Investigation of the Applicability of Raman Spectroscopy as Online Process Control during Consumer Milk Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
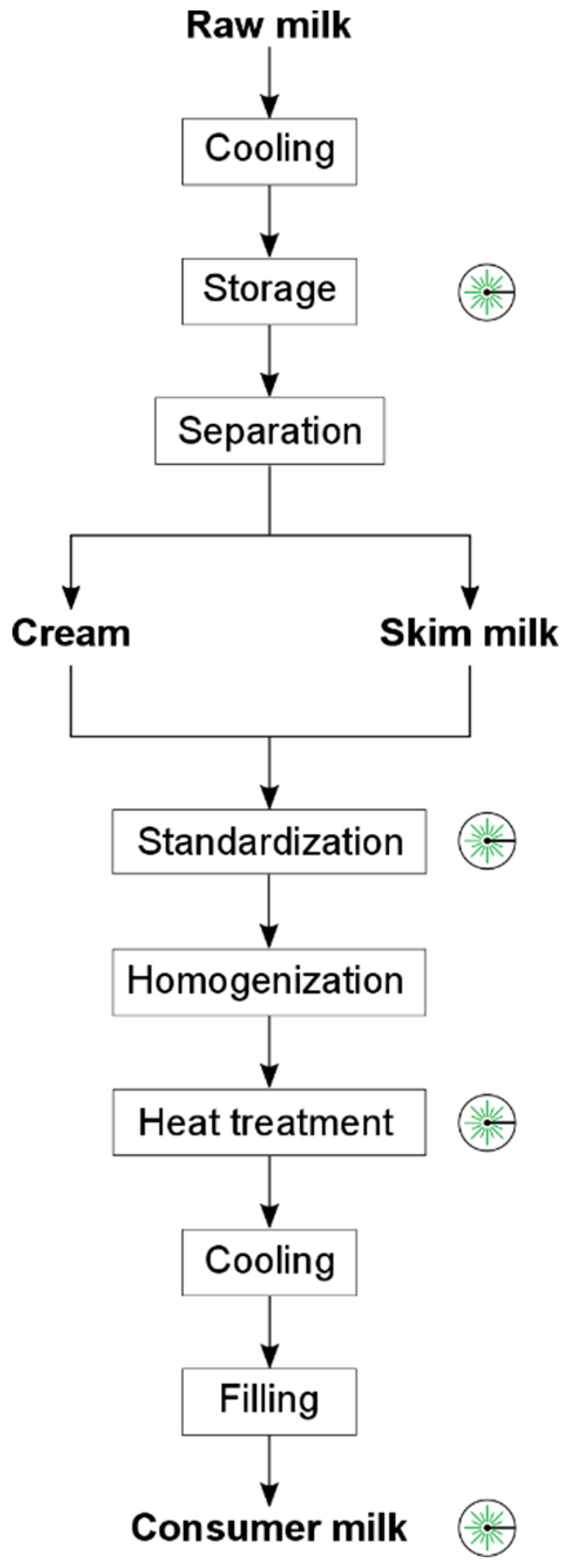
2.1. Samples
2.2. Raman Spectroscopic Measurements
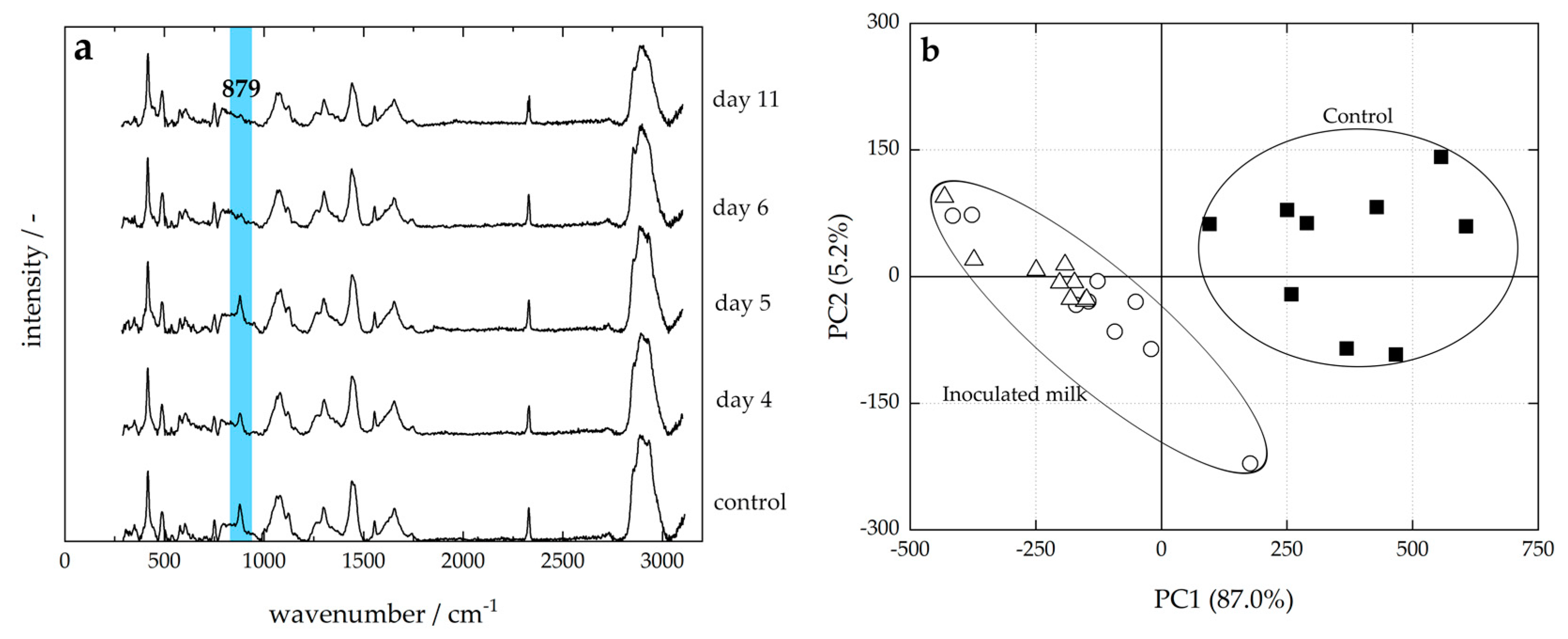
2.3. Inoculation with Pseudomonas sp. and Storage Test
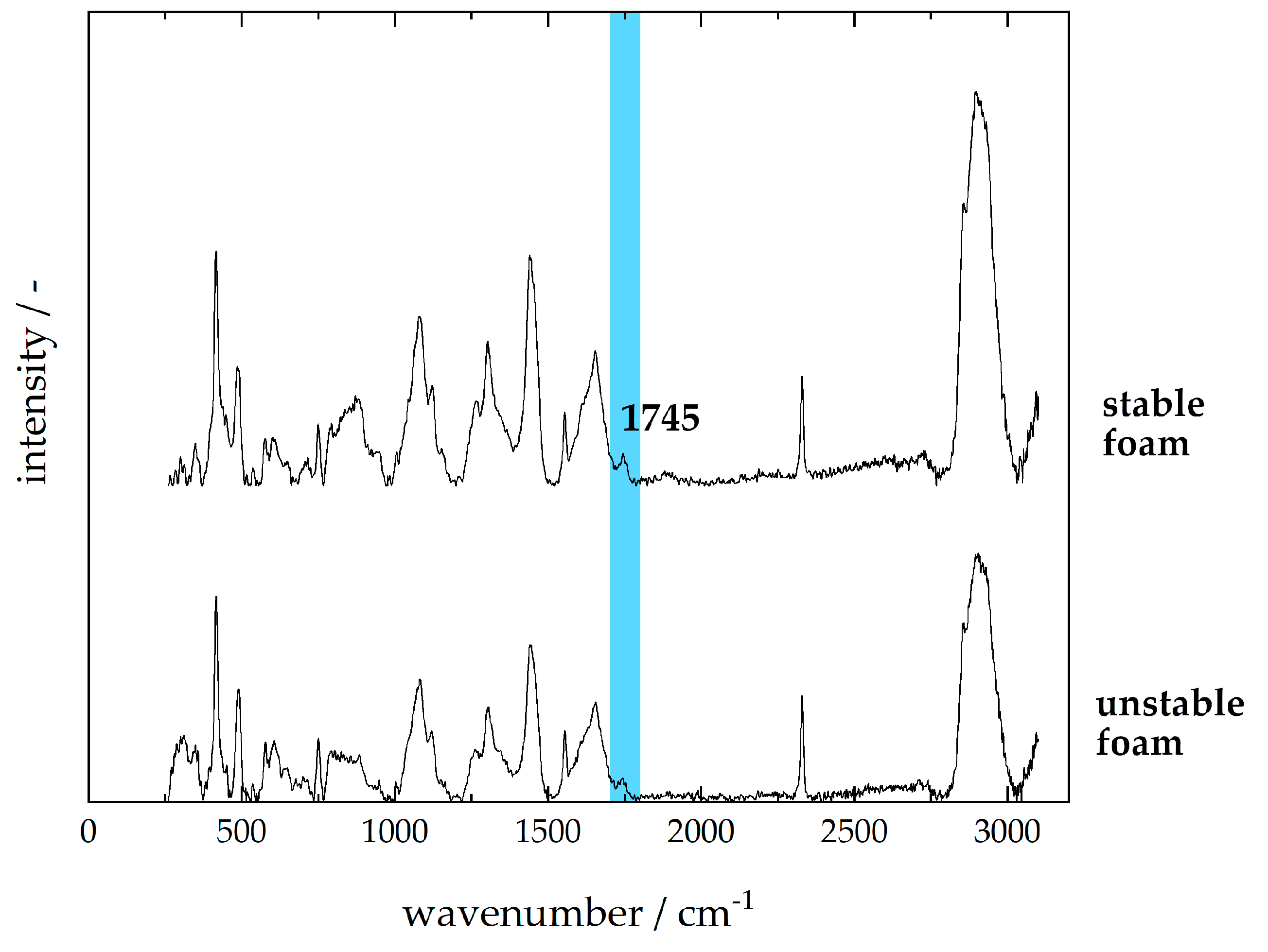
2.4. Preparation and Analysis of Milk Foam
- V15 ≥ 150 mL → good foam stability
- V15 < 150 mL → bad foam stability
2.5. Chemical Composition
2.6. Spectral Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
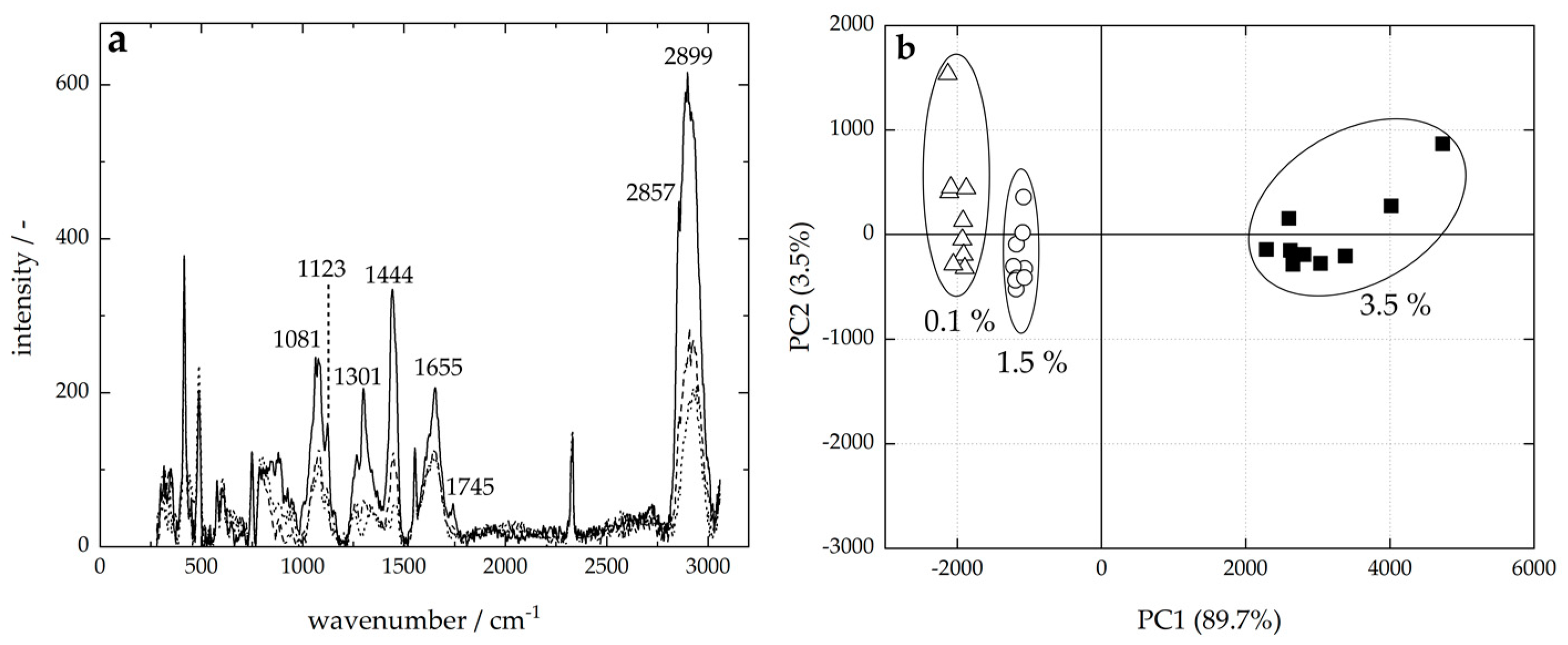
3.1. Standardization
3.1.1. Fat Content
3.1.2. Lactose
3.2. Raw Milk Storage
3.3. Heat Treatment
3.4. Consumer Milk—Foam Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript: | |
| ESL | Extended shelf life |
| ESL-MF | Extended shelf life-microfiltration |
| ESL-HHST | Extended shelf life-higher-heat shorter time |
| FFA | Free fatty acids |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| PC | Principal component |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| UHT | Ultrahigh temperature |
Appendix A
| Sample Code | Fat Content (%) | Protein Content (%) | Dry Matter (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 3.73 | 3.34 | 12.45 |
| C2 | 3.51 | 3.37 | 12.26 |
| C3 | 3.57 | 3.37 | 12.33 |
| C4 | 3.49 | 3.34 | 12.16 |
| C5 | 3.97 | 3.35 | 12.75 |
| C6 | 3.80 | 3.29 | 12.51 |
| C7 | 3.49 | 3.35 | 12.17 |
| C8 | 3.48 | 3.35 | 12.15 |
| C9 | 3.50 | 3.41 | 12.35 |
| C10 | 3.53 | 3.40 | 12.35 |
| C11 | 3.52 | 3.37 | 12.29 |
| C12 | 3.55 | 3.36 | 12.29 |
| C13 | 3.57 | 3.44 | 12.53 |
| C14 | 3.52 | 3.35 | 12.19 |
| C15 | 3.54 | 3.40 | 12.36 |
References
- Bradley, R.L. Effect of Light on Alteration of Nutritional Value and Flavor of Milk: A Review. J. Food Prot. 1980, 43, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.; Espiga, A.; Niranjan, K.; Livings, S.; Gumy, J.-C.; Sher, A. Formation and Stability of Milk Foams. In Bubbles in Food 2; Campbell, G., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 153–161. ISBN 9781891127595. [Google Scholar]
- Madimutsa, O.N.M.; Gwala, W.; Mujuru, F.; Nyambi, C. Investigation of Factors Affecting Frothing Capacity of Pasteurised Whole Milk for Cappuccino Coffee. Int. J. Latest Technol. Eng. Manag. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ponte, S. The ‘Latte Revolution’? Regulation, Markets and Consumption in the Global Coffee Chain. World Dev. 2002, 30, 1099–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, R.C. Dairy processing and quality assurance: An overview. In Dairy Processing & Quality Assurance, 2nd ed.; Chichester: West Sussex, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–40. ISBN 978-1-118-81031-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lafarge, V.; Ogier, J.-C.; Girard, V.; Maladen, V.; Leveau, J.-Y.; Gruss, A.; Delacroix-Buchet, A. Raw cow milk bacterial population shifts attributable to refrigeration. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5644–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonghe, V.; Coorevits, A.; van Hoorde, K.; Messens, W.; van Landschoot, A.; de Vos, P.; Heyndrickx, M. Influence of storage conditions on the growth of Pseudomonas species in refrigerated raw milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, T.M. A review of heat resistant lipases and proteinases and the quality of dairy products. Ir. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1977, 1, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, M.W.; Phillips, J.D.; West, I.G.; Muir, D.D. The effect of extended low-temperature storage of raw milk on the quality of pasteurized and UHT milk. Food Microbiol. 1988, 5, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckel, M.; Lidolt, M.; Achberger, V.; Glück, C.; Krewinkel, M.; Stressler, T.; von Neubeck, M.; Wenning, M.; Scherer, S.; Fischer, L.; et al. Growth of Pseudomonas weihenstephanensis, Pseudomonas proteolytica and Pseudomonas sp. in raw milk: Impact of residual heat-stable enzyme activity on stability of UHT milk during shelf-life. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 59, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, H.G. Lebensmittel- und Bioverfahrenstechnik: Molkereitechnologie; Verlag A. Kessler: Freising, Germany, 1996; ISBN 9783980237840. [Google Scholar]
- Huppertz, T. Foaming properties of milk: A review of the influence of composition and processing. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2010, 63, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstra, P. Principles of Foam Formation and Stability. Foams: Physics, Chemistry and Structure; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Oetjen, K.; Bilke-Krause, C.; Madani, M.; Willers, T. Temperature effect on foamability, foam stability, and foam structure of milk. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Engingeeing Asp. 2014, 460, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailing, P.J.; Walstra, P. Protein-stabilized foams and emulsions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1981, 15, 155–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, D.K.; Wilde, P.J.; Clark, D.C. Control of surfactant-induced destabilization of foams through polyphenol-mediated protein-protein interactions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, S.; Szostak, R.; Czaja, T.; Zachwieja, A. Analysis of milk by FT-Raman spectroscopy. Talanta 2015, 138, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.R.; Oliveira, K.d.S.; Stephani, R.; de Oliveira, L.F.C. Fourier-transform Raman analysis of milk powder: A potential method for rapid quality screening. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2011, 42, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwoudt, M.K.; Holroyd, S.E.; McGoverin, C.M.; Simpson, M.C.; Williams, D.E. Rapid, sensitive, and reproducible screening of liquid milk for adulterants using a portable Raman spectrometer and a simple, optimized sample well. J. Dairy Science. 2016, 99, 7821–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Chan, E.C.Y. The applications of Raman spectroscopy in food science. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha, R.A.; Paiva, I.M.; Anjos, V.; Furtado, M.A.M.; Bell, M.J.V. Quantification of whey in fluid milk using confocal Raman microscopy and artificial neural network. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3559–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Rodda, T.; Haynes, C.L.; Deschaines, T.; Strother, T.; Diez-Gonzalez, F.; Labuza, T.P. Detection of a Foreign Protein in Milk Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Coupled with Antibody-Modified Silver Dendrites. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1510–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Zou, M.-Q.; Qi, X.-H.; Liu, F.; Zhu, X.-H.; Zhao, B.-H. Detection of melamine in liquid milk using surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwoudt, M.K.; Holroyd, S.E.; McGoverin, C.M.; Simpson, M.C.; Williams, D.E. Raman spectroscopy as an effective screening method for detecting adulteration of milk with small nitrogen-rich molecules and sucrose. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2520–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Abassy, R.; Eravuchira, P.J.; Donfack, P.; von der Kammer, B.; Materny, A. Fast determination of milk fat content using Raman spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2011, 56, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, T.O.; Junqueira, G.M.A.; Porto, B.L.S.; Brito, C.D.; Sato, F.; de Oliveira, M.A.L.; Anjos, V.; Bell, M.J.V. Vibrational spectroscopy for milk fat quantification: Line shape analysis of the Raman and infrared spectra. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2016, 47, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gu, J.; Xiang, G.; Xu, J.; Fu, S.; Gong, H. Detection of total protein in milk using phosphomolybdic acid-mediated surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Abassy, R.M.; Eravuchira, P.J.; Donfack, P.; von der Kammer, B.; Materny, A. Direct determination of unsaturation level of milk fat using Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2012, 66, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, N.; Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. Fourier transform infrared and Raman spectroscopies for the rapid detection, enumeration, and growth interaction of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris in milk. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5681–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, S.; Stöckel, S.; Elschner, M.; Melzer, F.; Rösch, P.; Popp, J. Raman spectroscopy as a potential tool for detection of Brucella spp. in milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5575–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Feng, J.; Chen, J.C.; Du, X.-j.; Luo, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, S. Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes in milk using confocal micro-Raman spectroscopy and chemometric analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 204, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidemaier, K.; Carruthers, E.; Curry, A.; Kuroda, M.; Fallows, E.; Thomas, J.; Sherman, D.; Muldoon, M. Real-time pathogen monitoring during enrichment: A novel nanotechnology-based approach to food safety testing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 198, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernuy, B.; Meurens, M.; Mignolet, E.; Larondelle, Y. Performance Comparison of UV and FT-Raman Spectroscopy in the Determination of Conjugated Linoleic Acids in Cow Milk Fat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, J.R.; Bell, S.E.J.; Moss, B.W. A critical evaluation of Raman spectroscopy for the analysis of lipids: Fatty acid methyl esters. Lipids 2004, 39, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallier, S.; Gordon, K.C.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; Everett, D.W. Composition of bovine milk fat globules by confocal Raman microscopy. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.H.; Dann, S.E.; Blatchford, C.G. Lactose: A definitive guide to polymorph determination. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 334, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGoverin, C.M.; Clark, A.S.S.; Holroyd, S.E.; Gordon, K.C. Raman spectroscopic quantification of milk powder constituents. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 673, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattiasson, B.; Danielsson, B. Calorimetric analysis of sugars and sugar derivatives with aid of an enzyme thermistor. Carbohydr. Res. 1982, 102, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indyk, H. High performance liquid chromatographic analysis of lactose-hydrolysed milk. Food Chem. 1996, 57, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.S.; Jeon, I.J. Comparison of High Performance Liquid Chromatography and Enzymatic Method for the Measurement of Lactose in Milk. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 975–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Kuballa, T.; Leitz, J.; Andlauer, C.; Lachenmeier, D.W. NMR spectroscopy as a screening tool to validate nutrition labeling of milk, lactose-free milk, and milk substitutes based on soy and grains. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2012, 92, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 9780470093078. [Google Scholar]
- Li-Chan, E.; Nakai, S.; Hirotsuka, M. Raman spectroscopy as a probe of protein structure in food systems. In Protein Structure-Function Relationships in Foods; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 163–197. [Google Scholar]
- Nevin, A.; Osticioli, I.; Anglos, D.; Burnstock, A.; Cather, S.; Castellucci, E. Raman spectra of proteinaceous materials used in paintings: A multivariate analytical approach for classification and identification. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6143–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, M.; Li-Chan, E.; Nakai, S. Raman spectroscopic study of thermally induced gelation of whey proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Chan, E.; Nakai, S. Raman spectroscopic study of thermally and/or dithiothreitol induced gelation of lysozyme. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, J.E. Dehydrated foods, chemistry of browning reactions in model systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1953, 1, 928–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.P.; Kessler, H.-G. Über die Reaktionskinetik der Sporenabtötung und chemischer Veränderungen bei der thermischen Haltbarmachung von Milch zur Optimierung von Erhitzungsverfahren. Chem. Ing. Tech. 1982, 54, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, V.; Scherer, S.; Kulozik, U. Verfahren zur Verlängerung der Haltbarkeit von Konsummilch und ihre stofflichen Veränderungen: ESL-Milch. J. Für Verbrauch. Und Lebensm. 2010, 5, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, V.; Kulozik, U. Verfahrenskonzepte zur Herstellung von ESL-Milch. Dtsch. Milchwirtwirtschaft 2007, 58, 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, V.; Kulozik, U. Kombination von Mikrofiltration und thermischen Verfahren zur Haltbarkeitsverlängerung von Lebensmitteln. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2006, 78, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, S.; Huppertz, T.; Houlihan, A.V.; Deeth, H. The influence of temperature on the foaming of milk. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, S.; Huppertz, T.; Houlihan, A.V.; Deeth, H. Relationship between surface tension, free fatty acid concentration and foaming properties of milk. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töpel, A. Chemie und Physik der Milch: Naturstoff - Rohstoff - Lebensmittel; Behr’s Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Law, B.A. Enzymes of psychrotrophic bacteria and their effects on milk and milk products. J. Dairy Res. 1979, 46, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, A.W.; Deeth, H.C.; MacRae, I.C. Growth of lipolytic psychrotrophic pseudomonads in raw and ultra-heat-treated milk. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1986, 61, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, R.A. Lipolysis and the frothing of milk. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 1965, 20, 62. [Google Scholar]



| Manufacturers of Milk Samples |
|---|
| Arla Foods A.m.b.A., Viby, Denmark |
| FrieslandCampina, Amersfoort, The Netherlands |
| Hohenloher Molkerei eG, Schwäbisch Hall, Germany |
| Molkerei Weihenstephan GmbH & Co. KG, Freising, Germany |
| OMIRA GmbH, Ravensburg, Germany |
| Sample Code | V15 (mL) | FFA (meq/100 g fat) | Area (-) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 105 ± 4 | 2.8 | 514 ± 36 | |
| C2 | 108 ± 2 | 2.7 | 543 ± 35 | |
| C3 | 175 ± 0 | 1.9 | 671 ± 49 | |
| C4 | 103 ± 2 | 2.6 | 456 ± 44 | |
| C5 | 172 ± 2 | 1.1 | 695 ± 91 | |
| C6 | 172 ± 2 | 1.1 | 725 ± 76 | |
| C7 | 100 ± 0 | 3.1 | 498 ± 30 | |
| C8 | 100 ± 0 | 3.2 | 496 ± 37 | |
| C9 | 170 ± 4 | 1.0 | 591 ± 5 | |
| C10 | 170 ± 4 | 1.1 | 688 ± 55 | |
| C11 | 172 ± 2 | 0.9 | 585 ± 54 | |
| C12 | 100 ± 4 | 2.4 | 536 ± 10 | |
| C13 | 183 ± 2 | 1.1 | 629 ± 70 | |
| C14 | 102 ± 2 | 3.0 | 488 ± 50 | |
| C15 | 178 ± 5 | 1.0 | 818 ± 48 | |
| Spearman-Rho correlation coefficient | 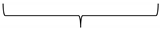 | 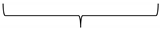 | ||
| −0.775 | −0.741 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reiner, J.; Protte, K.; Hinrichs, J. Investigation of the Applicability of Raman Spectroscopy as Online Process Control during Consumer Milk Production. ChemEngineering 2020, 4, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4030045
Reiner J, Protte K, Hinrichs J. Investigation of the Applicability of Raman Spectroscopy as Online Process Control during Consumer Milk Production. ChemEngineering. 2020; 4(3):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4030045
Chicago/Turabian StyleReiner, Jasmin, Kristin Protte, and Jörg Hinrichs. 2020. "Investigation of the Applicability of Raman Spectroscopy as Online Process Control during Consumer Milk Production" ChemEngineering 4, no. 3: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4030045
APA StyleReiner, J., Protte, K., & Hinrichs, J. (2020). Investigation of the Applicability of Raman Spectroscopy as Online Process Control during Consumer Milk Production. ChemEngineering, 4(3), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4030045






