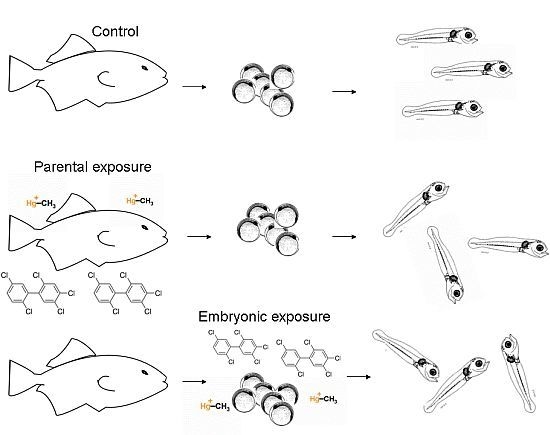
Delayed Behavioral Effects of Early Life Toxicant Exposures in Aquatic Biota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Environmental Chemicals
2.1. Mercury
2.2. Other Metals
2.3. Pesticides
2.4. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and Dioxins
2.5. Contaminants of Emerging Concern: Flame Retardants
2.6. Contaminants of Emerging Concern: Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products
2.7. Oil and Hydrocarbons
3. Discussion of Possible Mechanisms
3.1. Neurotransmitters and Brain Development
3.2. Sense Organs
3.3. Endocrine System
3.4. Mechanisms of Transgenerational Effects
4. Discussion, Conclusions, and Recommendations for Future Research
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimmel, C.A. Behavioral teratology: Overview. Environ. Health Persp. 1976, 18, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.; Levine, T.E. Studies on the behavioral toxicology of environmental contaminants. Environ. Health Persp. 1976, 13, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiard-Triquet, C. Behavioural disturbances: The missing link between sub-organismal and supra-organismal responses to stress? Prospects based on aquatic research. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2009, 15, 87–110. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, J.S.; Smith, G.; Zhou, T.; Santiago-Bass, C.; Weis, P. Effects of contaminants on behavior: Biochemical mechanisms and ecological consequences. BioScience 2001, 51, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mathias, J. The critical period of high mortality of larval fish—A discussion based on current research. Chin. J. Oceanog. Limnol. 1987, 5, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, M.; Linse, J.; Cairncross, C.; Francendese, L.; Kocan, R.M. Reproductive and transgenerational effects of methylmercury or Aroclor 1268 on Fundulus. heteroclitus. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.H. Effects of Prenatal Methylmercury Poisoning upon Growth and Development of Fetal Nervous System. In Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity of Metals; Clarkson, T.W., Nordberg, G.F., Sager, P.R., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 473–495. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, T.W. Mercury: Major issues in environmental health. Environ. Health Persp. 1992, 100, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.S.; Weis, P. Effects of embryonic exposure to methylmercury on larval prey capture ability in the mummichog, Fundulus. heteroclitus. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1995, 14, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.S.; Weis, P. Effects of embryonic and larval exposure to methylmercury on larval swimming performance and predator avoidance in the mummichog, Fundulus. heteroclitus. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Weis, J.S. Swimming behavior and predator avoidance in three populations of Fundulus. heteroclitus larvae after embryonic and/or larval exposure to methylmercury. Aquat. Toxicol. 1998, 43, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Scali, R.; Weis, J.S. Effects of methylmercury on ontogeny of prey capture ability and growth in three populations of larval Fundulus. heteroclitus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Scali, R.; Weis, P.; Weis, J.S. Behavioral effects in mummichog larvae (Fundulus. heteroclitus) following embryonic exposure to methylmercury. Mar. Environ. Res. 1996, 42, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ososkov, I.; Weis, J.S. Development of social behavior in larval mummichogs after embryonic exposure to methylmercury. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1996, 125, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, J.C.; Goodridge, R.; Olubatuyi, F.; Weis, J.S. Delayed effects of embryonic exposure of zebrafish (Danio. rerio) to methylmercury (MeHg). Aquat. Toxicol. 2001, 51, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.E.; Carvan, M.J.; Dellinger, J.A.; Ghorai, J.K.; White, D.B.; Williams, F.E.; Weber, D.N. Developmental selenomethionine and methylmercury exposures affect zebrafish learning. Neurotox. Teratol. 2010, 32, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lamb, C.; Smith, M.; Schaefer, L.; Carvan, M.J., III.; Weber, D.N. Developmental methylmercury exposure affects avoidance learning outcomes in adult zebrafish. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2012, 4, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, M.C.; Murphy, C.A.; Rose, K.A.; McCarthy, I.D.; Fuiman, L.A. Maternal body burden of methylmercury impairs survival skills of offspring in Atlantic croaker (Micropogonias. undulatus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeld, E.; Haugen, T.O.; Vollestad, L.A. Permanent impairment in the feeding behavior of grayling (Thymallus. thymallus) exposed to methylmercury during embryogenesis. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 213, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, C.; Ghorai, J.K.; Zalewski, K.; Weber, D.N. Developmental lead exposure causes startle response deficits in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, O.P.; Rice, K.C. Acid Rain. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1993, 21, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staurnes, M.; Kroglund, F.; Rosseland, B.O. Water quality requirement of Atlantic salmon (Salmo. salar) in water undergoing acidification or liming in Norway. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1996, 85, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staurnes, M.; Hansen, L.P.; Fugelli, K.; Haraldstad, O. Short-term exposure to acid water impairs osmoregulation, seawater tolerance, and subsequent marine survival of smolt of Atlantic salmon (Salmo. salar L.). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1996, 53, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmala, K.; Oshima, Y.; Lee, R.; Imada, N.; Honjo, T.; Kobayashi, K. Transgenerational toxicity of tributyltin and its combined effects with polychlorinated biphenyls on reproductive processes in Japanese medaka (Oryzias. latipes). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, C.M.; Yen, J.; Linney, E.A.; Seidler, F.; Slotkin, T. Silver exposure in developing zebrafish (Danio. rerio): Persistent effects on larval behavior and survival. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.W. Latent behavioural toxicity of copper to sea catfish, Arius felis and sheepshead, Archosargus. probatocephalus. J. Fish. Biol. 1985, 27, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulk, C.K.; Fuiman, L.; Thomas, P. Parental exposure to ortho, para-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane impairs survival skills of Atlantic croaker (Micropogonias. undulatus) larvae. Envir. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 254–262. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.E.; Forward, R.B.; Costlow, J.D. Effects of Embryonic Exposure to Sublethal Concentrations of Dimilin® on the Photobehavior of Grass Shrimp Larvae. In Marine Pollution and Physiology: Recent Advances; Vernberg, F.J., Thurberg, F.P., Calabrese, A., Vernberg, W.B., Eds.; University of South Carolina Press: Columbia, SC, USA, 1985; pp. 377–396. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.E.; Forward, R.B.; Costlow, J.D. Delayed Effects of Diflubenzuron on the Swimming and Vertical Distribution of Palaemonetes. pugio Larvae. In Pollution Physiology of Estuarine Organisms; Vernberg, W.B., Calabrese, A., Thurberg, F.P., Vernberg, F.J., Eds.; University of South Carolina Press: Columbia, SC, USA, 1987; pp. 351–371. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, E.; Baldwin, L.A. Defining hormesis. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2002, 21, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, I.; Fuiman, L.A.; Alvarez, M.C. Aroclor 1254 affects growth and survival skills of Atlantic croaker Micropogonias. undulatus larvae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 252, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollett, D.; Perez, K.E.; King-Heiden, T.C. Embryonic exposure to 2,3,7,8, TCDD impairs prey capture by zebrafish larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couillard, C.M.; Légaré, B.; Bernier, A.; Dionne, Z. Embryonic exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of PCB126 affect prey capture ability of Fundulus. heteroclitus larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaud, C.; Couillard, C.M.; Pellerin, J.; Légaré, B.; Gonzalez, P.; Hodson, P.V. Relative potency of PCB 126 to TCDD for sublethal embryotoxicity in the mummichog (Fundulus. heteroclitus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 129, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Marit, J.S.; Weber, L.P. Persistent effects on adult swim performance and energetics in zebrafish developmentally exposed to 2,3,7,8 tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 106–107, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ross, D.G.; de Vito, M.J.; Crofton, K. Effect of short-term in vivo exposure to polybrominated diphenylethers on thyroid hormones and hepatic enzyme activities in weanling rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 61, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timme-Laragy, A.R.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Developmental and behavioral effects of embryonic exposure to the polybrominated diphenyl mixture DE-71 in the killifish (Fundulus. heteroclitus). Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Reyero, N. Effects of BDE-209 contaminated sediments on zebrafish development and potential implications for human health. Environ. Int. 2014, 63, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Liao, J.; Xu, T.; Bai, C.; Chen, J.; Lin, K.; Huang, C.; Dong, Q. Chronic zebrafish low dose decabrominateddiphenyl ether (BDE-209) exposure affected parental gonad development and locomotion in F1 offspring. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.; Winter, M.J.; Tyler, C.R. Pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: A critical review of the evidence for health effects in fish. Crit. Revs. Toxicol. 2010, 40, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffker, M.; Tyler, C.R. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and sexual behaviours in fish—A critical review on effects and possible consequences. Crit. Revs. Toxicol. 2012, 42, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunder, R.J.; Matthiessen, P.; Sumpter, J.P.; Pottinger, T.G. Impaired reproduction in three-spined sticklebacks exposed to ethinyletradiol as juveniles. Biol. Repro. 2007, 77, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, M.; Rangarajan, S.; Lai, A.; Shaya, L.; Balshine, S.; Wilson, J.Y. Effects of chronic, parental pharmaceutical exposure on zebrafish (Danio. rerio) offspring. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 151, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.M.; Furlong, E.T.; Kolpin, D.W.; Werner, S.L.; Schoenfuss, H.L.; Barber, L.B.; Blazer, V.S.; Norris, D.O.; Vajda, A.M. Antidepressant pharmaceuticals in two U.S. effluent-impacted streams: Occurrence and fate in water and sediment, and selective uptake in fish neural tissue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, M.M.; Buerkley, M.A.; Julius, M.L.; Vajda, A.M.; Norris, D.O.; Barber, L.B.; Furlong, E.T.; Schultz, M.M.; Schoenfuss, H.L. Antidepressants at environmentally relevant concentrations affect predator avoidance behavior of larval fathead minnows (Pimephales. promelas). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 28, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, P.P.; Ford, A.T. The biological effects of antidepressants on the Molluscs and Crustaceans: A review. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 151, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Poi, C.; Darmaillacq, A.-S.; Dickel, L.; Boulouard, M.; Bellanger, C. Effects of perinatal exposure to waterborne fluoxetine on memory processing in the cuttlefish Sepia officianalis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 132–133, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, R.; Short, J.W.; Rice, S.D. Sensitivity of fish embryos to weathered crude oil: Part II. Increased mortality of pink salmon (Oncorhynchus. gorbuscha) embryos incubating downstream from weathered Exxon Valdez crude oil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, R.A.; Rice, S.D.; Wertheimer, A.C.; Bradshaw, R.F.; Thrower, F.P.; Joyce, J.E.; Short, J.W. Delayed effects on growth and marine survival of pink salmon Oncorhynchus. gorbuscha after exposure to crude oil during embryonic development. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 208, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carls, M.G.; Heintz, R.A.; Marty, G.D.; Rice, S.D. Cytochrome P4501A induction in oil exposed pink salmon Oncorhynchus gorbuscha embryos predicts reduced survival potential. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 301, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Sugahara, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Irie, K.; Ishida, M.; Kurokawa, D.; Kitamura, S.; Takata, H.; Handoh, I.C.; Nakayama, K.; et al. Nervous system disruption and concomitant behavioral abnormality in early hatched pufferfish larvae exposed to heavy oil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2488–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrander, G.K.; Landolt, M.; Kocan, R. The ontogeny of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus. kisutch) behavior following embryonic exposure to benzo[a]pyrene. Aquat. Toxicol. 1988, 13, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemby, A.; Smith, R.J. A behavioral assay for assessing effects of pollutants on fish chemoreception. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1986, 11, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colborn, T.; Vom Saal, F.; Soto, A. Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ. Health Persp. 1993, 101, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.R.; Sloman, K.A. The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: Integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.; Donerly, S.; Levin, E.D.; Linney, E.A. Differential acetylcholinesterase inhibition of chlorpyrifos, diazinon and parathion in larval zebrafish. Neurotox. Teratol. 2011, 33, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.M.; Khan, A.T.; Weis, J.S.; Weis, P. Behavior and brain correlates in mummichogs (Fundulus. heteroclitus) from polluted and unpolluted environments. Mar. Environ. Res. 1995, 39, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Rademacher, D.; Steinpreis, R.E.; Weis, J.S. Neurotransmitter levels in two populations of larval Fundulus. heteroclitus after methylmercury exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 1999, 124, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingerman, S.W.; Russell, L.C. Effects of the polychlorinated biphenyl Aroclor 1242 on locomotor activity and the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain of Gulf killifish, Fundulus. grandis. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1980, 25, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Wang, X.; Zuo, Z.; Cai, J.; Wang, C. Tributyltin exposure influences predatory behavior, neurotransmitter content and receptor expression in Sebastiscus. marmoratus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 128–129, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, D.; Williams, P.; Limney, E.; Levin, E.D. Zebrafish provide a sensitive model of persisting neurobehavioral effects of developmental chlorpyrifos exposure: Comparison with nicotine and pilocarpine effects and relationship to dopamine deficits. Neurotox. Teratol. 2010, 32, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Chrysanthis, E.; Yacisin, E.; Linney, E. Chlorpyrifos exposure of developing zebrafish: effects on survival and long-term effects on response latency and spatial discrimination. Neurotox. Teratol. 2003, 25, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, Z.; Li, T.; Jia-Yun, H.; Qiu, J.; Ping-Yao, Z.; Houyan, S. Trans-2-phenyl-cyclopropylamine induces nerve cells apoptosis in zebrafish mediated by depression of LSD1 activity. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.; Zhang, J. Effects of lead on neurogenesis during zebrafish embryonic brain development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 194, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, C.; Zheng, L.; Simonich, M.; Bai, C.; Tanguay, R.; Dong, Q. Trimethyltin chloride (TMT) neurobehavioral toxicity in embryonic zebrafish. Neurotox. Teratol. 2011, 33, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.; Howard, C.V.; Strahle, U.; Cossins, A. Neurodevelopmental defects in zebrafish (Danio. rerio) at environmentally relevant dioxin (TCDD) concentrations. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 76, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.S.; Weis, P. Effects of environmental pollutants on early fish development. Revs. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 1, 45–74. [Google Scholar]
- Baatrup, E.; Doving, K.B.; Winberg, S. Differential effects of mercurial compounds on the electro-olfactogram (EOG) of salmon (Salmo. salar L.). Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 1990, 20, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, K.H. Effects of Pollutants on Olfactory Related Behaviors in Fish and Crustaceans. In Chemical Communications in Crustaceans; Breithaupt, T., Thiel, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 507–529. [Google Scholar]
- Rehnberg, B.C.; Schreck, C.B. Acute metal toxicology of olfaction in coho salmon: Behavior, receptors, and odor-metal complexation. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1986, 36, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, J.; Baldwin, D.H.; Beauchamp, D.A.; Scholz, N.L. Low-level copper exposures increase visibility and vulnerability of juvenile coho salmon to cutthroat trout predators. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreau, N.D.; Pyle, G.G. Effect of copper exposure during embryonic development on chemosensory function of juvenile fathead minnows (Pimephales. promelas). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz, C.J.; Krone, P.H. Cell death, stress-responsive transgene activation, and deficits in the olfactory system of larval zebrafish following cadmium exposure. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2007, 41, 5143–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancalon, P. Degeneration and regeneration of olfactory cells induced by ZnSO4 and other chemicals. Tissue Cell 1982, 14, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.J.; Duff, A.J.; Horsfall, J.S.; Currie, S. Scents and scents-ability: Pollution disrupts social recognition and shoaling in fish. Proc. Biol. Soc. 2008, 275, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Carew, E.; Sloman, K.A. The effects of copper on the morphological and functional development of zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 84, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarria, M.; Santos, M.; Reis-Henriques, M.A.; Viera, N.; Monteiro, N.M. The unpredictable effects of mixtures of androgenic and estrogenic chemicals on fish early life. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 416–424. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, P.S.; Tillitt, D.E. 2,3,7,8-TCDD effects on visual structure and function in swim-up rainbow trout. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2004, 38, 6300–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, M.R.; Julius, M.L.; Vajda, A.M.; Norris, D.O.; Barber, L.B.; Schenfuss, H.L. Predator avoidance performance of larval fathead minnow (Pimephales. promelas) following short-term exposure to estrogen mixtures. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 91, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bistodeau, T.J.; Barber, L.B.; Bartell, S.E.; Cediel, R.A.; Grove, K.J.; Klaustermeier, J.; Woodard, J.C.; Lee, K.E.; Schoenfuss, H.L. Larval exposure to environmentally relevant mixtures of alkylphenolethoxylates reduces reproductive competence in male fathead minnows. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 79, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.B.; Adams, A.; Cyr, D.G.; Eales, G. Contaminant effects on the teleost fish thyroid. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 1680–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, S.M.; Alkindi, A.Y.; Waring, C.; Brown, J.A. Corticolsteroid and thyroid responses of larval and juvenile turbot exposed to the water-soluble fraction of crude oil. J. Fish. Biol. 1997, 50, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spachmo, B.; Arukwe, A. Endocrine and developmental effects in Atlantic salmon (Salmo. salar) exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonic or perfluorooctane carboxylic acids. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 108, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; John-Alder, H.B.; Weis, P.; Weis, J.S. Thyroidal status of mummichogs (Fundulus. heteroclitus) from a polluted versus a reference habitat. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 2817–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossniklaus, U.; Kelly, W.G.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; Pembrey, M.; Lindquist, S. Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: How important is it? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Whitelaw, E. The case for transgenerational epigenetic inheritance in humans. Mamm. Genome 2008, 19, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, D.; Gore, A. Epigenetic synthesis: A need for a new paradigm for evolution in a contaminated world. F 1000 Biol. Rep. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöikki, M.; Kangassalo, K.; Rantala, M. Transgenerational effects of heavy metal pollution on immune defense of the blowfly, Protophormia. terraenovaei. PLoS One 2012, 7, e38832. [Google Scholar]
- Crews, D.; Gore, A.C.; Hsu, T.S.; Dangleben, N.L.; Spinetta, M.; Schallert, T.; Anway, M.D.; Skinner, M.K. Transgenerational epigenetic imprints on mate preference. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5942–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anway, M.D.; Cupp, A.S.; Uzumcu, M.; Skinner, M.K. Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors and male fertility. Science 2005, 308, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, J.T.; Edwards, M.; Shetty, S.R.; Gatewood, J.D.; Taylor, J.A.; Rissman, E.F.; Connelly, J.J. Gestational exposure to bisphenol a produces transgenerational changes in behaviors and gene expression. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, J.A.; Dolinoy, D.; Basu, N. Epigenetics for ecotoxicologists. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, A. Developmental programming and endocrine disruptor effects on reproductive neuroendocrine systems. Front. Neuroendocrin. 2008, 29, 358–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.; Gore, A. Transgenerational neuroendocrine disruption of reproduction. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.J.; Sweatt, J.D. DNA methylation and memory formation. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1319–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Campbell, S.L.; Le, T.; Li, E.; Sweatt, J.D.; Silva, A.J.; Fan, G. Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a maintain DNA methylation and regulate synaptic function in adult forebrain neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.; Ezra-Nevo, G.; Regev, L.; Neufeld-Cohen, A.; Chen, A. Resilience to social stress coincides with functional DNA methylation of the Crf. gene in adult mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1351–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Devel. Dynam. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J.; Weis, P. Effects of exposure to lead on behavior of mummichog larvae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1998, 222, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuiman, L.A.; Cowan, J.; Smith, M.E.; O’Neal, J.P. Behavior and recruitment success in fish larvae: Variation with growth rate and the batch effect. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.M.; Weis, J.S. Predator/prey interactions of the mummichog, Fundulus. heteroclitus: Effects of living in a polluted environment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1997, 209, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmuth, J.M.; Roudez, R.; Glover, T.; Weis, J.S. Differences in prey capture behavior in populations of blue crab (Callinectes. sapidus Rathbun) from contaminated and clean estuaries in New Jersey. Estuaries Coasts 2009, 32, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Weis, J.S. Delayed Behavioral Effects of Early Life Toxicant Exposures in Aquatic Biota. Toxics 2014, 2, 165-187. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics2020165
Weis JS. Delayed Behavioral Effects of Early Life Toxicant Exposures in Aquatic Biota. Toxics. 2014; 2(2):165-187. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics2020165
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeis, Judith S. 2014. "Delayed Behavioral Effects of Early Life Toxicant Exposures in Aquatic Biota" Toxics 2, no. 2: 165-187. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics2020165
APA StyleWeis, J. S. (2014). Delayed Behavioral Effects of Early Life Toxicant Exposures in Aquatic Biota. Toxics, 2(2), 165-187. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics2020165