Micronization for Enhancement of Curcumin Dissolution via Electrospraying Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
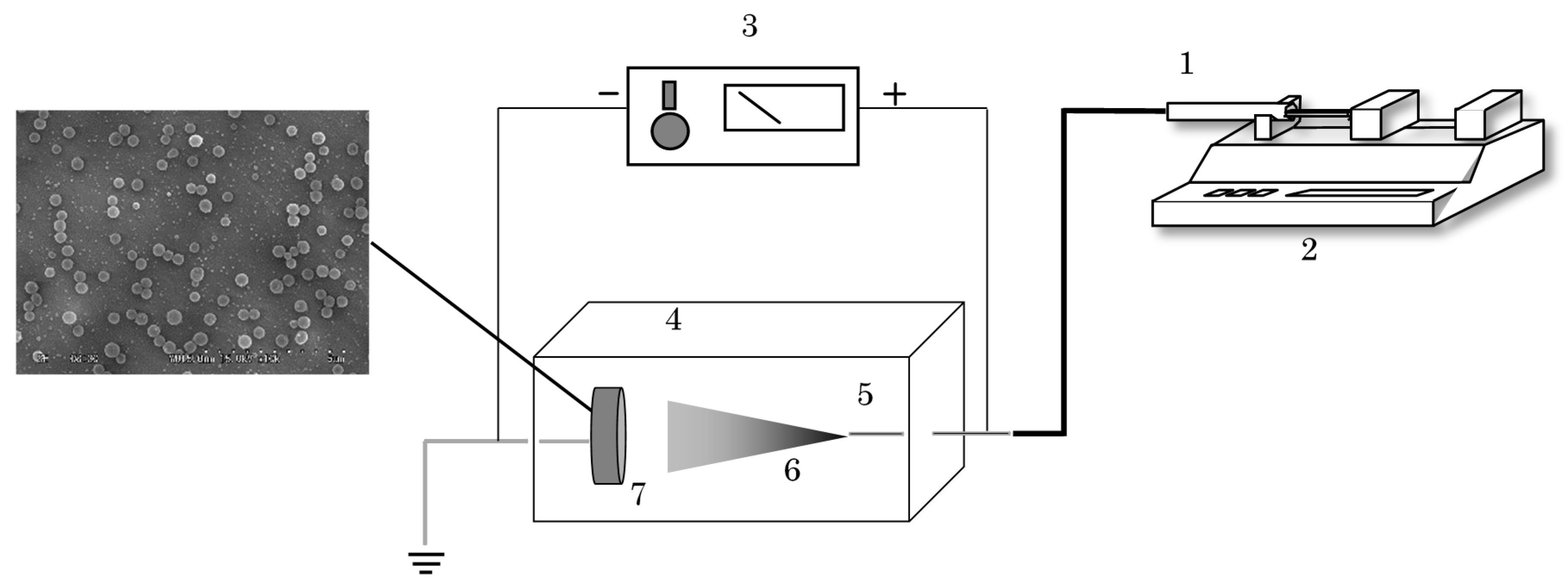
2.2. Experimental Setup and Procedure
2.3. Characterization of Products
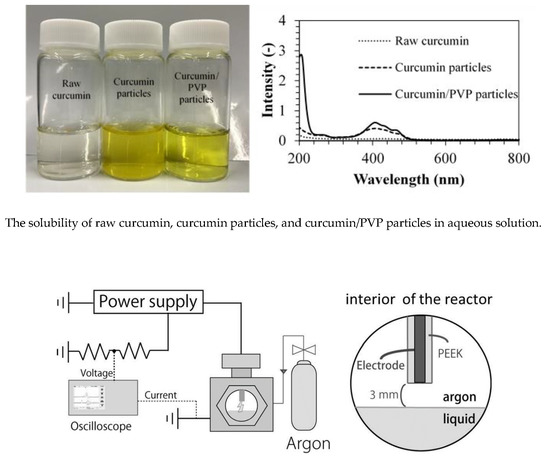
2.4. Dissolution Study
3. Results and Discussion
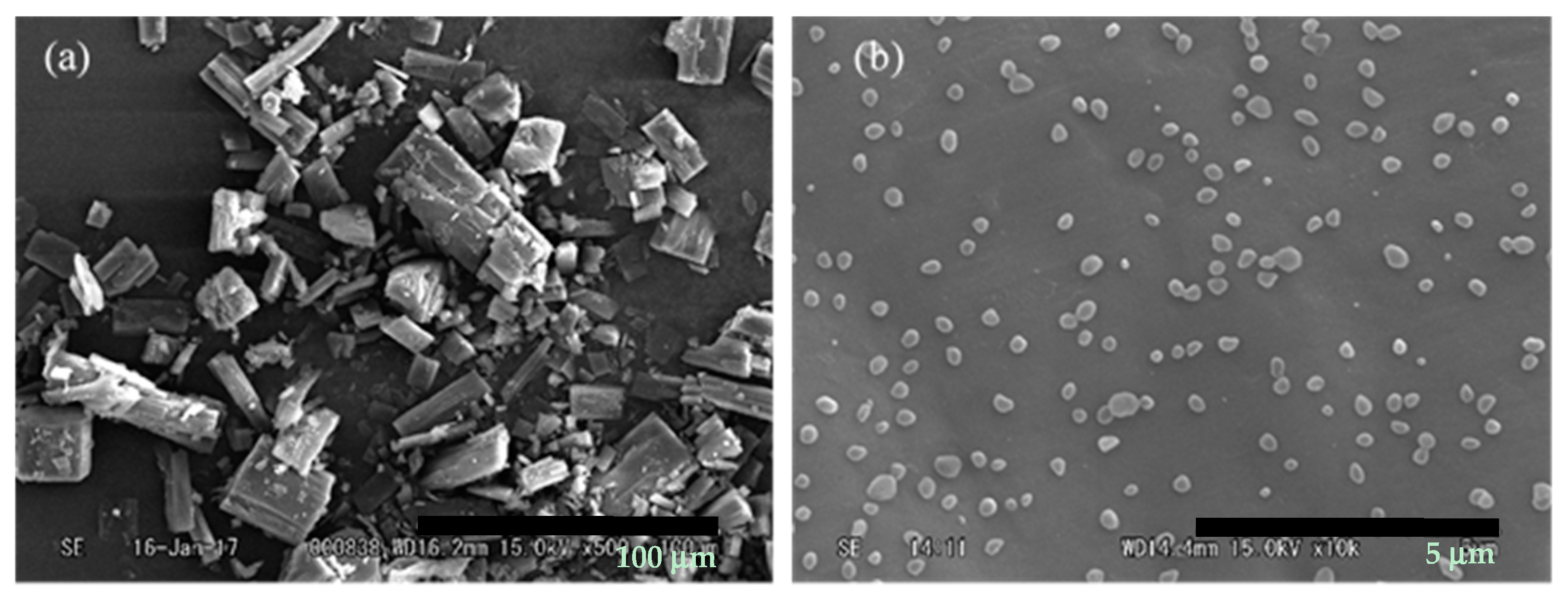
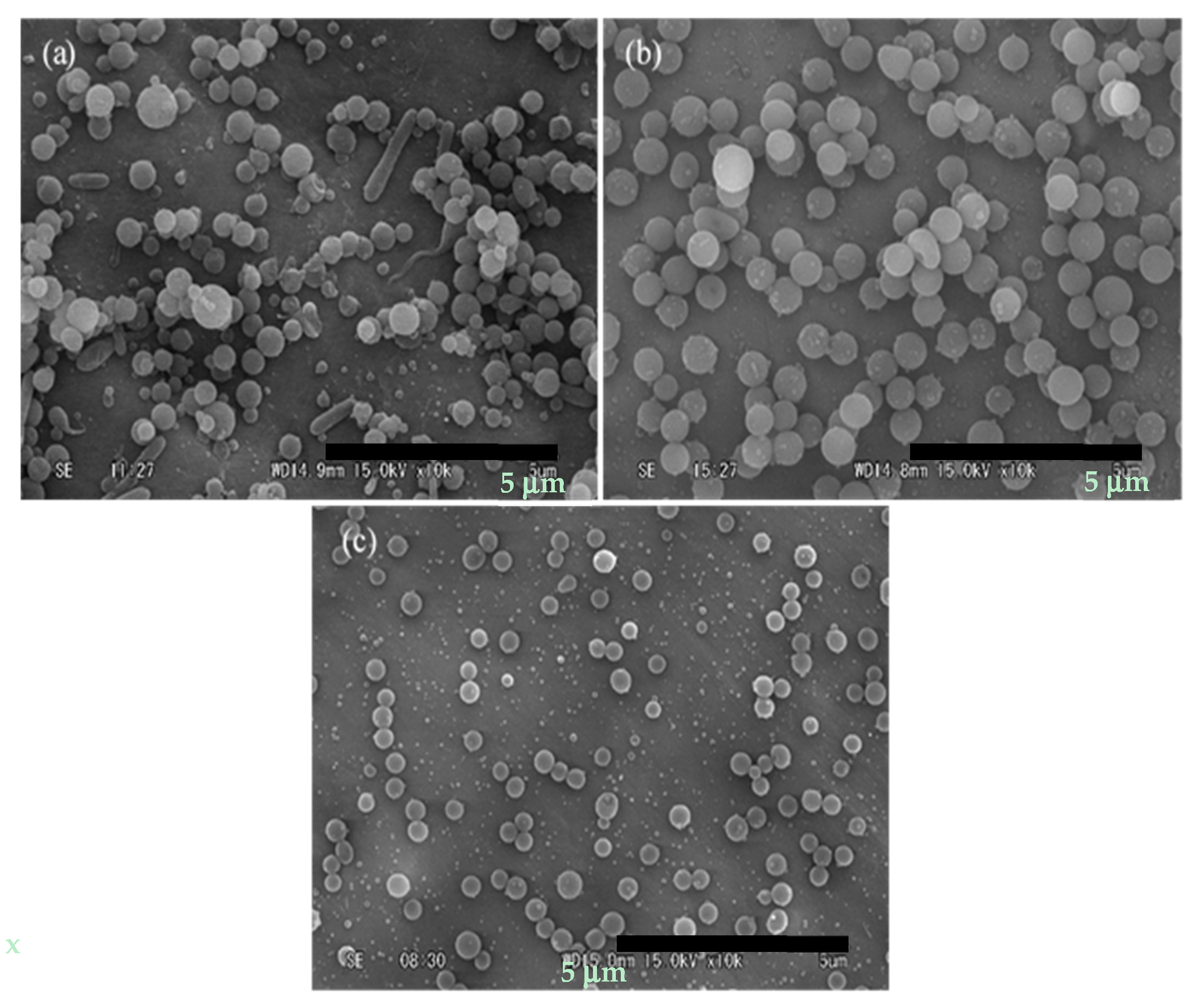
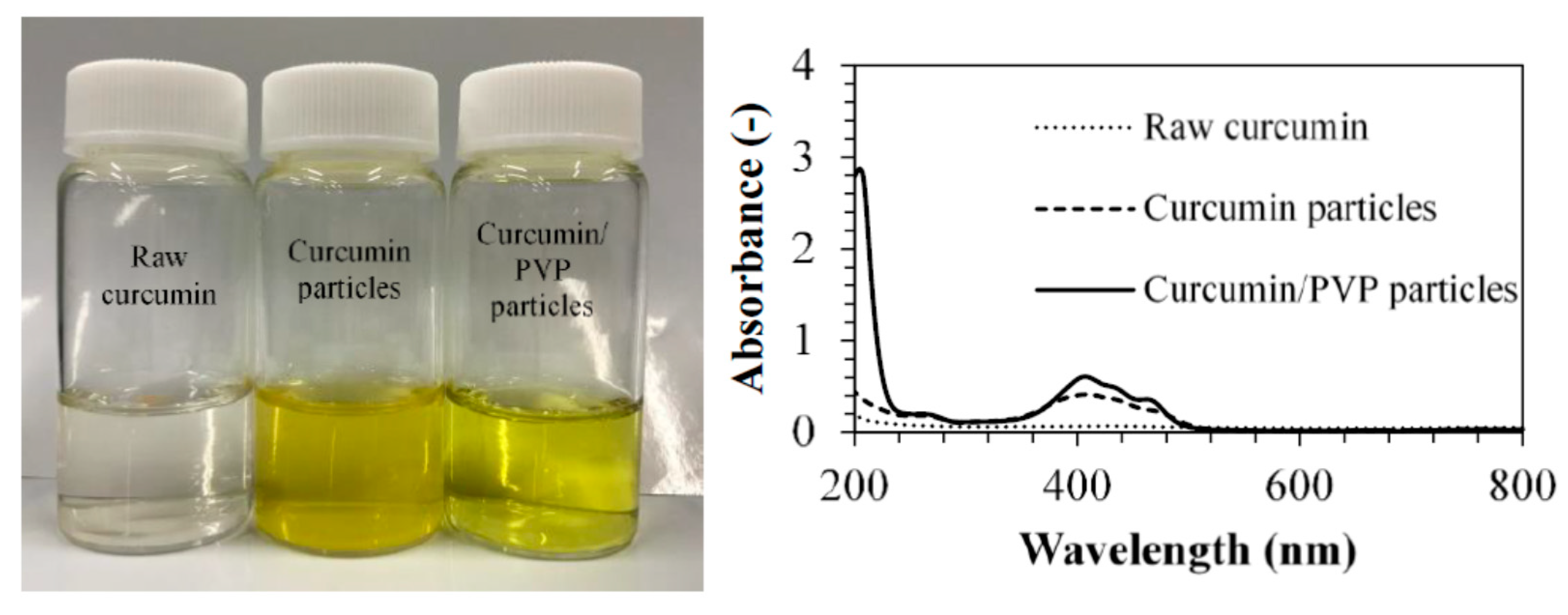
3.1. Micronization of Curcumin by Electrospraying
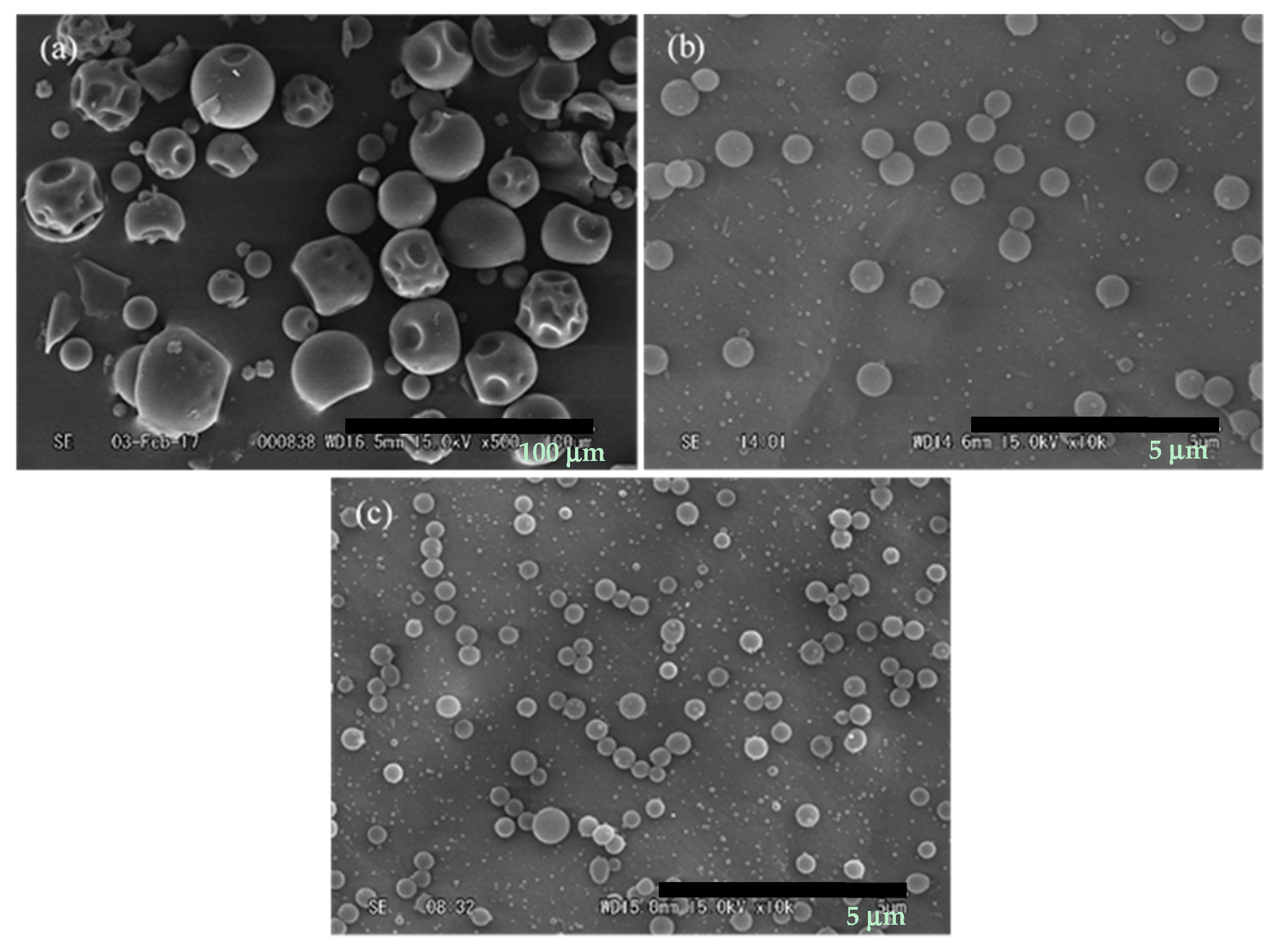
3.2. Encapsulation of Curcumin with PVP by Electrospraying
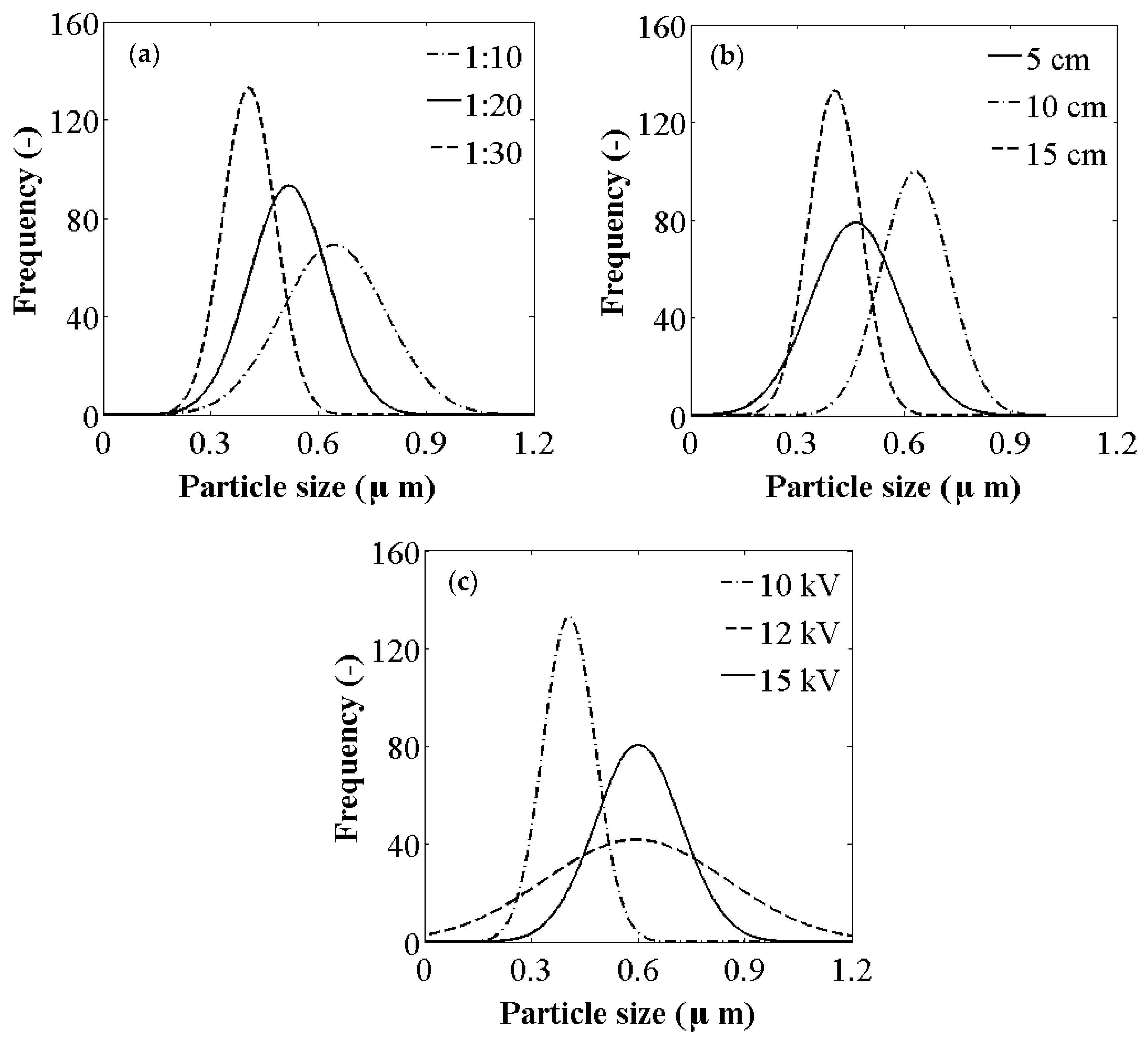
3.3. Effect of Curcumin/PVP Ratio
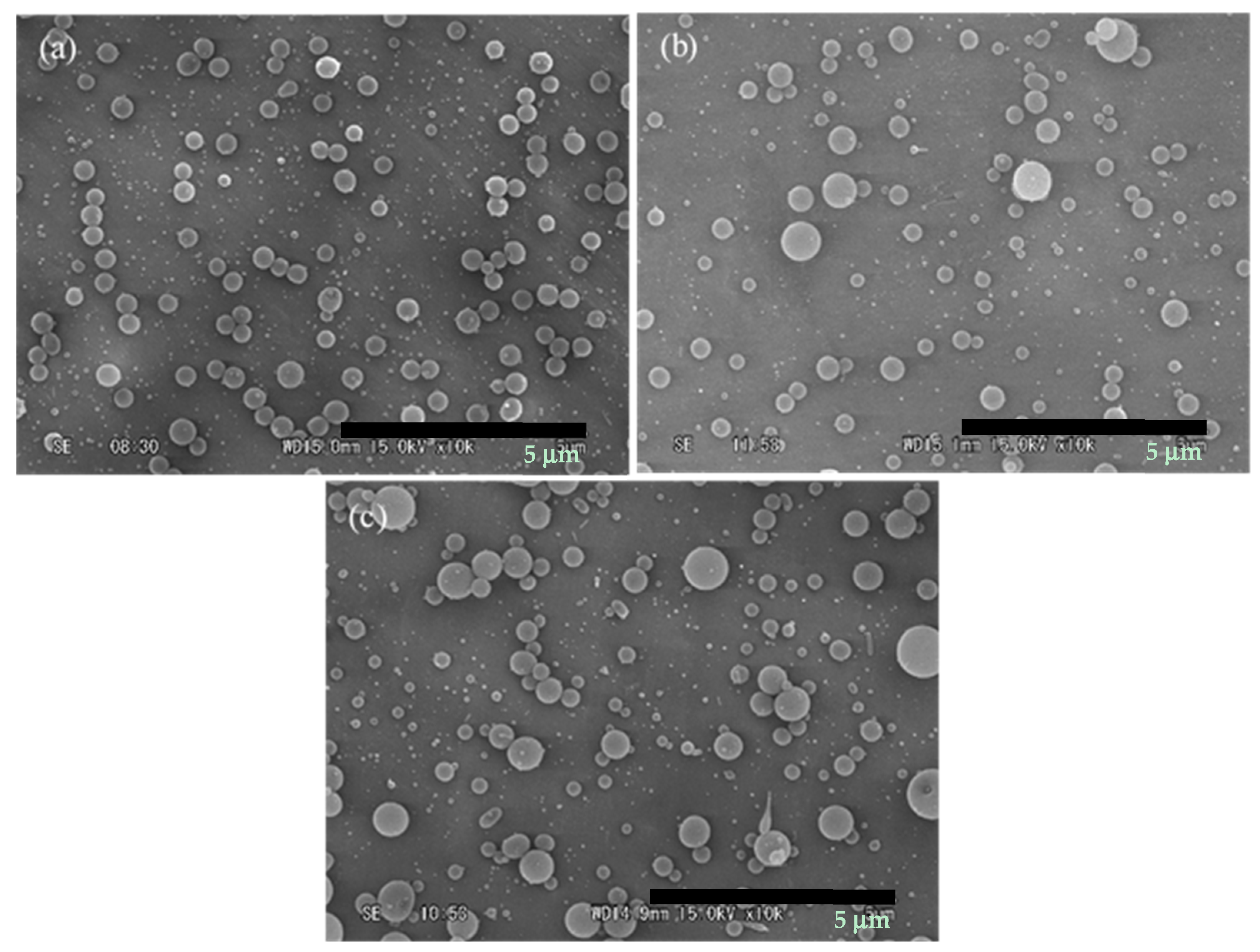
3.4. Effect of Tip to Collector Distance
3.5. Effect of Electric Voltage
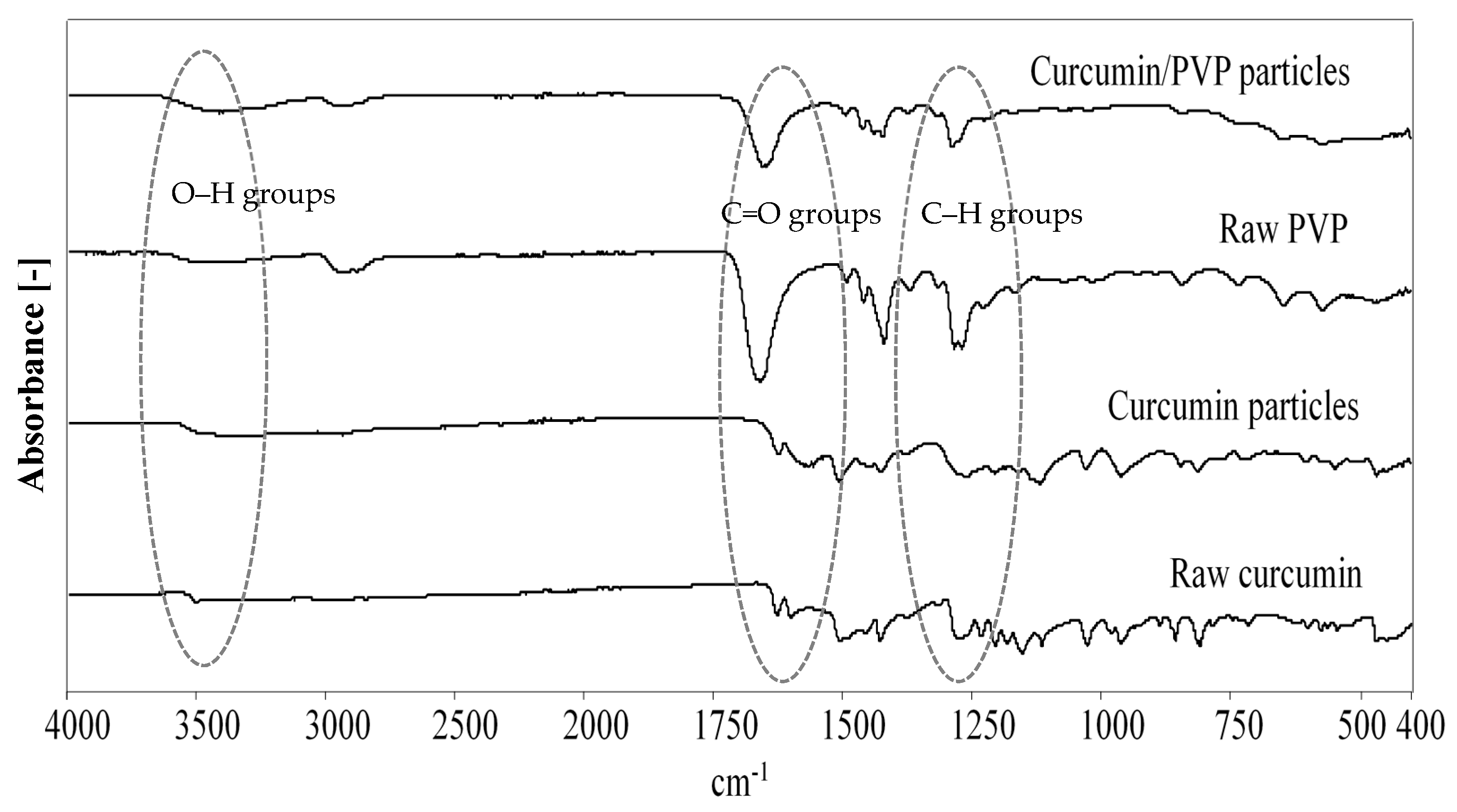
3.6. FTIR Analysis
3.7. Dissolution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Hassandarvish, P.; Tajik, H.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin. BioMed Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Fan, D.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Chen, A.; Li, J.; Lin, X.; et al. Nano–curcumin prepared via supercritical: Improve anti–bacterial, anti–oxidant and anti–cancer efficacy. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimthet, C.; Diono, W.; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Extraction of curcumin from Curcuma longa L. using ultrasound assisted supercritical carbon dioxide. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1840, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of curcumin: Problems and promise. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhouk, K.; Diono, W.; Kanda, H.; Kawasaki, S.; Goto, M. Micronization of curcumin with biodegradable polymer by supercritical anti-solvent using micro swirl mixer. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasekh, M.; Karavasili, C.; Soong, Y.L.; Bouropoulos, N.; Morries, M.; Armitage, D.; Li, X.; Fatourous, D.G.; Ahmad, Z. Electrospun PVP-indomethacin constituents for transdermal dressings and drug delivery devices. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosapio, V.; Marco, I.D.; Scognamiglio, M.; Reverchon, E. Folic acid-PVP nanostructured composite microparticles by supercritical antisolvent precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 277, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paximada, P.; Echegoyen, Y.; Koutinas, A.A.; Mandala, L.G.; Lagaron, J.M. Encapsulation of hydrophilic and lipophilized catechin into nanoparticles through emulsion electrospraying. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 64, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Estaca, J.; Balaguer, M.P.; Gavara, R.; Hernandez-Muooz, P. Formation of zein nanoparticles by electrohydrodynamic atomization: Effect of the main processing variables and suitability for encapsulating the food coloring and active ingredient curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Estaca, J.; Gavara, R.; Hernandez-Muooz, P. Encapsulation of curcumin in electrosprayed gelatin microspheres enhances its bioaccessibility and widens its uses in food applications. IFSET 2015, 29, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, A.M.; Mustapha, O.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, K.S.; Jin, S.G.; Yong, C.S.; Youn, Y.S.; Oh, Y.; Kim, J.O.; et al. Novel electrosprayed nanospherule for enhanced aqueous solubility and oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble fenofibrate. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona-Sanchez, V.A.; Calderon-Dominguez, G.; Morales-Sanchez, E.; Chanona-Perez, J.J.; Arzate-Vazquez, I.; Terres-Rojas, E. Pectin-based films produced by electrospraying. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 43779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Jin, L.; Ahmad, Z.; Huang, J.; Chang, L.J. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide loaded sodium alginate micro-particles prepared via electrospraying in controlled deposition environments. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 524, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Y. Integrating micromixer precipitation and electrospray drying toward the continuous production of drug nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Lei, F.; Liu, Z.; Tong, Q.; Si, T.; Xu, R.X. Coaxial electrospray of curcumin–loaded microparticles for sustained drug release. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, Z.; Chen, J.; He, T.; Hu, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, W.; Ko, F.; Zhou, W. Electrospray biodegradable microcapsules loaded with curcumin for drug delivery system with high bioactivity. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, C.; Wu, Z.; Liang, H.; Yan, P.; Song, J.; Ma, N.; Zhao, Q. Enhanced bioavailability and anticancer effect of curcumin–loaded electrospun nanofiber: In vitro and in vivo study. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Y.; Yu, D.G.; Brandfor-White, C.; Zhu, L.M. Sustained release of ethyl cellulose micro-particulate drug delivery systems prepared using electrospraying. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songsurang, K.; Praphairaksit, N.; Siraleartmukul, K.; Muangsin, N. Electrospray fabrication of doxorubicin-Chitosan-Tripolyphosphate nanoparticles for delivery of doxorubicin. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.L.; Cristinacce, P.L.H.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Parker, G.J.M. Preparation and characterization of polycaprolactone microspheres by electrospraying. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2016, l50, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, F.L.; Wu, T.; Tzeng, C.W.; Lin, L.; Lin, C. Curcumin nanoparticle improve the physicochemical properties of curcumin and effectively enhance its antioxidant and antithepatoma activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7376–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrut, M.; Jung, J.; Leboeuf, F. Enhancement of dissolution rate of poorly–soluble active ingredients by supercritical fluid processes: Part 1: Micronization of neat particles. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 288, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chhouk, K.; Diono, W.; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Micronization for Enhancement of Curcumin Dissolution via Electrospraying Technique. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2040060
Chhouk K, Diono W, Kanda H, Goto M. Micronization for Enhancement of Curcumin Dissolution via Electrospraying Technique. ChemEngineering. 2018; 2(4):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2040060
Chicago/Turabian StyleChhouk, Kimthet, Wahyu Diono, Hideki Kanda, and Motonobu Goto. 2018. "Micronization for Enhancement of Curcumin Dissolution via Electrospraying Technique" ChemEngineering 2, no. 4: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2040060
APA StyleChhouk, K., Diono, W., Kanda, H., & Goto, M. (2018). Micronization for Enhancement of Curcumin Dissolution via Electrospraying Technique. ChemEngineering, 2(4), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2040060