Integration of Microalgae Cultivation in a Biogas Production Process from Organic Municipal Solid Waste: From Laboratory to Pilot Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microalgae Species
2.2. Laboratory-Scale Experimental Setup
2.3. Pilot-Scale Experimental Setup
2.3.1. Inoculum
2.3.2. CO2 Injection
2.4. Monitoring and Analytical Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Laboratory-Scale Experiments
3.2. Pilot-Scale Experiments
3.2.1. TSS Concentration and Chlorophyll Content
3.2.2. COD and P Removal
3.2.3. Nitrogen Removal
3.2.4. Dissolved Oxygen
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Logan, M.; Visvanathan, C. Management strategies for anaerobic digestate of organic fraction of municipal solid waste: Current status and future prospects. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzano, R.; González-Martínez, S. Characteristics of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste and methane production: A review. Waste Manag. 2016, 54, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanna, M. Anaerobic Digestion of the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste. In Management of Microbial Resources in the Environment; Malik, A., Grohmann, E., Alves, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 313–340. ISBN 978-94-007-5931-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sisto, R.; Sica, E.; Lombardi, M.; Prosperi, M. Organic fraction of municipal solid waste valorisation in southern Italy: The stakeholders’ contribution to a long-term strategy definition. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlat, N.; Dallemand, J.-F.; Fahl, F. Biogas: Developments and perspectives in Europe. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, E.; Menegon, S.; Banzato, D.; D’alpaos, C.; Bertucco, A. From biogas to biomethane: A process simulation-based techno-economic comparison of different upgrading technologies in the Italian context. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Treu, L.; Tsapekos, P.; Luo, G.; Campanaro, S.; Wenzel, H.; Kougias, P.G. Biogas upgrading and utilization: Current status and perspectives. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.J.; Chesshire, M.; Heaven, S.; Arnold, R. Anaerobic digestion of source-segregated domestic food waste: Performance assessment by mass and energy balance. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuka-ogwude, D.; Ogbonna, J.; Moheimani, N.R. A review on microalgal culture to treat anaerobic digestate food waste effluent. Algal Res. 2020, 47, 101841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Newman, D.; Cepeda-Márquez, R.; Zeller, K. Global Food Waste Management: An Implementation Guide for Cities; World Biogas Association: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–145. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, A.; Murphy, J.D. Microalgal Cultivation in Treating Liquid Digestate from Biogas Systems. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, L.; Massé, D.I.; Pellerin, Y. The effect of pH on the separation of manure nutrients with reverse osmosis membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 325, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Maza, A.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.J. Ammonia removal in food waste anaerobic digestion using a side-stream stripping process. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Bowers, K.E.; Harrison, J.H.; Chen, S. Releasing Phosphorus from Calcium for Struvite Fertilizer Production from Anaerobically Digested Dairy Effluent. Water Environ. Res. 2010, 82, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrí, A.; Béline, F.; Dabert, P. Feasibility and interest of the anammox process as treatment alternative for anaerobic digester supernatants in manure processing—An overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornsson, W.J.; Nicol, R.W.; Dickinson, K.E.; McGinn, P.J. Anaerobic digestates are useful nutrient sources for microalgae cultivation: Functional coupling of energy and biomass production. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, Q.; Fang, F.; Luo, R.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, W.; Huo, S.; Cheng, P.; Liu, J.; Addy, M.; et al. Microalgae-based wastewater treatment for nutrients recovery: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, C.; Sialve, B.; Molinuevo-Salces, B. Anaerobic digestion of microalgal biomass: Challenges, opportunities and research needs. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Ge, X.; Park, S.Y.; Li, Y. Comparison of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 and Nannochloropsis salina for lipid production using artificial seawater and nutrients from anaerobic digestion effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara, C.; García-Encina, P.A.; Muñoz, R. Evaluation of the simultaneous biogas upgrading and treatment of centrates in a high-rate algal pond through C, N and P mass balances. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Min, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ruan, R.R. Anaerobic digested dairy manure as a nutrient supplement for cultivation of oil-rich green microalgae Chlorella sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2623–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisossadati, M.; Vadiveloo, A.; Bahri, P.A.; Parlevliet, D.; Moheimani, N.R. Treating anaerobically digested piggery effluent (ADPE) using microalgae in thin layer reactor and raceway pond. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayre, J.M.; Moheimani, N.R.; Borowitzka, M.A. Growth of microalgae on undiluted anaerobic digestate of piggery effluent with high ammonium concentrations. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Reynolds, D.L.; Das, K.C. Microalgal system for treatment of effluent from poultry litter anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10841–10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi Nguyen, M.L.; Lin, C.Y.; Lay, C.H. Microalgae cultivation using biogas and digestate carbon sources. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 122, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bona, D.; Papurello, D.; Flaim, G.; Cerasino, L.; Biasioli, F.; Silvestri, S. Management of Digestate and Exhausts from Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Produced in the Dry Anaerobic Digestion Pilot Plant: Microalgae Cultivation Approach. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanna, L.; Guldhe, A.; Rawat, I.; Bux, F. The optimization of biomass and lipid yields of Chlorella sorokiniana when using wastewater supplemented with different nitrogen sources. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.; Naseera, K.; Ram, A.; Meena, R.M.; Ramaiah, N. Bioremediation of tannery wastewater by a salt-tolerant strain of Chlorella vulgaris. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, G.; Bertucco, A.; Sforza, E. Mixotrophy in Synechocystis sp. for the treatment of wastewater with high nutrient content: Effect of CO2 and light. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 42, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, V.C.; Velasquez-Orta, S.B.; Hernández-García, A.; Monje-Ramírez, I.; Orta-Ledesma, M.T. Kinetic modelling of microalgae cultivation for wastewater treatment and carbon dioxide sequestration. Algal Res. 2018, 32, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Photovoltaic Geographical Information System (PVGIS). Available online: http://re.jrc.ec.europa.eu/pvgis/ (accessed on 25 September 2018).
- Bryant, D.A. The Molecular Biology of Cyanobacteria; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; ISBN 978-0-7923-3273-2. [Google Scholar]
- de Godos, I.; Arbib, Z.; Lara, E.; Rogalla, F. Evaluation of High Rate Algae Ponds for treatment of anaerobically digested wastewater: Effect of CO2 addition and modification of dilution rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collos, Y.; Harrison, P.J. Acclimation and toxicity of high ammonium concentrations to unicellular algae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 80, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbera, E.; Sforza, E.; Bertucco, A. Maximizing the production of Scenedesmus obliquus in photobioreactors under different irradiation regimes: Experiments and modeling. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takache, H.; Pruvost, J.; Cornet, J.F. Kinetic modeling of the photosynthetic growth of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in a photobioreactor. Biotechnol. Prog. 2012, 28, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.C. On the Proportions of Organic Derivatives in Sea Water and Their Relation to the Composition of Plankton. James Johnstone Meml. Vol. 1934, 176–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos Tercero, E.A.; Sforza, E.; Morandini, M.; Bertucco, A. Cultivation of Chlorella protothecoides with Urban Wastewater in Continuous Photobioreactor: Biomass Productivity and Nutrient Removal. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 1470–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebali, A.; Acién, F.G.; Rodriguez Barradas, E.; Olguín, E.J.; Sayadi, S.; Molina Grima, E. Pilot-scale outdoor production of Scenedesmus sp. in raceways using flue gases and centrate from anaerobic digestion as the sole culture medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 262, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Villegas, G.I.; Fiamengo, M.; Acién-Fernández, F.G.; Molina-Grima, E. Utilization of centrate for the outdoor production of marine microalgae at the pilot-scale in raceway photobioreactors. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-amaral, M.; Gómez-serrano, C.; Acién, F.G.; Fernández-sevilla, J.M.; Molina-grima, E. Outdoor production of Scenedesmus sp. in thin-layer and raceway reactors using centrate from anaerobic digestion as the sole nutrient source. ALGAL 2015, 12, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, E.; Muñoz, A.; García-González, M.C.; Muñoz, R.; García-Encina, P.A. A case study of a pilot high rate algal pond for the treatment of fish farm and domestic wastewaters. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, I.M.; Ghazi, T.I.M.; Omar, R. Production of biogas from solid organic wastes through anaerobic digestion: A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 95, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Min, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, R. Cultivation of green algae Chlorella sp. in different wastewaters from municipal wastewater treatment plant. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuellar-Bermudez, S.P.; Aleman-Nava, G.S.; Chandra, R.; Garcia-Perez, J.S.; Contreras-Angulo, J.R.; Markou, G.; Muylaert, K.; Rittmann, B.E.; Parra-Saldivar, R. Nutrients utilization and contaminants removal. A review of two approaches of algae and cyanobacteria in wastewater. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, E.; Marín, D.; Blanco, S.; Lebrero, R.; Muñoz, R. Simultaneous biogas upgrading and centrate treatment in an outdoors pilot scale high rate algal pond. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-fernández, C.; Molinuevo-salces, B.; García-gonzález, M.C. Nitrogen transformations under different conditions in open ponds by means of microalgae–bacteria consortium treating pig slurry. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 960–966. [Google Scholar]
- Molinuevo-salces, B.; García-gonzález, M.C.; González-fernández, C. Performance comparison of two photobioreactors configurations (open and closed to the atmosphere ) treating anaerobically degraded swine slurry. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5144–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Martinez, A.; Martin Garcia, N.; Romero, I.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J. Microalgae cultivation in wastewater: Nutrient removal from anaerobic membrane bioreactor effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 126, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, G.; Vandamme, D.; Muylaert, K. Microalgal and cyanobacterial cultivation: The supply of nutrients. Water Res. 2014, 65, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, J.L.; Granados, M.R.; de Godos, I.; Acién, F.G.; Molina, E.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.J. Oxygen transfer and evolution in microalgal culture in open raceways. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliphuis, A.M.J.; Janssen, M.; van den End, E.J.; Martens, D.E.; Wijffels, R.H. Light respiration in Chlorella sorokiniana. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Cossío, B.R.; Niell, F.X. Relationship between physicochemical variables and productivity in open ponds for the production of Spirulina: A predictive model of algal yield. Aquaculture 2003, 221, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 , Semi-continuous operation in orange,
, Semi-continuous operation in orange,  , and the transition stage in grey,
, and the transition stage in grey,  . Green
. Green  represents the period of feeding with membrane filtered digestate (MFD), while violet
represents the period of feeding with membrane filtered digestate (MFD), while violet  with filtered digestate (FD). Green dotted line (....) represents the change in the feeding mode (from manual to automatic). Violet dotted line (....) represents the shift in the water depth.
with filtered digestate (FD). Green dotted line (....) represents the change in the feeding mode (from manual to automatic). Violet dotted line (....) represents the shift in the water depth.
 , Semi-continuous operation in orange,
, Semi-continuous operation in orange,  , and the transition stage in grey,
, and the transition stage in grey,  . Green
. Green  represents the period of feeding with membrane filtered digestate (MFD), while violet
represents the period of feeding with membrane filtered digestate (MFD), while violet  with filtered digestate (FD). Green dotted line (....) represents the change in the feeding mode (from manual to automatic). Violet dotted line (....) represents the shift in the water depth.
with filtered digestate (FD). Green dotted line (....) represents the change in the feeding mode (from manual to automatic). Violet dotted line (....) represents the shift in the water depth.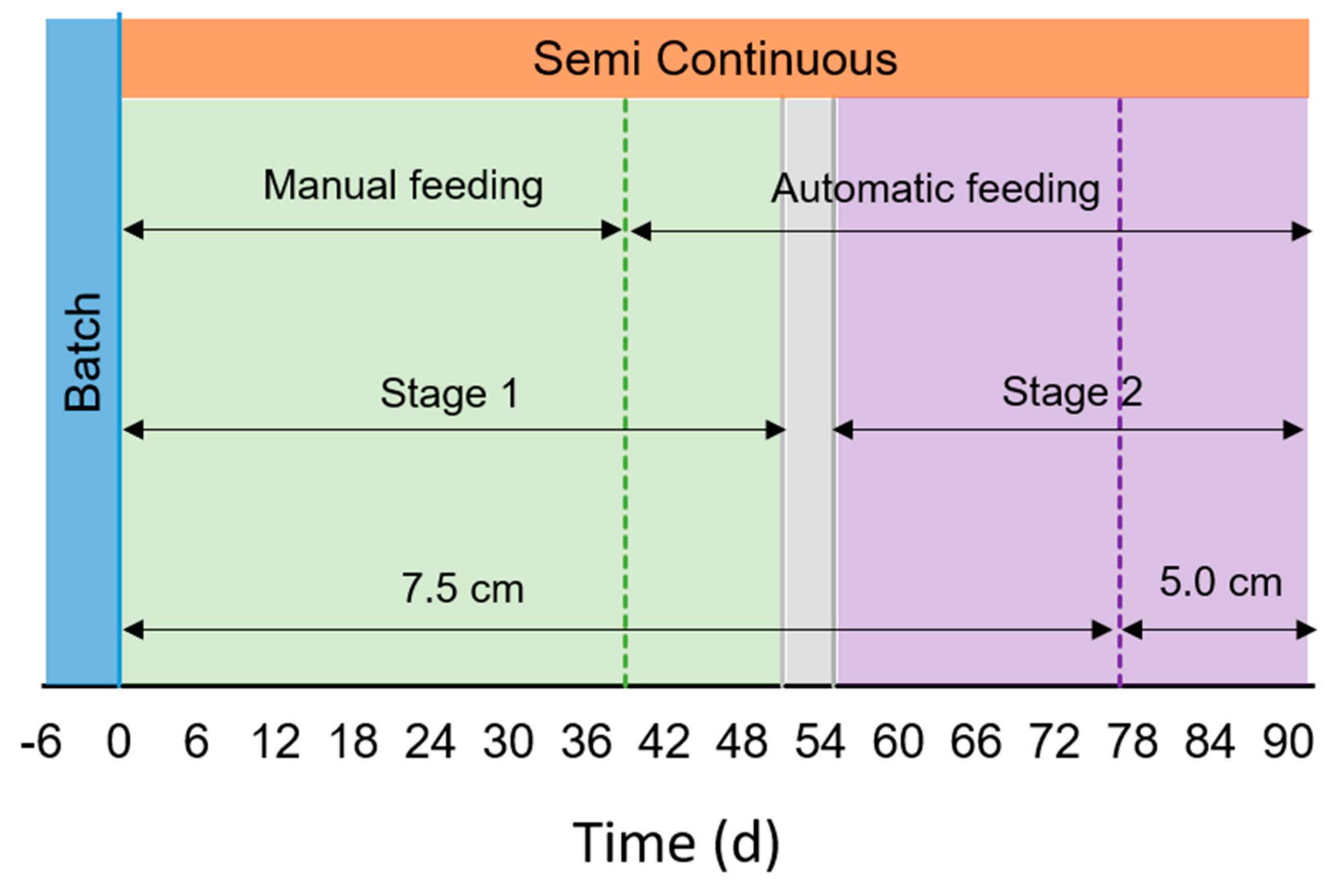
 , and the transition stage in grey,
, and the transition stage in grey,  . Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.
. Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.
 , and the transition stage in grey,
, and the transition stage in grey,  . Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.
. Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.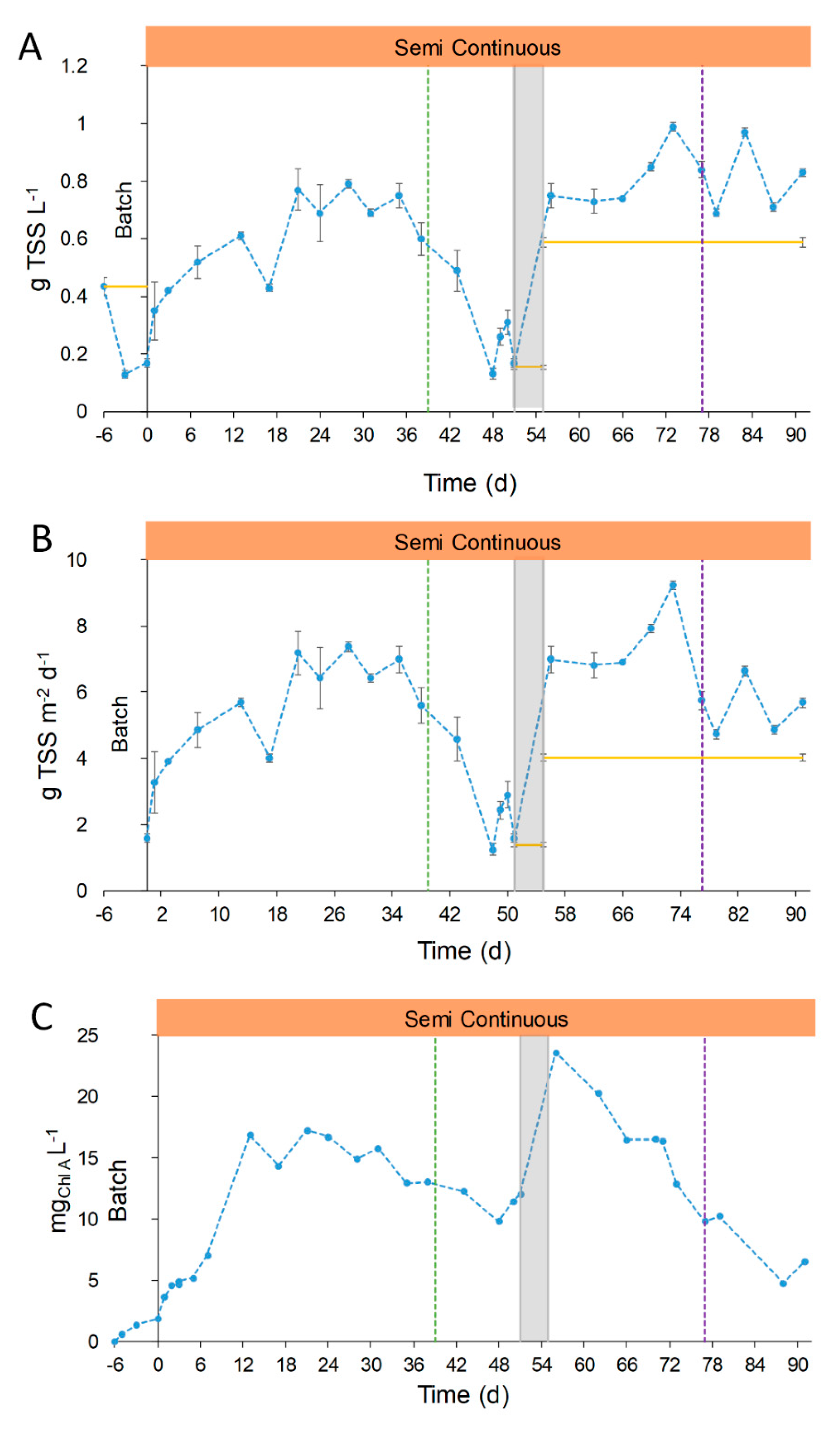
 , and the transition stage in grey,
, and the transition stage in grey,  . Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.
. Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.
 , and the transition stage in grey,
, and the transition stage in grey,  . Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.
. Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.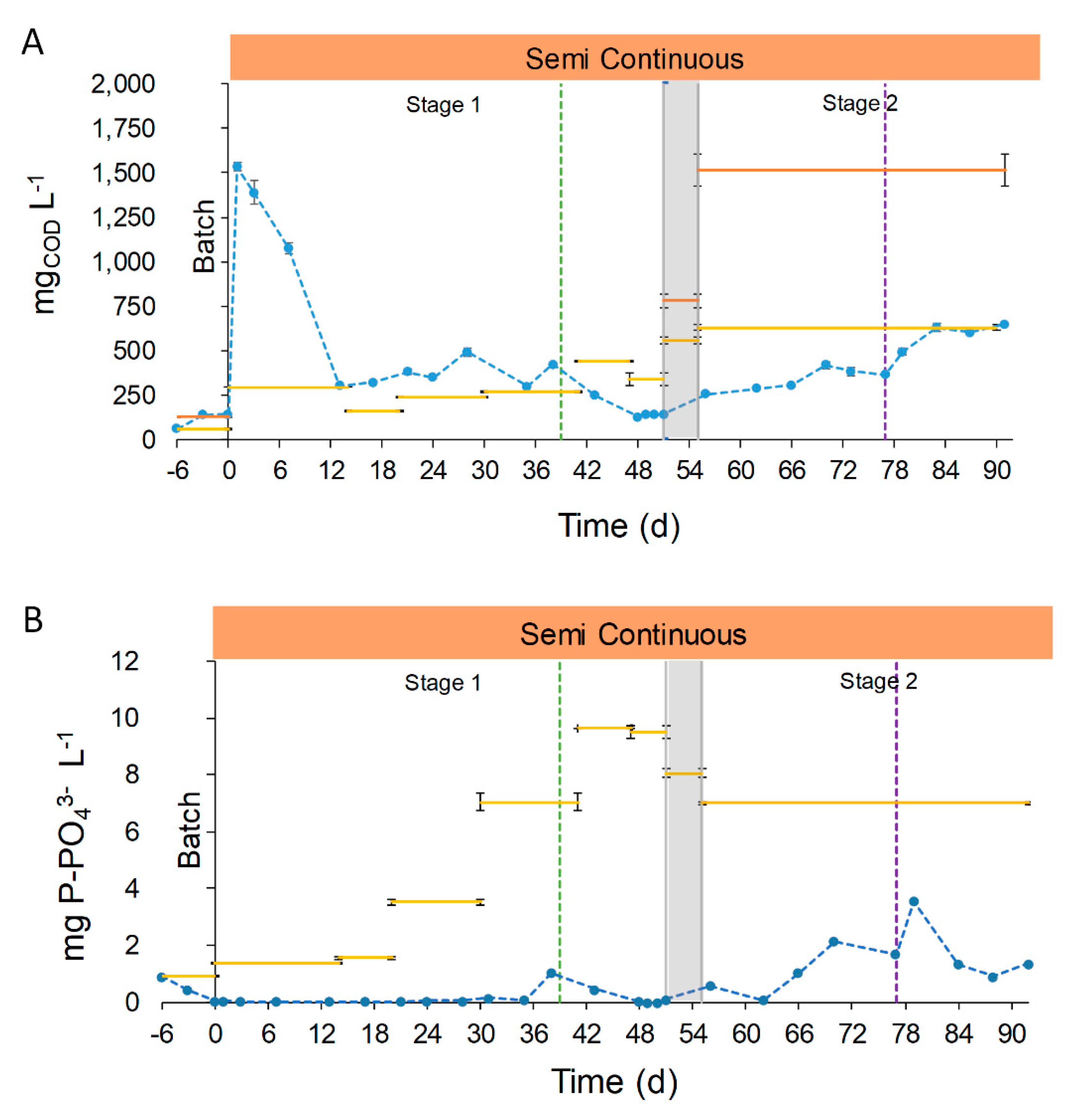
 , and the transitional stage in grey,
, and the transitional stage in grey,  . Green dotted line (....) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (....) represents the shift in the column depth.
. Green dotted line (....) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (....) represents the shift in the column depth.
 , and the transitional stage in grey,
, and the transitional stage in grey,  . Green dotted line (....) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (....) represents the shift in the column depth.
. Green dotted line (....) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (....) represents the shift in the column depth.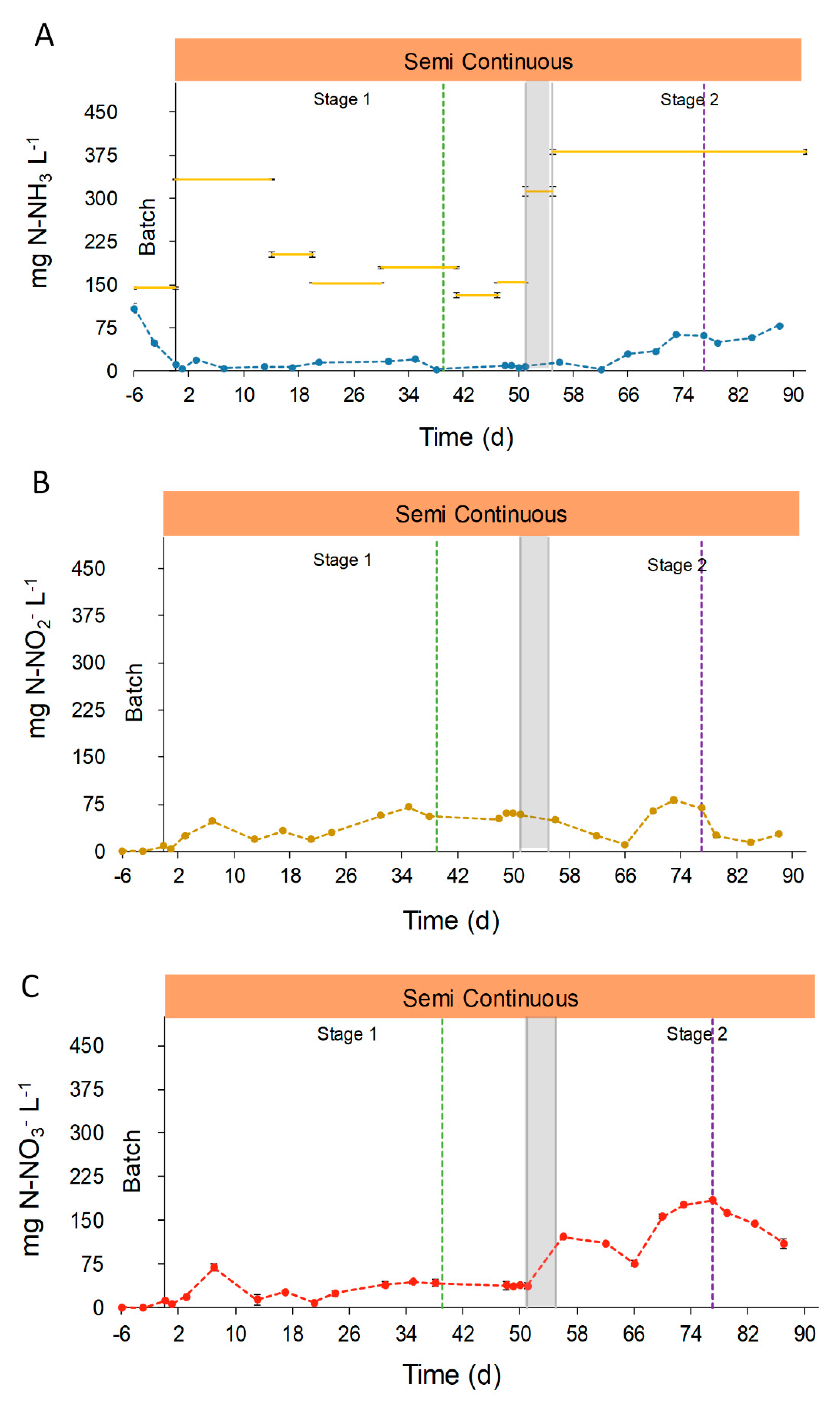
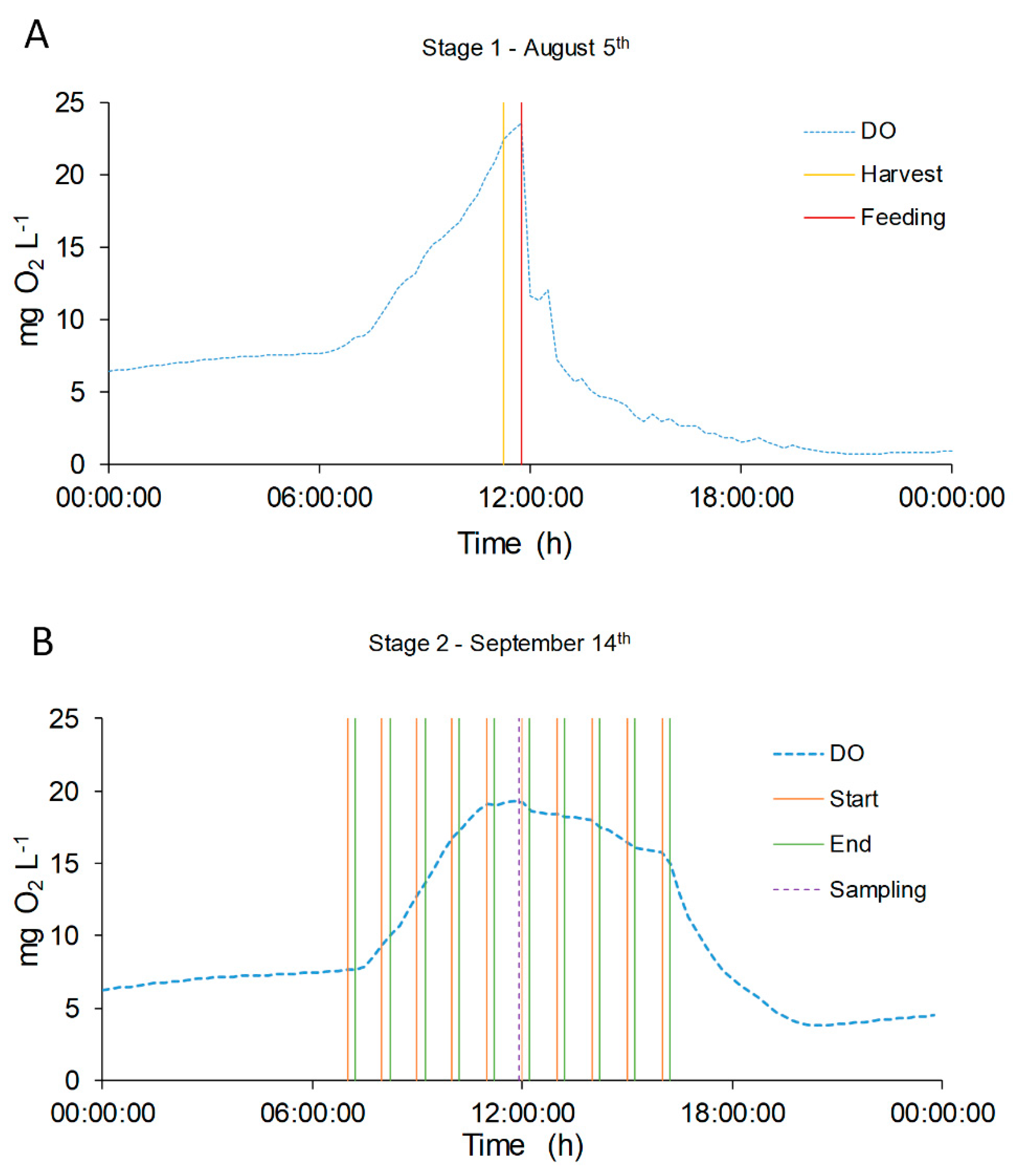
 , and the transitional stage in grey,
, and the transitional stage in grey,  . Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.
. Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.
 , and the transitional stage in grey,
, and the transitional stage in grey,  . Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.
. Green dotted line (●●●) represents the change in the feeding mode. Violet dotted line (●●●) represents the shift in the column depth.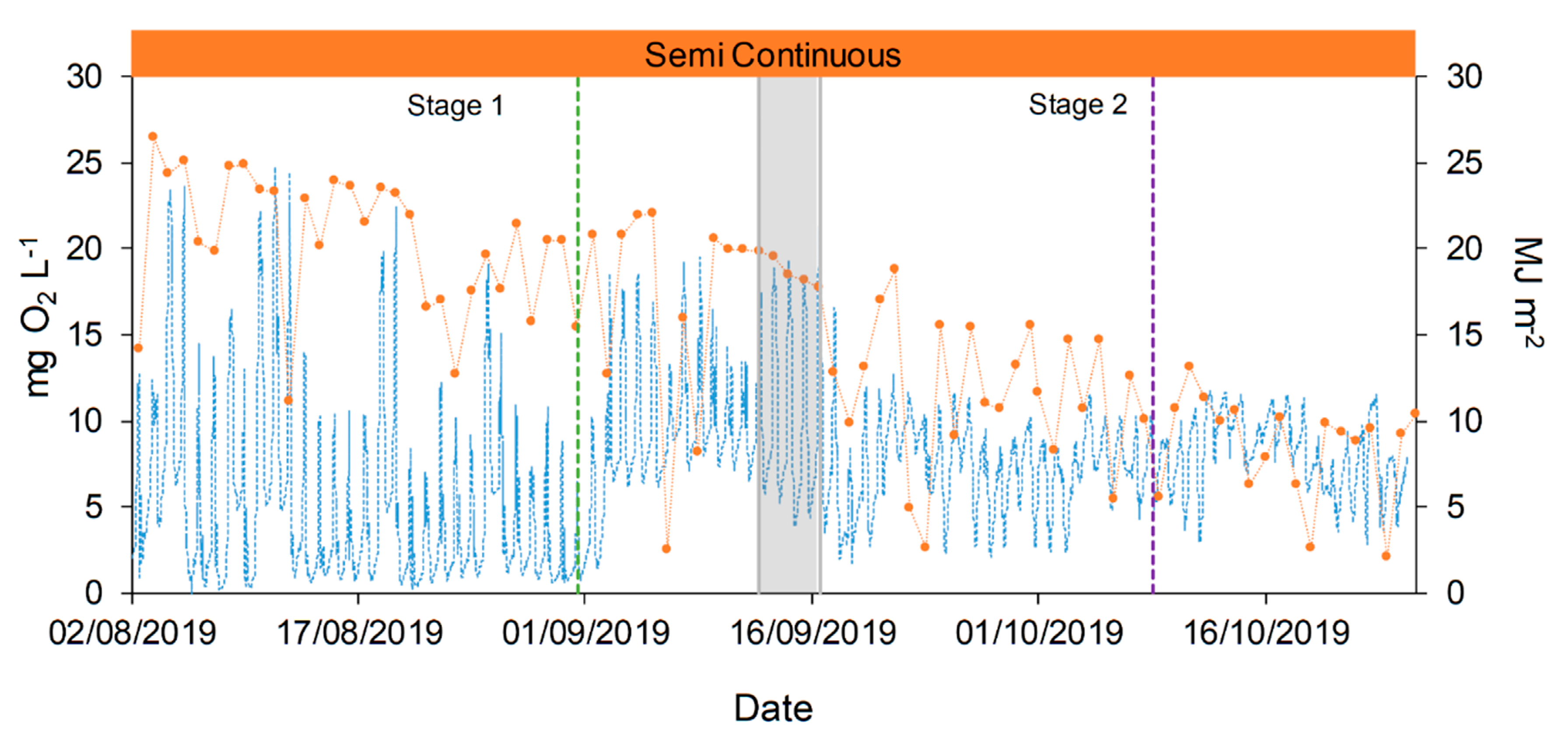
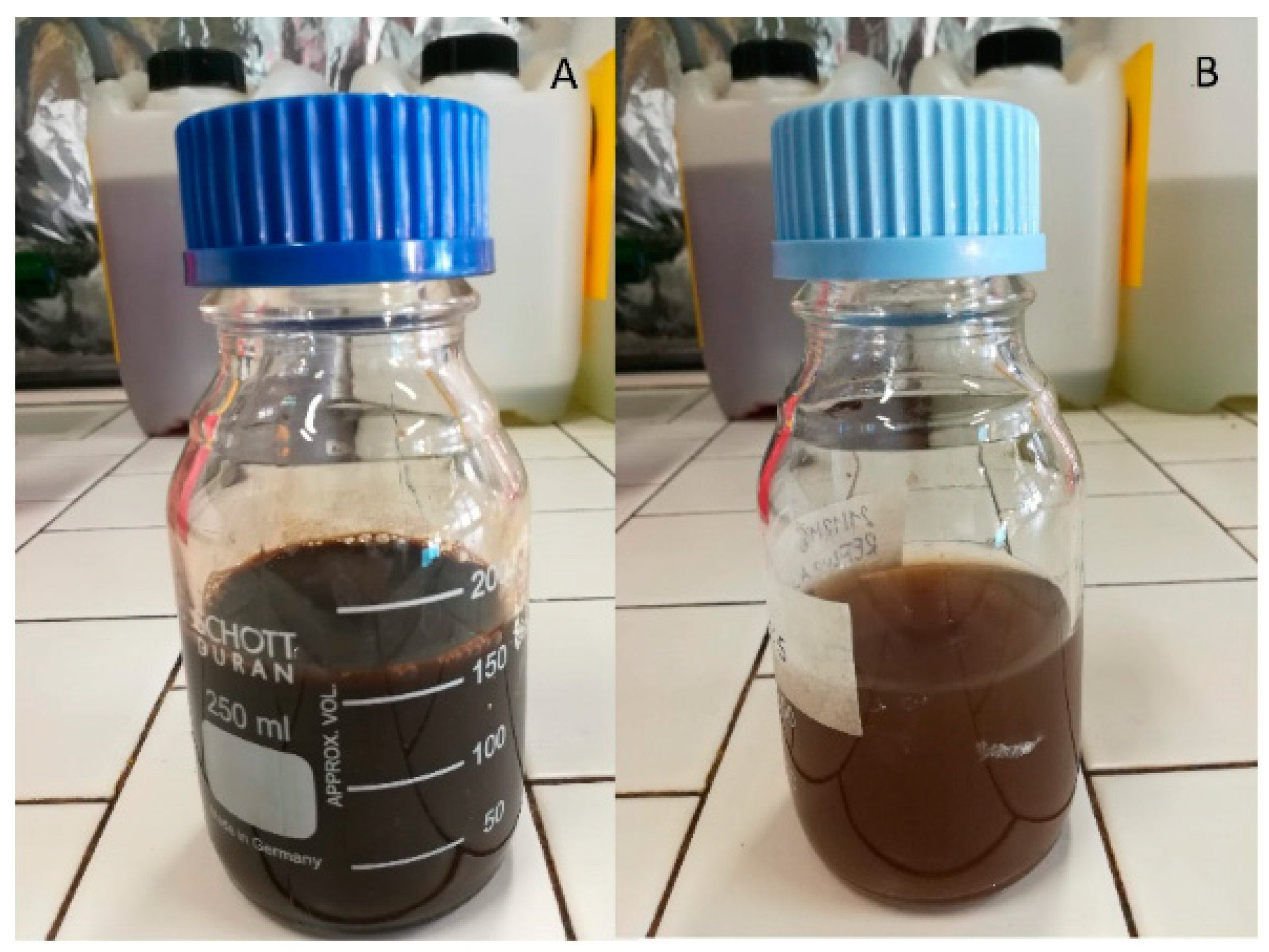
| Analysis | Centrifuged Digestate (CF) | Filtered Digestate (FD) |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonium, N-NH3 (mg L−1) | 2933 ± 141 | 3195 ± 140 |
| Nitrates, N-NO3 (mg L−1) | 200 ± 8 | 15 ± 2 |
| Nitrites, N-NO2 (mg L−1) | 2.5 ± 0.24 | n.d. |
| Phosphates, P-PO4 (mg L−1) | 51 ± 2 | 85 ± 1.5 |
| COD (mg L−1) | 11,947 ± 1312 | 12,383 ± 1528 |
| Total suspended solids (g L−1) | 4.2 ± 2.3 | 9.05 |
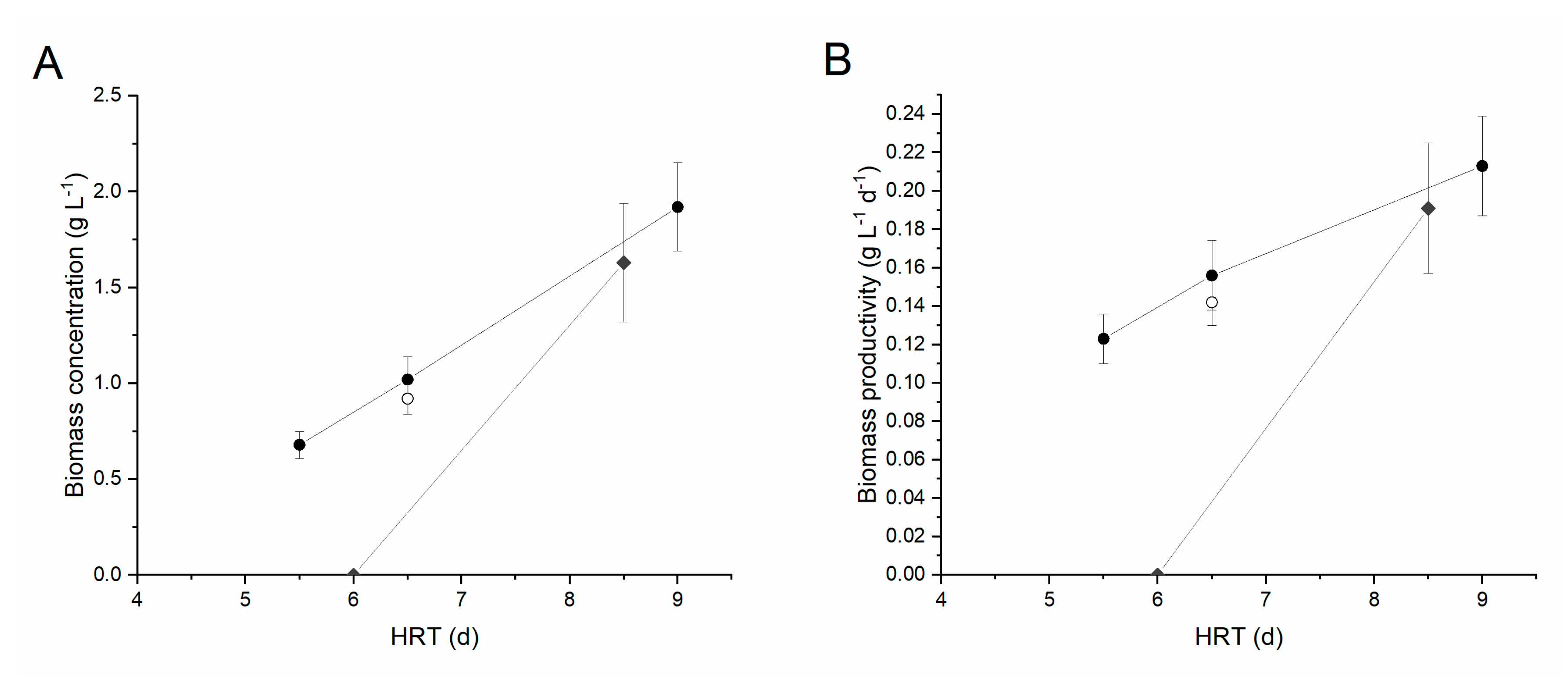
| Experimental Conditions | HRT (d) | pH | T (°C) | cx (g L−1) | Px (g L−1 d−1) | ΔN (%) | ΔP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifuged digestate 1:5 | 5.5 | 7.9 ± 0.2 | 25.0 ± 1.0 | 0.68 ± 0.07 | 0.123 ± 0.013 | 2.8% | 52.6% |
| 6.5 | 7.5 ± 0.2 | 25.6 ± 1.2 | 1.02 ± 0.12 | 0.156 ± 0.018 | 12.4% | 94.7% | |
| 9 | 7.7 ± 0.1 | 24.3 ± 0.6 | 1.92 ± 0.23 | 0.213 ± 0.026 | 12.6% | 96.7% | |
| Centrifuged digestate 1:2 | 6 | 7.9 ± 0.1 | 27.2 ± 1.5 | - | - | - | - |
| 8.5 | 7.6 ± 0.1 | 26.2 ± 1.0 | 1.63 ± 0.31 | 0.191 ± 0.034 | 12.3% | 59.6% | |
| Filtered digestate 1:2 | 6.5 | 7.7 ± 0.1 | 25.0 ± 1.6 | 0.92 ± 0.08 | 0.142 ± 0.012 | 3.96% | 84.1% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barreiro-Vescovo, S.; Barbera, E.; Bertucco, A.; Sforza, E. Integration of Microalgae Cultivation in a Biogas Production Process from Organic Municipal Solid Waste: From Laboratory to Pilot Scale. ChemEngineering 2020, 4, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4020025
Barreiro-Vescovo S, Barbera E, Bertucco A, Sforza E. Integration of Microalgae Cultivation in a Biogas Production Process from Organic Municipal Solid Waste: From Laboratory to Pilot Scale. ChemEngineering. 2020; 4(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarreiro-Vescovo, Santiago, Elena Barbera, Alberto Bertucco, and Eleonora Sforza. 2020. "Integration of Microalgae Cultivation in a Biogas Production Process from Organic Municipal Solid Waste: From Laboratory to Pilot Scale" ChemEngineering 4, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4020025
APA StyleBarreiro-Vescovo, S., Barbera, E., Bertucco, A., & Sforza, E. (2020). Integration of Microalgae Cultivation in a Biogas Production Process from Organic Municipal Solid Waste: From Laboratory to Pilot Scale. ChemEngineering, 4(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4020025






