Degradation of Low-Molecular-Weight Diesel Fractions (C10−C16 Alkane) Drives Cd Stabilization and Pb Activation in Calcareous Soils from Karst Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Soil Incubation
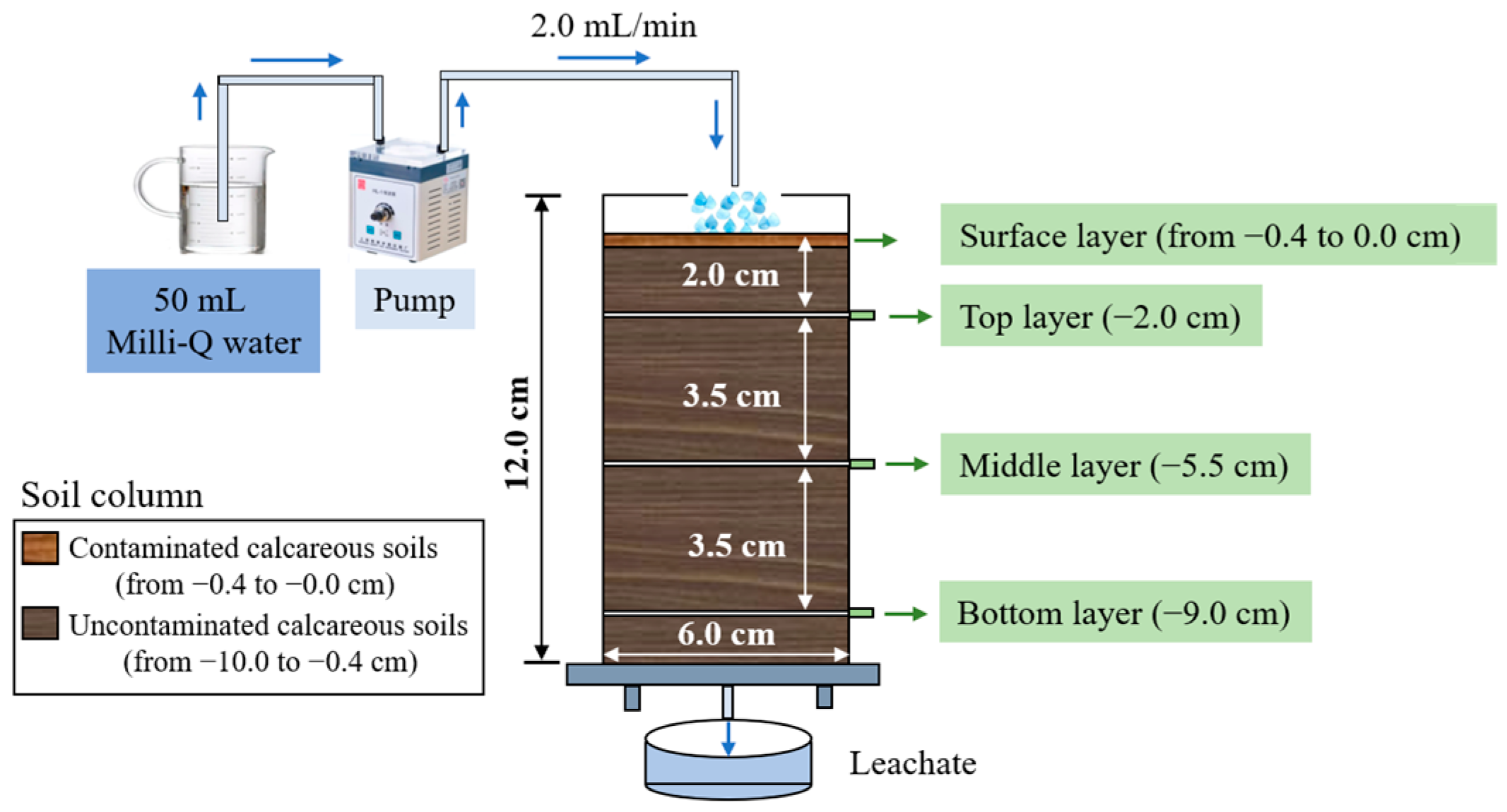
2.3. Column Setup
2.4. Leaching Experiments and Sample Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
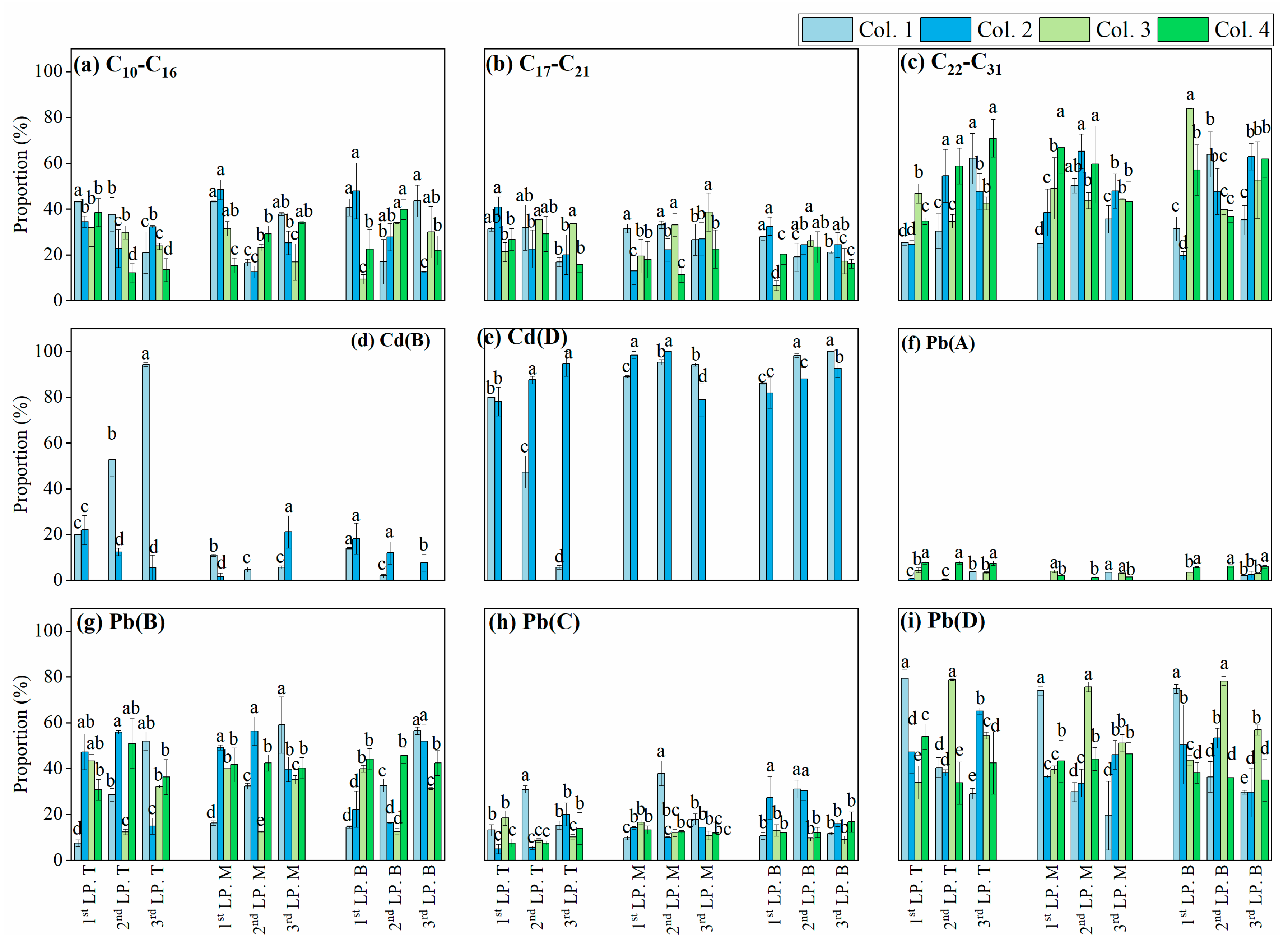
3.1. The Distribution of Cd and Pb in Diesel-Fuel-Contaminated Soils
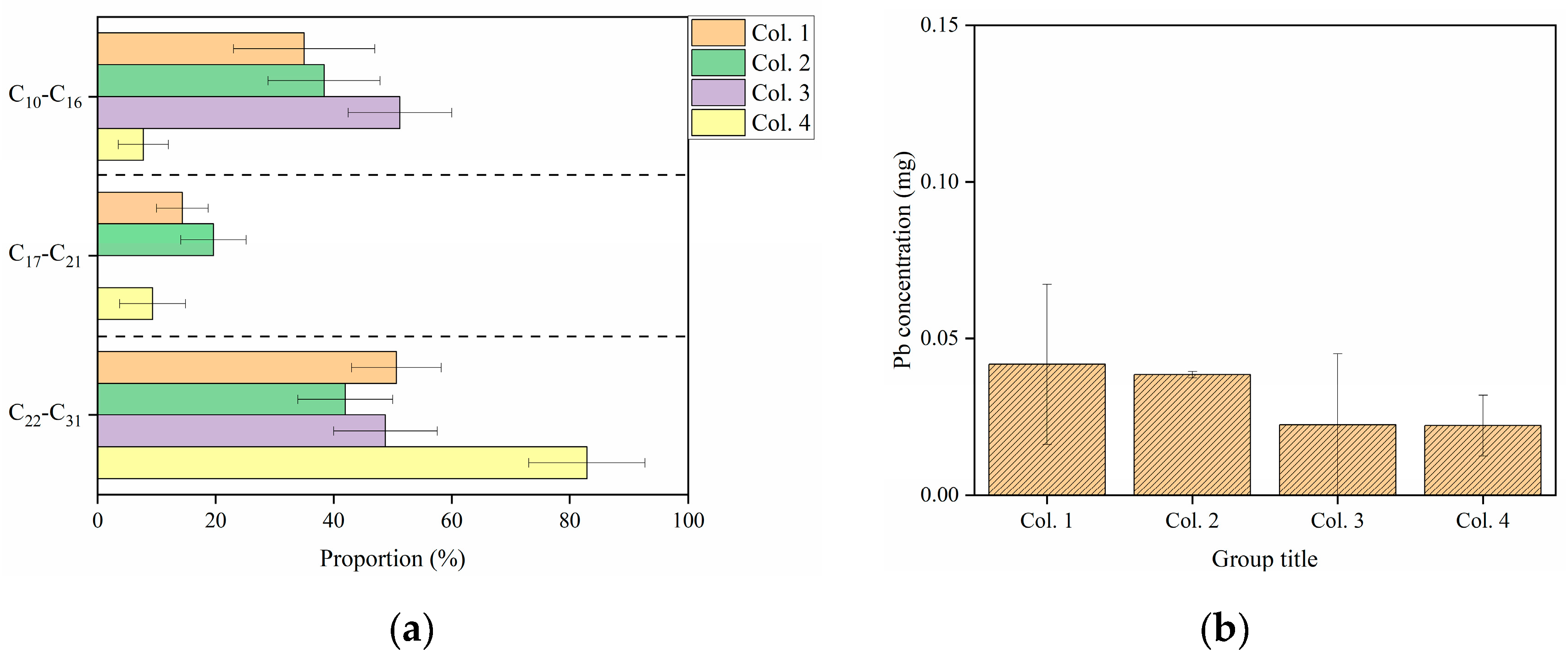
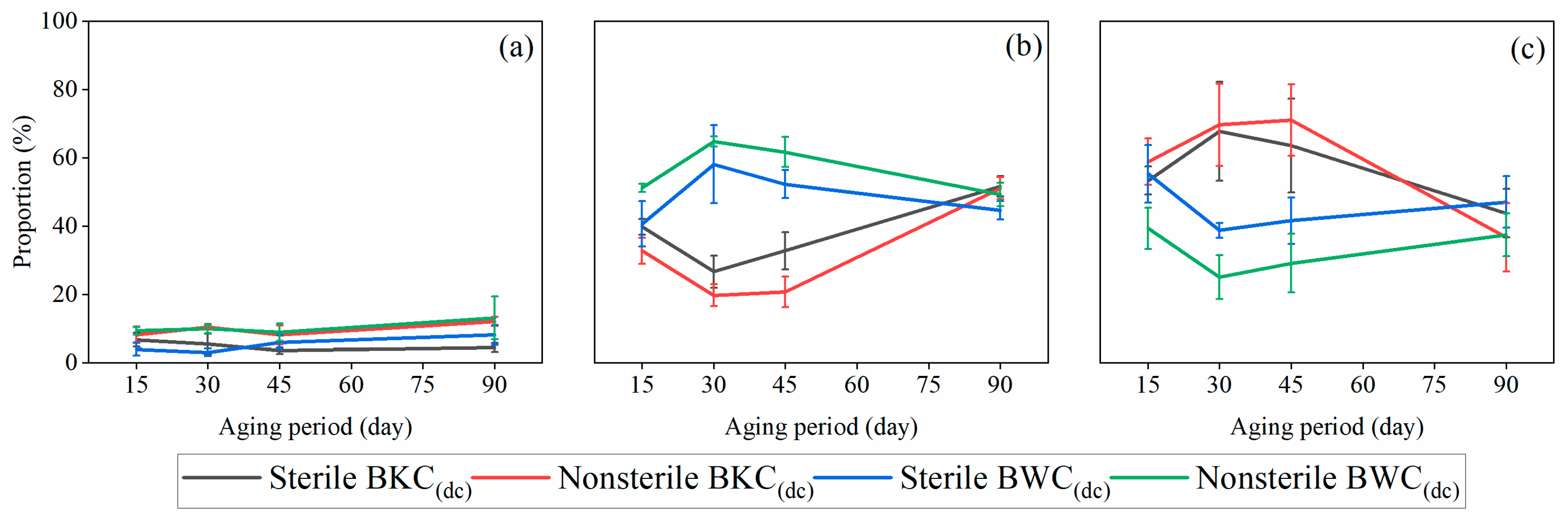
3.2. Effects of C10−C31 in Diesel Fuel
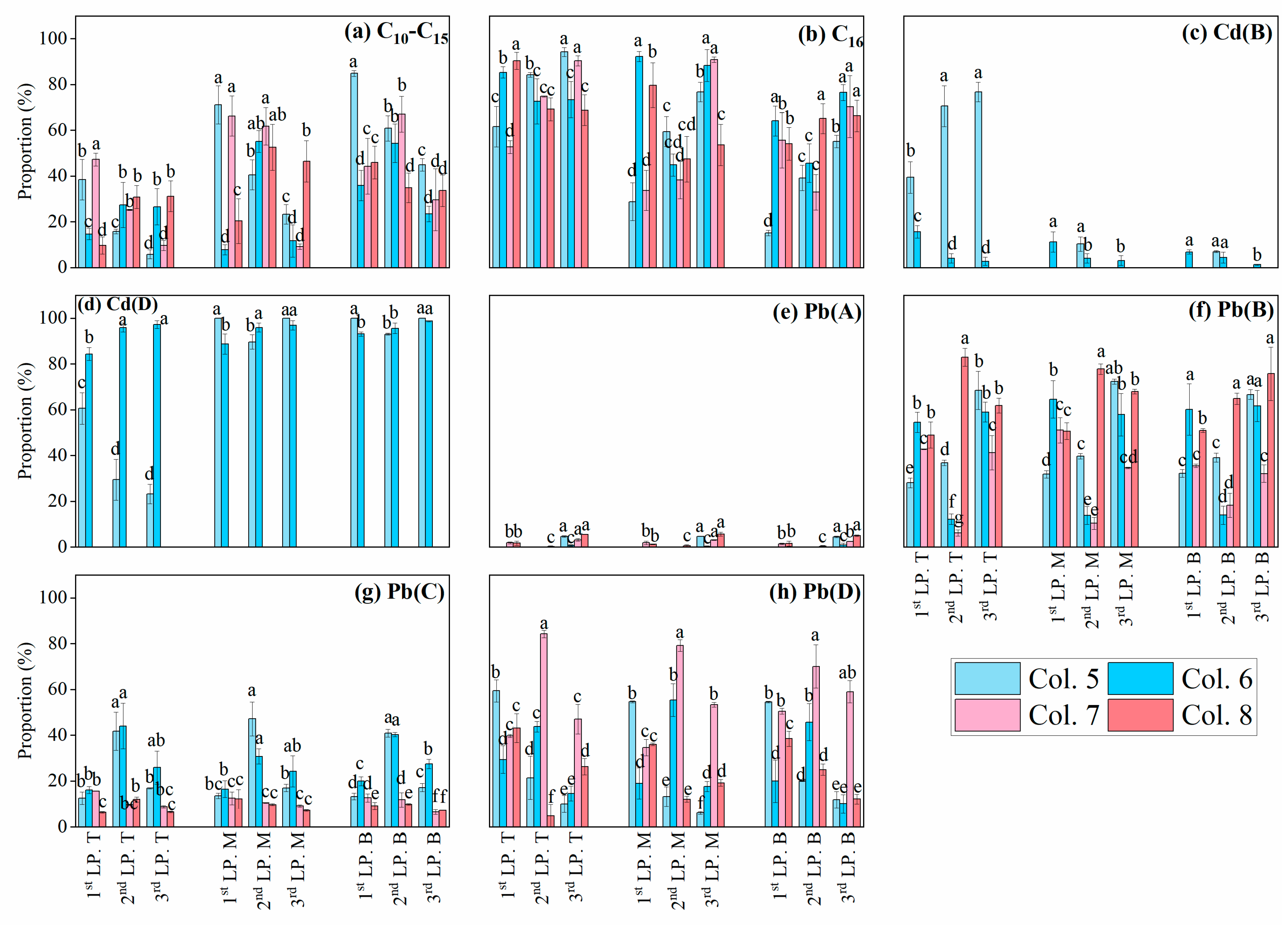
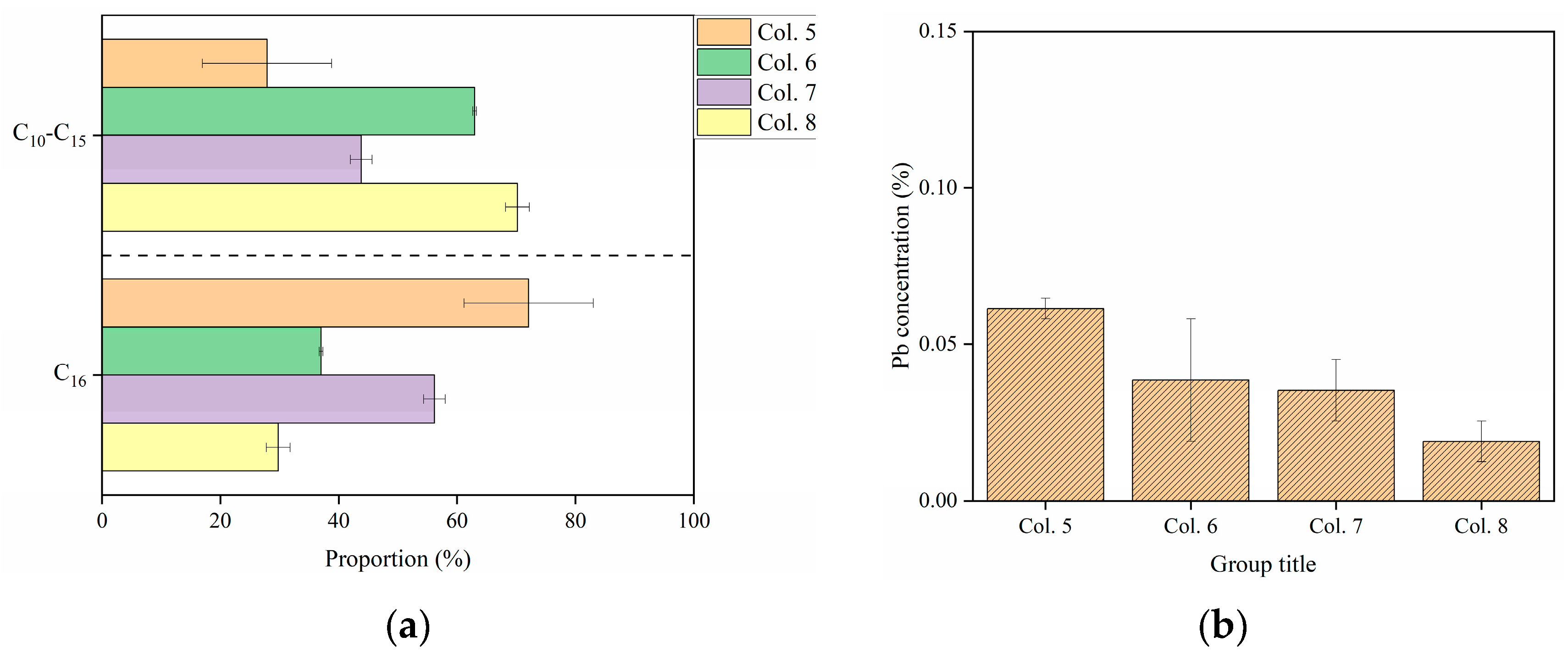
3.3. Retention of Cd and Pb in C16-Contaminated Soils
3.4. Effects of C16
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, Y.; Bai, L.; Li, C.; He, Z.; Liu, X. Assessment of heavy metal contamination levels and health risks in environmental media in the northeast region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, D.; Gao, P.; Gu, W.; He, X.; Yang, W.; Tang, W. Analysis of biosorption and biotransformation mechanism of Pseudomonas chengduensis strain MBR under Cd(II) stress from genomic perspective. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Yi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, D.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Song, S.; Wu, L.; Sáncheze, R.M.T.; Farías, M.E. Montmorillonite facilitated Pb(II) biomineralization by Chlorella sorokiniana FK in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Ding, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, W.; Chai, L. Advances in mechanism for the microbial transformation of heavy metals: Implications for bioremediation strategies. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 12315–12332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Zeng, G.M.; Niu, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, L.H.; Tan, X.F.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M. Bioremediation mechanisms of combined pollution of PAHs and heavy metals by bacteria and fungi: A mini review. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gu, T.; Yi, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y. The release mechanism of heavy metals from lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands treating road runoff. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16588–16595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, H.A.; Li, X.; Jeyakumar, P.; Wei, L.; Huang, L.; Huang, Q.; Kamran, M.; Shaheen, S.M.; Hou, D.; Rinklebe, J.; et al. Influence of biochar and soil properties on soil and plant tissue concentrations of Cd and Pb: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudur, L.S.; Gleeson, D.B.; Ryan, M.H.; Shahsavari, E.; Haleyur, N.; Nugegoda, D.; Ball, A.S. Implications of co-contamination with aged heavy metals and total petroleum hydrocarbons on natural attenuation and ecotoxicity in Australian soils. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, J.; Chen, H.; Du, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, R. Petroleum contamination in groundwater/air and its effects on farmland soil in the outskirt of an industrial city in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 118, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shen, Z.; Tian, T.; Liu, R.; Qiu, J. Temporal variation of heavy metal pollution in urban stormwater runoff. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Zhang, L.; Tan, Z.; Huang, Q. Effect mechanism of biochar’s zeta potential on farmland soil’s cadmium immobilization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19738–19748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y. Interactions between pyrene and heavy metals and their fates in a soil-maize (Zea mays L.) system: Perspectives from the root physiological functions and rhizosphere microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, R.; Shi, J.; Han, K.; Xu, D.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; Xue, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J. Response relationship of environmental factors caused by toluene concentration during leaching of capillary zone. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jakada, H. Contamination and natural attenuation characteristics of petroleum hydrocarbons in a fractured karst aquifer, North China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22780–22794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Liu, M. Effectiveness and mechanism of natural attenuation at a petroleum-hydrocarbon contaminated site. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Long, L.L.; Zhu, Q.R.; Chen, C.; Xu, M.; Wu, J.; Yang, G. Mechanism and ecological environmental risk assessment of peroxymonosulfate for the treatment of heavy metals in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Li, M.; Su, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Ali, E.F.; Shaheen, S.M. Brevundimonas diminuta isolated from mines polluted soil immobilized cadmium (Cd2+) and zinc (Zn2+) through calcium carbonate precipitation: Microscopic and spectroscopic investigations. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Han, R.; Chen, Q.; Shen, D.; Shentu, J. Soil heterogeneity influence on the distribution of heavy metals in soil during acid rain infiltration: Experimental and numerical modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Sharma, P.; Li, B.; Liu, K.; Liu, J.; Flury, M.; Shang, J. Effect of naphthalene on transport and retention of biochar colloids through saturated porous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 530, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, B.; Pazos, M.; Figueiredo, H.; Tavares, T.; Sanromán, M.A. Desorption kinetics of phenanthrene and lead from historically contaminated soil. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Cao, X.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z. Modeling the transport behavior of Pb(II), Ni(II) and Cd(II) in the complex heavy metal pollution site under the influence of coexisting ions. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 162, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhong, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Shao, B.; Liu, Z. Advances in applications of rhamnolipids biosurfactant in environmental remediation: A review. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 115, 796–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logeshwaran, P.; Megharaj, M.; Chadalavada, S.; Bowman, M.; Naidu, R. Petroleum hydrocarbons (PH) in groundwater aquifers: An overview of environmental fate, toxicity, microbial degradation and risk-based remediation approaches. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 10, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, B.; Yang, Y.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, X. Soil microbial ecological effect of shale gas oil-based drilling cuttings pyrolysis residue used as soil covering material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, Z.; Lan, J.; Li, T.; Yuan, D.; Yang, H.; Xing, B. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil seepage water in karst terrains, southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, Q.; Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhong, J. Response of microbial communities and their metabolic functions to calcareous succession process. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Liu, P.W.G.; Whang, L.M. Effects of natural organic matters on bioavailability of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil-water environments. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, B.; Nambi, I.M.; Govindarajan, S.K. Investigating the degradation of nC12 to nC23 alkanes and PAHs in petroleum- contaminated water by electrochemical advanced oxidation process using an inexpensive Ti/Sb-SnO2/PbO2 anode. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 125268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Ji, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Shi, H. Carbonate bedrock control of soil Cd background in Southwestern China: Its extent and influencing factors based on spatial analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, H.; Sui, Q.; Du, W.Y. Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soils by nZVI coupled with electrokinetic activation of persulfate. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 459, 142514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Cui, Z.; Zang, G. Migration, speciation and distribution of heavy metals in an oil-polluted soil affected by crude oil extraction processes. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB36600-2018; Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/trhj/201807/t20180703_446027.shtml (accessed on 1 August 2018).
- Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Ren, J.; Bekele, T.G.; Zhao, H. Effect of cyclodextrin on desorption of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 160, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wang, L.; Cao, D.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, S.; Shi, J. Remediation of petroleum contaminated soil by persulfate oxidation coupled with microbial degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Ye, X. Effect of bioaugmentation and biostimulation on hydrocarbon degradation and microbial community composition in petroleum-contaminated loessal soil. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, Q.; Yang, M.; Wang, S. A novel evaluation method-based effect analysis of urbanization on extreme precipitation in Guangxi, South China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 5957–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, R.; Smettem, K. Runoff change induced by vegetation recovery and climate change over carbonate and non-carbonate areas in the karst region of South-west China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Xing, L.; Liu, L.; Xing, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, C. Time-lag characteristics of the response of karst springs to precipitation in the northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, J. Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.S.; Park, J.W. A novel total petroleum hydrocarbon fractionation strategy for human health risk assessment for petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated site management. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, C.J.; Liu, N.; Li, J.; Ahmed, A. Experimental thawing events enhance petroleum hydrocarbons attenuation and enzymatic activities in polluted temperate soils. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Ren, Y.; Dong, Y. Effects of total organic carbon content and leaching water volume on migration behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils by column leaching tests. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Pan, J.R.; Lang, M.F.; Guo, X.T. Vertical migration and variation of crude oil in soil around typical oilfields under natural leaching. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 3073–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Bai, X.; Wen, X.; Liu, L.; Xiong, J.; Yang, C. A large and overlooked Cd source in karst areas: The migration and origin of Cd during soil formation and erosion. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 895, 165126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Perkins, R.B.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Ning, Z. Geogenic cadmium pollution and potential health risks, with emphasis on black shale. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 176, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaman, R.; Peng, C.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, X. Identifying sources and transport routes of heavy metals in soil with different land uses around a smelting site by GIS based PCA and PMF. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, A.; Li, L.; Xu, H. Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkodie, E.K.; Jiang, L.; Li, K.; Guo, Z.; Yang, J.; Shi, J.; Peng, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, S.; Deng, Y.; et al. The influence of cysteine in transformation of Cd fractionation and microbial community structure and functional profile in contaminated paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, J.; Fu, X.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, Q. Factors affecting the transport of petroleum colloids in saturated porous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 585, 124134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, L. Removal mechanisms of Cd from water and soil using Fe–Mn oxides modified biochar. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Dötterl, S.; Xu, J.; Garland, G.; Liu, X. The critical role of organic matter for cadmium-lead interactions in soil: Mechanisms and risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, M.F.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Saupe, G.B.; Dokken, K.M.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Using FTIR to corroborate the identity of functional groups involved in the binding of Cd and Cr to saltbush (Atriplex canescens) biomass. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjani, S.J. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, B.; He, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, X. A novel constructed carbonate-mineralized functional bacterial consortium for high-efficiency cadmium biomineralization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Li, Z.; Huang, M.; Wen, J.; Ding, X.; Zhou, M.; Cai, C. Laboratory and simulation study on the Cd(Ⅱ) adsorption by lake sediment: Mechanism and influencing factors. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, W. Effects of macromolecular humic/fulvic acid on Cd(II) adsorption onto reed-derived biochar as compared with tannic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Gu, P.; Deng, M.; Liu, Q. Periodical changes of dissolved organic matter (DOM) properties induced by biochar application and its impact on downward migration of heavy metals under flood conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huang, G.H.; An, C.H.; Wei, J. Combined effects of DOM extracted from site soil/compost and biosurfactant on the sorption and desorption of PAHs in a soil–water system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Wang, P.; Hu, B.; Jin, Q.; Zheng, T.; Li, D. Adsorption and distribution of heavy metals in aquatic environments: The role of colloids and effects of environmental factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Lu, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, W. Aging effect of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil under different attenuation conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 149, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrasse, B.; Hennebert, P.; Doumenq, P. Mobility of PAHs, PCBs and TPHs from Fresh and Aged Dredged Sediments. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Han, L.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Hu, F.; Li, H. The effects of aging time on the fraction distribution and bioavailability of PAH. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frescura, L.M.; de Menezes, B.B.; Duarte, R.; da Rosa, M.B. Application of multivariate analysis on naphthalene adsorption in aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 3329–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. The nutrient, total petroleum hydrocarbon and heavy metal contents in the seawater of Bohai Bay, China: Temporal–spatial variations, sources, pollution statuses, and ecological risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Ye, Z.; Ge, X. Characteristics, sources and health risks of toxic species (PCDD/Fs, PAHs and heavy metals) in PM2.5 during fall and winter in an industrial area. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, S.; Nie, S.; Jiang, T. Transport and retention of n-hexadecane in cadmium-/naphthalene-contaminated calcareous soil sampled in a karst area. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 8881–8895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W.; Cao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xian, Q. The effects of Cu-phenanthrene co-contamination on adsorption-desorption behaviors of phenanthrene in soils. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Camara, A.Y.; Li, H. Effects of the addition and aging of humic acid-based amendments on the solubility of Cd in soil solution and its accumulation in rice. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Dong, A.; Liu, J.; Su, J.; Hu, P.; Xu, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q. Relevance of dissolved organic matter generated from green manuring of Chinese milk vetch in relation to water-soluble cadmium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16409–16421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Tian, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, M. Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient levels on heavy metal contents and fractions in river surface sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, S.; Song, J.; Wu, S. Human health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urban soils of Nanjing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 889-2017; Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Soil Quality-Determination of Cation Exchange Capacity(CEC)-Hexamminecobalt Trichloride Solution-Spectrophotometric Method. Available online: https://english.mee.gov.cn/Resources/standards/Soil/Method_Standard4/201801/t20180105_429211.shtml (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Q.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of spectral responses of dissolved organic matter (DOM) for atrazine binding during the sorption process onto black soil. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HJ 911-2017; Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Soil and Sediment-Extraction of Organic compounds-Ultrasonic Extraction. Available online: https://codeofchina.com/standard/HJ911-2017.html (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- HJ 894-2017; Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Water Quality-Determination of Extractable Petroleum Hydrocarbons (C10–C40) Gas Chromatography. Available online: https://english.mee.gov.cn/Resources/standards/water_environment/method_standard2/201801/t20180105_429205.shtml (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Qureshi, A.A.; Kazi, T.G.; Baig, J.A.; Arain, M.B.; Afridi, H.I. Exposure of heavy metals in coal gangue soil, in and outside the mining area using BCR conventional and vortex assisted and single step extraction methods. Impact on orchard grass. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yan, Y.; Yu, R.; Hu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, H. Source apportionment and health risks of the bioavailable and residual fractions of heavy metals in the park soils in a coastal city of China using a receptor model combined with Pb isotopes. CATENA 2020, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 832–2017; Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Soil and Sediment-Digestion of Total Metal Elements- Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion Method. Available online: https://english.mee.gov.cn/Resources/standards/Soil/Method_Standard4/201708/t20170830_420636.shtml (accessed on 1 September 2017).
- HJ 678–2013; Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Water Quality-Digestion of Total Metals-Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion Method. Available online: https://www.codeofchina.com/standard/HJ678-2013.html (accessed on 1 February 2014).
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J. Micro-bubbles enhanced removal of diesel oil from the contaminated soil in washing/flushing with surfactant and additives. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group Number | Pollutants in the Surface Soils of the Column (−0.4 cm~0.0 cm) | Uncontaminated Soils (Filled from −10 cm to −0.4 cm) | Aging Periods for Contaminated Soils in the Surface Layer of the Column (−0.4 cm~0.0 cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Col. 1 | 4500 mg/kg diesel fuel + 20 mg/kg Cd | BKC | 30 days |
| Col. 2 | 90 days | ||
| Col. 3 | BWC | 30 days | |
| Col. 4 | 90 days | ||
| Col. 5 | 4500 mg/kg n-hexadecane (abbreviated as C16) + 20 mg/kg Cd | BKC | 30 days |
| Col. 6 | 90 days | ||
| Col. 7 | BWC | 30 days | |
| Col. 8 | 90 days |
| Col. 1 | Col. 2 | Col. 3 | Col. 4 | BKC | BWC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeta potential (mV) | −12.30 | −17.22 | −11.91 | −15.13 | −20.81 | −13.58 |
| CEC (cmol+/kg) | 57.20 | 70.71 | 13.34 | 8.31 | 86.91 | 7.55 |
| pH | 8.10 | 8.00 | 5.81 | 6.00 | 8.10 | 5.35 |
| Group | Equation |
|---|---|
| Col. 1 | (R2 = 0.53) (R2 = 0.71) |
| Col. 2 | (R2 = 0.31) (R2 = 0.45) |
| Col. 3 | (R2 = 0.54) |
| Col. 4 | (R2 = 0.64) |
| Col. 5 | Col. 6 | Col. 7 | Col. 8 | BKC | BWC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeta potential (mV) | −13.5 | −15.8 | −9.11 | −14.55 | −20.81 | −13.58 |
| CEC (cmol+/kg) | 45.8 | 61.3 | 12.69 | 8.83 | 86.91 | 7.55 |
| pH | 7.91 | 8.00 | 5.70 | 6.00 | 8.10 | 5.35 |
| Group | Equation |
|---|---|
| Col. 5 | (R2 = 0.78) (R2 = 0.33) (R2 = 0.46) |
| Col. 6 | (R2 = 0.13) |
| Col. 7 | (R2 = 0.31) (R2 = 0.34) |
| Col. 8 | (R2 = 0.28) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Nie, S. Degradation of Low-Molecular-Weight Diesel Fractions (C10−C16 Alkane) Drives Cd Stabilization and Pb Activation in Calcareous Soils from Karst Areas. Toxics 2025, 13, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060496
Huang Y, Tang Y, Xie Z, Wu J, Huang J, Nie S. Degradation of Low-Molecular-Weight Diesel Fractions (C10−C16 Alkane) Drives Cd Stabilization and Pb Activation in Calcareous Soils from Karst Areas. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060496
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yiting, Yankui Tang, Zhenze Xie, Jipeng Wu, Jiajie Huang, and Shaojiang Nie. 2025. "Degradation of Low-Molecular-Weight Diesel Fractions (C10−C16 Alkane) Drives Cd Stabilization and Pb Activation in Calcareous Soils from Karst Areas" Toxics 13, no. 6: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060496
APA StyleHuang, Y., Tang, Y., Xie, Z., Wu, J., Huang, J., & Nie, S. (2025). Degradation of Low-Molecular-Weight Diesel Fractions (C10−C16 Alkane) Drives Cd Stabilization and Pb Activation in Calcareous Soils from Karst Areas. Toxics, 13(6), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060496






