Are Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids the Link between the Immune System and the Microbiome towards Modulating Cancer?
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.1.1. Triggering and Regulating Inflammation
1.1.2. Microbes and Inflammation
1.1.3. Immune System and Inflammation
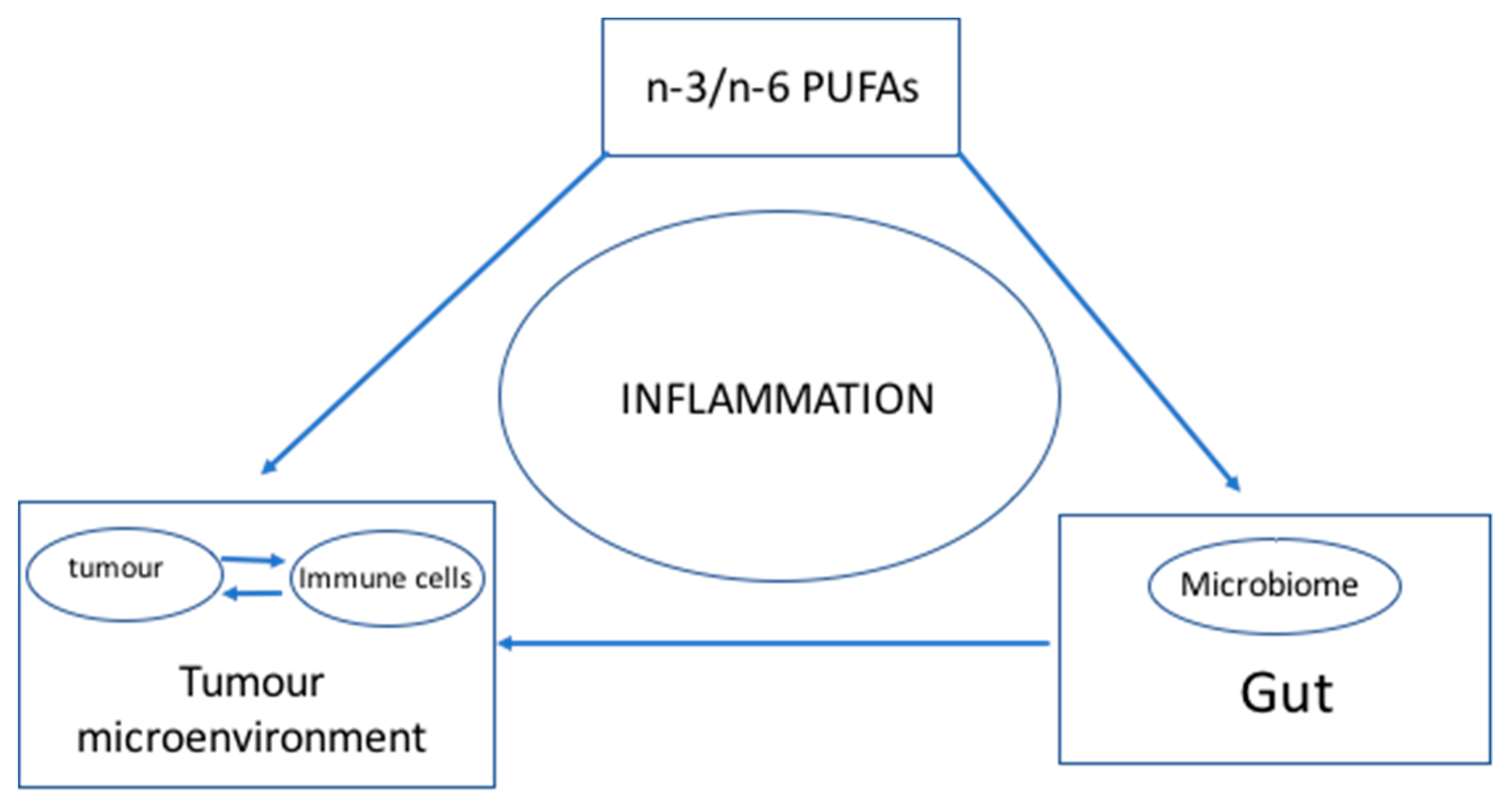
1.2. Connecting the Dots
2. Hypothesis: n-3 and n-6 PUFAs Modulate the Microbiome and Inflammation to Activate the Immune System—Optimal n-3 and n-6 PUFA Levels Lower Inflammation and Help Achieve a Balanced Microbiome to Enhance the Immune System
2.1. Rationale behind the Hypothesis
2.1.1. n-3/n-6 PUFAs and Cancer
2.1.2. n-3 PUFAs and the Microbiome
2.1.3. n-3 PUFAs and the Immune System
2.2. Testing the Hypothesis
2.2.1. Measuring the Levels of PUFAs and IAP: Omega-3 Index, AA/EPA Ratio and IAP
2.2.2. The Need to Measure Baseline and Endpoints
2.2.3. Validating the Hypothesis
3. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, J.; Chehrazi-Raffle, A.; Reddi, S.; Salgia, R. Development of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors as a form of cancer immunotherapy: A comprehensive review of registration trials and future considerations. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Routy, B.; Le Chatelier, E.; Derosa, L.; Duong, C.P.M.; Alou, M.T.; Daillère, R.; Fluckiger, A.; Messaoudene, M.; Rauber, C.; Roberti, M.P.; et al. Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science 2018, 359, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Spencer, C.N.; Nezi, L.; Reuben, A.; Andrews, M.C.; Karpinets, T.V.; Prieto, P.A.; Vicente, D.; Hoffman, K.; Wei, S.C.; et al. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matson, V.; Fessler, J.; Bao, R.; Chongsuwat, T.; Zha, Y.; Alegre, M.-L.; Luke, J.J.; Gajewski, T.F. The commensal microbiome is associated with anti-PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawelec, G.; Goldeck, D.; Derhovanessian, E. Inflammation, ageing and chronic disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 29, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiktorowska-Owczarek, A.; Malgorzata, B.; Nowak, J.Z. PUFAs: Structures, Metabolism and Functions. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.S. Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Dietary sources, metabolism, and significance—A review. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougle, D.R.; Watson, J.E.; Abdeen, A.A.; Adili, R.; Caputo, M.P.; Krapf, J.E.; Johnson, R.W.; Kilian, K.A.; Holinstat, M.; Das, A. Anti-inflammatory ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6034–E6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.M.; Montorfano, G.; Negroni, M.; Adorni, L.; Berselli, P.; Corsetto, P.; Wahle, K.; Berra, B. A rapid method for determining arachidonic: Eicosapentaenoic acid ratios in whole blood lipids: Correlation with erythrocyte membrane ratios and validation in a large Italian population of various ages and pathologies. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Díaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Vilchez-Padial, L.M.; Gil, A. Evidence of the anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics and synbiotics in intestinal chronic diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, L.; Molinari, R.; Farinon, B.; Merendino, N. Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szebeni, G.J.; Vizler, C.; Kitajka, K.; Puskas, L.G. Inflammation and cancer: Extra-and intracellular determinants of tumor-associated macrophages as tumor promoters. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9294018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; DuBois, R.N. Immunosuppression associated with chronic inflammation in the tumor microenvironment. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, L.F. William Bradley Coley, MD, and the phenomenon of spontaneous regression. Immunotargets Ther. 2018, 7, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-M.; Jeong, M.; Kim, E.-H.; Han, Y.-M.; Kwon, S.H.; Hahm, K.-B. Omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids intake to regulate helicobacter pylori associated gastric diseases as nonantimicrobial dietary approach. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayyedi, P.; Yuhong, Y.; Baharith, H.; Ford, A.C. Faecal microbiota transplantation for Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Med. J. Aust. 2017, 207, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpato, M.; Hull, M.A. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids as adjuvant therapy of colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Bilotto, S.; Russo, G.L.; Orhan, I.E.; Habtemariam, S.; Daglia, M.; Devi, K.P.; Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; Nabavi, S.M. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cancer: Lessons learned from clinical trials. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 359–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Eliseo, D.; Velotti, F. Omega-3 fatty acids and cancer cell cytotoxicity: Implications for multi-targeted cancer therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, J.; Watson, J.E.; Hong, I.S.; Fan, T.M.; Das, A. Anti-tumorigenic properties of omega-3 endocannabinoid epoxides. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5569–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morland, S.L.; Martins, K.J.B.; Mazurak, V.C. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation during cancer chemotherapy. J Nutr. Intermed. Metab. 2016, 5, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachtel, N.; Rohwer, N.; Pietzner, A.; Loew, A.; Weylandt, K.H. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation—A possible dietary adjunct to 2 enhance immune therapy in cancer? Preprints 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M.; Hata, J.; Hirakawa, Y.; Mukai, N.; Yoshida, D.; Ohara, T.; Kishimoto, H.; Kawano, H.; Kitazono, T.; Kiyohara, Y.; et al. The ratio of serum eicosapentaenoic acid to arachidonic acid and risk of cancer death in a Japanese community: The hisayama study. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, H.; Mitra, S.; Croden, F.C.; Taylor, M.; Wood, H.M.; Perry, S.L.; Spencer, J.A.; Quirke, P.; Toogood, G.J.; Lawton, C.L.; et al. A randomised trial of the effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplements on the human intestinal microbiota. Gut 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, P.N.T.; Desbois, A.P. Antibacterial effect of eicosapentaenoic acid against bacillus cereus and staphylococcus aureus: Killing kinetics, selection for resistance and potential cellular target. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaliannan, K.; Wang, B.; Li, X.Y.; Kim, K.J.; Kang, J.X. A host microbiome interaction mediates the opposing effects of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids on metabolic endotoxemia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.H.; Heithoff, D.M.; Aziz, P.V.; Sperandio, M.; Nizet, V.; Mahan, M.J.; Marth, J.D. Recurrent infection progressively disables host protection against intestinal inflammation. Science 2017, 358, eaao5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malo, M.S. A high level of intestinal alkaline phosphatase is protective against type 2 diabetes mellitus irrespective of obesity. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 2016–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.D.; Peng, K.C.; Wu, J.L.; Chen, J.Y. Transgenic expression of salmon delta-5 and delta-6 desaturase in zebrafish muscle inhibits the growth of Vibrio alginolyticus and affects fish immunomodulatory activity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 39, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Spinetti, T.; Tardivel, A.; Castillo, R.; Bourquin, C.; Guarda, G.; Tian, Z.; Tschopp, J.; Zhou, R. Omega 3 fatty acids prevent inflammation and metabolic disorder through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Immunity 2013, 38, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkanfi, M.; Kanneganti, T.D. The inflammasome: A remote control for metabolic syndrome. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menni, C.; Zierer, J.; Pallister, T.; Jackson, M.A.; Long, T.; Mohney, R.P.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; Valdes, A.M. Omega-3 fatty acids correlate with gut microbiome diversity and production of N-carbamylglutamate in middle aged and elderly women. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noriega, B.S.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Salyakina, D.; Coffman, J. Understanding the impact of omega-3 rich diet on the gut microbiota. Case Rep. Med. 2016, 3089303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guesdon, W.; Kosaraju, R.; Brophy, P.; Clark, A.; Dillingham, S.; Aziz, S.; Moyer, F.; Willson, K.; Dick, J.R.; Patil, S.P.; et al. Effects of fish oils on ex vivo B-cell responses of obese subjects upon BCR/TLR stimulation: A pilot study. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 53, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.Y.; McMurray, D.N.; Chapkin, R.S. Omega-3 fatty acids, lipid rafts, and T cell signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katan, M.B.; Deslypere, J.P.; van Birgelen, A.P.; Penders, M.; Zegwaard, M. Kinetics of the incorporation of dietary fatty acids into serum cholesteryl esters, erythrocyte membranes, and adipose tissue: An 18-month controlled study. J. Lipid Res. 1997, 38, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marangoni, F.; Colombo, C.; Galli, C. A method for the direct evaluation of the fatty acid status in a drop of blood from a fingertip in humans: Applicability to nutritional and epidemiological studies. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 326, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Mühlhäusler, B.S.; Gibson, R.A. A method for long term stabilisation of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in dried blood spots and its clinical application. Prostaglandins Leukotriences Essent. Fatty Acids 2014, 91, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.S. Assessing fatty acid biostatus: Red blood cells or plasma? Lipid Technol. 2013, 25, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.S. Theomega-3 index: Clinical utility for therapeutic intervention. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2010, 12, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, B.B.; Derraik, J.G.; Brennan, C.M.; Biggs, J.B.; Smith, G.C.; Garg, M.L.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Hofman, P.L.; Cutfield, W.S. Higher omega-3 index is associated with increased insulin sensitivity and more favourable metabolic profile in middle-aged overweight men. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, T.; Halsey, J.; Kromhout, D.; Gerstein, H.C.; Marchioli, R.; Tavazzi, L.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Rauch, B.; Ness, A.; Galan, P.; et al. Omega-3 treatment trialists’ collaboration. associations of omega-3 fatty acid supplement use with cardiovascular disease risks: Meta-analysis of 10 trials involving 77,917 individuals. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, T.; Halsey, J.; Kromhout, D.; Gerstein, H.C.; Marchioli, R.; Tavazzi, L.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Rauch, B.; Ness, A.; Galan, P.; et al. Associations of omega-3 fatty acid supplement use with cardiovascular disease risks: Meta-analysis of 10 trials involving 77,917 individuals. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2018, 24, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weylandt, K.H.; Serini, S.; Chen, Y.Q.; Su, H.M.; Lim, K.; Cittadini, A.; Calviello, G. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: The way forward in times of mixed evidence. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 143109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, J.; Conte, C.; Fontana, L.; Mittendorfer, B.; Imai, S.; Schechtman, K.B.; Gu, C.; Kunz, I.; Rossi Fanelli, F.; Patterson, B.W.; et al. Resveratrol supplementation does not improve metabolic function in nonobese women with normal glucose tolerance. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, T.P.; Wright, A.G.; Clifton, P.M.; Ilag, L.L. Postprandial insulin and glucose levels are reduced in healthy subjects when a standardised breakfast meal is supplemented with a filtered sugarcane molasses concentrate. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalho, S.M.; de Alvares Goulart, R.; Quesada, K.; Bechara, M.D.; de Cássio Alves de Carvalho, A. Inflammatory bowel disease: Can omega-3 fatty acids really help. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2016, 29, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hemmings, S.M.J.; Malan-Müller, S.; van den Heuvel, L.L.; Demmitt, B.A.; Stanislawski, M.A.; Smith, D.G.; Bohr, A.D.; Stamper, C.E.; Hyde, E.R.; Morton, J.T.; et al. The microbiome in posttraumatic stress disorder and trauma-exposed controls: An exploratory study. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, K.; Noguchi, H.; Nishi, D.; Hamazaki, K.; Hamazaki, T.; Matsuoka, Y.J. Effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on psychophysiological symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder in accident urvivors: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Affect Disord. 2017, 224, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, G.; Kettle, C.; Hayes, D.; Dennis, C.; Tucci, J. Omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and the treatment of depression. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Lehto, S.M.; Harty, S.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Burnet, P.W.J. Psychobiotics and the manipulation of bacteria-gut-brain signals. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Chang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Han, X.; Han, Y.; Yao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Cui, H.; Zheng, L.; Han, T.; et al. ω-3 PUFAs ameliorate liver fibrosis and inhibit hepatic stellate cells proliferation and activation by promoting YAP/TAZ degradation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaswant, M.; Poudyal, H.; Brown, L. Mechanisms of enhanced insulin secretion and sensitivity with n-3 unsaturated fatty acids. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilag, L.L. Are Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids the Link between the Immune System and the Microbiome towards Modulating Cancer? Medicines 2018, 5, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030102
Ilag LL. Are Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids the Link between the Immune System and the Microbiome towards Modulating Cancer? Medicines. 2018; 5(3):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030102
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlag, Leodevico L. 2018. "Are Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids the Link between the Immune System and the Microbiome towards Modulating Cancer?" Medicines 5, no. 3: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030102
APA StyleIlag, L. L. (2018). Are Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids the Link between the Immune System and the Microbiome towards Modulating Cancer? Medicines, 5(3), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030102




