Addressing the Global Challenge of Nitrous Oxide Misuse Through a Multidisciplinary Approach: Example of the PROTOSIDE Network
Abstract
1. Context, State of the Art, and Challenges
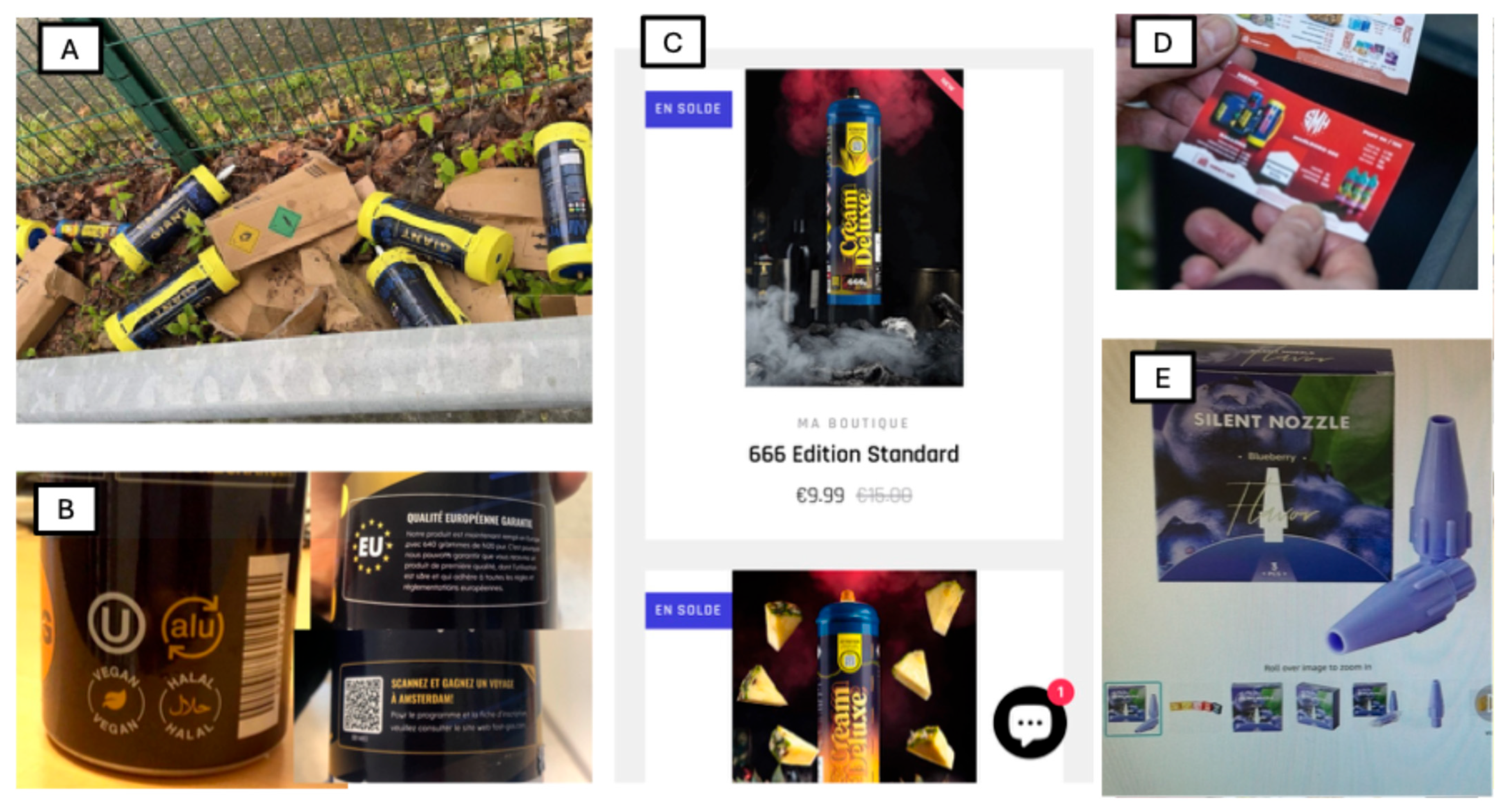
1.1. A Historical Shift: From Medical Use to Recreational Misuse
- Origins of medical use and early recreational consumption
- The shift to mass recreational use
- The role of unregulated distribution channels
1.2. The Epidemiological Surge: A Growing Global Concern
1.2.1. Europe: A Hub for Nitrous Oxide Consumption
- Key epidemiological findings according to the EMCDDA report
- Regulatory responses and effectiveness
1.2.2. Emerging Concerns: From Acute to Chronic Health Consequences
1.3. Clinical and Biological Consequences of Nitrous Oxide Misuse [1]
1.3.1. Neurological Manifestations: Myeloneuropathy and Central Nervous System Impairment
- Clinical presentations
1.3.2. Biochemical and Metabolic Disruptions: Methylmalonic Acid and Homocysteine Dysregulation
- -
- Methionine synthase, which requires methylcobalamin as a cofactor, catalyzes the remethylation of homocysteine into methionine. When MS activity is blocked, homocysteine accumulates in plasma—a biochemical hallmark of impaired one-carbon metabolism. This elevation is clinically relevant due to its association with vascular and neurological complications.
- -
- Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, on the other hand, depends on adenosylcobalamin (another active form of vitamin B12) and facilitates the conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA in mitochondria. Inactivation of this enzyme leads to accumulation of methylmalonic acid (MMA), a marker of intracellular B12 dysfunction.
- As a consequence, nitrous oxide intoxication can lead to (Table 1):
- Reduction in methionine synthesis, affecting myelin integrity [30].
| Biological Markers | Pathophysiological Significance |
|---|---|
| Plasma homocysteine | Sensitive marker of N2O exposure; reflects impaired methionine metabolism [10]. |
| Methylmalonic acid (MMA) | More specific to B12-related neurological dysfunction; correlated with clinical severity [10]. |
| Methionine levels | Low methionine is associated with myelin damage, linked to neurological outcomes [30]. |
- Key Takeaways:
- Vitamin B12 levels alone are unreliable, as they may appear normal despite severe toxicity [10].
1.3.3. Hematological and Bone Marrow Effects
1.3.4. Cardiovascular and Thromboembolic Complications
1.3.5. Psychiatric and Cognitive Consequences
1.4. Road Safety and Neurocognitive Risks of Nitrous Oxide Use
- Current challenges in detection:
- Public health implications:
2. Why a Global Network Was Needed
3. Multidisciplinary Competence Centers: The Foundation of PROTOSIDE
- Emergency physicians, to identify users, manage acute complications, and refer them to the right specialists;
- Neurologists, to diagnose and treat neurological injuries, including myelopathies [51];
- Specialists in laboratory medicine, equipped to perform advanced biochemical analyses such as total plasma homocysteine and MMA concentration measurements (4,6);
- Addiction specialists, to provide long-term support for individuals struggling with dependency [52];
- Addictovigilance coordinators, to monitor and report emerging trends, ensuring early warnings.
4. Comprehensive Patient Care and Prevention
- Early detection and diagnosis, leveraging multidisciplinary expertise and advanced analytical tools.
- Management, addressing acute complications, metabolic impairments, and neurological damage.
- Addiction support, including tailored programs to help patients overcome dependency on nitrous oxide.
- Long-term follow-up and coordination with primary care to ensure continuity of care through collaboration with general practitioners and specialists.
5. Knowledge Sharing and Global Collaboration
- Scientific conferences, bringing together experts to share research, discuss best practices, and align strategies to manage N2O misuse.
- Training programs for healthcare professionals, providing comprehensive modules on diagnosing, treating, and preventing N2O-related complications.
- Publications and research, contributing to the medical literature on mechanisms, health impacts, and management of N2O misuse.
6. A Global Model for Public Health Action
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lucas, A.; Noyce, A.J.; Gernez, E.; Khoury, J.M.E.; Garcon, G.; Cavalier, E.; Antherieu, S.; Grzych, G. Nitrous Oxide Abuse Direct Measurement for Diagnosis and Follow-up: Update on Kinetics and Impact on Metabolic Pathways. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2024, 62, 2356–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recreational Use of Nitrous Oxide—A Growing Concern for Europe | www.emcdda.europa.eu. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/rapid-communication/recreational-use-nitrous-oxide-growing-concern-europe_en (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Back, S.; Kroon, E.; Colyer-Patel, K.; Cousijn, J. Does Nitrous Oxide Addiction Exist? An Evaluation of the Evidence for the Presence and Prevalence of Substance Use Disorder Symptoms in Recreational Nitrous Oxide Users. Addiction 2024, 119, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Lanz, L.A.; Liebs, T.R.; Kaiser, N.; Zindel, M.; Berger, S.M. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Immersive Virtual Reality Games versus Nitrous Oxide for Pain Reduction in Common Outpatient Procedures in Pediatric Surgery. Trials 2025, 26, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, G.; Schoretsanitis, G.; Seifritz, E.; Olbrich, S. The Boon and Bane of Nitrous Oxide. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hout, M.C.V.; Bingham, T. ‘Surfing the Silk Road’: A Study of Users’ Experiences. Int. J. Drug Policy 2013, 24, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, S.J.; Riddell, O.; Herold, M.D.; Frank, V.A. Becoming a Nitrous Oxide User on Social Media: Learning to Maximise Pleasures and Minimise Harms. Int. J. Drug Policy 2022, 109, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benschop, A.; van Bakkum, F.; Noijen, J. Changing Patterns of Substance Use During the Coronavirus Pandemic: Self-Reported Use of Tobacco, Alcohol, Cannabis, and Other Drugs. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 633551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, J.; John, T.; Crossin, R.; Ward, R.D. Consuming and Thinking About Nangs: A Survey of Nitrous Oxide Use, Knowledge, Attitudes and Perceptions in Aotearoa New Zealand. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzych, G.; Deheul, S.; Gernez, E.; Davion, J.-B.; Dobbelaere, D.; Carton, L.; Kim, I.; Guichard, J.C.; Girot, M.; Humbert, L.; et al. Comparison of Biomarker for Diagnosis of Nitrous Oxide Abuse: Challenge of Cobalamin Metabolic Parameters, a Retrospective Study. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largeau, B.; Karam, A.; Potey, C.; Caous, A.-S.; Tard, C.; Carton, L.; Kuchcinski, G.; Gautier, S.; Deheul, S.; Bordet, R. Myeloneuropathy Induced by Recreational Nitrous Oxide Use with Variable Exposure Levels. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerlais, M.; Deheul, S.; Le Boisselier, R.; Victorri-Vigneau, C. Non-Medical Nitrous Oxide Misuse: From Identifying a Signal to Unprecedented Addictovigilance Network Communication. Therapies 2024, 80, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netherlands to Ban Laughing Gas from January 2022. Available online: https://www.rijksoverheid.nl/onderwerpen/drugs/documenten/brochures/2022/12/07/lachgasverbod-per-1-januari-2023 (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Gernez, E.; Lee, G.R.; Niguet, J.-P.; Zerimech, F.; Bennis, A.; Grzych, G. Nitrous Oxide Abuse: Clinical Outcomes, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity and Impact on Metabolism. Toxics 2023, 11, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortanier, E.; Delmont, E.; Corazza, G.; Kouton, L.; Micallef, J.; Attarian, S. Longitudinal Follow-up and Prognostic Factors in Nitrous Oxide-Induced Neuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2024, 29, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berling, E.; Fargeot, G.; Aure, K.; Tran, T.H.; Kubis, N.; Lozeron, P.; Zanin, A. Nitrous Oxide-Induced Predominantly Motor Neuropathies: A Follow-up Study. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 2720–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaloum, S.A.; Paris, A.; Mair, D.; Gutteridge, C.; Ayling, R.M.; Onen, B.L.; Walton, J.; Workman, A.; Villanueva, N.; Noyce, A.J. Evaluation of an Ambulatory Care Pathway for Patients with Nitrous Oxide-Induced Myeloneuropathy. BMJ Neurol. Open 2024, 6, e000737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.Y.; Klein, J.P. Subacute Combined Degeneration from Nitrous Oxide Use. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meißner, J.N.; Neuneier, J.; Bartzokis, I.; Rehm, M.; Al-Hayali, A.; Müller, M.; Paus, S.; Limmroth, V.; Fink, G.R.; Petzold, G.C.; et al. Increase of Nitrous Oxide-Induced Neurological Disorders—A German Multicenter Experience. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2025, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzych, G.; Scuccimarra, M.; Plasse, L.; Gernez, E.; Cassim, F.; Touze, B.; Girot, M.; Bossaert, C.; Tard, C. Understanding Neuropathy Features in the Context of Nitrous Oxide Abuse: A Combined Electrophysiological and Metabolic Approach. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, M.C.; Wijnhoven, A.M.; Maessen, G.C.; Blankensteijn, S.R.; van der Heyden, M.A.G. Does Vitamin B12 Deficiency Explain Psychiatric Symptoms in Recreational Nitrous Oxide Users? A Narrative Review. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, J.D. Hallucinations and Vitamin B12 Deficiency: A Systematic Review. Psychopathology 2024, 57, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménétrier, T.; Denimal, D. Vitamin B12 Status in Recreational Users of Nitrous Oxide: A Systematic Review Focusing on the Prevalence of Laboratory Abnormalities. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Osborne, M.L.; Kolhouse, J.F.; Binder, M.J.; Podell, E.R.; Utley, C.S.; Abrams, R.S.; Allen, R.H. Nitrous Oxide Has Multiple Deleterious Effects on Cobalamin Metabolism and Causes Decreases in Activities of Both Mammalian Cobalamin-Dependent Enzymes in Rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 67, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabler, S.P. Vitamin B12 Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzych, G.; Zerimech, F.; Touze, B.; Descamps, C.; Bout, M.-A.; Joncquel, M.; Douillard, C.; Kim, I.; Tard, C.; Brousseau, T. Enhancing Differential Diagnosis Related to Oxidative Stress, Nitrous Oxide, and Nutrition by Rapid Plasma Homocysteine Measurement. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzych, G.; Douillard, C.; Lannoy, J.; Joncquel Chevalier Curt, M. Very High Plasma Homocysteine without Malnutrition or Inherited Disorder. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1468–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waclawik, A.J.; Luzzio, C.C.; Juhasz-Pocsine, K.; Hamilton, V. Myeloneuropathy from Nitrous Oxide Abuse: Unusually High Methylmalonic Acid and Homocysteine Levels. WMJ 2003, 102, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Francisco, C.; Pattengale, P.; O’Gorman, M.R.; Mitchell, W.G. An Adolescent with Increased Plasma Methylmalonic Acid and Total Homocysteine. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernez, E.; Deheul, S.; Tard, C.; Joncquel, M.; Douillard, C.; Grzych, G. Plasma Methionine and Clinical Severity in Nitrous Oxide Consumption. Toxics 2023, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontiera, M.S.; Stabler, S.P.; Kolhouse, J.F.; Allen, R.H. Regulation of Methionine Metabolism: Effects of Nitrous Oxide and Excess Dietary Methionine. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1994, 5, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, L.C.; Grobelny, A.; Hahn, K.; Audebert, H.J.; Krause, P.; Franke, C.; Ruprecht, K. Severe Subacute Combined Degeneration of the Spinal Cord Resulting from Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Abuse: A Case Series. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2025, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, K.Y.; Lwin, M.T.; Lwin, Z.T. Correlation Between Nitrous Oxide and Functional Vitamin B12 Deficiency Resulting in Subacute Combined Degeneration of the Spinal Cord: A Case Report. Cureus 2024, 16, e74383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amess, J.A.L.; Rees, G.M.; Burman, J.F.; Nancekievill, D.G.; Mollin, D.L. Megaloblastic Hæmopoiesis in Patients Receiving Nitrous Oxide. Lancet 1978, 312, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lan, L.; Xu, L.; Zhu, B.; Huang, Y. A Retrospective Cohort Study on Red Blood Cell Morphology Changes in Pre-School Age Children under Nitrous Oxide Anesthesia. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patyjewicz, M.; Mair, D.; Zaloum, S.A.; Onen, B.; Walton, J.; Dobson, R.; Joerres, C.; Shah, A.M.; MacCallum, P.; Massey, T.H.; et al. Recreational Nitrous Oxide and Thrombotic Events: A Case Series. BMJ Neurol. Open 2024, 6, e000619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulkadi, S.; Peters, B.; Vliegen, A.-S. Thromboembolic Complications of Recreational Nitrous Oxide (Ab)Use: A Systematic Review. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2022, 54, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukhi, D.; Siguret, V.; Vodovar, D.; Delrue, M.; Reiner, P.; Aghetti, A.; Guey, S.; Mazighi, M.; Crassard, I. Cerebral Venous Thrombosis and Nitrous Oxide Intoxication: Report of Two Cases and Review of the Literature. Brain Behav. 2025, 15, e70394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizouard, T.; Caplette, C.; Duval, D.; Savary, D.; Douillet, D. Right Iliac Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Associated with Recreational Nitrous Oxide: A Case Report. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 17, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, D.; Agrawal, A.; Gupta, S.; Bajaj, S.; Bajaj, D.; Agrawal, A.; Gupta, S.; Bajaj, S. Recreational Nitrous Oxide Abuse Causing Ischemic Stroke in a Young Patient: A Rare Case Report. Cureus 2018, 10, e3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueant, J.-L.; Gueant-Rodriguez, R.-M.; Oussalah, A.; Zuily, S.; Rosenberg, I. Hyperhomocysteinemia in Cardiovascular Diseases: Revisiting Observational Studies and Clinical Trials. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 123, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, M.E.; Lander, S.J.; Park, J.; Chae, C. Recreational Nitrous Oxide Causing Deep Vein Thrombosis and Subacute Combined Degeneration: Whip It Real Good. Cureus 2024, 16, e65155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, G.; Lönnberg, F.; Gautam, G.; Ågren, A.; Nordmark Grass, J.; Siddiqui, A.J. Life-Threatening Thrombosis After Large Amounts of Nitrous Oxide Use. JACC Case Rep. 2024, 29, 102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Suryadi, J.; Yang, Y.; Kucukkal, T.G.; Cao, W.; Alexov, E. Mutations in the KDM5C ARID Domain and Their Plausible Association with Syndromic Claes-Jensen-Type Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27270–27287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posthuma, J.J.; Reesink, K.D.; Schütten, M.; Ghossein, C.; Spaanderman, M.E.; ten Cate, H.; Schep, G. A Rare Case of Intermittent Claudication Associated with Impaired Arterial Vasodilation. Case Rep. Vasc. Med. 2017, 2017, 4868123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, J.; Hines, L.A.; Bonell, C.; Hickman, M.; Adara, L.; Townson, J.; Cannings-John, R.; Moore, L.; White, J. Association of Volatile Substance, Nitrous Oxide and Alkyl Nitrate Use with Mental Health in UK Adolescents. Br. J. Psychiatry 2025, 226, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, E.E.; Warner, L.L.; Brakke, B.D.; Davis, P.R.; Finkel, D.M.; Burkle, C.M.; Hanson, A.C.; Pompeian, R.J.; Arendt, K.W.; Butler Tobah, Y.S.; et al. Impact of Nitrous Oxide Use on Parturient Recall of Neuraxial Analgesia Risks. J. Clin. Anesth. 2024, 98, 111579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzych, G.; Megarbane, B.; Diesnis, R.; Chauvin, A.; Denimal, D.; Diesnis, R.; Gernez, E.; Redonnet-Vernhet, I.; Blin, J.; Kim, I.; et al. Nitrous oxide and road safety: Challenges and opportunities for biological screening. SPECTRA Diagn. 2024; ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Gernez, E.; Bennis, A.; Diesnis, R.; Niguet, J.P.; Grzych, G. Awareness of Health Care Related to Nitrous Oxide Abuse for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 192, 3087–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaloum, S.A.; Mair, D.; Paris, A.; Smith, L.J.; Patyjewicz, M.; Onen, B.L.; Noyce, A.J. Tackling the Growing Burden of Nitrous Oxide-Induced Public Health Harms. Lancet Public Health 2025, 10, e257–e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, A.; Lake, L.; Joseph, A.; Workman, A.; Walton, J.; Hayton, T.; Evangelou, N.; Lilleker, J.B.; Ayling, R.M.; Nicholl, D.; et al. Nitrous Oxide-Induced Subacute Combined Degeneration of the Cord: Diagnosis and Treatment. Pract. Neurol. 2023, 23, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesing, D.; Neu, P. Trenddroge Lachgas (Distickstoffmonoxid, N2O) und die Abhängigkeitskriterien nach ICD-10. Nervenarzt 2024, 96, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grzych, G.; Diesnis, R.; Dupré, T.; Niguet, J.P.; Gernez, E.; Denimal, D.; Deheul, S.; Guichard, J.C.; Scliffet, D.; Mégarbane, B.; et al. Addressing the Global Challenge of Nitrous Oxide Misuse Through a Multidisciplinary Approach: Example of the PROTOSIDE Network. Toxics 2025, 13, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060466
Grzych G, Diesnis R, Dupré T, Niguet JP, Gernez E, Denimal D, Deheul S, Guichard JC, Scliffet D, Mégarbane B, et al. Addressing the Global Challenge of Nitrous Oxide Misuse Through a Multidisciplinary Approach: Example of the PROTOSIDE Network. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060466
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrzych, Guillaume, Remy Diesnis, Thierry Dupré, Jean Paul Niguet, Emeline Gernez, Damien Denimal, Sylvie Deheul, Jean Claude Guichard, Damien Scliffet, Bruno Mégarbane, and et al. 2025. "Addressing the Global Challenge of Nitrous Oxide Misuse Through a Multidisciplinary Approach: Example of the PROTOSIDE Network" Toxics 13, no. 6: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060466
APA StyleGrzych, G., Diesnis, R., Dupré, T., Niguet, J. P., Gernez, E., Denimal, D., Deheul, S., Guichard, J. C., Scliffet, D., Mégarbane, B., Redonnet-Vernhet, I., Boucher, A., Bennis, A., Karila, L., Cavalier, E., Rolland, B., Riou, C., Bossaert, C., & Chauvin, A., on behalf of the multidisciplinary network PROTOSIDE. (2025). Addressing the Global Challenge of Nitrous Oxide Misuse Through a Multidisciplinary Approach: Example of the PROTOSIDE Network. Toxics, 13(6), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060466







