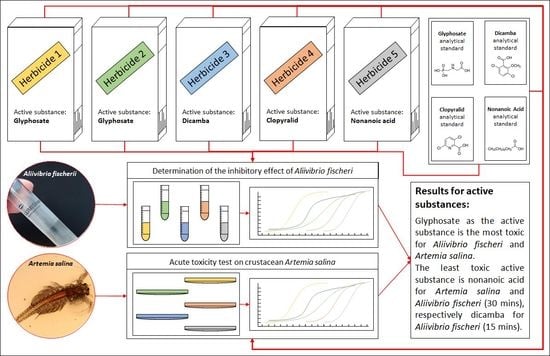
The Influence of Herbicides to Marine Organisms Aliivibrio fischeri and Artemia salina
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Organisms
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Luminescent Bacteria Test
3.2. Crustacea Bioassay Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varanasi, A.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Jugulam, M. Impact of Climate Change Factors on Weeds and Herbicide Efficacy. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Volume 135, pp. 107–146. [Google Scholar]
- Matzenbacher, F.O.; Vidal, R.A.; Merotto, A.; Trezzi, M.M. Environmental and Physiological Factors that Affect the Efficacy of Herbicides that Inhibit the Enzyme Protoporphyrinogen oxidase: A Literature Review. Planta Daninha 2014, 32, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, X.J.; Pedersen, T.; Fischer, M.; White, R.; Young, T.M. Herbicide runoff along highways. 1. Field observations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Isensee, A.; Shirmohammadi, A. Influence of Soil Texture and Tillage on Herbicide Transport. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, L. Determining the Selectivity of Herbicides and Assessing Their Effect on Plant Roots—A Case Study with Indaziflam and Glyphosate Herbicides. In Herbicides, Physiology of Action and Safety; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.G.; Somers, K.M.; Dillon, P.J.; Paterson, C.; Reid, R.A. Impacts of golf courses on macroinvertebrate community structure in Precambrian Shield streams. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, J.A.; Yeager, M.A.; Suffet, I.H. Organophosphorus insecticides in agricultural and residential runoff: Field observations and implications for total maximum daily load development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodeur, J.C.; Suarez, R.P.; Natale, G.S.; Ronco, A.E.; Zaccagnini, M.E. Reduced body condition and enzymatic alterations in frogs inhabiting intensive crop production areas. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haith, D.A. Ecological Risk Assessment of Pesticide Runoff from Grass Surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6496–6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, K.R.; Dalhoff, K.; Volz, D.; Van Der Kraak, G. 7—Effects of Herbicides on Fish. In Fish Physiology; Tierney, K.B., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 33, pp. 369–409. [Google Scholar]
- Catania, P.; Inglese, P.; Pipitone, F.; Vallone, M. Assessment of the Wind Influence on Spray Application using an Artificial Vineyard. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2011, 76, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Baetens, K.; Ho, Q.T.; Nuyttens, D.; De Schampheleire, M.; Endalew, A.M.; Hertog, M.; Nicolai, B.; Ramon, H.; Verboven, P. A validated 2-D diffusion-advection model for prediction of drift from ground boom sprayers. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baio, F.H.R.; Antuniassi, U.R.; Castilho, B.R.; Teodoro, P.E.; da Silva, E.E. Factors affecting aerial spray drift in the Brazilian Cerrado. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouse, L.F. Effect of nozzle type and operation on spray droplet size. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.K.; Franti, T.G.; Comfort, S.D. Impact of Initial Soil Water Content, Crop Residue Cover, and Post–herbicide Irrigation on Herbicide Runoff. Trans. ASAE 2002, 45, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postigo, C.; de Alda, M.J.L.; Barcelo, D.; Ginebreda, A.; Garrido, T.; Fraile, J. Analysis and occurrence of selected medium to highly polar pesticides in groundwater of Catalonia (NE Spain): An approach based on on-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry detection. J. Hydrol. 2010, 383, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, D.; Saidov, N.; Jaliov, A.; El Bouhssini, M.; Kennelly, M.; Bahlai, C.; Landis, J.; Maredia, K. Demonstration of an Integrated Pest Management Program for Wheat in Tajikistan. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2016, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cozad, A.; Mudge, C.; Diaz, R. Integrated management of giant salvinia using herbicides and the salvinia weevil. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2019, 57, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jannoyer, M.; Le Bellec, F.; Lavigne, C.; Achard, R.; Malézieux, E. Choosing cover crops to enhance ecological services in orchards: A multiple criteria and systemic approach applied to tropical areas. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 9, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, C.A.; Chen, J.; Fine, J.D.; Frazier, M.T.; Frazier, J.L. The formulation makes the honey bee poison. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 120, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagi, T. Surfactant effects on environmental behavior of pesticides. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 194, 71–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnage, R.; Antoniou, M.N. Ignoring Adjuvant Toxicity Falsifies the Safety Profile of Commercial Pesticides. Front. Public Health 2018, 5, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, K.A.; Halling-Sørensen, B.; Mogensen, B.B.; Vejrup, K.V. Environmental properties and effects of nonionic surfactant adjuvants in pesticides: A review. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 871–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlman, P.W.; Phillips, W.M. Inhibition of Glyphosate Phytotoxicity. Weed Sci. 1979, 27, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowles, R.S.; Cowles, E.A.; Mcdermott, A.M.; Ramoutar, D.N. “Inert” Formulation Ingredients with Activity: Toxicity of Trisiloxane Surfactant Solutions to Twospotted Spider Mites (Acari: Tetranychidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, S.; Luthy, R.G. Effects of nonionic surfactants on the solubilization and mineralization of phenanthrene in soil-water systems. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1992, 40, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Camazano, M.; Arienzo, M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Crisanto, T. Effect of different surfactants on the mobility of selected non-ionic pesticides in soil. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 3793–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, M.; Messina, C.; Abbate, C.; Baglieri, A.; Boursier, C. Solubility and adsorption behaviors of chlorpyriphos-methyl in the presence of surfactants. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2009, 44, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Cruz, M.S.; Sanchez-Martin, M.J.; Sanchez-Camazano, M. Surfactant-enhanced desorption of atrazine and linuron residues as affected by aging of herbicides in soil. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 50, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freydier, L.; Lundgren, J.G. Unintended effects of the herbicides 2,4-D and dicamba on lady beetles. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Schmehl, D.R.; Mullin, C.A.; Frazier, J.L. Four common pesticides, their mixtures and a formulation solvent in the hive environment have high oral toxicity to honey bee larvae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e77547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, S.N.; Christiansen, L.B.; Pedersen, K.L.; Korsgaard, B.; Bjerregaard, P. In vivo estrogenic activity of branched and linear alkylphenols in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 233, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.; Aparicio, V.C.; Bastos, M.C.; De Geronimo, E.; Labanowski, J.; Prestes, O.D.; Zanella, R.; dos Santos, D.R. Indiscriminate use of glyphosate impregnates river epilithic biofilms in southern Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, A.L.; Dayan, F.E. Fate of Glyphosate during Production and Processing of Glyphosate-Resistant Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2061–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqueda, C.; Undabeytia, T.; Villaverde, J.; Morillo, E. Behaviour of glyphosate in a reservoir and the surrounding agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglin, W.A.; Meyer, M.; Kuivila, K.; Dietze, J. Glyphosate and its degradation product AMPA occur frequently and widely in US soils, surface water, groundwater, and precipitation. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeff, W.; Neumann, C.; Schulz-Bull, D.E. Glyphosate and AMPA in the estuaries of the Baltic Sea method optimization and field study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, M.A.; Schulz-Bull, D.E.; Kanwischer, M. The challenge of detecting the herbicide glyphosate and its metabolite AMPA in seawater—Method development and application in the Baltic Sea. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matozzo, V.; Marin, M.G.; Masiero, L.; Tremonti, M.; Biamonte, S.; Viale, S.; Finos, L.; Lovato, G.; Pastore, P.; Bogialli, S. Effects of aminomethylphosphonic acid, the main breakdown product of glyphosate, on cellular and biochemical parameters of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matozzo, V.; Munari, M.; Masiero, L.; Finos, L.; Marin, M.G. Ecotoxicological hazard of a mixture of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid to the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck 1819). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajnaiova, L.; Vurm, R.; Kholomyeva, M.; Kobera, M.; Koci, V. Determination of the Ecotoxicity of Herbicides Roundup (R) Classic Pro and Garlon New in Aquatic and Terrestrial Environments. Plants 2020, 9, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, F.A.; Samojeden, C.G.; Rutkoski, C.F.; Folador, A.; Da Fre, S.P.; Muller, C.; Hartmann, P.A.; Hartmann, M.T. Morphological, behavioral and genotoxic effects of glyphosate and 2,4-D mixture in tadpoles of two native species of South American amphibians. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 85, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.B.; Dong, C.Y.; Zhai, Z.Z.; Tang, L.; Wang, L. Glyphosate-induced lipid metabolism disorder contributes to hepatotoxicity in juvenile common carp. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Dai, P.Y.; Perveen, A.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, L.Y.; Jia, X.; Li, Y.S.; Li, C.M. Effects of chronic glyphosate exposure to pregnant mice on hepatic lipid metabolism in offspring. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, T.M.; Hal, J. Mechanism of action of natural auxins and the auxinic herbicides. Rev. Toxicol. 1997, 1, 111–142. [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann, K. Auxin herbicides: Current status of mechanism and mode of action. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quareshy, M.; Prusinska, J.; Li, J.; Napier, R. A cheminformatics review of auxins as herbicides. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flasiński, M.; Hąc-Wydro, K. Natural vs. synthetic auxin: Studies on the interactions between plant hormones and biological membrane lipids. Environ. Res. 2014, 133, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Dryhurst, G. Electrochemical and peroxidase O2-mediated oxidation of indole-3-acetic acid at physiological pH. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1997, 432, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaepen, S.; Vanderleyden, J. Auxin and plant-microbe interactions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a001438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, J.P.; Butz, R.G.; Cork, D.J. Use of dicamba-degrading microorganisms to protect dicamba susceptible plant species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Qiu, J.; He, Q.; Zhu, J.; He, J. Enhanced degradation of dicamba by an anaerobic sludge acclimated from river sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlund, P.; Nasuhoglu, D.; Isazadeh, S.; Yargeau, V. Investigation of Acute and Chronic Toxicity Trends of Pesticides Using High-Throughput Bioluminescence Assay Based on the Test Organism Vibrio fischeri. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 74, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro Marcato, A.C.; de Souza, C.P.; Fontanetti, C.S. Herbicide 2,4-D: A Review of Toxicity on Non-Target Organisms. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.C.M.; Moreira, R.A.; Pinto, T.J.S.; Ogura, A.P.; Yoshii, M.P.C.; Lopes, L.F.P.; Montagner, C.C.; Goulart, B.V.; Daam, M.A.; Espíndola, E.L.G. Acute and chronic toxicity of 2,4-D and fipronil formulations (individually and in mixture) to the Neotropical cladoceran Ceriodaphnia silvestrii. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filkowski, J.; Besplug, J.; Burke, P.; Kovalchuk, I.; Kovalchuk, O. Genotoxicity of 2, 4-D and dicamba revealed by transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants harboring recombination and point mutation markers. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2003, 542, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.F.; Li, W.; Zha, J.M.; Wang, Z.J. Dicamba affects sex steroid hormone level and mRNA expression of related genes in adult rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus) at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 30, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corredor, M.; Mellado, J.R.; Montoya, M.R. EC (EE) process in the reduction of the herbicide clopyralid on mercury electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 4302–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, D.B.; Cessna, A.J.; Sverko, E.; Glozier, N.E. Pesticides in surface drinking-water supplies of the northern Great Plains. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizaoui, C.; Mezughi, K.; Bickley, R. Heterogeneous photocatalytic removal of the herbicide clopyralid and its comparison with UV/H2O2 and ozone oxidation techniques. Desalination 2011, 273, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, R.; Ikenaga, O.; Ishihara, S.; Shibata, H.; Iwafune, T.; Sato, T.; Yamashita, Y. Determination of herbicide clopyralid residues in crops grown in clopyralid-contaminated soils. J. Pestic. Sci. 2010, 35, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Tamura, K.; Seike, N. Change of clopyralid concentration in recycled beef cattle compost. Anim. Sci. J. 2021, 92, e13568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebato, M.; Uegaki, R.; Sutoh, M. Dynamics of clopyralid herbicide during composting in small composting experiment units. J. Pestic. Sci. 2015, 40, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, E.; Seike, N.; Namiki, S. Highly sensitive analytical method for herbicide clopyralid residue in cattle manure compost with ultraperformance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pestic. Sci. 2019, 44, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltner, E.; Bary, A.; Cogger, C. Clopyralid and compost: Formulation and mowing effects on herbicide content of grass clippings. Compost Sci. Util. 2003, 11, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furia, T.E. CRC Handbook of Food Additives; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1973; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg, J.E.; Lindberg, M. Nonanoic acid—An experimental irritant. Contact Dermat. 2003, 49, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Fidalgo, A.; Ilharco, L.M.; Pagliaro, M. Herbicides based on pelargonic acid: Herbicides of the bioeconomy. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin.-Biofpr 2019, 13, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, S.; Yamada, S.; Hosomi, M. Anti-cyanobacterial fatty acids released from Myriophyllum spicatum. Hydrobiologia 2005, 543, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotti, S.; Ferri, E.N.; Fumo, M.G.; Maiolini, E. Monitoring of environmental pollutants by bioluminescent bacteria. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 608, 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarque, S.; Masner, P.; Klánová, J.; Prokeš, R.; Bláha, L. Bioluminescent Vibrio fischeri Assays in the Assessment of Seasonal and Spatial Patterns in Toxicity of Contaminated River Sediments. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, B.; Lafuente, C.; Lapeña, D.; Errazquin, D.; Lomba, L. QSAR study for predicting the ecotoxicity of NADES towards Aliivibrio fischeri. Exploring the use of mixing rules. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, S.; Venkataraman, C.; Mukherji, S. A review on advantages of implementing luminescence inhibition test (Vibrio fischeri) for acute toxicity prediction of chemicals. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inouye, S. NAD(P)H-Flavin Oxidoreductase from the Bioluminescent Bacterium, Vibrio-Fischeri ATCC-7744, IS A Flavoprotein. FEBS Lett. 1994, 347, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ji, Y.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, K.; Hu, X.; Ye, J. Comparison of organics and heavy metals acute toxicities to Vibrio fischeri. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2016, 81, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, B.S.; Carvalho, F.D.; Guilhermino, L.M.; Van Stappen, G. Use of the genus Artemia in ecotoxicity testing. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persoone, G.; Wells, P.G. Artemia in aquatic toxicology: A review. Artemia Res. Appl. 1987, 1, 259–275. [Google Scholar]
- Asem, A.; Rastegar-Pouyani, N.; De Los Rios-Escalante, P. The genus Artemia Leach, 1819 (Crustacea: Branchiopoda). I. True and false taxonomical descriptions. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2010, 38, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaecke, P.; Persoone, G.; Claus, C.; Sorgeloos, P. Proposal for a short-term toxicity test with Artemia nauplii. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1981, 5, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Osborne, W.J. Heavy metal determination and aquatic toxicity evaluation of textile dyes and effluents using Artemia salina. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 25, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllidis, G.V.; Abatzopoulos, T.J.; Sorgeloos, P. Review of the biogeography of the genus Artemia (Crustacea, Anostraca). J. Biogeogr. 1998, 25, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, S.T.; Buoncristiani, M.R.; Carl, J.R. Artemia Habitats—Ion Concentrations Tolerated by One Superspecies. Hydrobiologia 1988, 158, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amat, F. Biología de Artemia. Inf. Téc. Inst. Investig. Pesq. 1985, 126, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Barahona, M.V.; Sanchez-Fortun, S. Toxicity of carbamates to the brine shrimp Artemia salina and the effect of atropine, BW284c51, iso-OMPA and 2-PAM on carbaryl toxicity. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 104, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umarani, R.; Kumaraguru, A.K.; Nagarani, N. Investigation of acute toxicity of heavy metals in Artemia salina acclimated to different salinity. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2012, 94, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, C.M.; Simoniello, P.; Arena, C.; Capriello, T.; Panzuto, R.; Vitale, E.; Agnisola, C.; Tizzano, M.; Avallone, B.; Ferrandino, I. Effects of four food dyes on development of three model species, Cucumis sativus, Artemia salina and Danio rerio: Assessment of potential risk for the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulvasu, C.; Jennifer, S.M.; Prabhu, D.; Chandhirasekar, D. Toxicity Effect of Silver Nanoparticles in Brine Shrimp Artemia. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 256919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Bayo, F. Comparative acute toxicity of organic pollutants and reference values for crustaceans. I. Branchlopoda, Copepoda and Ostracoda. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 385–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, F.; Delame, N.; Vita, J.L.; Huyghe, C.; Reboud, X. The micro-economic impacts of a ban on glyphosate and its replacement with mechanical weeding in French vineyards. Crop Prot. 2021, 150, 105778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, K.A.; Nicola, V.B.; Dudas, R.T.; Demetrio, W.C.; Maia, L.d.S.; Cunha, L.; Bartz, M.L.C.; Brown, G.G.; Pasini, A.; Kille, P.; et al. Pesticides in a case study on no-tillage farming systems and surrounding forest patches in Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S.O. The history and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czech Standards Institute. Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio fischeri (Luminiscent bacteria Test)—Part 2: Method Using Liquid-Dried Bacteria (ISO 11348-2: 1998); Czech Standards Institute: Prague, Czech Republic, 2000; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis. J. Inst. Actuar. 1952, 78, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mesnage, R.; Bernay, B.; Seralini, G.E. Ethoxylated adjuvants of glyphosate-based herbicides are active principles of human cell toxicity. Toxicology 2013, 313, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament, Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L 353, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Amoros, I.; Alonso, J.L.; Romaguera, S.; Carrasco, J.M. Assessment of toxicity of a glyphosate-based formulation using bacterial systems in lake water. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, J.L.; Bonnemoy, F.; Dusser, M.; Bohatier, J. Assessment of the potential toxicity of herbicides and their degradation products to nontarget cells using two microorganisms, the bacteria Vibrio fischeri and the ciliate Tetrahymena pyriformis. Environ. Toxicol. 2007, 22, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, M.D.; Vettori, S.; Bueno, M.J.M.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R. Toxicity evaluation with Vibrio fischeri test of organic chemicals used in aquaculture. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, M.T.; Mariscal, A.; Carnero-Varo, M.; Fernandez-Crehuet, J. Correlation of two bioluminescence and one fluorogenic bioassay for the detection of toxic chemicals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2002, 53, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberidou, C.; Kitsiou, V.; Karahanidou, S.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Kouras, A.; Kosma, C.I.; Albanis, T.A.; Poulios, I. Photocatalytic degradation of the herbicide clopyralid: Kinetics, degradation pathways andecotoxicity evaluation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 2510–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Scarlett, A.G.; West, C.E.; Rowland, S.J. Toxicity of Individual Naphthenic Acids to Vibrio fischeri. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9776–9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.D.; de Oliveira, R.; Abe, F.R.; Brito, L.B.; Moura, D.S.; Valadares, M.C.; Grisolia, C.K.; de Oliveira, D.P.; de Oliveira, G.A.R. Ecotoxicological Assesment of Glyphosate-based Herbicides: Effects on Different Organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawahar Ali, A.; Mohamed, A.J.; Kumar, M.A.; John, B.A. Organophosphorus pesticides toxicity on brine shrimp artemia. J. CleanWAS 2018, 1, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchnitz, N.; Kurzius, F.; Rupp, H.; Schmidt, G.; Hauser, B.; Schrodter, M.; Meissner, R. Assessment of pesticide inputs into surface waters by agricultural and urban sources—A case study in the Querne/Weida catchment, central Germany. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.J.; Fong, S.; Deanovic, L.; Young, T.A. Toxicity of herbicides in highway runoff. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 2336–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, A.E.; Marino, D.J.G.; Abelando, M.; Almada, P.; Apartin, C.D. Water quality of the main tributaries of the Parana Basin: Glyphosate and AMPA in surface water and bottom sediments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruzzo, P.J.; Porta, A.A.; Ronco, A.E. Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glozier, N.E.; Struger, J.; Cessna, A.J.; Gledhill, M.; Rondeau, M.; Ernst, W.R.; Sekela, M.A.; Cagampan, S.J.; Sverko, E.; Murphy, C.; et al. Occurrence of glyphosate and acidic herbicides in select urban rivers and streams in Canada, 2007. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, L.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Glyphosate, aminomethylphosphonic acid, and glufosinate ammonium in agricultural groundwater and surface water in China from 2017 to 2018: Occurrence, main drivers, and environmental risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Du-Carrée, J.; Boukhari, R.; Cachot, J.; Cabon, J.; Louboutin, L.; Morin, T.; Danion, M. Generational effects of a chronic exposure to a low environmentally relevant concentration of glyphosate on rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, B.B.; Nascimento, N.F.; Santos, M.P.; Bertolini, R.M.; Yasui, G.S.; Giaquinto, P.C. Low concentrations of glyphosate-based herbicide cause complete loss of sperm motility of yellowtail tetra fish Astyanax lacustris. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 92, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, S.; Santos, M.A.; Barroso, C.; Gaivão, I.; Pacheco, M. Differential genotoxicity of Roundup(®) formulation and its constituents in blood cells of fish (Anguilla anguilla): Considerations on chemical interactions and DNA damaging mechanisms. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, N.S. Oxidative stress responses of rats exposed to Roundup and its active ingredient glyphosate. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 28, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owagboriaye, F.; Dedeke, G.; Ademolu, K.; Olujimi, O.; Aladesida, A.; Adeleke, M. Comparative studies on endogenic stress hormones, antioxidant, biochemical and hematological status of metabolic disturbance in albino rat exposed to roundup herbicide and its active ingredient glyphosate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 14502–14512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.; Benvindo-Souza, M.; Carvalho, W.F.; Nunes, H.F.; de Lima, P.N.; Costa, M.S.; Benetti, E.J.; Guerra, V.; Saboia-Morais, S.M.T.; Santos, C.E.; et al. Evaluation of the genotoxic, mutagenic, and histopathological hepatic effects of polyoxyethylene amine (POEA) and glyphosate on Dendropsophus minutus tadpoles. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, M.T.K.; Chu, L.M. Aquatic toxicity of glyphosate-based formulations: Comparison between different organisms and the effects of environmental factors. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, E.; Raymann, K.; Moran, N. Glyphosate perturbs the gut microbiota of honey bees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 201803880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, L.T.; Vázquez, D.E.; Arenas, A.; Farina, W.M. Effects of field-realistic doses of glyphosate on honeybee appetitive behaviour. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.H.; Gao, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.Z.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Dai, P.L.; Hou, C.S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Diao, Q.Y. Effects of a commercially formulated glyphosate solutions at recommended concentrations on honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) behaviours. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attademo, A.M.; Lajmanovich, R.C.; Peltzer, P.M.; Boccioni, A.P.C.; Martinuzzi, C.; Simonielo, F.; Repetti, M.R. Effects of the emulsifiable herbicide Dicamba on amphibian tadpoles: An underestimated toxicity risk? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 31962–31974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz de Arcaute, C.; Larramendy, M.L.; Soloneski, S. Genotoxicity by long-term exposure to the auxinic herbicides 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and dicamba on Cnesterodon decemmaculatus (Pisces: Poeciliidae). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.V.; Soloneski, S.; Larramendy, M.L. The chlorophenoxy herbicide dicamba and its commercial formulation banvel induce genotoxicity and cytotoxicity in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Mutat. Res. 2007, 634, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espandiari, P.; Thomas, V.A.; Glauert, H.P.; O’Brien, M.; Noonan, D.; Robertson, L.W. The herbicide dicamba (2-methoxy-3,6-dichlorobenzoic acid) is a peroxisome proliferator in rats. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1995, 26, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairchild, J.F.; Allert, A.L.; Feltz, K.P.; Nelson, K.J.; Valle, J.A. An ecological risk assessment of the acute and chronic effects of the herbicide clopyralid to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 57, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, W.C.; Smith, F.A.; John, J.A.; Rao, K.S. Teratologic evaluation of 3,6-Dichloropicolinic acid in rats and rabbits. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1984, 4, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, J.; Allert, A.; Sappington, L.; Nelson, K.; Valle, J. Using Accelerated Life Testing Procedures to Compare the Relative Sensitivity of Rainbow Trout and the Federally-Listed Threatened Bull Trout to Three Commonly-Used Rangeland Herbicides (Picloram, 2,4-D, and Clopyralid). Environ. Toxicol. Chem./SETAC 2008, 27, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stehr, C.M.; Linbo, T.L.; Baldwin, D.H.; Scholz, N.L.; Incardona, J.P. Evaluating the effects of forestry herbicides on fish development using rapid phenotypic screens. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2009, 29, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sura, S.; Waiser, M.J.; Tumber, V.; Raina-Fulton, R.; Cessna, A.J. Effects of a herbicide mixture on primary and bacterial productivity in four prairie wetlands with varying salinities: An enclosure approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydy, M.; Belden, J.; Wheelock, C.; Hammock, B.; Denton, D. Challenges in regulating pesticide mixtures. Ecol. Soc. 2004, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Chemical Agency. Candidate List of Substances of very High Concern for Authorisation. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/candidate-list-table (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- European Food Safety Authority. Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the potential endocrine disrupting properties of glyphosate. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04979. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Status under Reg. (EC) No 1107/2009. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/active-substances/?event=as.details&as_id=811 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- European Food Safety Authority. Conclusion on the Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Glyphosate. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/4302 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
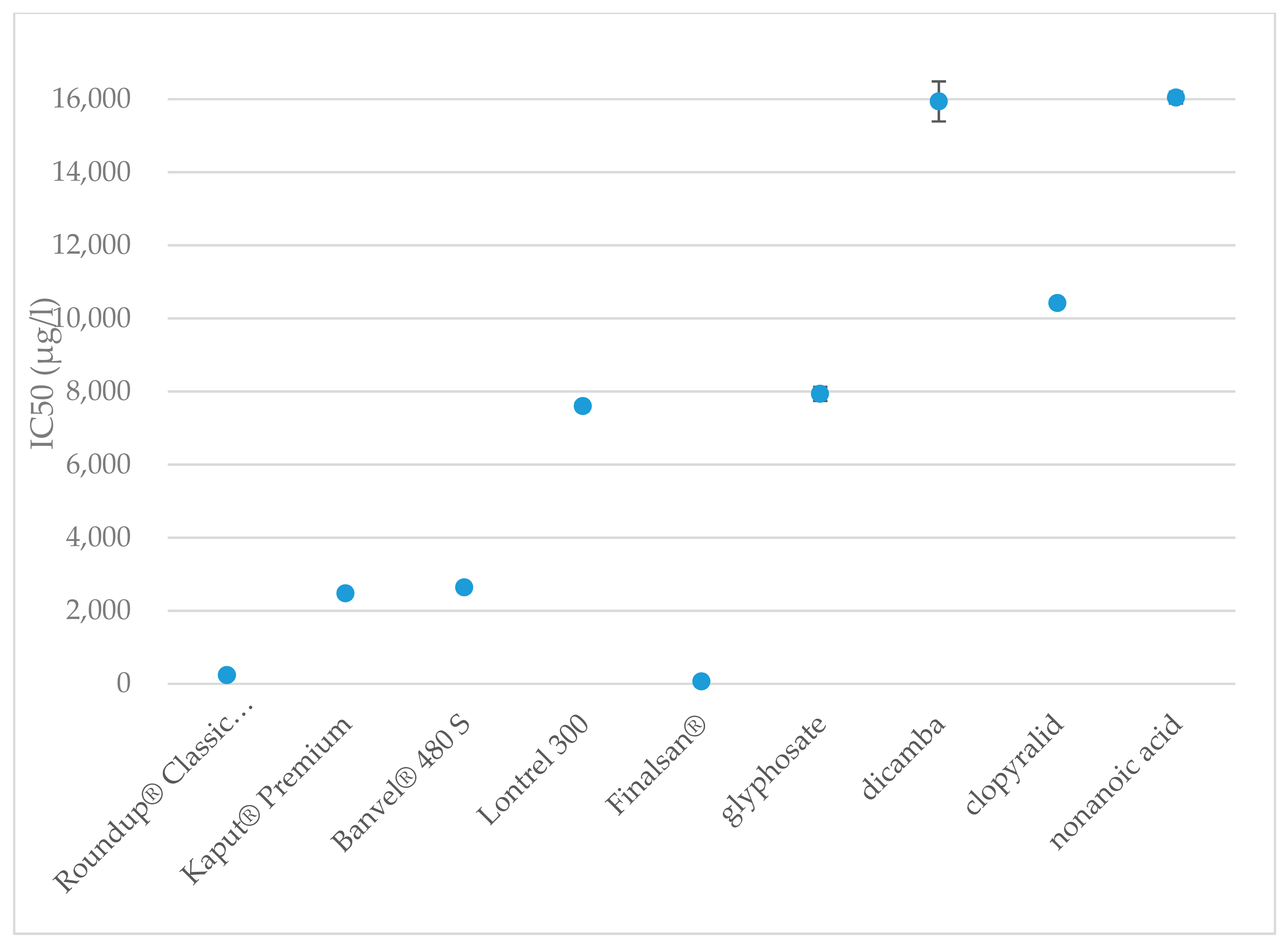

| Tested Substances | Time (min) | IC Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 ( μg·L−1) | 95% Fiducial CI | IC90 ( μg·L−1) | 95% Fiducial CI | ||||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | ||||
| Roundup® Classic Pro | 15 | 236 | 194 | 288 | 494 | 405 | 602 |
| 30 | 243 | 203 | 290 | 467 | 391 | 557 | |
| Kaput® Premium | 15 | 2475 | 1887 | 3247 | 7438 | 5670 | 9757 |
| 30 | 2598 | 2005 | 3368 | 7400 | 5709 | 9591 | |
| Banvel® 480 S | 15 | 2637 | 1859 | 3740 | 14,469 | 10,201 | 20,521 |
| 30 | 2286 | 1624 | 3217 | 11,748 | 8348 | 16,532 | |
| Lontrel 300 | 15 | 7596 | 5023 | 11,488 | 38,749 | 25,623 | 58,600 |
| 30 | 8740 | 6017 | 12,696 | 37,188 | 25,601 | 54,019 | |
| Finalsan® | 15 | 64 | 31 | 130 | 1096 | 542 | 2216 |
| 30 | 66 | 30 | 144 | 1567 | 723 | 3395 | |
| Glyphosate | 15 | 7934 | 3836 | 16,410 | 145,009 | 70,116 | 299,896 |
| 30 | 2928 | 1421 | 6033 | 42,507 | 20,633 | 87,570 | |
| Dicamba | 15 | 15,937 | 10,267 | 24,738 | 87,040 | 56,073 | 135,109 |
| 30 | 9220 | 5558 | 15,296 | 63,817 | 38,468 | 105,868 | |
| Clopyralid | 15 | 10,417 | 6685 | 16,231 | 58,985 | 37,855 | 91,910 |
| 30 | 5071 | 3107 | 8276 | 31,126 | 19,072 | 50,800 | |
| Nonanoic acid | 15 | 16,040 | 8105 | 31,745 | 228,878 | 115,649 | 452,965 |
| 30 | 14,039 | 7,444 | 26,476 | 163,374 | 86,631 | 308,100 | |
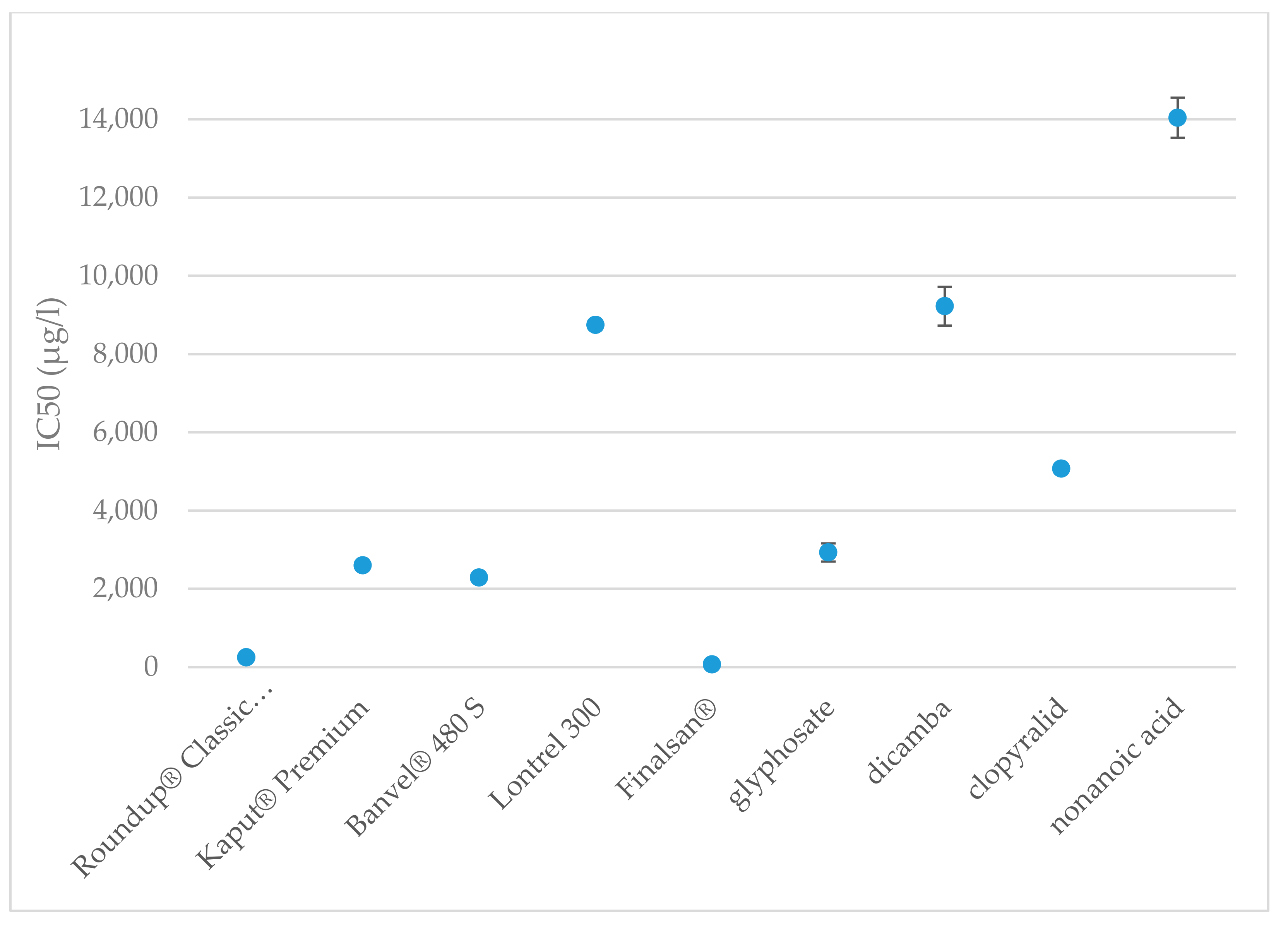
| Tested Substances | LC Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 ( μg·L−1) | 95% Fiducial CI | LC90 ( μg·L−1) | 95% Fiducial CI | |||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||
| Roundup® Classic Pro | 18 | 16 | 21 | 28 | 24 | 32 |
| Kaput® Premium | 19 | 16 | 23 | 31 | 26 | 36 |
| Banvel® 480 S | 2519 | 2083 | 3046 | 4669 | 3861 | 5647 |
| Lontrel 300 | 1796 | 1304 | 2473 | 5776 | 4194 | 7955 |
| Finalsan® | 100 | 59 | 169 | 649 | 383 | 1100 |
| Glyphosate | 811 | 729 | 902 | 1060 | 952 | 1179 |
| Dicamba | 3705 | 2793 | 4914 | 8628 | 6505 | 11,444 |
| Clopyralid | 2800 | 2565 | 3056 | 3797 | 3478 | 4144 |
| Nonanoic acid | 7493 | 6568 | 8549 | 12,516 | 10,971 | 14,278 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vurm, R.; Tajnaiová, L.; Kofroňová, J. The Influence of Herbicides to Marine Organisms Aliivibrio fischeri and Artemia salina. Toxics 2021, 9, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9110275
Vurm R, Tajnaiová L, Kofroňová J. The Influence of Herbicides to Marine Organisms Aliivibrio fischeri and Artemia salina. Toxics. 2021; 9(11):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9110275
Chicago/Turabian StyleVurm, Radek, Lucia Tajnaiová, and Jana Kofroňová. 2021. "The Influence of Herbicides to Marine Organisms Aliivibrio fischeri and Artemia salina" Toxics 9, no. 11: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9110275
APA StyleVurm, R., Tajnaiová, L., & Kofroňová, J. (2021). The Influence of Herbicides to Marine Organisms Aliivibrio fischeri and Artemia salina. Toxics, 9(11), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9110275