S.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Pereiro, A.B. Synthesis and Characterization of Fluorinated Phosphonium Ionic Liquids to Use as New Engineering Solvents. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6030038
Naranjo MC, Redondo AE, Acuña JC, Vieira NSM, Araújo JMM, Pereiro AB. Synthesis and Characterization of Fluorinated Phosphonium Ionic Liquids to Use as New Engineering Solvents. ChemEngineering. 2022; 6(3):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6030038
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaranjo, María C., Andres E. Redondo, Jacqueline C. Acuña, Nicole S. M. Vieira, João M. M. Araújo, and Ana B. Pereiro. 2022. "Synthesis and Characterization of Fluorinated Phosphonium Ionic Liquids to Use as New Engineering Solvents" ChemEngineering 6, no. 3: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6030038
APA StyleNaranjo, M. C., Redondo, A. E., Acuña, J. C., Vieira, N. S. M., Araújo, J. M. M., & Pereiro, A. B. (2022). Synthesis and Characterization of Fluorinated Phosphonium Ionic Liquids to Use as New Engineering Solvents. ChemEngineering, 6(3), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6030038








