Abstract
Several hydrotalcite-type compounds with different divalent (Mg2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+) and trivalent (Al3+, Cr3+) cations and different ratio compositions were tested for the isomerization of linoleic acid in order to study their role on the obtention of specific conjugated linoleic acids (CLAs) with anticarcinogenic and nutritional properties. This is a complex reaction due to the high number of possible isomers of linoleic acid together with the significant competition of the isomerization reaction with other secondary undesired reactions. All catalysts showed very high conversions of linoleic acid, but condensation products were mainly obtained, especially for the hydrotalcite-type compounds with higher Mg/Al ratios due to their higher Brønsted basicity and for the catalysts with higher Ni2+ content or with the presence of Cu2+, Zn2+ in the layers because of the influence of the higher acidity of these cations on the Brønsted basicity of the hydroxides. The best results were achieved for the catalysts with Mg/Al ratio around 2.5–3, resulting in 29–38% of selectivity to the identified CLAs.
1. Introduction
Linoleic acid (cis-9, cis-12-octadecanoic acid) can have 56 isomers as a result of the combination of 14 isomers in position with conjugated double bonds located from carbons 2, 4 until carbons 15, 17, with the corresponding combinations cis/cis, cis/trans, trans/cis, or trans/trans. However, only about 20 conjugated linoleic acid isomers (CLAs) have been identified, mainly in meat and dairy products, using analytical techniques such as gas or liquid chromatography or 13C NMR. Figure 1 depicts the main isomers of linoleic acid (LA).
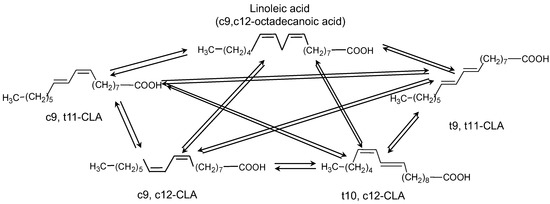
Figure 1.
Main isomers of linoleic acid (c9, c12-octadecanoic acid).
A significant number of studies reported that certain CLAs have anticarcinogenic and nutritional properties, so they can be applied as functional foods. Specifically, the isomer cis-9, trans-11-CLA (c9, t11-CLA) was proposed as a potential antitumor agent, while the isomer trans-10, cis-12-CLA (t10, c12-CLA) was related to the regulation of lipids and body mass [1,2,3,4].
Ruminant animals can synthesize CLAs from linoleic acid by means of rumen bacteria. For this reason, CLAs can be found naturally in dairy products and meat [2]. Regarding CLA production processes, the use of biotechnology, purification of fatty acid mixtures, and chemical synthesis methods did not allow a good separation of the isomers. At the industrial level, the production of CLA is usually performed by isomerization in alkaline conditions employing alkali bases or potassium alkoxides [5]. However, the use of solvents, alkali bases, and the necessary subsequent neutralization with acid becomes an economic and ecological drawback.
There are few publications related to the use of heterogeneous catalysis for the selective obtention of CLA isomers. Bernas et al. tested a great variety of supported-metal catalysts (Ru, Ni, Pd, Pt, Rh, Ir, Os, Pt-Rh supported on C, Al2O3, SiO2Al2O3, H-MCM-41, MCM-22, H-Y, and H-beta), previous activation or not under hydrogen, for the isomerization of linoleic acid in the liquid phase [6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. Previous publications reported that hydrogenation of linoleic acid is a competing reaction with respect to the isomerization reaction. The isomerization of linoleic acid involves a change in the position of one of the C–C double bonds in the initial linoleic acid molecule. The activation of this transformation can take place either through the C–H bonds adjacent to the double bonds or through the π-bonds along the carbon chain. In general, double bond migration proceeds via half-hydrogenated intermediates when hydrogen is present [13].
Claus et al. reported the synthesis of CLAs over Ag/SiO2 catalyst in the presence of hydrogen taking into account that silver is the metal with the lowest hydrogen-binding energy [14]. The catalytic results with Ag/SiO2 at 438 K showed the best selectivity values achieved until now of 35% to c9, t11-CLA, and 26% to t10, c12-CLA for a 69% of conversion with 12% of selectivity to the hydrogenation products at 438 K for 90 min of reaction.
These two research groups also investigated the use of gold catalysts supported in a wide variety of supports, such as Al2O3, SiO2, Fe2O3, CeO2, MnO2, TiO2, ZrO2, active carbon, and Ti-silicalite (TS-1), but the results did not improve those previously obtained [15,16]. Au increased activity but favoured the formation of undesired hydrogenation products. This reveals the high difficulty to convert selectively linoleic acid to the desired products. It is well-known that isomerization reactions can be catalysed either by acidic, basic, or supported metal catalysts [17].
In a previous work, we studied the role of catalyst acidity and porosity on the isomerization of linoleic acid to CLAs [18]. Conversion of linoleic acid increased in the presence of higher amounts of weak-moderate acid centres (Brønsted and Lewis) together with a higher accessibility of the acid sites. Additionally, the synergic effect between Brønsted and Lewis centres led to higher selectivity to the isomer cis-9, trans-11-CLA (9–13%), whereas higher selectivity to trans-10, cis-12-CLA (4–6%) was achieved with higher amounts of Brønsted acidity [18]. Additionally, other uninteresting CLAs, and some hydrogenation and condensation products were obtained. The presence of hydrogenation products was explained by hydride transfer type reactions that take place on the acid sites. Regarding condensation products, it is well-known that olefins can undergo proton-catalysed reactions on acid sites, such as isomerization, polymerisation, and cyclisation [19].
More recently, a series of Ru-MgAl composite oxides catalysts prepared by calcining the ruthenium grafted hydrotalcite-like precursor at various temperatures were tested for the isomerization of linoleic acid in the absence of hydrogen [20]. The basic sites of Ru-MgAl catalyst together with the ruthenium sites seem to have a synergic effect resulting in a selectivity to cis-9, trans-11-CLA of 14% and trans-10, cis-12-CLA of 16%. However, there are not studies about the use of basic materials without metallic phase as catalysts for this reaction. In this case, a competition between the isomerization reaction and possible secondary condensation reactions should be expected.
Hydrotalcite-like compounds, a class of layered materials having the general formula [M(II)1−xM(III)x(OH)2][Ax/nn−]·mH2O (where M(II) and M(III) are divalent and trivalent cations and A is the interlayer anion), showed significant applications as basic catalysts, ion exchangers, supports, and precursors for composite materials [21,22,23]. Calcination of hydrotalcites gives to high-area mixed oxides, which also have numerous catalytic applications [24,25,26]. The acid-base properties of these layered double hydroxides (LDHs) can be modulated by modifying the nature and amount of structural cations and compensating anions in addition to their method of synthesis [21].
The aim of this work was to study the role of the nature of cations, divalent (Mg2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+) and trivalent (Al3+, Cr3+), and the cations ratio employed to prepare the hydrotalcite-type compounds on the isomerization of linoleic acid to CLAs. Additionally, two calcined LDHs, one synthesized brucite and one commercial MgO were tested for comparison. Fresh and used catalysts were characterized by several techniques.
2. Materials and Methods
Several layered double hydroxides with different cation and ratio composition were prepared by coprecipitation at constant pH under vigorous magnetic stirring.
One hydrotalcite with Mg2+/Al3+ ratio of 9/1 was synthesized at pH 9 (pH = 9 ± 0.1) (HTMgAl1) and two hydrotalcites with Mg2+/Al3+ ratio of 9/1 and 3/1 were synthesized at pH 10 (pH = 10 ± 0.1) using an aqueous solution containing in appropriate amounts Mg(NO3)2·6H2O and Al(NO3)3·9H2O, and a 1 M NH3 titrating solution which were simultaneously added to an aqueous solution of (NH4)2CO3 0.05 M (HTMgAl2 and HTMgAl3, respectively).
Two Ni/Mg/Al LDHs were prepared at pH 8 (pH = 8 ± 0.1) both with M2+/Al3+ ratio of 3, but with Ni2+/Mg2+ ratio of 10 (HTNiMgAl1) and Ni2+/Mg2+ ratio of 0.25 (HTNiMgAl2), respectively. In this procedure, an aqueous solution containing in appropriate amounts Ni(NO3)2·6H2O, Mg(NO3)2·6H2O and Al(NO3)3·9H2O, and a 1 M NaOH titrating solution, which were simultaneously added to an aqueous solution of Na2CO3·10H2O.
Finally, one Cu/Zn/Cr sample with M2+/Cr3+ ratio of 2 and Cu2+/Zn2+ ratio of 1 (HTCuZnCr), and one Cu/Cr sample with Cu2+/Cr3+ ratio of 4 (HTCuCr) were synthesized at pH 10 (pH = 10 ± 0.1) using an aqueous solution containing in appropriate amounts CuCl2, ZnSO4·7H2O and CrCl3·6H2O, and a 1 M NaOH titrating solution which were simultaneously added to an aqueous solution of Na2CO3·10H2O following a synthesis method reported for preparing Cu/Mg/Cr LDHs [26].
After complete precipitation, the corresponding gels were aged by refluxing at 343 K for 18 h in Mg/Al and Ni/Mg/Al samples, and at room temperature for 4 h in Cu/Zn/Cr and Cu/Cr samples. All samples were filtered and washed several times with deionized water until neutral pH. Solids were dried in an oven at 393 K overnight.
HTMgAl1 and HTNiMgAl1 were calcined at 623 K for 4 h obtaining samples cHTMgAl1 and cHTNiMgAl1, respectively. Commercial MgO (MgO) was supplied by Panreac (≥99%).
One brucite was synthesized by rapid addition of NH3 10 N to MgCl2 solution and later adjust of pH to 11, maintaining stirring for 30 min (B).
Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the different samples were obtained with a Siemens D5000 diffractometer using nickel-filtered CuKα radiation. Samples were dusted on double-sided sticky tape and mounted on glass microscope slides. The patterns were recorded over a range of 2θ angles from 10° to 90° and crystalline phases were identified using the Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS) files (089-0460 corresponds to the hydrotalcite phase and 44-1482 to the brucite). From the diffraction data, the cell parameters (c and a) were calculated from (003) and (110) peaks, respectively using a matching profile with WIN FIT 1.2 software. Crystallite size of the layers was calculated from (110) plane for hydrotalcite-type compounds and from (001) plane for brucite by using the Debye-Scherrer equation. For calcined hydrotalcites and MgO, crystallite size was calculated from (200) plane.
N2 adsorption-desorption measurements were performed on a Quadrasorb SI at 77 K to determine the specific BET area. Before measurement, the samples were degassed at 363 K.
Elemental analyses of the different samples were obtained with a Hitachi Z-8200 Polarized Zeeman Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer. The digestion of all hydrotalcites was carried out with concentrated HNO3. All measures were made by triplicate.
Scanning electron micrographs (SEM) were obtained with a JEOL JSM-35 C scanning microscope operating at an accelerating voltage in the range 15–30 kV, work distance of 14 mm, and magnification values between 5000 and 30,000·.
Transmission electron micrograph (TEM) was done using JEOL 1011 transmission electron microscope operating at an accelerating voltage of 80 kV and magnification of 200 k. Sample (0.1 mg) was dispersed in ethanol (50 µL) with the aid of an ultrasounds. It was then deposited on a carbon coated copper grid and air dried.
Linoleic acid (C18H32O2) (>99.9% purity) and n-decane (>95% purity) were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich. Decane (70 mL) and linoleic acid (0.2 g) were charged into a 200 mL stirred glass reactor, which was provided with a reflux condenser and a heating jacket. The solution was deoxygenated before catalyst addition bubbling nitrogen (100 mL/min) through it for 10 min. Catalysts were dried prior to the catalytic tests. The system was stirred at 700 rpm in all experiments to keep the catalyst uniformly dispersed in the reaction medium and to eliminate external mass-transfer problems. Catalytic tests were performed under N2 at 438 K and the reaction products were taken at 10 h of reaction. Each catalytic point was made by triplicate in order to ensure the reproducibility of the results.
Reaction products were silylated following the method reported elsewhere [8,13], and identified by gas chromatography (GC) on a Shimadzu GC-2010 instrument equipped with a 25 m capillary HP-5 column (i.d. 0.20 mm, film thickness 0.11 μm) and a FID detector operating at 563 K. In the silylation procedures, 10 μL of samples from the reactor were added into glass tubes that had been washed with methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE, 99.8% of purity from Sigma-Aldrich). An amount of 50 μL of 0.5 mg/mL C17:0 fatty acid solution (98% of purity, Sigma Aldrich) was added to each sample as internal standard. MTBE and the solvent were evaporated in a stream of nitrogen with water as heating medium and the samples were furthermore dried at 313 K for 20 min. Then, samples were dissolved in 20 μL pyridine (98% of purity, Sigma-Aldrich) and 80 μL N, O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) of >99% of purity and 40 μL trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS) of 98% purity were added, both supplied by Sigma-Aldrich. Solutions were kept in an oven at 343 K for 45 min.
An aliquot of 2 μL of the samples was injected into the GC at the injector temperature 533 K. Helium served as a carrier gas with a flow rate of 0.9 mL/min and a split ratio of 1:20. The temperature program was 423 K (0.5 min)-7 K/min-503 K-10 K/min-563 K (10 min). Peaks corresponding to linoleic acid and conjugated dyonic isomers of linoleic acid were identified and quantified from the calibration lines obtained by injecting the silylated standards of linoleic acid, supplied by Sigma-Aldrich, and trans-10, cis-12, cis-9, trans-11 and trans-9, trans-11 CLA isomers, supplied by Matreya Inc (98% of purity). Conversion and selectivity values were calculated following the equations:
Conversion (%) = (mols of transformed linoleic acid/initial mols of linoleic acid) × 100
Selectivity (%) = (mols of linoleic acid transformed to one reaction product/mols of transformed linoleic acid) × 100.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Catalysts
XRD patterns of the Mg/Al and Ni/Mg/Al samples showed only one crystalline phase identified as hydrotalcite. For the CuZnCr and CuCr samples, a less crystalline hydrotalcite phase was observed, probably due the lower aging time used (Figure 2).
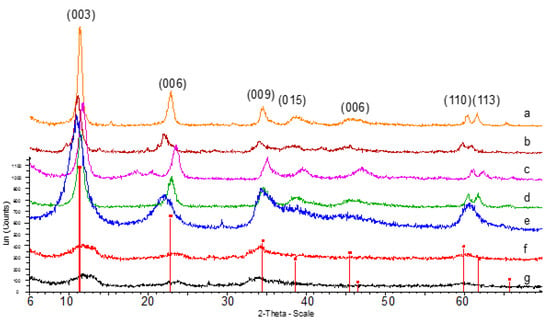
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of the hydrotalcite-type samples. (a) HTMgAl1, (b) HTMgAl2, (c) HTMgAl3, (d)HTNiMgAl1, (e) HTNiMgAl2, (f) HTCuZnCr and (g) HTCuCr. Red line: JCPDS file (089-0460 hydrotalcite).
A better resolution of the peaks appeared at higher 2θ values, specifically, those which correspond to the (110) and (113) planes, was observed for Mg/Al samples and for the Ni/Mg/Al sample with higher Ni content (HTNiMgAl1), thus demonstrating a higher intralayer ordering. This was confirmed by the higher layer crystallite size obtained for these samples when calculated from the (110) plane by using the Scherrer equation (Table 1). The full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the basal reflection plane (003) is usually taken to evaluate the crystallinity in the stacking direction. Mg/Al samples and sample HTNiMgAl1 showed lower FWHM values according to their higher crystallinity.

Table 1.
Characterization of the catalysts by XRD and N2 physisorption.
Cell parameters (a and c) were calculated from the interplanar distances (110) and (003), respectively (Table 1). The differences observed for the lattice parameter a can be related to the isomorphic substitution between M2+ (Ni2+, Mg2+, Zn2+) and M3+ (Al3+, Cr3+). Parameter c mainly depends on the charge, size, and number of anions between the brucite layers. Thus, the slight differences observed between the samples for cell parameter c can be attributed to the different type of anions used (CO32−, NO3−, Cl−, SO42−) together with some differences in the hydration degree.
XRD of the calcined hydrotalcites cHTMgAl1 and cHTNiMgAl1 exhibited the presence of an amorphous phase due to the expected mixture of magnesium (nickel) and aluminium oxides Mg(Ni)(Al)Ox with periclase structure and crystallite sizes lower than commercial MgO (Table 1). Finally, high-crystalline brucite was identified by XRD for sample B (Figure 3).
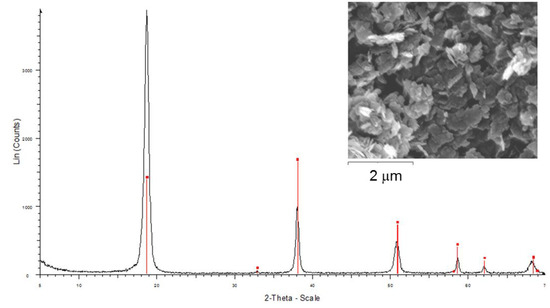
Figure 3.
XRD pattern and SEM of the brucite sample (B).
The Mg/Al molar ratio values calculated by XRF for the Mg/Al hydrotalcites precipitated at pH 10 were near the theoretical value whereas for the sample synthesized at pH 9 (HTMgAl1), the Mg/Al value was lower (Table 2). This can be explained by the different optimum pH value for precipitating magnesium hydroxide (pH 10) with respect to aluminium hydroxide (pH 8–9). For the Ni/Mg/Al, Cu/Zn/Cr and Cu/Cr hydrotalcites, the cationic ratios calculated by XRF almost matched the theoretical values (Table 2).

Table 2.
Characterization of the hydrotalcite-type compounds by XRF.
N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of the hydrotalcite-type compounds were type IV, according to IUPAC classification, with average pore diameters in the range of mesopores and hysteresis type B according to de Boer classification, characteristic of ordered or disordered distribution of the lamellas (Figure 4). This is in agreement with the porosity obtained for the hydrotalcites prepared by conventional refluxing [23]. Calcined hydrotalcites and MgO also presented nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms of type IV while brucite (B) exhibited a mixture of the isotherm type II and IV with hysteresis type D, according to the Boer classification.
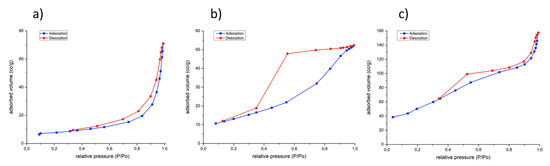
Figure 4.
N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms for samples: (a) HTMgAl1, (b) HTNiMgAl1 and (c) HTCuZnCr.
Regarding BET surface areas, Cu/Cr and Cu/Zn/Cr hydrotalcites had higher surface areas than Mg/Al and Mg/Ni/Al samples (Table 1). This can be explained by their lower crystallinity, as observed by XRD (Figure 2). The increase of the surface area observed after calcination for the samples cHTMgAl1 and cHTNiMgAl1 can be related to the rapid release of gases occurred during decomposition of the hydrotalcite structure due to the loss of anions and water from the interlayer space.
The SEM and TEM of the samples exhibited the presence of thin regular hexagonal crystals characteristic of the hydrotalcite-type compounds with some overlay of the layers (Figure 5).
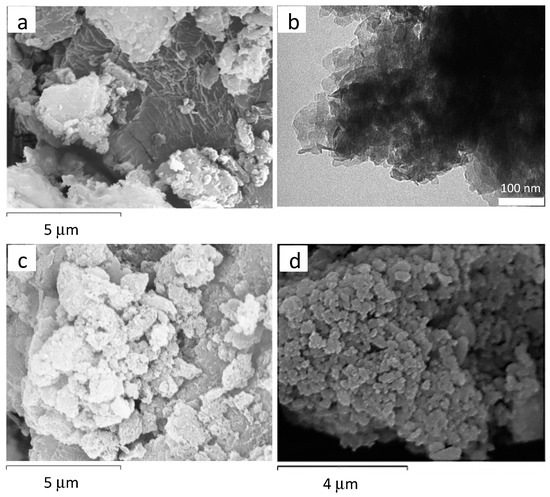

Figure 5.
Several representative micrographs of the hydrotalcite-type compounds: (a) SEM of HTMgAl1, (b) TEM of HTMgAl3, (c) SEM of HTNiMgAl1, and (d) SEM of HTCuZnCr.
Calcined samples maintained the hexagonal morphology of their precursors, the hydrotalcite-type compounds, which is in agreement with the literature [27]. This means that the crystal morphology of the particles did not change significantly despite the changes suffered by the structure with the temperature (loss of water, anions, and dihydroxylation processes). Finally, SEM of synthesized brucite showed layered particles with higher particle size (Figure 3) than the hydrotalcite-type compounds.
3.2. Catalytic Activity
Table 3 shows the conversion and selectivity values to the identified CLA isomers: cis-9, trans-11-CLA, trans-10, cis-12-CLA, and trans-9, trans-11-CLA for all catalysts. The difference between 100% and the selectivity to these isomers was named in Table 3 along with other products, which are the sum of other nonidentified CLA isomers and condensation products.

Table 3.
Catalytic results for the isomerization of linoleic acid.
All basic materials showed very high conversions of linoleic acid. However, the presence of Brønsted basic sites related to OH− (in the case of brucite) or the presence of Lewis basic sites related to the O2− (in commercial MgO (M) and in the Mg/(Ni)(Al)Ox of calcined hydrotalcites (cHTMgAl1, cHTNiMgAl1)) led to very low selectivity to conjugation. Thus, condensation products were mainly obtained. The presence of condensation products was confirmed by the appearance of peaks at higher retention times than those corresponding to the CLAs in the chromatograms. It is well-known that the Lewis basic sites generated after calcining hydrotalcites have higher basicity strength than the Brønsted basic sites related to the OH− of their precursors [28,29].
Regarding Mg/Al hydrotalcite type-compounds, the hydrotalcites with higher Mg/Al ratio (HTMgAl1 and HTMgAl2). Therefore Brønsted basic sites with similar strengths to brucite also led to lower amounts of conjugation products (3.9–13.6%). However, for the hydrotalcite HTMgAl3 with lower Mg/Al ratio, higher selectivity to conjugation products (38.4%) was achieved. This can be attributed to the higher amounts of Al3+, which decreased the basicity strength of the resulting hydrotalcite when compared with those with higher Mg/Al ratio or even with brucite although some contribution to isomerization of the Lewis acidity related to the presence of Al3+ cannot be discarded [18,30,31,32]. Additionally, for HTMgAl1 and HTMgAl2, the other products detected were completely condensation products, while for HTMgAl3, the other products observed in the chromatogram were other CLA products together with condensation products.
The two Ni/MgAl hydrotalcites synthesized showed important differences in their catalytic behaviour, since HTNiMgAl2 resulted in significant higher selectivity to conjugation products than HTNiMgAl1. Taking into account the different cation composition of their layers (Table 2), the presence of higher amounts of Ni2+ in the layers of HTNiMgAl1 did not favour conjugation of linoleic acid. On the other hand, a higher Mg/Al content (around 2.4), and therefore, moderate-weak Brønsted basic sites, could be related to the higher selectivity to the identified conjugation products (28.8%) observed for catalyst HTNiMgAl2, which was comparable to that obtained for the catalyst HTMgAl3 with a Mg/Al ratio of 2.91 (38.4%) (Table 2). Interestingly, higher amounts of Ni2+ with higher acidity than Mg2+ in catalyst HTNiMgAl1 did not favour isomerization, mainly considering that the amount of M2+/Al3+ ratio was slightly lower than that of HTNiMgAl2 (2.59 compared to 2.9). This allowed us to conclude that the main contribution to the isomerization reaction should be attributed to the Brønsted basic sites with moderate-weak basicity related to the OH−.
Finally, HTCuZnCr and HTCuCr catalysts led to null or practically null selectivity to CLAs. The incorporation of cations with higher acidity in the hydrotalcite structure, such as Cu2+ or Zn2+, decreased their Brønsted basicity favouring the formation of condensation/polymerization products, as previously observed for the hydrotalcite with higher Ni2+ content.
From these results, we can conclude that the low selectivity to the conjugation products of linoleic acid (CLAs) observed for these hydrotalcite-type catalysts could be related to: a) The different acid-basic properties derived from the presence of different cations and different cations ratio in the hydrotalcite layers, and b) the particular porosity of the layered hydrotalcite-type compounds, which can involve some steric hindrance to the formation of these isomers due to their conformation, taking into account that the accessibility of the reagents to the interlayer space should be low or null compared with other materials with higher porosity. The major CLA product was always the trans-9, trans-11-CLA isomer, which is the most thermodynamically favourable.
The selectivity results to the desired CLA products obtained with the best hydrotalcite-type catalyst tested in this study (10.7–15.6%) were much lower than those reported for supported-metal catalysts (e.g., 61% for Ag/SiO2 [14]) but comparable to those obtained when acid catalysts were used for this reaction (e.g., 16.6% for NiNa-mordenite [18]). It was not possible to compare with other basic catalysts since, to our knowledge, there are not references about their use for this reaction.
Some of the used catalysts were characterized by XRD and nitrogen physisorption. After reaction, catalysts maintained their hydrotalcite structure, with some increase of crystallinity, which can explained by some aging of the hydrotalcite during the 10 h of reaction performed at 438 K (e.g., Figure 6). However, a decrease of their surface area was observed in all cases (e.g., from 48 to 22 m2/g for catalyst HTMgAl3). In order to evaluate the possible presence of reaction products in the catalytic pores, these catalysts were submitted to extraction with ether for 10 h under refluxing. The products were separated from the ether phase by rota-evaporation, silylated following the procedure described in the experimental section and analysed by gas chromatography. The results mainly showed the presence of condensation products. This is in agreement with the change of colour observed for catalysts after reaction from white to beige-brown.
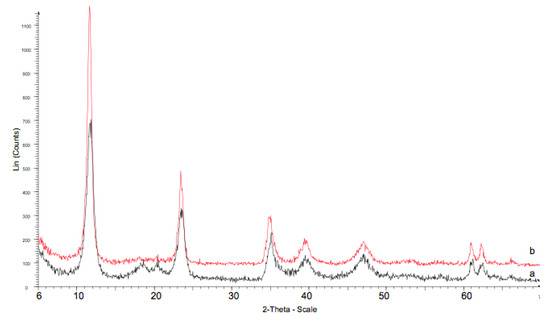
Figure 6.
XRD pattern of the catalyst HTMgAl3 a) before, and b) after reaction.
The catalytic life of catalyst HTMgAl3 was evaluated in three consecutive runs at the same reaction conditions (Figure 7). After each run, catalyst was recovered by filtration, washed in ether at room temperature, and dried. Catalytic reuses resulted in a significant loss of conversion and a progressive loss of selectivity to the identified isomerization products at expenses of the formation of other unidentified CLAs and mainly condensation products. The results confirmed that despite the cleaning of catalyst after each use with the purpose to eliminate the retained products, basic centres were strongly affected from the first use. Therefore, the values of conversion and selectivity to the desired products decreased.
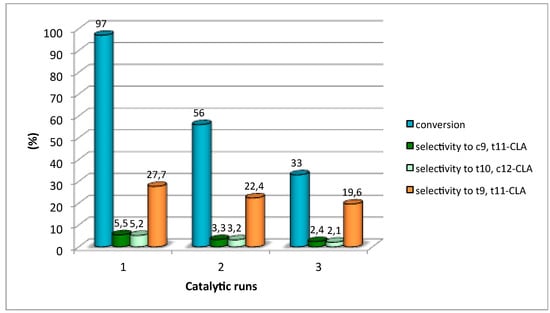
Figure 7.
Catalytic life of catalyst HTMgAl3.
With respect to the reaction mechanism on basic sites, we believe that the initiation of the isomerization reaction of linoleic acid can be similar to that previously reported for the 1-butene isomerization reaction on heterogeneous basic catalysts [33]. In that study, H. Hattori proposed the initiation of reaction by abstraction of allylic H by basic sites to form cis or trans forms of the allyl anion (double bond migration). However, more studies are needed to optimize the composition and cation ratio in LDHs or even modify the acid-base properties of these materials, e.g., by doping with other compounds in order to improve the selectivity to the conjugated products.
4. Conclusions
All basic materials showed very high conversion of linoleic acid. Brønsted basic sites of brucite or the presence of Lewis basic sites in calcined hydrotalcites and MgO led to very low selectivity to conjugation, and condensation products were mainly obtained. The best results were achieved for the catalysts with Mg/Al ratio around 2.5–3, which had the appropriate acid-base properties, resulting in 29–38 % of selectivity to the identified CLAs.
Author Contributions
Methodology, X.C.; validation, P.S. and Y.C.; investigation, X.C.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.C.; supervision, P.S. and Y.C.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- O’Quinn, P.R.; Nelssen, J.L.; Goodband, R.D.; Tokach, M.D. Conjugated linoleic acid. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2000, 1, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whigham, L.D.; Cook, M.E.; Atkinson, R.L. Conjugated linoleic acid: Implications for human health. Pharmacol. Res. 2000, 42, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mougios, V.; Matsakas, A.; Petridou, A.; Ring, S.; Sagredos, A.; Melissopoulou, A.; Tsigilis, N.; Nikolaidis, M.J. Effect of supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid on human serum lipids and body fat. Nutr. Biochem. 2001, 12, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombo, J.D.; Ganguly, A.; Bistrian, B.R.; Menard, M.P. The antiproliferative effects of biologically active isomers of conjugated linoleic acid on human colorectal and prostatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2002, 177, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.; Zander, L.; Albiez, W.; Horlacher, P.; Westfechtel, A. Method for the production of conjugated linoleic acids. EP1527153A1, 4 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bernas, A.; Kumar, N.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Laine, E.; Holmbom, B.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D. Conjugation of linoleic acid over a hydrogen pre-activated heterogeneous catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2002, 10, 1142–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernas, A.; Laukkanen, P.; Kumar, N.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Väyrynen, J.; Laine, E.; Holmbom, B.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D. A new heterogeneously catalytic pathway for isomerization of linoleic acid over Ru/C and Ni/H–MCM-41 catalysts. J. Catal. 2002, 210, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernas, A.; Kumar, N.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Kul’kova, N.V.; Holmbom, B.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D. Isomerization of linoleic acid over supported metal catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 245, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernas, A.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Kumar, N.; Holmbom, B.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D. Heterogeneously catalytic isomerization of linoleic acid over supported ruthenium catalysts for production of anticarcinogenic food constituents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernas, A.; Murzin, D. Influence of hydrogen preactivation on the linoleic acid isomerization properties of supported ruthenium catalyst. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2003, 78, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernas, A.; Kumar, N.; Laukkanen, P.; Väyrynen, J.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D. Influence of ruthenium precursor on catalytic activity of Ru/Al2O3 catalyst in selective isomerization of linoleic acid to cis-9,trans-11- andtrans-10,cis-12-conjugated linoleic acid. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 267, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernas, A.; Kumar, N.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Holmbom, B.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D. Heterogeneous catalytic production of conjugated linoleic acid. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2004, 8, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, K.S.; Hilaire, L.; Le Normand, F.; Touroude, R.; Paul-Boncour, V.; Percheron-Guegan, A. Catalysis by palladium–rare-earth-metal (REPd3) intermetallic compounds: hydrogenation of but-1-ene, buta-1,3-diene and but-1-yne. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1991, 87, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreich, M.; Claus, P. Direct Conversion of Linoleic Acid over Silver Catalysts in the Presence of H2: An Unusual Way towards Conjugated Linoleic Acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7800–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, P.; Horlacher, P.; Claus, P. Direct isomerization of linoleic acid to conjugated linoleic acids (CLA) using gold catalysts. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2009, 32, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simakova, O.; Lleino, A.; Campo, B.; Maki-Arvela, P.; Kordas, K.; Mikkola, J.; Murzin, D. Linoleic acid isomerization over mesoporous carbon supported gold catalysts. Catal. Today 2010, 150, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K.; Hölderich, W. Industrial application of solid acid–base catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1999, 181, 399–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardó, X.; Bergadà, O.; Cesteros, Y.; Salagre, P. Effect of catalyst acidity and porosity on the catalytic isomerization of linoleic acid to obtain conjugated linoleic acids (CLAs). Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oukaci, R.; Wu, J.C.S. Secondary reactions during CO hydrogenation on zeolite-supported metal catalysts: Influence of alkali cations. J. Catal. 1987, 107, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q. Synergetic effect of ruthenium and basicity sites in the Ru–MgAl catalyst for hydrogen-free production of conjugated linoleic acids. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 20248–20255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, A. Clays and catalysis: A promising future. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 14, 161–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rives, V.; Ulibarri, M.A. Layered double hydroxides (LDH) intercalated with metal coordination compounds and oxometalates. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 181, 61–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavani, F.; Trifiro, F.; Vaccari, A. Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: Preparation, properties and applications. Catal. Today 1991, 11, 173–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesteros, Y.; Salagre, P.; Medina, F.; Sueiras, J.E.; Tichit, D.; Coq, B. Hydrodechlorination of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene on nickel-based catalysts prepared from several Ni/Mg/Al hydrotalcite-like precursors. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 32, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, F.; Fornasari, G.; Rosetti, V.; Trifirò, F.; Vaccari, A. Effect of the Mg/Al ratio of the hydrotalcite-type precursor on the dispersion and activity of Rh and Ru catalysts for the partial oxidation of methane. Catal. Today 2004, 91–92, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelló, S.; Medina, F.; Tichit, D.; Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Groen, J.C.; Sueiras, J.E.; Salagre, P.; Cesteros, Y. Aldol Condensations Over Reconstructed Mg–Al Hydrotalcites: Structure–Activity Relationships Related to the Rehydration Method. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debecker, D.P.; Gaigneaux, E.M.; Busca, G. Exploring, Tuning, and Exploiting the Basicity of Hydrotalcites for Applications in Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chemistry 2009, 15, 3920–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climent, M.J.; Corma, A.; Iborra, S.; Epping, K.; Velty, A. Increasing the basicity and catalytic activity of hydrotalcites by different synthesis procedures. J. Catal. 2004, 225, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cosimo, J.I.; Apesteguia, C.R.; Ginés, M.J.L.; Iglesia, E. Structural Requirements and Reaction Pathways in Condensation Reactions of Alcohols on MgyAlOx Catalysts. J. Catal. 2000, 190, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A. Inorganic Solid Acids and Their Use in Acid-Catalyzed Hydrocarbon Reactions. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 559–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, S.M.; Zong, Z.; Chatzidimitriou, A.; Avci, L.E.; Bond, J.Q.; Carreon, M.A.; Wettstein, S.G. Small pore zeolite catalysts for furfural synthesis from xylose and switchgrass in a γ-valerolactone/water solvent. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 422, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.J.; Iglesia, E. The strength of Brønsted acid sites in microporous aluminosilicates. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5741–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, H. Heterogeneous basic catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 537–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).