Economic Evaluation of Drying of Soot Sludge and Sawdust Mixture at Low Temperatures Using the Characteristic Drying Curve Method †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
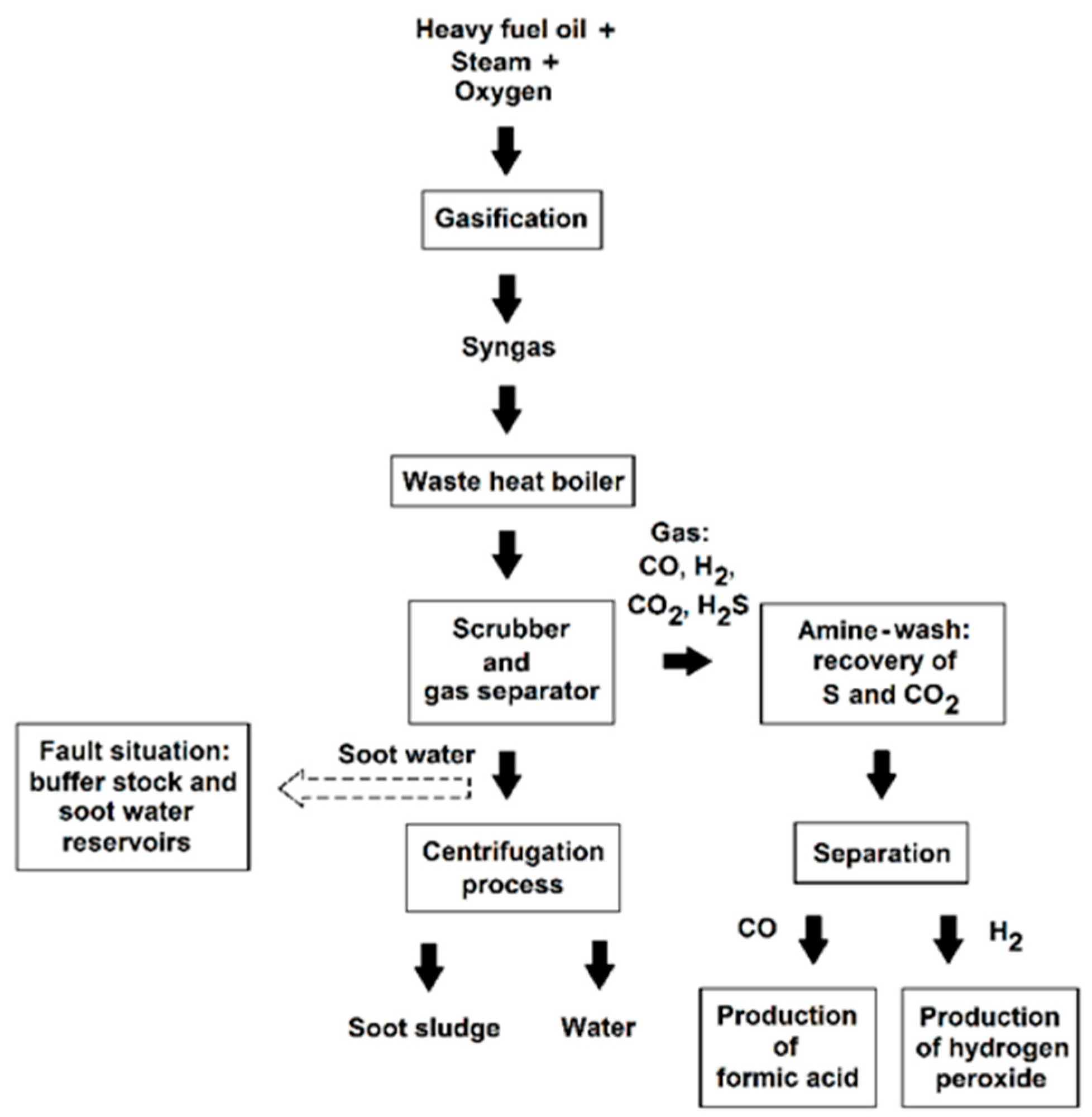
2.1. Generation of the Soot Sludge
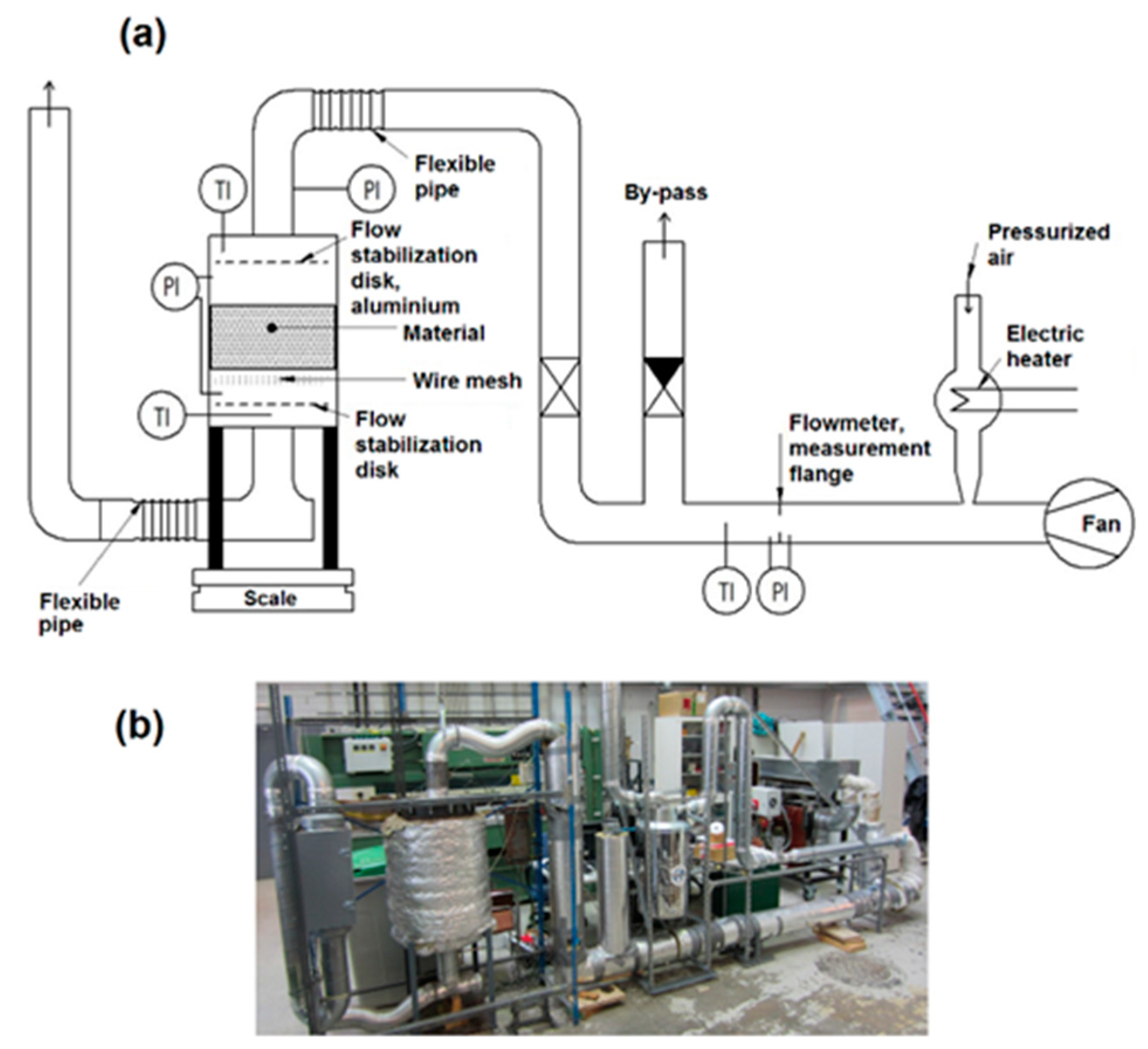
2.2. Experimental Test Equipment
2.3. Soot Sludge and Sawdust Mixture
2.4. Characteristic Drying Curve
2.5. Economic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
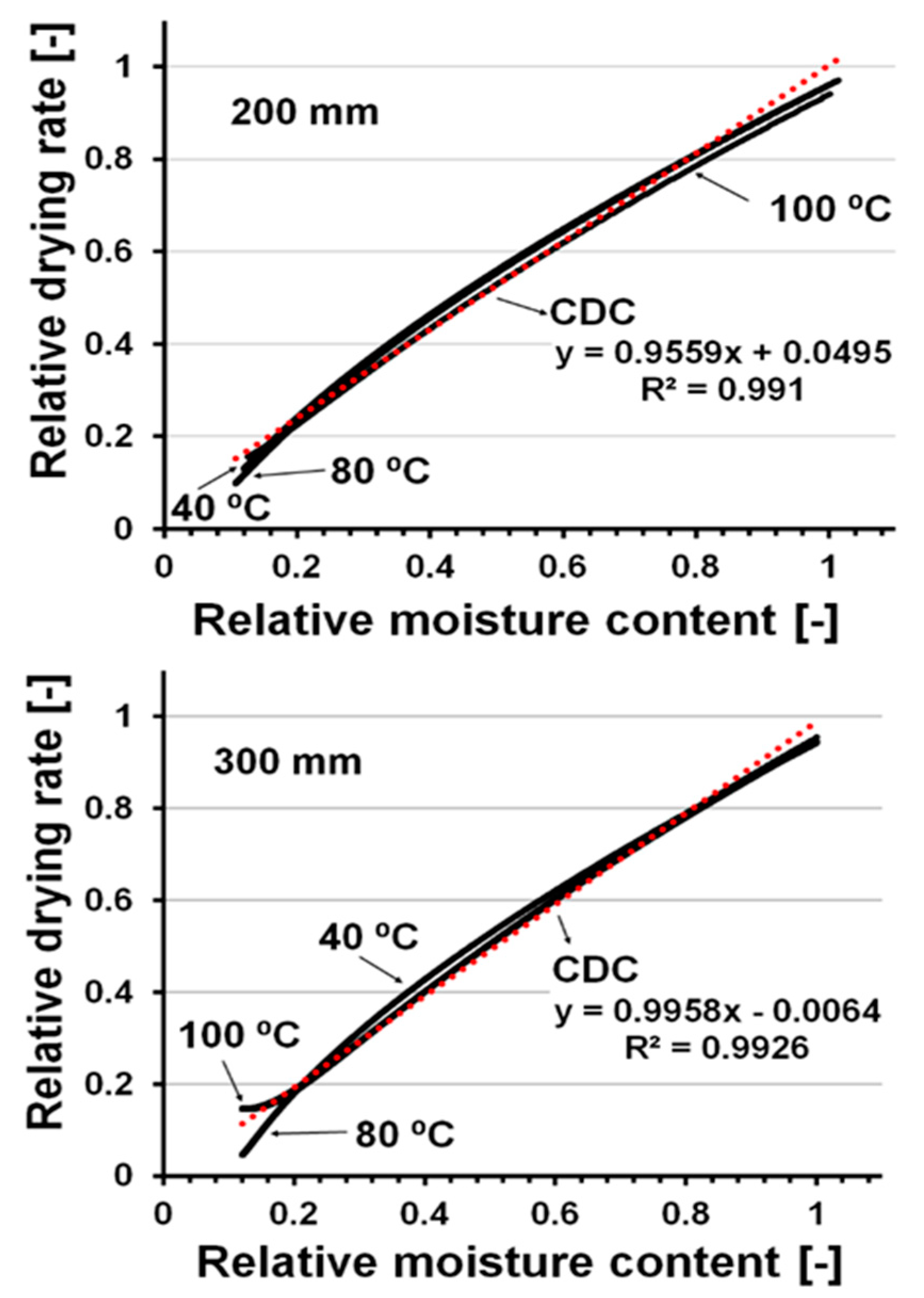
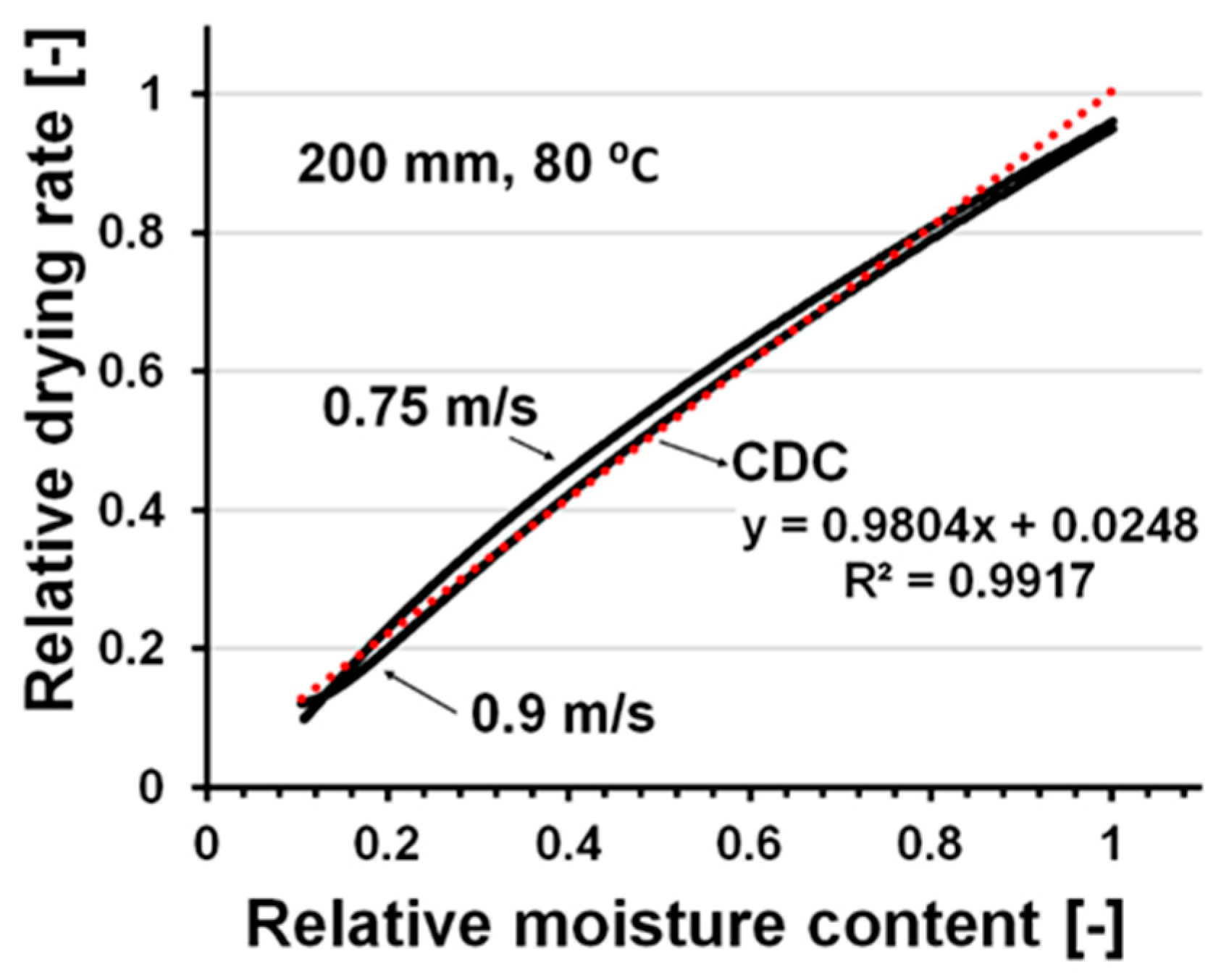
3.1. Determination of Characteristic Drying Curves
3.2. Determination of the Volumetric Heat Transfer Coefficient
3.3. Economic Analysis
3.3.1. Base Case
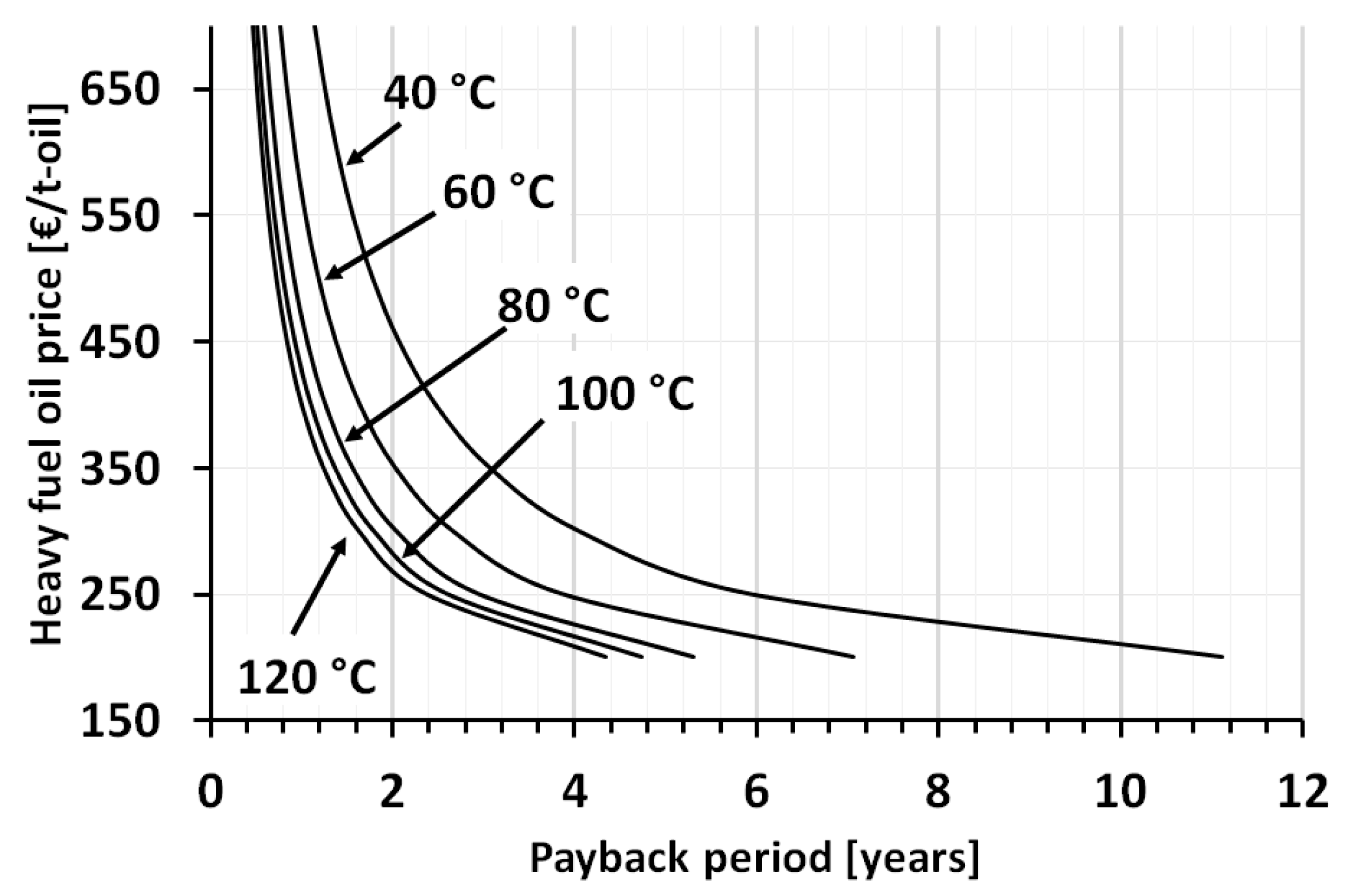
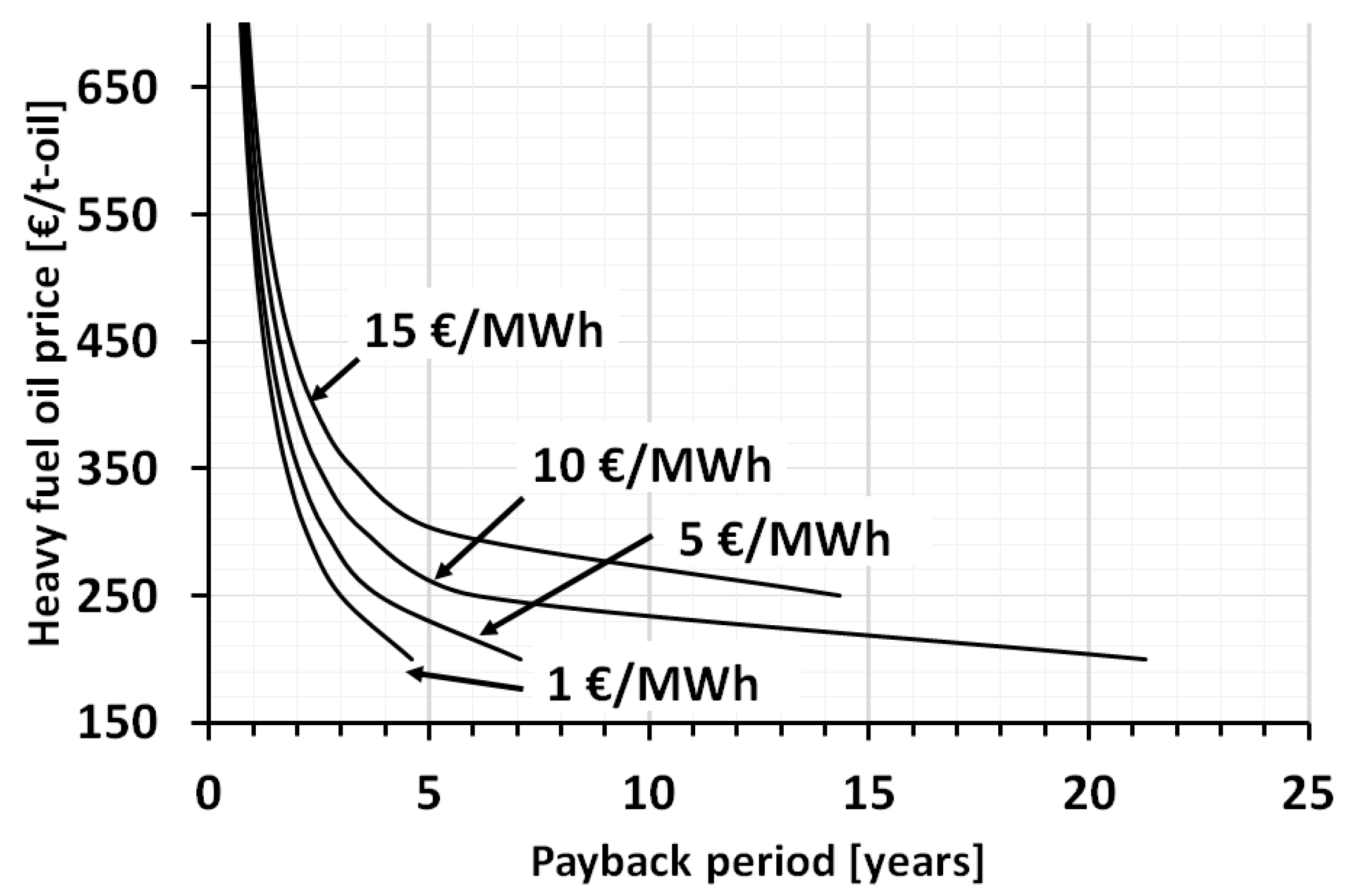
3.3.2. Sensitivity Analysis: Influence of the Heat Price
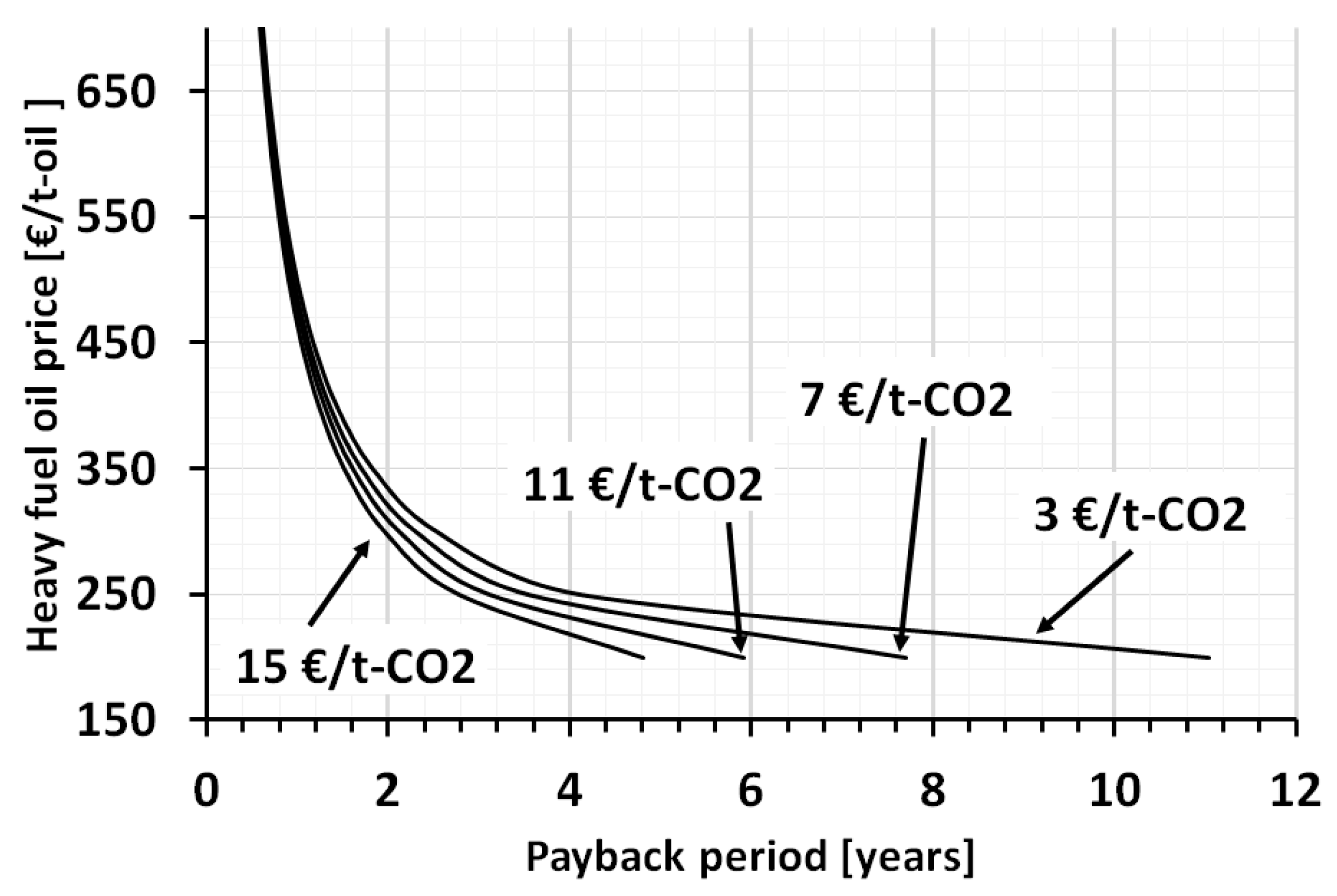
3.3.3. Sensitivity Analysis: Influence of the CO2 Emission Price
3.3.4. Sensitivity Analysis: Influence of the Sawdust Price
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| cross-sectional area of a continuous-working belt dryer [m2] | |
| specific volumetric heat transfer area/evaporation surface [m2/m3] | |
| price of the CO2 emissions [€/t-CO2] | |
| price of the electricity [€/MWh] | |
| price of the heavy fuel oil [€/t-oil] | |
| price of the heat [€/MWh] | |
| price of the sawdust [€/MWh] | |
| specific heat capacity of dry air [kJ/kg°C] | |
| specific heat capacity of water vapor [kJ/kg°C] | |
| enthalpy of humid air [kJ/kgda] | |
| total investment costs of the dryer [€] | |
| vaporization heat [J/kg] | |
| drying rate during the constant drying period [kgH2O/(kgdbs)] | |
| mass flow rate of dry air [kgda/s] | |
| mass flow rate of material [kgdb/s] | |
| mass flow rate of sawdust [kgdb/s] | |
| mass flow rate of the soot sludge [kgdb/s] | |
| reduced heavy fuel oil consumption [kg/h] | |
| electricity consumption of the dryer’s fans [MW] | |
| annual operational costs [€/years] | |
| annual savings from reduced CO2-emissions [€/years] | |
| annual savings in fuel consumption [€/years] | |
| annual costs of sawdust [€/years] | |
| pressure drop over the plate heat exchanger(s) and the air duct system [Pa] | |
| pressure drop over the material bed [Pa] | |
| total pressure drop over the dryer configuration/pressure difference [Pa] | |
| heating value of heavy fuel oil [MJ/kg-oil] | |
| lower heating value of sawdust [MJ/kgdb] | |
| mass ratio (dry basis) of sawdust to soot sludge in the mixture [-] | |
| CO2 emission factor of heavy fuel oil [kg-CO2/MWh] | |
| annual net savings [€/years] | |
| T | air temperature [K] |
| air temperature [°C] | |
| wet bulb temperature [°C] | |
| u | moisture content of material [kgH2O/kgdb] |
| moisture content of the moist soot sludge [kgH2O/kgdb] | |
| moisture content of the soot sludge and sawdust mixture after drying [kgH2O/kgdb] | |
| velocity of air before the fan(s) [m/s] | |
| moisture content of air [kg/kgda] | |
| critical moisture content [kgH2O/kgdb] | |
| bed height of material inside the dryer [m] | |
| α | heat transfer coefficient for the heat transfer between the bed and drying air in the boundary layer (convective) [W/m2K] |
| density of dry air [kgda/m3] | |
| bulk density of dry material [kgdb/m3] | |
| residence time of material inside the dryer/drying time [s] | |
| annual operating time of the dryer [h/years] | |
| heat consumption of the dryer [MW] | |
| efficiency of the fan(s) [-] | |
| CDC | Characteristic Drying Curve |
| CHP | Combined Heat and Power plant |
| da | dry air |
| db | dry basis |
| DC | drying curve |
| PBP | payback period without interest [years] |
| wb | wet basis |
| vol-% | volume-% |
References
- Eastman Chemical Company. Available online: www.eastman.com (accessed on 10 November 2018).
- Chen, G.; Yue, P.L.; Mujumdar, A.S. Sludge dewatering and drying. Dry. Technol. 2002, 20, 883–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunçal, T.; Uslu, O. A review of dehydration of various industrial sludges. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 1642–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippinen, I.; Ahtila, P. Drying of activated sludge under partial vacuum conditions—An experimental study. Dry. Technol. 2004, 22, 2119–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllymaa, T.; Holmberg, H.; Arhippainen, P.; Ahtila, P. Upgrading of soot sludge from waste to fuel by means of low temperature drying in fixed beds. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 138, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudra, T.; Gawrzynski, Z.; Glaser, R.; Stanislawski, J.; Poirier, M. Drying of pulp and paper sludge in a pulsed fluid bed dryer. Dry. Technol. 2002, 20, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, A.; Elustondo, D.; Mäkelä, M.; Segerström, M.; Kalén, G.; Fraikin, L.; Léonard, A.; Larsson, S.H. Drying recycled fiber rejects in a bench-scale cyclone: Influence of device geometry and operational parameters on drying mechanisms. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiec, J. Drying of waste sludges in a fluidized bed dryer with a mixer. Dry. Technol. 2002, 20, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San José, M.J.; Alvarez, S.; López, R. Drying of industrial sludge waste in a conical spouted bed dryer. Effect of air temperature and air velocity. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keey, R.B. Drying: Principles and Practice. International Series of Monographs in Chemical Engineering; Pergamon: Oxford, NY, USA, 1972; p. 193. [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg, H.; Ahtila, P.; Ahtila, O. Experimental study on drying of bark in fixed beds. Dry. Technol. 2011, 29, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannot, Y.; Batsale, J.-C.; Ahouannou, C.; Kanmogne, A.; Talla, A. Measurement errors processing by covariance analysis for an improved estimation of drying characteristic curve parameters. Dry. Technol. 2002, 20, 1919–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhila, M.; Kechaou, N.; Otmani, M.; Fliyou, M.; Lahsasni, S. Experimental study of sorption isotherms and drying kinetics of Moroccan eucalyptus globulus. Dry. Technol. 2002, 20, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannot, Y.; Talla, A.; Nganhou, J.; Puiggali, J.-R. Modeling of banana convective drying by the drying characteristic curve (DCC) method. Dry. Technol. 2004, 22, 1949–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, U.S.; Khan, M.K.; Mohanty, S.N. Heat pump drying of green sweet pepper. Dry. Technol. 2008, 26, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahsasni, S.; Kouhila, M.; Mahrouz, M.; Ait Mohamed, L.; Agorram, B. Characteristic drying curve and mathematical modeling of thin-layer solar drying of prickly pear cladode (Opuntia ficus indica). J. Food Process Eng. 2004, 27, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, M.; Ben Mabrouk, S.; Zouari, I.; Bellagi, A. Kinetic study of the convective drying of spearmint. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2014, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahsasni, S.; Kouhila, M.; Mahrouz, M.; Jaouhari, J.T. Drying kinetics of prickly pear fruit (Opuntia ficus indica). J. Food Eng. 2004, 61, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mghazli, S.; Ouhammou, M.; Hidar, N.; Lahnine, L.; Idlimam, A.; Mahrouz, M. Drying characteristics and kinetics solar drying of Moroccan rosemary leaves. Renew. Energy 2017, 108, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langrish, T.A.G. Characteristic drying curves for cellulosic fibres. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaleno, R.O.; Castro, L.M.; Coelho Pinheiro, M.N. Drying kinetics of granulated cork: Effect of air drying stream conditions and granule size. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 107, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langrish, T.A.G. An assessment of the use of characteristic drying for the high-temperature drying of softwood timber. Dry. Technol. 1999, 17, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzell, E.; Melander, O.; Rasmuson, A. The drying kinetics and equilibrium moisture content of MDF fibers. Dry. Technol. 2009, 27, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellagha, S.; Amami, E.; Farhat, A.; Kechaou, N. Drying kinetics and characteristic drying curve of lightly salted sardine (Sardinella aurita). Dry. Technol. 2002, 20, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdour, L.; Desmorieux, H.; Andrieu, J. A contribution to the characteristic drying curve concept: Application to the drying of plaster. Dry. Technol. 2000, 18, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decision for the Environmental Licence Application. Pohjois-Pohjanmaan Ympäristökeskus 2007, PPO-2005-Y-1-111 2007. Available online: https://www.google.fi/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&ved=0ahUKEwiKh7CfyOPXAhVkJpoKHUbEBiIQFgguMAE&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.ymparisto.fi%2Fdownload%2Fnoname%2F%257BF5A71E5F-1300-47F5-BC13-C64649E0192E%257D%2F88395&usg=AOvVaw0qAKdVuFr257X5bctTKnaa (accessed on 29 November 2017).
- Myllymaa, T.; Holmberg, H.; Hillamo, H.; Laajalehto, T.; Ahtila, P. Wood chip drying in fixed beds: Drying kinetics and economics of drying at a municipal combined heat and power plant site. Dry. Technol. 2015, 33, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllymaa, T.; Holmberg, H.; Ahtila, P. Techno-Economic Evaluation of Biomass Drying in Moving Beds: The Effect of Drying Kinetics on Drying Costs. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CO2 European Emission Allowances. MarketsInsider. 2018. Available online: http://markets.businessinsider.com/commodities/CO2-emissionsrechte (accessed on 3 September 2018).
- Sawdust Price in Finland. 2018. Metsäkustannus. Available online: https://www.metsalehti.fi/puunhinta/metsaenergian-kayttopaikkahinnat/ (accessed on 3 September 2018).
- Oil Price, 2018. Statistics Finland, Energy Prices, ISSN=1799-800X. 4th Quarter 2017, Appendix Figure 1. Import Prices of Oil, Helsinki. Available online: http://www.stat.fi/til/ehi/2017/04/ehi_2017_04_2018-03-13_kuv_001_en.html (accessed on 3 September 2018).
- Holmberg, H.; Isaksson, J.; Lahdelma, R. Minimization of total drying costs for a continuous packed-bed biomass dryer operating at an integrated chemical pulp and paper mill. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 71, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Moisture Content (% w.b.) | C (% in d.b.) | H | N | S | O | Cl | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soot Sludge | 95 | 65.9 | 0.66 | 0.35 | 1.34 | 4.50 | - | 27.2 |
| Sawdust | 56 | 48–50 | 6–6.5 | 0.5–2.3 | 0.05 | 38–42 | <0.01 | 0.4–0.6 |
| The Comparison of the Drying Times | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mm | 300 mm | |||||
| Drying Time, DC [s] | Drying Time, CDC [s] | * Relative Error | Drying Time, DC [s] | Drying Time, CDC [s] | * Relative Error | |
| 40 °C | 17,870 | 18,347 | 2.7 | 27,930 | 28,308 | 1.4 |
| 80 °C | 7840 | 7790 | 0.6 | 13,010 | 13,219 | 1.6 |
| 100 °C | 6650 | 6526 | 1.9 | 10,360 | 10,408 | 0.5 |
| 0.75 m/s; 80 °C | 7840 | 8137 | 3.8 | |||
| 0.9 m/s; 80 °C | 7650 | 7453 | 2.6 | |||
| The Critical Moisture Contents[kgH2O/kgdb] | ||||||
| 200 mm; 0.75 m/s | 300 mm; 0.75 m/s | |||||
| 40 °C | 4.50 | 4.16 | ||||
| 80 °C | 5.04 | 4.34 | ||||
| 100 °C | 4.30 | 4.46 | ||||
| 200 mm; 0.9 m/s | ||||||
| 80 °C | 4.51 | |||||
| Air Velocity: [m/s] | tair,in [°C] | tair,out [°C] | xin [kgH2O/kgda] | twb [°C] | [kgH2O/(kgdbs)] | αa [W/(m3K)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.75 m/s | 40.9 | 21.3 | 0.0057 | 19.4 | 0.000461 | 16,160 |
| 0.75 m/s | 81.4 | 31.1 | 0.0026 | 27.6 | 0.001190 | 18,274 |
| 0.75 m/s | 101.7 | 37.4 | 0.0055 | 32.9 | 0.001249 | 14,895 |
| Average: | 16,443 | |||||
| 0.9 m/s | 81.5 | 34.5 | 0.0041 | 28.4 | 0.001177 | 15,309 |
| tair, in [°C] | tair, out [°C] | xin [kgH2O/kgda] | twb [°C] | [kgH2O/(kgdbs)] | αa [W/(m3K)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40.7 | 20.0 | 0.0046 | 18.5 | 0.000308 | 11,435 |
| 80.0 | 31.3 | 0.0031 | 27.6 | 0.000685 | 10,534 |
| 103.4 | 35.1 | 0.0055 | 33.2 | 0.000893 | 13,266 |
| Average: | 11,745 |
| Parameters | Initial Value |
|---|---|
| Volume ratio of the sludge and sawdust mixture | 50%soot sludge:50%sawdust |
| Bed height of the mixture inside the dryer | 200 mm |
| Inlet air velocity before the bed | 0.75 m/s |
| Mass flow rate of moist soot sludge | 20 t/d |
| Moisture content of pure soot sludge | 95% wb |
| Mass flow rate of moist sawdust | 7.8 t/d |
| Moisture content of pure sawdust | 56% wb |
| Initial moisture content of the mixture | 5.3 kgH2O/kgdb (84% wb) |
| Final moisture content of the mixture after drying | 0.7 kgH2O/kgdb (41% wb) |
| Bulk density of the mixture | 116 kgdb/m3 |
| Total pressure drop of the dryer for the bed height of 200 mm | 318 Pa (from the drying data, average value between the pressure drops in the beginning and at the end of the tests [5]) |
| Total pressure drop over the heat exchanger and air duct | 400 Pa |
| Drying air temperature before the fans and before heating it to the desired drying air temperature | 15 °C |
| Moisture content of air | 0.004 kgH2O/kgda (average value from the drying tests [5]) |
| Efficiency of the fan (η) | 0.8 |
| Heating value of heavy fuel oil | 41 MJ/kg |
| Emission factor of heavy fuel oil | 284 kgCO2/MWh |
| Price of the CO2 ton | 13 €/tCO2 (current price [29], base case) |
| Lower heating value of dry sawdust | 19 MJ/kgdb |
| Lower heating value of dry soot sludge | 22.65 MJ/kgdb |
| Mass ratio of sawdust to soot sludge in the mixture () | 3.4 kgdb, sawdust/kgdb,soot sludge |
| Price of electricity | 40 €/MWh |
| Price of heat | 5 €/MWh (base case) |
| Price of sawdust | 19 €/MWh (current price in Finland [30], base case) |
| Operating time of the chemical plant and the dryer | 8000 h/year |
| 40 °C | 60 °C | 80 °C | 100 °C | 120 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-sectional area of the dryer | 39 m2 | 24 m2 | 17 m2 | 15 m2 | 13 m2 |
| Investment cost | 535,131 € | 359,705 € | 278,879 € | 244,024 € | 219,992 € |
| Savings in heavy fuel oil costs | 346,256 €/a | 346,256 €/a | 346,256 €/a | 346,256 €/a | 346,256 €/a |
| Savings in CO2 emissions | 35,510 €/a | 35,510 €/a | 35,510 €/a | 35,510 €/a | 35,510 €/a |
| Cost of sawdust | 114,391 €/a | 114,391 €/a | 114,391 €/a | 114,391 €/a | 114,391 €/a |
| Cost of electricity | 8492 €/a | 5117 €/a | 3726 €/a | 3160 €/a | 2783 €/a |
| Cost of heat | 33,355 €/a | 34,007 €/a | 33,738 €/a | 35,417 €/a | 36,571 €/a |
| Payback period | 2.4 years | 1.6 years | 1.2 years | 1.1 years | 1.0 years |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Myllymaa, T.; Holmberg, H.; Ahtila, P. Economic Evaluation of Drying of Soot Sludge and Sawdust Mixture at Low Temperatures Using the Characteristic Drying Curve Method. ChemEngineering 2020, 4, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4010006
Myllymaa T, Holmberg H, Ahtila P. Economic Evaluation of Drying of Soot Sludge and Sawdust Mixture at Low Temperatures Using the Characteristic Drying Curve Method. ChemEngineering. 2020; 4(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleMyllymaa, Tiina, Henrik Holmberg, and Pekka Ahtila. 2020. "Economic Evaluation of Drying of Soot Sludge and Sawdust Mixture at Low Temperatures Using the Characteristic Drying Curve Method" ChemEngineering 4, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4010006
APA StyleMyllymaa, T., Holmberg, H., & Ahtila, P. (2020). Economic Evaluation of Drying of Soot Sludge and Sawdust Mixture at Low Temperatures Using the Characteristic Drying Curve Method. ChemEngineering, 4(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4010006




