Real-Time Assessment of E-Cigarettes and Conventional Cigarettes Emissions: Aerosol Size Distributions, Mass and Number Concentrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Real-Time Measurement of Aerosols in a Closed Room
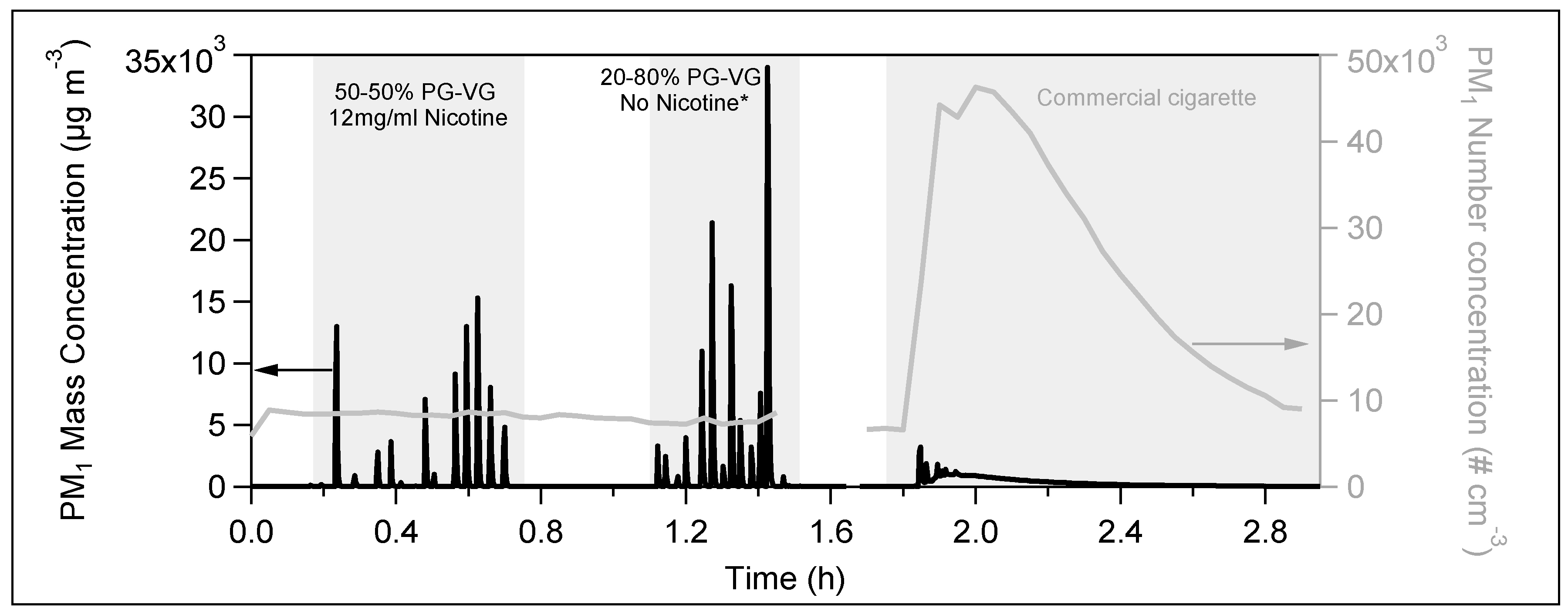
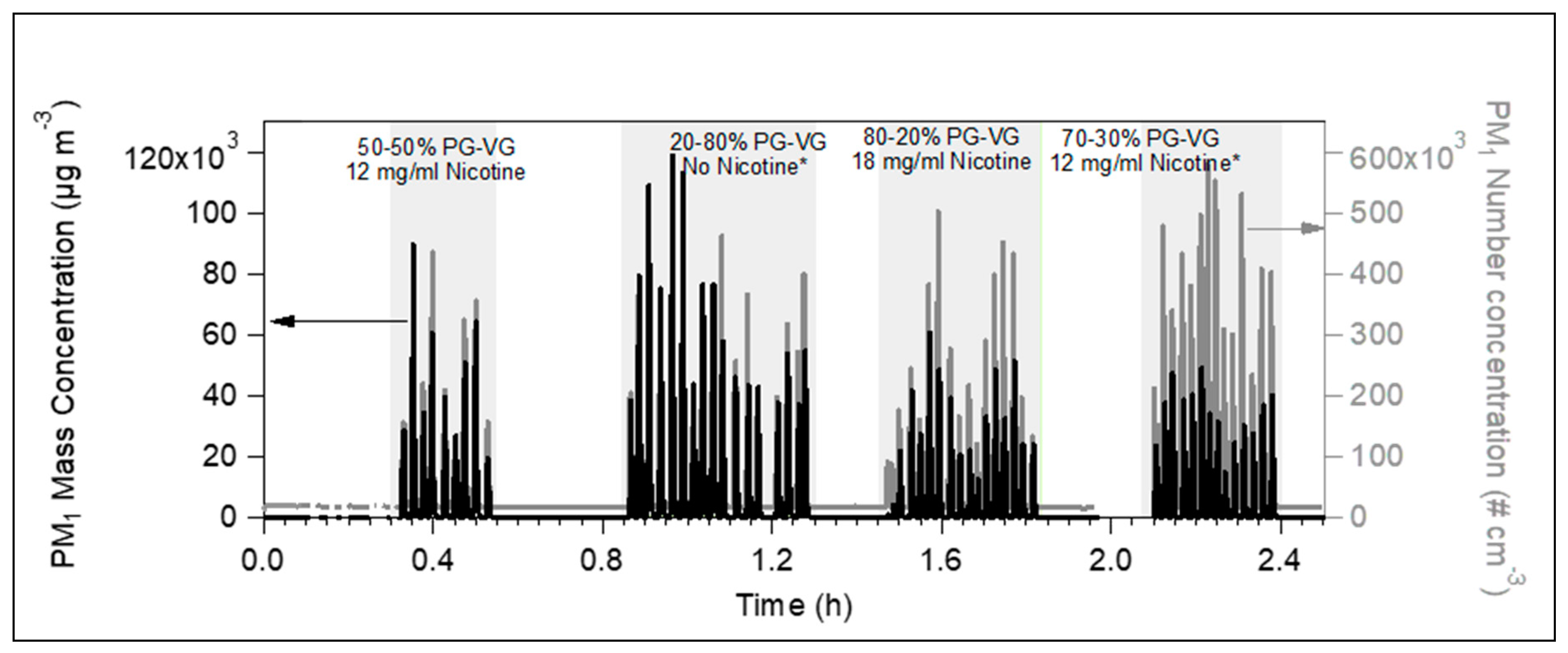
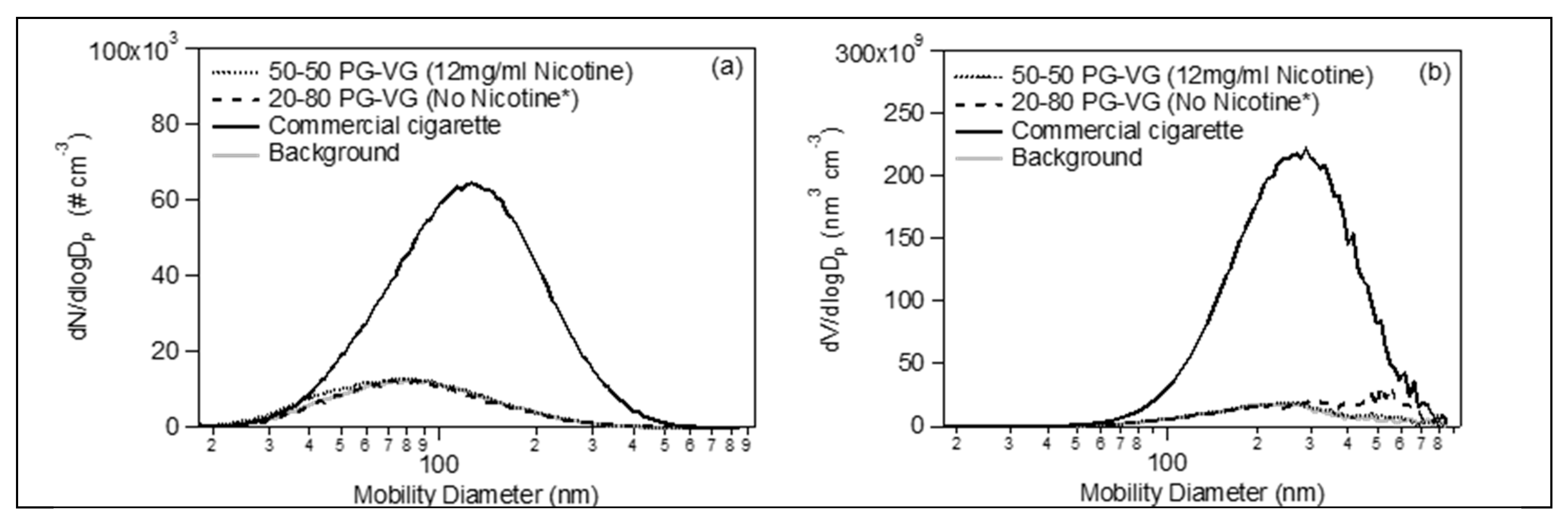
3. Results
E-Cigs Particulate Matter Emissions in a Closed Room
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hajek, P.; Etter, J.-F.; Benowitz, N.; Eissenberg, T.; McRobbie, H. Electronic cigarettes: Review of use, content, safety, effects on smokers, and potential for harm and benefit. Addiction 2014, 109, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgman, A.; Perfetti, T.A. The Chemical Components of Tobacco and Tobacco Smoke; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rom, O.; Pecorelli, A.; Valacchi, G.; Reznick, A.Z. Are E-cigarettes a safe and good alternative to cigarette smoking? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1340, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famele, M.; Ferranti, C.; Abenavoli, C.; Palleschi, L.; Mancinelli, R.; Draisci, R. The Chemical Components of Electronic Cigarette Cartridges and Refill Fluids: Review of Analytical Methods. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2015, 17, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farsalinos, K.E.; Polosa, R. Safety evaluation and risk assessment of electronic cigarettes as tobacco cigarette substitutes: A systematic review. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.J.; Cheng, J.M. Electronic cigarettes: Product characterisation and design considerations. Tob. Control 2014, 23, ii4–ii10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farsalinos, K.E.; Gillman, G. Carbonyl Emissions in E-cigarette Aerosol: A Systematic Review and Methodological Considerations. Front. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinou, E.; Fotopoulou, F.; Drosos, A.; Dimakopoulou, N.; Zagoriti, Z.; Niarchos, A.; Makrynioti, D.; Kouretas, D.; Farsalinos, K.; Lagoumintzis, G.; et al. Tobacco-specific nitrosamines: A literature review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamilari, E.; Farsalinos, K.; Poulas, K.; Kontoyannis, C.G.; Orkoula, M.G. Detection and quantitative determination of heavy metals in electronic cigarette refill liquids using Total Reflection X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 116, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mubarak, M.A.; Danika, C.; Vlachos, N.S.; Farsalinos, K.; Poulas, K.; Sivolapenko, G. Development and validation of analytical methodology for the quantification of aldehydes in e-cigarette aerosols using UHPLC-UV. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 116, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowski, T.R.; Jabłczyńska, K.; Odziomek, M.; Schlage, W.K.; Kuczaj, A.K. Physicochemical studies of direct interactions between lung surfactant and components of electronic cigarettes liquid mixtures. Inhal. Toxicol. 2018, 30, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czogala, J.; Goniewicz, M.L.; Fidelus, B.; Zielinska-Danch, W.; Travers, M.J.; Sobczak, A. Secondhand Exposure to Vapors from Electronic Cigarettes. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2014, 16, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.M.; Tinghino, B.; Mangiaracina, G.; Marani, A.; Vitali, M.; Protano, C.; Osborn, J.F.; Cattaruzza, M.S. Electronic cigarettes: An evaluation of exposure to chemicals and fine particulate matter (PM). Ann. Ig. 2012, 24, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Demokritou, P. Development and characterization of electronic-cigarette exposure generation system (Ecig-EGS) for the physico-chemical and toxicological assessment of electronic cigarette emissions. Inhal. Toxicol. 2016, 28, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schripp, T.; Markewitz, D.; Uhde, E.; Salthammer, T. Does e-cigarette consumption cause passive vaping? Indoor Air 2013, 23, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuoco, F.; Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; Vigo, P. Influential parameters on particle concentration and size distribution in the mainstream of e-cigarettes. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.A. Comparison of Select Analytes in Exhaled Aerosol from E-Cigarettes with Exhaled Smoke from a Conventional Cigarette and Exhaled Breaths. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 11177–11191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scungio, M.; Stabile, L.; Buonanno, G. Measurements of electronic cigarette-generated particles for the evaluation of lung cancer risk of active and passive users. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 115, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingebrethsen, B.J.; Cole, S.K.; Alderman, S.L. Electronic cigarette aerosol particle size distribution measurements. Inhal. Toxicol. 2012, 24, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheev, V.B.; Brinkman, M.C.; Granville, C.A.; Gordon, S.M.; Clark, P.I. Real-Time Measurement of Electronic Cigarette Aerosol Size Distribution and Metals Content Analysis. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2016, 18, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sumner, W.; Chen, D.-R. In vitro particle size distributions in electronic and conventional cigarette aerosols suggest comparable deposition patterns. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2013, 15, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, S.; Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; Ficco, G. Short-term effects of electronic and tobacco cigarettes on exhaled nitric oxide. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 278, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahab, L.; Goniewicz, M.L.; Blount, B.C.; Brown, J.; McNeill, A.; Alwis, K.U.; Feng, J.; Wang, L.; West, R. Nicotine, Carcinogen, and Toxin Exposure in Long-Term E-Cigarette and Nicotine Replacement Therapy Users: A Cross-sectional Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 166, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, W.; Szendrei, K.; Matzen, W.; Osiander-Fuchs, H.; Heitmann, D.; Schettgen, T.; Jörres, R.A.; Fromme, H. Use of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) impairs indoor air quality and increases FeNO levels of e-cigarette consumers. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Exp. Number: | e-Liquids/Cigarette Type |
|---|---|
| 1 | 80% PG–20% VG 18 mg/mL nicotine |
| 2 | 50% PG–50% VG 12 mg/mL nicotine |
| 3 | 80% PG–20% VG 12 mg/mL nicotine |
| 4 | 70% PG–30% VG 12 mg/mL nicotine 1 |
| 5 | 20% PG–80% VG without nicotine 1 |
| 6 | Hand-rolling cigarette |
| 7 | Conventional tobacco cigarette |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lampos, S.; Kostenidou, E.; Farsalinos, K.; Zagoriti, Z.; Ntoukas, A.; Dalamarinis, K.; Savranakis, P.; Lagoumintzis, G.; Poulas, K. Real-Time Assessment of E-Cigarettes and Conventional Cigarettes Emissions: Aerosol Size Distributions, Mass and Number Concentrations. Toxics 2019, 7, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7030045
Lampos S, Kostenidou E, Farsalinos K, Zagoriti Z, Ntoukas A, Dalamarinis K, Savranakis P, Lagoumintzis G, Poulas K. Real-Time Assessment of E-Cigarettes and Conventional Cigarettes Emissions: Aerosol Size Distributions, Mass and Number Concentrations. Toxics. 2019; 7(3):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7030045
Chicago/Turabian StyleLampos, Spyros, Evangelia Kostenidou, Konstantinos Farsalinos, Zoi Zagoriti, Aristeidis Ntoukas, Konstantinos Dalamarinis, Panagiotis Savranakis, George Lagoumintzis, and Konstantinos Poulas. 2019. "Real-Time Assessment of E-Cigarettes and Conventional Cigarettes Emissions: Aerosol Size Distributions, Mass and Number Concentrations" Toxics 7, no. 3: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7030045
APA StyleLampos, S., Kostenidou, E., Farsalinos, K., Zagoriti, Z., Ntoukas, A., Dalamarinis, K., Savranakis, P., Lagoumintzis, G., & Poulas, K. (2019). Real-Time Assessment of E-Cigarettes and Conventional Cigarettes Emissions: Aerosol Size Distributions, Mass and Number Concentrations. Toxics, 7(3), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics7030045








