Degradation of Typical PPCPs During Anaerobic Digestion and in Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standards and Chemicals
2.2. Anaerobic Digestion of Compounds in Sludge
2.3. Degradation of Compounds in Soil
2.4. Instrumental Analysis of Residual Compounds
2.4.1. Extraction of Dissolved Compounds in Supernatant Fraction of Sludge
2.4.2. Extraction of Extractable Adsorbed Compounds in Solid Fraction of Sludge
2.4.3. Extraction of Residual Compounds in Soil
2.4.4. Instrumental Conditions
2.5. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
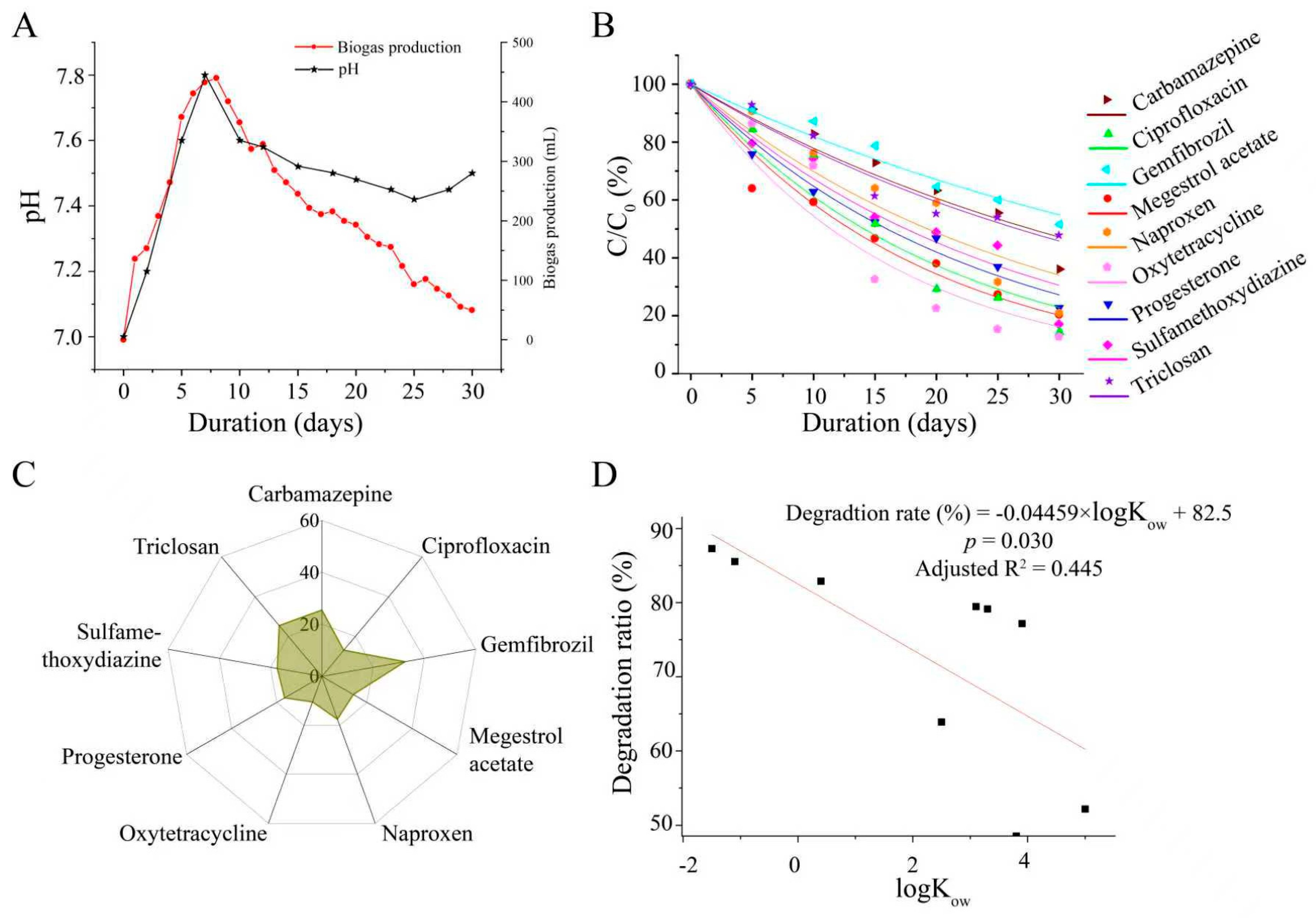
3.1. Anaerobic Degradation of the Targeted PPCPs in Anaerobic Sludge
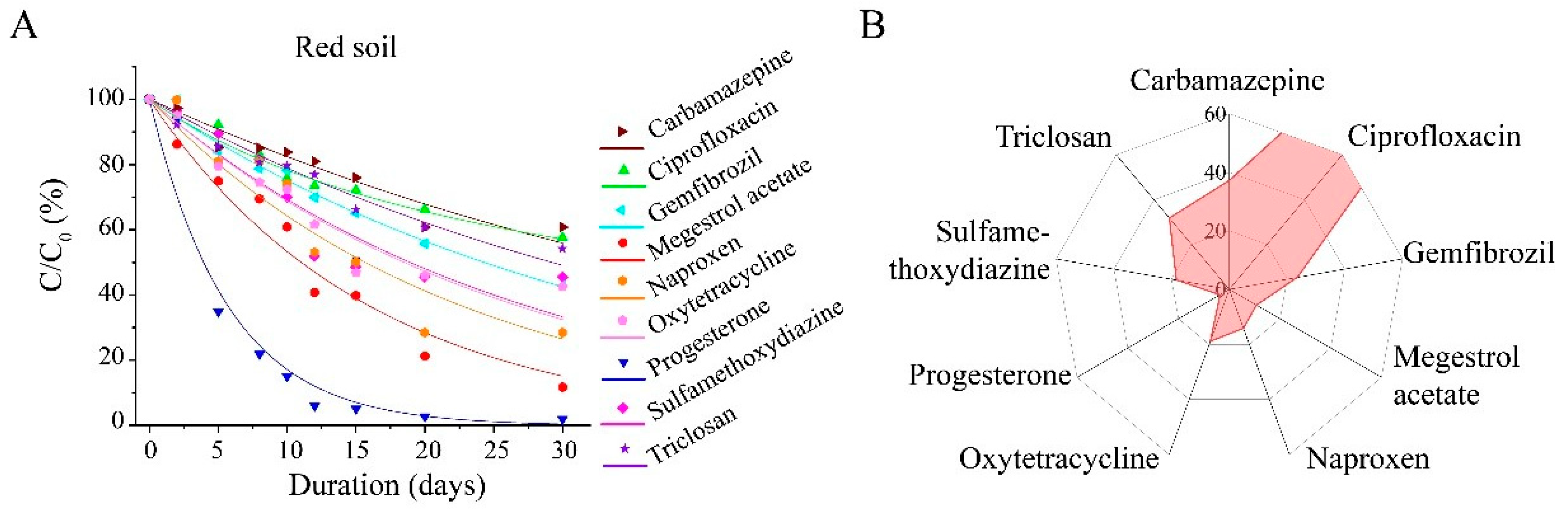
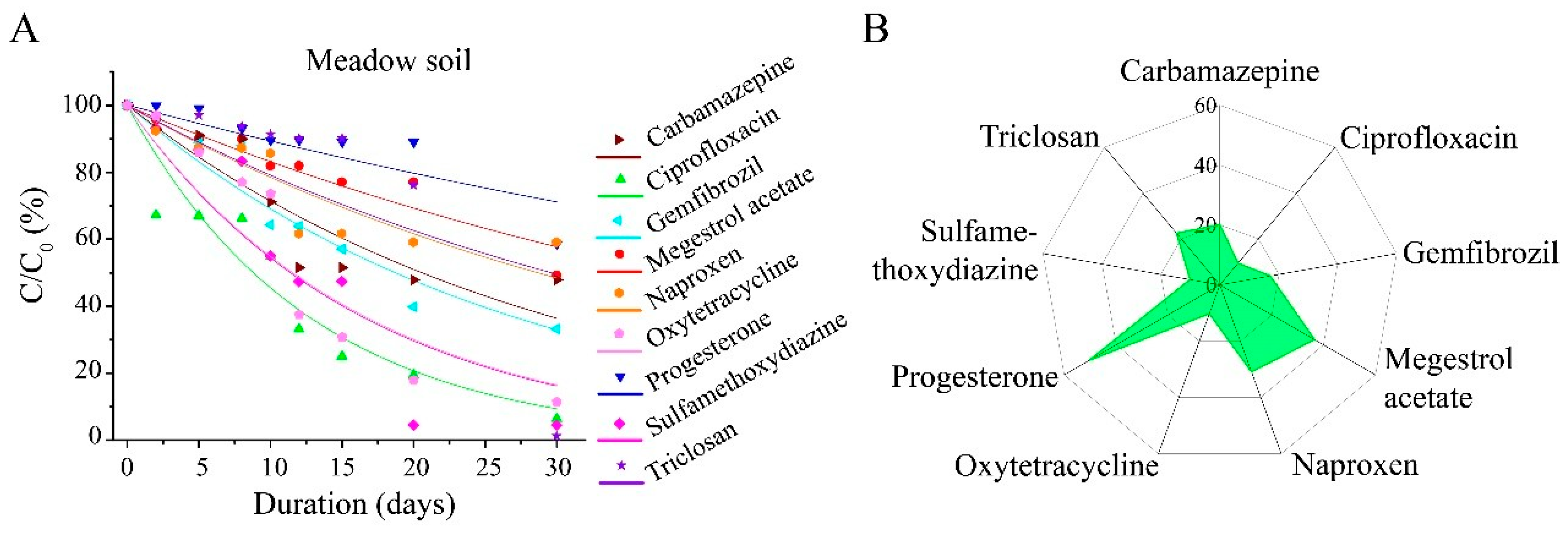
3.2. Degradation of PPCPs in Three Soils
3.3. Impact of Soil Physicochemical Properties on the Degradability of Nine PPCPs
3.4. Fate of Degradation of Nine PPCPs in Anaerobic Sludge Digestion and Land Use Scenarios
4. Environmental Implications and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Tian, L.X.; Zhu, T.T.; Zhao, Y.X.; Tong, Y.D.; Yang, Y.K.; Sun, P.Z.; Liu, Y.W. Effect, fate and remediation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) during anaerobic sludge treatment: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 19095–19114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, S.; Sevda, S. Biological Treatment of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs). In Biotechnology for Environmental Protection; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevin, B.; Pierre, B.; Laure, M.; Dominique, P. Transformation of PPCPs in the environment: Review of knowledge and classification of pathways according to parent molecule structures. Crit. Rev. Eeviron. Sci. Technol. 2022, 53, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.F.; Powers, S.M.; Hampton, S.E. An evidence synthesis of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the environment: Imbalances among compounds, sewage treatment techniques, and ecosystem types. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12961–12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, G. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the aquatic environment in China: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizmas, L.; Sharma, V.K.; Gray, C.M.; McDonald, T.J. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in waters: Occurrence, toxicity, and risk. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenborn, R.; Brorström-Lundén, E.; Reiersen, L.-O.; Wilson, S. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Arctic environments: Indicator contaminants for assessing local and remote anthropogenic sources in a pristine ecosystem in change. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 33001–33013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Sanderson, H.; Roy, K.; Benfenati, E.; Leszczynski, J. Ecotoxicological assessment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products using predictive toxicology approaches. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brausch, J.M.; Connors, K.A.; Brooks, B.W.; Rand, G.M. Human Pharmaceuticals in the Aquatic Environment: A Review of Recent Toxicological Studies and Considerations for Toxicity Testing. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 218, pp. 1–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.K.; Rehman, M.Y.A.; Malik, R.N. Fate and toxicity of pharmaceuticals in water environment: An insight on their occurrence in South Asia. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 111030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xi, H.; Xu, L.; Jin, M.; Zhao, W.; Liu, H. Ecotoxicological effects, environmental fate and risks of pharmaceutical and personal care products in the water environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, R.B.; Gil-Solsona, R.; Subirats, J.; Restrepo-Montes, E.; Zaiat, M.; Santos-Neto, Á.J.; Gago-Ferrero, P. Biotransformation pathways of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) during acidogenesis and methanogenesis of anaerobic digestion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozhdeh, A.; Hossein, A.; Chen, C.; Besalatpour, A.A. Fate of organic pollutants in sewage sludge during thermal treatments: Elimination of PCBs, PAHs, and PPCPs. Fuel 2022, 319, 123864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biel-Maeso, M.; Corada-Fernández, C.; Lara-Martín, P.A. Monitoring the occurrence of pharmaceuticals in soils irrigated with reclaimed wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Mao, R.; Cao, Z.; Song, S. Contamination, transport, and ecological risks of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a large irrigation region. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Snyder, S.A.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Which Micropollutants in Water Environments Deserve More Attention Globally? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 31270.1-2014; Test Guidelines on Environmental Safety Assessment for Chemical Pesticides-Part 1: Transformation in soils. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Bohaty, R.; Eckel, W.; Shamim, M.; Spatz, D.; White, W.; Young, D. Standard Operating Procedure for Using the NAFTA Guidance to Calculate Representative Half-Life Values and Characterizing Pesticide Degradation. 2015. Available online: https://19january2017snapshot.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-08/documents/ftt_sop_using_nafta_guidance_version2.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2015).
- Dai, X.; Duan, N.; Dong, B.; Dai, L. High-solids anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste in comparison with mono digestions: Stability and performance. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.A.; Mehta, C.M.; Batstone, D.J. Low pH anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge for enhanced phosphorous release. Water Res. 2015, 81, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Chen, Y.; Ndegwa, P. Association between methane yield and microbiota abundance in the anaerobic digestion process: A meta-regression. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.; Flowers, R.; McAvoy, D.; Dickenson, E. Biotransformation of trace organic compounds by activated sludge from a biological nutrient removal treatment system. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Patrolecco, L.; Ademollo, N.; Tolomei, A.; Barra Caracciolo, A. Degradation of Gemfibrozil and Naproxen in a river water ecosystem. Microchem. J. 2013, 107, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.; Sindhu, R.; Chaturvedi Bhargava, P. Biodegradation of emerging organic pollutant gemfibrozil: Mechanism, kinetics and pathway modelling. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 374, 128749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, H.; Xue, Y.; Wang, H.; Dai, X. Partition and fate analysis of fluoroquinolones in sewage sludge during anaerobic digestion with thermal hydrolysis pretreatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, R. Variation of antibiotics in sludge pretreatment and anaerobic digestion processes: Degradation and solid-liquid distribution. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 255, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebele, A.J.; Abou-Elwafa Abdallah, M.; Harrad, S. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the freshwater aquatic environment. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, V.G.; Stasinakis, A.S.; Mamais, D.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Lekkas, T.D. Fate of selected pharmaceuticals and synthetic endocrine disrupting compounds during wastewater treatment and sludge anaerobic digestion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizel, A.; Schlüsener, M.P.; Dierkes, G.; Wick, A.; Ternes, T.A. Ternes. Analysis of the aerobic biodegradation of glucocorticoids: Elucidation of the kinetics and transformation reactions. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brausch, J.M.; Rand, G.M. Rand. A review of personal care products in the aquatic environment: Environmental concentrations and toxicity. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spongberg, A.L.; Witter, J.D.; Acuña, J.; Vargas, J.; Murillo, M.; Umaña, G.; Gómez, E.; Perez, G. Reconnaissance of selected PPCP compounds in Costa Rican surface waters. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6709–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.C.; Mohamad-Nasir, N.; Hashim, S.N.; Lokman, N.F.; Wong, K.K. Biodegradation of carbamazepine by bacterial mixed culture: An enzymatic insight. Curr. Top. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Yun, R.; Li, L.; Chilouch, C. Study on the occurrence forms of oxytetracycline and sulfamethoxazole in saline soil and their influencing factors. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, G.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, X. Biotransformation of cyproterone acetate, drospirenone, and megestrol acetate in agriculture soils: Kinetics, microbial community dynamics, transformation products, and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; He, Z.; Li, Y. Sorption, desorption, and transformation of synthetic progestins in soil and sediment systems. Geoderma 2020, 362, 114141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xue, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Liang, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, X. Biotransformation kinetics and pathway of typical synthetic progestins in soil microcosms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, W.; Price, G.; Jamieson, R.; Lake, C. Biodegradation kinetics of individual and mixture non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in an agriculture soil receiving alkaline treated biosolids. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Yang, K.; Jia, R.; Tian, C.; Zhu, Y. Degradation of triclosan and carbamazepine in two agriculture and garden soils with different textures amended with composted sewage sludge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of sewage application in agricultural on soil environment. Sichuan Environ. 2011, 30, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Davidson, R.; Jones, K. Screening the environmental fate of organic contaminants in sewage sludge applied to agricultural soils: II. The potential for transfers to plants and grazing animals. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 185, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Duarte-Davidson, R.; Jones, K. Screening the environmental fate of organic contaminants in sewage sludges applied to agricultural soils: 1. The potential for downward movement to groundwaters. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 185, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Ying, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Field dissipation of benzotriazole and 5-methyl-1H-benzotriazole in biosolids-amended soils. Guangzhou Chem. 2017, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soil Type | pH | Organic Matter (%) | Cation Substitution Amount (cmol(+)/kg) | Soil Particle Content ᴡ/% | Texture | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Grain (2–0.05 mm) | Powder Particles (0.05–0.002 mm) | Viscous Particles (<0.002 mm) | |||||
| Red Soil | 4.60 | 1.36 | 11.53 | 15.00 | 42.76 | 42.24 | Chalk clay |
| Black Earth | 7.28 | 6.54 | 28.87 | 39.04 | 38.80 | 22.16 | Loamy soil |
| Meadow soil | 7.96 | 6.85 | 22.13 | 11.96 | 73.20 | 14.84 | Powdered sandy loam |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Xu, L.; Guo, L.; Hu, J.; Liu, R. Degradation of Typical PPCPs During Anaerobic Digestion and in Soil. Toxics 2025, 13, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090780
Guo M, Xu L, Guo L, Hu J, Liu R. Degradation of Typical PPCPs During Anaerobic Digestion and in Soil. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090780
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Min, Linyue Xu, Liguo Guo, Jie Hu, and Ru Liu. 2025. "Degradation of Typical PPCPs During Anaerobic Digestion and in Soil" Toxics 13, no. 9: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090780
APA StyleGuo, M., Xu, L., Guo, L., Hu, J., & Liu, R. (2025). Degradation of Typical PPCPs During Anaerobic Digestion and in Soil. Toxics, 13(9), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090780






