Removal of the Recalcitrant Artificial Sweetener Sucralose and Its By-Products from Industrial Wastewater Using Microbial Reduction/Oxidation of Iron
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enrichment Culture
2.2. Wastewater Treatment
2.3. Analysis
3. Results
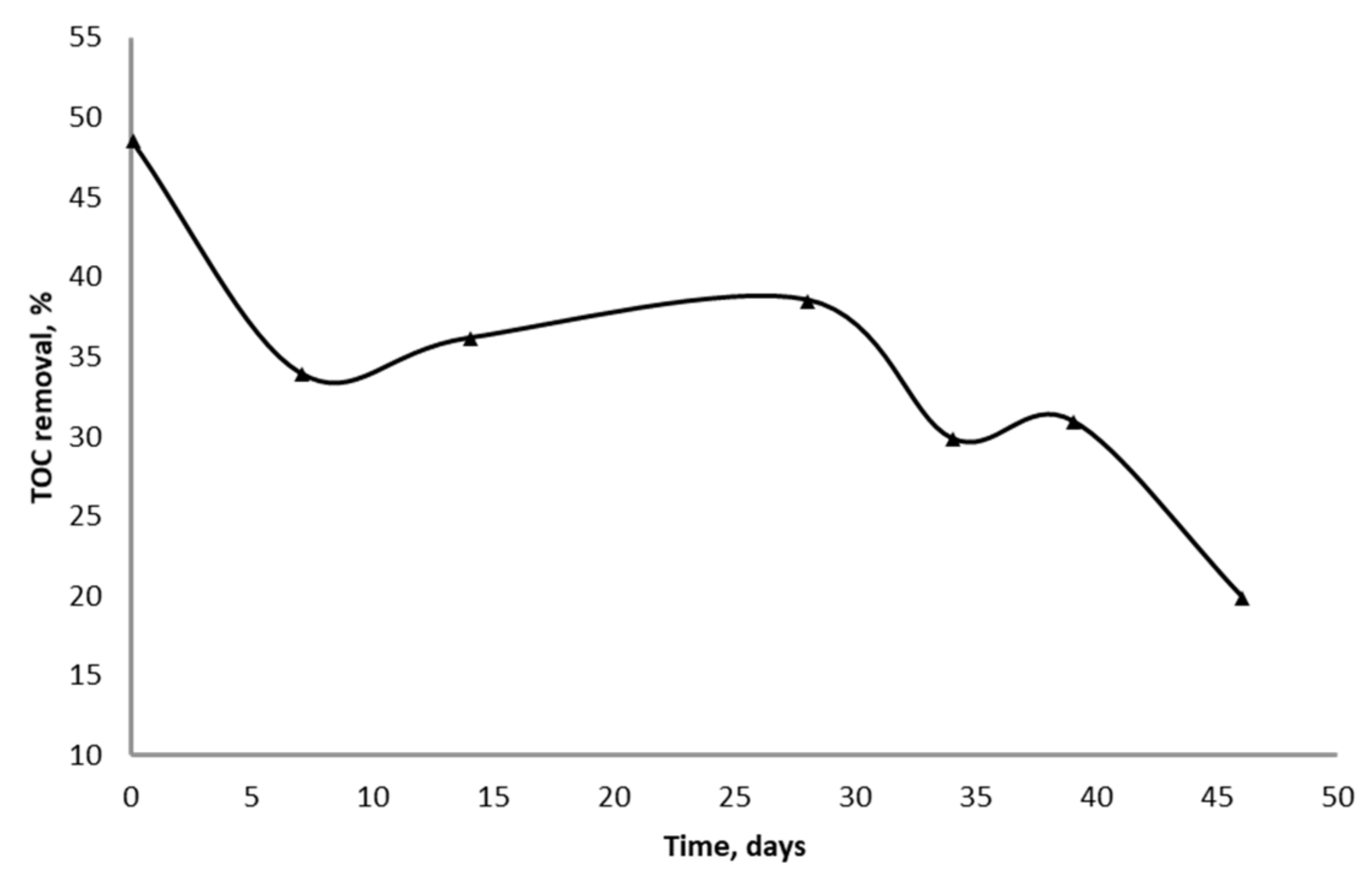
3.1. Batch Treatment of Wastewater
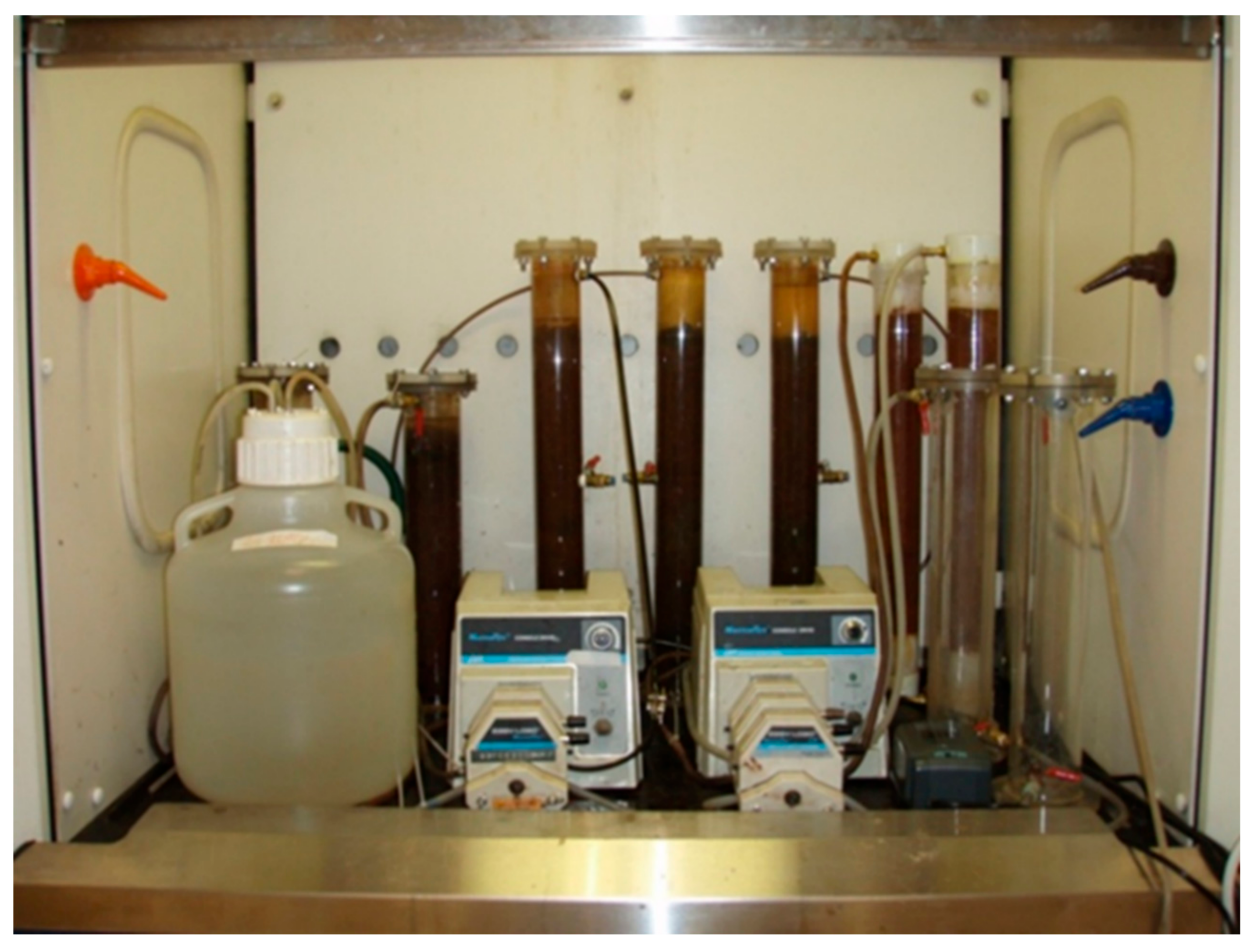
3.2. Continuous Treatment of Wastewater
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivanov, V.; Stabnikov, V.; Guo, C.H.; Stabnikova, O.; Ahmed, Z.; Kim, I.S.; Shuy, E.B. Wastewater engineering applications of BioIronTech process based on the biogeochemical cycle of iron bioreduction and (bio)oxidation. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2014, 1, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V. Environmental Microbiology for Engineers, 2nd ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, J.H.; Tay, S.T.L.; Ivanov, V.; Stabnikova, O.; Wang, J.-Y. Compositions and Methods for the Treatment of Wastewater and Other Waste. U.S. Patent 7,393,452, 1 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, J.H.; Tay, S.T.L.; Ivanov, V.; Hung, Y.C. Application of biotechnology for industrial waste treatment. In Handbook of Industrial Wastes Treatment, 2nd ed.; Revised and Expanded by Marcel Dekker; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 585–618. [Google Scholar]
- Roussel, J.; Carliell-Marquet, C. Significance of vivianite precipitation on the mobility of iron in anaerobically digested sludge. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.H.; Stabnikov, V.; Ivanov, V. The removal of phosphate from wastewater using anoxic reduction of iron ore in the rotating reactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 46, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, L. Effectiveness of phosphate removal during anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge by dosing iron (III). J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, V.; Lim, J.J.W.; Stabnikova, O.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Biodegradation of estrogens by facultative anaerobic iron-reducing bacteria. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Sustainable strategy for enhancing anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: Driving dissimilatory iron reduction with fenton sludge. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2220–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.; Stabnikova, E.V.; Stabnikov, V.P.; Kim, I.S.; Zubair, A. Effects of iron compounds on the treatment of fat-containing wastewaters. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2002, 38, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.; Wang, J.-Y.; Stabnikov, V.; Xing, Z.; Tay, J.-H. Improvement of sludge quality by iron-reducing bacteria. J. Residuals Sci. Tech. 2004, 1, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Stabnikov, V.P.; Ivanov, V.N. The effect of various iron hydroxide concentrations on the anaerobic fermentation of sulfate-containing model wastewater. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, J.; Quan, X.; Li, Q. Biological sulfate reduction in the acidogenic phase of anaerobic digestion under dissimilatory Fe (III)-reducing conditions. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuzir, A.; Yaacob, S.S.; Tijani, H.I.; Abdullah, N.; Ahmed, Z. Addition of ferric chloride in anaerobic digesters to enhance sulphide removal and methanogenesis. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 79, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.; Stabnikov, V. Construction Biotechnology: Biogeochemistry, Microbiology and Biotechnology of Construction Materials and Processes; Springer Science & Business Media: Singapore, 2017; 317p. [Google Scholar]
- Stabnikov, V.; Ivanov, V. Biotechnological production of biogrout from iron ore and cellulose. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, C.; Keim, K. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Use of nutritive and nonnutritive sweeteners. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheimer, J.; Eaton, A.; Badruzzaman, M.; Haghani, A.W.; Jacangelo, J.G. Occurrence and suitability of sucralose as an indicator compound of wastewater loading to surface waters in urbanized regions. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4019–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tsoi, Y.-K.; Leung, K.S.-Y. Evaluating the environmental impact of artificial sweeteners: A study of their distributions, photodegradation and toxicities. Water Res. 2014, 52, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Singer, H.; Berg, M.; Müller, B.; Pernet-Coudrier, B.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Elimination of polar micropollutants and anthropogenic markers by wastewater treatment in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenck, K.; Rosenblum, L.; Ramakrishan, B.; Carson, J., Jr.; Macke, D.; Nietcha, C. Correlation of trace contaminants to wastewater management practices in small watersheds. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.; Gawlik, B.; Boettcher, K.; Locoro, G.; Contini, S.; Bidoglio, G. Sucralose screening in European surface waters using a solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography–triple quadrupole mass spectrometry method. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, R.N.; Morgan, J.B.; Avery, G.B.; Kieber, R.J.; Kirk, A.M.; Skrabal, S.A.; Willey, J.D. Occurrence of the artificial sweetener sucralose in coastal and marine waters of the United States. Mar. Chem. 2009, 116, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefsen, K.E.; Nizzettj, L.; Huggett, D.B. Presence, fate and effects of the intense sweetener sucralose in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-L.; Mahan, T.A.; Farley, E. Microbial Consortia for Biodegradation of Sucralose and Other Chlorinated Carbohydrates. U.S. Patent 8,557,976B2, 15 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, C.I.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chiu, C.-A.; Nelson, K.G.; Westerhoff, P.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Fate of sucralose during wastewater treatment. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2011, 28, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Time of Treatment, Days | Parameters of Treatment Efficiency | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC | COD | Color | ||||
| mg/L | % of Removal | mg/L | % of Removal | Unit | % of Removal | |
| 0 | 1200 | 0 | 2192 | 0 | 3084 | 0 |
| 1 | 889 | 26 | 1654 | 24 | 2450 | 21 |
| 8 | 575 | 52 | 1062 | 52 | 920 | 71 |
| 14 | 449 | 63 | 871 | 60 | 785 | 75 |
| 21 | 361 | 70 | 700 | 68 | 743 | 76 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanov, V.; Stabnikov, V.; Tay, J.H. Removal of the Recalcitrant Artificial Sweetener Sucralose and Its By-Products from Industrial Wastewater Using Microbial Reduction/Oxidation of Iron. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2030037
Ivanov V, Stabnikov V, Tay JH. Removal of the Recalcitrant Artificial Sweetener Sucralose and Its By-Products from Industrial Wastewater Using Microbial Reduction/Oxidation of Iron. ChemEngineering. 2018; 2(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanov, Volodymyr, Viktor Stabnikov, and Joo Hwa Tay. 2018. "Removal of the Recalcitrant Artificial Sweetener Sucralose and Its By-Products from Industrial Wastewater Using Microbial Reduction/Oxidation of Iron" ChemEngineering 2, no. 3: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2030037
APA StyleIvanov, V., Stabnikov, V., & Tay, J. H. (2018). Removal of the Recalcitrant Artificial Sweetener Sucralose and Its By-Products from Industrial Wastewater Using Microbial Reduction/Oxidation of Iron. ChemEngineering, 2(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2030037






