Using Geochemistry, Stable Isotopes and Statistical Tools to Estimate the Sources and Transformation of Nitrate in Groundwater in Jinan Spring Catchment, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
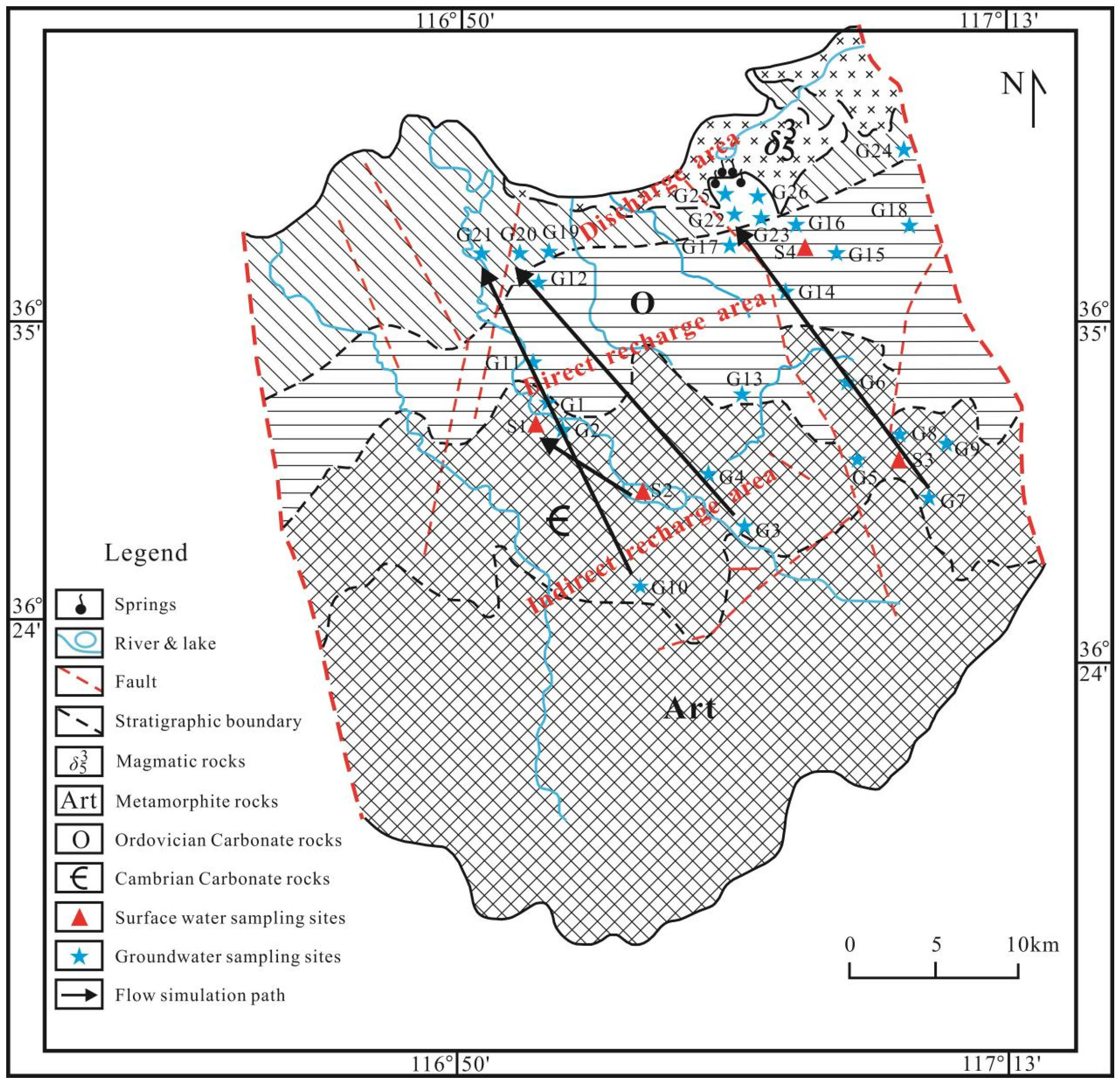
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
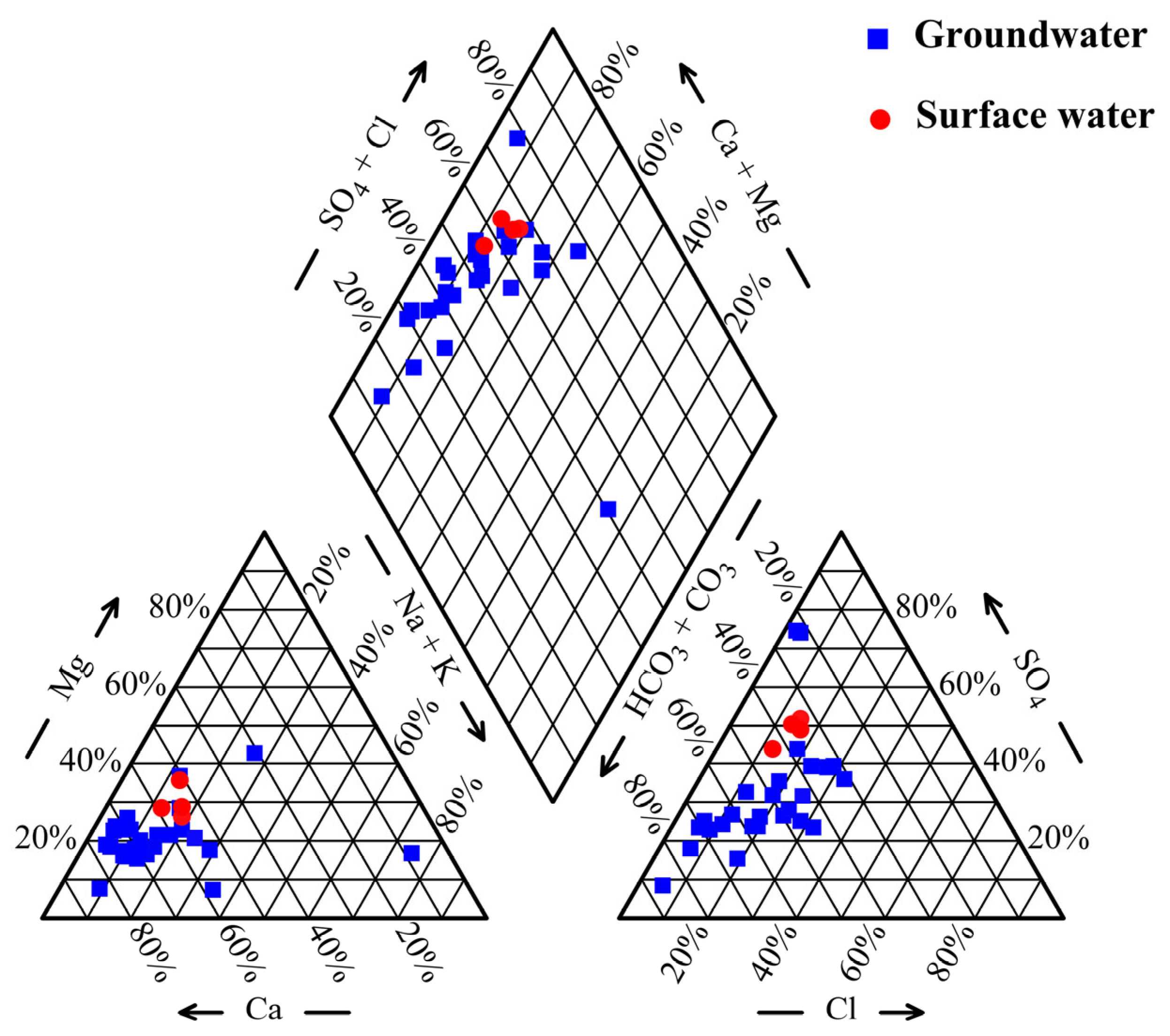
3.1. Hydrochemistry and Nitrate Pollution Characteristics
3.1.1. Hydrochemistry Characteristics
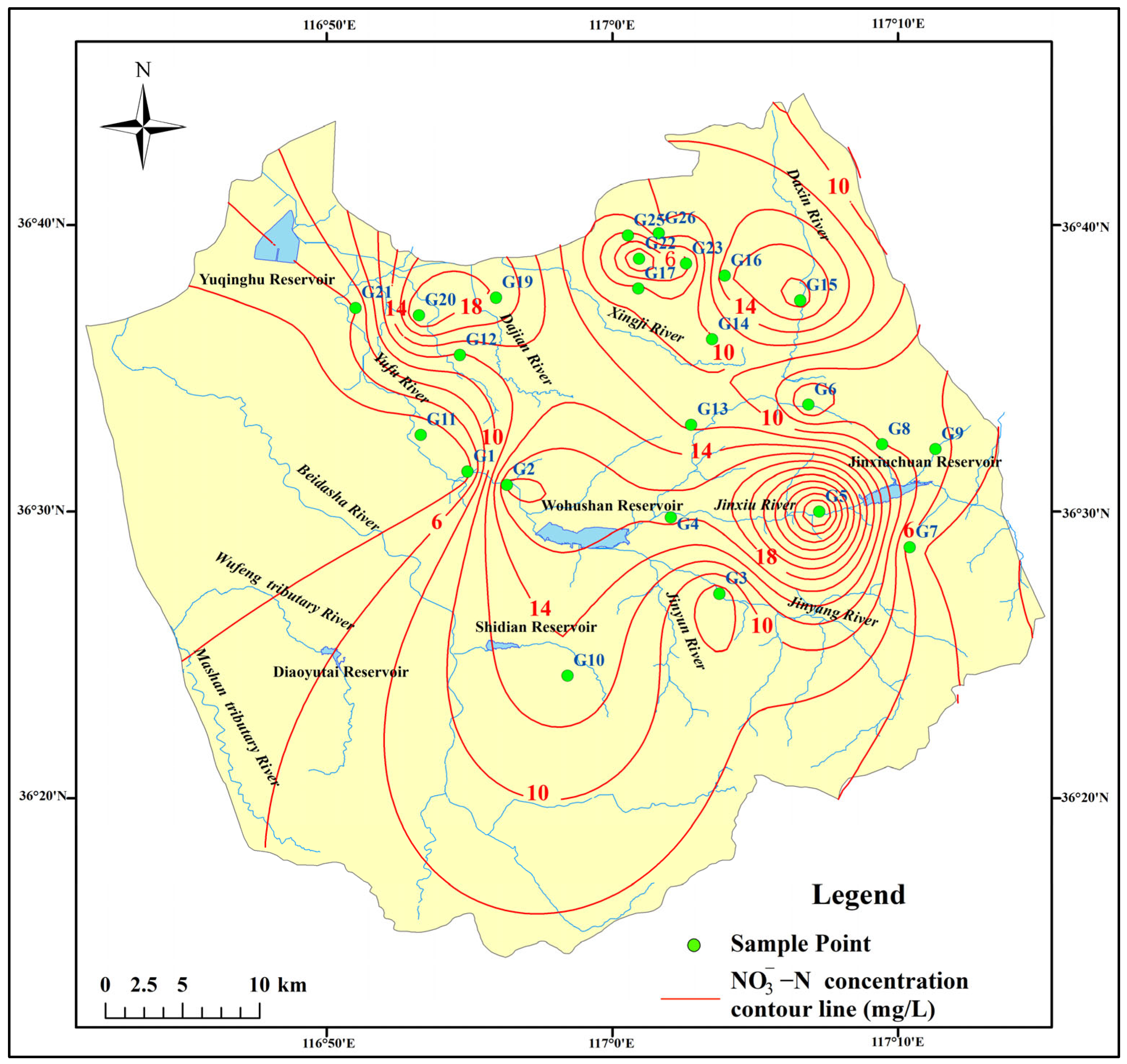
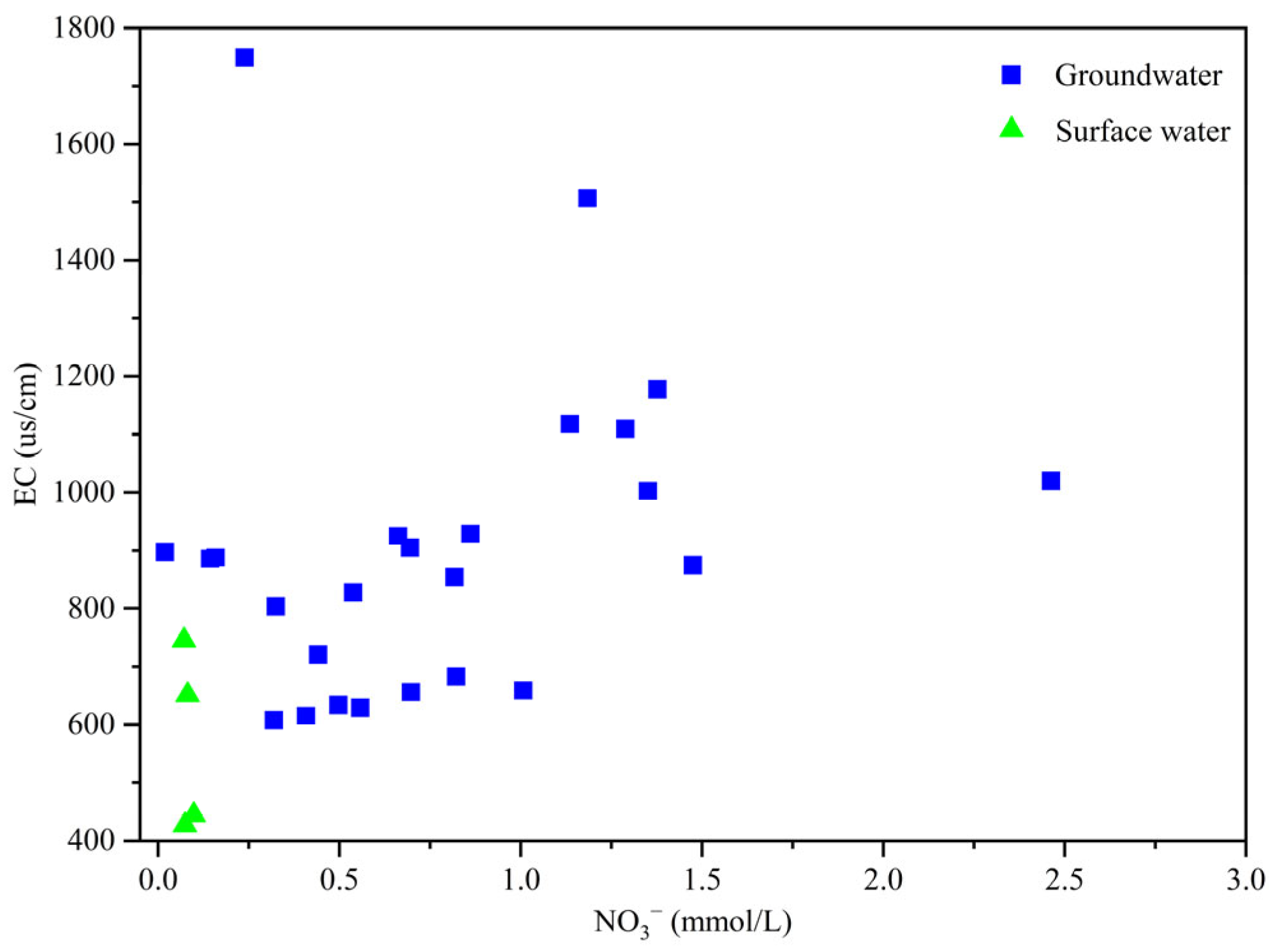
3.1.2. Nitrate Pollution Characteristics
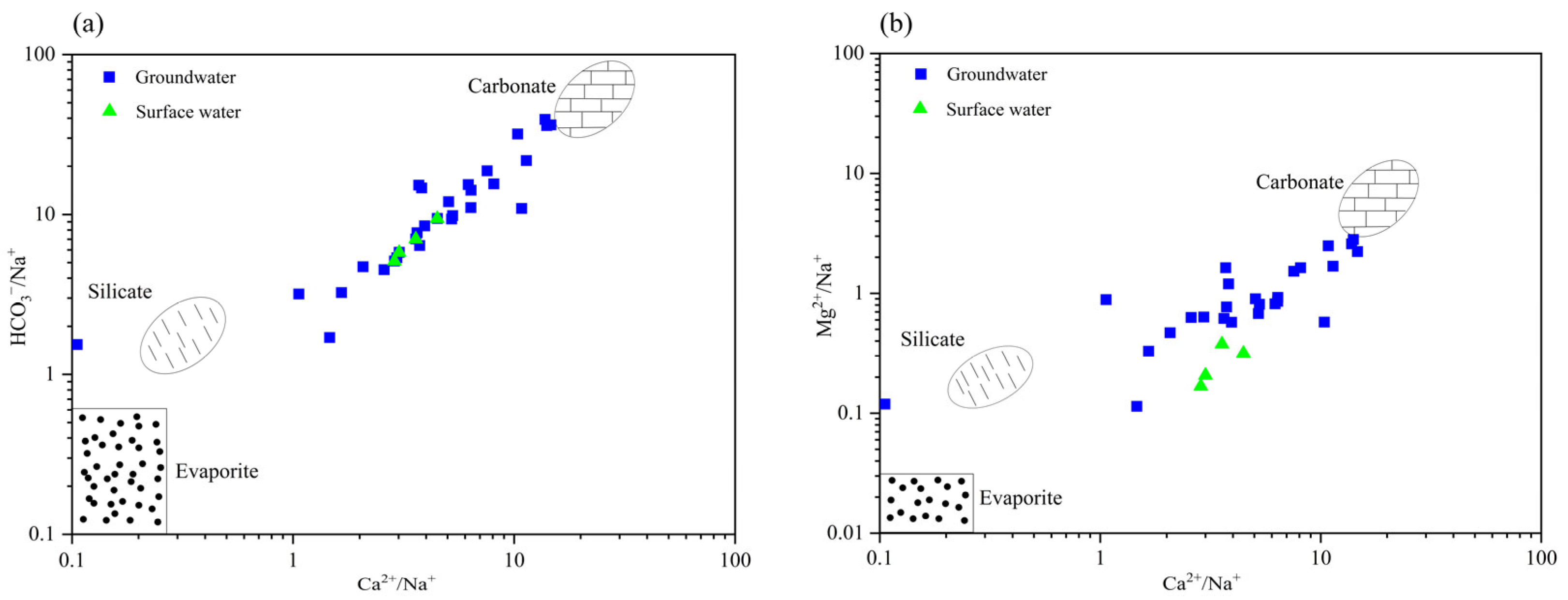
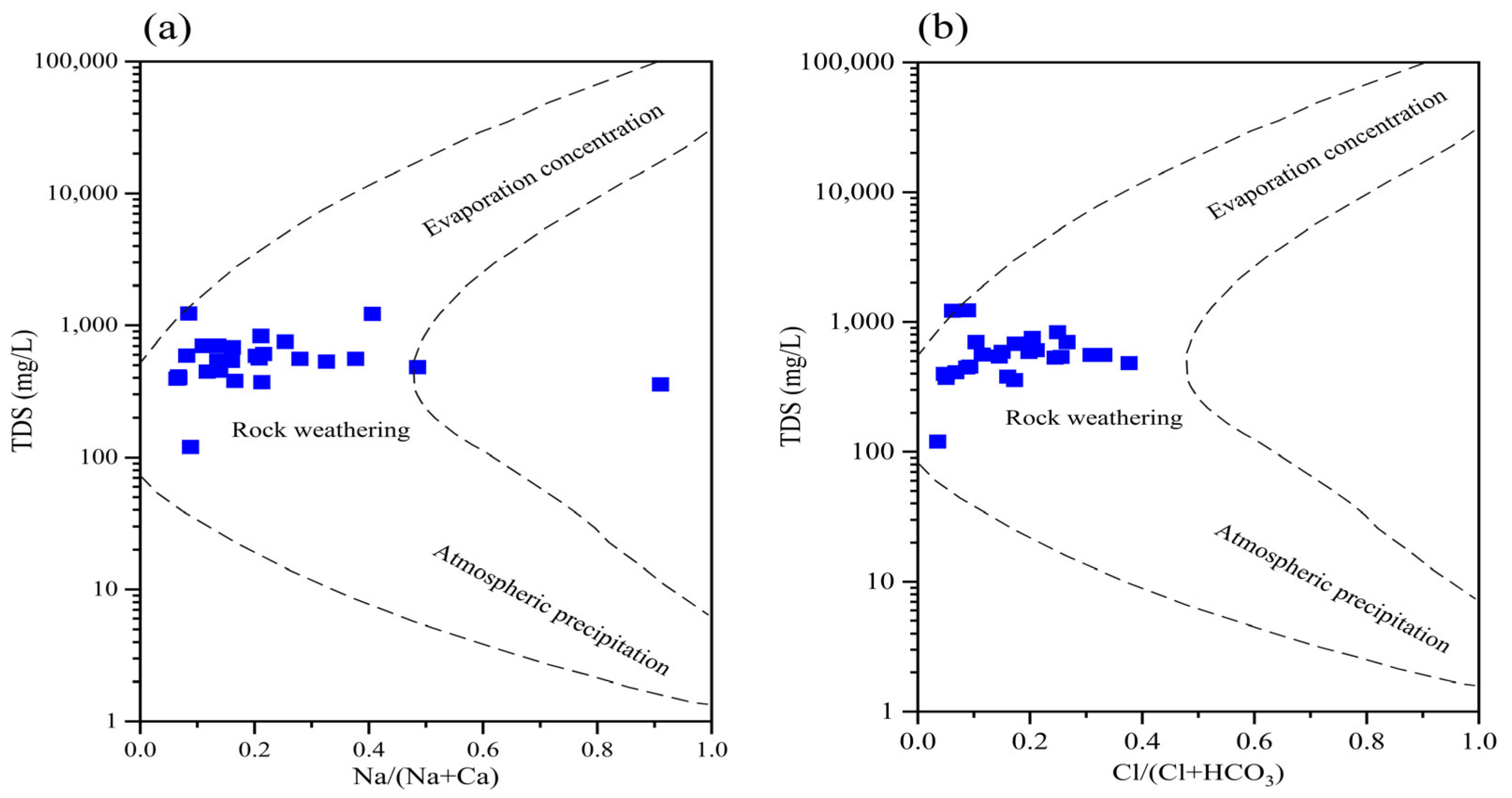
3.2. Genesis and Evolution of Hydrochemistry Characteristics
3.3. Nitrate Traceability Analysis
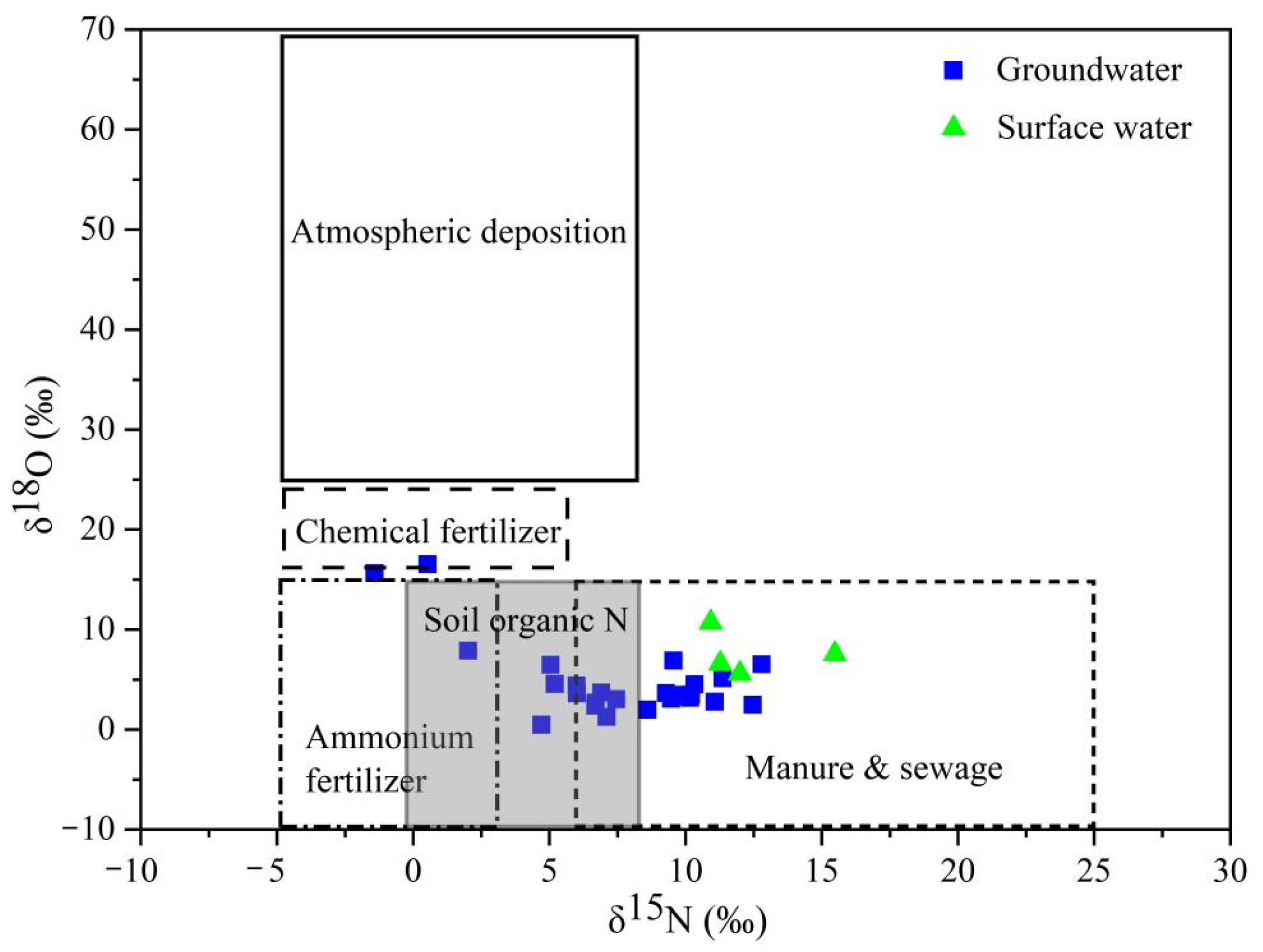
3.3.1. Qualitative Identification of Nitrate Sources
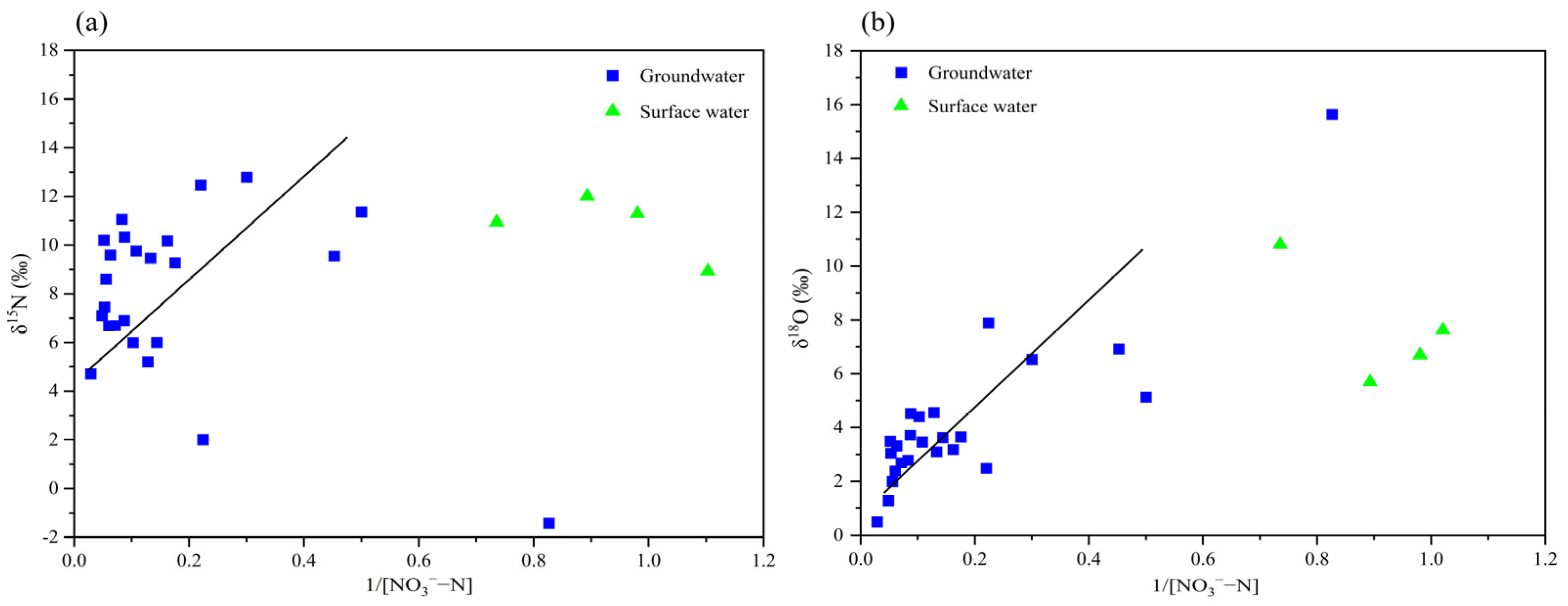
3.3.2. Identification of Denitrification
3.3.3. Quantitative Analysis of Nitrate Sources
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, F.X.; Jin, M.G.; Qin, P.R. Sustainable yield of a karst aquifer system: A case study of Jinan springs in Northern China. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qin, D.J.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Li, F.L.; Huang, J.W. A complicated Karst spring system: Identified by karst springs using water level, hydrogeochemical, and isotopic data in Jinan, China. Water 2019, 11, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Han, C.H.; Li, S.X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Guan, Q.H.; Zhang, W.J. Exploring the Hydrogeochemical Formation and Evolution of the Karst Aquifer System in the Yufu River Based on Hydrochemistry and Isotopes. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.A.; Li, C.; Niu, Y.; Jiang, X. Seasonal nitrate input drives the spatiotemporal variability of regional surface water-groundwater interactions, nitrate sources and transformations. J. Hydrol. 2025, 655, 132973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, S.K.; Hiscock, K.M.; Dennis, P.F. Microbial and hydrological influences on nitrate isotopic composition in an agricultural lowland catchment. J. Hydrol. 2012, 468–469, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Yu, S.Y.; Kang, H.J.; Hyun, I.H.; Song, Y.C.; Kim, H.; Yun, S.T. Shift of nitrate sources in groundwater due to intensive livestock farming on Jeju Island, South Korea: With emphasis on legacy effects on water management. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Daesslé, L.W.; Cervantes-Avilés, P.A.; Ledesma, R.R. Estimation of nitrate pollution sources and transformations in groundwater of an intensive livestock-agricultural area (Comarca Lagunera), combining major ions, stable isotopes and MixSIAR model. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 115445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.R.; Chen, X.Q.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.S.; Wang, H.B. Traceability and Biogeochemical Process of Nitrate in the Jinan karst Spring Catchment, North China. Water 2023, 15, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.P.; Wang, W.T.; Zhao, C.H.; Wang, W.; Tang, C.L. Variations of karst water and environmental problems in North China. Carsologica Sin. 2013, 32, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Biddau, R.; Dore, E.; Pelo, S.D.; Lorrai, M.; Botti, P.; Testa, M.; Cidu, R. Geochemistry, stable isotopes and statistic tools to estimate threshold and source of nitrate in groundwater (Sardinia, Italy). Water Res. 2023, 232, 119663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.R.; Guo, F.; Jiang, G.H.; Bian, H.Y. Application of 15N and 18O to nitrogen pollution source in karst water in Eastern Guilin. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.P.; Gao, X.B.; Zhao, C.H.; Tang, C.L.; Shen, H.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, Y.X. Review: Characterization, evolution, and environmental issues of karst water systems in Northern China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.H.; Jiang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Wu, W.; Peng, X.Y.; Liu, J.C. Sources of nitrate in groundwater and its environmental effects in karst trough valleys: A case study of an underground river system in the Longfeng trough valley, Chongqing. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Han, Z.W.; Shen, C.H.; Zhang, S.; Tu, H.; Guo, Y.L. Identifying nitrate sources in a typical karst underground river basin. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 2664–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Wu, P.; Zha, X.F.; He, S.Y.; Wu, L.N.; Han, Z.W. Tracing nitrate sources in urban waters of karst mountainous area using hydrochemistry and stable isotope. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2021, 41, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, K.; Pan, X.D.; Yuan, D.X.; Zeng, J.; Liang, J.P.; Peng, C. Nitrate sources and nitrogen dynamics in a karst aquifer with mixed nitrogen inputs (Southwest China): Revealed by multiple stable isotopic and hydro-chemical proxies. Water Res. 2022, 210, 118000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, M.D.; Jin, M.G.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Kang, F.X. Identifying the source and transformation of riverine nitrates in a karst watershed, North China: Comprehensive use of major ions, multiple isotopes and a Bayesian model. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 246, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Wang, W.P.; Qu, S.S.; Huang, Q.; Liu, S.; Xu, Q.Y.; Ni, L.D. A new perspective to explore the hydraulic connectivity of Karst aquifer system in Jinan spring catchment, China. Water 2018, 10, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, C.S.; Jia, C.; Zhang, H.L.; Guan, Q.; Wu, X.C.; Wang, J.X.; Lv, M.H. Health risk assessment of groundwater nitrate contamination: A case study of a typical karst hydrogeological unit in East China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 9274–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.L.; Jin, M.G.; Ma, H.K.; Liu, H.R.; Peng, T. Hydrodynamic characteristics of Jinan karst spring system identified by hydrologic time-series data. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.J.; Xu, J.X.; Wang, S.C.; Li, C.S.; Han, K.; Li, J.J.; Luo, F.; Ma, H.K. The distribution characteristics and hydrogeological significance of trace elements in karst water, Jinan, China. Earth Sci. Front. 2014, 21, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Xing, L.T.; Zhang, F.J.; Han, Z. Chemical characteristics research on karst water in Jinan spring area. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1092, 593–596. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Xing, L.T.; Li, C.S. Variation of typical pollution components and pollution way of karst water in Baotu Spring region. Carsologica Sin. 2018, 37, 810–818. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q.H.; Li, F.L.; Wang, A.Q.; Feng, P.; Tian, C.J.; Chen, X.Q.; Liu, D. Hydrochemistry characteristics and evolution of karst spring groundwater system in Jinan. Carsologica Sin. 2019, 38, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wang, W.Z.; Li, Z. Nitrate dynamics in the streamwater-groundwater interaction system: Sources, fate, and controls. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, H.X.; Yu, C.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.P.; Yang, Y. Tracing nitrate origins and transformation processes in groundwater of the Hohhot Basin’s Piedmont strong runoff zone through dual isotopes and hydro-chemical analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, H.Y.; Fu, B.; Yan, H.; Hu, W.L.; Liu, G.C.; Chen, A.Q. Shifts in the sources and fates of nitrate in shallow groundwater caused by agricultural intensification intensity: Revealed by hydrochemistry, stable isotopic composition and source contribution. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 345, 108337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, C.L.; Zheng, L.G.; Dong, X.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, C. Identification of nitrate sources and transformations in basin using dual isotopes and hydrochemistry combined with a Bayesian mixing model: Application in a typical mining city. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Shu, L.L.; Chen, W.L.; Chen, Z.; Shang, X.; Yang, Y.; Randy, A.D.; Zhang, M.H. Nitrate pollution source apportionment, uncertainty and sensitivity analysis across a rural-urban river network based on δ15N/δ18O-NO3− isotopes and SIAR modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.T.; Zhou, J.; Song, G.Z.; Xing, X.R. Mixing ratios of recharging water sources for the four largest spring groups in Jinan. Earth Sci. Front. 2018, 25, 260–272. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.L.; Wang, Q.B.; Feng, W. Hydro-chemical and isotopic study of the Karst spring catchment in Jinan. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Li, C.S.; Jia, C.; Sun, B.; Zhang, H.L.; Pang, W. Spatiotemporal difference study of Karst hydrochemical characteristics in the Baotu Spring area of Jinan. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Z.; Li, W.P.; Yin, X.L.; Duan, X.M.; Gao, Z.D.; Wang, Q.B. Hydrochemistry and isotopes of shallow groundwater in the Jinan spring catchment. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2008, 35, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Jin, M.G. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation causes of karst water in Jinan spring catchment. Earth Sci. 2017, 42, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zheng, T.Y.; Zheng, X.L.; Hao, Y.J.; Yuan, R.Y. Nitrate source apportionment in groundwater using Bayesian isotope mixing model based on nitrogen isotope fractionation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiatos, I. Nitrate source identification in groundwater of multiple land-use areas by combining isotopes and multivariate statistical analysis: A case study of Asopos Basin (Central Greece). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macilwain, C. US report raises fears over nitrate levels in water. Nature 1995, 377, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.F.; Hu, J.; Wu, A.J.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, W.L.; Li, F.L. Identify the nitrate sources in different land use areas based on multiple isotopes. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, P.H.; Zhang, J.R. Sources and biogeochemical processes of nitrate in the Laolongdong karst underground river basin, Chongqing. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4470–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.L.; Song, X.F.; Yang, L.H.; Yang, S.T. River–spring connectivity and hydrogeochemical processes in a karst water system of Northern China: A case study of Jinan Spring Catchment. Water 2024, 16, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.F.; Liu, C.Q. Water geochemistry of the Xijiang Basin rivers, South China: Chemical weathering and CO2 consumption. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marandi, A.; Shand, P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs diagram. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 97, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.H. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of Karst groundwater in the Baiquan spring catchment. Carsologica Sin. 2021, 40, 398–408. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.Z.; Yang, X.P. Hydrochemical compositions of natural waters in Ordos Deserts and their influencing factors. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2224–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswarlu, T.; Anmala, J.; Dharwa, M. PCA, CCA, and ANN modeling of climate and land-use effects on stream water quality of karst watershed in Upper Green River, Kentucky. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 6, 05020008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yue, F.J.; Wang, X.D.; Chen, S.N.; Li, X.Z.; Liu, T.Z.; Yang, C. Antecedent rainfall and land use controlling the fate of nitrogen in Karst urban rivers, elucidated by an isotopic approach. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.R.; Chen, H.W.; Li, F.L.; Guo, F.; Jiang, G.H. Spatial distribution characteristics of nitrogen pollution in a typical Karst groundwater system. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Xie, R.T.; Hao, Y.; Lu, J. Quantitative identification of nitrate pollution sources and uncertainty analysis based on dual isotope approach in an agricultural watershed. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, T.; Yang, P.H.; Xie, G.W.; Hong, A.H.; Cao, C.; Xie, S.Y.; Shi, W.Y. Nitrate-nitrogen pollution sources of an underground river in Karst agricultural area using 15N and 18O isotope technique. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 4547–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, N.S.; Clough, T.J.; Johnson-Beebout, S.E.; Elberling, B.; Baisden, W.T. Effects of denitrification and transport on the isotopic composition of nitrate (δ18O, δ15N) in freshwater systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2228–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Chang, L.R.; Brian, H.; Song, L.S.; Chris, G. Nitrate sources and biogeochemical processes in Karst underground rivers impacted by different anthropogenic input characteristics. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Dai, E.F.; Cheng, Q.D.; Wu, Z.Z. The sources and fate of nitrogen in groundwater under different land use types: Stable isotope combined with a hydrochemical approach. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1878–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, X.X.; Chris, G.; Wu, X.Y.; Chang, L.R.; Zheng, Y.L.; Yang, P.H. Nitrate migration and transformations in groundwater quantified by dual nitrate isotopes and hydrochemistry in a karst World Heritage site. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 138907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, G.; Joseph, R.F.; Samuel, G.; Dickson, A.; Geophrey, A.; Nafisatu, Z. Nitrate contamination and source apportionment in surface and groundwater in Ghana using dual isotopes (15N and 18O-NO3) and a Bayesian isotope mixing model. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2020, 233, 103658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Water Samples | T /(°C) | pH | EC (µS/cm) | DO | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | NH4+−N | Cl− | HCO3− | SO42− | NO2−−N | NO3−−N | Total Hardness | TDS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ/(mg/L) | |||||||||||||||||
| Indirect recharge area | G1 | 24.4 | 7.57 | 886 | 4.75 | 3.19 | 42.04 | 108.41 | 26.50 | 0.03 | 94.24 | 190.06 | 173.51 | <0.005 | 2.00 | 379.87 | 559.51 |
| G2 | 17.9 | 7.29 | 1003 | 6.81 | 8.28 | 30.74 | 160.26 | 20.92 | 0.06 | 60.64 | 288.79 | 157.71 | <0.005 | 18.90 | 486.36 | 681.89 | |
| G3 | 24.8 | 7.2 | 721 | 5.74 | 1.67 | 18.73 | 116.17 | 15.36 | 0.05 | 29.47 | 288.79 | 87.62 | <0.005 | 6.17 | 353.35 | 454.59 | |
| G4 | 22.7 | 7.32 | 1507 | 6.52 | 5.27 | 24.17 | 261.26 | 60.28 | 0.05 | 25.69 | 264.11 | 629.37 | 0.01 | 16.57 | 900.66 | 1231.09 | |
| G5 | 17.5 | 7.25 | 1020 | 6.66 | 2.85 | 19.67 | 159.15 | 32.18 | 0.02 | 35.27 | 306.07 | 127.82 | 0.02 | 34.47 | 529.95 | 701.22 | |
| G6 | 23.9 | 7.67 | 1749 | 7.24 | 1.82 | 155.22 | 227.01 | 17.78 | 0.04 | 17.33 | 264.11 | 650.49 | 0.01 | 3.33 | 640.13 | 1226.05 | |
| G7 | 23.0 | 7.9 | 608 | 7.48 | 1.41 | 18.90 | 69.95 | 30.92 | <0.01 | 15.20 | 288.79 | 53.42 | <0.005 | 4.46 | 302.01 | 372.18 | |
| G8 | 21.9 | 7.68 | 629 | 8.35 | 1.03 | 7.26 | 106.49 | 16.21 | 0.05 | 14.12 | 264.11 | 73.31 | <0.005 | 7.80 | 332.71 | 395.28 | |
| G9 | 25 | 7.48 | 634 | 7.48 | 0.77 | 7.34 | 101.21 | 19.03 | 0.06 | 14.19 | 288.79 | 70.68 | <0.005 | 6.95 | 331.12 | 399.59 | |
| G10 | 16.3 | 7.51 | 659 | 8.69 | 1.59 | 13.93 | 105.12 | 21.32 | 0.06 | 24.85 | 261.64 | 73.19 | <0.005 | 14.09 | 350.31 | 446.96 | |
| Direct recharge area | G11 | 23.3 | 7.57 | 888 | 4.52 | 2.47 | 60.69 | 100.38 | 19.98 | 0.03 | 88.12 | 197.46 | 170.47 | <0.005 | 2.21 | 332.95 | 560.64 |
| G12 | 24.7 | 7.43 | 854 | 7.69 | 0.45 | 21.56 | 137.52 | 19.97 | 0.05 | 51.88 | 306.07 | 90.87 | <0.005 | 11.44 | 425.67 | 543.68 | |
| G13 | 21.6 | 7.6 | 683 | 8.07 | 0.61 | 96.21 | 9.46 | 11.49 | 0.06 | 30.79 | 148.10 | 71.34 | <0.005 | 11.50 | 70.94 | 357.02 | |
| G14 | 24.6 | 7.71 | 905 | 8.25 | 1.07 | 25.05 | 131.81 | 20.37 | 0.05 | 84.48 | 246.83 | 100.75 | <0.005 | 9.72 | 413.05 | 540.99 | |
| G15 | 18.3 | 7.26 | 1178 | 7.48 | 2.34 | 46.67 | 174.43 | 36.07 | 0.07 | 98.96 | 298.66 | 224.58 | <0.005 | 19.27 | 584.12 | 833.23 | |
| G16 | 18.7 | 7.4 | 1118 | 7.04 | 1.63 | 50.54 | 148.74 | 32.13 | 0.04 | 69.53 | 271.51 | 226.50 | <0.005 | 15.89 | 503.76 | 752.80 | |
| G17 | 21.5 | 7.24 | 925 | 6.15 | 1.18 | 35.15 | 138.21 | 20.24 | 0.04 | 73.67 | 298.66 | 112.17 | <0.005 | 9.26 | 428.50 | 589.82 | |
| G18 | 22.8 | 7.73 | 656 | 8.60 | 0.62 | 7.47 | 104.81 | 21.06 | 0.04 | 19.50 | 269.05 | 68.87 | <0.005 | 9.75 | 348.48 | 411.46 | |
| Discharge area | G19 | 18.3 | 7.14 | 1110 | 5.77 | 0.38 | 27.70 | 176.52 | 23.79 | 0.04 | 110.86 | 306.07 | 109.86 | <0.005 | 18.03 | 538.80 | 700.83 |
| G20 | 20.8 | 7.32 | 875 | 8.02 | 0.72 | 13.26 | 150.47 | 22.36 | 0.08 | 50.96 | 288.36 | 97.62 | <0.005 | 20.64 | 486.82 | 592.64 | |
| G21 | 21.6 | 7.74 | 615 | 2.58 | 1.01 | 17.85 | 90.11 | 16.11 | 0.05 | 40.92 | 214.74 | 68.49 | <0.005 | 5.70 | 291.35 | 380.70 | |
| G22 | 19.9 | 6.85 | 897 | 2.32 | 18.13 | 30.62 | 116.75 | 36.82 | 1.12 | 58.20 | 449.23 | 63.12 | <0.005 | 0.26 | 443.18 | 564.68 | |
| G23 | 22.8 | 8.03 | 804 | 4.92 | 4.19 | 48.82 | 51.79 | 43.32 | 0.09 | 93.89 | 155.50 | 138.87 | <0.005 | 4.54 | 307.73 | 484.20 | |
| G24 | 18.1 | 7.95 | 204 | 5.86 | 1.75 | 3.48 | 36.10 | 2.01 | 0.05 | 4.05 | 111.07 | 8.43 | <0.005 | 1.21 | 98.43 | 119.97 | |
| G25 | 21.9 | 7.45 | 828 | 6.22 | 2.73 | 48.68 | 100.80 | 22.86 | 0.06 | 74.26 | 229.55 | 123.78 | <0.005 | 7.52 | 345.88 | 532.96 | |
| G26 | 20.2 | 7.35 | 929 | 5.70 | 1.23 | 37.54 | 136.51 | 23.25 | 0.04 | 77.24 | 288.79 | 121.21 | <0.005 | 12.05 | 436.63 | 610.12 | |
| Surface water | S1 | 27.6 | 8.72 | 698 | 17.25 | 4.86 | 29.76 | 85.56 | 24.62 | 0.06 | 40.75 | 152.54 | 190.24 | <0.005 | 0.98 | 286.42 | 405.26 |
| S2 | 30.9 | 8.56 | 617 | 12.98 | 3.83 | 23.36 | 70.54 | 22.64 | 0.39 | 37.69 | 135.76 | 151.34 | 0.09 | 1.12 | 269.37 | 392.35 | |
| S3 | 24.5 | 8.62 | 425 | 12.58 | 2.25 | 11.65 | 52.35 | 15.46 | 0.04 | 18.86 | 110.25 | 88.76 | 0.01 | 1.02 | 208.75 | 250.26 | |
| S4 | 26.2 | 8.67 | 440 | 11.82 | 1.32 | 12.97 | 46.53 | 19.68 | 0.11 | 20.66 | 91.33 | 102.12 | 0.02 | 1.36 | 197.24 | 264.03 | |
| Water Samples | NO3−−N/(mg/L) | Locations |
|---|---|---|
| G2 | 18.90 | Indirect recharge area |
| G4 | 16.57 | Indirect recharge area |
| G5 | 34.47 | Indirect recharge area |
| G10 | 14.09 | Indirect recharge area |
| G12 | 11.44 | Direct recharge area |
| G13 | 11.50 | Direct recharge area |
| G15 | 19.27 | Direct recharge area |
| G16 | 15.89 | Direct recharge area |
| G19 | 18.03 | Discharge area |
| G20 | 20.64 | Discharge area |
| G26 | 12.05 | Discharge area |
| pH | EC | TDS | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | HCO3− | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | −0.3915 | −0.3823 | −0.4588 | 0.0681 | −0.5124 | −0.2533 | −0.7598 | −0.2821 | −0.4145 | −0.0757 |
| EC | −0.3915 | 1 | 0.9825 | 0.1585 | 0.6002 | 0.8625 | 0.5348 | 0.3346 | 0.2852 | 0.3159 | 0.8704 |
| TDS | −0.3823 | 0.9825 | 1 | 0.1651 | 0.5103 | 0.9041 | 0.5908 | 0.3221 | 0.1913 | 0.3443 | 0.9130 |
| K+ | −0.4588 | 0.1585 | 0.1651 | 1 | 0.0076 | 0.1108 | 0.4103 | 0.4813 | 0.1052 | −0.1558 | 0.0756 |
| Na+ | 0.0681 | 0.6002 | 0.5103 | 0.0076 | 1 | 0.1719 | −0.0187 | −0.1796 | 0.1385 | −0.1705 | 0.5933 |
| Ca2+ | −0.5124 | 0.8625 | 0.9041 | 0.1108 | 0.1719 | 1 | 0.4885 | 0.5054 | 0.1414 | 0.4514 | 0.7496 |
| Mg2+ | −0.2533 | 0.5348 | 0.5908 | 0.4103 | −0.0187 | 0.4885 | 1 | 0.3186 | 0.2684 | 0.2730 | 0.4873 |
| HCO3− | −0.7598 | 0.3346 | 0.3221 | 0.4813 | −0.1796 | 0.5054 | 0.3186 | 1 | 0.0515 | 0.2671 | 0.0296 |
| Cl− | −0.2821 | 0.2852 | 0.1913 | 0.1052 | 0.1385 | 0.1414 | 0.2684 | 0.0515 | 1 | 0.0993 | −0.0415 |
| NO3− | −0.4145 | 0.3159 | 0.3443 | −0.1558 | −0.1705 | 0.4514 | 0.2730 | 0.2671 | 0.0993 | 1 | 0.0843 |
| SO42− | −0.0757 | 0.8704 | 0.9130 | 0.0756 | 0.5933 | 0.7496 | 0.4873 | 0.0296 | −0.0415 | 0.0843 | 1 |
| Sources | Contribution Rate/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groundwater | Surface Water | |||||
| Min | Max | Mean ± SD | Min | Max | Mean ± SD | |
| Domestic sewage & manure | 8.5 | 59.4 | 37.1 ± 13.4 | 47.7 | 74.7 | 56.9 ± 11.0 |
| Soil organic nitrogen | 14.0 | 33.8 | 25.2 ± 5.3 | 8.2 | 17.4 | 14.3 ± 4.2 |
| NH4+ in rainfall and fertilizer | 10.5 | 33.5 | 21.0 ± 5.8 | 6.1 | 13.1 | 10.7 ± 3.2 |
| Chemical fertilizer | 5.7 | 29.5 | 11.4 ± 5.5 | 6.6 | 14.2 | 10.7 ± 3.1 |
| Atmospheric deposition | 1.8 | 18.5 | 5.3 ± 3.8 | 5.7 | 11.0 | 7.4 ± 2.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Fan, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, M. Using Geochemistry, Stable Isotopes and Statistical Tools to Estimate the Sources and Transformation of Nitrate in Groundwater in Jinan Spring Catchment, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050393
Wang K, Fan M, Wu Z, Zhang X, Wang H, Chen X, Wang M. Using Geochemistry, Stable Isotopes and Statistical Tools to Estimate the Sources and Transformation of Nitrate in Groundwater in Jinan Spring Catchment, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050393
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kairan, Mingyuan Fan, Zhen Wu, Xin Zhang, Hongbo Wang, Xuequn Chen, and Mingsen Wang. 2025. "Using Geochemistry, Stable Isotopes and Statistical Tools to Estimate the Sources and Transformation of Nitrate in Groundwater in Jinan Spring Catchment, China" Toxics 13, no. 5: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050393
APA StyleWang, K., Fan, M., Wu, Z., Zhang, X., Wang, H., Chen, X., & Wang, M. (2025). Using Geochemistry, Stable Isotopes and Statistical Tools to Estimate the Sources and Transformation of Nitrate in Groundwater in Jinan Spring Catchment, China. Toxics, 13(5), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050393






