Coupled In Silico Toxicology Models Reveal Equivalent Ecological Risks from BPA and Its Alternatives in Chinese Surface Waters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Toxicity Data and Environmental Concentrations
2.2. Development of Coupled In Silico Toxicology Models
2.3. Calculation of HC5s and PNECs
2.4. Ecological Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
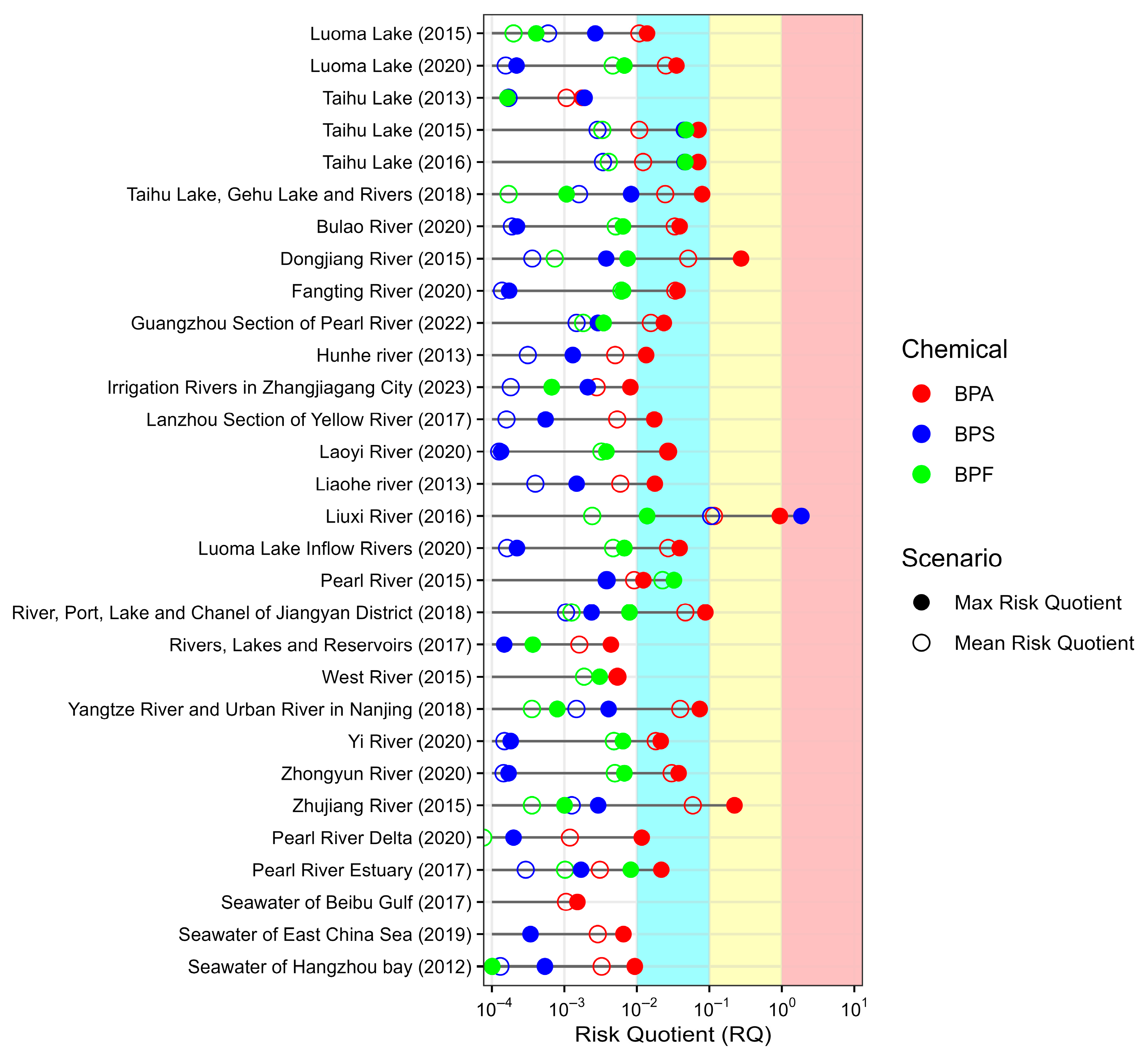
3.1. Occurrence of BPA, BPS, and BPF in Chinese Surface Waters
| No. | Location | Sampling Year | Pre-Treatment and Detection Method | Concentration (Range with Mean Value, ng/L) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | BPS | BPF | |||||
| 1 | Luoma Lake | 2015 | SPE + HPLC-MS/MS | 49–110 (86) | 0–94 (21) | 3.5–14 (6.8) | [50] |
| 2 | Luoma Lake | 2020 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 120–280 (200) | 3.2–7.7 (5.45) | 87.4–230 (159) | [51] |
| 3 | Taihu Lake | 2013 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 4.2–14 (8.5) | 0.28–67 (6) | 0–5.6 (0.83) | [52] |
| 4 | Taihu Lake | 2015 | SPE + HPLC-MS/MS | 27–565 (86) | 4.5–1569 (101) | 0–1634 (114) | [53] |
| 5 | Taihu Lake | 2016 | SPE + HPLC-MS/MS | 28–560 (97) | 4.5–1600 (120) | 0–1600 (140) | [50] |
| 6 | Taihu Lake | 2016 | SPE + HPLC-MS/MS | 19–68 (26) | 4.1–160 (16) | 26–720 (78) | [54] |
| 7 | Taihu Lake, Gehu Lake and Rivers | 2018 | SPE + LC-MS/MS | 47.8–633 (196) | 6.56–293 (56.1) | 0.48–36.7 (5.82) | [55] |
| 8 | Bulao River | 2020 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 220–310 (265) | 5.5–7.8 (6.65) | 130–220 (175) | [51] |
| 9 | Dongjiang River | 2015 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 23.7–2180 (406) | 0.07–133 (12.7) | 0.98–255 (25.2) | [2] |
| 10 | Fangting River | 2020 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 250–290 (270) | 3.6–6.1 (4.85) | 200–220 (210) | [51] |
| 11 | Guangzhou Section of Pearl River | 2022 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 60.5–187.5 (124) | 1.7–102.1 (51.9) | 5.4–118.8 (62.1) | [56] |
| 12 | Hunhe river | 2013 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 4.4–107 (40) | 0.61–46 (11) | ND | [52] |
| 13 | Irrigation Rivers in Zhangjiagang City | 2023 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 4.66–64.77 (22.19) | 0–74.04 (6.42) | 0–22.88 (1.04) | [57] |
| 14 | Lanzhou Section of Yellow River | 2017 | SPE + HPLC-MS/MS | 7.8–138.5 (42.6) | 0–19.4 (5.6) | / | [58] |
| 15 | Laoyi River | 2020 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 210–220 (215) | 4.2–4.7 (4.45) | 91.9–130 (111) | [51] |
| 16 | Liaohe river | 2013 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 5.9–141 (47) | 0.22–52 (14) | ND | [52] |
| 17 | Liuxi River | 2016 | LLE/SPE + HPLC-MS/MS | 75.6–7480 (922) | 19.9–65,600 (3720) | 0–474 (82.8) | [59] |
| 18 | Luoma Lake Inflow Rivers | 2020 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 120–310 (215) | 3.6–7.8 (5.7) | 91.9–230 (161) | [60] |
| 19 | Pearl River | 2015 | SPE + LC-MS/MS | 0–98 (73) | 0–135 (135) | 448–1110 (773) | [49] |
| 20 | River, Port, Lake and Chanel of Jiangyan District | 2018 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 19–702 (371.5) | 3.4–83.5 (37.1) | 0–270.6 (42.9) | [61] |
| 21 | Rivers, Lakes and Reservoirs | 2017 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 0–34.9 (12.8) | 0–5.2 (1.1) | 0–12.56 (2.18) | [62] |
| 22 | West River | 2015 | SPE + LC-MS/MS | 0–43 (43) | ND | 0–105 (64) | [49] |
| 23 | Yangtze River and Urban River in Nanjing | 2018 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 85.9–586.4 (315.8) | 12.9–143.4 (51.6) | 1.4–27.3 (12.2) | [63] |
| 24 | Yangtze River and Urban River in Nanjing | 2018 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 120–554 (253) | 2.24–73.3 (39.2) | 0–4.76 (2.2) | [64] |
| 25 | Yi River | 2020 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 120–170 (145) | 4.1–6.4 (5.25) | 110–220 (165) | [51] |
| 26 | Zhongyun River | 2020 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 180–300 (240) | 4.2–6 (5.1) | 110–230 (170) | [51] |
| 27 | Zhujiang River | 2015 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 118–1770 (471) | 16.6–103 (44.5) | 6.54–34.4 (12.2) | [2] |
| 28 | Pearl River Delta | 2020 | SPE + HPLC-MS/MS | 1.7–93 (9.5) | 0.039–7 (0.54) | 0–1.6 (0.016) | [65] |
| 29 | Pearl River Estuary | 2017 | SPE + UPLC- Q-Exactive Orbitrap MS | 9.48–173 (24.6) | 1.6–59.8 (10.3) | 2.37–282 (35) | [66] |
| 30 | Seawater of Beibu Gulf | 2017 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 5.26–12.04 (8.38) | 0.07–0.63 (0.34) | ND | [67] |
| 31 | Seawater of East China Sea | 2019 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 2.7–52 (23) | 0.15–12 (2.2) | ND | [68] |
| 32 | Seawater of Hangzhou bay | 2012 | SPE + UPLC-MS/MS | 6.59–74.58 (26) | 0.29–18.99 (4.6) | 0–3.47 (3.2) | [69] |
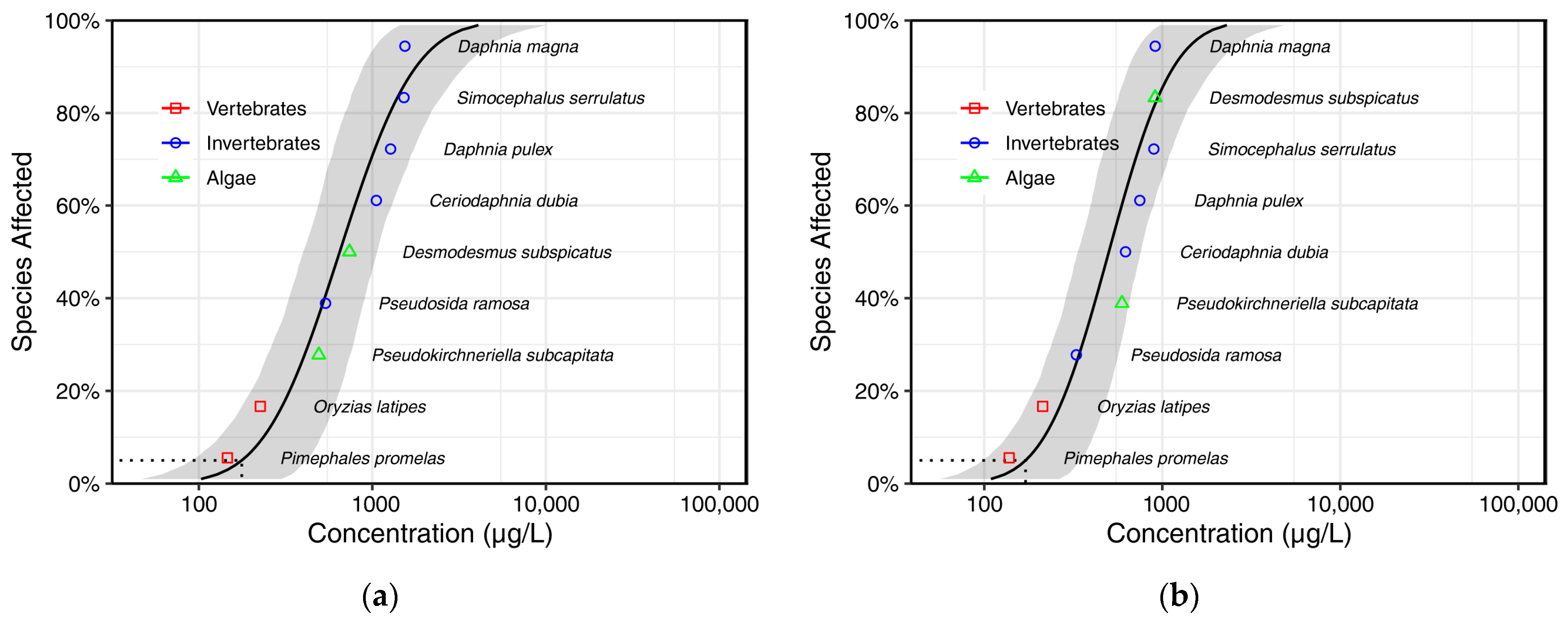
3.2. Validation of Coupled In Silico Toxicology Models and Calculation of PNECs
3.3. Ecological Risk of BPA, BPS, and BPF in Chinese Surface Waters
3.4. Implications and Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, D.; Yuan, K.; Ai, F.; Li, M.; Zhu, N.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, K.; Yin, D.; Bu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Occurrence, spatial distributions, and temporal trends of bisphenol analogues in an E-waste dismantling area: Implications for risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, J.-L.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Jia, Y.-W.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Chen, C.-E.; Liu, Y.-S.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Ying, G.-G. Occurrence, mass loads and risks of bisphenol analogues in the Pearl River Delta region, South China: Urban rainfall runoff as a potential source for receiving rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Chen, W.-Q.; Zeng, X.; Tang, L. Dynamic stocks and flows analysis of bisphenol A (BPA) in China: 2000–2014. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Zheng, C.; Wang, K.-J. The comparative toxicities of BPA, BPB, BPS, BPF, and BPAF on the reproductive neuroendocrine system of zebrafish embryos and its mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Tan, T.; Liang, H.; Huang, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, P.; Su, X. Occurrence and distribution of bisphenol compounds in different categories of animal feeds used in China. Emerg. Contam. 2021, 7, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousoumah, R.; Leso, V.; Iavicoli, I.; Huuskonen, P.; Viegas, S.; Porras, S.P.; Santonen, T.; Frery, N.; Robert, A.; Ndaw, S. Biomonitoring of occupational exposure to bisphenol A, bisphenol S and bisphenol F: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tišler, T.; Krel, A.; Gerželj, U.; Erjavec, B.; Dolenc, M.S.; Pintar, A. Hazard identification and risk characterization of bisphenols A, F and AF to aquatic organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Fol, V.; Aït-Aïssa, S.; Sonavane, M.; Porcher, J.-M.; Balaguer, P.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Zalko, D.; Brion, F. In vitro and in vivo estrogenic activity of BPA, BPF and BPS in zebrafish-specific assays. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreman, J.; Lee, O.; Trznadel, M.; David, A.; Kudoh, T.; Tyler, C.R. Acute toxicity, teratogenic, and estrogenic effects of Bisphenol A and its alternative replacements Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F, and Bisphenol AF in Zebrafish embryo-larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12796–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, G.; Jiang, R.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y. Occurrence, toxicity and ecological risk of Bisphenol A analogues in aquatic environment—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Kannan, K.; Tan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.; Widelka, M. Bisphenol analogues other than BPA: Environmental occurrence, human exposure, and toxicity—A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5438–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, J.R.; Bolden, A.L. Bisphenol S and F: A Systematic Review and Comparison of the Hormonal Activity of Bisphenol A Substitutes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eladak, S.; Grisin, T.; Moison, D.; Guerquin, M.-J.; N’Tumba-Byn, T.; Pozzi-Gaudin, S.; Benachi, A.; Livera, G.; Rouiller-Fabre, V.; Habert, R. A new chapter in the bisphenol A story: Bisphenol S and bisphenol F are not safe alternatives to this compound. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-L.; Li, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; Kong, X.-Z.; Qin, N.; Liu, W.-X.; Wu, W.-J.; Jorgensen, S.E. Key issues for the development and application of the species sensitivity distribution (SSD) model for ecological risk assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 54, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthuma, L.; Suter, G.W., II; Traas, T.P. Species Sensitivity Distributions in Ecotoxicology; CRC Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hiki, K.; Iwasaki, Y. Can we reasonably predict chronic species sensitivity distributions from acute species sensitivity distributions? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13131–13136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roveri, V.; Lopes Guimarães, L. In silico prediction of persistent, mobile, and toxic pharmaceuticals (PMT): A case study in São Paulo Metropolitan Region, Brazil. Comput. Toxicol. 2023, 25, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.; Ojha, P.K.; Roy, K. Computational modeling of aquatic toxicity of polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) employing 2D-QSAR and chemical read-across. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 257, 106429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Abdullayev, R.; Jillella, G.K.; Nair, V.G.; Bousily, M.; Kar, S.; Gajewicz-Skretna, A. Decoding cyanide toxicity: Integrating Quantitative Structure-Toxicity Relationships (QSTR) with species sensitivity distributions and q-RASTR modeling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 291, 117824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, L.G. In silico toxicology for the pharmaceutical sciences. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 241, 356–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerich, J.; Ecker, G.F. In silico toxicology: From structure–activity relationships towards deep learning and adverse outcome pathways. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2020, 10, e1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Feng, C.; Jin, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, N.; Bai, Y.; Wu, F.; Raimondo, S. A QSAR–ICE–SSD model prediction of the PNECs for alkylphenol substances and application in ecological risk assessment for rivers of a megacity. Environ. Int. 2022, 167, 107367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasteel, E.E.J. Next Generation Risk Assessment of Chemicals: In Vitro and in Silico Approaches to Work Towards Enough Precision to Make a Decision. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, M.; Dyer, S.D.; Belanger, S.E.; Wu, F. The combined QSAR-ICE models: Practical application in ecological risk assessment and water quality criteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8877–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douziech, M.; Ragas, A.M.J.; van Zelm, R.; Oldenkamp, R.; Jan Hendriks, A.; King, H.; Oktivaningrum, R.; Huijbregts, M.A.J. Reliable and representative in silico predictions of freshwater ecotoxicological hazardous concentrations. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, P.; Povinelli, R.J.; White, S.; Merrill, S.J. An ensemble model of QSAR tools for regulatory risk assessment. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunghini, F.; Marcou, G.; Azam, P.; Enrici, M.H.; Van Miert, E.; Varnek, A. Consensus QSAR models estimating acute toxicity to aquatic organisms from different trophic levels: Algae, Daphnia and fish. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2020, 31, 655–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, J.; Figuière, R.; Dekker, S.C.; van Wezel, A.P.; Cousins, I.T. Managing PMT/vPvM substances in consumer products through the concepts of essential-use and functional substitution: A case-study for cosmetics. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2023, 25, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vračko, M.; Lagares, L.M. Clustering of bisphenols based on toxicity predictions for key aquatic species: Daphnia magna, Pimephales promelas, and Oryzias latipes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 295, 118149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wu, F.; Mu, Y.; Meng, W.; Dyer, S.D.; Fan, M.; Raimondo, S.; Barron, M.G. Interspecies Correlation Estimation–Applications in Water Quality Criteria and Ecological Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11382–11383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, S.; Barron, M.G. Application of interspecies correlation estimation (ICE) models and QSAR in estimating species sensitivity to pesticides. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2020, 31, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.-y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ge, H.; Ji, X.; Meng, Y. ICE-SSD Model: Bridging the Ecological Risk Assessment Gap between Plasticizer and the Substitute. ACS EST Water 2025, 5, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M.G.; Jackson, C.R.; Awkerman, J.A. Evaluation of in silico development of aquatic toxicity species sensitivity distributions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 116, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Tao, H.; Qi, G.; Guo, W.; Ge, H.; Shi, J. A QSAR–ICE–SSD model prediction of the PNECs for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and their ecological risks in an area of electroplating factories. Molecules 2021, 26, 6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Xie, H.; Jin, X.; Naraginti, S.; Xu, D.; Guo, C.; Feng, C.; Wu, F.; Giesy, J.P. Prediction of HC5s for phthalate esters by use of the QSAR–ICE model and ecological risk assessment in Chinese surface waters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 467, 133642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoondert, R.P.J.; Oldenkamp, R.; de Zwart, D.; van de Meent, D.; Posthuma, L. QSAR-based estimation of species sensitivity distribution parameters: An exploratory investigation. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 2764–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, A.; Zhang, X.; Niu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Application of combined QSAR-ICE models in calculation of hazardous concentrations for linear alkylbenzene sulfonate. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ge, H.; Shi, J.; Tao, H.; Li, B.; Yu, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, R.; Li, X. A tiered probabilistic approach to assess antibiotic ecological and resistance development risks in the fresh surface waters of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 114018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Ge, H.; Tao, H.; Guo, W.; Yu, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Xiao, R.; Xu, Z.; et al. Tiered ecological risk assessment of nonylphenol and tetrabromobisphenol A in the surface waters of China based on the augmented species sensitivity distribution models. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, S.; Lilavois, C.R.; Barron, M.G. Web-Based Interspecies Correlation Estimation (Web-ICE) for Acute Toxicity: User Manual, Version 3.3; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development: Gulf Breeze, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, D.R.; van Dam, R.A.; Fisher, R.; Batley, G.E.; Tillmanns, A.R.; Thorley, J.; Schwarz, C.J.; Spry, D.J.; McTavish, K. Recent developments in species sensitivity distribution modeling. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, S.E.; Carr, G.J. SSDs revisited: Part II—Practical considerations in the development and use of application factors applied to species sensitivity distributions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 1526–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, G.J.; Belanger, S.E. SSDs revisited: Part I—A framework for sample size guidance on species sensitivity distribution analysis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 1514–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Qin, N.; Kong, X.; Liu, W.; Wu, W.; He, Q.; Yang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, B.; et al. Ecological risk assessment and priority setting for typical toxic pollutants in the water from Beijing-Tianjin-Bohai area using Bayesian matbugs calculator (BMC). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorley, J.; Schwarz, C. ssdtools: An R package to fit species sensitivity distributions. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Hecker, M.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H. A comparison of statistical methods for deriving freshwater quality criteria for the protection of aquatic organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, M.; Meng, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Peng, S.; Rong, X.; Wang, L. Residue level, occurrence characteristics and ecological risk of pesticides in typical farmland-river interlaced area of Baiyang Lake upstream, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, J.; Lam, P.K.S.; Moon, H.-B.; Jeong, Y.; Kannan, P.; Achyuthan, H.; Munuswamy, N.; et al. Bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues including BPS and BPF in surface water samples from Japan, China, Korea and India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yan, K.; Wu, S.; Han, Z.; Guo, R.; Chen, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Bisphenol analogues in surface water and sediment from the shallow Chinese freshwater lakes: Occurrence, distribution, source apportionment, and ecological and human health risk. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Hu, G.; Gao, Z.; Meng, Q.; Zhu, X. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of bisphenol analogues in Luoma Lake and its inflow rivers in Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 1430–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhu, L. Occurrence and partitioning of bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from Liaohe River Basin and Taihu Lake, China. Water Res. 2016, 103, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Guo, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, D.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Shi, L. Distribution Characteristics and Potential Risk of Bisphenol Analogues in Surface Water and Sediments of Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 2793–2800. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, N.; Guo, R.; Chen, M.; Mai, D.; Yan, Z.; Han, Z.; Chen, J. Occurrence, distribution and sources of bisphenol analogues in a shallow Chinese freshwater lake (Taihu Lake): Implications for ecological and human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, W.; Cai, Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, C.; Ning, L. Investigating the role of colloids on the distribution of bisphenol analogues in surface water from an ecological demonstration area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ying, G. Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risks of Bisphenol Compounds in Guangzhou Section of the Pearl River, River Swell and Pipeline Runoff. J. South China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 56, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, L.; Ren, J.; Jing, C.; Lu, G.; Yang, X. Medium distribution, source characteristics and ecological risk of bisphenol compounds in agricultural environment. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.-l.; Wang, X.-c.; Shen, J.-m. Spatial and temporal distributions of bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wu, L.-H.; Liu, G.-Q.; Shi, L.; Guo, Y. Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment of Eight Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Urban River Water and Sediments of South China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 75, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, Q.; Hu, G.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Epua Epri, J. Simultaneous determination of seven bisphenol analogues in surface water by solid-phase extraction and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ren, J.; You, Z.; Liu, J.; Lu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, J. The sinking behavior of micro–nano particulate matter for bisphenol analogues in the surface water of an ecological demonstration zone, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, M. Occurrence and exposure assessment of bisphenol analogues in source water and drinking water in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Cai, Y.; Ren, J.; Lu, G.; Li, Y.; Ji, Y. Multimedia distribution and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues in the urban rivers and their bioaccumulation in wild fish with different dietary habits. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 164, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Liu, J.; Ren, J.; Shen, J.; Fan, J.; Xi, R.; Chen, W.; Chen, Q. Occurrence, Distribution and Ecological Risk of Bisphenol Analogues in the Surface Water from a Water Diversion Project in Nanjing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xie, R.; He, Y.; Li, W.; Du, B.; Zeng, L. Broadening the lens on bisphenols in coastal waters: Occurrence, partitioning, and input fluxes of multiple novel bisphenol S derivatives along with BPA and BPA analogues in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qiu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Xiong, J.; Gao, C.; Hu, S. Occurrence, distribution, bioaccumulation, and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues, parabens and their metabolites in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiao, S.-K.; Wu, Q.; Pan, C.-G. Bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea: Occurrence, partitioning and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhao, M.; Jin, H. Occurrence and partitioning of bisphenol analogues, triclocarban, and triclosan in seawater and sediment from East China Sea. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shao, B. Simultaneous determination of seven bisphenols in environmental water and solid samples by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1328, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattullo, C.E.; Bährs, H.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Loffredo, E. Removal of bisphenol A by the freshwater green alga Monoraphidium braunii and the role of natural organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plahuta, M.; Tišler, T.; Pintar, A.; Toman, M.J. Adverse effects of bisphenol A on water louse (Asellus aquaticus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 117, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladewig, V.; Jungmann, D.; Köhler, H.R.; Licht, O.; Ludwichowski, K.U.; Schirling, M.; Triebskorn, R.; Nagel, R. Effects of bisphenol A on Gammarus fossarum and Lumbriculus variegatus in artificial indoor streams. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2006, 88, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaich, E.M.; Friederich, U.; Caspers, N.; Hall, A.T.; Klecka, G.M.; Dimond, S.S.; Staples, C.A.; Ortego, L.S.; Hentges, S.G. Acute and chronic toxicity testing of bisphenol A with aquatic invertebrates and plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnaire, B.; Gagné, F.; André, C.; Blaise, C.; Abbaci, K.; Budzinski, H.; Dévier, M.-H.; Garric, J. Development of biomarkers of stress related to endocrine disruption in gastropods: Alkali-labile phosphates, protein-bound lipids and vitellogenin-like proteins. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 92, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkowicz, I.R.H.; Herkovits, J.; Pérez Coll, C.S. Stage-dependent toxicity of bisphenol a on Rhinella arenarum (anura, bufonidae) embryos and larvae. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloas, W.; Lutz, I.; Einspanier, R. Amphibians as a model to study endocrine disruptors: II. Estrogenic activity of environmental chemicals in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Liang, D.; Liang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Jiang, G. Assessing developmental toxicity and estrogenic activity of halogenated bisphenol A on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2014, 112, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Lin, X.; Jin, R.; Peng, T.; Peng, Z.; Fu, Z. Toxic Effects of Bisphenol A on Early Life Stages of Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 93, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihaich, E.; Rhodes, J.; Wolf, J.; van der Hoeven, N.; Dietrich, D.; Hall, A.T.; Caspers, N.; Ortego, L.; Staples, C.; Dimond, S.; et al. Adult fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas, partial life-cycle reproductive and gonadal histopathology study with bisphenol A. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2525–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Bu, Q.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, R.; Huang, H.; Yang, L.; Tang, J.; Ma, Y. Emerging Contaminants in the Effluent of Wastewater Should Be Regulated: Which and to What Extent? Toxics 2024, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Jin, X.; Wang, J. Tiered probabilistic assessment of organohalogen compounds in the Han River and Danjiangkou Reservoir, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Chemical | Abbr. | Structure | CAS Number | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Solubility in Water (mg/L) | Log Kow | Log Koc | Half-Life in Water (days) | BCF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bisphenol A | BPA | 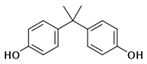 | 80-05-7 | C15H16O2 | 228.29 | 300 | 3.41 | 4.88 | 37.5 | 71.9 |
| Bisphenol S | BPS | 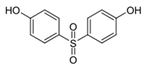 | 80-09-1 | C12H10O4S | 250.27 | 1100 | 1.65 | 2.5 | 37.5 | 3.16 |
| Bisphenol F | BPF | 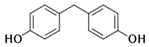 | 620-92-8 | C13H12O2 | 200.24 | 540 | 2.91 | 4.47 | 15 | 34.7 |
| Predicted Species | Surrogate Species | R2 | p-Value | MSE | Cross-Validation Success (%) | Slope | Intercept |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pimephales promelas | Oryzias latipes | 0.92 | <0.001 | 0.26 | 78 | 1.01 | −0.21 |
| Ceriodaphnia dubia | Daphnia magna | 0.95 | <0.001 | 0.26 | 81 | 1 | −0.19 |
| Daphnia pulex | Daphnia magna | 0.97 | <0.001 | 0.12 | 90 | 1.01 | −0.14 |
| Simocephalus serrulatus | Daphnia magna | 0.88 | <0.001 | 0.21 | 87 | 1 | −0.03 |
| Pseudosida ramosa | Daphnia magna | 0.87 | 0.006 | 0.57 | 67 | 0.93 | −0.24 |
| Desmodesmus subspicatus | Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata | 0.96 | <0.001 | 0.31 | 84 | 1.1 | −0.11 |
| No. | Species | Group | Concentration (μg/L) | Observed Duration (days) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chlorolobion braunii | Algae | 3995 | 4 | [70] |
| 2. | Asellus aquaticus | Crustaceans | 2000 | 21 | [71] |
| 3. | Daphnia magna | Crustaceans | 5000 | 21 | [8] |
| 4. | Gammarus fossarum | Crustaceans | 500 | 103 | [72] |
| 5. | Chironomus tentans | Insects | 1400 | 4 | [73] |
| 6. | Potamopyrgus antipodarum | Molluscs | 100 | 28 | [74] |
| 7. | Valvata piscinalis | Molluscs | 100 | 28 | [74] |
| 8. | Rhinella arenarum | Amphibians | 1799 | 14 | [75] |
| 9. | Xenopus laevis | Amphibians | 23 | 84 | [76] |
| 10 | Danio rerio | Fish | 1500 | 21 | [77] |
| 11. | Oryzias latipes | Fish | 598 | 44 | [78] |
| 12. | Pimephales promelas | Fish | 130 | 164 | [79] |
| Chemical | Dataset of SSD | HC5 and Its 95% CI (μg/L) | Assessment Factor | PNEC (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | Experimental toxicity data | 39.8 (12.1–186) | 5 | 7.96 |
| BPA | Predicted toxicity data from the coupled in silico toxicology models | 40.2 (16.2–129) | 5 | 8.04 |
| BPS | Predicted toxicity data from the coupled in silico toxicology models | 176 (90.5–415) | 5 | 35.2 |
| BPF | Predicted toxicity data from the coupled in silico toxicology models | 171 (98.1–347) | 5 | 34.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Xiao, J.; Tao, H.; Zhang, M.; Lu, L.; Qin, C. Coupled In Silico Toxicology Models Reveal Equivalent Ecological Risks from BPA and Its Alternatives in Chinese Surface Waters. Toxics 2025, 13, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080671
Zhang J, Xiao J, Tao H, Zhang M, Lu L, Qin C. Coupled In Silico Toxicology Models Reveal Equivalent Ecological Risks from BPA and Its Alternatives in Chinese Surface Waters. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080671
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiawei, Jingzi Xiao, Huanyu Tao, Mengtao Zhang, Lu Lu, and Changbo Qin. 2025. "Coupled In Silico Toxicology Models Reveal Equivalent Ecological Risks from BPA and Its Alternatives in Chinese Surface Waters" Toxics 13, no. 8: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080671
APA StyleZhang, J., Xiao, J., Tao, H., Zhang, M., Lu, L., & Qin, C. (2025). Coupled In Silico Toxicology Models Reveal Equivalent Ecological Risks from BPA and Its Alternatives in Chinese Surface Waters. Toxics, 13(8), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080671







