Kidneys Under Siege: Pesticides Impact Renal Health in the Freshwater Fish Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio Linnaeus, 1758)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish
2.2. Experimental Pesticides
2.3. Experimental Set-Up
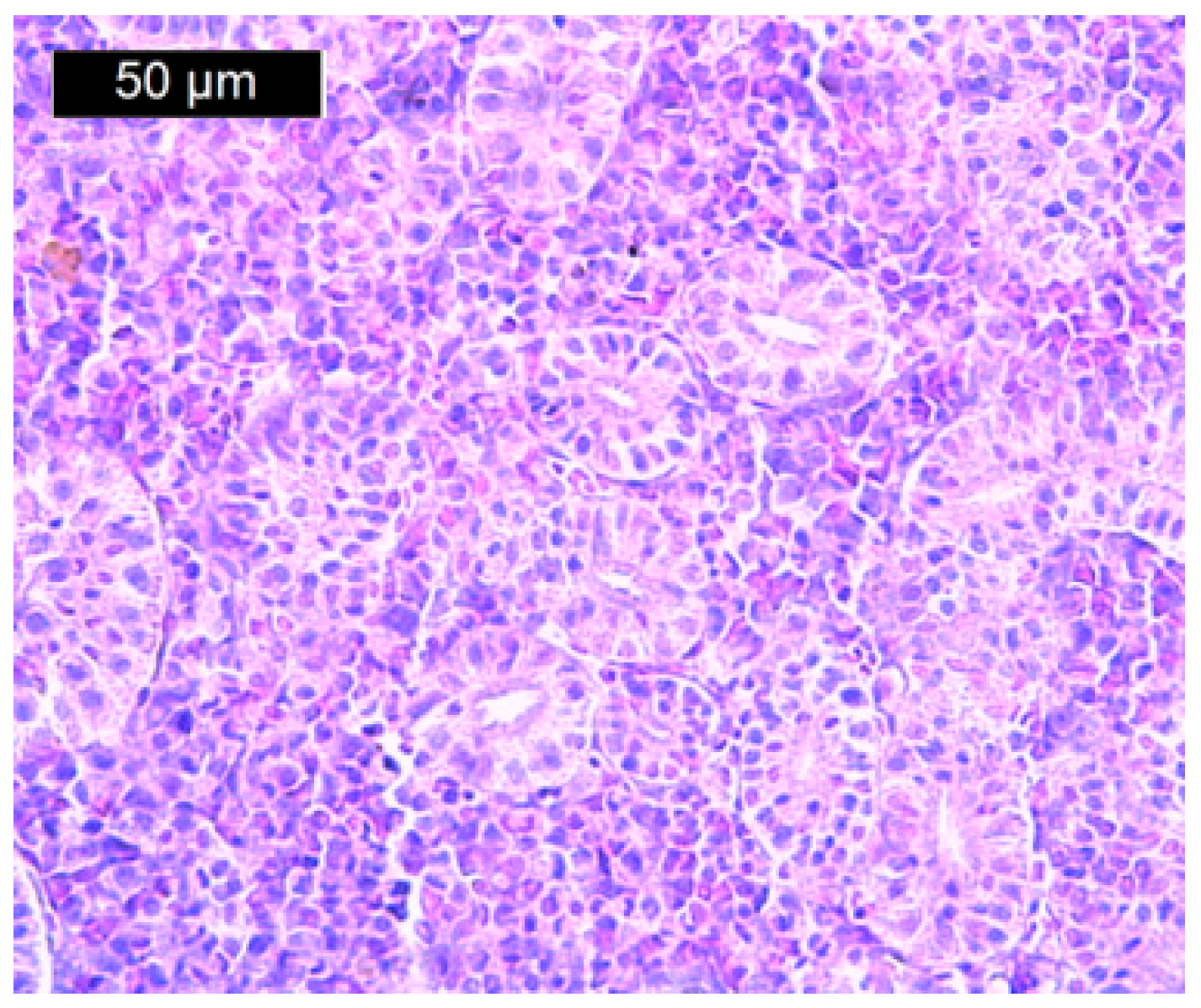
2.4. Histopathological Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- US EPA. What Is a Pesticide? Chapter 6—Insecticides and Environmental Pesticide Control Subchapter II—Environmental Pesticide Control. Se. 136—Definitions; US EPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.H.M.; Lenzen, M.; McBratney, A.; Maggi, F. Risk of pesticide pollution at the global scale. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaller, J.G. Daily Poison: Pesticides—An Underestimated Danger; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hvezdova, M.; Kosubova, P.; Kosikova, M.; Scherr, K.E.; Simek, Z.; Brodsky, L.; Sudoma, M.; Skulcova, L.; Sanka, M.; Svobodova, M.; et al. Currently and recently used pesticides in Central European arable soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, A.S.A.; Hidayah, N. Global Trade and Pesticide Use. In The Interplay of Pesticides and Climate Change: Environmental Dynamics and Challenges; Babaniyi, B.R., Babaniyi, E.E., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Bali, A.S.; Parihar, R.D.; et al. Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjerps, R.M.A.; Kooij, P.J.F.; van Loon, A.; Van Wezel, A.P. Occurrence of pesticides in Dutch drinking water sources. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Monzon, J.P.; Ernst, O. Cropping system-imposed yield gap: Proof of concept on soybean cropping systems in Uruguay. Field Crops Res. 2021, 260, 107944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-Onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in Drinking Water-A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Parada, A.; Goyenola, G.; Teixeira de Mello, F.; Heinzen, H. Recent advances and open questions around pesticide dynamics and effects on freshwater fishes. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 4, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.M.; Seibert, D.; Quesada, H.B.; de Jesus Bassetti, F.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Bergamasco, R. Occurrence, impacts and general aspects of pesticides in surface water: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 135, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Bastos, L.R.; Bastos, L.P.; Carneiro, P.C.F.; Guiloski, I.C.; Silva de Assis, H.C.; Padial, A.A.; Freire, C.A. Evaluation of the water quality of the upper reaches of the main Southern Brazil river (Iguacu river) through in situ exposure of the native siluriform Rhamdia quelen in cages. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.B.; De Canales, M.L.G.; Sarasquete, C. Histopathological changes induced by lindane (γ-HCH) in various organs of fishes. Sci. Mar. 2003, 67, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, F.; Qureshi, I.; Ali, M. Histopathological changes in the kidney of common carp, Cyprinus carpio following nitrate exposure. J. Res. Sci 2004, 15, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Sachi, I.T.C.; Bonomo, M.M.; Sakuragui, M.M.; Modena, P.Z.; Paulino, M.G.; Carlos, R.M.; Fernandes, J.B.; Fernandes, M.N. Biochemical and morphological biomarker responses in the gills of a Neotropical fish exposed to a new flavonoid metal-insecticide. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.J.; Brown, M.L. Relationships among invasive common carp, native fishes and physicochemical characteristics in upper Midwest (USA) lakes. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2011, 20, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloskowski, J. Impact of common carp Cyprinus carpio on aquatic communities: Direct trophic effects versus habitat deterioration. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. Arch. Für Hydrobiol. 2011, 178, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Yousafzai, A.M.; Siraj, M.; Ahmad, R.; Ahmad, I.; Nadeem, M.S.; Ahmad, W.; Akbar, N.; Muhammad, K. Pollution problem in River Kabul: Accumulation estimates of heavy metals in native fish species. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 537368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, X. Oxidative stress response and histopathological changes due to atrazine and chlorpyrifos exposure in common carp. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 103, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhadhbi, L.; Beiras, R. Acute toxicity of seven selected pesticides (Alachlor, Atrazine, Dieldrin, Diuron, Pirimiphos-Methyl, Chlorpyrifos, Diazinon) to the marine fish (turbot, Psetta maxima). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 5917–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepic, S.; Hackenberger, B.K.; Velki, M.; Loncaric, Z.; Hackenberger, D.K. Effects of individual and binary-combined commercial insecticides endosulfan, temephos, malathion and pirimiphos-methyl on biomarker responses in earthworm Eisenia andrei. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleurat-Lessard, F.; Chaurand, M.; Marchegay, G.; Abecassis, J. Effects of processing on the distribution of pirimiphos-methyl residues in milling fractions of durum wheat. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2007, 43, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxborough, R.M. Trends in US President’s malaria initiative-funded indoor residual spray coverage and insecticide choice in sub-Saharan Africa (2008–2015): Urgent need for affordable, long-lasting insecticides. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengela, D.; Seyoum, A.; Lucas, B.; Johns, B.; George, K.; Belemvire, A.; Caranci, A.; Norris, L.C.; Fornadel, C.M. Multi-country assessment of residual bio-efficacy of insecticides used for indoor residual spraying in malaria control on different surface types: Results from program monitoring in 17 PMI/USAID-supported IRS countries. Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakeshott, J.G.; Devonshire, A.L.; Claudianos, C.; Sutherland, T.D.; Horne, I.; Campbell, P.M.; Ollis, D.L.; Russell, R.J. Comparing the organophosphorus and carbamate insecticide resistance mutations in cholin- and carboxyl-esterases. Chem. Biol. Interact 2005, 157–158, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donarski, W.J.; Dumas, D.P.; Heitmeyer, D.P.; Lewis, V.E.; Raushel, F.M. Structure-activity relationships in the hydrolysis of substrates by the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 4650–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elersek, T.; Filipic, M. Organophosphorous Pesticides—Mechanisms of Their Toxicity; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.A.A. Variation in susceptibility to insecticides and synergistic effect of enzyme inhibitors in Pakistani strains of Trogoderma granarium. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2021, 91, 101775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, H.; Balszuweit, F.; Kehe, K.; Worek, F.; Thiermann, H. Chapter 56—Toxicokinetic aspects of nerve agents and vesicants. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents; 2nd ed.; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 817–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieroh, E.A.; Krass, W.; Hemmen, C. Propamocarb, einneues Fungizid zur Abwehr von Oomyceten im Zierpflanzen- und Gemüsebau. Meded. Fac. Landbouw. Rijksuniv. Gent 1978, 43, 933–942. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.C.; Hird, S.J.; Sykes, M.D.; Startin, J.R. Determination of residues of propamocarb in wine by liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry with direct injection. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, M.; de Kok, A. Determination of propamocarb in vegetables using polymer-based high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 972, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Battu, R.S.; Singh, B. Development and validation of QuEChERS Method for estimation of propamocarb residues in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) and soil. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 2, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alrahman, S.H.; Almaz, M.M. Degradation of propamocarb-hydrochloride in tomatoes, potatoes and cucumber using HPLC-DAD and QuEChERS methodology. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.; Mpina, F.H. Fenamidone + Propamocarb hydrochloride: A promising package for the control of early and late blights of tomatoes in Northern Tanzania. Int. J. Agr. For. 2016, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Xi, Z. Exogenous 24-epibrassinolide regulates antioxidant and pesticide detoxification systems in grapevine after chlorothalonil treatment. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 81, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, H.; Juhasz, A.L.; Cui, X.; Ma, L.Q. Predicting the relative bioavailability of DDT and its metabolites in historically contaminated soils using a Tenax-improved physiologically based extraction test (TI-PBET). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Propamocarb Hydrochloride R.E.D. FACTS—Prevention; P.a.T.S.W. USEPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, M.; Shamoun, S.F.; Sumampong, G. Effects of systemic and contact fungicides on life stages and symptom expression of Phytophthora ramorum in vitro and in planta. Crop Prot. 2015, 67, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnert, G.K.; Freitas, M.B.; DeQuattro, Z.A.; Barry, T.; Karasov, W.H. Effects of low, subchronic exposure of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and commercial 2,4-D formulations on early life stages of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2550–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I. The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database. 2022. Available online: https://www.weedscience.org (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- USEPA. 20152017. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Pesticides Industry Sales and Usage 2008–2012 Market Estimates. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2017-01/documents/pesticides-industry-sales-usage-2016_0.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Islam, F.; Farooq, M.A.; Gill, R.A.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Ali, B.; Wang, G.X.; Zhou, W. 2,4-D attenuates salinity-induced toxicity by mediating anatomical changes, antioxidant capacity and cation transporters in the roots of rice cultivars. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y. Insight into the mode of action of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) as an herbicide. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Stackelberg, K. A Systematic review of carcinogenic outcomes and potential mechanisms from exposure to 2,4-D and MCPA in the environment. J. Toxicol. 2013, 2013, 371610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RED. Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) 2; USEPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- da Fonseca, M.B.; Glusczak, L.; Moraes, B.S.; de Menezes, C.C.; Pretto, A.; Tierno, M.A.; Zanella, R.; Goncalves, F.F.; Loro, V.L. The 2,4-D herbicide effects on acetylcholinesterase activity and metabolic parameters of piava freshwater fish (Leporinus obtusidens). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 69, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiljanek, T.; Niewiadowska, A.; Semeniuk, S.; Gawel, M.; Borzecka, M.; Posyniak, A. Multi-residue method for the determination of pesticides and pesticide metabolites in honeybees by liquid and gas chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry--Honeybee poisoning incidents. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1435, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, F.L.; Saéz, C.; Llanos, J.; Lanza, M.R.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Solar-powered electrokinetic remediation for the treatment of soil polluted with the herbicide 2,4-D. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 190, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, U.; Silah, H. Monitoring 2,4-D removal by filamentous fungi using electrochemical methods. Biotech Stud. 2025, 34, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Wang, J.; Farooq, M.A.; Khan, M.S.S.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, M.; Munos, S.; Li, Q.X.; Zhou, W. Potential impact of the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on human and ecosystems. Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartczak, P.; Żółtowska, S.; Norman, M.; Klapiszewski, Ł.; Zdarta, J.; Komosa, A.; Kitowski, I.; Ciesielczyk, F.; Jesionowski, T. Saw-sedge Cladium mariscus as a functional low-cost adsorbent for effective removal of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous systems. Adsorption 2016, 22, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rosseland, B.O.; Rognerud, S.; Collen, P.; Grimalt, J.O.; Vives, I.; Massabuau, J.-C.; Lackner, R.; Hofer, R.; Raddum, G.G.; Fjellheim, A.; et al. Brown Trout in Lochnagar: Population and contamination by metals and organic micropollutants. In Lochnagar: The Natural History of a Mountain Lake; Rose, N.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 253–285. [Google Scholar]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 276, 33–79. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32010L0063 (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Romeis, B. Mikroskopische Technik; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2015; p. 697. Available online: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=NDOnDwAAQBAJ (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Bernet, D.; Schmidt, H.; Meier, W.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Wahli, T. Histopathology in fish: Proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J. Fish Dis. 1999, 22, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, A.; Costa, J.; Serrão, J.; Cruz, C.; Eiras, J.C. A histology-based fish health assessment of farmed seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Aquaculture 2015, 448, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerli, S.; Bernet, D.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Vonlanthen, P.; Wahli, T.; Segner, H. Assessment of fish health status in four Swiss rivers showing a decline of brown trout catches. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 69, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a test of whether one of two random variables is stochastically larger than the other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, F.; Hibiya, T. An Atlas of Fish Histology: Normal and Pathological Features; Kodansha Limited: Tokyo, Japan, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, E.M. Pituitary-Interrenal Axis as an Indicator of Stress in Fish; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. The stress response in fish. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 591–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorova, S.; Miyamoto, R.; Harada, T.; Isogai, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Ozato, K.; Wakamatsu, Y. Renal glomerulogenesis in medaka fish, Oryzias latipes. Dev. Dyn. 2008, 237, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobjerg, N.; Jespersen, A.; Wilkinson, M. Morphology of the kidney in the West African caecilian, Geotrypetes seraphini (Amphibia, Gymnophiona, Caeciliidae). J. Morphol. 2004, 262, 583–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cengiz, E.I. Gill and kidney histopathology in the freshwater fish Cyprinus carpio after acute exposure to deltamethrin. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 22, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Otaibi, A.M.; Al-Balawi, H.F.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Suliman, E.M. Toxicity bioassay and sub-lethal effects of diazinon on blood profile and histology of liver, gills and kidney of catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Braz. J. Biol. 2019, 79, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Hussain, R.; Abbas, G.; Kalim, M.; Khan, A.; Ferrando, S.; Gallus, L.; Ahmed, Z. Fipronil (Phenylpyrazole) induces hemato-biochemical, histological and genetic damage at low doses in common carp, Cyprinus carpio (Linnaeus, 1758). Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Bu, Y.; Li, X. Immunological and histopathological responses of the kidney of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) sublethally exposed to glyphosate. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boran, H.; Capkin, E.; Altinok, I.; Terzi, E. Assessment of acute toxicity and histopathology of the fungicide captan in rainbow trout. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, S.; Islam, M.T.; Sadat, M.A.; Jannat, R.; Alam, M.R.; Shahjahan, M. Sumithion induced structural erythrocyte alteration and damage to the liver and kidney of Nile tilapia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 36695–36706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Sarkar, C.; Khatun, S.; Sumon, K. Toxic effects of agro-pesticide cypermethrin on histological changes of kidney in Tengra, Mystus tengara. Asian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 3, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, E.I.; Unlu, E. Sublethal effects of commercial deltamethrin on the structure of the gill, liver and gut tissues of mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis: A microscopic study. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 21, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamanickam, V.; Narayanan, M. Heavy metal induced histopathological alterations in selected organs of the Cyprinus carpio L. (Common Carp). Int. J. Environ. Res. 2009, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammod Mostakim, G.; Zahangir, M.M.; Monir Mishu, M.; Rahman, M.K.; Islam, M.S. Alteration of blood parameters and histoarchitecture of liver and kidney of Silver Barb after chronic exposure to quinalphos. J. Toxicol. 2015, 2015, 415984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigamani, D. Effect of herbicides on fish and histological evaluation. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2015, 1, 437–440. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoola, S.O.; Ajani, E.K. Histopathological effect of cypermethrin on juvenile African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). World J. Biol. Res. 2008, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, J.B.; Gonzáles de Canales, M.L.; Sarasquete, C. Histopathological changes induced by lindane (γ-HCH)in various organs of fishes. Sci. Mar. 2003, 67, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Mukherjee, S. A histopathological study of carp (Labeo rohita) exposed to hexachlorocyclohexane. Vet. Arh. 2000, 70, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Tilak, K.; Veeraiah, K.; Yacobu, K. Studies on histopathological changes in the gill, liver and kidney of Ctenopharyngodon idellus (Valenciennes) exposed totechnical fenvalerate and EC 20%. Pollut. Res. 2001, 20, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Velmurugan, B.; Selvanayagam, M.; Cengiz, E.I.; Unlu, E. The effects of monocrotophos to different tissues of freshwater fish Cirrhinus mrigala. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 78, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatubi, O.K.; Ojokoh, A. Effects of fermentation and extrusion on the proximate composition of corn-groundnut flour blends. Niger. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 30, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Indicator | Control | Pirimiphos-Methyl | Propamocarb Hydrochloride | 2,4-D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 μg/L | 60 μg/L | 40 μg/L | 80 μg/L | 50 μg/L | 100 μg/L | ||
| Total length (cm) | 9.16 ± 0.4 | 10.44 ± 0.8 | 11.49 ± 0.5 | 9.64 ± 0.63 | 8.67 ± 2.9 | 9.31 ± 0.2 | 11.13 ± 0.3 |
| Weight (g) | 18.83 ± 5.7 | 19.25 ± 2.8 | 18.89 ± 2.4 | 19.11 ± 3.1 | 19.57 ± 2.7 | 16.28 ± 2.5 | 15.87 ± 3.5 |
| Pesticide | Recommended Dose | Dilution Relative to LC50 | Experimental Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pirimiphos-methyl | 0.00015 mL/m3–1 mL/dka | ×60,000 | 10 μg/L |
| ×10,000 | 60 μg/L | ||
| Propamocarb hydrochloride | 0.01–0.3 mL/dka | ×2000 | 40 μg/L |
| ×1000 | 80 μg/L | ||
| 2,4-D | 120–200 mL/dka | ×2000 | 50 μg/L |
| ×1000 | 100 μg/L |
| Pirimiphos-Methyl | pH | Temperature °C | Dissolved Oxygen mg/L | Electrical Conductivity μS/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8.3 ± 0.05 | 17.5 ± 0.05 | 9 ± 0.05 | 365 ± 0.05 |
| 10 μg/L | 8.2 ± 0.05 | 17 ± 0.05 | 8.5 ± 0.05 | 426 ± 0.05 |
| 60 μg/L | 8.1 ± 0.05 | 17.5 ± 0.05 | 7.3 ± 0.05 | 473 ± 0.05 |
| Propamocarb Hydrochloride | pH | Temperature °C | Dissolved Oxygen mg/L | Electrical Conductivity μS/cm |
| Control | 8.5 ± 0.05 | 17.5 ± 0.05 | 9 ± 0.05 | 365 ± 0.05 |
| 40 μg/L | 8.1 ± 0.05 | 18 ± 0.05 | 8.1 ± 0.05 | 433 ± 0.05 |
| 80 μg/L | 7.9 ± 0.05 | 18.5 ± 0.05 | 7.5 ± 0.05 | 485 ± 0.05 |
| 2,4-D | pH | Temperature °C | Dissolved Oxygen mg/L | Electrical Conductivity μS/cm |
| Control | 8.5 ± 0.05 | 17.5 ± 0.05 | 9 ± 0.05 | 365 ± 0.05 |
| 50 μg/L | 7.5 ± 0.05 | 17.5 ± 0.05 | 8.2 ± 0.05 | 451 ± 0.05 |
| 100 μg/L | 6.9 ± 0.05 | 18.5 ± 0.05 | 7.7 ± 0.05 | 469 ± 0.05 |
| Reaction Pattern | Organ | Alteration | Importance Factor | Score Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Pirimiphos-Methyl | |||||
| 10 μg/L | 60 μg/L | |||||
| Changes in the circulatory system | Kidney | Haemorrhage | WKC1 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A |
| Hyperaemia | WKC2 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Aneurysms | WKC3 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Index for the circulatory system | IKC = 0 A | IKC = 0 A | IKC = 0 A | |||
| Degenerative changes | Tubule | Vacuolar degeneration | WKR1 = 1 | 0 A | 2 B | 2 B |
| Hyaline degeneration | WKR2 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 1 B | ||
| Necrobiosis | WKR3 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 1 B | ||
| Necrosis | WKR4 = 3 | 0 A | 0 A | 1 B | ||
| Glomerulus | Dilatation of the Bowman’s capsule | WKR5 = 1 | 0 A | 2 B | 3 C | |
| Contraction | WKR6 = 1 | 0 A | 1 B | 1 B | ||
| Necrobiosis * | WKR7 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Necrosis | WKR8 = 3 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Interstitial tissue | Necrosis | WKR9 = 3 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | |
| Index for the degenerative changes | IKR = 0 A | IKR = 5 B | IKR = 12 C | |||
| Proliferative changes | Tubule | Hypertrophy | WKP1 = 1 | 0 A | 2 B | 2 B |
| Hyperplasia | WKP2 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Glomerulus | Hypertrophy | WKP3 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | |
| Hyperplasia | WKP4 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Thickening of Bowman’s capsular membrane | WKP5 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 1 B | ||
| Interstitial tissue | Hypertrophy | WKP6 = 1 | 0 A | 3 B | 3 B | |
| Edema | WKP7 = 2 | 0 A | 1 B | 1 B | ||
| Index for the proliferative changes | IKP = 0 A | IKP = 7 B | IKP = 9 B | |||
| Inflammation | Kidney | Infiltration | WKI1 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A |
| Activation of melanomacrophages | WKI2 = 2 | 0 A | 3 B | 3 B | ||
| Index for the inflammatory processes | IKI = 0 A | IKI =6 B | IKI =6 B | |||
| Index for the organ | IK = 0 A | IK = 18 B | IK = 27 C | |||
| Reaction Pattern | Organ | Alteration | Importance Factor | Score Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Propamocarb Hydrochloride | |||||
| 40 μg/L | 80 μg/L | |||||
| Changes in the circulatory system | Kidney | Haemorrhage | WKC1 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A |
| Hyperaemia | WKC2 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Aneurysms | WKC3 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Index for changes in the circulatory system | IKC = 0 A | IKC = 0 A | IKC = 0 A | |||
| Degenerative changes | Tubule | Vacuolar degeneration | WKR1 = 1 | 0 A | 1 B | 3 C |
| Hyaline degeneration | WKR2 = 1 | 0 A | 1 B | 2 C | ||
| Necrobiosis | WKR3 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Necrosis | WKR4 = 3 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Glomerulus | Dilatation of the Bowman’s capsule | WKR5 = 1 | 0 A | 2 B | 2 B | |
| Contraction | WKR6 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Necrobiosis * | WKR7 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Necrosis | WKR8 = 3 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Interstitial tissue | Necrosis | WKR9 = 3 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | |
| Index for the degenerative changes | IKR = 0 A | IKR = 4 B | IKR = 7 C | |||
| Proliferative changes | Tubule | Hypertrophy | WKP1 = 1 | 0 A | 1 B | 1 B |
| Hyperplasia | WKP2 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Glomerulus | Hypertrophy | WKP3 = 1 | 0 A | 1 B | 1 B | |
| Hyperplasia | WKP4 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Thickening of Bowman’s capsular membrane | WKP5 = 2 | 0 A | 0 B | 1 B | ||
| Interstitial tissue | Hypertrophy | WKP6 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | |
| Edema | WKP7 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Index for the proliferative changes | IKP = 0 A | IKP = 2 B | IKP = 4 C | |||
| Inflammation | Kidney | Infiltration | WKI1 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A |
| Activation of melano-macrophages | WKI2 = 2 | 0 A | 1 B | 2 C | ||
| Index for inflammatory processes | IKI = 0 A | IKI = 2 B | IKI = 4 B | |||
| Index for organ IK | IK = 0 A | IK = 8 B | IK = 15 C | |||
| Reaction Pattern | Organ | Alteration | Importance Factor | Score Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2,4-D | |||||
| 50 μg/L | 100 μg/L | |||||
| Changes in the circulatory system | Kidney | Haemorrhage | WKC1 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A |
| Hyperaemia | WKC2 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Aneurysms | WKC3 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Index for changes in the circulatory system | IKC = 0 A | IKC = 0 A | IKC = 0 A | |||
| Degenerative changes | Tubule | Vacuolar degeneration | WKR1 = 1 | 0 A | 2 B | 4 C |
| Hyaline degeneration | WKR2 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Necrobiosis | WKR3 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Necrosis | WKR4 = 3 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Glomerulus | Dilatation of the Bowman’s capsule | WKR5 = 1 | 0 A | 1 B | 2 C | |
| Contraction | WKR6 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 1 B | ||
| Necrobiosis * | WKR7 = 2 | 0 A | 1 B | 1 B | ||
| Necrosis | WKR8 = 3 | 0 A | 1 B | 1 B | ||
| Interstitial tissue | Necrosis | WKR9 = 3 | 0 A | 0 A | 1 B | |
| Index for the degenerative changes | IKR = 0 A | IKR = 5 B | IKR = 15 C | |||
| Proliferative changes | Tubule | Hypertrophy | WKP1 = 1 | 0 A | 0 A | 1 B |
| Hyperplasia | WKP2 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Glomerulus | Hypertrophy | WKP3 = 1 | 0 A | 1 B | 3 C | |
| Hyperplasia | WKP4 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 1 B | ||
| Thickening of Bowman’s capsular membrane | WKP5 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | ||
| Interstitial tissue | Hypertrophy | WKP6 = 1 | 0 A | 1 B | 1 B | |
| Edema | WKP7 = 2 | 0 A | 2 B | 4 C | ||
| Index for the proliferative changes | IKP = 0 A | IKP = 6 B | IKP = 15 C | |||
| Inflammation | Kidney | Infiltration | WKI1 = 2 | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A |
| Activation of melano-macrophages | WKI2 = 2 | 0 A | 2 B | 2 B | ||
| Index for the inflammatory processes | IKI = 0 A | IKI =4 B | IKI =4 B | |||
| Index for organ IK | IK = 0 A | IK = 15 B | IK = 34 C | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stoyanova, S.; Georgieva, E.; Kovacheva, E.; Antal, L.; Somogyi, D.; Uzochukwu, I.E.; Nagy, L.; Nyeste, K.; Yancheva, V. Kidneys Under Siege: Pesticides Impact Renal Health in the Freshwater Fish Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio Linnaeus, 1758). Toxics 2025, 13, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070518
Stoyanova S, Georgieva E, Kovacheva E, Antal L, Somogyi D, Uzochukwu IE, Nagy L, Nyeste K, Yancheva V. Kidneys Under Siege: Pesticides Impact Renal Health in the Freshwater Fish Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio Linnaeus, 1758). Toxics. 2025; 13(7):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070518
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoyanova, Stela, Elenka Georgieva, Eleonora Kovacheva, László Antal, Dóra Somogyi, Ifeanyi Emmanuel Uzochukwu, László Nagy, Krisztián Nyeste, and Vesela Yancheva. 2025. "Kidneys Under Siege: Pesticides Impact Renal Health in the Freshwater Fish Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio Linnaeus, 1758)" Toxics 13, no. 7: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070518
APA StyleStoyanova, S., Georgieva, E., Kovacheva, E., Antal, L., Somogyi, D., Uzochukwu, I. E., Nagy, L., Nyeste, K., & Yancheva, V. (2025). Kidneys Under Siege: Pesticides Impact Renal Health in the Freshwater Fish Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio Linnaeus, 1758). Toxics, 13(7), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070518









