Integrated Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods Reveal Heavy Metal-Induced Health Risks in Guizhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Contamination Assessment
2.4. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
2.5. Health Risk Assessment
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution
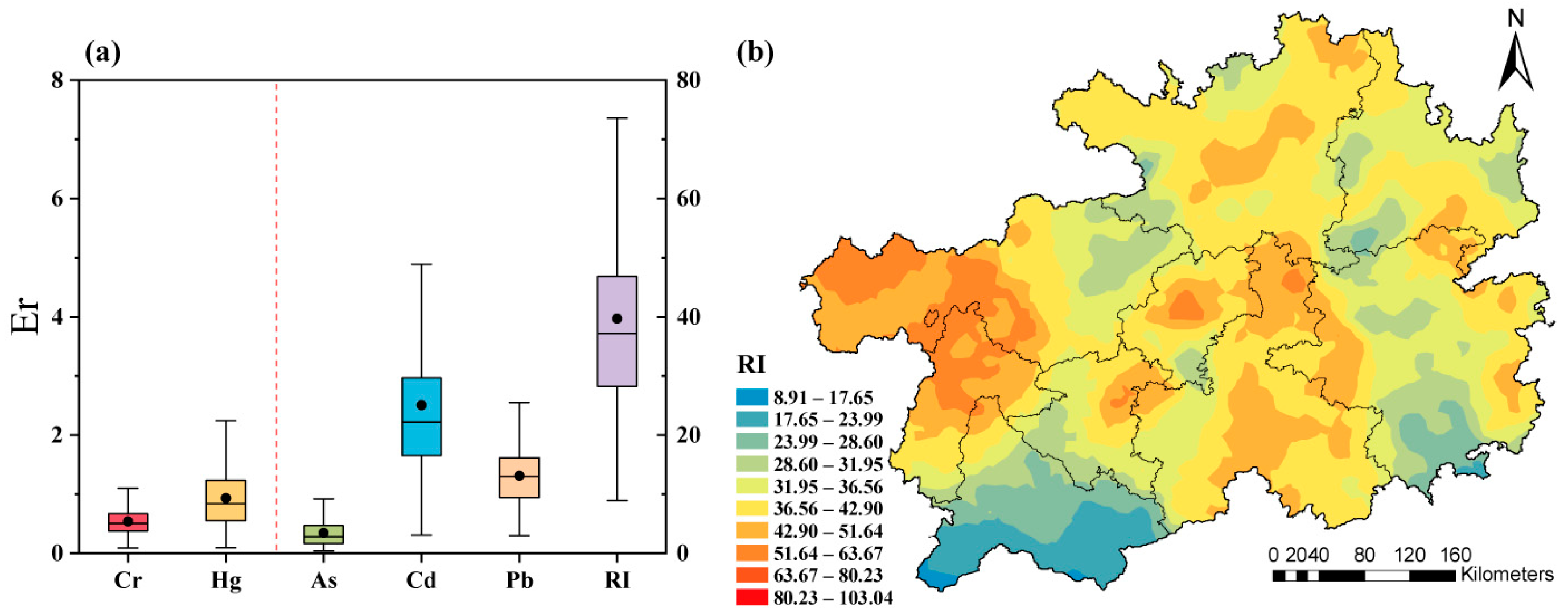
3.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
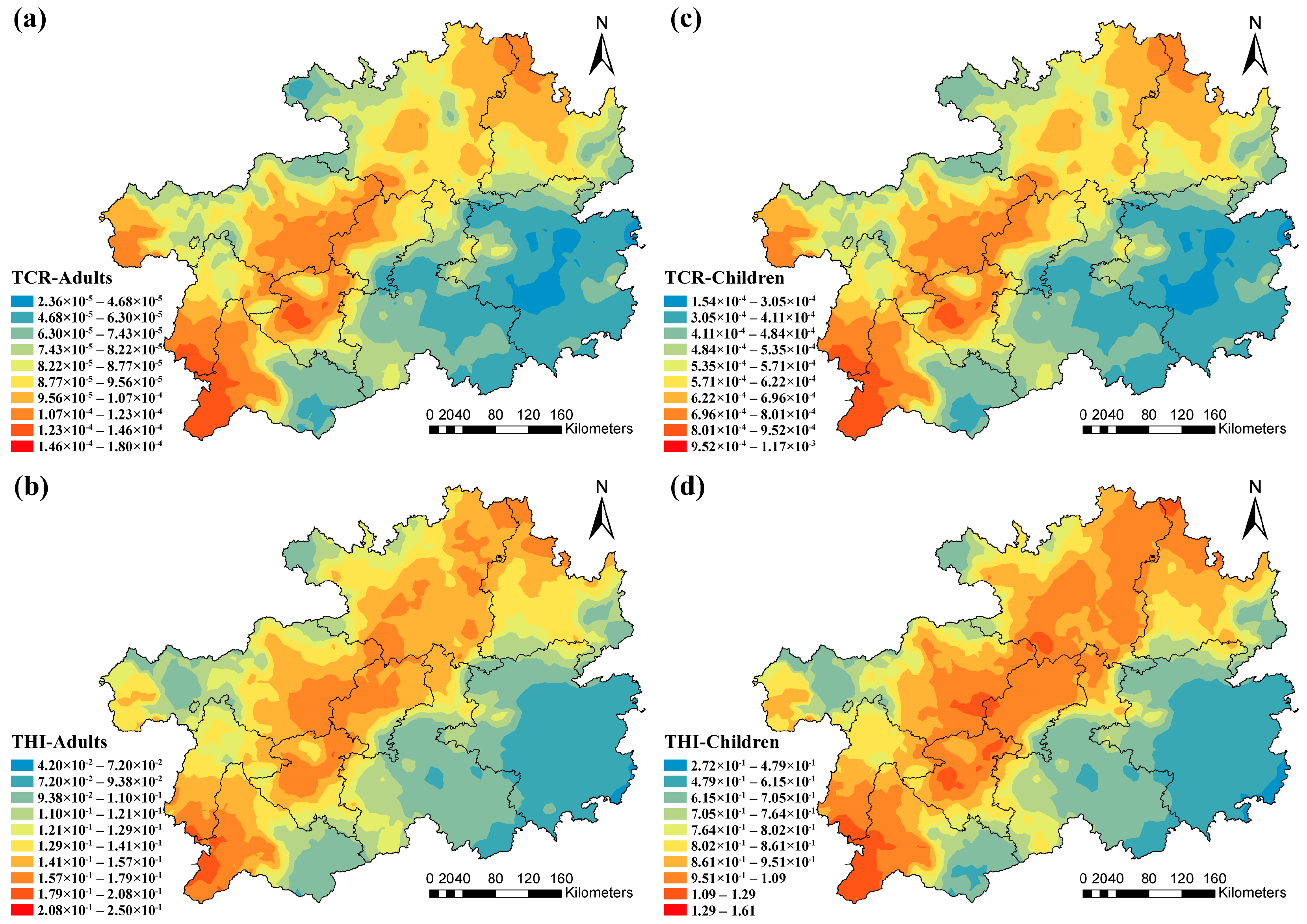
3.3. Deterministic Risk Assessment
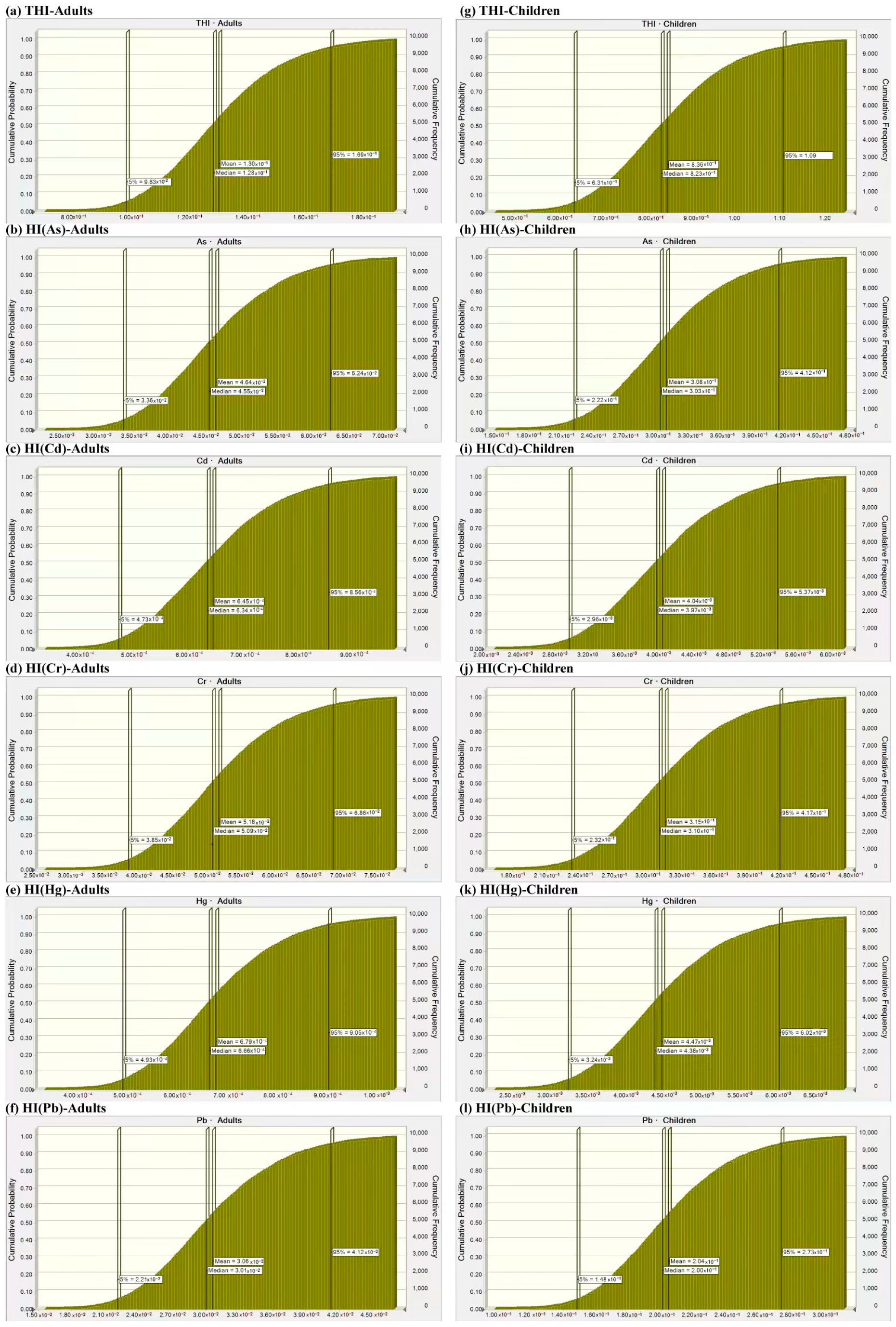
3.4. Probabilistic Risk Assessment
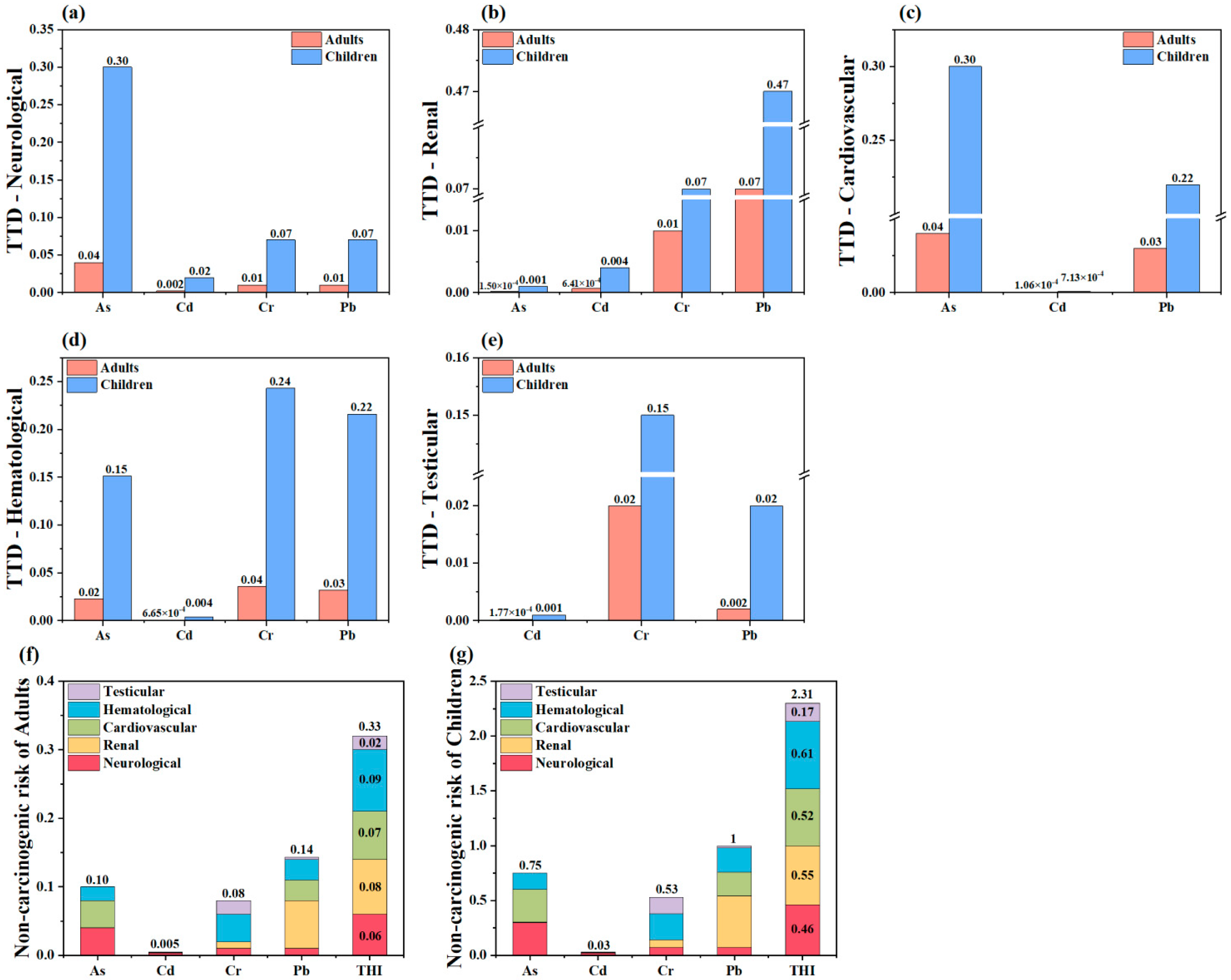
3.5. Health Risk Assessment Based on the TTD Method
4. Discussion
4.1. Heavy Metals Pollution Analysis
4.2. Deterministic and Probabilistic Risk Assessment
4.3. Health Risk Assessment Modified by the TTD Method
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Meng, J.; Yin, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T. Sources and health risks of heavy metals in soils and vegetables from intensive human intervention areas in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vareda, J.P.; Valente, A.J.M.; Durães, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wang, K.; Noguera, D.R.; Jiang, J.; Oyserman, B.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, Q.; Cui, F. Transformation and speciation of typical heavy metals in soil aquifer treatment system during long time recharging with secondary effluent: Depth distribution and combination. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konyshev, A.A.; Sidkina, E.S.; Cherkasova, E.V.; Mironenko, M.V.; Gridasov, A.G.; Zhilkina, A.V.; Bugaev, I.A. Migration Forms of Heavy Metals and Chemical Composition of Surface Waters in the “Arsenic” Shaft Area (Pitkäranta Ore District, South Karelia). Geochem. Int. 2020, 58, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, J. Research on Heavy Metal Pollution and Comprehensive Treatment of Farmland Soil. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Fu, R.; Liu, H.; Guo, X. Current knowledge from heavy metal pollution in Chinese smelter contaminated soils, health risk implications and associated remediation progress in recent decades: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhuo, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, L.; Wei, X.; Ji, J. Ecological risk assessment of Cd and other heavy metals in soil-rice system in the karst areas with high geochemical background of Guangxi, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, J. Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Han, H.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Cadmium risk in the soil-plant system caused by weathering of carbonate bedrock. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Tu, Y.; Yu, E.; Xing, D. Cadmium accumulation and migration of 3 peppers varieties in yellow and limestone soils under geochemical anomaly. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, W.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.; Wen, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, C. Effects of copper mining on heavy metal contamination in a rice agrosystem in the Xiaojiang River Basin, southwest China. Acta Geochim. 2019, 38, 753–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, R.; Guo, C.; Lv, J.; Wu, L.; Xu, J. Occurrence, sources and risk of heavy metals in soil from a typical antimony mining area in Guizhou Province, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 45, 3637–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Mei, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X. Health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution and its sources in agricultural soils near Hongfeng Lake in the mining area of Guizhou Province, China. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1276925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Lu, G.; Fan, B.; Xiang, W.; Bao, Z. Bioaccumulation and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-crop systems in Liujiang karst area, Southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 9657–9669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xue, S.; Ma, T.; Yu, L. Heavy Metal Pollution and Source Contributions in Agricultural Soils Developed from Karst Landform in the Southwestern Region of China. Toxics 2022, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Chen, J.; Qian, H. Spatial characteristics of heavy metal contamination and potential human health risk assessment of urban soils: A case study from an urban region of South India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, L. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: Case study in Jiangsu Province. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 134953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Yue, W.; Teng, Y. Source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments and soils in an interconnected river-soil system based on a composite fingerprint screening approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, B.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Potential driving forces and probabilistic health risks of heavy metal accumulation in the soils from an e-waste area, southeast China. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. New Perspectives about Health Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution-Origin and Prospects of Probabilistic Risk Analysis. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, W.; Xiong, J.; Yang, J.; Huang, R.; Xie, P. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil of Lalu Wetland Based on Monte Carlo Simulation and ACPS-MLR. Water 2023, 15, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudi, M.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Yang, L.; Tong, S.; Yu, Q.J.; Ruan, H.D.; Atabila, A.; et al. Exposure Routes and Health Risks Associated with Pesticide Application. Toxics 2022, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Kong, L.; Jiang, D.; Wei, J.; Cao, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, L.; Deng, S. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of chemicals of concern in soil, water and sediment at a large strontium slag pile area. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, Z.; Mahdavi, V.; Tajdar-oranj, B. Probabilistic health risk assessment based on Monte Carlo simulation for pesticide residues in date fruits of Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 42037–42050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Cai, Y.; Wang, T.; Xiao, R.; Chen, W. Regional probabilistic risk assessment of heavy metals in different environmental media and land uses: An urbanization-affected drinking water supply area. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbur, S.B.; Hansen, H.; Pohl, H.; Colman, J.; McClure, P. Using the ATSDR Guidance Manual for the Assessment of Joint Toxic Action of Chemical Mixtures. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 18, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Liu, T.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lei, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S. Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation in Rice from a High Geological Background Area in Guizhou Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Specification of Land Quality Geochemical Assessment; Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. The Technical Specification for Soil Environmental Monitoring; Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Soil and Sediment—Digestion of Total Metal Elements—Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion Method; Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 2017.
- He, S.; Niu, Y.; Xing, L.; Liang, Z.; Song, X.; Ding, M.; Huang, W. Research progress of the detection and analysis methods of heavy metals in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1310328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine. Soil Quality—Determination of Total Mercury, Total Arsenic, Total Lead—Atomic Fluorescence Part I: Determination of Total Mercury in Soil; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine: Beijing, China, 2008.
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine. Soil Quality—Determination of Total Mercury, Total Arsenic, Total Lead—Atomic Fluorescence Part II: Determination of Total Arsenic in Soil; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Ya, Y.; Mo, L.; Fan, Y.; Liao, J.; Huang, D.; Tan, H. Determination of Arsenic and Mercury in Soil by Microwave Digestion and Hidride GenerationAtomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 14, 651–653. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemerow, N.L. Stream, Lake, Estuary, and Ocean Pollution; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land; Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Förstner, U.; Ahlf, W.; Calmano, W.; Kersten, M. Sediment Criteria Development. In Sediments and Environmental Geochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- CNEMC. The Backgrounds of Soil Environment of Guizhou, China; China National Environmental Monitoring Center: Beijing, China, 1990.
- Loska, K.; Wiechula, D.; Korus, I. Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA; Exposure Analysis and Risk Characterization Group; Moya, J. Exposure Factors Handbook; USEPA National Center for Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- USEPA. Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Chinese Population Exposure Parameter Manual; Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; He, K.; Zhang, Q. Risk assessment, spatial distribution, and source apportionment of heavy metals in Chinese surface soils from a typically tobacco cultivated area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 16852–16863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MohseniBandpi, A.; Eslami, A.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Shahsavani, A.; Jeihooni, A.K.; Ghaderpoury, A.; Alinejad, A. Health risk assessment of heavy metals on PM2.5 in Tehran air, Iran. Data Brief 2018, 17, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (RAGS); U.S. Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Sarwar, T.; Shahid, M.; Natasha, N.; Khalid, S.; Haidar Shah, A.; Ahmad, N.; Naeem, M.A.; Khan, Z.U.H.; Murtaza, B.; Bakhat, H. Quantification and risk assessment of heavy metal build-up in soil–plant system after irrigation with untreated city wastewater in Vehari, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 4281–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L. Heavy metal contamination assessment and probabilistic health risks in soil and maize near coal mines. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1004579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Du, Q.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Shan, Y.; Shao, W. A Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of an oasis agricultural region in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Cao, S. Highlights of the Chinese Exposure Factors Handbook (Adults); Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Chen, H.; Song, L.; Yao, Z.; Meng, F.; Teng, Y. Characterization and source apportionment of heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Tai (China) and its surrounding soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition; National Center for Environmental Assessment Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Liu, L.; Han, J.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, S. Assessment of heavy metal non-carcinogenic health risk in solidified fly ash using TTD and WOE methods. Environ. Chem. 2019, 38, 1014–1020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Guidance Manual for the Assessment of Joint Toxic Action of Chemical Mixtures; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2001.
- ATSDR. Interaction Profile for Arsenic, Cadmium, Chromium and Lead [Online]; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2004.
- Vega, F.A.; Covelo, E.F.; Andrade, M.L. Competitive sorption and desorption of heavy metals in mine soils: Influence of mine soil characteristics. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Song, J.; Cheng, Y.; McBride, M.B. Derivation of regional risk screening values and intervention values for cadmium-contaminated agricultural land in the Guizhou Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2366–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, R. Effects of As pollutant in soil on crop growth and safety of agricultural products under Cd stress. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 2132–2136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Qu, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y. Comparison of the concentrations, sources, and distributions of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils of two provinces in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; An, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, L.; Lv, S. Geochemical characteristics and health risks of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from a coal mining area in Anhui province, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiri-Nyarko, F.; Duah, A.A.; Karikari, A.Y.; Agyekum, W.A.; Manu, E.; Tagoe, R. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils at the Kpone landfill site, Ghana: Implication for ecological and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, A.A.; Varvani, J.; Zare, R. Assessment and zoning of environmental hazard of heavy metals using the Nemerow integrated pollution index in the vineyards of Malayer city. Acta Geophys. 2020, 69, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, Y.; Hou, H.; Shangguan, Y.; Li, F. Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhou, L.; Song, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y. Mercury Pollution in Dryland Soil and Evaluation of Maize Safety Production in Guizhou Province. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 2868–2878. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kyere, V.N.; Greve, K.; Atiemo, S.M.; Amoako, D.; Aboh, I.J.K.; Cheabu, B.S. Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Exposure to Heavy Metals in Soils from Informal E-Waste Recycling Site in Ghana. Emerg. Sci. J. 2018, 2, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtepe, H. Soil Contamination by Metals/Metalloids around an Industrial Region and Associated Human Health Risk Assessment. J. Adv. Res. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2024, 10, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Alharthy, R.D.; Zubair, M.; Ahmed, M.; Hameed, A.; Rafique, S. Toxic and heavy metals contamination assessment in soil and water to evaluate human health risk. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, B.; Fang, G.; Wang, L.; Xiang, B. A review of heavy metal pollution levels and health risk assessment of urban soils in Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena-Fernandez, A.; Gonzalez-Munoz, M.J.; Lobo-Bedmar, M.C. Establishing the importance of human health risk assessment for metals and metalloids in urban environments. Environ. Int. 2014, 72, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Qing, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. Characterization and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil of Mine Area in the Yunnan-Guizhou Area. Environ. Sci. 2024, 1–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ling, J.; Chang, B.; Zhao, G. Assessment of heavy metal content, distribution, and sources in Nansi Lake sediments, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 30929–30942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihedioha, J.N.; Ogili, E.O.; Ekere, N.R.; Ezeofor, C.C. Risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of paddy soil and rice (Oryza sativa) from Abakaliki, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Chang, S.X.; Collins, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Status assessment and probabilistic health risk modeling of metals accumulation in agriculture soils across China: A synthesis. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tian, J.; Ren, J.; Lin, K.; Cui, C. Heavy metals in daily meals and food ingredients in the Yangtze River Delta and their probabilistic health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y. Metals in exposed-lawn soils from 18 urban parks and its human health implications in southern China’s largest city, Guangzhou. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, H. Assessment and amendment methods of heavy metal non-carcinogenic health risks in agricultural land around smelters. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2024, 14, 112–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Items | As | Cd | Cr | Hg | Pb | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 1.19 | 0.08 | 15.97 | 0.02 | 11.42 | 3.84 |
| Max | 24.87 | 0.75 | 149.82 | 0.29 | 49.38 | 8.06 |
| Mean | 9.08 | 0.36 | 73.06 | 0.13 | 28.14 | 6.14 |
| SD | 5.38 | 0.16 | 29.21 | 0.06 | 8.09 | 0.96 |
| CV% | 59.25 | 44.44 | 39.98 | 46.15 | 28.75 | 15.64 |
| pH ≤ 5.5 | 30 | 0.30 | 250 | 0.50 | 80 | - |
| Exceeded(%) a | 0 | 37.39 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| 5.5 < pH ≤ 6.5 | 30 | 0.4 | 250 | 0.50 | 100 | - |
| Exceeded(%) a | 0 | 32.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| 6.5 < pH ≤ 7.5 | 25 | 0.6 | 300 | 0.6 | 140 | - |
| Exceeded(%) a | 0 | 9.47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| pH > 7.5 | 20 | 0.8 | 350 | 1.0 | 240 | - |
| Exceeded(%) a | 9.88 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| BV b | 20 | 0.66 | 95.9 | 0.1 | 35.2 | - |
| Exceeded(%) b | 4.46 | 5.54 | 20.95 | 62.03 | 18.92 | - |
| Non-Carcinogenic Risks | Carcinogenic Risks | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIing | HIinh | HIdermal | HI | CRing | CRinh | CRdermal | CR | ||
| As | Adults | 4.51 × 10−2 | 3.36 × 10−4 | 4.35 × 10−4 | 4.59 × 10−2 | 2.03 × 10−5 | 2.18 × 10−8 | 8.09 × 10−8 | 2.04 × 10−5 |
| Children | 3.02 × 10−1 | 5.83 × 10−4 | 2.05 × 10−3 | 3.05 × 10−1 | 1.36 × 10−4 | 3.78 × 10−8 | 3.81 × 10−7 | 1.36 × 10−4 | |
| Cd | Adults | 5.32 × 10−4 | 1.98 × 10−5 | 8.49 × 10−5 | 6.42 × 10−4 | 3.27 × 10−6 | 3.57 × 10−10 | 3.27 × 10−6 | |
| Children | 3.57 × 10−3 | 3.44 × 10−5 | 3.99 × 10−4 | 4.03 × 10−3 | 2.19 × 10−5 | 6.19 × 10−10 | 2.19 × 10−5 | ||
| Cr | Adults | 3.63 × 10−2 | 4.06 × 10−4 | 1.45 × 10−2 | 5.12 × 10−2 | 5.45 × 10−5 | 4.87 × 10−9 | 8.68 × 10−6 | 6.32 × 10−5 |
| Children | 2.43 × 10−1 | 7.04 × 10−4 | 6.81 × 10−2 | 3.12 × 10−1 | 3.66 × 10−4 | 8.45 × 10−9 | 4.09 × 10−5 | 4.06 × 10−4 | |
| Hg | Adults | 6.36 × 10−4 | 3.61 × 10−5 | 6.82 × 10−4 | |||||
| Children | 4.26 × 10−3 | 1.70 × 10−4 | 4.50 × 10−3 | ||||||
| Pb | Adults | 2.99 × 10−2 | 3.19 × 10−4 | 3.03 × 10−2 | 3.56 × 10−7 | 1.88 × 10−10 | 3.56 × 10−7 | ||
| Children | 2.01 × 10−1 | 1.50 × 10−3 | 2.02 × 10−1 | 2.39 × 10−6 | 3.26 × 10−10 | 2.39 × 10−6 | |||
| THI/TCR | Adults | 1.12 × 10−1 | 7.62 × 10−4 | 1.54 × 10−2 | 1.29 × 10−1 | 7.52 × 10−5 | 2.72 × 10−8 | 8.77 × 10−6 | 8.40 × 10−5 |
| Children | 7.54 × 10−1 | 1.32 × 10−3 | 7.22 × 10−2 | 8.28 × 10−1 | 5.04 × 10−4 | 4.72 × 10−8 | 4.12 × 10−5 | 5.45 × 10−4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Sun, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q. Integrated Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods Reveal Heavy Metal-Induced Health Risks in Guizhou, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060515
Li Q, Li D, Wang Z, Sun D, Zhang T, Zhang Q. Integrated Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods Reveal Heavy Metal-Induced Health Risks in Guizhou, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060515
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qinju, Dashuan Li, Zelan Wang, Dali Sun, Ting Zhang, and Qinghai Zhang. 2025. "Integrated Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods Reveal Heavy Metal-Induced Health Risks in Guizhou, China" Toxics 13, no. 6: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060515
APA StyleLi, Q., Li, D., Wang, Z., Sun, D., Zhang, T., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Integrated Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods Reveal Heavy Metal-Induced Health Risks in Guizhou, China. Toxics, 13(6), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060515







