Associations between Urinary, Dietary, and Water Fluoride Concentrations among Children in Mexico and Canada
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample
2.2. Childhood Urinary Fluoride (CUF)
2.3. Dietary Fluoride Concentration (for the PROGRESS Cohort Only)
2.4. Measurement of Municipal Drinking Water Fluoride Levels (for the MIREC Cohort Only)
2.5. Covariates and Modifiers of Exposure Levels
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
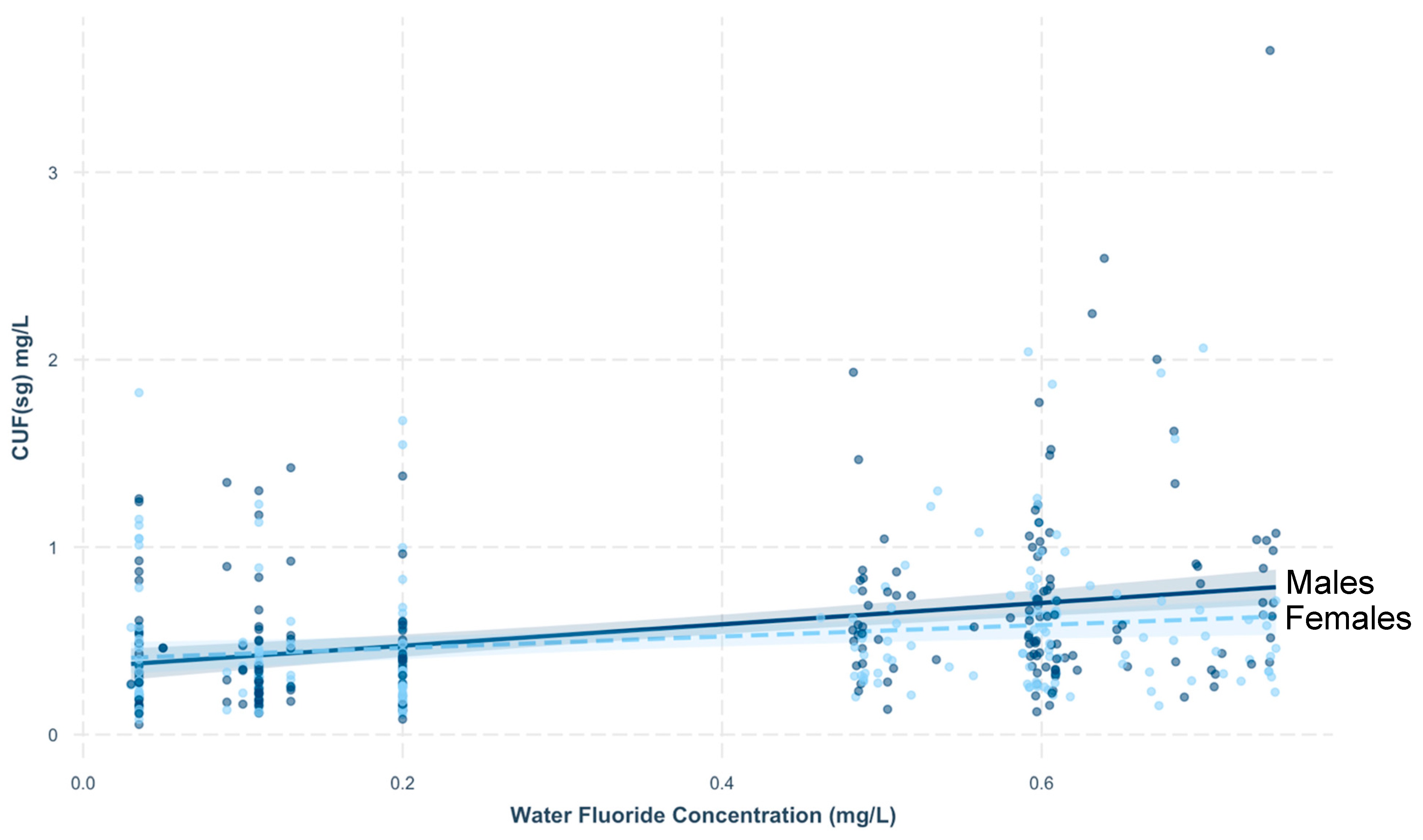
3.1. Association between CUFSG and Covariates
3.2. Association between Fluoride Sources and Covariates
3.3. CUF in Relation to Fluoride Sources
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Marinho, V.C.C. Cochrane reviews of randomized trials of fluoride therapies for preventing dental caries. Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2009, 10, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Public Health Capacity and Knowledge Management Unit, Quebec Region for the Office of the Chief Dental Officer of Canada, Public Health Agency of Canada. The State of Community Water Fluoridation (CWF) across Canada. 2017. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/services/health/publications/healthy-living/community-water-fluoridation-across-canada-2017.html (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Community Water Fluoridation. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fluoridation/basics/index.htm (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Fluoride: Exposure and Relative Source Contribution Analysis; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Secretaría-de-Salud. Norma Oficial Mexicana Nom-040-Ssa1-1993. Sal Yodatada y Sal Fluorada; Ministry of Health: Mexico City, Mexico, 1995.
- Nutrient Data Laboratory, Beltsville Human Nutrition Research Center, Agricultural Research Service. USDA National Fluoride Database of Selected Beverages and Foods Release 2; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2005.
- Zohoori, F.V.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Cardoso, C.A.B.; Olympio, K.P.K.; Levy, F.M.; Grizzo, L.T.; Mangueira, D.F.B.; Sampaio, F.C.; Maguire, A. Total fluoride intake and excretion in children up to 4 years of age living in fluoridated and non-fluoridated areas. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2013, 121, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Mondal, N.K. Dental fluorosis and urinary fluoride concentration as a reflection of fluoride exposure and its impact on IQ level and BMI of children of Laxmisagar, Simlapal Block of Bankura District, W.B., India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Till, C.; Green, R.; Grundy, J.; Hornung, R.; Neufeld, R.; Martinez-Mier, E.A.; Ayotte, P.; Muckle, G.; Lanphear, B. Community water fluoridation and urinary fluoride concentrations in a national sample of pregnant women in Canada. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, T.; Vengosh, A.; Jeuland, M.; Tekle-Haimanot, R.; Weinthal, E.; Kravchenko, J.; Paul, C.; McCornick, P. Fluoride exposure from groundwater as reflected by urinary fluoride and children’s dental fluorosis in the main ethiopian rift valley. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Rafique, T.; Hasan, S.K.; Khan, N.; Khan, M.H.; Usmani, T.H. Correlation of fluoride in drinking water with urine, blood plasma, and serum fluoride levels of people consuming high and low fluoride drinking water in Pakistan. Fluoride 2012, 45, 384–388. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.B. Concentrations of fluoride in water and plasma for US children and adolescents: Data from NHANES 2013–2014. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 50, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, L. Fluoridation exposure status based on location of data collection in the Canadian health measures survey: Is it valid? J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2016, 82, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Gaur, S.; Garg, V.K. Fluoride in drinking water and human urine in Southern Haryana, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberio, A.M.; Quiñonez, C.; Hosein, F.S.; McLaren, L. Fluoride exposure and reported learning disability diagnosis among Canadian children: Implications for community water fluoridation. Can. J. Public Health 2017, 108, e229–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Lata, S.; Yadav, J.; Yadav, J.P. Relationship between water, urine and serum fluoride and fluorosis in school children of Jhajjar District, Haryana, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3377–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoral, A.; Luna-Villa, L.C.; Mantilla-Rodriguez, A.A.; Mercado, A.; Lippert, F.; Liu, Y.; Peterson, K.E.; Hu, H.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M.; Martinez-Mier, E.A. Fluoride content in foods and beverages from Mexico City markets and supermarkets. Food Nutr. Bull. 2019, 40, 514–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddell, J.K.; Malin, A.; Flora, D.; McCague, H.; Till, C. Association of water fluoride and urinary fluoride concentrations with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in Canadian youth. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Till, C.; Green, R.; Lanphear, B. Association between maternal fluoride exposure and child IQ—Reply. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.; Lanphear, B.; Hornung, R.; Flora, D.; Martinez-Mier, E.A.; Neufeld, R.; Ayotte, P.; Muckle, G.; Till, C. Fluoride exposure during fetal development and intellectual abilities in a Canadian birth cohort. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashash, M.; Marchand, M.; Hu, H.; Till, C.; Martinez-Mier, E.A.; Sanchez, B.N.; Basu, N.; Peterson, K.E.; Green, R.; Schnaas, L.; et al. Prenatal fluoride exposure and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms in children at 6–12 years of age in Mexico City. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashash, M.; Thomas, D.; Hu, H.; Martinez-Mier, E.A.; Sanchez, B.N.; Basu, N.; Peterson, K.E.; Ettinger, A.S.; Wright, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Prenatal fluoride exposure and cognitive outcomes in children at 4 and 6–12 years of age in Mexico. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 097017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Toxicology Program (NTP). Draft NTP Monograph on the Systematic Review of Fluoride Exposure and Neurodevelopmental and Cognitive Health Effects; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Farmus, L.; Till, C.; Green, R.; Hornung, R.; Martinez-Mier, E.A.; Ayotte, P.; Muckle, G.; Lanphear, B.; Flora, D. Critical windows of fluoride neurotoxicity in Canadian children. Environment 2020. in revision. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, J.M.; Thomson, W.M.; Ramrakha, S.; Moffitt, T.E.; Zeng, J.; Foster Page, L.A.; Poulton, R. Community water fluoridation and intelligence: Prospective study in New Zealand. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Whitford, G.M. Fluoride intake, metabolism and toxicity. In Fluoride and the Oral Environment; Buzalaf, M.A.R., Ed.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 22, pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Villa, A.; Anabalon, M.; Zohouri, V.; Maguire, A.; Franco, A.M.; Rugg-Gunn, A. Relationships between fluoride intake, urinary fluoride excretion and fluoride retention in children and adults: An analysis of available data. Caries Res. 2010, 44, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton-Evans, G.; Junger, M.L.; Lin, M.; Wei, L.; Espinoza, L.; Beltran-Aguilar, E. Use of toothpaste and toothbrushing patterns among children and adolescents—United States, 2013–2016. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada. Second Report on Human Biomonitoring of Environmental Chemicals in Canada; Authority of the Minister of Health: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013.
- Abduweli Uyghurturk, D.; Goin, D.E.; Martinez-Mier, E.A.; Woodruff, T.J.; DenBesten, P.K. Maternal and fetal exposures to fluoride during mid-gestation among pregnant women in Northern California. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketley, C.E.; Cochran, J.A.; Holbrook, W.P.; Sanches, L.; Van Loveren, C.; Oila, A.M.; O’Mullane, D.M. Urinary fluoride excretion by preschool children in six European countries. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2004, 32, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, T.E.; Fraser, W.D.; Fisher, M.; Davis, K.; Liang, C.L.; Lupien, N.; Bastien, S.; Velez, M.P.; Von Dadelszen, P.; Hemmings, D.G.; et al. Cohort profile: The maternal-infant research on environmental chemicals research platform. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2013, 27, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.M.; Wright, R.J.; Just, A.C.; Power, M.C.; Tamayo y Ortiz, M.; Schnaas, L.; Hu, H.; Wright, R.O.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M. Relationships between lead biomarkers and diurnal salivary cortisol indices in pregnant women from Mexico City: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burris, H.H.; Braun, J.M.; Byun, H.M.; Tarantini, L.; Mercado, A.; Wright, R.J.; Schnaas, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Wright, R.O.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M. Association between birth weight and DNA methylation of IGF2, glucocorticoid receptor and repetitive elements LINE-1 and Alu. Epigenomics 2013, 5, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Mier, E.A.; Cury, J.A.; Heilman, J.R.; Katz, B.P.; Levy, S.M.; Li, Y.; Maguire, A.; Margineda, J.; O’Mullane, D.; Phantumvanit, P.; et al. Development of gold standard ion-selective electrode-based methods for fluoride analysis. Caries Res. 2011, 45, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Mier, E.A.; Soto-Rojas, A.E.; Buckley, C.M.; Margineda, J.; Zero, D.T. Evaluation of the direct and diffusion methods for the determination of fluoride content in table salt. Community Dent. Health 2009, 26, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, R.; Meeker, J.D.; Park, S.; Silva, M.J.; Calafat, A.M. Temporal variability of urinary phthalate metabolite levels in men of reproductive age. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ramírez, S.; Mundo-Rosas, V.; Jiménez-Aguilar, A.; Shamah-Levy, T. Methodology for the analysis of dietary data from the Mexican National Health and Nutrition Survey 2006. Salud Publ. Mex. 2009, 51, S523–S529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada. Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality: Guideline Technical Document—Fluoride; Water, Air and Climate Change Bureau, Healthy Environments and Consumer Safety Branch, Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2010.
- Aylward, L.L.; Hays, S.M.; Vezina, A.; Deveau, M.; St-Amand, A.; Nong, A. Biomonitoring equivalents for interpretation of urinary fluoride. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakens, D. Equivalence tests: A practical primer for t tests, correlations, and meta-analyses. Soc. Psychol. Personal. Sci. 2017, 8, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A. Package “Equivalence”: Provides Tests and Graphics for Assessing Tests of Equivalence; CRAN: Melbourne, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Forte, F.D.S.; Moimaz, S.A.S.; Sampaio, F.C. Urinary fluoride excretion in children exposed to fluoride toothpaste and to different water fluoride levels in a tropical area of Brazil. Braz. Dent. J. 2008, 19, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marthaler, T.M. Salt fluoridation and oral health. Acta Med. Acad. 2013, 42, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographic Variables | MIREC (n = 645) | PROGRESS (n = 551) |
|---|---|---|
| Child Variables | ||
| Sex; N (%) male Age (y); M (SD) | 326 (50.5) | 282 (51.2) |
| 3.66 (0.87) | 4.80 (0.56) | |
| Weight (kg) or BMI (kg/m2) | 15.82 (1.88) kg | 15.71 (1.71) kg/m2 |
| Maternal Variables | ||
| Education; N (%) | ||
| ≥University Degree; 455 (70.9) | <secondary school; 217 (39.4) | |
| ≤College Degree; 187 (29.1) | secondary school; 202 (36.7) | |
| >secondary school; 132 (24) | ||
| Race (n, % white) a | 564, 87.9% | N/A |
| Fluoride Matrix | N | Arithmetic Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | 5th Percentile; 95th Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUFSG (mg/L) | ||||
| MIREC: Overall | 645 a | 0.55 (0.43) | 0.43 (0.39) | 0.15; 1.35 |
| Fluoridated | 219 | 0.66 (0.47) * | 0.53 (0.43) | 0.22; 1.58 |
| Non-fluoridated | 231 | 0.42 (0.31) * | 0.33 (0.27) | 0.12; 1.14 |
| MIREC (2–3-years) | ||||
| Fluoridated | 140 | 0.50 (0.39) * | 0.50 (0.39) | 0.22; 1.47 |
| Non-fluoridated | 170 | 0.41 (0.32) * | 0.32 (0.28) | 0.12; 1.13 |
| MIREC (4–6 years) | ||||
| Fluoridated | 79 | 0.79 (0.56) * | 0.64 (0.59) | 0.25; 1.63 |
| Non-fluoridated | 61 | 0.46 (0.29) * | 0.37 (0.29) | 0.17; 1.15 |
| PROGRESS (4–6 years) | 551 | 0.74 (0.42) | 0.67 (0.36) | 0.30; 1.32 |
| Water Fluoride (mg/L) | ||||
| MIREC: Overall | 516 a | 0.35 (0.25) | 0.20 (0.49) | 0.035; 0.73 |
| Fluoridated | 244 | 0.60 (0.08) | 0.60 (0.09) | 0.49; 0.74 |
| Non-fluoridated | 272 | 0.12 (0.06) | 0.11 (0.17) | 0.04; 0.2 |
| Dietary Fluoride (mcg/d) | ||||
| PROGRESS | 561 | 693.89 (311.67) | 630.64 (372.73) | 321.27; 1261.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Green, R.; Till, C.; Cantoral, A.; Lanphear, B.; Martinez-Mier, E.A.; Ayotte, P.; Wright, R.O.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Malin, A.J. Associations between Urinary, Dietary, and Water Fluoride Concentrations among Children in Mexico and Canada. Toxics 2020, 8, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040110
Green R, Till C, Cantoral A, Lanphear B, Martinez-Mier EA, Ayotte P, Wright RO, Tellez-Rojo MM, Malin AJ. Associations between Urinary, Dietary, and Water Fluoride Concentrations among Children in Mexico and Canada. Toxics. 2020; 8(4):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040110
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreen, Rivka, Christine Till, Alejandra Cantoral, Bruce Lanphear, E. Angeles Martinez-Mier, Pierre Ayotte, Robert O. Wright, Martha M. Tellez-Rojo, and Ashley J. Malin. 2020. "Associations between Urinary, Dietary, and Water Fluoride Concentrations among Children in Mexico and Canada" Toxics 8, no. 4: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040110
APA StyleGreen, R., Till, C., Cantoral, A., Lanphear, B., Martinez-Mier, E. A., Ayotte, P., Wright, R. O., Tellez-Rojo, M. M., & Malin, A. J. (2020). Associations between Urinary, Dietary, and Water Fluoride Concentrations among Children in Mexico and Canada. Toxics, 8(4), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040110









