Human Health Consumption Risk Assessment of Trace Metal Content in the Triggerfish Balistes spp. from the RAMSAR Site 1826 San Ignacio-Navachiste-Macapule Lagoon Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
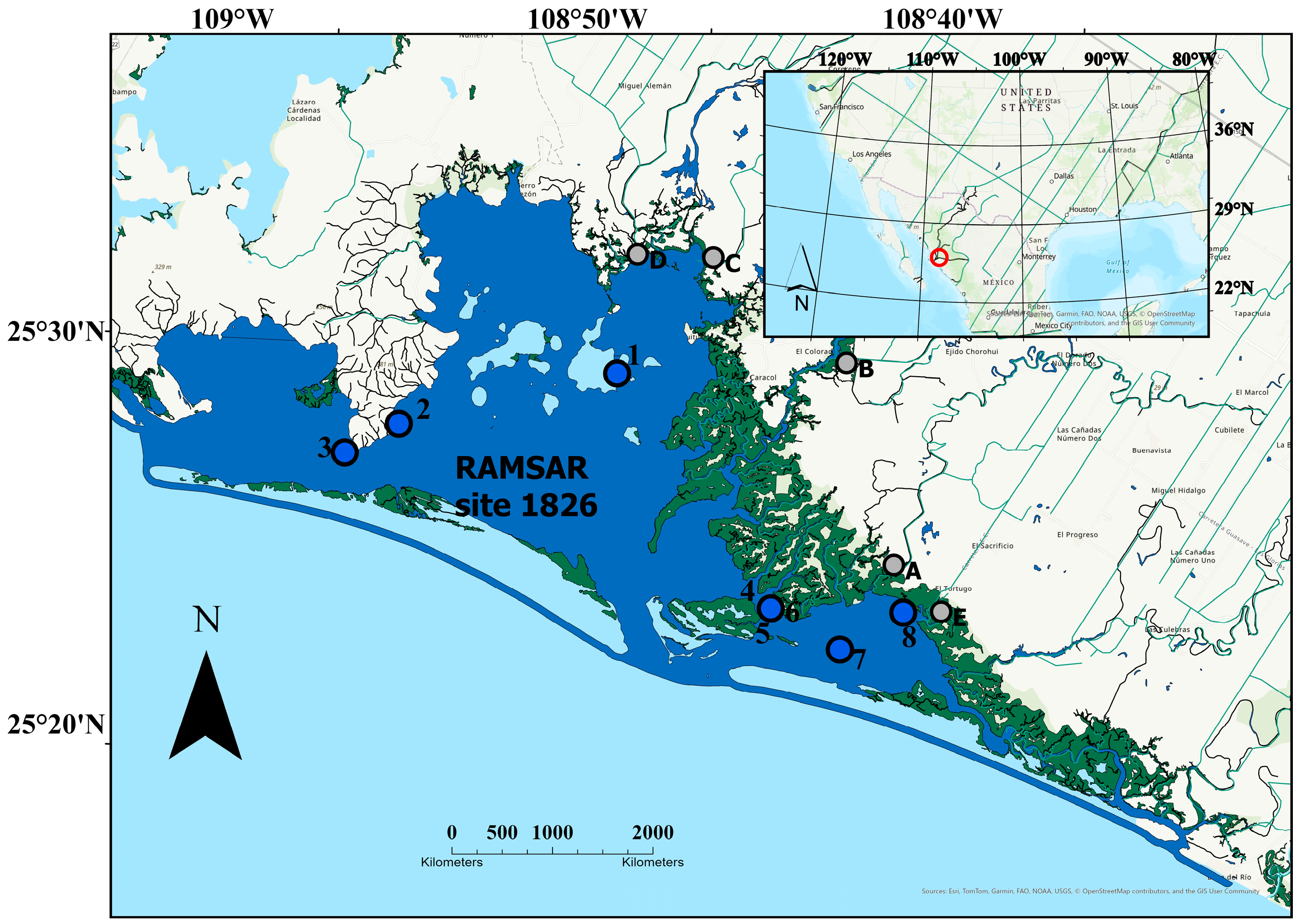
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. TM Analysis
2.5. Estimated Daily Intake (EDI)
2.6. Non-Carcinogenic Risk (THQ)
Hazzard Index (HI)
2.7. Carcinogenic Risk
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
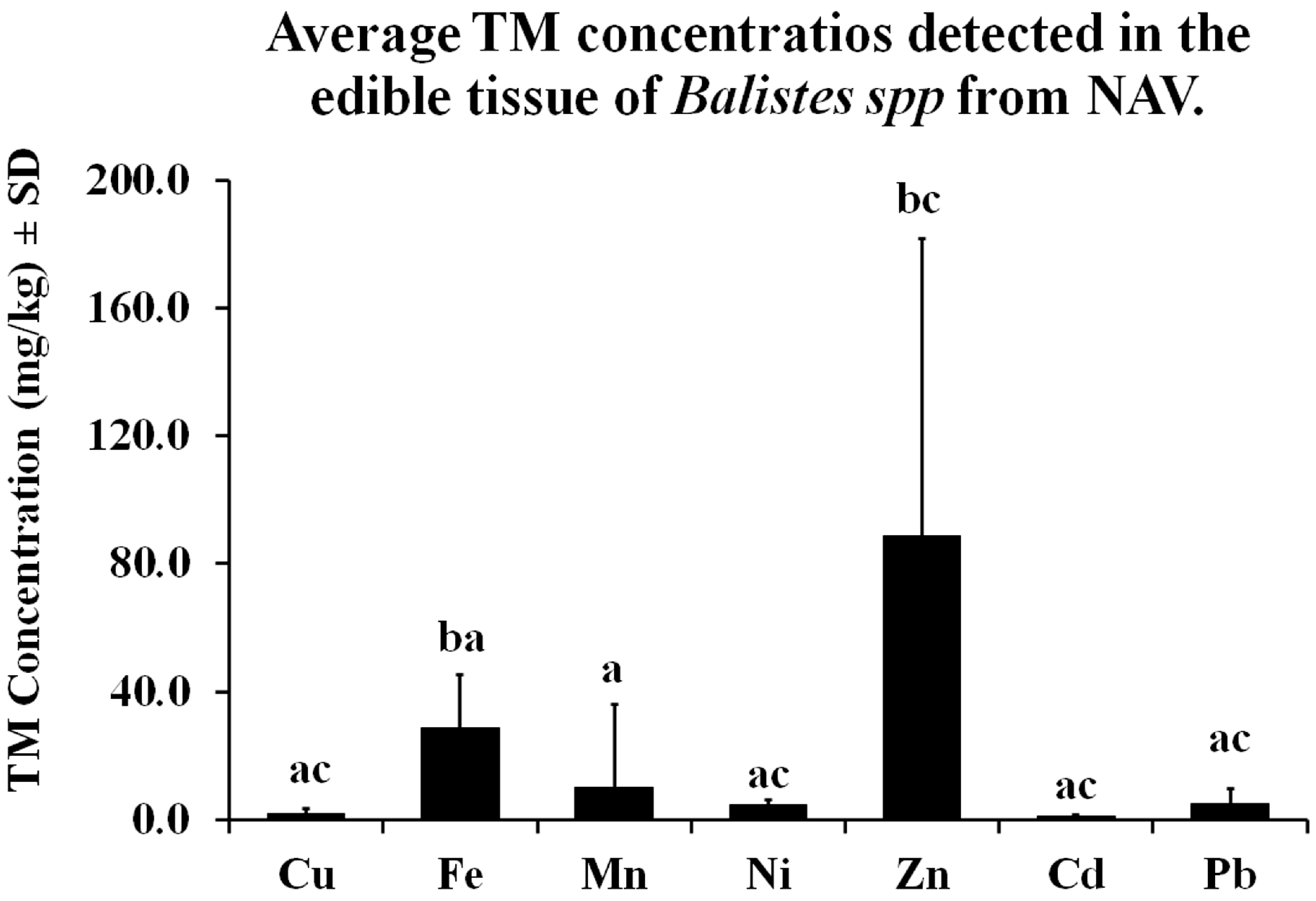
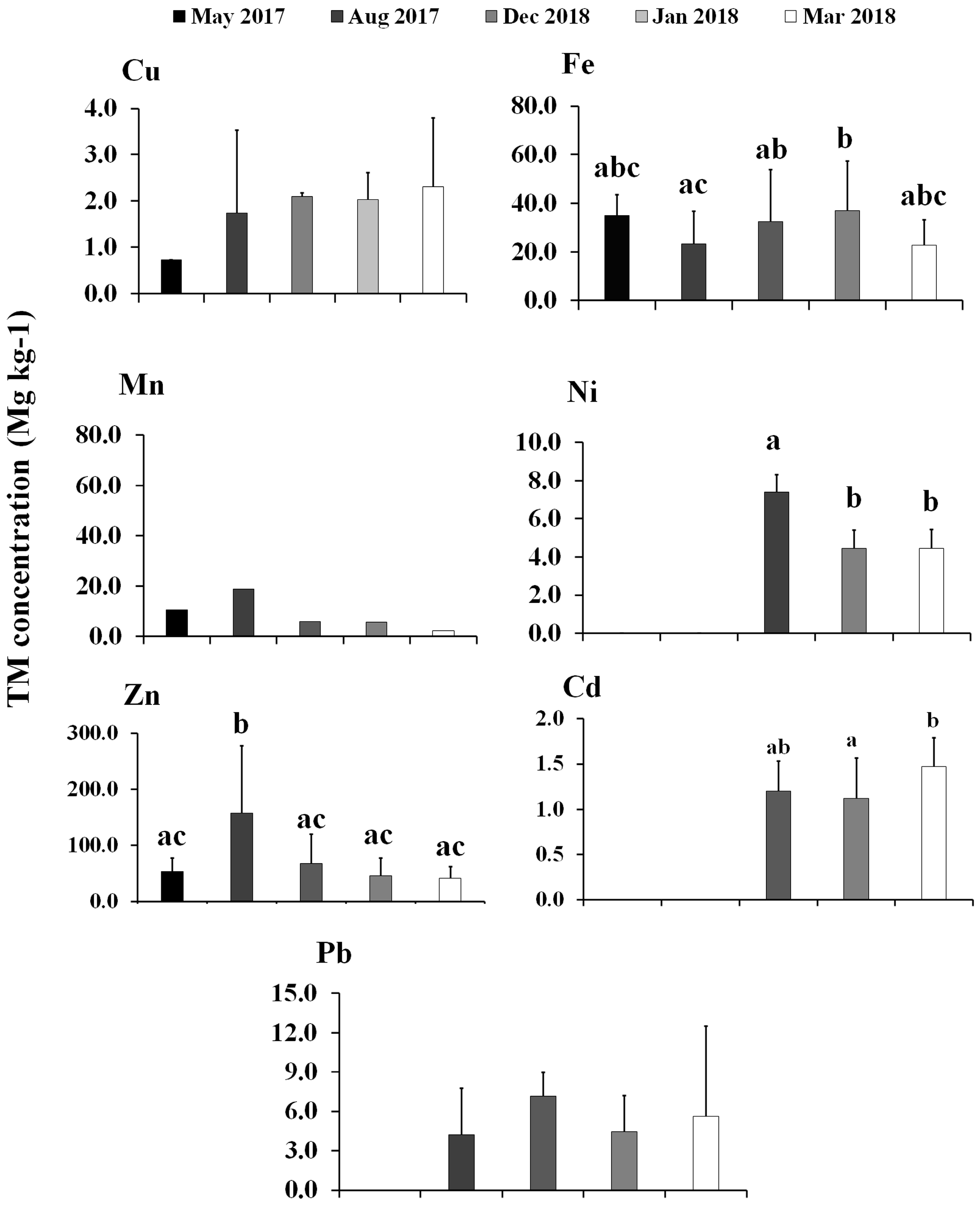
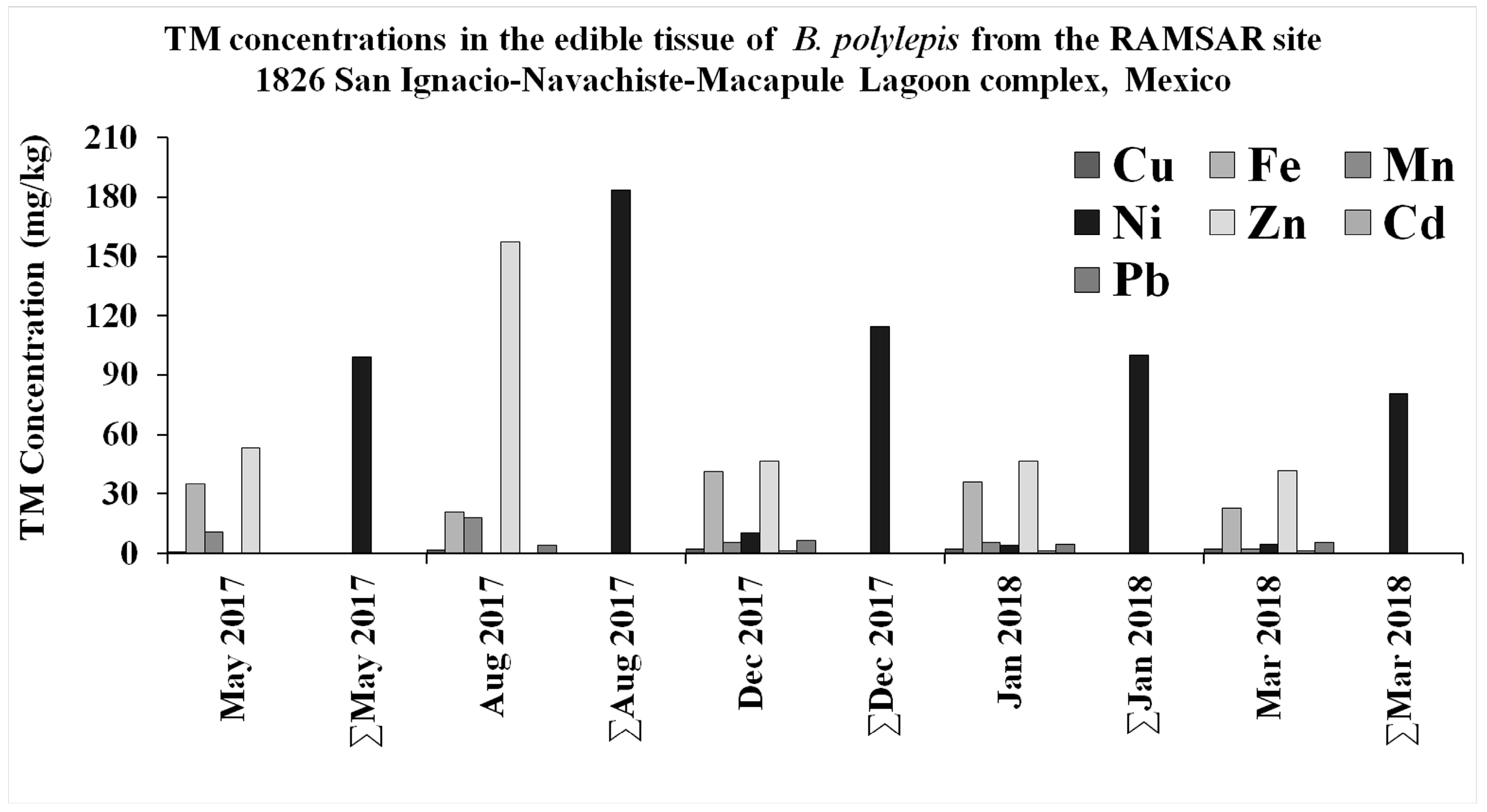
3.1. Trace Metal Concentrations
3.2. Estimated Daily Intake
3.3. Non-Carcinogenic (THQ) and HI
3.4. Carcinogenic Risk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Sun, G. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Contamination in Black Soil at Sanjiang Plain: From Source Analysis to Health Risk Assessment. Processes 2024, 12, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Prieto, M.C.; Luna-González, A.; Espinoza-Tenorio, A.; González-Ocampo, H.A. Planning ecotourism in coastal protected areas; projecting temporal management scenarios. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simou, A.; Sarti, O.; Abdelfattah, B.; Mrabet, A.; Khaddor, M.; Allali, N. Assessing ecological and health risks of potentially toxic elements in marine and beach sediments of Tangier Bay, Southwestern Mediterranean sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, P.A.R.; Alonso, R.Á.; Valsero, J.J.D.; García, R.M.; Cabrera, F.Á.; Cosío, E.L.; Laforet, S.D. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in marine sediments from southwest of Mallorca island, Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 16852–16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, M.; Melo, R.C.B.; Whitfield, A.K. Past and present conservation of south American estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 295, 108542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Pachón, T.A.; López-Vivas, J.M.; Mazariegos-Villarreal, A.; León-Cisneros, K.; Medina-López, M.A.; Barjau González, E.; Serviere-Zaragoza, E. Diet of the finescale triggerfish, Balistes polylepis (Steindachner), in the Gulf of California. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2023, 74, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez-Osuna, F.; Osuna-Martínez, C.C. Bioavailability of cadmium, copper, mercury, lead, and zinc in subtropical coastal lagoons from the southeast Gulf of California using mangrove oysters (Crassostrea corteziensis and Crassostrea palmula). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abelardo Gonzalez-Ocampo, H.; Parra-Olivas, M.C.; Pérez-González, E.; Rodríguez-Meza, G.D. Rhizophora mangle L. bioindicator of environmental exposure to heavy metals in the Navachiste lagoon complex, Sinaloa, Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granados-Galván, I.A.; Rodríguez-Meza, D.G.; Luna-González, A.; González-Ocampo, H.A. Human health risk assessment of pesticide residues in snappers (Lutjanus) fish from the Navachiste Lagoon complex, Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Armenta, G.; Pérez-González, E.; Rodríguez-Meza, G.D.; González-Ocampo, H.A. Health risk of consuming Sphoeroides spp. from the Navachiste Lagoon complex due to its trace metals and organochlorine pesticides content. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Montiel, N.J.; Santamaría-Miranda, A.; Rodríguez-Meza, G.D.; Galindo-Reyes, J.G.; González-Ocampo, H.A. Concentrations of organochlorine pesticides in fish (Mugil cephalus) from a coastal ecosystem in the southwestern gulf of California. Biol. Environ. Proc. R. Ir. Acad. 2013, 113B, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, C.H.; Sotelo-Gonzalez, M.I.; Osuna-Martínez, C.C.; Frías-Espericueta, M.G.; Sánchez-Cárdenas, R.; Bergés-Tiznado, M.E.; Góngora-Gómez, A.M.; García-Ulloa, M. Biomonitoring of potentially toxic elements through oysters (Saccostrea palmula and Crassostrea corteziensis) from coastal lagoons of Southeast Gulf of California, Mexico: Health risk assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 2329–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eschmeyer, W.N.; Herald, E.S. A Field Guide to Pacific Coast Fishes: North America; Houghton Mifflin Harcourt: Boston, MA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Humann, P.; DeLoach, N. Reef Fish Identification: Galápagos; New World Publications, Inc.: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Barroso-Soto, I.; Castillo-Gallardo, E.; Quiñonez-Velázquez, C.; Morán-Angulo, R.E. Age and growth of the finescale triggerfish, Balistes polylepis (Teleostei: Balistidae), on the coast of Mazatlán, Sinaloa, Mexico. Pac. Sci. 2007, 61, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, J.; Herrera-Valdivia, E.; Nevárez-López, C.A.; Rodríguez-Romero, J. Population aspects of the cochito fish Balistes (Steindachner, 1876) as a component of the accompanying fauna of shrimp in the Gulf of California, Mexico. [Aspectos poblacionales del pez cochito Balistes (Steindachner, 1876) como componente de la fauna de acompañamiento del camarón en el Golfo de California, México). In Effects of Trawling in the Gulf of California [Efectos de la Pesca de Arrastre en el Golfo de California], 1st ed.; López Martínez, J., Morales Bojórquez, E., Eds.; Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas del Noroeste, SC y Fundación Produce Sonora: Sonora, México, 2012; pp. 205–215. Available online: https://www.cibnor.mx/images/stories/posgrado/otros/capitulo%2011.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Pauly, D.; Froese, R. FishBase. A Global Information System on Fishes. 2025. Available online: https://www.fishbase.us/ (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Serviere-Zaragoza, E.; Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Mazariegos-Villarreal, A.; Balart, E.F.; Valencia-Valdez, H.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C. Cadmium, lead, copper, zinc, and iron concentration patterns in three marine fish species from two different mining sites inside the Gulf of California, Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serviere-Zaragoza, E.; Mazariegos-Villarreal, A.; Balart, E.F.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Acosta-Pachón, T.A. Diet and trophic position of three common rocky reef fish at two locations in the Gulf of California. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 47, 101964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasquilla-Henao, M.; González Ocampo, H.A.; Luna González, A.; Rodríguez Quiroz, G. Mangrove forest and artisanal fishery in the southern part of the Gulf of California, Mexico. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 83, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RAMSAR. RAMSAR Sites Information Service. In Ficha Informativa de los Humedales de Ramsar (FIR)—Sistema Lagunar San Ignacio-Navachist-Macapule, 2006–2008 ed.; The Secretariat of the Convention on Wetlands: Gland, Switzerland, 2025; p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo-Urias, D.; Martinez-Lopez, A. Eutrophication Process on Coastal Lagoons of North of Sinaloa, Mexico. In Proceedings of AGU Spring Meeting Abstracts, Acapulco, Mexico, 22 May 2007; p. OS34B-03. [Google Scholar]
- CONAPESCA. Commercial Fishing Permit [Permiso Para Pesca Comercial]. In CONAPESCA-01-068, ONAPESCA, Ed. 2025; SAGARPA: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2025; Available online: https://www.gob.mx/public/tramites/detalleTramite.xhtml?homoclave=CONAPESCA-01-068 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Lockwood, A.P.M. Effects of Pollutants on Aquatic Organisms; CUP Archive; Cambrigde University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1976; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Botello, A.V. Golfo de México: Contaminación e Impacto Ambiental: Diagnóstico y Tendencias; Universidad Juarez Autónoma de Tabasco: Villahermosa, Mexico, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- DOF. NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-117-SSA1-1994, Bienes y Servicios. Método de Prueba para la Determinación de Cadmio, Arsénico, Plomo, Estaño, Cobre, Fierro, Zinc y Mercurio en Alimentos, Agua Potable y Agua Purificada por Espectrometrí a de Absorción Atómica; Federación, D.O.d.l., Ed.; Secretaria de Gobernación: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 1995; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, N.; Mollah, M.Z.I.; Alam, M.F.; Safiur Rahman, M. Seasonal investigation of heavy metals in marine fishes captured from the Bay of Bengal and the implications for human health risk assessment. Food Control 2016, 70, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Human Health Risk Assessment Protocol for Hazardous Waste Combustion Facilities, Appendix C, Risk Characterization Equations; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 810. [Google Scholar]
- CONAPO. Demographic Reconciliation Databases 1950 to 2019 and Projections of the Population of Mexico 2020 to 2070 [Bases de Datos de la Conciliación Demográfica 1950 a 2019 y Proyecciones de la Población de México 2020 a 2070]; Consejo Nacional de Población [Census Bureau]: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2023; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- DGSIAP. Agri-Food Panorama [Panorama Agroalimentario], 1st ed.; General Directorate of the Agri-Food and Fisheries Information Service [Dirección General del Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera]: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2025; 232p. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Vol. I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; p. 291. [Google Scholar]
- Gnonsoro, U.P.; Ake Assi, Y.E.D.; Sangare, N.S.; Kouakou, Y.U.; Trokourey, A. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals (Pb, Cd, Hg) in Hydroalcoholic Gels of Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 2510–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATSDR. Public Health Assessment Guidance Manual; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Guidance for Assessing Chemical Contaminant Data for Use in Fish Advisories: Risk Assessment and Fish Consumption Limit, 3rd ed.; Unites States Environmental Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; p. 383. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-06/documents/volume2.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Wang, C.-x.; Liu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, L.; Wu, H. Investigation and Evaluation of the Healthy Risk of Heavy Metal Contents in Astragalus membranaceus of Shaanxi Province. J. Food Prot. 2025, 88, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasavada, N. One-Way ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) with Post-Hoc Tukey HSD (Honestly Significant Difference). Test Calculator for Comparing Multiple Treatments. Available online: https://astatsa.com/OneWay_Anova_with_TukeyHSD/ (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- EUC. European Commission Regulation, No. 1881/2006. Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nauen, C.E. Compilation of legal limits for hazardous substances in fish and fishery products. FAO Fish. Circ. (FAO) 1983, 764, 102. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Toxicological Review of Zinc and Compounds; Unites States Environmental Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 6, pp. 7440–7466. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. IRIS Assessments. List of Substances on IRIS 2025. 30 July 2025. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/iris (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Gochis, D.J.; Brito-Castillo, L.; Shuttleworth, W.J. Hydroclimatology of the North American Monsoon region in northwest Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2006, 316, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higareda, C.E.R.; Guevara, L.I.P.; León, S.C.; Zazueta, J.G.S.; Martínez, J.C. Analysis of rainfall variables trends and potential vegetation responses in Sinaloa, México. Am. J. Clim. Change 2014, 3, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peinado Guevara, H.J.; Espinoza Ortiz, M.; Peinado Guevara, V.M.; Herrera Barrientos, J.; Peinado Guevara, J.A.; Delgado Rodríguez, O.; Pellegrini Cervantes, M.d.J.; Sánchez Morales, M. Potential Flood Risk in the City of Guasave, Sinaloa, the Effects of Population Growth, and Modifications to the Topographic Relief. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Pesticide Residues in Food and Feed. Pesticide Index. 2013. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/343b0b84-d8fd-4c94-9327-5df9d543f18f/content (accessed on 10 August 2013).
- Peana, M.; Pelucelli, A.; Medici, S.; Cappai, R.; Nurchi, V.M.; Zoroddu, M.A. Metal toxicity and speciation: A review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 7190–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Elenes, M.; Rodríguez-Meza, G.D.; Pérez-González, E.; González-Ocampo, H.A. Trace Metal Residues in Swimming Warrior Crab Callinectes bellicosus: A Consumption Risk. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 772221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Hossain, M.B.; Choudhury, T.R.; Yu, J.; Rana, M.S.; Noman, M.A.; Hosen, M.M.; Paray, B.A.; Arai, T. Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Cultured Shrimp and Aquaculture Sludge. Toxics 2022, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuksezgin, F.; Pazi, I.; Gonul, L.T. Environmental impact of fish farming: Assessment of metal contamination and sediment geochemistry at three aquaculture areas from the eastern Aegean coast. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, S.; Song, Y.; Pan, J.; Guo, P. Bioavailability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of marine aquaculture in Zhelin Bay. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2019, 39, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogruyol, H.; Can Tunçelli, İ.; Özden, Ö.; Erkan, N.; Karakulak, F.S. Bioaccumulation of Mercury, Cadmium, Lead, and Arsenic in Whiting and Tub Gurnard From the Sea of Marmara: Implications for Human Health. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Chao, L.; Hou, L.; Wang, Y.; Chu, J.; Sun, J. Distribution, trophic magnification and risk of trace metals and perfluoroalkyl acids in marine organisms from Haizhou Bay. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalipci, E.; Cüce, H.; Ustaoğlu, F.; Dereli, M.A.; Türkmen, M. Toxicological health risk analysis of hazardous trace elements accumulation in the edible fish species of the Black Sea in Türkiye using multivariate statistical and spatial assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 97, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucuksezgin, F.; Altay, O.; Uluturhan, E.; Kontas, E. Trace metal and organochlorine residue levels in red mullet (Mullus barbatus) from the eastern Aesgean, Turkey. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2327–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauffret, A.; Chouvelon, T.; Wessel, N.; Cresson, P.; Bănaru, D.; Baudrier, J.; Bustamante, P.; Chekri, R.; Jitaru, P.; Le Loc’h, F.; et al. Trace elements, dioxins and PCBs in different fish species and marine regions: Importance of the taxon and regional features. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Fuentes, E.; Moity, N.; Ramírez-González, J.; Andrade-Vera, S.; Hardisson, A.; González-Weller, D.; Paz, S.; Rubio, C.; Gutiérrez, Á.J. Metals in commercial fish in the Galapagos Marine Reserve: Contribution to food security and toxic risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Yasmina, B.; Redouane, B.; Samir, R.; Samir, B.; Mostefa, B. Bioaccumulation Assessment of Trace Metals by Three Main Demersal Fish from Algerian Coast; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, X. Nutritional value and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in nine commercial fish species from Dachen Fishing Ground, East China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Yusoff Abd Samad, M.; Uddin, M.K.; Quddus, M.A.; Hossain, M.M. Recent trends in the foliar spraying of zinc nutrient and zinc oxide nanoparticles in tomato production. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Bhatti, H.N.; Khan, A.; Zafar, L.; Iqbal, M. Zinc oxide nano-fertilizer application (foliar and soil) effect on the growth, photosynthetic pigments and antioxidant system of maize cultivar. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 102343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okyere, E.Y.; Adu-Boahen, K.; Boateng, I.; Dadson, I.Y.; Boanu, N.Y.; Kyeremeh, S. Analysis of ecological health status of the Muni Lagoon: Evidence from heavy metal content in its water and fish samples. Geo Geogr. Environ. 2023, 10, e00115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genova, G.; Della Chiesa, S.; Mimmo, T.; Borruso, L.; Cesco, S.; Tasser, E.; Matteazzi, A.; Niedrist, G. Copper and zinc as a window to past agricultural land-use. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 126631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-López, A.; Escobedo-Urías, D.; Reyes-Salinas, A.; Hernández-Real, M.T. Phytoplankton response to nutrient runoff in a large lagoon system in the Gulf of California. Hidrobiológica 2007, 17, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-López, A.; Pérez-Morales, A.; Ayala-Rodríguez, G.A.; Escobedo-Urías, D.; Hakspiel-Segura, C. Abundance and seasonal variability of aloricate ciliates and tintinnids in a eutrophic coastal lagoon system of the Gulf of California, Mexico. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 32, 100814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjahan, M.; Taslima, K.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Emran, M.; Alam, S.I.; Faggio, C. Effects of heavy metals on fish physiology—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, S.S.; Karuppasamy, R.; Poongodi, K.; Puvaneswari, S. Bioaccumulation pattern of zinc in freshwater fish Channa punctatus (Bloch.) after chronic exposure. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 8, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, A.L.D.; Damien, P.; McCoy, D.; Mar, M.; Kessouri, F.; McWilliams, J.C.; Moffett, J.; Bianchi, D. The Shelf-To-Basin Transport of Iron From the Northern U.S. West Coast to the Pacific Ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2024, 38, e2023GB008029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.B.; Souza, I.C.; Soares, M.P.; Monferrán, M.V.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Matsumoto, S.T.; Fernandes, M.N. Metal/metalloid concentrations and multi-biomarkers in blood of Nile tilapia living in coastal lagoons near metallurgical industrial areas: An integrated evaluation. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2025, 44, 1596–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, E.; Mamdouh, A.Z.; Elbahnaswy, S.; El-Son, M.M.A.; Risha, E.; ElSayed, A.; Barbary, M.I.E.; Sebaei, M.G.E. The impact of heavy metal pollution: Bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, and histopathological alterations in fish across diverse habitats. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaj, M.A.; Esmaeili, S.; Sayyad-Amin, P. Combinations of Iron and Manganese Have Variable Effects on the Quantitative and Qualitative Traits of Tuberose (Polianthes tuberosa L.). Int. J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2025, 12, 245–262. [Google Scholar]
- Barats, A.; Renac, C.; Garrido- Hoyos, S.; Gonzalez-Perez, B.; Garcia-Mendoza, K.; Esteller-Alberich, M.V.; Jara-Marini, M.E.; Aguilar-Chavez, A. Assessment of the water quality in the coastal Yaqui valley (Mexico): Implications for human health and ecological risks. Environ Res 2025, 264, 120275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arole, K.; Velhal, M.; Tajedini, M.; Xavier, P.G.; Bardasz, E.; Green, M.J.; Liang, H. Impacts of particles released from vehicles on environment and health. Tribol. Int. 2023, 184, 108417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, S.; Hassanzadeh, N.; Sohrabi, M.; Loppi, S. Biomonitoring of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Urban Atmosphere of Tehran Metropolis Using the Lichen Anaptychia setifera (Mereschk.) Räsänen. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEGI. Registered Motor Vehicles in Circulation [Vehículos de Motor Registrados en Circulación]; Información Económica: Aguascalientes, Mexico, 2023; Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/programas/vehiculosmotor/#tabulados (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Xian, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Bennion, H.; Jeppesen, E.; Dong, X. Coastal lagoons as a transitional zone between land and sea: Insight from trace element pollution in southern China. Water Res. 2025, 286, 124192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakulthaew, C.; Chokejaroenrat, C.; Panya, S.; Songsasen, A.; Poomipuen, K.; Imman, S.; Suriyachai, N.; Kreetachat, T.; Comfort, S. Developing a Slow-Release Permanganate Composite for Degrading Aquaculture Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, K.S. Toxicity of some chemical therapeutics to the commercial shrimp, Penaeus californiensis. Aquaculture 1976, 7, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapalan, T.; Kwong, R.W. Functional significance and physiological regulation of essential trace metals in fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb238790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosseland, B.O.; Teien, H.C.; Basnet, S.; Borgstrøm, R.; Sharma, C.M. Trace elements and organochlorine pollutants in selected fish species from Lake Phewa, Nepal. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2017, 99, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, S.P.; Kaushik, S.J. Nutrition and metabolism of minerals in fish. Animals 2021, 11, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauliutė, G.; Svecevičius, G. Heavy metal interactions during accumulation via direct route in fish: A review. Zool. Ecol. 2015, 25, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.-M.; Gu, Y.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J.; Wang, P. Iron–manganese (oxyhydro) oxides, rather than oxidation of sulfides, determine mobilization of Cd during soil drainage in paddy soil systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frías-Espericueta, M.G.; Osuna-López, J.; Aguilar-Juárez, M.; Voltolina, D. Cadmio y plomo en organismos de importancia comercial de la zona costera de Sinaloa, México: 20 años de estudios. CICIMAR Oceánides 2010, 25, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.A.; Newth, J.L. Swans and lead fishing weights: A systematic review of deposition, impacts and regulations in Europe. Wildfowl 2024, 7, 27–56. [Google Scholar]
- Soroldoni, S.; Castro, Í.B.; Abreu, F.; Duarte, F.A.; Choueri, R.B.; Möller, O.O.; Fillmann, G.; Pinho, G.L.L. Antifouling paint particles: Sources, occurrence, composition and dynamics. Water Res. 2018, 137, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RNPA. List of Economic Units and Assets, Larger and Smaller Vessels and Aquaculture Facilities [Relación de Unidades Económicas y Activos Embarcaciones Mayores, Menores e Instalaciones Acuícolas]; Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca Sinaloa: Mazatlán, Mexico, 2025; Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conapesca (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- FA. FishAngler; FishAngler, LLC.: Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 2025; Available online: https://www.fishangler.com/ (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Quintela, F.M.; da Silva, F.A.; Correa, F.; Carvalho, F.R.; Galiano, D.; Pires, M.C.O.; Galatti, U. Essential and Non-Essential Elements Levels in Fish Species Highly Consumed in the Middle Miranda River, Brazilian Pantanal. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 87, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Mohiuddin, S.; Panhwar, S.K. Metal transportation mechanism by rainfall runoff as a contribution to the bioaccumulation in seafood. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.T.; El-Nady, H.; Gomaa, R.M.; Salman, S.A.; Khalifa, I.H. Contamination and sediment quality evaluation of toxic metals enrichment in heavy mineral-rich beach sands of Arish City, Northeastern Egypt. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2024, 9, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Morales, J.B.; Bastidas-Bastidas, P.d.J.; Rodríguez-Aguilar, B.A.; Davizon, Y.A.; Márquez-Pacheco, H.; Amillano-Cisneros, J.M.; Godínez-Siordia, D.E.; Lorente Adame, R.G.; González-Márquez, L.-C.; Camacho, L.L. Health risk assessment from pesticide exposure through tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) consumption in Guasave, Sinaloa, Mexico [Evaluación del riesgo a la salud por la exposición a plaguicidas a través del consumo de tomate (Solanum lycopersicum L.), en Guasave, Sinaloa, México]. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2025, 41, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, H.E.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Abdel-Wahab, M.; Almadani, S.; Alfaifi, H.; Youssef, M. Assessment of sediment quality using different pollution indicators and statistical analyses, Hurghada area, Red Sea coast, Egypt. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, L.; Thuerig, B.; Apostolov, S.; Blogg, H.; Borgo, E.; Corneo, P.E.; Fittje, S.; de Palma, M.; Donko, A.; Experton, C.; et al. Use of Copper-Based Fungicides in Organic Agriculture in Twelve European Countries. Agronomy 2022, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavé, K.; Lodeiros, C.; Freites-Valbuena, L.; Vélez-Falcones, J.; Zapata-Vívenes, É.; Arrieche, D.; Guevara, M.; Pinto, R. The use of copper sulfate to control mussel (Mytella strigata) invasive events in the Penaeus vannamei shrimp farming: Doses, effects, and depuration. Aquaculture 2025, 598, 741964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, J.; Machado-Neto, J.; Brossi-Garcia, A.; Marques, H.; Kubo, E. Acute toxicity of the fungicide copper oxychloride to the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii De Man. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 65, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakimska-Nagórska, A.; Konieczka, P.; Skóra, K.; Namieśnik, J. Bioaccumulation of metals in tissues of marine animals, part I: The role and impact of heavy metals on organisms. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar]
| Element | Mass Fraction (mg/kg) |
|---|---|
| Cd | 42.3 ± 1.8 |
| Cu | 497 ± 22 |
| Fe | 179 ± 8 |
| Mn | 15.6 ± 1.0 |
| Ni | 5.30 ± 0.24 |
| Zn | 136 ± 6 |
| Pb | 0.225 ± 0.018 |
| TM | MRLs | Average | Maximum | Minimum | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 5 *–30 ** | 1.39 | 9.62 | 0.16 | 1.38 |
| Fe | - | 25.47 | 84.32 | 6.15 | 28.47 |
| Mn | 0.14 **** | 8.98 | 238.38 | 0.10 | 26.14 |
| Ni | 70 ** | 0.38 | 10.59 | 2.097 | 1.54 |
| Zn | 0.3 *** | 87.53 | 656.30 | 11.33 | 92.48 |
| Cd | 0.003 **** | 1.151 | 2.17 | 0.30 | 0.41 |
| Pb | 0.30 * | 1.23 | 31.45 | 0.64 | 4.72 |
| Metal | Average Concentration (mg/kg) | Reference Dose (RfD) | EDI | THQ | HI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 1.39 | NR | 0.006 | 2.9 | |
| Zn | 87.53 | 0.003 *–0.3 ** | 0.399 | 1.329 | |
| Ni | 0.38 | 0.02 * | 0.002 | 0.101 | |
| Fe | 25.47 | NR | 0.116 | ||
| Mn | 8.98 | 0.14 * | 0.041 | 0.292 | |
| Cd | 2.17 | 0.0004 *–0.05 ** | 0.005 | 1.752 | |
| Pb | 1.23 | 0.30 * | 0.022 | 2.577 |
| TM | EDI | RfD | ILRC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.006 | NR | |
| Zn | 0.399 | 3 × 10−1 | 1.2 × 10−1 |
| Ni | 0.002 | 2 × 10−2 | 4.02 × 10−5 |
| Fe | 0.116 | NR | |
| Mn | 0.041 | 1.4 × 10−1 | 5.72 × 10−3 |
| Cd | 0.001 | 3 × 10−3 | 1.58 × 10−4 |
| Pb | 0.006 | 3 × 10−3 | 1.85 × 10−4 |
| Species | Cu | Fe | Mn | Ni | Zn | Cd | Pb | Habitat [17] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balistes polylepis * | 1.39 | 25.39 | 8.95 | 0.44 | 87.36 | 1.15 | 1.39 | A |
| Amblychaeturichthys hexanema 3 | 7.9 | 71.7 | 0.45 | A | ||||
| Caulolatilus princeps 7 | 1.19 | 0.39 | 0.44 | A | ||||
| Chelidonichthys lucerne 2 | 0.003 | 0.04 | A | |||||
| Collichthys lucidus 9 | 2.8 | 15.15 | 0.067 | 0.1 | A | |||
| Conger myriaster 3 | 4.78 | 29.8 | 0.22 | A | ||||
| Cynoglossus joyneri 3 | 6.95 | 44.9 | 0.36 | A | ||||
| Hexagrammos otakii 3 | 5.81 | 60.8 | 0.19 | A | ||||
| Johnius belangerii 3 | 4.66 | 67.4 | 0.38 | A | ||||
| Larimichthys crocea 9 | 2.0 | 12.55 | 0.067 | 0.025 | B | |||
| Larimichthys polyactis 3 | 5.9 | 56.1 | 0.39 | B | ||||
| Lateolabrax maculatus 9 | 5.1 | 12.85 | 0.067 | 0.1 | C | |||
| Lepturacanthus savala 3 | 4.752 | 36.6 | 0.28 | C | ||||
| Merlangius merlangus 2 | 0.003 | 0.04 | D | |||||
| Merlangius merlangus 4 | 0.5 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.01 | 3.4 | 0.02 | D | |
| Merlangius merlangus 4 | 1.32 | 98.1 | 0.16 | 0.135 | 65.4 | 0.21 | 0.53 | D |
| Merlangius merlangus 6 | 0.0055 | 0.0064 | D | |||||
| Merluccius merluccius 8 | 3.16 | 7.69 | 33.77 | E | ||||
| Miichthys miiuy 3 | 2.7 | 53.4 | 0.22 | E | ||||
| Mullus barbatus 4 | 0.5 | 2.3 | 3.2 | 0.02 | 0.05 | E | ||
| Mullus barbatus 5 | 0.00249 | 0.13 | E | |||||
| Mullus surmuletus8 | 5.31 | 15.13 | 31.99 | A | ||||
| Muraenesox cinereus 3 | 4.16 | 14.5 | 0.14 | E | ||||
| Muraenesox cinereus 9 | 2.3 | 21.4 | 0.068 | 0.1 | E | |||
| Mycteroperca olfax 7 | 0.48 | 2.54 | 0.25 | F | ||||
| Pagellus erythrinus 8 | 2.54 | 12.14 | 34.29 | F | ||||
| Saurida elongate 3 | 7.43 | 82.9 | 0.48 | F | ||||
| Sebastiscus marmoratus 3 | 3.4 | 94.5 | 0.15 | E | ||||
| Sebastiscus marmoratus 9 | 2.4 | 27.15 | 0.067 | 1.1 | E | |||
| Sphoeroides spp. 1 | 1.45 | 80.52 | 6.13 | 8.06 | 189.55 | 1.45 | 18.42 | E |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Ocampo, H.A.; Michel-Rubio, A.A.; Pérez-Gonzalez, E.; Rodríguez-Meza, G.D. Human Health Consumption Risk Assessment of Trace Metal Content in the Triggerfish Balistes spp. from the RAMSAR Site 1826 San Ignacio-Navachiste-Macapule Lagoon Complex. Toxics 2025, 13, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090718
González-Ocampo HA, Michel-Rubio AA, Pérez-Gonzalez E, Rodríguez-Meza GD. Human Health Consumption Risk Assessment of Trace Metal Content in the Triggerfish Balistes spp. from the RAMSAR Site 1826 San Ignacio-Navachiste-Macapule Lagoon Complex. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090718
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Ocampo, Héctor Abelardo, Adán Alfonso Michel-Rubio, Ernestina Pérez-Gonzalez, and Guadalupe Durga Rodríguez-Meza. 2025. "Human Health Consumption Risk Assessment of Trace Metal Content in the Triggerfish Balistes spp. from the RAMSAR Site 1826 San Ignacio-Navachiste-Macapule Lagoon Complex" Toxics 13, no. 9: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090718
APA StyleGonzález-Ocampo, H. A., Michel-Rubio, A. A., Pérez-Gonzalez, E., & Rodríguez-Meza, G. D. (2025). Human Health Consumption Risk Assessment of Trace Metal Content in the Triggerfish Balistes spp. from the RAMSAR Site 1826 San Ignacio-Navachiste-Macapule Lagoon Complex. Toxics, 13(9), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090718








