Arsenic Exposure and Neuropsychological Outcomes in Children: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection and Screening
2.4. Data Extraction and Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Main Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.2. Exposure Assessment and Analytical Techniques
3.3. Markers of Exposure
3.4. Neuropsychological Function and Assessment Methods
3.5. Arsenic Exposure and Neuropsychological Function
3.6. Confounding Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| As | Arsenic |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| iAs | Inorganic arsenic |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Fatoki, J.O.; Badmus, J.A. Arsenic as an Environmental and Human Health Antagonist: A Review of Its Toxicity and Disease Initiation. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 5, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, B.; Djamgoz, M.B.A.; Akün, E. ARSENIC: A Review on Exposure Pathways, Accumulation, Mobility and Transmission into the Human Food Chain. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 243, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Costa, M. Arsenic: A Global Environmental Challenge. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 61, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcella, D.; Cascio, C.; Gómez Ruiz, J. Ángel Chronic Dietary Exposure to Inorganic Arsenic. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, S.Y.; Javaid, D.; Hajam, Y.A.; Reshi, M.S. Arsenic Toxicity: Sources, Pathophysiology and Mechanism. Toxicol. Res. 2023, 13, tfad111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodovnik, A. Environmental Neurotoxicants and Developing Brain. Mt. Sinai J. Med. A J. Transl. Pers. Med. 2011, 78, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punshon, T.; Davis, M.A.; Marsit, C.J.; Theiler, S.K.; Baker, E.R.; Jackson, B.P.; Conway, D.C.; Karagas, M.R. Placental Arsenic Concentrations in Relation to Both Maternal and Infant Biomarkers of Exposure in a US Cohort. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Garcia, N.Y.; Ramírez, A.I.C.; Juarez, K.; Galindo, J.B.; Briceño, G.; Martinez, E.C. Maternal Exposure to Arsenic and Its Impact on Maternal and Fetal Health: A Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e49177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.J. Arsenic Methylation-Lessons from Three Decades of Research. Toxicology 2021, 457, 152800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Xi, S.; Li, X.; Lu, C.; Li, G.; Xu, Y.; Qu, C.; Niu, Y.; Sun, G. Arsenic Speciation Transported Through the Placenta from Mother Mice to Their Newborn Pups. Environ. Res. 2006, 101, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Ghosh, S.; Biswas, B.; Pramanik, S.; Nriagu, J.; Bhowmick, S. Epigenetic Modifications from Arsenic Exposure: A Comprehensive Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 151218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likhar, A.; Patil, M.S. Importance of Maternal Nutrition in the First 1000 Days of Life and Its Effects on Child Development: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, M.S. “The First Thousand Days” Define a Fetal/Neonatal Neurology Program. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 683138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadani, J.D.; Tofail, F.; Nermell, B.; Gardner, R.; Shiraji, S.; Bottai, M.; Arifeen, S.E.; Huda, S.N.; Vahter, M. Critical Windows of Exposure for Arsenic-Associated Impairment of Cognitive Function in Pre-School Girls and Boys: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 1593–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signes-Pastor, A.J.; Vioque, J.; Navarrete-Muñoz, E.M.; Carey, M.; Garc-Villarino, M.; Fernández-Somoano, A.; Tardón, A.; Santa-Marina, L.; Irizar, A.; Casas, M.; et al. Inorganic Arsenic Exposure and Neuropsychological Development of Children of 4–5 Years of Age Living in Spain. Environ. Res. 2019, 174, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signes-Pastor, A.J.; Romano, M.E.; Jackson, B.; Braun, J.M.; Yolton, K.; Chen, A.; Lanphear, B.; Karagas, M.R. Associations of Maternal Urinary Arsenic Concentrations During Pregnancy with Childhood Cognitive Abilities: The HOME Study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 245, 114009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadani, J.D.; Grantham-McGregor, S.M.; Tofail, F.; Nermell, B.; Fängström, B.; Huda, S.N.; Yesmin, S.; Rahman, M.; Vera-Hernández, M.; Arifeen, S.E.; et al. Pre- and Postnatal Arsenic Exposure and Child Development at 18 Months of Age: A Cohort Study in Rural Bangladesh. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofail, F.; Vahter, M.; Hamadani, J.D.; Nermell, B.; Huda, S.N.; Yunus, M.; Rahman, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.M. Effect of Arsenic Exposure During Pregnancy on Infant Development at 7 Months in Rural Matlab, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margiana, R.; Alshahrani, S.H.; Kayumova, D.; Alawadi, A.H.R.; Hjazi, A.; Alsalamy, A.; Qasim, Q.A.; Juyal, A.; Garousi, N. Association Between Maternal Exposure to Arsenic by Drinking Water During Pregnancy and Risk of Preterm Birth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2023, 34, 2947–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, J.S.; Garry, M.R.; Perez, V.; Chang, E.T. Low-Level Arsenic Exposure and Developmental Neurotoxicity in Children: A Systematic Review and Risk Assessment. Toxicology 2015, 337, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, K.K.; Mazumder, D.N.G. Effect of Drinking Arsenic-Contaminated Water in Children. Indian J. Public Health 2012, 56, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quansah, R.; Armah, F.A.; Essumang, D.K.; Luginaah, I.; Clarke, E.; Marfoh, K.; Cobbina, S.J.; Nketiah-Amponsah, E.; Namujju, P.B.; Obiri, S.; et al. Association of Arsenic with Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes/Infant Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Gil, F.; Hernández, A.F.; Alguacil, J.; Lorca, A.; Mendoza, R.; Gómez, I.; Molina-Villalba, I.; González-Alzaga, B.; Aguilar-Garduño, C.; et al. Postnatal Arsenic Exposure and Attention Impairment in School Children. Cortex 2016, 74, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.A.; Fruh, V.; Howe, C.G.; White, R.F.; Henn, B.C. Associations of Metals and Neurodevelopment: A Review of Recent Evidence on Susceptibility Factors. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2020, 7, 237–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanvand, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Khoshnamvand, N.; Jafari, A.; Palangi, H.S.; Mokhayeri, Y. Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Arsenic Exposure in Drinking Water and Intelligence Quotient. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, H.; Charlotte, B. What’s in My Baby’s Food? Healthy Babies Bright Futures: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, K.; Meghan, L. Results of Lifetime IQ Decrement Analysis from Dietary Exposures to Lead and Inorganic Arsenic for Children 0 to <2 Years of Age; Abt Global: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, D.; Thomas, J.; Oliver, S. Clarifying Differences Between Review Designs and Methods. Syst. Rev. 2012, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Peters, M.D.J.; Stern, C.; Tufanaru, C.; McArthur, A.; Aromataris, E. Systematic Review or Scoping Review? Guidance for Authors When Choosing Between a Systematic or Scoping Review Approach. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P. (Ed.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.4 (Updated August 2023); Cochrane: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bramer, W.M.; Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kleijnen, J.; Franco, O.H. Optimal Database Combinations for Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews: A Prospective Exploratory Study. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.R.; Wu, H.; Bellinger, D.C.; Smith, D.R.; Wolff, M.S.; Savitz, D.A. Exposure to Metal Mixtures and Neuropsychological Functioning in Middle Childhood. Neurotoxicology 2022, 93, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, V.K.; Ford-Jones, E.L. Spotlight on Middle Childhood: Rejuvenating the ‘Forgotten Years’. Paediatr. Child Health 2012, 17, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, M.L.; Claeson, M.; Bremberg, S.; Peterson, S.S.; Alfvén, T.; Ndeezi, G. The Missing Middle of Childhood. Glob. Health Action 2023, 16, 2242196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forns, J.; Aranbarri, A.; Grellier, J.; Julvez, J.; Vrijheid, M.; Sunyer, J. A Conceptual Framework in the Study of Neuropsychological Development in Epidemiological Studies. Neuroepidemiology 2012, 38, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, E.; Culakova, E.; Meng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Mohile, S.; Flannery, M.A. Overview of Sankey Flow Diagrams: Focusing on Symptom Trajectories in Older Adults with Advanced Cancer. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2022, 13, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-González, E.; García-Esquinas, E.; de Larrea-Baz, N.F.; Salcedo-Bellido, I.; Navas-Acien, A.; Lope, V.; Gómez-Ariza, J.L.; Pastor, R.; Pollán, M.; Pérez-Gómez, B. Toenails as Biomarker of Exposure to Essential Trace Metals: A Review. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritschl, V.; Ferreira, R.J.O.; Santos, E.J.F.; Fernandes, R.; Juutila, E.; Mosor, E.; Santos-Costa, P.; Fligelstone, K.; Schraven, L.; Stummvoll, G.; et al. Suitability for e-Health of Non-Pharmacological Interventions in Connective Tissue Diseases: Scoping Review with a Descriptive Analysis. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibble, T.; Pansell, T. Clinical Characteristics of Visual Motion Hypersensitivity: A Systematic Review. Exp. Brain Res. 2023, 241, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, W.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, B.; Zhang, Z. A Scoping Review of the Self-Reported Compassion Measurement Tools. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Loiacono, N.J.; Kline, J.; Factor-Litvak, P.; van Geen, A.; Mey, J.L.; Levy, D.; Abramson, R.; Schwartz, A.; et al. A Cross-Sectional Study of Well Water Arsenic and Child IQ in Maine Schoolchildren. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, R.O.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Woolf, A.D.; Jim, R.; Bellinger, D.C. Neuropsychological Correlates of Hair Arsenic, Manganese, and Cadmium Levels in School-Age Children Residing Near a Hazardous Waste Site. Neurotoxicology 2006, 27, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlowe, M.; Stellern, J.; Errera, J.; Moon, C. Main and Interaction Effects of Metal Pollutants on Visual-Motor Performance. Arch. Environ. Health 1985, 40, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.A.; Romano, M.E.; Jackson, B.P.; Bellinger, D.; Korrick, S.; Karagas, M.R. Associations of Perinatal Metal and Metalloid Exposures with Early Child Behavioral Development over Time in the New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study. Expo. Health 2024, 16, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, J.; Nelson, C.; Waldron, C.; Bergeron, M.; Samson, A.; Valentovic, M. Effect of Umbilical Cord Essential and Toxic Elements, Thyroid Levels, and Vitamin d on Childhood Development. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, W.; Colicino, E.; Levin-Schwartz, Y.; Enlow, M.B.; Amarasiriwardena, C.; Andra, S.S.; Gennings, C.; Wright, R.O.; Wright, R.J. Prenatal Metal Mixtures and Sex-Specific Infant Negative Affectivity. Environ. Epidemiol. 2021, 5, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, B.T.; Romano, M.E.; Gui, J.; Punshon, T.; Jackson, B.P.; Karagas, M.R.; Korrick, S.A. Periconceptional and Prenatal Exposure to Metal Mixtures in Relation to Behavioral Development at 3 Years of Age. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 4, e0106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlowe, M.; Cossairt, A.; Moon, C.; Errera, J.; MacNeel, A.; Peak, R.; Ray, J.; Schroeder, C. Main and Interaction Effects of Metallic Toxins on Classroom Behavior. J. Abnorm. Child. Psychol. 1985, 13, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.; Marlowe, M.; Stellern, J.; Errera, J. Main and Interaction Effects of Metallic Pollutants on Cognitive Functioning. J. Learn. Disabil. 1985, 18, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, E.E.; Karagas, M.R.; Demidenko, E.; Bellinger, D.C.; Korrick, S.A. In Utero Arsenic Exposure and Early Childhood Motor Development in the New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study. Front. Epidemiol. 2023, 3, 1139337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.J.; Pedretti, N.F.; Goldson, B.; Mathews, N.; Merced-Nieves, F.; Xhani, N.; Enlow, M.B.; Gershon, R.; Ho, E.; Huddleston, K.; et al. Integrating Data Across Multiple Sites in the Northeastern United States to Examine Associations Between a Prenatal Metal Mixture and Child Cognition. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 193, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilakaratne, R.; Lin, P.I.D.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Landero, J.; Wright, R.O.; Bellinger, D.; Oken, E.; Cardenas, A. Cross-Sectional and Prospective Associations of Early Childhood Circulating Metals with Early and Mid-Childhood Cognition in the Project Viva Cohort. Environ. Res. 2024, 246, 118068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, L.; Mazumdar, M.M.; Bobb, J.F.; Henn, B.C.; Rodrigues, E.; Sharif, O.I.A.; Kile, M.L.; Quamruzzaman, Q.; Afroz, S.; Golam, M.; et al. The Joint Effect of Prenatal Exposure to Metal Mixtures on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes at 20–40 Months of Age: Evidence from Rural Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 067015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, E.G.; Bellinger, D.C.; Valeri, L.; Hasan, M.O.S.I.; Quamruzzaman, Q.; Golam, M.; Kile, M.L.; Christiani, D.C.; Wright, R.O.; Mazumdar, M. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Among 2- to 3-Year-Old Children in Bangladesh with Elevated Blood Lead and Exposure to Arsenic and Manganese in Drinking Water. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2016, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Kline, J.; Siddique, A.B.; Shahriar, H.; Uddin, M.N.; van Geen, A.; Mey, J.L.; et al. Child Intelligence and Reductions in Water Arsenic and Manganese: A Two-Year Follow-up Study in Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect 2016, 124, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nahar, M.N.; Inaoka, T.; Fujimura, M. A Consecutive Study on Arsenic Exposure and Intelligence Quotient (IQ) of Children in Bangladesh. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2014, 19, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, F.; Wasserman, G.A.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Liu, X.; Slavkovich, V.; Siddique, A.B.; Sultana, R.; Sultana, R.; Islam, T.; Levy, D.; et al. Arsenic Exposure and Motor Function Among Children in Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Ahmed, E.; Parvez, F.; Slavkovich, V.; Levy, D.; Mey, J.; van Geen, A.; et al. Manganese Exposure from Drinking Water and Children’s Classroom Behavior in Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Ahsan, H.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Kline, J.; van Geen, A.; Slavkovich, V.; Loiacono, N.J.; Levy, D.; et al. Water Arsenic Exposure and Intellectual Function in 6-Year-Old Children in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Ahsan, H.; Factor-Litvak, P.; van Geen, A.; Slavkovich, V.; LoIacono, N.J.; Cheng, Z.; Hussain, I.; et al. Water Arsenic Exposure and Children’s Intellectual Function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahter, M.; Skröder, H.; Rahman, S.M.; Levi, M.; Hamadani, J.D.; Kippler, M. Prenatal and Childhood Arsenic Exposure Through Drinking Water and Food and Cognitive Abilities at 10 Years of Age: A Prospective Cohort Study. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Ahsan, H.; Levy, D.; Kline, J.; van Geen, A.; Mey, J.; Slavkovich, V.; et al. Arsenic and Manganese Exposure and Children’s Intellectual Function. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Lin, L.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, J.; Dong, G.; Yang, B.; Jing, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, G.; Yu, Z.; et al. Effects of Lead, Cadmium, Arsenic, and Mercury Co-Exposure on Children’s Intelligence Quotient in an Industrialized Area of Southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-X.; Wang, Z.-H.; Cheng, X.-T.; Li, J.; Sang, Z.-P.; Zhang, X.-D.; Han, L.-L.; Qiao, X.-Y.; Wu, Z.-M.; Wang, Z.-Q. Arsenic and Fluoride Exposure in Drinking Water: Children’s IQ and Growth in Shanyin County, Shanxi Province, China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Wu, X.; Huang, K.; Yan, S.; Li, Z.; Xia, X.; Pan, W.; Sheng, J.; Tao, R.; Tao, Y.; et al. Domain- and Sex-Specific Effects of Prenatal Exposure to Low Levels of Arsenic on Children’s Development at 6 Months of Age: Findings from the Ma’anshan Birth Cohort Study in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, C. Gender Differences in Trace Element Exposures with Cognitive Abilities of School-Aged Children: A Cohort Study in Wujiang City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 64807–64821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-D.; Yan, C.-H.; Shen, X.-M.; Tian, Y.; Cao, L.-L.; Yu, X.-G.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.-X. Prenatal Exposure to Multiple Toxic Heavy Metals and Neonatal Neurobehavioral Development in Shanghai, China. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2011, 33, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Zheng, T.; Xia, W.; et al. Prenatal Arsenic Exposure, Arsenic Metabolism and Neurocognitive Development of 2-Year-Old Children in Low-Arsenic Areas. Environ. Int. 2023, 174, 107918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, H.; Qi, X.; Wu, C.; Chang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z. Sex-Specific Differences in Cognitive Abilities Associated with Childhood Cadmium and Manganese Exposures in School-Age Children: A Prospective Cohort Study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Yu, X. Prenatal Exposure to Arsenic and Neurobehavioral Development of Newborns in China. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Geng, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Han, L.; Yao, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, L.; Wen, J. Exposure to Metal Mixtures and Young Children’s Growth and Development: A Biomonitoring-Based Study in Eastern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Qi, X.; Chang, X.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Z. Sex-Specific Associations of Maternal and Childhood Urinary Arsenic Levels with Emotional Problems Among 6-Year-Age Children: Evidence from a Longitudinal Cohort Study in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merced-Nieves, F.M.; Chelonis, J.; Pantic, I.; Schnass, L.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M.; Braun, J.M.; Paule, M.G.; Wright, R.J.; Wright, R.O.; Curtin, P. Prenatal Trace Elements Mixture Is Associated with Learning Deficits on a Behavioral Acquisition Task Among Young Children. New Dir. Child. Adolesc. Dev. 2022, 2022, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozadi, S.S.; Li, L.; Luo, L.; Mackenzie, D.; Erdei, E.; Du, R.; Roman, C.W.; Hoover, J.; O’donald, E.; Burnette, C.; et al. Prenatal Metal Exposures and Infants’ Developmental Outcomes in a Navajo Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Water, E.; Curtin, P.; Gennings, C.; Chelonis, J.J.; Paule, M.; Bixby, M.; McRae, N.; Svensson, K.; Schnaas, L.; Pantic, I.; et al. Prenatal Metal Mixture Concentrations and Reward Motivation in Children. Neurotoxicology 2022, 88, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin-Schwartz, Y.; Gennings, C.; Schnaas, L.; Chávez, M.D.C.H.; Bellinger, D.C.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Wright, R.O. Time-Varying Associations Between Prenatal Metal Mixtures and Rapid Visual Processing in Children. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Kordas, K.; Lopez, P.; Rosado, J.L.; Cebrian, M.E.; Vargas, G.G.; Ronquillo, D.; Stoltzfus, R.J. Association Between Arsenic Exposure and Behavior Among First-Graders from Torreón, Mexico. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, J.L.; Ronquillo, D.; Kordas, K.; Rojas, O.; Alatorre, J.; Lopez, P.; Garcia-Vargas, G.; Caamaño, M.C.; Cebrián, M.E.; Stoltzfus, R.J. Arsenic Exposure and Cognitive Performance in Mexican Schoolchildren. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, J.; Navarro, M.E.; Jimenez-Capdeville, M.E.; Santos-Diaz, M.A.; Golden, A.; Rodriguez-Leyva, I.; Borja-Aburto, V.; Díaz-Barriga, F. Exposure to Arsenic and Lead and Neuropsychological Development in Mexican Children. Environ. Res. 2001, 85, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Amador, D.; Navarro, M.E.; Carrizales, L.; Morales, R.; Calderón, J. Decreased Intelligence in Children and Exposure to Fluoride and Arsenic in Drinking Water. Cad. Saude Publica 2007, 23 (Suppl. S4), S579–S587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, N.; Holla, B.; Heron, J.; Sharma, E.; Zhang, Y.; Fernandes, G.; Iyengar, U.; Spiers, A.; Yadav, A.; Das, S.; et al. Neurocognitive Analysis of Low-Level Arsenic Exposure and Executive Function Mediated by Brain Anomalies Among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults in India. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, E2312810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyanza, E.C.; Bernier, F.P.; Martin, J.W.; Manyama, M.; Hatfield, J.; Dewey, D. Effects of Prenatal Exposure and Co-Exposure to Metallic or Metalloid Elements on Early Infant Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Areas with Small-Scale Gold Mining Activities in Northern Tanzania. Environ. Int. 2021, 149, 106104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.S.D.A.; de Figueiredo, N.D.; Froes-Asmus, C.I.R. Prenatal Exposure to Metals and Neurodevelopment in Infants at Six Months: Rio Birth Cohort Study of Environmental Exposure and Childhood Development (PIPA Project). ISEE Conf. Abstr. 2022, 2022, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Su, F.-C.; Lin, C.-M.; Liao, H.-F.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Jeng, S.-F.; Su, Y.-N.; Chen, P.-C. In Utero Exposure to Environmental Lead and Manganese and Neurodevelopment at 2 Years of Age. Environ. Res. 2013, 123, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Blasco, R.; Murcia, M.; Lozano, M.; Sarzo, B.; Esplugues, A.; Riutort-Mayol, G.; Vioque, J.; Lertxundi, N.; Marina, L.S.; Lertxundi, A.; et al. Prenatal Arsenic Exposure, Arsenic Methylation Efficiency, and Neuropsychological Development Among Preschool Children in a Spanish Birth Cohort. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, C.; Amaya, E.; Gil, F.; Fernández, M.F.; Murcia, M.; Llop, S.; Andiarena, A.; Aurrekoetxea, J.; Bustamante, M.; Guxens, M.; et al. Prenatal Co-Exposure to Neurotoxic Metals and Neurodevelopment in Preschool Children: The Environment and Childhood (INMA) Project. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forns, J.; Fort, M.; Casas, M.; Cáceres, A.; Guxens, M.; Gascon, M.; Garcia-Esteban, R.; Julvez, J.; Grimalt, J.O.; Sunyer, J. Exposure to Metals During Pregnancy and Neuropsychological Development at the Age of 4 Years. Neurotoxicology 2014, 40, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, M.A.; Kelsey, K.T.; MacFarlane, A.J.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Ashley-Martin, J.; Fisher, M.; Fraser, W.D.; Lanphear, B.P.; Muckle, G.; et al. Maternal Folate Status and the Relation Between Gestational Arsenic Exposure and Child Health Outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, R.P.; Fujiwara, T.; Umezaki, M.; Watanabe, C. Home Environment and Cord Blood Levels of Lead, Arsenic, and Zinc on Neurodevelopment of 24 Months Children Living in Chitwan Valley, Nepal. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 29, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, R.P.; Fujiwara, T.; Umezaki, M.; Furusawa, H.; Watanabe, C. Home Environment and Prenatal Exposure to Lead, Arsenic and Zinc on the Neurodevelopment of Six-Month-Old Infants Living in Chitwan Valley, Nepal. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2014, 41, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, R.P.; Fujiwara, T.; Umezaki, M.; Watanabe, C. Association of Cord Blood Levels of Lead, Arsenic, and Zinc with Neurodevelopmental Indicators in Newborns: A Birth Cohort Study in Chitwan Valley, Nepal. Environ. Res. 2013, 121, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.B.; Kao, C.S.; Chien, L.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Liao, K.W. Associations Among Prenatal and Postnatal Arsenic, Lead, and Cadmium Exposures and Motor Development in 3-Year-Old Children: A Longitudinal Birth Cohort Study in Taiwan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 43191–43200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, R.P.; Umezaki, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Watanabe, C. Association of Cord Blood Levels of Lead, Arsenic, and Zinc and Home Environment with Children Neurodevelopment at 36 Months Living in Chitwan Valley, Nepal. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.B.; Hsueh, Y.M.; Kuo, G.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Chang, J.H.; Chien, L.C. Preliminary Study of Urinary Arsenic Concentration and Arsenic Methylation Capacity Effects on Neurodevelopment in Very Low Birth Weight Preterm Children Under 24 Months of Corrected Age. Medicine 2018, 97, e12800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notario-Barandiaran, L.; Díaz-Coto, S.; Jimenez-Redondo, N.; Guxens, M.; Vrijheid, M.; Andiarena, A.; Irizar, A.; Riaño-Galan, I.; Fernández-Somoano, A.; Llop, S.; et al. Latent Childhood Exposure to Mixtures of Metals and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in 4–5-Year-Old Children Living in Spain. Expo. Health 2023, 16, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, G.; Barg, G.; Queirolo, E.I.; Vahter, M.; Peregalli, F.; Mañay, N.; Kordas, K. A Cross-Sectional Study of General Cognitive Abilities Among Uruguayan School Children with Low-Level Arsenic Exposure, Potential Effect Modification by Methylation Capacity and Dietary Folate. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, R.; Hegde, A.M.; Parlees, P.; Keshan, A. Environmental Arsenic Contamination and Its Effect on Intelligence Quotient of School Children in a Historic Gold Mining Area Hutti, North Karnataka, India: A Pilot Study. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2017, 8, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordas, K.; Ardoino, G.; Coffman, D.L.; Queirolo, E.I.; Ciccariello, D.; Mañay, N.; Ettinger, A.S. Patterns of Exposure to Multiple Metals and Associations with Neurodevelopment of Preschool Children from Montevideo, Uruguay. J. Environ. Public Health 2015, 2015, 493471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Ossa, C.A.D.; Ramírez-Giraldo, A.F.; Arroyo-Alvis, K.; Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Díez, S. Neuropsychological Effects and Cognitive Deficits Associated with Exposure to Mercury and Arsenic in Children and Adolescents of the Mojana Region, Colombia. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunwittaya, S.; Ruksee, N.; Khamnong, T.; Jiawiwatkul, A.; Kleebpung, N.; Chumchua, V.; Plitponkarnpim, A.; Nopparat, C.; Permpoonputtana, K. Inorganic Arsenic Contamination and the Health of Children Living Near an Inactive Mining Site: Northern Thailand. EXCLI J. 2022, 21, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Ehrenstein, O.S.; Poddar, S.; Yuan, Y.; Mazumder, D.G.; Eskenazi, B.; Basu, A.; Hira-Smith, M.; Ghosh, N.; Lahiri, S.; Haque, R.; et al. Children’s Intellectual Function in Relation to Arsenic Exposure. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Rahman, M.S.; Kumar, R.; Ali, M.; Niraj, P.K.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, S.K.; Ghosh, A.K. Arsenic Contamination in Groundwater Causing Impaired Memory and Intelligence in School Children of Simri Village of Buxar District of Bihar. J. Ment. Health Hum. Behav. 2019, 24, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.B.; Chakraborty, D.; Mondal, N.K. Effect of Arsenic and Manganese Exposure on Intellectual Function of Children in Arsenic Stress Area of Purbasthali, Burdwan, West Bengal. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzetti, S.; Cagna, G.; Calza, S.; Conversano, M.; Fedrighi, C.; Forte, G.; Giorgino, A.; Guazzetti, S.; Majorani, C.; Oppini, M.; et al. The Effects of the Exposure to Neurotoxic Elements on Italian Schoolchildren Behavior. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, G.; Barg, G.; Vahter, M.; Queirolo, E.I.; Peregalli, F.; Mañay, N.; Millen, A.E.; Yu, J.; Kordas, K. Executive Functions in School Children from Montevideo, Uruguay and Their Associations with Concurrent Low-Level Arsenic Exposure. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, G.; Barg, G.; Vahter, M.; Queirolo, E.I.; Peregalli, F.; Mañay, N.; Millen, A.E.; Yu, J.; Browne, R.W.; Kordas, K. Low Level Arsenic Exposure, b-Vitamins, and Achievement Among Uruguayan School Children. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Guazzetti, S.; Renzetti, S.; Conversano, M.; Cagna, G.; Fedrighi, C.; Giorgino, A.; Peli, M.; Placidi, D.; Zoni, S.; et al. Neurocognitive Impact of Metal Exposure and Social Stressors Among Schoolchildren in Taranto, Italy. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2019, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egwunye, J.; Cardoso, B.R.; Braat, S.; Ha, T.; Hanieh, S.; Hare, D.; Duan, A.X.; Doronila, A.; Tran, T.; Tuan, T.; et al. The Role of Fingernail Selenium in the Association Between Arsenic, Lead and Mercury and Child Development in Rural Vietnam: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 129, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Pan, S.; Chin, W.; Hsu, J.; Guo, Y.L. Urinary Heavy Metals and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Symptoms of Preschool Children: A Mixed-Exposure Analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.S.; Fan, Y.T.; Chien, L.C.; Liao, K.W.; Chang, J.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Jiang, C.B. Effects of Preterm Birth and Postnatal Exposure to Metal Mixtures on Neurodevelopment in Children at 24 Months of Age. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 86856–86865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D. Arsenic Consumption in the United States. J. Environ. Health 2015, 78, 8–44. [Google Scholar]
- Nachman, K.E.; Ginsberg, G.L.; Miller, M.D.; Murray, C.J.; Nigra, A.E.; Pendergrast, C.B. Mitigating Dietary Arsenic Exposure: Current Status in the United States and Recommendations for an Improved Path Forward. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaji, E.; Santosh, M.; Sarath, K.V.; Prakash, P.; Deepchand, V.; Divya, B.V. Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater: A Global Synopsis with Focus on the Indian Peninsula. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, A.; Khan, M.Z.K.; Renzaho, A.M.N. Human Health Risks and Socio-Economic Perspectives of Arsenic Exposure in Bangladesh: A Scoping Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, M.S.; Mise, N.; Ichihara, S. Arsenic Contamination in Food Chain in Bangladesh: A Review on Health Hazards, Socioeconomic Impacts and Implications. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2022, 2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsasuluk, P.; Chotpantarat, S.; Siriwong, W.; Robson, M. Human Biomarkers Associated with Low Concentrations of Arsenic (as) and Lead (Pb) in Groundwater in Agricultural Areas of Thailand. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 13896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Morata, I.; Sobel, M.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; Navas-Acien, A.; Howe, C.G.; Sanchez, T.R. A State-of-the-Science Review on Metal Biomarkers. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2023, 10, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, J. Urinary Arsenic as a Biomarker: Speciation Analysis for the Assessment of Dietary Exposure. In Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Jenisova, Z.; Feszterova, M.; Baros, S.; Liska, J.; Hudecova, D.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Arsenic: Toxicity, Oxidative Stress and Human Disease. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, R.K.; Garla, R.; Kaushal, N.; Bansal, M.P.; Garg, M.L.; Mohanty, B.P. The Relevance of Arsenic Speciation Analysis in Health & Medicine. Chemosphere 2023, 316, 137735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.M.; Chakraborty, R.; Bundschuh, J.; Bhattacharya, P.; Parvez, F. Health Effects of Arsenic Exposure in Latin America: An Overview of the Past Eight Years of Research. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha, G.; Vogler, G.; Lezcano, D.; Nermell, B.; Vahter, M. Exposure to Inorganic Arsenic Metabolites During Early Human Development. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 1998, 44, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolins, M.; Ruchirawat, M.; Landrigan, P. The Developmental Neurotoxicity of Arsenic: Cognitive and Behavioral Consequences of Early Life Exposure. Ann. Glob. Health 2014, 80, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, G.I.V.; Esquivel, D.F.G.; Ortega, D.R.; Ayala, T.B.; Chávez, L.A.R.; López-López, H.E.; Salazar, A.; Flores, I.; Pineda, B.; Gómez-Manzo, S.; et al. Mechanisms Associated with Cognitive and Behavioral Impairment Induced by Arsenic Exposure. Cells 2023, 12, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.R.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; Vaidya, D.; Grau, M.; Francesconi, K.A.; Goessler, W.; Guallar, E.; Post, W.S.; Kaufman, J.D.; Navas-Acien, A. Estimation of Inorganic Arsenic Exposure in Populations with Frequent Seafood Intake: Evidence from MESA and NHANES. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 184, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, J.E.H.; Donovan, S.M.; Snetselaar, L.; Dewey, K.G.; Novotny, R.; Stang, J.; Taveras, E.M.; Kleinman, R.E.; Bailey, R.L.; Raghavan, R.; et al. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Dietary Supplements Consumed During Pregnancy and Lactation and Child Neurodevelopment: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3483–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherzai, D.; Moness, R.; Sherzai, S.; Sherzai, A. A Systematic Review of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Consumption and Cognitive Outcomes in Neurodevelopment. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2022, 17, 649–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Mallick, R.; Duttaroy, A.K. Maternal Docosahexaenoic Acid Status During Pregnancy and Its Impact on Infant Neurodevelopment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated Methodological Guidance for the Conduct of Scoping Reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
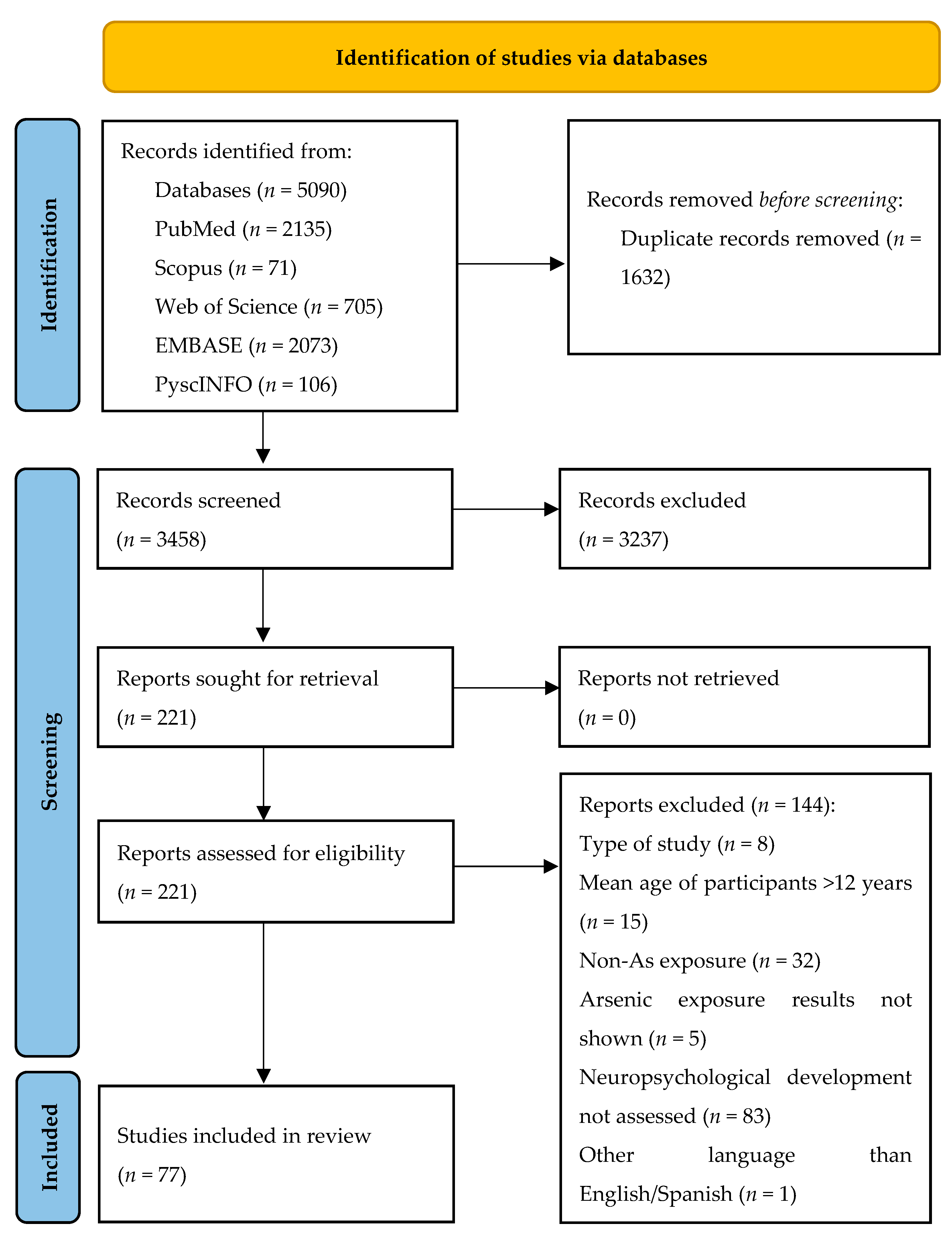


| Study Design | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Cross-sectional | 40 (51.9) |
| Longitudinal | 37 (48.1) |
| Number of participants | median (IQR) |
| 301 (148–439) | |
| Age of participants in months | median (IQR) |
| Minimum age | 60.0 (30.6–72.0) |
| Median age | 78.8 (44.6–81.0) |
| Maximum age | 96 (45.3–131.4) |
| Evaluated metal exposure | n (%) |
| As | 27 (35.1) |
| As + other metals | 50 (64.9) |
| Exposure window | n (%) |
| Perinatal/prenatal | 23 (29.9) |
| Childhood | 44 (57.2) |
| Both | 10 (12.9) |
| Main source of exposure | n (%) |
| Water | 20 (25.9) |
| Food | 21 (27.3) |
| Food and water | 8 (10.4) |
| Industry | 14 (18.2) |
| Not described | 14 (18.2) |
| Neuropsychological assessment | n (%) |
| Single test | 52 (67.5) |
| Multiple tests | 25 (32.5) |
| Main exposure effects | n (%) |
| Beneficial | 1 (1.3) |
| Harmful | 57 (74.0) |
| Null | 21 (27.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Notario-Barandiaran, L.; Compañ-Gabucio, L.M.; Bauer, J.A.; Vioque, J.; Karagas, M.R.; Signes-Pastor, A.J. Arsenic Exposure and Neuropsychological Outcomes in Children: A Scoping Review. Toxics 2025, 13, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070542
Notario-Barandiaran L, Compañ-Gabucio LM, Bauer JA, Vioque J, Karagas MR, Signes-Pastor AJ. Arsenic Exposure and Neuropsychological Outcomes in Children: A Scoping Review. Toxics. 2025; 13(7):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070542
Chicago/Turabian StyleNotario-Barandiaran, Leyre, Laura M. Compañ-Gabucio, Julia A. Bauer, Jesús Vioque, Margaret R. Karagas, and Antonio J. Signes-Pastor. 2025. "Arsenic Exposure and Neuropsychological Outcomes in Children: A Scoping Review" Toxics 13, no. 7: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070542
APA StyleNotario-Barandiaran, L., Compañ-Gabucio, L. M., Bauer, J. A., Vioque, J., Karagas, M. R., & Signes-Pastor, A. J. (2025). Arsenic Exposure and Neuropsychological Outcomes in Children: A Scoping Review. Toxics, 13(7), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070542








