Acute Dermatotoxicity of Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) in Zebrafish Epidermis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Maintenance and Experimental Set-Up
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Maltose-Reduced Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs)
2.4. Toxicity Testing of AgNPs
2.5. Preparation of Engineered Silver Nanoparticle Suspensions (eAg-NPs)
2.6. Sample Fixation and Tissue Processing
2.7. Tissue Histochemistry
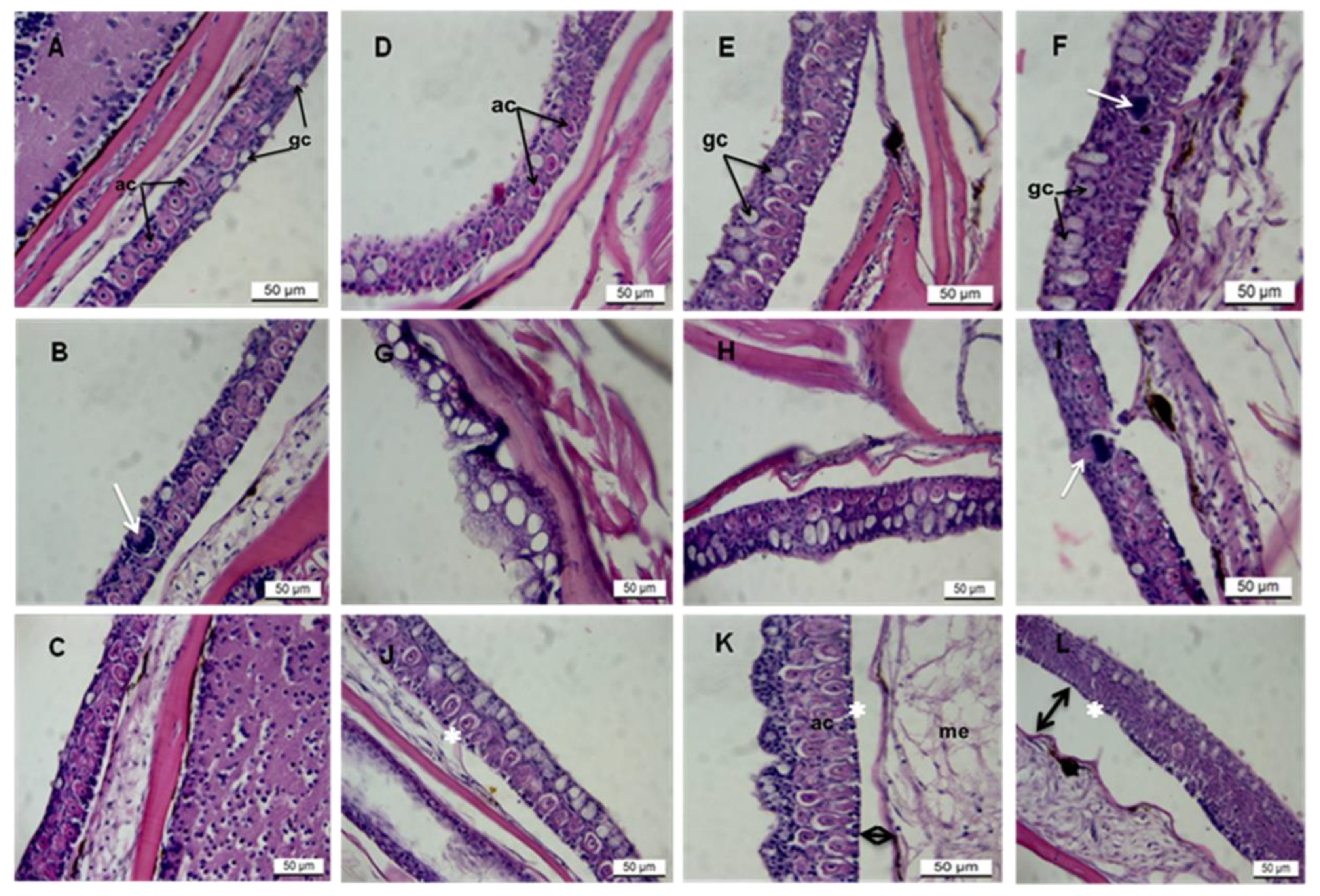
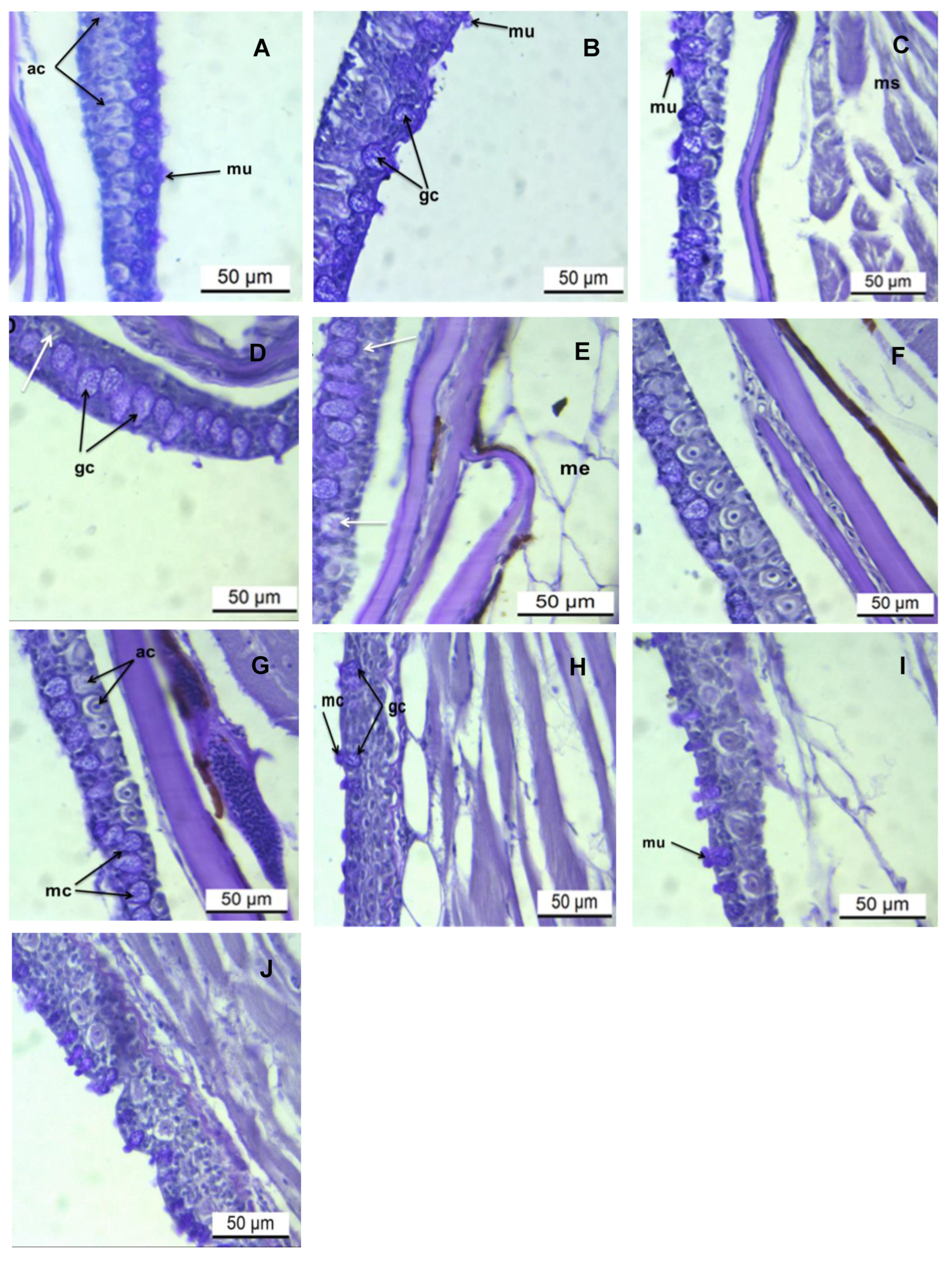
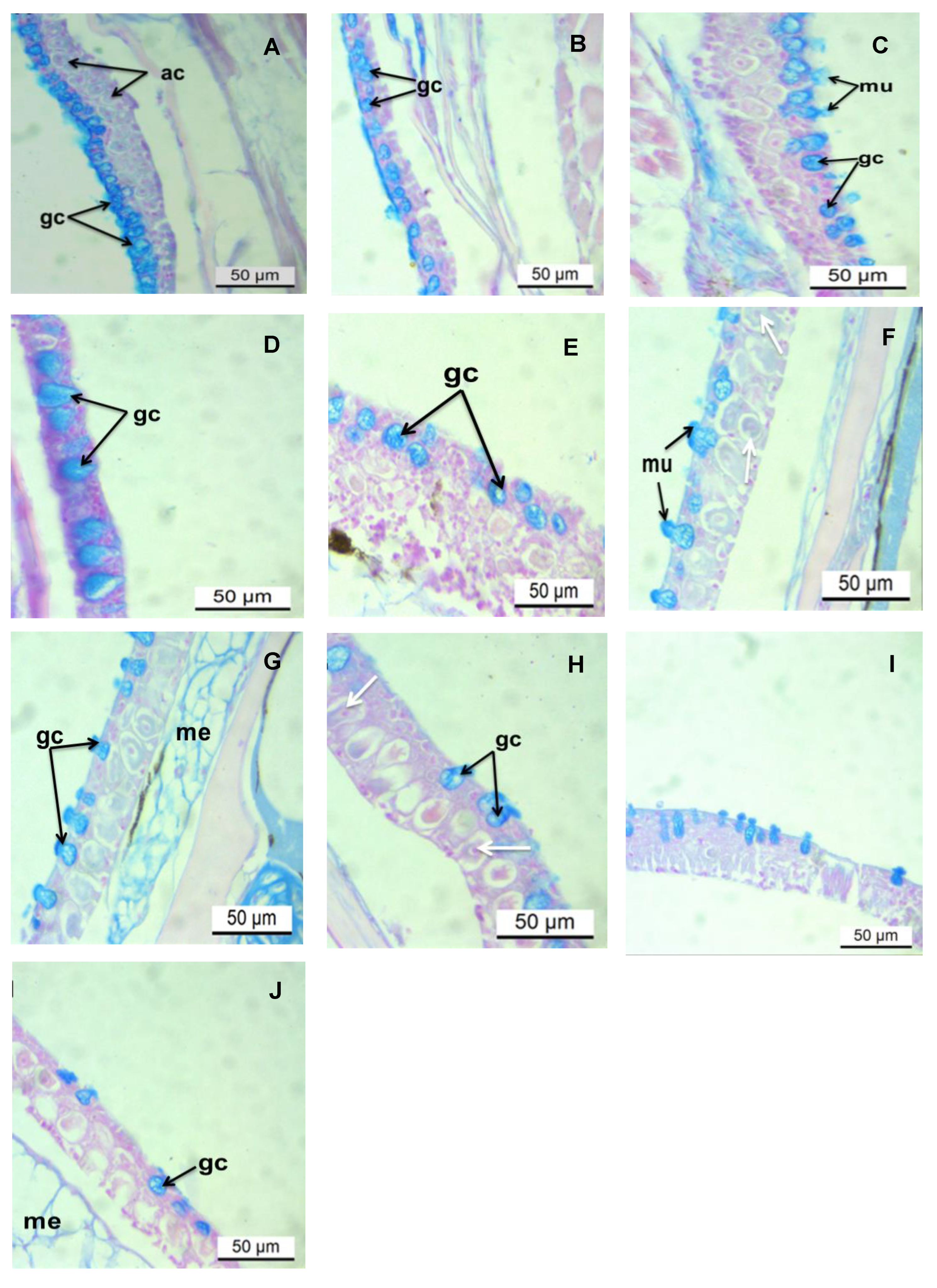
3. Results
3.1. Histopathology of AgNPs on Zebrafish Skin
3.2. Histochemical Analysis of the Epidermis PAS/AB pH 2.5 Stains
4. Discussion
4.1. Rapid Mucus Production as a Fish Stress Response to AgNP Exposure
4.2. Goblet Cell Dynamics and Epidermal Integrity in Response to AgNP Exposure
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Khawaga, A.M.; Zidan, A.; El-Mageed, A.I.A. Preparation methods of different nanomaterials for various potential applications: A review. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1281, 135148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M. Nanomaterials: Types, properties, recent advances, and toxicity concerns. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health. 2022, 25, 00319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.S.; Hammad, E.N.; Mohamed, A.A.; El-Dougdoug, W. A comprehensive review of nanomaterials: Types, synthesis, characterization, and applications. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorowicz, A.; Margarita, V.; Fais, G.; Pantaleo, A.; Manca, A.; Concas, A.; Rappelli, P.; Fiori, P.L.; Cao, G. Characterization of nanomaterials synthesized from Spirulina platensis extract and their potential antifungal activity. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcolea-Rodriguez, V.; Simeone, F.C.; Dumit, V.I.; Faccani, L.; Toledo, V.; Haase, A.; Coca-López, N.; Portela, R.; Bañares, M.A. A refined dose metric for nanotoxicology based on surface site reactivity for oxidative potential of engineered nanomaterials. Nanoscale Adv. 2025, 7, 2929–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bañares, M.A.; Alcolea-Rodriguez, V.; Portela, R. A catalytic perspective to nanomaterials reactivity-based toxicity; implications for single-and multiple-component nanomaterials (nanocomposites). NanoImpact 2025, 37, 100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Song, Y. Mechanistic insight on nanomaterial-induced reactive oxygen species formation. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 151, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allará, C.; Ciccone, G.; Ciocca, M.; Vasquez, S.; Ibba, P.; Maver, M.; Mimmo, T.; Lugli, P.; Petti, L. Electronic Nanomaterials for Plants: A Review on Current Advances and Future Prospects. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2025, 2500080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.A.; Abd-Elaziem, W.; Elsheikh, A.; Zayed, A.A. Advancements in nanomaterials for nanosensors: A comprehensive review. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 4015–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azani, M.R.; Hassanpour, A. Nanotechnology in the fabrication of advanced paints and coatings: Dispersion and stabilization mechanisms for enhanced performance. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202400844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitha, V.S.; Jeyasubramanian, K.; Prabhin, V.S.; Dhanabalan, S.; Thirumurugan, A. Nanomaterials in paints. In Handbook of Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; Volume 1, pp. 693–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciğeroğlu, Z.; El Messaoudi, N.; Şenol, Z.M.; Başkan, G.; Georgin, J.; Gubernat, S. Clay-based nanomaterials and their adsorptive removal efficiency for dyes and antibiotics: A review. Mater Today Sustain. 2024, 26, 100735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Roy, A.; Bhasin, S.; Emran, T.B.; Khusro, A.; Eftekhari, A.; Moradi, O.; Rokni, H.; Karimi, F. Nanomaterials: An alternative source for biodegradation of toxic dyes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 164, 112996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borase, H.; Sharma, A.; Patel, P.; Patil, S. Nanomaterials: A Backbone to Various Biological Applications. In Advanced Nanomaterials for Biological, Nutraceutical, and Medicinal Applications; Apple Academic Press: Waretown, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 205–232. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.; Pires, P.C.; Fonseca, M.; Costa, G.; Giram, P.S.; Mazzola, P.G.; Bell, V.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Veiga, F.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Nanomaterials in cosmetics: An outlook for European regulatory requirements and a step forward in sustainability. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Shenoy, S.; Shetty, S.; Zulfa, S.; Haseena, T. Nanomaterials in cosmetics. In Handbook of Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; Volume 2, pp. 497–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.M.; Hayes, A.W. Mechanisms and Assessment of Genotoxicity of Metallic Engineered nanomaterials in the human environment. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadiq, S.; Khan, S.; Khan, I.; Khan, A.; Humayun, M.; Wu, P.; Usman, M.; Khan, A.; Alanazi, A.F.; Bououdina, M. A critical review on metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) based nanomaterials for biomedical applications: Designing, recent trends, challenges, and prospects. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varaprasad, K.; Jayaramudu, T.; Kartikeyan, C.; Congreve, R.C.; Reddy, G.V.S. Development, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications of PVP–AgCl Nanomaterials: Antibacterial and Anticancer Properties. ChemistrySelect 2025, 10, e202404398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yue, H. Two-dimensional nanomaterials induced nano-bio interfacial effects and biomedical applications in cancer treatment. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Li, S.; Ho, S.H. How do nanomaterials influence the spread of antibiotic resistance genes in aquatic environments? Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 111183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, A.; Cazzagon, V.; Faraggiana, E.; Bettiol, C.; Picone, M.; Marcomini, A.; Badetti, E. An overview on dispersion procedures and testing methods for the ecotoxicity testing of nanomaterials in the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrowiec, B. Nanowaste in the aquatic environment–threats and risk countermeasures. Desalination Water Treat. 2025, 322, 101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Liu, H.; Bao, Y.; Liu, G. Toxicological impacts of nanomaterials on marine bivalves. In Marine Bivalve Mollusks and Emerging Pollutants; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thit, A.; Skjolding, L.M.; Hansen, S.F. Ecotoxicity testing of nanomaterials in sediment–suggestions to improve science and regulation. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2024, 11, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, J.; Shen, N.; Wang, L.; Hu, C. Effects of Engineered Nanomaterials on Aquatic Plants: Current Status, Trends, and Challenges; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 1–25. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/698_2024_1179 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Babakhani, N.; Sobhanardakani, S.; Mansouri, B.; Cheraghi, M.; Lorestani, B. Bioaccumulation of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) Co-Exposed with Graphene Oxide Nanosheets (GNs) in the Gill and Intestine Tissues of Guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2025, 114, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiarashi, M.; Mahamed, P.; Ghotbi, N.; Tadayonfard, A.; Nasiri, K.; Kazemi, P.; Badkoobeh, A.; Yasamineh, S.; Joudaki, A. Spotlight on therapeutic efficiency of green synthesis metals and their oxide nanoparticles in periodontitis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Kumar, A.; Singh, N. Optimized conditions for phytoinspired fabrication of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and exploring their photo-and chemocatalytic routes of methylene blue (MB) dye degradation. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 13563–13594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Ramírez, S.F.; Ramírez-Anguiano, A.C.; Minjarez-Ibañez, A.D.C.; Sánchez-Toscano, Y.G.; Cavazos-Garduño, A.; Serrano-Niño, J.C.; García-Bustos, E.D.; Rosales, D.A.L.; Velázquez-Juárez, G.; Zamudio-Ojeda, A. Biological toxicity, safety issues, and environmental hazards associated with silver nanoparticles. In Silver Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 341–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, K.; Singh, A.K.; Lyndem, S.; Kumari, K.; Jha, A.N.; Singha Roy, A. Fundamental Understanding of Bio-Nano Interface of Lysozyme on Psidium guajava Polyphenol Coated Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanistic Insights into the Effect of Protein Corona on the Antibacterial Efficacy. Langmuir 2025, 41, 2899–2915. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c04832 (accessed on 23 May 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shi, L.; Song, Z.; Geng, Z.; Yan, Y. The antibacterial activity and formation mechanism of quercetin-coated silver nanoparticles and protein complex. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1334, 141878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Green Silver Nanoparticles: An Antibacterial Mechanism. Antibiotics 2024, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkasa, D.P.; Arozal, W.; Kusmardi, K.; Syaifudin, M.; Purwanti, T.; Laksmana, R.I.; Pratama, A.A.; Sugoro, I.; Rahayu, D.P. Toxicity and biodistribution of alginate-stabilized AgNPs upon 14-days repeated dose oral administration in mice. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 14, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sati, A.; Ranade, T.N.; Mali, S.N.; Ahmad Yasin, H.K.; Pratap, A. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs): Comprehensive insights into bio/synthesis, key influencing factors, multifaceted applications, and toxicity—A 2024 update. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 7549–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Vohra, N. A Comprehensive Review of Silver Nanoparticles: Classification, Synthesis, Properties, Applications, and Toxicity. Pexacy Com. 2024, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Ullah, K.; Bibi, N.; Ahmad, B.; Shah, K.; Qiang, T.Y. The potential toxicity of chemically fabricated silver nanomaterials based on accumulation and histological changes in fish (Cyprinus carpio). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2024, 87, 2292–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernick, M.; Kennedy, A.J.; Thomas, T.; Scott, K.C.; Sipe, J.M.; Hendren, C.O.; Wiesner, M.R.; Hinton, D.E. Morphologic alterations across three levels of biological organisation following oral exposure to silver-polymer nanocomposites in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Sci. Nano 2024, 11, 3317–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannam, H.E.; Khedr, A.I.; El-Sayed, R.; Ahmed, N.M.; Salaah, S.M. Oxidative stress responses and histological changes in the liver of Nile tilapia exposed to silver bulk and nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15390. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-97731-8#citeas (accessed on 23 May 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuthe, G.E.; Siguba, B. Silver nanoparticle-induced nephrotoxicity in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffitt, R.J.; Lavelle, C.M.; Kane, A.S.; Denslow, N.D.; Barber, D.S. Chronic nanoparticulate silver exposure results in tissue accumulation and transcriptomic changes in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 130, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, K.W.; Auffan, M.; Badireddy, A.R.; Nelson, C.M.; Wiesner, M.R.; Chilkoti, A.; Liu, J.; Marinakos, S.M.; Hinton, D.E. Uptake of silver nanoparticles and toxicity to early life stages of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes): Effect of coating materials. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 120, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Q. Silver nanoparticles cause oxidative damage and histological changes in medaka (Oryzias latipes) after 14 days of exposure. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.; Ogulata, R.T.; Sezgin Bozok, S. Silver nanoparticles against SARS-CoV-2 and its potential application in medical protective clothing–a review. J. Text. Inst. 2022, 113, 2825–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, N.; Ramesh, S.; Shanmugam, R. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica and Syzygium aromaticum extract and its antibacterial action against Enterococcus faecalis: An in vitro study. Cureus. 2024, 16, e65044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Yadav, P.; Bala, S.; Kaur, J. Probing the Fascinating Role of Eu-AgNPs in the Synthesis of Bioactive Substituted Chalcones as a Green Matrix and Study of Their Biological Potential. J. Organomet. Chem. 2025, 1028, 123528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, E.; Okuthe, G.E. Engineered nanoparticles in aquatic systems: Toxicity and mechanism of toxicity in fish. Emerg. Contam. 2023, 9, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyaf Dezfuli, B.; Lorenzoni, M.; Carosi, A.; Giari, L.; Bosi, G. Teleost innate immunity, an intricate game between immune cells and parasites of fish organs: Who wins, who loses. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1250835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Hoz, M.F.T.; Flamini, M.A.; Portiansky, E.L.; Díaz, A.O. Analysis of glycoconjugates and morphological characterization of the descending colon and rectum of the plains viscacha, Lagostomus maximus. Zoology 2019, 135, 125691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabillon, N.A.R.; Lazado, C.C. Mucosal barrier functions of fish under changing environmental conditions. Fishes 2019, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiepanek, A.; Kuryk, Ł.; Garofalo, M.; Kumar, S.; Baran, J.; Musolf, P.; Siebenhaar, F.; Fluhr, J.W.; Kobiela, T.; Plasenzotti, R.; et al. The multifaceted roles of mast cells in immune homeostasis, infections and cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.X.; Xu, H.Y.; He, Q.L.; Yu, Y.Y.; Xu, Z. The crucial role of fish mucus in regulating progeny inflammation and microbial homeostasis. WatBS 2024, 3, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempuraj, D.; Mentor, S.; Thangavel, R.; Ahmed, M.E.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Raikwar, S.P.; Dubova, I.; Zaheer, S.; Iyer, S.S.; Zaheer, A. Mast cells in stress, pain, blood-brain barrier, neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvain, F.É.; Leroux, N.; Normandeau, É.; Holland, A.; Bouslama, S.; Mercier, P.L.; Luis Val, A.; Derome, N. Genomic and environmental factors shape the active gill bacterial community of an Amazonian teleost holobiont. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02064-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canosa, L.F.; Bertucci, J.I. The effect of environmental stressors on growth in fish and its endocrine control. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1109461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtak, G.; Nepal, R.; Bouras, G.; Shaghayegh, G.; Bennett, C.; Finnie, J.; Fenix, K.; Psaltis, A.J.; Wormald, P.J.; Vreugde, S. Staphylococcus aureus biofilm-secreted factors cause mucosal damage, mast cell infiltration, and goblet cell hyperplasia in a rat rhinosinusitis model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, T.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Yang, P.; He, S.; Zhang, H. Transcriptomic analysis on the effects of altered water temperature regime on the fish ovarian development of Coreius guichenoti under the impact of river damming. Biology 2022, 11, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, A. Alterations and resilience of intestinal microbiota to increased water temperature are accompanied by the recovery of immune function in Nile tilapia. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebi, M.; Yilmaz, Y. Epithelial barrier hypothesis in the context of nutrition, microbial dysbiosis, and immune dysregulation in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1575770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.M.; Li, P.; Chen, C.Z.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.H. Toxic effects of emerging pollutants on mucosal organs of teleost fish: A review focusing on mucosal microbiota, physical barrier and immune barrier. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 978, 179431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, H.; Longshaw, M.; Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, S.; Ren, M. Effects of replacing fishmeal with methanotroph (Methylococcus capsulatus, Bath) bacteria meal (FeedKind®) on growth and intestinal health status of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 122, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Puertas, R.; Adamek, M.; Mallavia, R.; Falco, A. Fish skin mucus extracts: An underexplored source of antimicrobial agents. Mar. Drugs. 2023, 21, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-López, F.E.; Ibarz, A.; Ordóñez-Grande, B.; Vallejos-Vidal, E.; Andree, K.B.; Balasch, J.C.; Fernández-Alacid, L.; Sanahuja, I.; Sánchez-Nuño, S.; Firmino, J.P.; et al. Skin multi-omics-based interactome analysis: Integrating the tissue and mucus exuded layer for a comprehensive understanding of the teleost mucosa functionality as a model of study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 613824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanahuja, I.; Guerreiro, P.M.; Girons, A.; Fernandez-Alacid, L.; Ibarz, A. Evaluating the repetitive mucus extraction effects on mucus biomarkers, mucous cells, and the skin-barrier status in a marine fish model. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1095246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baisakhi, B.; Das, B.K.; Mohanty, D.; Jena, K.; Pradhan, J. Nanotherapeutics: An Approach for Fish Disease Treatment. In Laboratory Techniques for Fish Disease Diagnosis; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 471–488. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-96-4620-3_20 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Collado-Gonzalez, M.; Esteban, M.Á. Chitosan-nanoparticles effects on mucosal immunity: A systematic review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 130, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidian, G.; Lazado, C.C.; Mahboub, H.H.; Mohammadi-Aloucheh, R.; Prokić, M.D.; Nada, H.S.; Faggio, C. Chemically and green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles alter key immunological molecules in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) skin mucus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Z.; Ai, F.; Du, W.; Yin, Y.; Guo, H. Multiple effects of ZnO nanoparticles on goldfish (Carassius auratus): Skin mucus, gut microbiota and stable isotope composition. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamad, N.; Kar, A.; Mehta, S.; Dewani, M.; Ravichandran, V.; Bhardwaj, P.; Sharma, S.; Banerjee, R. Immunomodulatory nanosystems for treating inflammatory diseases. Biomaterials 2021, 274, 120875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Mishra, A.K. Immunomodulation, toxicity, and therapeutic potential of nanoparticles. BioTech 2022, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sau, S.; Dey, A.; Pal, P.; Das, B.; Maity, K.K.; Dash, S.K.; Tamili, D.K.; Das, B. Immunomodulatory and immune-toxicological role of nanoparticles: Potential therapeutic applications. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 135, 112251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Kumawat, M.; Gogoi, H.; Madhyastha, H.; Lichtfouse, E.; Daima, H.K. Engineered nanomaterials for immunomodulation: A review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 727–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, E.; Hidouri, S.; Kechnebbou, M.; Amara, S. Ascorbic acid and glutamate as therapeutics for oxidative stress and behavioral dysfunction in rats exposed to zinc nanoparticles. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2025, 17, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, R.; Zaki, H.; Saeed, H. Health Risks and Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Rats: Assessment of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Effects. Future Perspect. Med. Pharm. Environ. Biotechnol. 2024, 1, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, Y.; Ijaz, N.; Maheen, A.; Mustafa, G.; Bafail, D.A.; Qamar, M.R.; Ahsan, M.A.; Masood, N.; Rajeh, N.; Mohiuddin, M. Multi-biomarker approach to assess oxidative stress and antioxidants profile in male albino rats exposed to ZnO nanoparticle. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2024, 4. Available online: https://asianjab.com/journal/index.php/ajab/article/view/658 (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Mohamed, A.S.; Ghannam, H.E.; El-Lahamy, A.A.; Soliman, H.A. The protective role of vitamins (E+ C) on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to ZnO NPs and Zn ions: Bioaccumulation and proximate chemical composition. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2022, 22, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batir-Marin, D.; Boev, M.; Cioanca, O.; Lungu, I.I.; Marin, G.A.; Burlec, A.F.; Mitran, A.M.; Mircea, C.; Hancianu, M. Exploring oxidative stress mechanisms of nanoparticles using Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Toxicological and pharmaceutical insights. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Lee, Y.H.; Chou, C.L.; Chang, Y.S.; Liu, W.C.; Chiu, H.W. Oxidative stress and potential effects of metal nanoparticles: A review of biocompatibility and toxicity concerns. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatami, M.; Ghorbanpour, M. Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles-induced reactive oxygen species: Phytotoxicity and detoxification mechanisms in plant cell. PPB 2024, 213, 108847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuthe, G. Investigation of apoptosis as a biomarker for earlier detection of impending sex inversion in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 2016, 71, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwafemi, O.S.; Lucwaba, Y.; Gura, A.; Masabeya, M.; Ncapayi, V.; Olujimi, O.O.; Songca, S.P. A facile completely ‘green’size tunable synthesis of maltose-reduced silver nanoparticles without the use of any accelerator. Colloid. Surf. B. 2013, 102, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.J.; Pham, C.H.; Lee, J.; Bae, E.; Yi, J.; Gu, M.B. Evaluation of the toxic impact of silver nanoparticles on Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 94, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuthe, G.E.; Bhomela, B. Morphology, histology and histochemistry of the digestive tract of the Banded tilapia, Tilapia sparrmanii (Perciformes: Cichlidae). Zoologia 2020, 37, e51043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuthe, G.E. DNA and RNA pattern of staining during oogenesis in zebrafish (Danio rerio): A confocal microscopy study. Acta Histochem. 2013, 115, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, R.; Krishnaraj, C.; Kumar, V.A.; Harper, S.L.; Kalaichelvan, T.P.; Yun, S.I. In vivo toxicity evaluation of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles and gold nanoparticles on adult zebrafish: A comparative study. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, J.; Vijver, M.G.; Ahmad, F.; Richardson, M.K.; Peijnenburg, W.J. Toxicity of different-sized copper nano-and submicron particles and their shed copper ions to zebrafish embryos. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwafemi, O.S.; Vuyelwa, N.; Scriba, M.; Songca, S.P. Green controlled synthesis of monodispersed, stable and smaller sized starch-capped silver nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2013, 106, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacci, S. The Evolution of Mast Cells Across All Vertebrate Classes: The Mystery Continues. 2025. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202502.2210/v2 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Benhamed, S.; Guardiola, F.A.; Martínez, S.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.J.; Pérez-Sirvent, C.; Mars, M.; Esteban, M.A. Exposure of the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) to sediments contaminated with heavy metals down-regulates the gene expression of stress biomarkers. Toxicol. Rep. 2016, 3, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.; Guo, R.; Pan, K.; Xu, H.; Chu, X. Mucus and mucin: Changes in the mucus barrier in disease states. Tissue Barriers 2025, 2499752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Cuesta, A.; Arizcun, M.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A. Comparative skin mucus and serum humoral defence mechanisms in the teleost gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Fleming, E.; Luo, Y. An overview of the biochemistry, synthesis, modification, and evaluation of mucoadhesive polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of bioactive compounds. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 2023, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, V.K.; Domouhtsidou, G.P.; Raftopoulou, E. Localization of Hg and Pb in the palps, the digestive gland and the gills in Mytilus galloprovincialis (L.) using autometallography and X-ray microanalysis. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 125, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marigómez, I.; Soto, M.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Angulo, E.; Giamberini, L. Cellular and subcellular distribution of metals in molluscs. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2002, 56, 358–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Reyero, N.; Thornton, C.; Hawkins, A.D.; Escalon, L.; Kennedy, A.J.; Steevens, J.A.; Willett, K.L. Assessing the exposure to nanosilver and silver nitrate on fathead minnow gill gene expression and mucus production. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2015, 4, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, A.D.; Thornton, C.; Steevens, J.A.; Willett, K.L. Alteration in Pimephales promelas mucus production after exposure to nanosilver or silver nitrate. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2869–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durai, U.; Athisuyambulingam, M.; Viswambaran, G.; Beevi, F.S.M. Cytopathological changes of Selected Tissues in Asian Sea Bass, Latescalcarifer (Bloch) Exposed to Mercury. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 1749–1772. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/cytopathological-changes-selected-tissues-asian/docview/2565223158/se-2 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Ghosh, S.; Nukavarapu, S.P.; Jala, V.R. Effects of heavy metals on gut barrier integrity and gut microbiota. Microbiota 2024, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, G.V.; Girons, A.; Okubamichael, M.A.; Pittman, K. Mucosal epithelial homeostasis: Reference intervals for skin, gill lamellae and filament for Atlantic salmon and other fish species. J. Fish. Dis. 2025, 48, e14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabssawy, A.N.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Azab, A.M.; Khalaf-Allah, H.M.; Ashry, A.S.; Ali, A.O.; Sabra, A.B.A.; Salem, S.S. Hindering the biofilm of microbial pathogens and cancer cell lines development using silver nanoparticles synthesized by epidermal mucus proteins from Clarias gariepinus. BMC Biotechnol. 2024, 24, 28. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12896-024-00852-7 (accessed on 23 May 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razmara, P.; Pyle, G.G. Effect of copper nanoparticles and copper ions on the architecture of rainbow trout olfactory mucosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzate-Díaz, H.A.; Fernández-Alacid, L.; Pardo-Carrasco, S.C. Biomarkers in Skin Mucus for a Minimally Invasive Approach to Stress in Red Tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) Fry. Biology 2025, 14, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Magalhães, C.R.; Farinha, A.P.; Carrilho, R.; Schrama, D.; Cerqueira, M.; Rodrigues, P.M. A new window into fish welfare: A proteomic discovery study of stress biomarkers in the skin mucus of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). J. Proteom. 2023, 281, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Martinez, L.; Brandts, I.; Reyes-López, F.; Tort, L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Teles, M. Skin mucus as a relevant low-invasive biological matrix for the measurement of an acute stress response in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Water 2022, 14, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keihani, R. Physiological and Endocrine Stress in Atlantic salmon (Salmo Salar): Validation of Alternative Matrices for Evaluating Fish Welfare in Captivity-Focus on Less Invasive Matrices of Mucus and Feces. 2025. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11250/3184695 (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Leonora, F.H.S.V.; Caipang, C.M.A. Exploring the Bioactive Properties and Potential Probionts in the Fish Mucosa. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 2025, 55, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD, T.N. 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section; OECD: Paris, France, 1992; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
| Item Group/Hour | Number of Goblet Cells/Hour | Size of Goblet Cells/(µm) Hour | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 96 h | 24 h | 48 h | 96 h | |
| Control 0 | 11.17 ± 3.148 | 12.67 ± 2.275 | 12.56 ± 2.617 | 12.71 ± 2.084 | 14.13 ± 2.453 | 13.9 ± 1.99 |
| 0.031 μg/L | 20.00 ± 2.275 a | 13.17 ± 2.065 | 10.83 ± 1.339 a | 7.07 ± 1.22 a | 15.85 ± 2.369 a | 15.25 ± 1.609 |
| 0.250 μg/L | 18.94 ± 2.287 a | 18.89 ± 2.298 a | 11.28 ± 1.074 | 13.13 ± 5.079 | 16.15 ± 2.298 | 13.73 ± 1.516 |
| 5.000 μg/L | 12.00 ± 2.086 | 9.556 ± 1.423 a | 14.67 ± 2.635 | 11.57 ± 4.236 | 8.256 ± 1.382 a | 6.403 ± 1.583 a |
| Organ | Pathological Lesion Types Observed | 0 μg/L | 0.031 μg/L | 0.250 μg/L | 5.000 μg/L | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| − | 24 h | 48 h | 96 h | 24 h | 48 h | 96 h | 24 h | 48 h | 96 h | ||
| Epidermal Tissues | Irregular structure of alarm cells | − | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Shrunk cytoplasm alarm cells | − | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | |
| PAS reaction | − | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | |
| AB (pH 2.5) | − | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okuthe, G.E.; Siguba, B. Acute Dermatotoxicity of Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) in Zebrafish Epidermis. Toxics 2025, 13, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070592
Okuthe GE, Siguba B. Acute Dermatotoxicity of Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) in Zebrafish Epidermis. Toxics. 2025; 13(7):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070592
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkuthe, Grace Emily, and Busiswa Siguba. 2025. "Acute Dermatotoxicity of Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) in Zebrafish Epidermis" Toxics 13, no. 7: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070592
APA StyleOkuthe, G. E., & Siguba, B. (2025). Acute Dermatotoxicity of Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) in Zebrafish Epidermis. Toxics, 13(7), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070592






