Intratracheal Administration of Polystyrene Micro(nano)plastics with a Mixed Particle Size Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats by Activating TGF-β1 Signaling and Destabilizing Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy in a Dose- and Time-Dependent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Preparation of the PS-MP Mixture
2.4. Exposure Method and Treatment
2.5. Observation of PS-MPs in the Lung Tissues of the Rats
2.6. Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) Staining
2.7. Masson’s Trichrome Staining
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Western Blotting (WB)
2.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.11. Real-Time PCR
2.12. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.13. Estimation of ATP Levels
2.14. Analysis of the BMD and BMDL of PS-MP Exposure in Rats
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
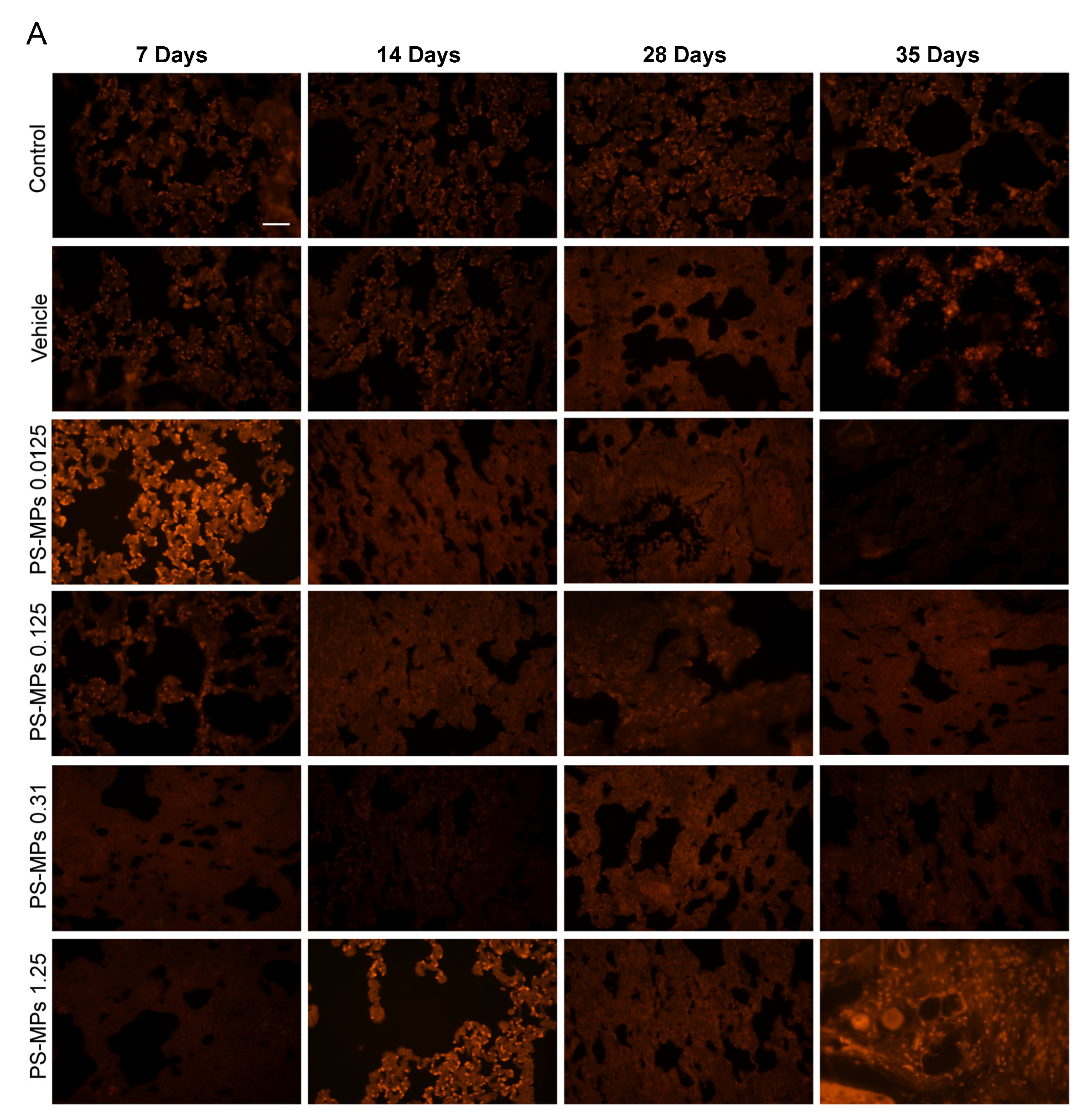
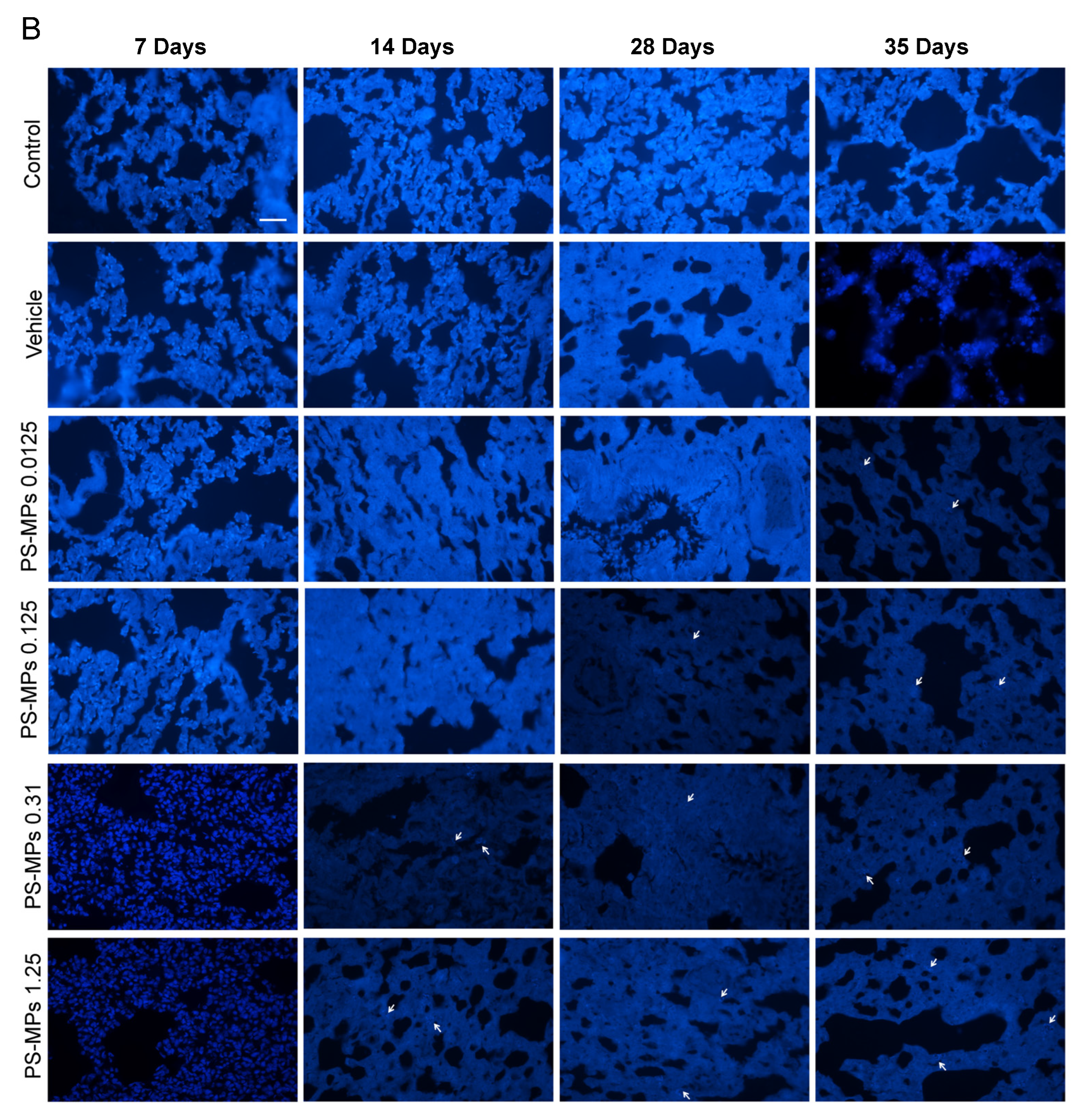
3.1. PS-MP Distribution in the Lung Tissues of the Rats
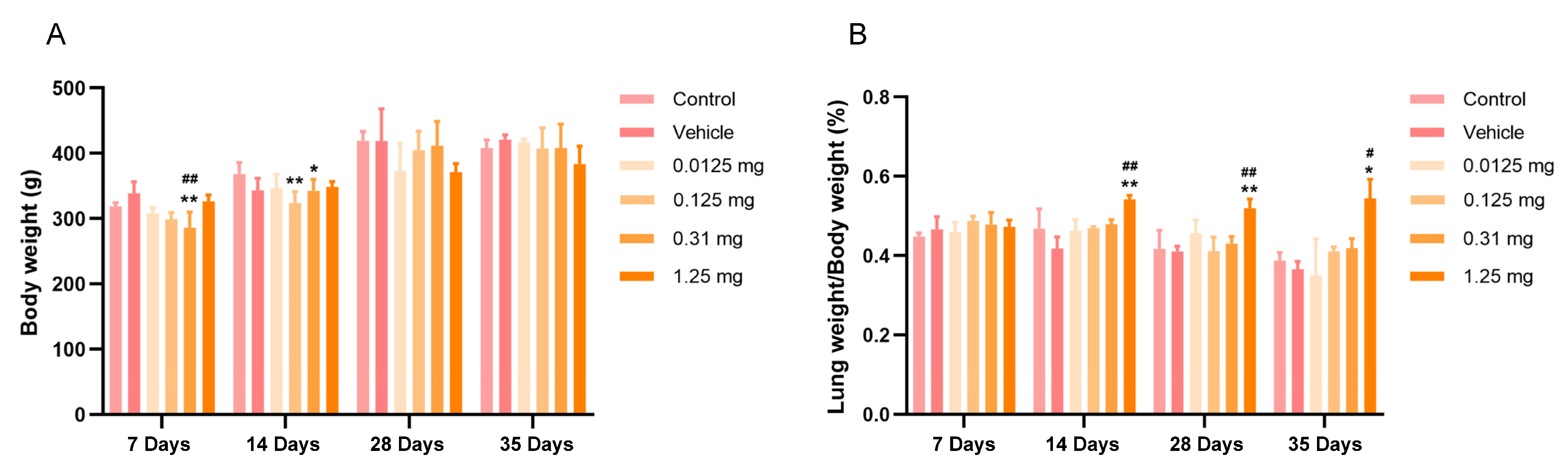
3.2. Intratracheal Administration of PS-MPs Affect the Body and Lung Weights of Rats
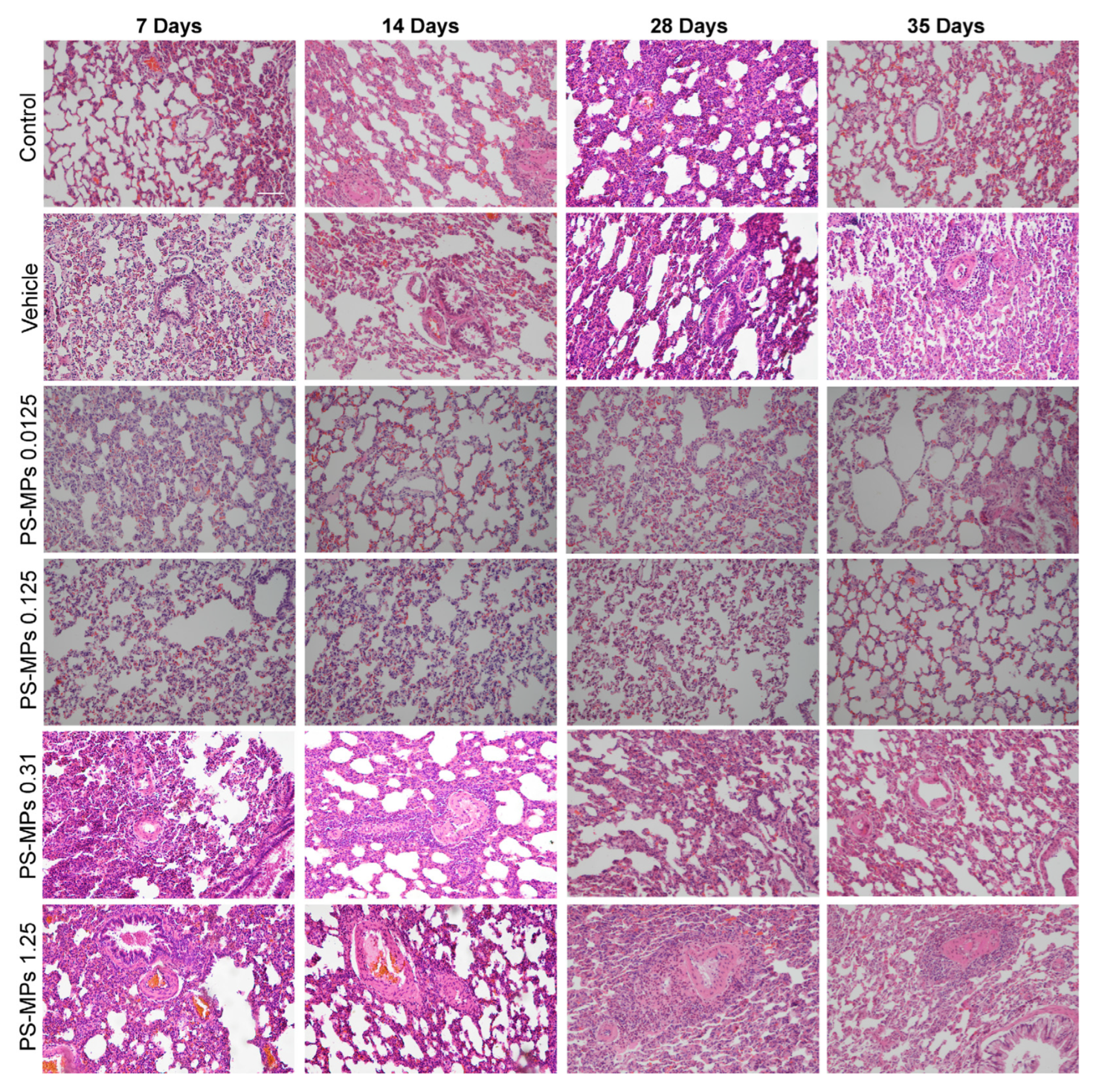
3.3. Intratracheal Administration of PS-MPs Induces Structural Damage in the Lungs of Rats
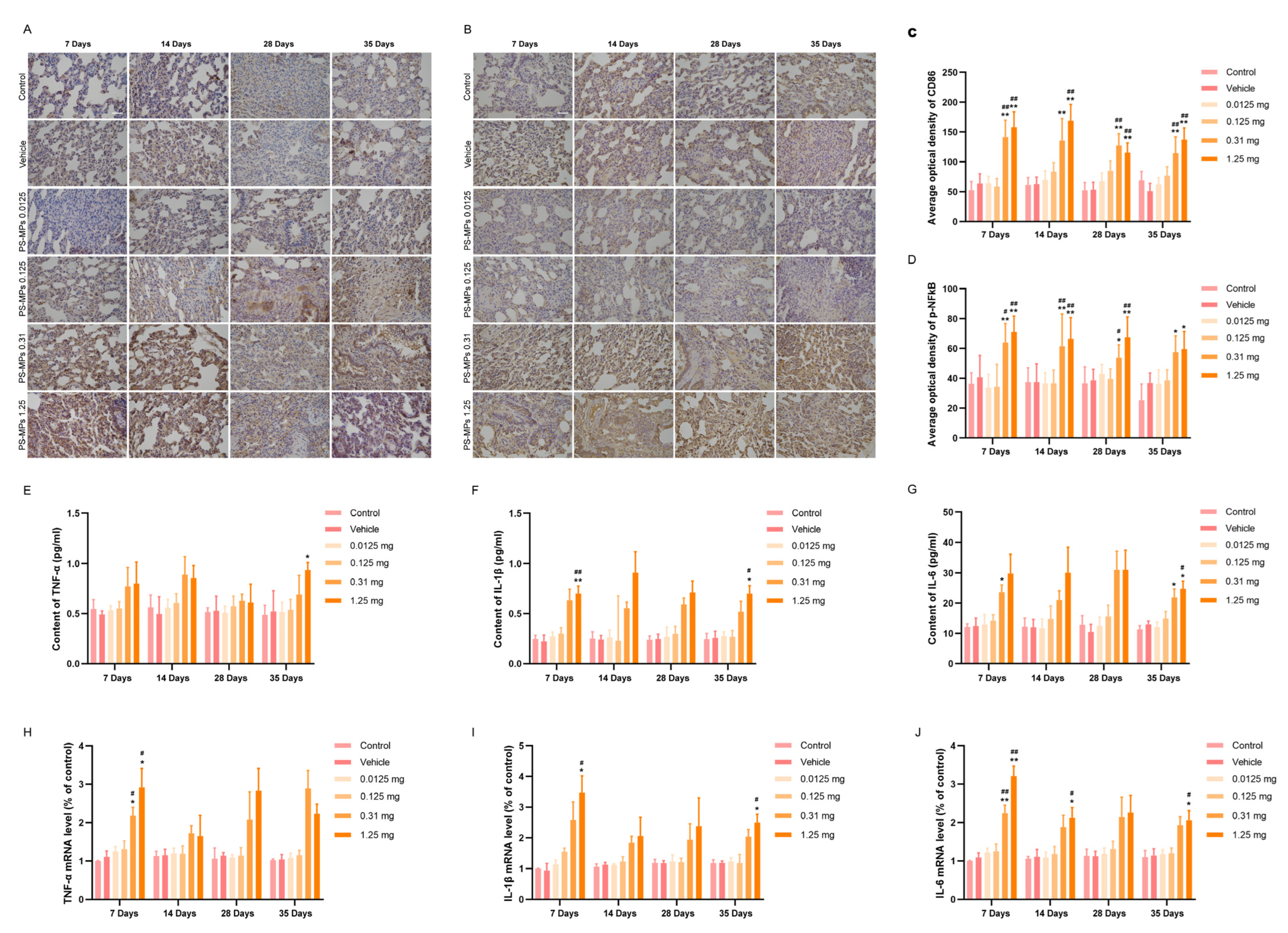
3.4. Intratracheal Administration of PS-MPs Activates NFκB-Mediated Pulmonary Inflammation in Rats
3.5. Intratracheal Administration of PS-MPs Activates TGF-β1/Smad Signaling to Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats
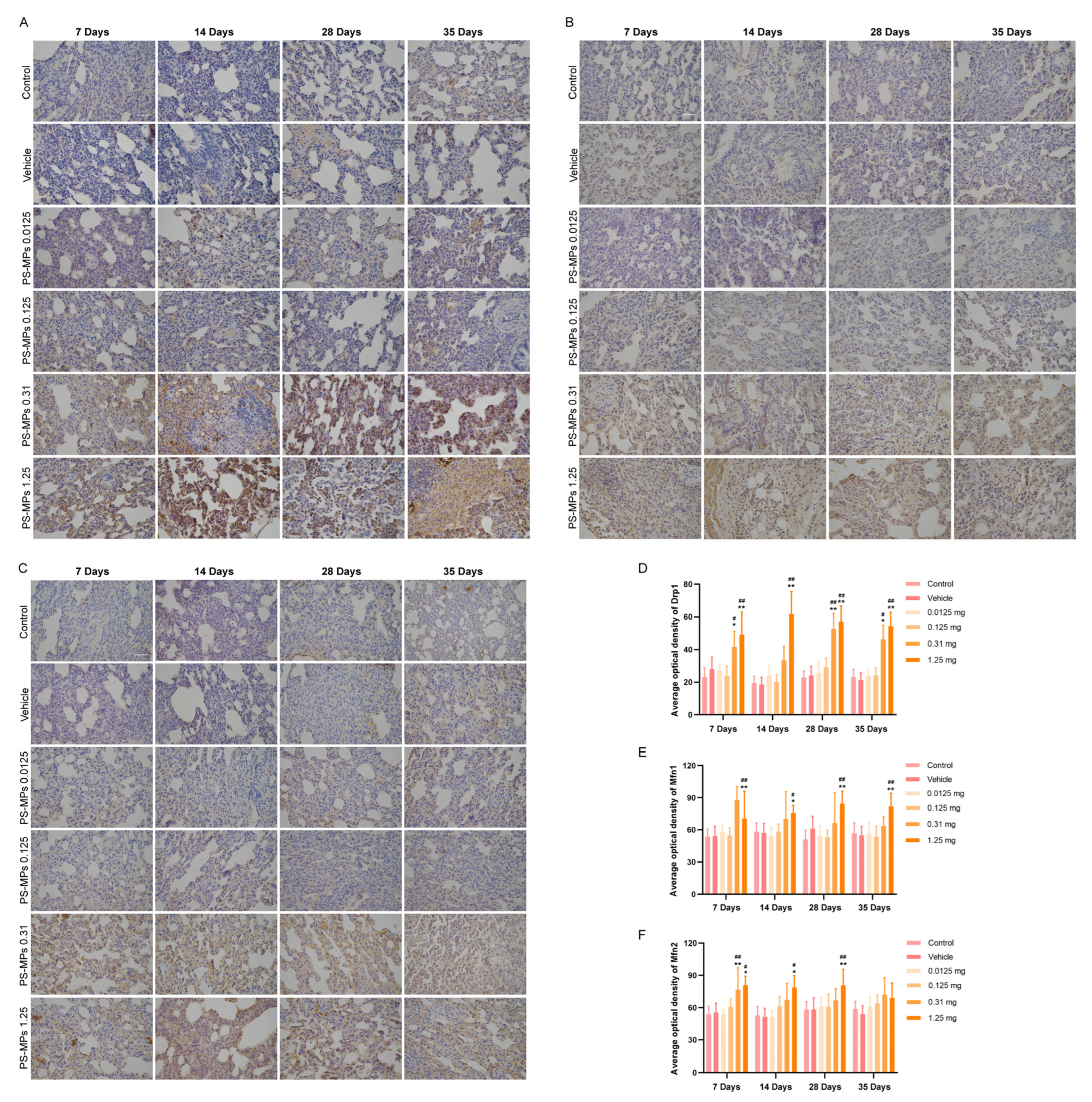
3.6. Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy Dysfunction Aggravate Pulmonary Fibrosis Induced by PS-MPs
3.7. Assessment of the BMD and BMDL by Evaluating the Lung Organ Coefficient and Proinflammatory Cytokine Contents in Rats Subjected to PS-MPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Akt | protein kinase B |
| AT-II cell | alveolar epithelial type II cell |
| BMD | benchmark dose |
| BMDL | benchmark dose lower confidence limit |
| Drp1 | dynamic associated protein 1 |
| EMT | epithelial mesenchymal transition |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| IκBα | Phospho inhibitor of κBα |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| LC3 | microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 |
| Mfn1/2 | mitochondrial fusion 1/2 |
| MPs | microplastics |
| NFκB | nuclear factor κB |
| NOAEL | no observed adverse effect level |
| NPs | nanoplastics |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase |
| PINK1 | PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 |
| PS-MPs | polystyrene microplastics |
| SMAD | small mothers against decapentaplegic proteins |
| SQSTM1/p62 | sequestosome-1 |
| TGF-β1 | transforming growth factor-β1 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
References
- Zolotova, N.; Kosyreva, A.; Dzhalilova, D.; Fokichev, N.; Makarova, O. Harmful effects of the microplastic pollution on animal health: A literature review. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, F.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, Y.; Ruan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Fate and transport of nanoplastics in complex natural aquifer media: Effect of particle size and surface functionalization. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güven, O.; Gökdağ, K.; Jovanović, B.; Kıdeyş, A.E. Microplastic litter composition of the Turkish territorial waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and its occurrence in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J. Mini-review of microplastics in the atmosphere and their risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Júnior, G.R.; Dos Santos Galvão, L.; Ando, R.A.; Mauad, T. Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of microplastics in human lung tissue using μFTIR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, B.D.; Bunn, W.B.; Hesterberg, T.W. Solubility of polymeric organic fibers and manmade vitreous fibers in gambles solution. Inhal. Toxicol. 1990, 2, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Lv, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Xu, Q.; Cai, H.; Dai, J. Intratracheal administration of polystyrene microplastics induces pulmonary fibrosis by activating oxidative stress and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Xiao, T.; Luo, H.; Chen, D.; Lu, K.; Shi, W.; Sun, C.; Bian, Q. A study on the roles of long non-coding RNA and circular RNA in the pulmonary injuries induced by polystyrene microplastics. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.D.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, H.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lin, C.H. Polystyrene microplastic particles: In vitro pulmonary toxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, T.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Liang, G. In vitro evaluation of nanoplastics using human lung epithelial cells, microarray analysis and co-culture model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Shi, X.; Xu, S. Di-(2-ethyl hexyl) phthalate induced oxidative stress promotes microplastics mediated apoptosis and necroptosis in mice skeletal muscle by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Toxicology 2022, 474, 153226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Yin, K.; Su, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, L.; Li, J.B.; Wang, Y.; Xing, M. Polystyrene microplastics induce autophagy and apoptosis in birds lungs via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR. Environ. Toxicol. 2023, 38, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Xia, P.F.; Yuan, X.Z.; Wang, S.G. Chlorine disinfection elevates the toxicity of polystyrene microplastics to human cells by inducing mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, M.; Su, X.; Yuan, P.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Wan, Z.; Zou, W. Photolytic degradation elevated the toxicity of polylactic acid microplastics to developing zebrafish by triggering mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Guo, W.B.; Liu, Y.Y.; Yang, L.; Miao, A.J. Perturbation of calcium homeostasis and multixenobiotic resistance by nanoplastics in the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, R.; Uzochukwu, D.; Di Giulio, R.T. PAH sorption to nanoplastics and the trojan horse effect as drivers of mitochondrial toxicity and PAH localization in zebrafish. Front Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hou, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce mitochondrial damage in mouse GC-2 cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, D.; Tanaka, A.; Suen, D.F.; Youle, R.J. Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.; Lai, Y.C.; Romero, Y.; Brands, J.; St Croix, C.M.; Kamga, C.; Corey, C.; Herazo-Maya, J.D.; Sembrat, J.; Lee, J.S.; et al. PINK1 deficiency impairs mitochondrial homeostasis and promotes lung fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, S.M.; Kluxen, F.M.; Ritz, C. A Review of Recent Advances in Benchmark Dose Methodology. Risk Anal. 2019, 39, 2295–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.F.; Gu, Z.G.; Fan, Y.H.; Li, X.L.; Niu, Z.M.; Duan, X.R.; Mallah, A.M.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.L.; Yao, W.; et al. Benchmark Dose Assessment for Coke Oven Emissions-Induced Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number Damage Effects. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2023, 36, 490–500. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, K.; Vimalkumar, K. A Review of Human Exposure to Microplastics and Insights Into Microplastics as Obesogens. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 724989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Hong, W.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Ran, P. Chronic exposure to biomass ambient particulate matter triggers alveolar macrophage polarization and activation in the rat lung. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.; Tabassum, S.; Sarwar, S.; Qureshi, R.; Sohaib Khalid, M.; Riaz, N.; Al-Qahtani, W.H.; Murtaza, I. Neuroprotective Effect of Otostegia limbata Against PTZ-Induced Mice Model of Epilepsy by Attenuated Expression of p-NFκB and TNF-α. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 779681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, H.; Chen, X.; Han, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, W.; Liang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Epigenetically upregulated oncoprotein PLCE1 drives esophageal carcinoma angiogenesis and proliferation via activating the PI-PLCε-NF-κB signaling pathway and VEGF-C/ Bcl-2 expression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Lu, M.L.; Wang, H.X. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inflammation by regulating CCN1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownell, R.; Kaminski, N.; Woodruff, P.G.; Bradford, W.Z.; Richeldi, L.; Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R. Precision Medicine: The New Frontier in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Wei, X.; Xie, T.; Lv, B.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X. Interaction of NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease and Potential Active Drug Treatments. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, M.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P.; Dasgupta, S. Mitochondrial fusion and fission: The fine-tune balance for cellular homeostasis. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T. Current understanding of bipolar disorder: Toward integration of biological basis and treatment strategies. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 73, 526–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.L.; Lian, L.; Chen, X.N.; Cai, W.H.; Fan, X.B.; Fan, Y.J.; Li, T.T.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.P. The role of mitochondria in myocardial damage caused by energy metabolism disorders: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 208, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Weng, J.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Xie, M.; Wang, X.; Chang, Q.; Li, M.; Chung, F.K.; Adcock Ian, M.; et al. Attenuation of PM2.5-induced alveolar epithelial cells and lung injury through regulation of mitochondrial fission and fusion. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2023, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.P.; Hsu, C.L.; Fan, L.C.; Huang, Z.; Bhatia, D.; Chen, Y.J.; Hisata, S.; Cho, S.J.; Nakahira, K.; Imamura, M.; et al. Mitofusins regulate lipid metabolism to mediate the development of lung fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant-Beuchot, L.; Mary, A.; Pardossi-Piquard, R.; Bourgeois, A.; Lauritzen, I.; Eysert, F.; Kinoshita, P.F.; Cazareth, J.; Badot, C.; Fragaki, K.; et al. Accumulation of amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragments triggers mitochondrial structure, function, and mitophagy defects in Alzheimer’s disease models and human brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Liu, D.; Ji, X.; Chi, T.; Guo, Z.; Li, L.; Zou, L. Prevention of Huntington’s Disease-Like Behavioral Deficits in R6/1 Mouse by Tolfenamic Acid Is Associated with Decreases in Mutant Huntingtin and Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 4032428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, J.; Wright, S.L.; Dris, R.; Collard, F.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Kelly, F.J.; Tassin, B. Microplastics in air: Are we breathing it in? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.K.; Ensor, D.S.; Sparks, L.E. Airborne particle sizes and sources found in indoor air. Atmos. Environ. A Gen Top. 1992, 26, 2149–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levermore, J.M.; Smith, T.E.L.; Kelly, F.J.; Wright, S.L. Detection of Microplastics in Ambient Particulate Matter Using Raman Spectral Imaging and Chemometric Analysis. Anal Chem. 2020, 92, 8732–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, S.; Rodriguez, C.; Sarrett, S.M.; Dayts, E.J.; Zeglis, B.M.; Keinänen, O. Unraveling the in vivo fate of inhaled micro- and nanoplastics with PET imaging. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dou, J.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, X. Bioeffects of Inhaled Nanoplastics on Neurons and Alteration of Animal Behaviors through Deposition in the Brain. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Olga, V.; Xue, Y.; Lv, S.; Diao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhou, H. The potential effects of microplastic pollution on human digestive tract cells. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 1, 132714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assas, M.; Qiu, X.; Chen, K.; Ogawa, H.; Xu, H.; Shimasaki, Y.; Oshima, Y. Bioaccumulation and reproductive effects of fluorescent microplastics in medaka fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, I.; Brenna, C.; Passaro, A.; Neri, L.M. Bioaccumulation Rate of Non-Biodegradable Polystyrene Microplastics in Human Epithelial Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remigante, A.; Spinelli, S.; Gambardella, L.; Bozzuto, G.; Vona, R.; Caruso, D.; Villari, V.; Cappello, T.; Maisano, M.; Dossena, S.; et al. Internalization of nano- and micro-plastics in human erythrocytes leads to oxidative stress and estrogen receptor-mediated cellular responses. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 223, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Geffen, C.; Deißler, A.; Quante, M.; Renz, H.; Hartl, D.; Kolahian, S. Regulatory Immune Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Friends or Foes? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 663203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lv, J.; Su, Z.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L. LRRK2 plays essential roles in maintaining lung homeostasis and preventing the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2106685118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Feng, C.; Gao, D.; Yao, B.; Wu, X.; Fu, X. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate inflammatory cytokine-induced impairment of AT-II cells through a keratinocyte growth factor-dependent PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3755–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plikus, M.V.; Wang, X.; Sinha, S.; Forte, E.; Thompson, S.M.; Herzog, E.L.; Driskell, R.R.; Rosenthal, N.; Biernaskie, J.; Horsley, V. Fibroblasts: Origins, definitions, and functions in health and disease. Cell 2021, 184, 3852–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Działo, E.; Czepiel, M.; Tkacz, K.; Siedlar, M.; Kania, G.; Błyszczuk, P. WNT/β-Catenin Signaling Promotes TGF-β-Mediated Activation of Human Cardiac Fibroblasts by Enhancing IL-11 Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciolà, A.; Visalli, G.; Pruiti Ciarello, M.; Di Pietro, A. Newly Emerging Airborne Pollutants: Current Knowledge of Health Impact of Micro and Nanoplastics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Ren, J.; Gui, Y.; Wei, W.; Shu, B.; Lu, Q.; Xue, X.; Sun, X.; He, W.; Yang, J.; et al. Wnt/β-Catenin-Promoted Macrophage Alternative Activation Contributes to Kidney Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gu, W.; Zhang, B.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Toxic effects of nanoplastics with different sizes and surface charges on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in A549 cells and the potential toxicological mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, T.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Xia, X.; Ji, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, R.; et al. Inhaled tire-wear microplastic particles induced pulmonary fibrotic injury via epithelial cytoskeleton rearrangement. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siekacz, K.; Piotrowski, W.J.; Iwański, M.A.; Górski, P.; Białas, A.J. The Role of Interaction between Mitochondria and the Extracellular Matrix in the Development of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9932442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Li, C.; Lu, Y.; Lei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Weng, D.; Chen, J. Dioscin Alleviates Crystalline Silica-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis through Promoting Alveolar Macrophage Autophagy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1878–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Hong, Q.; Lin, J.; Li, X.; Meng, Y. Cigarette smoke-inactivated SIRT1 promotes autophagy-dependent senescence of alveolar epithelial type 2 cells to induce pulmonary fibrosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 166, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Laar, V.S.; Berman, S.B. The interplay of neuronal mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 51, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maremanda, K.P.; Sundar, I.K.; Rahman, I. Role of inner mitochondrial protein OPA1 in mitochondrial dysfunction by tobacco smoking and in the pathogenesis of COPD. Redox Biol. 2021, 45, 102055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Dong, S.; Wu, L.; Wu, L.; Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, D. PI3K/Akt pathway-mediated HO-1 induction regulates mitochondrial quality control and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, D.; Chen, R.; Zhang, B.; Tan, Y.; Niu, Y.; Duan, H.; Mai, B.; et al. The development of a cell-based model for the assessment of carcinogenic potential upon long-term PM2.5 exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, S.F.; Zhou, Y.M.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.X.; Dai, Y.F.; Adamson, S.X.; Zheng, Y.X.; Bin, P. Assessment of Benchmark Dose in BEAS-2B Cells by Evaluating the Cell Relative Viability with Particulates in Motorcycle Exhaust via the Air-liquid Interface Exposure. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gutting, B.W.; Rukhin, A.; Marchette, D.; Mackie, R.S.; Thran, B. Dose-Response Modeling for Inhalational Anthrax in Rabbits Following Single or Multiple Exposures. Risk Anal. 2016, 36, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft, S.C.; Hines, S.A. Benchmark dose analysis for Bacillus anthracis inhalation exposures in the nonhuman primate. Risk Anal. 2012, 32, 1750–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; FitzGerald, R.; Wilks, M.F.; Barle, E.L.; Hopf, N.B. Use of the benchmark-dose (BMD) approach to derive occupational exposure limits (OELs) for genotoxic carcinogens: N-nitrosamines. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2023, 43, 1183–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.M.; Mole, M.L.; Chernoff, N.; Barbee, B.D.; Turner, C.I.; Logsdon, T.R.; Kavlock, R.J. The developmental toxicity of inhaled methanol in the CD-1 mouse, with quantitative dose-response modeling for estimation of benchmark doses. Teratology 1993, 47, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Genes | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|
| TNF-α | F: TGTTCATCCGTTCTCTACCCA |
| R: CACTACTTCAGCGTCTCGT | |
| IL-1β | F: CTATGGCAACTGTCCCTGAA |
| R: GGCTTGGAAGCAATCCTTAATC | |
| IL-6 | F: GAAGTTAGAGTCACAGAAGGAGTG |
| R: GTTTGCCGAGTAGACCTCATAG | |
| β-actin | F: TGCTATGTTGCCCTAGACTTCG |
| R: GTTGGCATAGAGGTCTTTACGG |
| Time Point | Model of Fit | Goodness of Fit p Value | AIC | BMD | BMDL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | ||||||
| 7 Days | ||||||
| Lung organ coefficient (%) | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | ExponentialM5 | 0.545 | −45.136 | 0.141 | 0.095 | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | |
| 14 Days | ||||||
| Lung organ coefficient (%) | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | |
| 28 Days | ||||||
| Lung organ coefficient (%) | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | NDR | |
| 35 Days | ||||||
| Lung organ coefficient (%) | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | Power | 0.594 | −24.876 | 0.151 | 0.031 | |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | ExponentialM5 | 0.490 | −43.294 | 0.205 | 0.115 | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | Polynomial 2° | 0.538 | 91.815 | 0.05 | 0.037 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, S.; Yuan, C.; Long, W.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Liu, P.; et al. Intratracheal Administration of Polystyrene Micro(nano)plastics with a Mixed Particle Size Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats by Activating TGF-β1 Signaling and Destabilizing Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy in a Dose- and Time-Dependent Manner. Toxics 2025, 13, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060487
Xia S, Yuan C, Long W, Wu Z, Li X, Wang N, Gao M, Li Z, Li P, Liu P, et al. Intratracheal Administration of Polystyrene Micro(nano)plastics with a Mixed Particle Size Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats by Activating TGF-β1 Signaling and Destabilizing Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy in a Dose- and Time-Dependent Manner. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060487
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Shuang, Chunli Yuan, Wei Long, Zongcheng Wu, Xiuqin Li, Nan Wang, Mumu Gao, Zhe Li, Peilun Li, Peng Liu, and et al. 2025. "Intratracheal Administration of Polystyrene Micro(nano)plastics with a Mixed Particle Size Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats by Activating TGF-β1 Signaling and Destabilizing Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy in a Dose- and Time-Dependent Manner" Toxics 13, no. 6: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060487
APA StyleXia, S., Yuan, C., Long, W., Wu, Z., Li, X., Wang, N., Gao, M., Li, Z., Li, P., Liu, P., Qu, X., & Sun, L. (2025). Intratracheal Administration of Polystyrene Micro(nano)plastics with a Mixed Particle Size Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats by Activating TGF-β1 Signaling and Destabilizing Mitochondrial Dynamics and Mitophagy in a Dose- and Time-Dependent Manner. Toxics, 13(6), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060487







