Diagnostic Workup and Evaluation of Patients with Prurigo Nodularis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Diagnosis
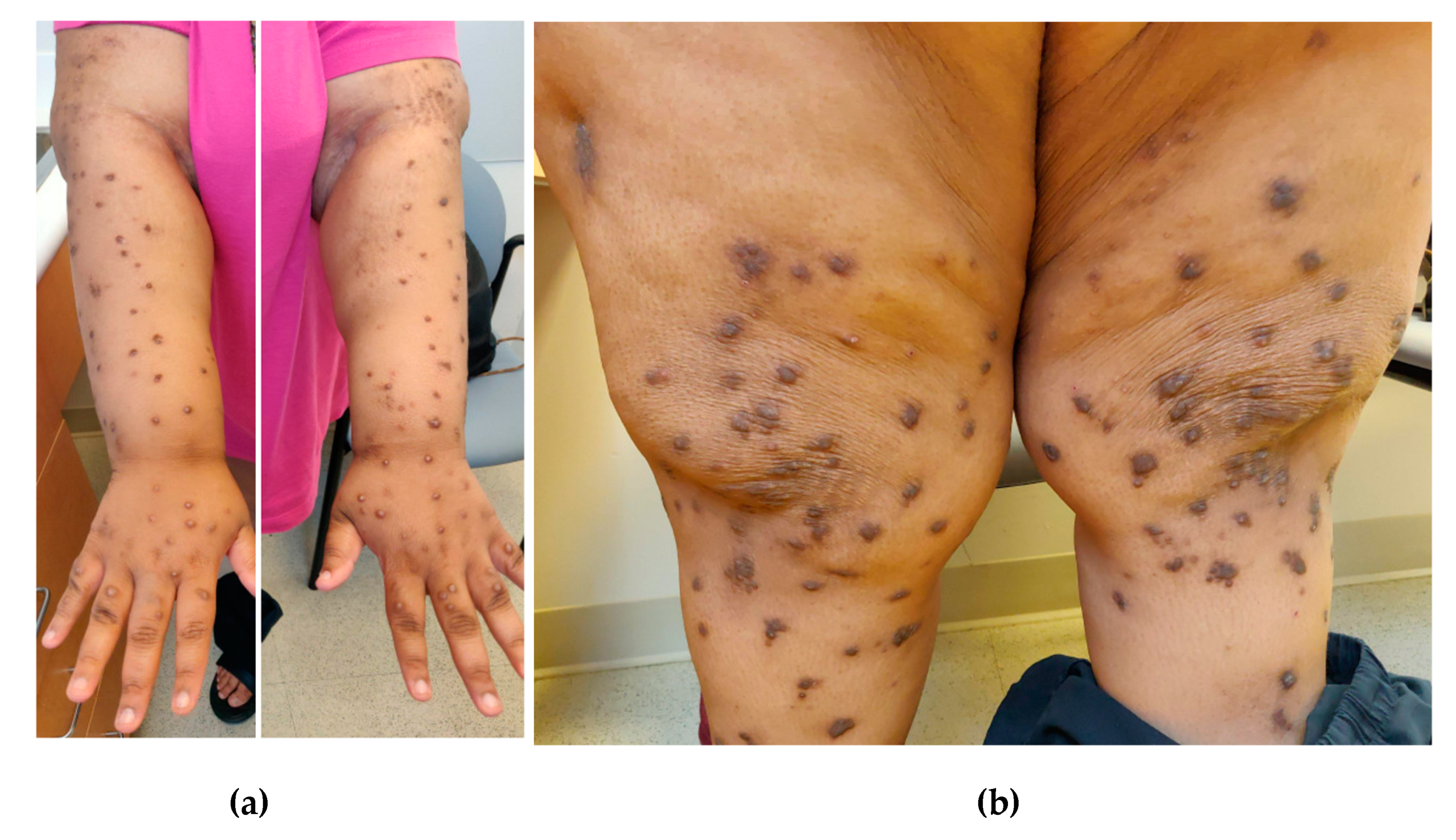
4.1. History and Physical
4.2. Differential Diagnoses
4.2.1. Pemphigoid Nodularis
4.2.2. Actinic Prurigo
4.2.3. Epidermolysis Bullosa
4.2.4. Hypertrophic Lichen Planus
4.2.5. Neurotic Excoriations
5. Etiologic Factors and Associated Diseases
5.1. Dermatoses
5.2. Systemic
5.3. Infectious
5.4. Medications
5.5. Psychiatric
5.6. Neurologic
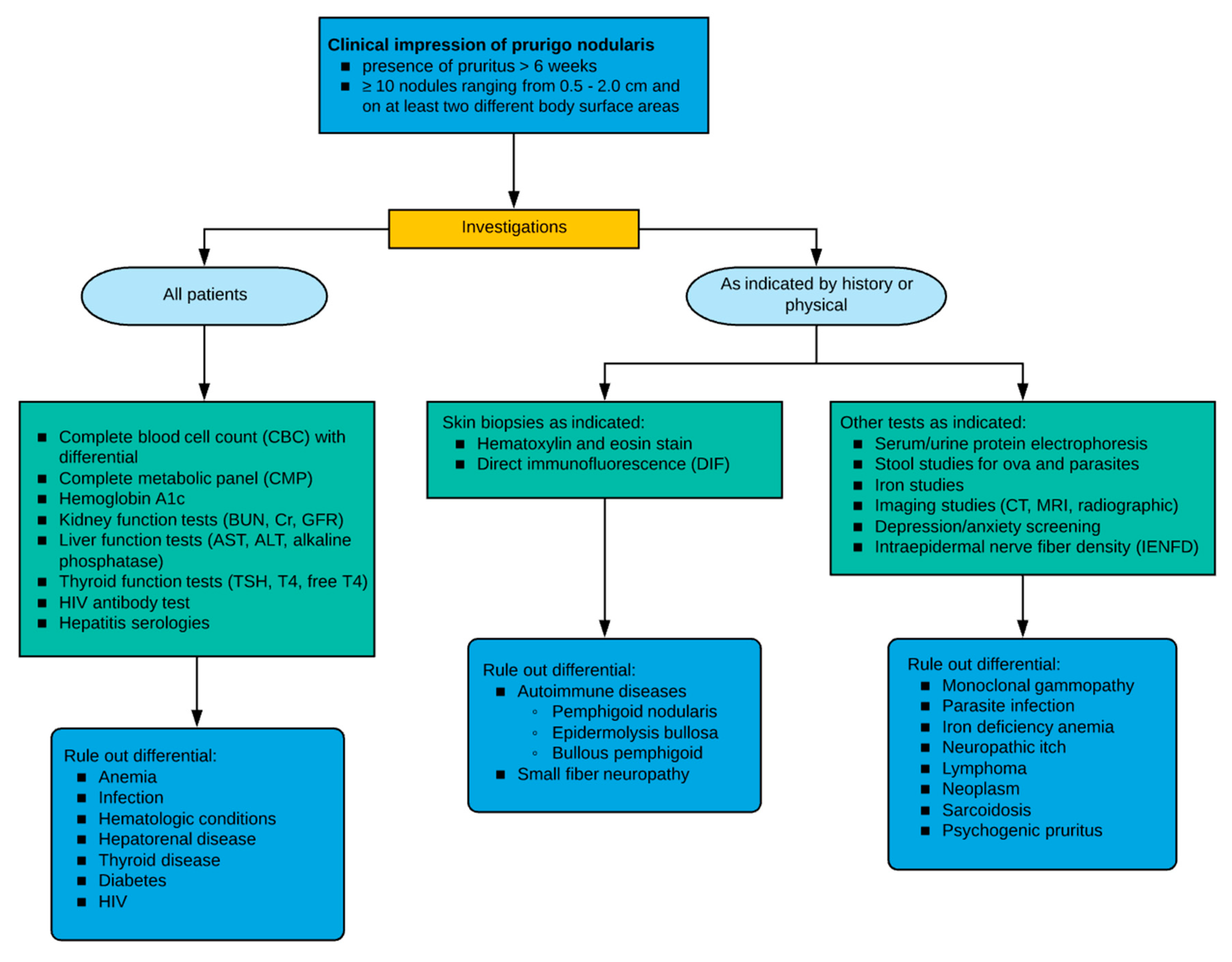
6. Evaluation
6.1. Biopsy
6.2. Laboratory Evaluation
6.3. Pruritic Intensity and Quality of Life
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boozalis, E.; Tang, O.; Patel, S.; Semenov, Y.R.; Pereira, M.P.; Ständer, S.; Kang, S.; Kwatra, S.G. Ethnic differences and comorbidities of 909 prurigo nodularis patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 714–719.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, V.A.; Tang, O.; Stander, S.; Miller, L.S.; Kang, S.; Kwatra, S.G. Association between prurigo nodularis and malignancy in middle-aged adults. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, K.A.; Kang, S.; Kwatra, S.G. Inpatient Burden of Prurigo Nodularis in the United States. Medicines 2019, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.H.; Canner, J.K.; Khanna, R.; Kang, S.; Kwatra, S.G. Real-world prevalence of prurigo nodularis and burden of associated diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iking, A.; Grundmann, S.; Chatzigeorgakidis, E.; Phan, N.Q.; Klein, D.; Ständer, S. Prurigo as a symptom of atopic and non-atopic diseases: Aetiological survey in a consecutive cohort of 108 patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidler, C.; Yosipovitch, G.; Ständer, S. Prurigo Nodularis and Its Management. Dermatol. Clin. 2018, 36, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedel, F.; Schürmann, C.; Metze, D.; Ständer, S. [Prurigo. Clinical definition and classification]. Hautarzt 2014, 65, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salhi, W.; Alharithy, R. Pemphigoid nodularis. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2015, 19, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, H.L.; Lim, S.P. Pemphigoid nodularis mimicking nodular prurigo in an immune-suppressed patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2015, 95, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.; Michael, C. Pemphigoid nodularis: Two new cases demonstrating distinguishing clinical clues from prurigo nodularis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 60, AB103–AB104. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, J.S.; McKee, P.H.; Smith, N.P.; Shimizu, H.; Griffiths, W.A.D.; Bhogal, B.S.; Black, M.M. Unusual variants of pemphigoid: From pruritus to pemphigoid nodularis. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1992, 19, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, A.M.; Albert, S.; Gratian, M.J.; Bittencourt, R.; Bhogal, B.S.; Black, M.M. Pemphigoid nodularis (non-bullous): A clinicopathological study of five cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 147, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.; Fischer, A. Actinic prurigo. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, AB224. [Google Scholar]
- Pustover, K.; Fivenson, D. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: A unique clinical presentation with Blaschkoid acral distribution. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, AB124. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, V.; Naveen, K.; Athanikar, S.; Rai, V.; Shastry, D. Epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa: A report of two cases. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 5, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankad, B.S.; Beergouder, S.L. Hypertrophic lichen planus versus prurigo nodularis: A dermoscopic perspective. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2016, 6, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werbel, T.; Hinds, B.R.; Cohen, P.R. Scabies presenting as cutaneous nodules or malar erythema: Reports of patients with scabies surrepticius masquerading as prurigo nodularis or systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatol. Online J. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wick, M.R. Psoriasiform dermatitides: A brief review. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 34, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.S.; Tey, H.L. Extensive prurigo nodularis: Characterization and etiology. Dermatology 2014, 228, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Wang, H.Y.; Kim, E.; Hwang, H.J.; Choi, E.; Lee, H.; Choi, E.H. Clinical characteristics and genetic variation in atopic dermatitis patients with and without allergic contact dermatitis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2018, 28, 637–643. [Google Scholar]
- Akarsu, S.; Ozbagcivan, O.; Ilknur, T.; Semiz, F.; Inci, B.B.; Fetil, E. Xerosis cutis and associated co-factors in women with prurigo nodularis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2018, 93, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyachi, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Furukawa, F.; Imamura, S. Prurigo nodularis. A possible relationship to atopy. J. Dermatol. 1980, 7, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roenigk, R.K.; Dahl, M.V. Bullous pemphigoid and prurigo nodularis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1986, 14 Pt 2, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.P.; Miller, K.; Cohen, D.E.; Stein, J.A. Keratoacanthomas arising in association with prurigo nodules in pruritic, actinically damaged skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland Payne, C.M.; Wilkinson, J.D.; McKee, P.H.; Jurecka, W.; Black, M.M. Nodular prurigo—A clinicopathological study of 46 patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 1985, 113, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winhoven, S.; Gawkrodger, D. Nodular prurigo: Metabolic diseases are a common association. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 32, 224–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, S.N.; Cockerell, C.J. Prurigo nodularis in HIV-infected individuals. Int. J. Dermatol. 1998, 37, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rien, B.E.; Lemont, H.; Cohen, R.S. Prurigo nodularis: As association with uremia. J. Am. Podiatry Assoc. 1982, 72, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishi, R.; Ringwala, S.; Tracy, J.; Fatteh, S. Prurigo nodularis and Hashimoto thyroiditis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 113, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, S.; Péchère, M.; Toutous Trellu, L. Chronic Prurigo: An Unusual Presentation of Hodgkin Lymphoma. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2018, 10, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, P.; Rajan, S.J.; George, I.A.; George, R. A sinister itch: Prurigo nodularis in Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2009, 57, 715–716. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parcheta, P.; Stepien, P.; Zarebska-Michaluk, D.; Krecisz, B. Nodular prurigo as first manifestation of primary biliary cholangitis successfully treated with rifampin and sertraline. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 97, 1056. [Google Scholar]
- Savoia, F.; Casadio, C.; Tabanelli, M.; Spadola, G.; Zago, S.; Maio, V.; Giacomoni, P.; Gaddoni, G.; Patrizi, A.; Lanzanova, G. Prurigo nodularis as the first manifestation of a chronic autoimmune cholestatic hepatitis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2011, 50, 1588–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, S.; Raciti, C.; D’Angelo, G.; Ierna, D.; Bruno, C.M. Hyde’s prurigo nodularis and chronic HCV hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1998, 28, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, T.; Heitkemper, T.; Mettang, T.; Phan, N.Q.; Ständer, S. [Clinical features and prurigo nodularis in nephrogenic pruritus]. Hautarzt 2014, 65, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, A.E.; Wolf, K.; Ständer, S. [Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Rare but important]. Hautarzt 2017, 68, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, V.A.; Tang, O.; Ständer, S.; Kang, S.; Kwatra, S.G. Association between itch and cancer in 16,925 patients with pruritus: Experience at a tertiary care center. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.T.; Wang, W.H.; Yen, C.C.; Yu, I.T.; Chen, P.M. Prurigo nodularis as initial presentation of metastatic transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 631–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fina, L.; Grimalt, R.; Berti, E.; Caputo, R. Nodular prurigo associated with Hodgkin’s disease. Dermatologica 1991, 182, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, G.F.; Resta, F.; Marsigli, L.; Gaddoni, G.; Baldassarri, L.; Caprio, G.P.; Degli Azzi, I.; Foschi, F.G.; Gasbarrini, G. Prurigo nodularis (Hyde’s prurigo) disclosing celiac disease. Hepatogastroenterology 1999, 46, 2281–2284. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, A.W.; Stubbing, D.G.; Elvy, B.L. Prurigo nodularis and gluten enteropathy. Br. J. Dermatol. 1976, 95, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saporito, L.; Florena, A.M.; Colomba, C.; Pampinella, D.; Di Carlo, P. Prurigo nodularis due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58 Pt 12, 1649–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulin, S.J.; Čeović, R.; Lončarić, D.; Ilić, I.; Radman, I. Nodular prurigo associated with mycosis fungoides—Case report. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2015, 23, 203. [Google Scholar]
- Menni, S.; Boccardi, D.; Gualandri, L.; Cainarca, M. Prurigo nodularis in a young child with a parasitic infestation with Ascaris lumbricoides. Eur. J. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2009, 19, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Guarneri, C.; Lotti, J.; Fioranelli, M.; Roccia, M.G.; Lotti, T.; Guarneri, F. Possible role of Helicobacter pylori in diseases of dermatological interest. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31 (Suppl. 2), 57–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neri, S.; Ierna, D.; D’Amico, R.A.; Giarratano, G.; Leotta, C. Helicobacter pylori and prurigo nodularis. Hepatogastroenterology 1999, 46, 2269–2272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacob, C.I.; Patten, S.F. Strongyloides stercoralis infection presenting as generalized prurigo nodularis and lichen simplex chronicus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1999, 41 Pt 2, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, J.O.; Katila, M.L.; Vornanen, M. Slowly growing mycobacteria and chronic skin disorders. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 23, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L.S.; Wu, T.S.; Wang, C.C.J.; Ku, C.L.; Hsu, Y.H.; Chang, P.Y. Mycobacterium mucogenicum infection presenting with generalized follicular hyperplasia and prurigo nodularis in an immunocompetent patient. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, S97–S98. [Google Scholar]
- De, D.; Dogra, S.; Kanwar, A.J. Prurigo nodularis in healed herpes zoster scar: An isotopic response. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2007, 21, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, S.G.; Mehta, R.D. Cutaneous Adverse Reactions of Chemotherapy in Cancer Patients: A Clinicoepidemiological Study. Indian J. Dermatol. 2018, 63, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattore, D.; Panariello, L.; Annunziata, M.C.; Fabbrocini, G. Prurigo nodularis and pembrolizumab: A therapeutic challenge. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 110, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanini, G.F.; Resta, F.; Marsigli, L.; Gaddoni, G.; Baldassarri, L.; Caprio, G.P.; Degli Azzi, I.; Foschi, F.G.; Gasbarrini, G. Clinical classification of itch: A position paper of the International Forum for the Study of Itch. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2007, 87, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.G.; Stull, C.; Yosipovitch, G. Psychiatric disorders and pruritus. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 35, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radmanesh, M.; Shafiei, S. Underlying psychopathologies of psychogenic pruritic disorders. Psychosom. Dermatol. Psychosom. 2001, 2, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dazzi, C.; Erma, D.; Piccinno, R.; Veraldi, S.; Caccialanza, M. Psychological factors involved in prurigo nodularis: A pilot study. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2011, 22, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotti, T.; Buggiani, G.; Prignano, F. Prurigo nodularis and lichen simplex chronicus. Dermatol. Ther. 2008, 21, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenaut, E.; Halvorsen, J.A.; Dalgard, F.J.; Lien, L.; Balieva, F.; Sampogna, F.; Linder, D.; Evers, A.W.; Jemec, G.B.; Gieler, U.; et al. The self-assessed psychological comorbidities of prurigo in European patients: A multicentre study in 13 countries. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieler, U.; Tomas-Aragones, L.; Linder, D.; Jemec, G.; Poot, F.; Szepietowski, J.; Korte, J.; Taube, K.; Lvov, A.; Consoli, S. Self-inflicted lesions in dermatology: Terminology and classification—A position paper from the European Society for Dermatology and Psychiatry (ESDaP). Acta Derm. Venereol. 2013, 93, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachisuka, J.; Chiang, M.C.; Ross, S.E. Itch and neuropathic itch. Pain 2018, 159, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misery, L.; Brenaut, E.; Le Garrec, R.; Abasq, C.; Genestet, S.; Marcorelles, P.; Zagnoli, F. Neuropathic pruritus. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigelt, N.; Metze, D.; Ständer, S. Prurigo nodularis: Systematic analysis of 58 histological criteria in 136 patients. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2010, 37, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuhknecht, B.; Marziniak, M.; Wissel, A.; Phan, N.; Pappai, D.; Dangelmaier, J.; Metze, D.; Ständer, S. Reduced intraepidermal nerve fibre density in lesional and nonlesional prurigo nodularis skin as a potential sign of subclinical cutaneous neuropathy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.P.; Pogatzki-Zahn, E.; Snels, C.; Vu, T.-H.; Üçeyler, N.; Loser, K.; Sommer, C.; Evers, A.W.M.; Van Laarhoven, A.I.M.; Agelopoulos, K.; et al. There is no functional small-fibre neuropathy in prurigo nodularis despite neuroanatomical alterations. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.P.; Ständer, S. Assessment of severity and burden of pruritus. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, A.; Heisig, M.; Phan, N.; Taneda, K.; Takamori, K.; Takeuchi, S.; Furue, M.; Blome, C.; Augustin, M.; Ständer, S.; et al. Visual analogue scale: Evaluation of the instrument for the assessment of pruritus. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2012, 92, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.; Blome, C.; Fritz, F.; Gerss, J.; Reich, A.; Ebata, T.; Augustin, M.; Szepietowski, J.; Ständer, S. Assessment of pruritus intensity: Prospective study on validity and reliability of the visual analogue scale, numerical rating scale and verbal rating scale in 471 patients with chronic pruritus. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2012, 92, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeski, C.J.; Johnson, J.A.; Davison, S.N.; Lauzon, C.J. Itch Severity Scale: A self-report instrument for the measurement of pruritus severity. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pölking, J.; Zeidler, C.; Schedel, F.; Osada, N.; Augustin, M.; Metze, D.; Pereira, M.P.; Yosipovitch, G.; Bernhard, J.D.; Ständer, S. Prurigo Activity Score (PAS): Validity and reliability of a new instrument to monitor chronic prurigo. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ständer, S.; Zeidler, C.; Riepe, C.; Steinke, S.; Fritz, F.; Bruland, P.; Soto-Rey, I.; Storck, M.; Agner, T.; Augustin, M.; et al. European EADV network on assessment of severity and burden of Pruritus (PruNet): First meeting on outcome tools. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1144–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, C. International experiences with the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale—A review of validation data and clinical results. J. Psychosom. Res. 1997, 42, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 1990, 40, 305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M. A rating scale for depression. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1960, 23, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Guth, D.; Steer, R.A.; Ball, R. Screening for major depression disorders in medical inpatients with the Beck Depression Inventory for Primary Care. Behav. Res. Ther. 1997, 35, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatos, C.R.; Dikeos, D.G.; Paparrigopoulos, T.J. Athens Insomnia Scale: Validation of an instrument based on ICD-10 criteria. J. Psychosom. Res. 2000, 48, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneh, B. Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Occup. Med. (Lond.) 2015, 65, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.A.; Hicks, G.; Nino-Murcia, G. Validity and reliability of a scale to assess fatigue. Psychiatry Res. 1991, 36, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, A.W.; Fekken, G.C.; Saskin, P.; Knowles, J.B. Psychometric evaluation of the Stanford Sleepiness Scale. J. Sleep Res. 1992, 1, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.S.; Poindexter, G.B.; Monthrope, Y.M.; Bendeck, S.E.; Swerlick, R.A.; Chen, S.C. A pilot quality-of-life instrument for pruritus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 59, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twiss, J.; Meads, D.M.; Preston, E.P.; Crawford, S.R.; McKenna, S.P. Can we rely on the Dermatology Life Quality Index as a measure of the impact of psoriasis or atopic dermatitis? J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.E.; Sherbourne, C.D. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med. Care 1992, 30, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, K.M.; Egeberg, A.; Gislason, G.H.; Skov, L.; Thyssen, J.P. Anxiety, depression and suicide in patients with prurigo nodularis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, e106–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, C.D.; Khanna, R.; Williams, K.A.; Kwatra, M.M.; Kwatra, S.G. Diagnostic Workup and Evaluation of Patients with Prurigo Nodularis. Medicines 2019, 6, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines6040097
Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, Kwatra MM, Kwatra SG. Diagnostic Workup and Evaluation of Patients with Prurigo Nodularis. Medicines. 2019; 6(4):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines6040097
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Christina D., Raveena Khanna, Kyle A. Williams, Madan M. Kwatra, and Shawn G. Kwatra. 2019. "Diagnostic Workup and Evaluation of Patients with Prurigo Nodularis" Medicines 6, no. 4: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines6040097
APA StyleKwon, C. D., Khanna, R., Williams, K. A., Kwatra, M. M., & Kwatra, S. G. (2019). Diagnostic Workup and Evaluation of Patients with Prurigo Nodularis. Medicines, 6(4), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines6040097





