Ecological Risk and Human Health Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Datong Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.3. Heavy Metal Pollution Evaluation Methods
2.3.1. Geo-Accumulation Index Method
2.3.2. Enrichment Factor Method
2.3.3. Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation Methodology
2.4. Health Risk Evaluation Methodology
2.5. Monte Carlo Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Sediment Heavy Metal Content
3.2. Characterization of Heavy Metal Contamination of Sediments
3.2.1. Geo-Accumulation Index
3.2.2. Enrichment Factor
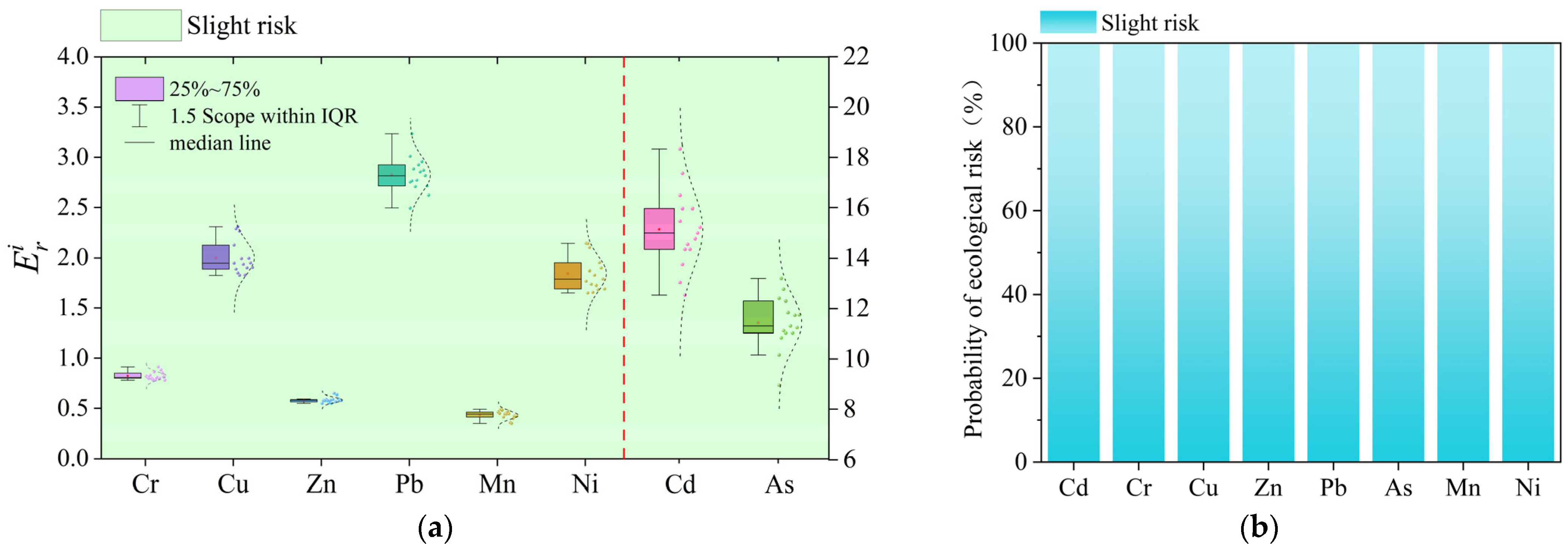
3.3. Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risks of Sediment Heavy Metals
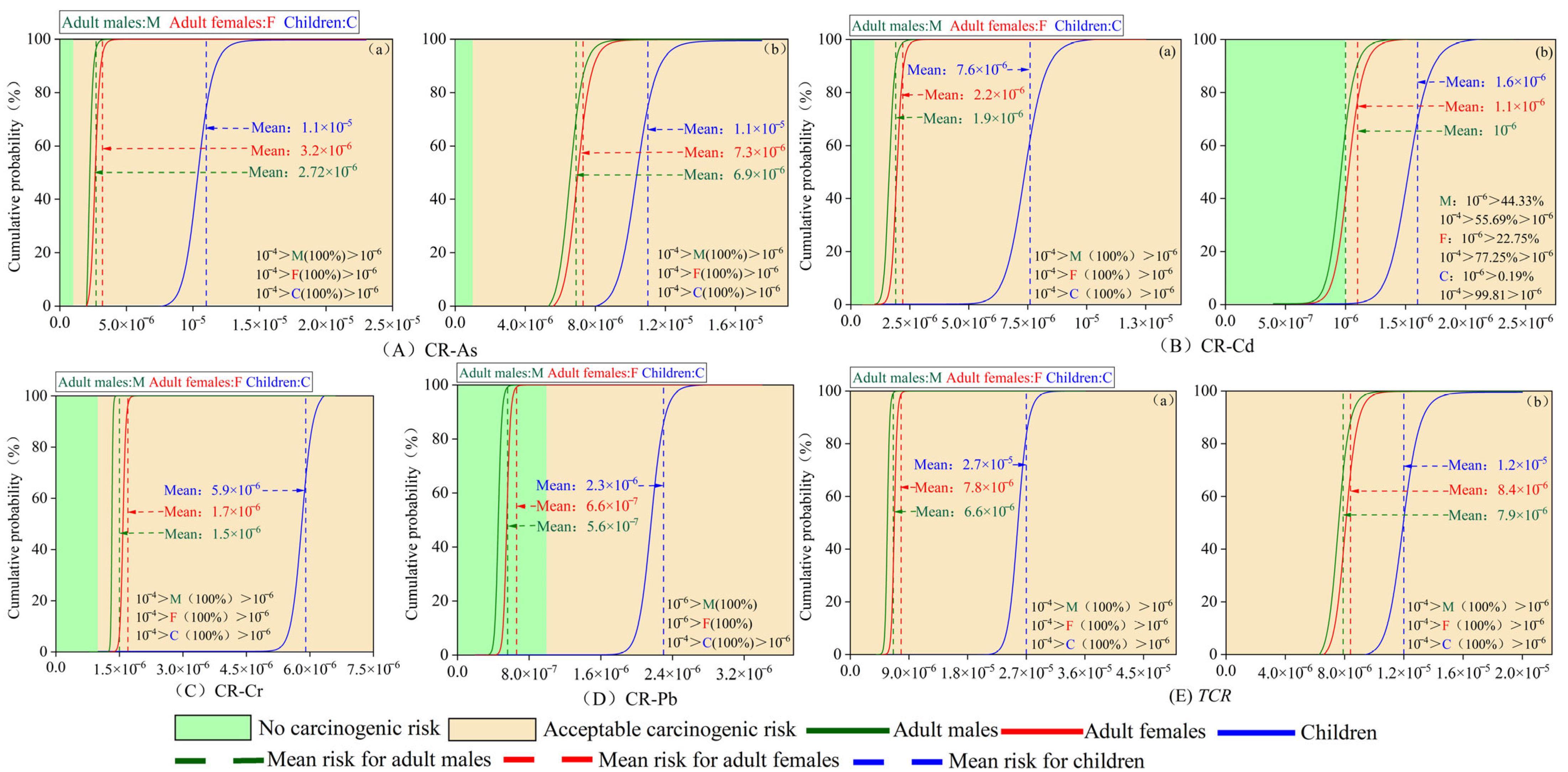
3.4. Human Health Evaluation
Carcinogenic and Non-Carcinogenic Health Risk Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion of the Causes of Heavy Metal Contamination of Sediments
4.1.1. Impact of Human Activities
4.1.2. Regulation by Natural Factors
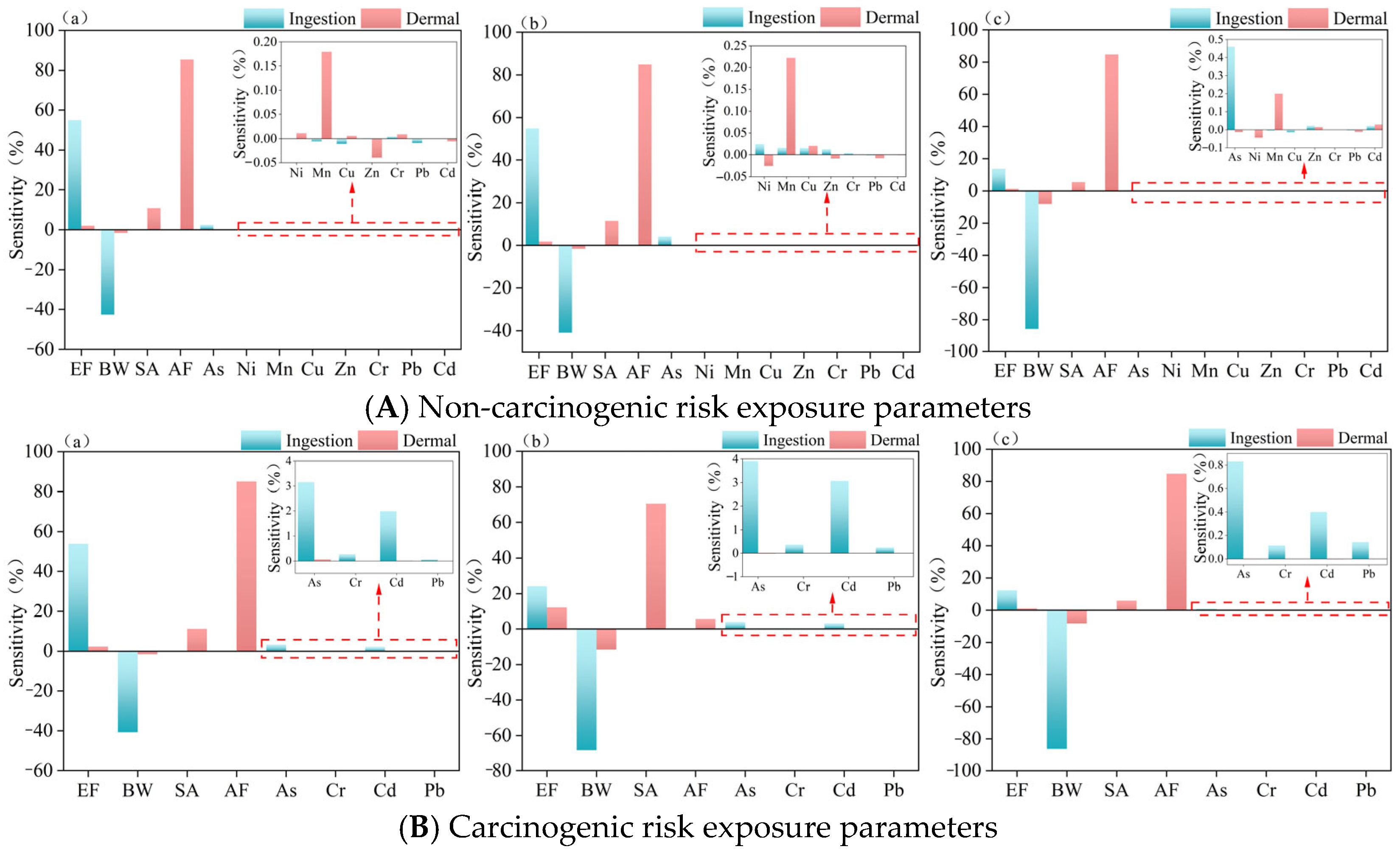
4.2. Major Factors Affecting Human Health in the Datong Lake Area
4.2.1. Main Factors Influencing the Health Risks of Different Population Groups in the Datong Lake District
4.2.2. Sensitivity Discussion of Human Health Risk Parameters
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The average values of Cd, Pb, Cr, Cu, Mn, Pb, Ni, and Zn contents in the sediments of Datong Lake were higher than the background values of soil elements in the sediments of Dongting Lake. The average value of As content in heavy metals was lower than the background value of soil, and the possibility of point-source contamination in the study area is slight.
- (2)
- According to the evaluation results of the Geo-cumulative index method and Enrichment factor method, the average values of Igeo and EF of heavy metal elements in the sediments of Daitong Lake were Ni > Cu > Cr > Mn > Cd > Pb > Zn > As, and the grading standards of the Igeo pollution level showed that all heavy metal elements were slightly polluted except As, which was not polluting. From the EF pollution level grading standard, Pb, Zn, and As are non- polluted, and Ni, Cu, Cr, Mn and Cd are slightly polluted. The combination of the two evaluation methods can verify each other and make up for the limitations of a single method.
- (3)
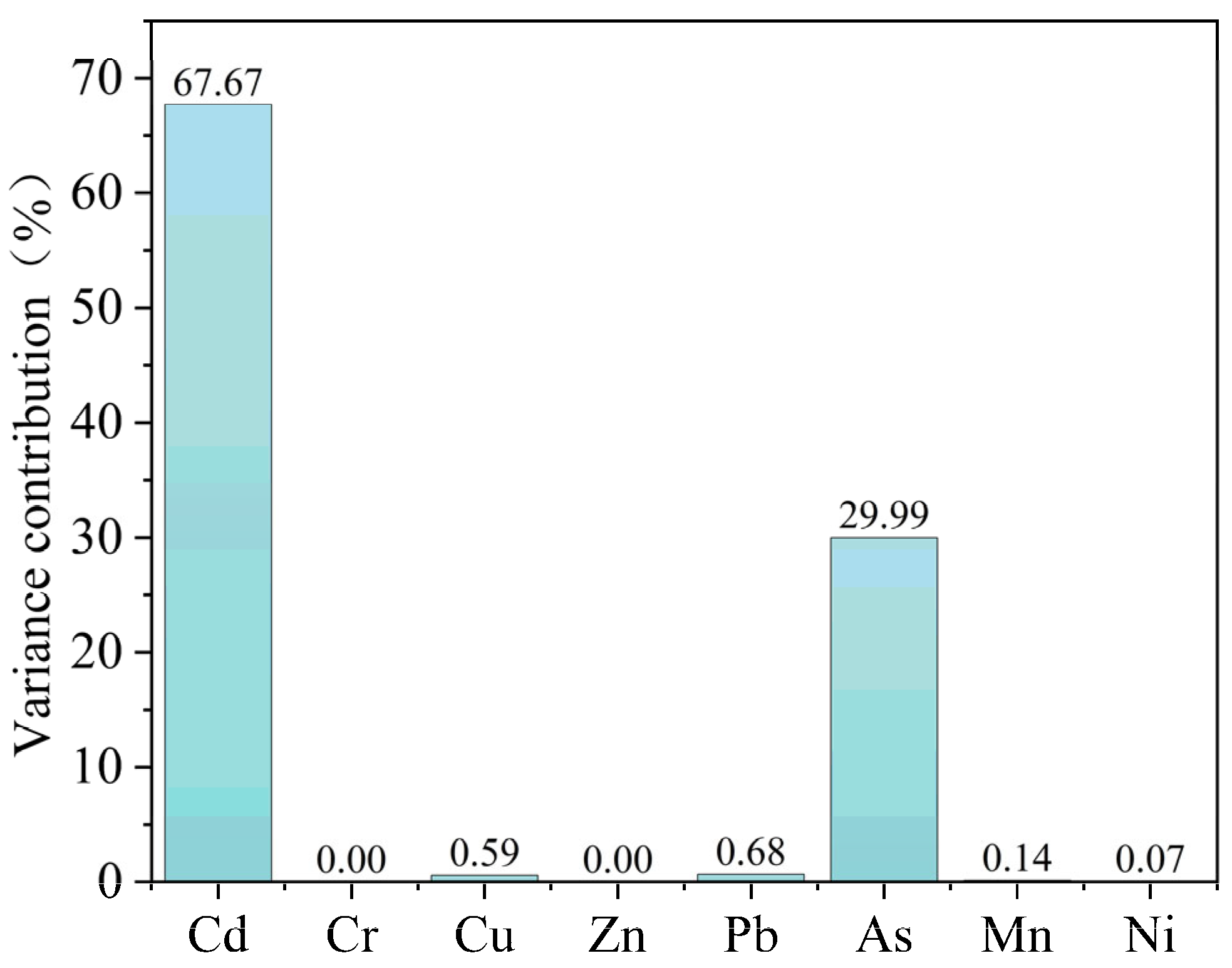
- The analysis of potential risk shows that the average value of for each heavy metal element in the sediments of Datong Lake was as follows: Cd > As > Pb > Cu > Ni > Cr > Zn > Mn, and all heavy metal elements are slightly polluted. Among them, Cd and As are the main contributing elements to the risk of heavy metals in the sediments of Datong Lake.
- (4)
- Both non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks for all populations in the study area remain low for heavy metal exposure via ingestion and dermal pathways. In the ecological and health risk assessments, As and Cd exhibited significantly higher sensitivity than the other heavy metals. Consequently, continuous monitoring and source-tracking of Cd and As are essential to safeguard long-term ecological integrity and public health in the region.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| USEPA | United States Environmental Protcction Agency |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| DLSHBV | Dongting Lake sediment hydrological background values |
| TF | Toxicity factor |
References
- Zheng, S.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, W. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and food crops in the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration of China. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanusi, I.O.; Olutona, G.O.; Wawata, I.G.; Onohuean, H. Heavy metals pollution, distribution and associated human health risks in groundwater and surface water: A case of Kampala and Mbarara districts, Uganda. Discov. Water 2024, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Tao, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, F.; Sui, S.; Jia, L. Assessment of the migration characteristics and source-oriented health risks of heavy metals in the soil and groundwater of a legacy contaminated by the chlor-alkali industry in central China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Shukla, R.; Srivastava, P.K.; Mishra, V.K. Assessment of heavy metal pollution level, ecological and human health risks in surface water of Narmada River, India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lang, Y. A national wide evaluation of heavy metals pollution in surface sediments from different marginal seas along China Mainland. Reg. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 42, 101637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyemang, J.; Gyimah, E.; Ofori, P.; Nimako, C.; Akoto, O. Pollution and Health Risk Implications of Heavy Metals in the Surface Soil of Asafo Auto-Mechanic Workshop in Kumasi, Ghana. Chem. Afr. 2022, 5, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamad, A.A.; Ghrefat, H.; Howari, F.; Khawaja, A.A.; Zoubi, A. Assessment of roadside pollution by heavy metals: A case study from the District of Bani Kinanah, Irbid, Northern Jordan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yuan, L.; Yifu, L.I.; Dandan, H.E.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of main water systems in Hunan Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 1934–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.; Islam, M.A.; Tamim, U.; Ahmed, F.T.; Hossen, M.B. Heavy metal analysis of water and sediments of the Kaptai Lake in Bangladesh: Contamination and concomitant health risk assessment. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2024, 210, 111358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.; Mahmood, S.; Khalid, A.; Shahzad, K.; Anjum, M.Z. Seasonal variation in non-point source heavy metal pollution in Satpara Lake and its toxicity in trout fish. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redwan, M.; Elhaddad, E. Heavy metal pollution in Manzala Lake sediments, Egypt: Sources, variability, and assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, D.; Castillo, F.; Nambi, I.; Sadhasivam, R.; Valleru, H.; Fohrer, N. Evaluating heavy metal levels and their toxicity risks in an urban lake in Chennai, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 1849–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, L.; Zhou, C.; Liu, G.; Yao, L. A study of environmental pollution and risk of heavy metals in the bottom water and sediment of the Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 19658–19673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Ren, B. Trends and Sources of Heavy Metal Pollution in Global River and Lake Sediments from 1970 to 2018. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 257, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, N.; Singh, S.P.; Sahu, S.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Maurya, A.S.; Kumar, N.; Rout, R.K.; Tripathy, G.R. Isotopic evidence of autochthonous organic matter acting as a major sink of anthropogenic heavy metals in modern lacustrine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Ge, Y.; Abuduwaili, J. Health risk of heavy metal exposure from dustfall and source apportionment with the PCA-MLR model: A case study in the Ebinur Lake Basin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 272, 118950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ge, J.; Yang, X.; Cheng, D.; Yuan, C.; Liu, Z.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Gu, Y. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Dajiuhu Lake Wetland in Shennongjia, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 30, 25999–26011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, Z.H.; Fahad, K.K. Study of the Heavy Metals Concentration Level in the Water and Sediment and some Tissues of the Grass Carp Ctenopharyngodon idella V. Cultured in Cages in the Euphrates River. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1262, 072064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Yang, F.; Du, H. Comparisons of heavy metals levels in water, sediment and crayfish under rice-crayfish co-culture and pond culture modes with correlation analysis and health risk assessment. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 5088–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshe, P.; Jugade, R. Influence of Fe/Al oxyhydroxides and soil organic matter on the adsorption of Pb onto natural stream sediment. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhan, W.Y. Control of phosphorus release from sediment by hydrous zirconium oxide combined with calcite, bentonite and zeolite. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, G.; Canl, O.; Aslan, E. Spatial distribution, source identification and ecological risk assessment of POPs and heavy metals in lake sediments of Istanbul, Turkey. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113172. [Google Scholar]
- Soomro, S.; Shi, X.; Guo, J.; Hu, C.; Zwain, H.M.; Liu, C.; Khan, M.Z.; Niu, C.; Zhao, C.; Ahmed, Z. Appraisal of climate change and source of heavy metals, sediments in water of the Kunhar River watershed, Pakistan. Nat. Hazards 2023, 116, 2191–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Xue, B.; Yang, H. Comparison of spatiotemporal burial and contamination of heavy metals in core sediments of two plateau lakes with contrasting environments: Implication for anthropogenic-driven processes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkelemi, M.J.; Mwaijengo, G.N.; Rwiza, M.J. Assessment of Physicochemical Profile and Heavy Metal Constituents in the Groundwaters of Rural Areas in Southwest Tanzania. Water Resour. 2024, 51, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amala, O.; Vara, L.K.; Dadhich, A.; Ramesh, M. Water Quality Index and Heavy Metal Pollution Index of Groundwater Quality: A case Study in Visakhapatnam District, AP. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2022, 26, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Xu, C.; Kang, S.; Huo, A.; Nover, D. Heavy metals in water and surface sediments of the Fenghe River Basin, China: Assessment and source analysis. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3072–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Yu, F.; Tao, X.; Guo, J.; Yu, Y. Contamination, Spatial Distribution and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Surface Soil of Anhui Chaohu Economic Development Zone, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Huang, X. Heavy Metal Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment in Sediments of the Xiling Channel Inland Waterway Guangdong Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 11, 40–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jonjev, M.; Mileti, Z.; Pavlovi, D.; Mati, M.; Akmak, D.; Mitrovi, M.; Pavlovi, P. Health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in the riparian zone of the Sava River (southeastern Europe): Effects of high and low water events. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Bhuyan, M.S.; Rahman, M.M. Toxic metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in water and sediment at ship breaking sites in the Bay of Bengal Coast, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smatti-Hamza, I.; Keddari, D.; Mehennaoui, S.; Afri-Mehennaoui, F.Z. Assessment of the level of heavy metals contamination via sediments quality indices of the Koudiet Medouar Dam and its tributary (Batna, Algeria). Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umroh; Bengen, D.G.; Prartono, T.; Riani, E. Heavy Metals Source Identification by Enrichment factor in Bangka Island Sediments, Indonesia. Environ. Asia 2022, 15, 120–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nijeje, E.; Senyonjo, A.; Sahan, S.J.; Byamugisha, D.; Ntambi, E. Speciation of Selected Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of River Rwizi, Mbarara City, Uganda. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, D.J. Quantitative risk analysis of sediment heavy metals using the positive matrix factorization-based ecological risk index method: A case of the Kuye River, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba, C. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Heavy Metals in Lake and Reservoir Sediments in China: A Pollution Status and Risk Assessment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, L.; Enguo, S.; Shenwen, C.; Ying, D.; Jun, Z.; Boping, Z. Spatial distribution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Hongfeng Lake. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1272. [Google Scholar]
- Okuku, E.O.; Peter, H.K. Choose of Heavy Metals Pollution Biomonitors: A Critic of the Method that uses Sediments total Metals Concentration as the Benchmark. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Afify, A.D.G.; Abdel-Satar, A.M. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in water, sediment and plants in the Nile River in the Cairo region, Egypt. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2020, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Wang, R.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, W.; Hao, J.; Huang, F. Historical co-enrichment, source attribution, and risk assessment of critical nutrients and heavy metal/metalloids in lake sediments: Insights from Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 390. [Google Scholar]
- Sishu, F.K.; Melese, T.B.; Aklog, D. Assessment of heavy metal and other chemical pollution in Lake Tana along urban peripheries, Ethiopia. Water Pract. Technol. 2024, 19, 1200–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelik, U.; Tekin-Zan, S. Evaluation of selected heavy metal and selenium pollution in water and sediments of Lake Eirdir (Isparta/Türkiye) using statistical analysis and pollution indices. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2024, 53, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Fan, Y.; Li, H. Rapid diagnosis of heavy metal pollution in lake sediments based on environmental magnetism and machine learning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slukovskii, Z.; Guzeva, A.; Malysheva, M.; Kudryavtseva, L. Pristine Tundra Lakes in the North of Murmansk Region (Arctic): Geochemistry of Sediments, Pollution Assessment and Heavy Metal Forms. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 18, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Hu, J. Soil heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment around Wangchun Industrial Park, Ningbo, China. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Anita; Kulsoom, M. Health risk assessment due to heavy metal contamination in groundwater of Basuhi River Basin, Jaunpur, India. Environ. Sustain. 2024, 7, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.C. Soil Geochemical Mapping of the Sal Island (Cape Verde): Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment. Land 2024, 13, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.; Fu, S.; Liu, H.; Song, H.; Ren, L. Soil heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment associated with development zones in Shandong, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 30016–30028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Bin, X.; Zhenjun, Z.; Tian, L.; Chuanxin, C.; Yang, L.; Chunhua, L.; Dan, Y. Drivers of organic carbon stocks in eutrophic lake sediments after reestablishment of submerged aquatic vegetation. Plant Soil 2024, 499, 639–653. [Google Scholar]
- Yan-Yu, S.U.; Chun-Hua, L.I.; Liao, Y.J.; Yan, L.I.; Dong, X.H. Application of “safe and just operating space” based on multi-source data in environmental management of datong lake catchment. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2021, 45, 197–205. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ze-Dong, Y.; Zhi-Heng, Q.; Zhong-Ke, B.; Yi-Cheng, H. The influence of land use change and socioeconomic factors on the water quality of typical reservoirs in Hunan Province, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 2270–2277. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.T.; Liu, D.; Zhong, W.J.; Ni, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Accumulation and composition characteristics of organic phosphorus in sediments from the Yangtze River–connected lakes, China. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 1800–1813. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Zhanggen, H.; Hongbin, L. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Dongting Lake Sediments from 2003 to 2021. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2025, 20, 281. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.; Yin, H.; Dong, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Lu, C. Analysis and probabilistic health risk assessment of vertical heavy metal pollution in the water environment of reservoir in the west coast new area of Qingdao, China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Hu, H.; Lin, H.; Xie, L. Bedding Slope Destabilization under Rainfall: A Case Study of Zhuquedong Slope in Hunan Province, China. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, R.T.T.; Loring, D.H. Determination of Lithium in the NRCC Marine Sediments: MESS-1, BCSS-1, PACS-1 and the NIST River Sediment: SRM 2704. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2010, 14, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.T.; Yao, T.; She, X.S.; Zhang, P.Q.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.Y.; Qi, N. Simultaneous determination of multiple elements of tea garden soil using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 267, 042023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, A.; Murava, R.T.; Norgbey, E.; Zhu, X. Spatial Distribution, Risk Index, and Correlation of Heavy Metals in the Chuhe River (Yangtze Tributary): Preliminary Research Analysis of Surface Water and Sediment Contamination. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Lu, S. Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediment, and fish from Dongting Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34076–34090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, G.; Deka, H. Crude oil associated heavy metals (HMs) contamination in agricultural land: Understanding risk factors and changes in soil biological properties. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.C.; Le, V.H.; Luong Van, T. Assessment of the accumulation level and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments of Bong Mieu River, Quang Nam Province, Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekperusi, A.O.; Asiwa, D.O. Trophodynamics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in seafood from a tropical estuary in the gulf of Guinea. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, F.U.; Umar, R. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment using deterministic and Monte Carlo simulation approaches in the Himalayan spring and surface water systems of Kulgam District, Kashmir valley, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.S.; Wang, Y.L.; Jiang, C.B.; Tai, P.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Chao, H.J.; Lo, Y.C.; Hseu, Z.Y.; Hsi, H.C.; Chien, L.C. Assessment of sources and health risks of heavy metals in metropolitan household dust among preschool children: The LEAPP-HIT study. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Elnabi, M.K.; Elkaliny, N.E.; Elyazied, M.M.; Azab, S.H.; Elkhalifa, S.A.; Elmasry, S.; Mouhamed, M.S.; Shalamesh, E.M.; Alhorieny, N.A.; Abd Elaty, A.E. Toxicity of Heavy Metals and Recent Advances in Their Removal: A Review. Toxics 2023, 11, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.; Shu, R.; Pang, S.Y. Temporal and Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk Assessment and source Identification of heavy Metals in the Surface Sediments of Lake Taihu Basin, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.Y.; Yan, G.H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, B.H. Trends and risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of river-connected lakes: A case study of Dongting Lake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209 Pt A, 117181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.G.; Geng, M.M.; Li, F.; Xie, Y.H.; Tian, T.; Chen, Q. Spatiotemporal characteristics and drivers of ecosystem service interactions in the Dongting Lake Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.Q.; Ye, C.; Li, C.H.; Wei, W.W.; Zheng, X.Y.; Hu, W. Characteristics of spatial and temporal distribution of water quality in Datong Lake and analysis of its influencing factors. Environ. Eng. 2022, 2, 34–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Li, T.; Huang, B.; Feng, Y.L.; Lei, M.J.; Zhuo, H.H.; Wu, Y.L. Evolutionary characteristics of water quality and eutrophication of typical lakes in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River and their drivers from 2016 to 2020. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.P.; Xu, G.X.; Yang, R.Q.; Dai, J.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.W. Responses of soil antibiotic resistance genes to the decrease in grain size of sediment discharged into Dongting Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.L. Constructing a novel pH-mediated magnetic relaxation sensor via the Mn(II)/Mn(IV) conversion. Microchem. J. 2024, 196, 109677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, A.; Akhtar, S.; Mohsin, F. Evaluating drinking water quality and associated health risks in primary schools of punjab: A multi-method approach combining conventional analysis, monte carlo simulation, and geospatial mapping. Environ. Earth Sci. 2025, 84, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K.; Li, F.; Chen, N.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, J. Analysis of Heavy Metal Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Dried Fish Marketed in Guangzhou, China. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 203, 2041–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.F.; Song, Y.X.; Li, W.; Wen, Y.B.; Ji, J.F. Health Risk of Heavy Metal and Implication for Ecological Threat in Soils Weathered from the Black Shale. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2025, 114, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Gao, Y.T.; Wang, C.K.; Gu, H.L.; Sun, M.K.; Dang, Y.H.; Ai, S.W. Heavy metal pollution status, children health risk assessment and source apportionment in farmland soils in a typical polluted area, Northwest China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2024, 38, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Level | Pollution Index | Pollution Category |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | ≤0 | Uncontaminated |
| 1 | (0,1] | Slightly |
| 2 | (1,2] | Moderately |
| 3 | (2,3] | Moderately/Heavily |
| 4 | (3,4] | Heavily |
| 5 | >4 | Extremely |
| Level | Pollution Index | Pollution Category |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | ≤1 | Uncontaminated |
| 1 | (1,2] | Slightly |
| 2 | (2,5] | Moderately |
| 3 | (5,20] | Moderately/Heavily |
| 4 | (20,40] | Heavily |
| 5 | >40 | Extremely |
| Level | Pollution Index | Risk Class |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | ≤150 | Slight risk |
| 1 | (150,300] | Moderate risk |
| 2 | (300,600] | Higher risk |
| 3 | (600,1200] | High risk |
| 5 | >1200 | Extremely high risk |
| Elements | RfD | SF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingestion | Dermal | Ingestion | Dermal | |
| As | 3.00 × 10−4 | 1.23 × 10−4 | 1.50 × 100 | 1.50 × 100 |
| Cd | 1.00 × 10−3 | 1.00 × 10−5 | 1.80 × 100 | 3.80 × 10−1 |
| Cr | 3.00 × 10−3 | 6.00 × 10−5 | 5.00 × 10−1 | - |
| Cu | 4.00 × 10−2 | 1.20 × 10−2 | - | - |
| Hg | 3.00 × 10−4 | 2.10 × 10−5 | - | - |
| Ni | 2.00 × 10−2 | 5.40 × 10−3 | - | - |
| Pb | 3.50 × 10−3 | 5.25 × 10−3 | 8.50 × 10−3 | - |
| Zn | 3.50 × 10−1 | 6.00 × 10−2 | - | - |
| Mn | 4.60 × 10−2 | 1.84 × 10−3 | - | - |
| Exposure Parameters | Unit | Probability Distribution | Adult Males | Adult Females | Children |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRing | mg/d | point | 114 | 114 | 200 |
| ED | a | point | 70 | 70 | 18 |
| EF | d/a | triangular | 345 (180–365) | 345 (180–365) | 345 (180–365) |
| BW | kg | logarithmic | 67.55 ± 8.72 | 57.59 ± 8.03 | - |
| BW | kg | triangular | - | - | 29.30 (5.20–56.80) |
| ABS | - | point | 0.03 (As), 0.14 (Cd), 0.001 (Cr), 0.1 (Cu), 0.35 (Ni), 0.006 (Pb), 0.02 (Zn), 0.01 (Mn) | ||
| SA | m2 | triangular | 0.169 (0.085–0.422) | 0.153 (0.076–0.382) | 0.086 (0.043–0.216) |
| AF | mg/cm2·d | logarithmic | 0.49 ± 0.54 | 0.49 ± 0.54 | 0.65 ± 1.2 |
| CF | - | point | 10 (−6) | 10 (−6) | 10 (−6) |
| AT (non-carcinogenic) | d | point | 365 × ED | 365 × ED | 365 × ED |
| AT (carcinogenic) | d | point | 365 × 70 | 365 × 70 | 365 × 70 |
| Cd | Cr | Cu | Zn | Pb | As | Mn | Ni | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min/(mg/kg) | 0.54 | 96.20 | 43.70 | 128.00 | 36.00 | 9.78 | 914.00 | 49.40 |
| Max/(mg/kg) | 0.79 | 112.42 | 55.30 | 151.00 | 46.70 | 14.40 | 1287.00 | 64.20 |
| Median/(mg/kg) | 0.66 | 109.00 | 51.90 | 143.00 | 41.38 | 11.40 | 1010.00 | 59.27 |
| Mean/(mg/kg) | 0.66 | 107.07 | 50.81 | 142.67 | 41.36 | 11.37 | 1046.13 | 57.99 |
| SD | 0.07 | 4.85 | 3.98 | 6.44 | 2.51 | 1.13 | 107.80 | 5.15 |
| CV/% | 10.13 | 4.53 | 7.84 | 4.52 | 6.08 | 9.94 | 10.30 | 8.89 |
| DLSHBV/(mg/kg) | 0.33 | 44.00 | 20.20 | 83.30 | 23.30 | 12.90 | 450.00 | 21.20 |
| TF | 30 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 5 |
| Distribution type | logistic | minimum extreme | minimum extreme | binomial | logistic | maximum extreme | maximum extreme | triangular |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Chen, R.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Xiang, K.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y. Ecological Risk and Human Health Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Datong Lake. Toxics 2025, 13, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070560
Li G, Chen R, Li Z, Wu X, Xiang K, Wang C, Peng Y. Ecological Risk and Human Health Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Datong Lake. Toxics. 2025; 13(7):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070560
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Gao, Rui Chen, Zhen Li, Xin Wu, Kui Xiang, Chiheng Wang, and Yi Peng. 2025. "Ecological Risk and Human Health Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Datong Lake" Toxics 13, no. 7: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070560
APA StyleLi, G., Chen, R., Li, Z., Wu, X., Xiang, K., Wang, C., & Peng, Y. (2025). Ecological Risk and Human Health Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Datong Lake. Toxics, 13(7), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070560







