HMGB1 as a Key Mediator in Malignant Mesothelioma and a Potential Target for Asbestos-Related Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Wound Healing Assay
2.5. Transwell Assay
2.6. Cell Cycle and Apoptosis
2.7. Xenograft Mouse Model and Tissue Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HMGB1 Is Highly Expressed in MM Cells and Xenograft Tumors
3.2. Interference with HMGB1 and TLR4 Reduces MM Cell Viability, Migration, and Invasion
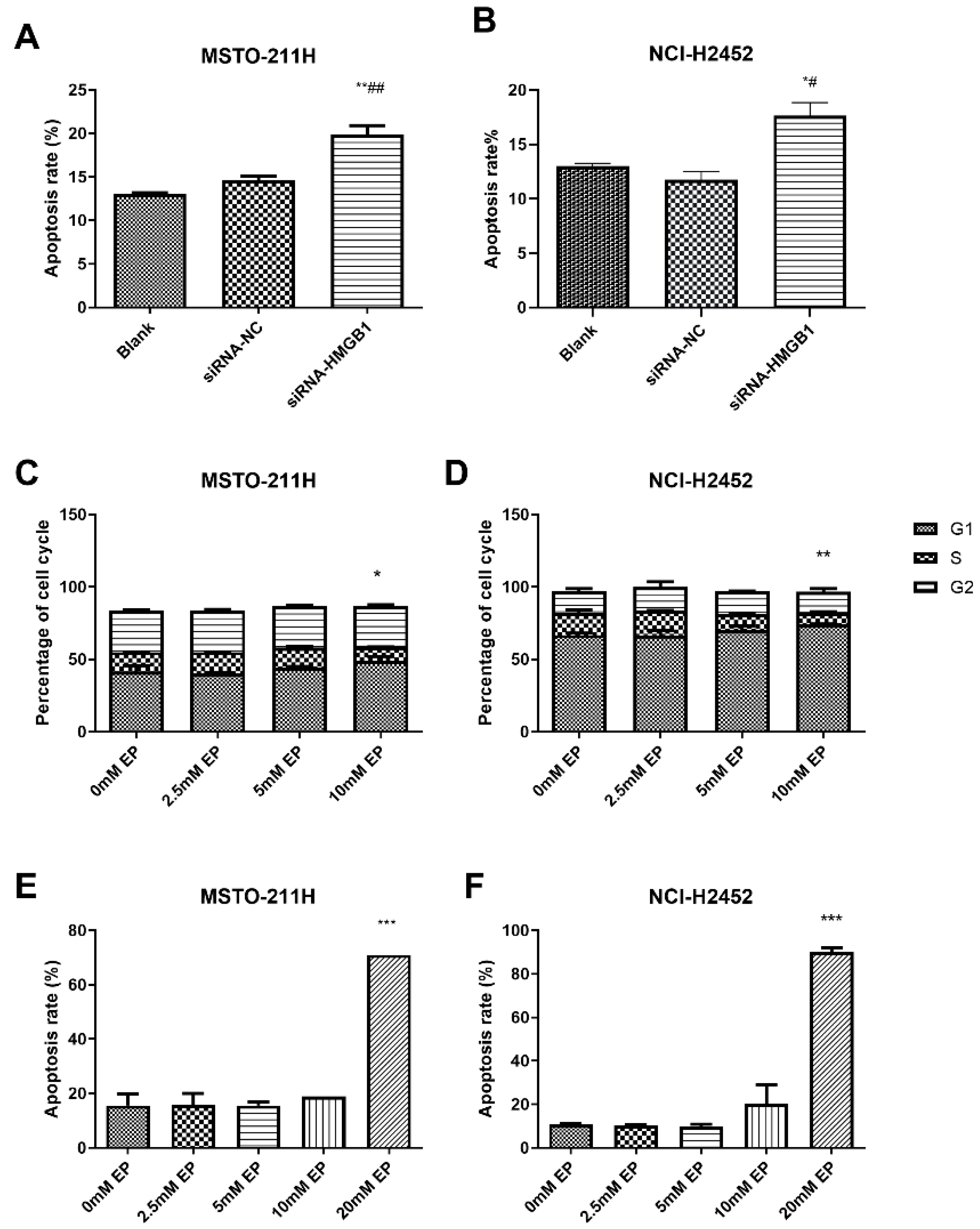
3.3. HMGB1 Inhibition Alters Cell Cycle Progression and Induces Apoptosis
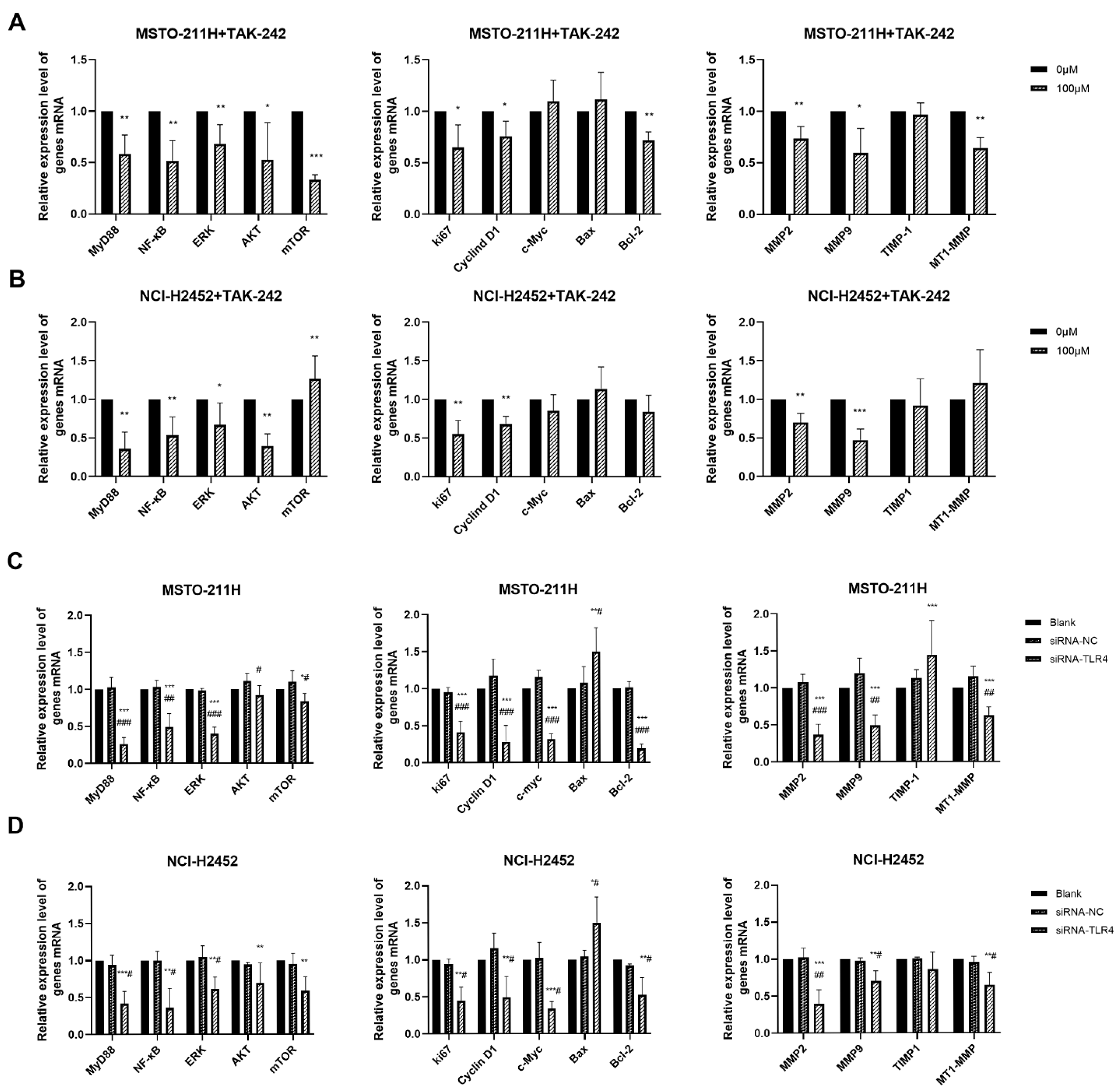
3.4. HMGB1-TLR4 Signaling Modulates Downstream Pathways
3.5. In Vivo Inhibition of HMGB1 Suppresses Tumor Growth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carbone, M.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Alexander, H.R.; Baas, P.; Bardelli, F.; Bononi, A.; Bueno, R.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Jablons, D.; et al. Mesothelioma: Scientific Clues for Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 402–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Ruan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xiang, D.; Li, N.; Hu, J.; Shen, J.; Deng, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhao, P.; et al. Assessment of Global Trends in the Diagnosis of Mesothelioma From 1990 to 2017. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2120360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zuo, T.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Xia, C.; Yang, Z.; Chen, W. Epidemiology and Trend Analysis on Malignant Mesothelioma in China. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 29, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Cai, Y.; Ou, T.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Cai, K. Global Burden of Mesothelioma Attributable to Occupational Asbestos Exposure in 204 Countries and Territories: 1990–2019. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimed-Ochir, O.; Rath, E.M.; Kubo, T.; Yumiya, Y.; Lin, R.T.; Furuya, S.; Brislane, K.; Klebe, S.; Nowak, A.K.; Kang, S.K.; et al. Must Countries Shoulder the Burden of Mesothelioma to Ban Asbestos? A Global Assessment. BMJ Global Health 2022, 7, e010553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lian, L.; Lei, Q.; Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Hemminki, K.; Ji, J.; Chen, T. Burden of Malignant Mesothelioma in China during 1990–2019 and the Projections through 2029. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2024, 4, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Pass, H.I.; Ak, G.; Alexander, H.R.; Baas, P.; Baumann, F.; Blakely, A.M.; Bueno, R.; Bzura, A.; Cardillo, G.; et al. Medical and Surgical Care of Patients With Mesothelioma and Their Relatives Carrying Germline BAP1 Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolami, I.; Lucenteforte, E.; Eccher, A.; Marletta, S.; Brunelli, M.; Graziano, P.; Pisapia, P.; Malapelle, U.; Troncone, G.; Scarpa, A.; et al. Evidence-Based Diagnostic Performance of Novel Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma in Effusion Cytology. Cancer Cytopathol. 2022, 130, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Crites, M.K.; Rich, P.; Bajantri, B. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, G.G.; John, T.; Ball, D.L. Controversies in the Role of Radiotherapy in Pleural Mesothelioma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Yang, H. Mesothelioma: Recent Highlights. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, F.; Bononi, A.; Wang, Q.; Bai, F.; Patergnani, S.; Kricek, F.; Haglund, E.; Suarez, J.S.; Tanji, M.; Xu, R.; et al. BAP1 Forms a Trimer with HMGB1 and HDAC1 That Modulates Gene × Environment Interaction with Asbestos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2111946118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. HMGB1 in Inflammation and Cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Koka, S.; Boini, K.M. High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1): Molecular Signaling and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Cells 2024, 13, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Rivera, Z.; Jube, S.; Nasu, M.; Bertino, P.; Goparaju, C.; Franzoso, G.; Lotze, M.T.; Krausz, T.; Pass, H.I.; et al. Programmed Necrosis Induced by Asbestos in Human Mesothelial Cells Causes High-Mobility Group Box 1 Protein Release and Resultant Inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12611–12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, J.S.; Novelli, F.; Goto, K.; Ehara, M.; Steele, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Zolondick, A.A.; Xue, J.; Xu, R.; Saito, M.; et al. HMGB1 Released by Mesothelial Cells Drives the Development of Asbestos-Induced Mesothelioma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2307999120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Patergnani, S.; Giorgi, C.; Suarez, J.; Goto, K.; Bononi, A.; Tanji, M.; Novelli, F.; Pastorino, S.; Xu, R.; et al. Asbestos Induces Mesothelial Cell Transformation via HMGB1-Driven Autophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 25543–25552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foelsch, K.; Pelczar, P.; Zierz, E.; Kondratowicz, S.; Qi, M.; Mueller, C.; Alawi, M.; Huebener, S.; Clauditz, T.; Gagliani, N.; et al. Intestinal Epithelia and Myeloid Immune Cells Shape Colitis Severity and Colorectal Carcinogenesis via High-Mobility Group Box Protein 1. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2024, 18, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Shang, Y. Sufentanil Suppresses Cell Carcinogenesis Via Targeting MiR-186-5p/HMGB1 Axis and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Biotechnol. 2025, 67, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athavale, D.; Barahona, I.; Song, Z.; Desert, R.; Chen, W.; Han, H.; Das, S.; Ge, X.; Komakula, S.S.B.; Gao, S.; et al. Overexpression of HMGB1 in Hepatocytes Accelerates PTEN Inactivation-Induced Liver Cancer. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, C.; Kanemura, S.; Tabata, R.; Masachika, E.; Shibata, E.; Otsuki, T.I.; Nishizaki, T.; Nakano, T. Serum HMGB1 as a Diagnostic Marker for Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, C.; Shibata, E.; Tabata, R.; Kanemura, S.; Mikami, K.; Nogi, Y.; Masachika, E.; Nishizaki, T.; Nakano, T. Serum HMGB1 as a Prognostic Marker for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, A.; Antoine, D.J.; Pellegrini, L.; Baumann, F.; Pagano, I.; Pastorino, S.; Goparaju, C.M.; Prokrym, K.; Canino, C.; Pass, H.I.; et al. HMGB1 and Its Hyperacetylated Isoform Are Sensitive and Specific Serum Biomarkers to Detect Asbestos Exposure and to Identify Mesothelioma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.; Jiang, Z.; He, X.; Yu, M.; Chen, R.; Chen, J.; Ru, G.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhu, L.; et al. Serum HMGB1 as a Potential Biomarker for Patients with Asbestos-Related Diseases. Dis. Markers 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Shen, W.; Ying, S.; Gao, Z.; He, X.; Chen, R.; Xia, H.; Guo, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Overexpression of Fibulin-3 in Tumor Tissue Predicts Poor Survival of Malignant Mesothelioma Patients from Hand-Spinning Asbestos Exposed Area in Eastern China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolondick, A.A.; Gaudino, G.; Xue, J.; Pass, H.I.; Carbone, M.; Yang, H. Asbestos-Induced Chronic Inflammation in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Related Therapeutic Approaches—A Narrative Review. Precis. Cancer Med. 2021, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, X.; Shen, G.; Teng, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, X.; Hu, Z.; et al. Autophagy-Based Unconventional Secretion of HMGB1 by Keratinocytes Plays a Pivotal Role in Psoriatic Skin Inflammation. Autophagy 2021, 17, 529–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punchoo, R.; Zhou, E.; Bhoora, S. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Apoptotic Biomarkers in Actinomycin D-Treated SiHa Cervical Cancer Cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 174, e62663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinska, A.; Adamczyk-Grochala, J.; Kwasniewicz, E.; Deregowska, A.; Semik, E.; Zabek, T.; Wnuk, M. Reduced Levels of Methyltransferase DNMT2 Sensitize Human Fibroblasts to Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage That Is Accompanied by Changes in Proliferation-Related MiRNA Expression. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, J.; Ying, S. HMGB1 as a Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Malignant Mesothelioma. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 4183157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, L.; Xue, J.; Larson, D.; Pastorino, S.; Jube, S.; Forest, K.H.; Saad-Jube, Z.S.; Napolitano, A.; Pagano, I.; Negi, V.S.; et al. HMGB1 Targeting by Ethyl Pyruvate Suppresses Malignant Phenotype of Human Mesothelioma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22649–22661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settayanon, S.; Chanvorachote, P.; Mutirangura, A. The Role of Box A of HMGB1 in Producing ΓH2AX Associated DNA Breaks in Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Sheng, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Jia, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Hu, T.; Ma, Y. Glycyrrhizin Ameliorates Colorectal Cancer Progression by Regulating NHEJ Pathway through Inhibiting HMGB1-Induced DNA Damage Response. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Roy, P.K.; Dey, A.; Mandal, M. Impact of HMGB1 on Cancer Development and Therapeutic Insights Focused on CNS Malignancy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Jiang, W.; Su, Y.; Huang, H.; Ye, J.; Wang, R.; Tang, Z.; Su, R. Asiatic Acid Alleviates LPS-Induced Pyroptosis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis via Inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in Broiler Hepatocytes. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2025, 109, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; He, S.; Xin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, F. HMGB1-Mediated Transcriptional Activation of Circadian Gene TIMELESS Contributes to Endometrial Cancer Progression through Wnt-β-Catenin Pathway. Cell Signal. 2024, 116, 111045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Islam, A.U.; Prakash, H.; Singh, S. Phytochemicals Targeting NF-ΚB Signaling: Potential Anti-Cancer Interventions. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Maeda, M.; Azimi, M.D.; Fayaz, S.H.; Chen, W.; Hamajima, N.; Kato, M. High Levels of Boron Promote Anchorage-Independent Growth of Nontumorigenic Cells. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.S.; Yang, Y.C.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, W.X.; Chen, N.W. Enhancing the Therapeutic Effects of Ethyl Pyruvate on Gastric Cancer through Knockdown of YAP1 Expression. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2013, 11, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Guan, X.-W.; Gribben, J.G.; Liu, F.-T.; Jia, L. Blockade of HMGB1 Signaling Pathway by Ethyl Pyruvate Inhibits Tumor Growth in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, G.; Xing, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C. TAK-242 Inhibits Glioblastoma Invasion, Migration, and Proneural–Mesenchymal Transition by Inhibiting TLR4 Signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 439, 114091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Qu, X.; Ke, H.; Gong, W.; Chen, R.; Yang, W.; Cheng, Z. Association between the HMGB1/TLR4 Signaling Pathway and the Clinicopathological Features of Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3093–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, W.; Chen, N.; Lin, Y.; Ma, H.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Pan, X.; Tian, X. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis via Activation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF Kappa B Axis. Cancer Lett. 2016, 375, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastille, E.; Faßnacht, T.; Adamczyk, A.; Ngo Thi Phuong, N.; Buer, J.; Westendorf, A.M. Inhibition of TLR4 Signaling Impedes Tumor Growth in Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 669747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Yang, Z.; Hao, X.; Tang, W.; Ma, W.; Zong, H. Roles of HMGB1 in Regulating Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Shi, H.; Zhang, B.; Ou, X.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shu, P.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as Immunosuppressive Regulators and Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrián, M.J.G.; Bauden, M.; Andersson, R.; Holdenrieder, S.; Ansari, D. Paradoxical Role of Hmgb1 in Pancreatic Cancer: Tumor Suppressor or Tumor Promoter? Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 4381–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, H.J.; Lee, K.-H.; Park, M.S.; Sun, E.-G.; Cho, S.H.; Chung, I.-J.; Shim, H.-J.; Bae, W.K. Dynamic Changes in Immune Cells in Humanized Liver Metastasis and Subcutaneous Xenograft Mouse Models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Pellegrini, L.; Napolitano, A.; Giorgi, C.; Jube, S.; Preti, A.; Jennings, C.J.; De Marchis, F.; Flores, E.G.; Larson, D.; et al. Aspirin Delays Mesothelioma Growth by Inhibiting HMGB1-Mediated Tumor Progression. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.-F.; Ding, C.; Yao, C.-J.; Wang, J.-C.; Feng, M.-Q.; Gong, X.-X.; Yu, L.; Xu, H.-D.; Xia, H.-L. HMGB1 as a Key Mediator in Malignant Mesothelioma and a Potential Target for Asbestos-Related Cancer Therapy. Toxics 2025, 13, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060448
Zhong Y-F, Ding C, Yao C-J, Wang J-C, Feng M-Q, Gong X-X, Yu L, Xu H-D, Xia H-L. HMGB1 as a Key Mediator in Malignant Mesothelioma and a Potential Target for Asbestos-Related Cancer Therapy. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060448
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yi-Fang, Chan Ding, Chun-Ji Yao, Jia-Chun Wang, Min-Qian Feng, Xiao-Xue Gong, Lin Yu, Hua-Dong Xu, and Hai-Ling Xia. 2025. "HMGB1 as a Key Mediator in Malignant Mesothelioma and a Potential Target for Asbestos-Related Cancer Therapy" Toxics 13, no. 6: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060448
APA StyleZhong, Y.-F., Ding, C., Yao, C.-J., Wang, J.-C., Feng, M.-Q., Gong, X.-X., Yu, L., Xu, H.-D., & Xia, H.-L. (2025). HMGB1 as a Key Mediator in Malignant Mesothelioma and a Potential Target for Asbestos-Related Cancer Therapy. Toxics, 13(6), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060448




