Environmental Risk and Management of Iron Tailings in Road Subgrade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Analytical Detection
2.2. Characterization of Pollutant Release
2.3. Characterization of Pollutant Migration and Diffusion
2.3.1. Soil Leaching and Dilution Factor (LF)
2.3.2. Groundwater Dilution and Attenuation Factor (DAF)
2.4. Representation of Uncertainty and Risk
3. Results and Discussion
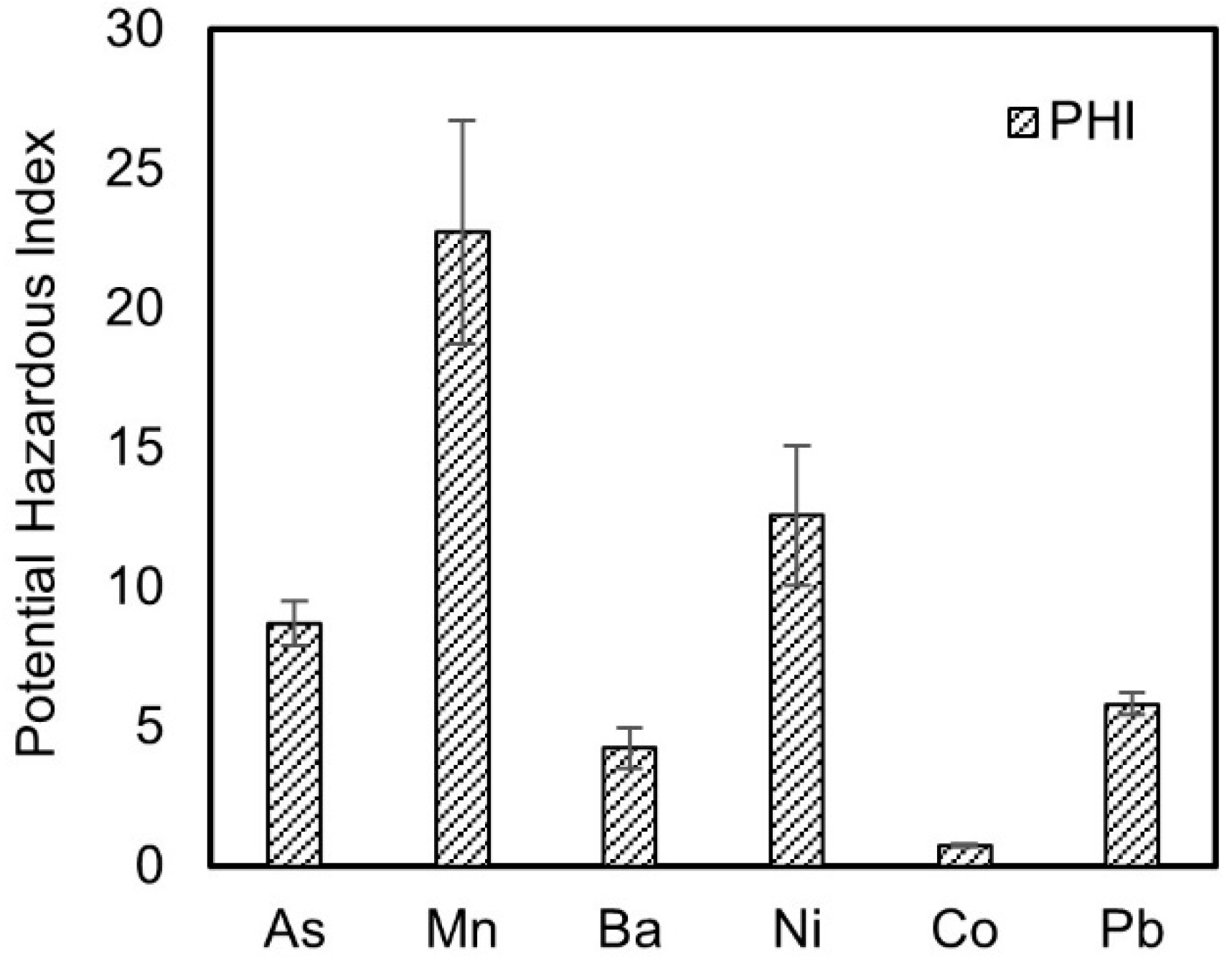
3.1. Release of Pollutants and Potential Environmental Risks
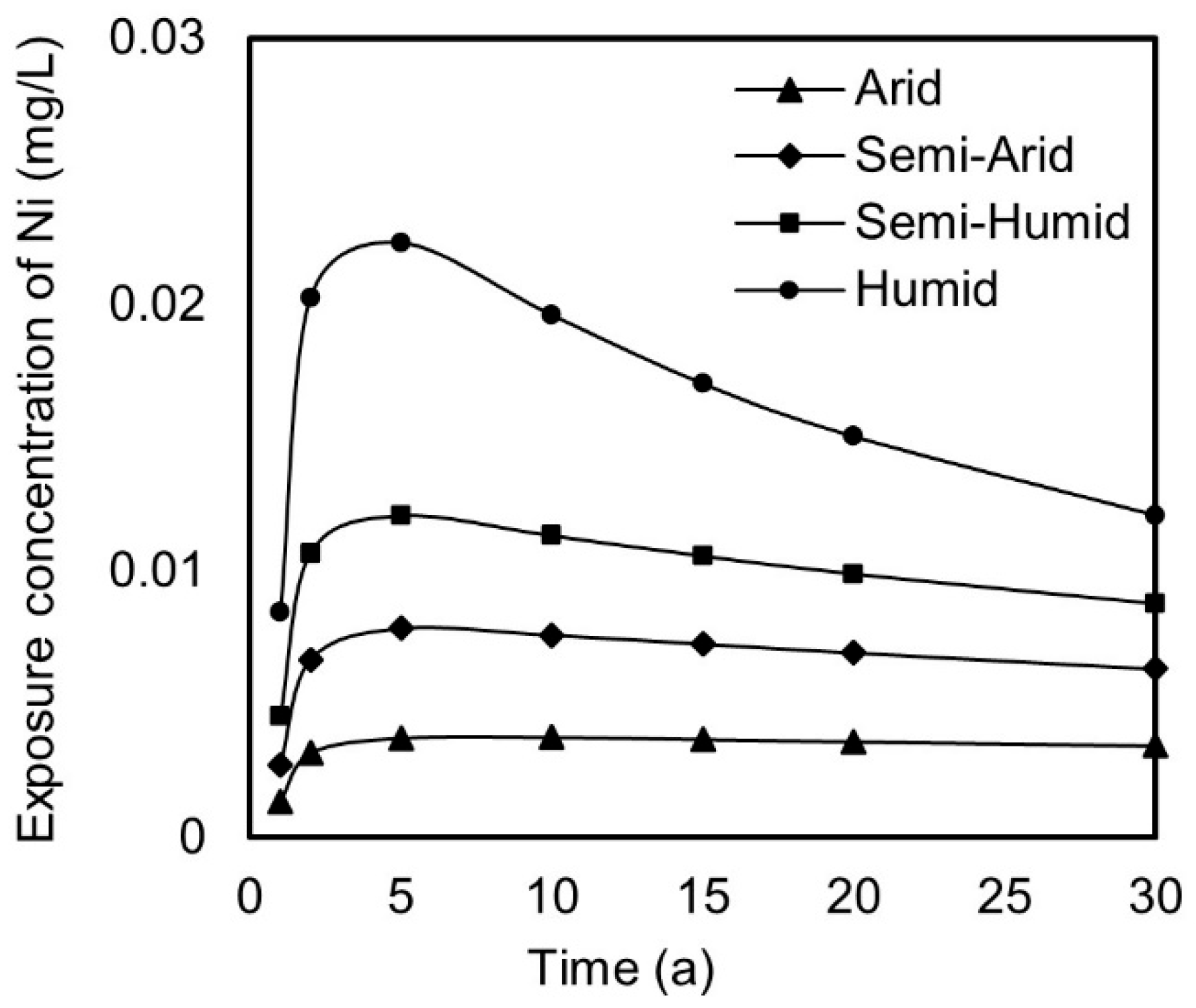
3.2. Exposure Risk and Evolution of Utilizing Iron Tailings in Road Construction
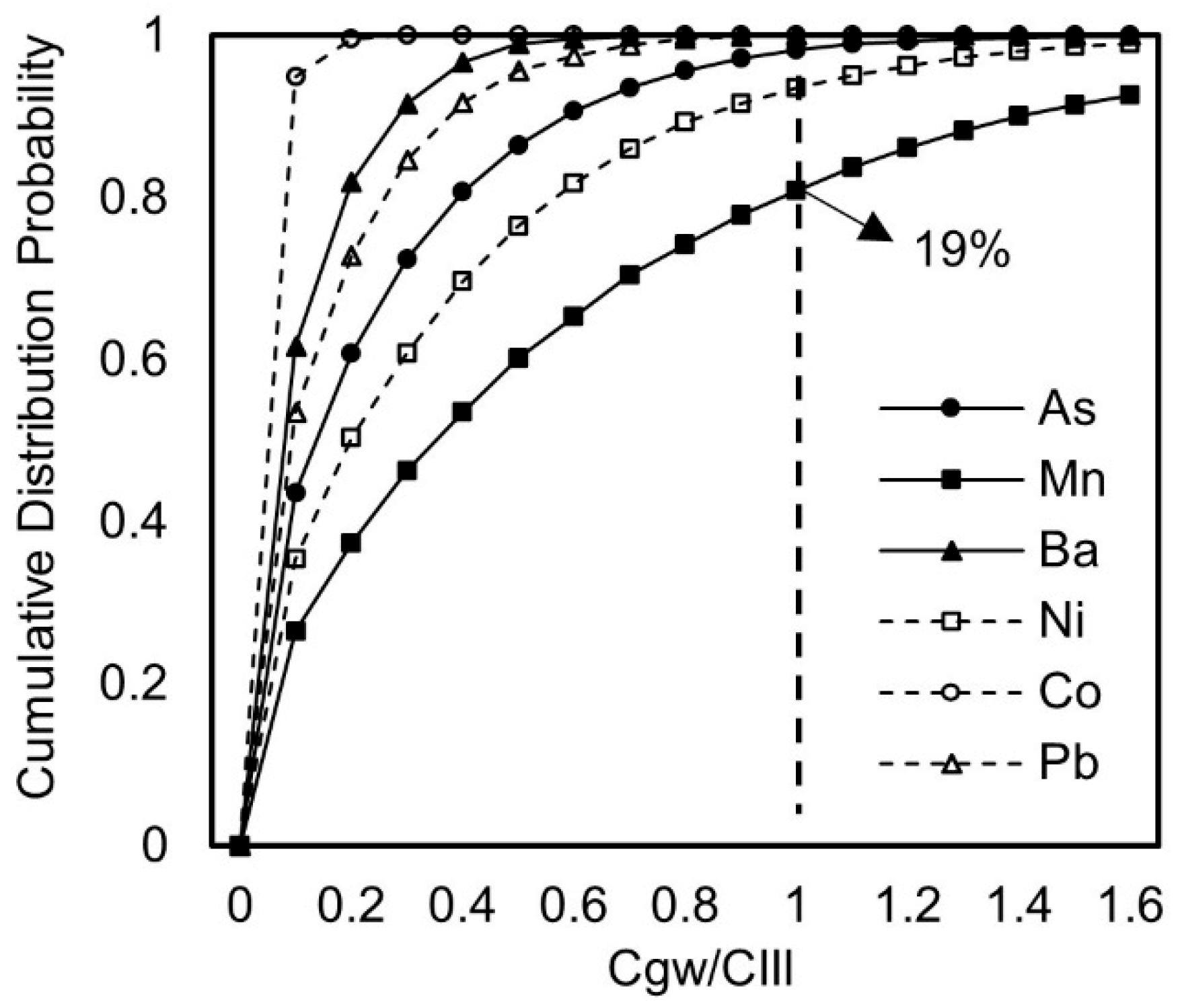
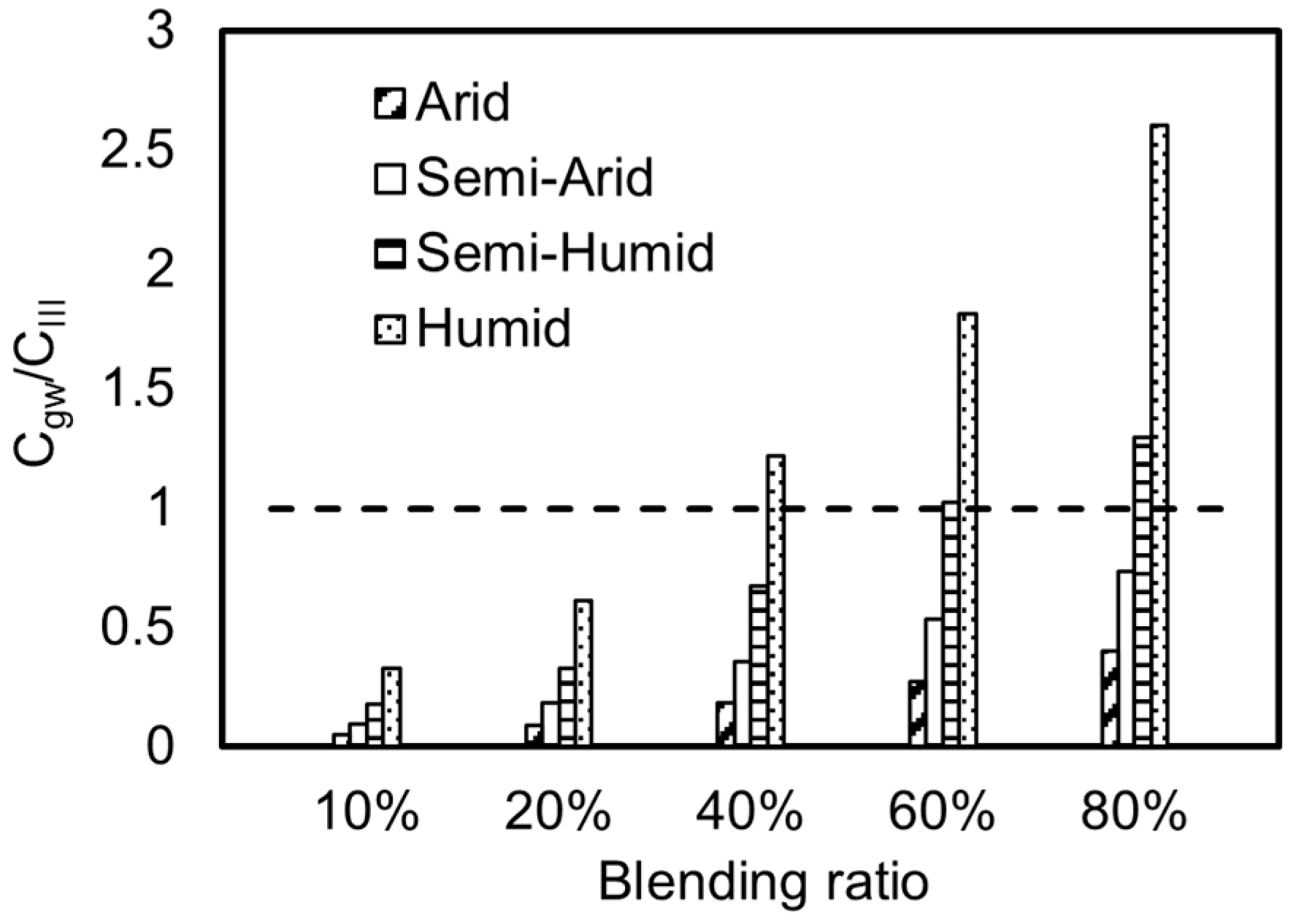
3.3. Regional Differences in Groundwater Pollution Risk from Utilizing Iron Tailings in Road Construction
3.4. Study on Regionalized Differential Management and Control of Iron Tailings
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, G.; Liu, F.; Xie, Q.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Kumar, E.R.; Sun, J. Exploration of Iron Ore Tailings with High Volume in Sustainable Cement and Ecofriendly Cementitious Material. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 19, 100482–100492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E. Grain-Size Composition Effect on Flexural Response and Pore Structure of Cementitious Tail-Rock Fills with Fiber Reinforcement. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 20, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Bian, P.; Zhang, S. Source and Migration Pathways of Heavy Metals in Soils from an Iron Mine in Baotou City, China. Minerals 2024, 14, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Quan, X.; Jing, W.; Xu, J.; Zhao, N.; Liu, B.; Ying, H. Industrial Byproduct Iron Ore Tailings as Ecofriendly Materials in the Utilization of Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 372, 130813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, M.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, X.; Tang, D.; Zeng, J.; Dai, F. Converting Iron Mine Tailings into Composite Aggregates for Ultrahigh-Performance Mortar. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2025, 37, 4024460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Road Base Materials Prepared by Multi-Industrial Solid Wastes in China: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 373, 130860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, W.; Xie, Q.; Chen, W.; Hui, J.; Li, S.; Liang, M. Splitting Behavior of Polyvinyl Alcohol Fiber Reinforced Iron Ore Tailings Concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, V.O.; Silvestro, L.; Gleize, P.J.P.; Kirchheim, A.P.; Schneider, I.A.H. Application of Leached Iron Ore Tailings to Produce Sustainable Cements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 377, 131095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela Farenzena, H.; Bruschi, G.J.; Schmitt Medina, G.; de Sousa Silva, J.P.; Lotero, A.; Consoli, N.C. Iron Ore Tailings Stabilization with Alternative Alkali-Activated Cement for Dry Stacking: Mechanical and Microstructural Insights. Can. Geotech. J. 2024, 61, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hu, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Jiang, M. Research Progress on Iron-Rich Industrial Waste as Environmentally Functional Material. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 42, 101772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Chen, H.; She, K.; Peng, X.; Yu, Z.; Yao, G.; Xu, Y. Environmental Risk Characteristics and Temporal and Spatial Differentiation Characteristics of Fly Ash Road Filling and Utilization. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, C.; Huang, H. Red Mud Modified Phosphogypsum Based Self-Leveling Mortar: Hydration Mechanism, Heavy Metal Migration Law and Spatial Distribution Characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 426, 136071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Lin, Y.; Meng, B.; Yue, B.; Liang, Y. Mechanical Properties and Leaching Toxicity of Electrolytic Manganese Residue—Red Mud—Coal Fly Ash Paving Bricks. Res. Environ. Sci. 2024, 37, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 298-2019; Technical Specifications on Identification for Hazardous Waste. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- GB 5085.3-2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes- Identification for Extraction Toxicity. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB 5085.6-2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes- Identification for Toxic Substance Content. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Deng, J.; Ning, X.; Qiu, G.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y. Optimizing Iron Separation and Recycling from Iron Tailings: A Synergistic Approach Combining Reduction Roasting and Alkaline Leaching. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathchandra, S.S.; Rengel, Z.; Solaiman, Z.M. A Review on Remediation of Iron Ore Mine Tailings via Organic Amendments Coupled with Phytoremediation. Plants 2023, 12, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, S. Regional Differences in Risks and Control Limits of Road Use of Oil and Gas Extraction Wastes in Yellow River Basin. Res. Environ. Sci. 2024, 37, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayla Kilgo, M.; Anctil, A.; Kennedy, M.S.; Powell, B.A. Metal Leaching from Lithium-Ion and Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries and Photovoltaic Modules in Simulated Landfill Leachates and Municipal Solid Waste Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ge, X.; Liu, P.; Song, G.; Hu, Z. Experimental Study on the Preparation of Cementitious Materials from Iron Ore Tailings by Activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 385, 131409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 25.3-2019; Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Soil Contamination of Land for Construction. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Schatzmayr Welp Sá, T.; Oda, S.; Karla Castelo Branco Louback Machado Balthar, V.; Dias Toledo Filho, R. Use of Iron Ore Tailings and Sediments on Pavement Structure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 128072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yilmaz, E.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, Y. Curing Conditions Effect on Pore Structure, Compressive Strength and Elastic Modulus of Cementitious Tailings Backfills. Powder Technol. 2023, 422, 118458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahi, F.S.; Ghanizadeh, A.R. Compressive Strength, Durability, and Resilient Modulus of Cement-Treated Magnetite and Hematite Iron Ore Tailings as Pavement Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 447, 138076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semyachkov, A.; Pochechun, V.; Semyachkov, K. Hydrogeoecological Conditions of Technogenic Groundwater in Waste Disposal Sites. J. Min. Inst. 2023, 260, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Du, B.; Zhao, M.; Yang, F. Buffering Distance between Drought Hazardous Waste Landfill and Water Source and Its Regulation Strategy. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Du, B.; Xu, Y.; Yang, F. Buffering distance between coastal hazardous waste landfill and water source and its regulation strategy. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Symbol | Unit | Input Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infiltration coefficient | α | Dimensionless | N (0.2, 0.05) |
| Subgrade layer thickness | d | m | U (0.3, 1.2) |
| Solid waste volume fraction | f | Dimensionless | U (0.1, 0.5) |
| Subgrade material density | ρ | kg/L | N (2, 0.2) |
| Soil bulk density | ρb | kg/L | 1.5 |
| Water content ratio of unsaturated zone | θws | Dimensionless | 0.3 |
| Groundwater Darcy velocity | Ugw | m/a | 25 |
| Groundwater mixing zone thickness | σgw | m | N (2, 0.082) |
| Soil permeability | I | m/a | 0.3 |
| Road width | W | m | U (3.5, 30) |
| Hydraulic conductivity | K | m/d | U (10, 50) |
| Hydraulic gradient | i | ‰ | U (3, 6) |
| Porosity | n | % | U (30, 50) |
| Longitudinal dispersion coefficient | DL | m2/d | U (5, 10) |
| Pollutant | As | Mn | Ba | Ni | Co | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.040 | 1.860 | 2.600 | 0.080 | 0.080 | 0.050 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.005 | 0.600 | 0.300 | 0.010 | 0.006 | 0.01 |
| Minimum | 0.030 | 0.253 | 1.691 | 0.057 | 0.057 | 0.025 |
| Maximum | 0.053 | 3.325 | 3.228 | 0.097 | 0.097 | 0.091 |
| Class III Limit | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Zhang, D.; Cao, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Hua, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Q. Environmental Risk and Management of Iron Tailings in Road Subgrade. Toxics 2025, 13, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070603
Xu X, Zhang D, Cao J, Wu C, Wang Y, Hua J, Zhao Z, Zhang J, Yu Q. Environmental Risk and Management of Iron Tailings in Road Subgrade. Toxics. 2025; 13(7):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070603
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaowei, Dapeng Zhang, Jie Cao, Chaoyue Wu, Yi Wang, Jing Hua, Zehua Zhao, Jun Zhang, and Qi Yu. 2025. "Environmental Risk and Management of Iron Tailings in Road Subgrade" Toxics 13, no. 7: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070603
APA StyleXu, X., Zhang, D., Cao, J., Wu, C., Wang, Y., Hua, J., Zhao, Z., Zhang, J., & Yu, Q. (2025). Environmental Risk and Management of Iron Tailings in Road Subgrade. Toxics, 13(7), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070603







