Estimating PM2.5 Exposures and Cardiovascular Disease Risks in the Yangtze River Delta Region Using a Spatiotemporal Convolutional Approach to Fill Gaps in Satellite Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
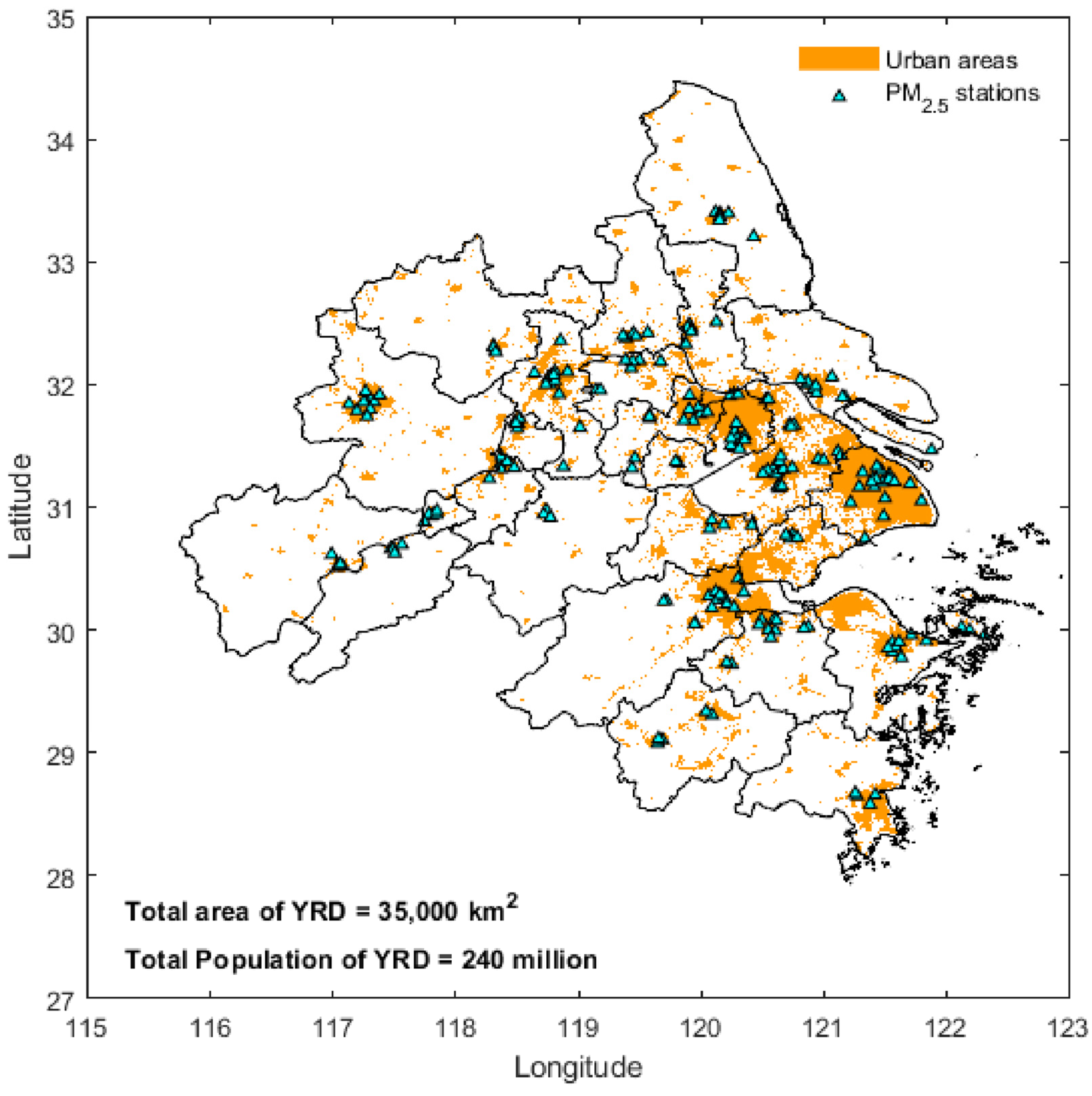
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data Sets
2.2.1. Ground-Based PM2.5 Measurements
2.2.2. Satellite Data Products
2.2.3. Meteorological Data
2.2.4. Population Data
2.3. Methods
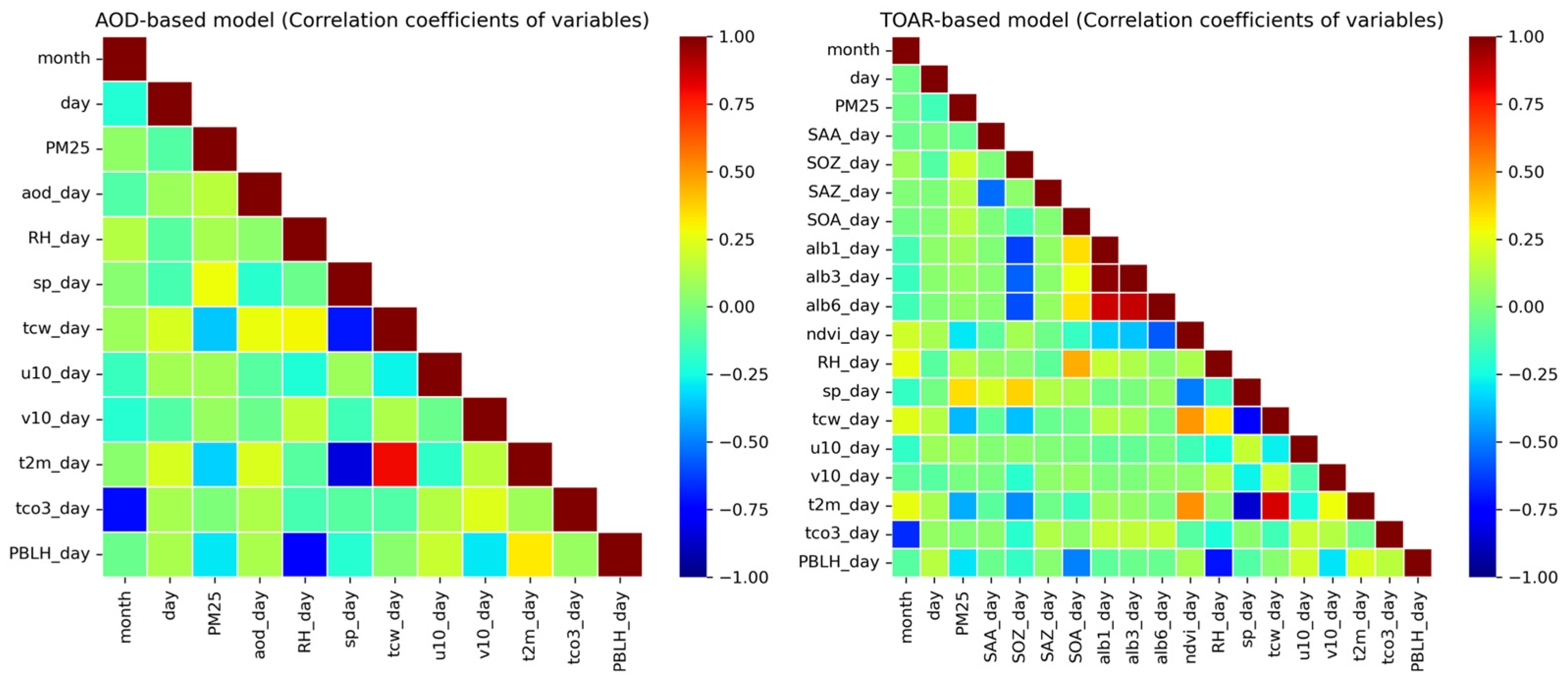
2.3.1. Data Preprocessing and Matching
2.3.2. Imputation Method for Missing Values
2.3.3. Model Implementation
Random Forest (RF) Model
Gradient-Boosting Regression (GBR) Model
Extreme Gradient-Boosting (XGBoost) Regression Model
Support Vector Regression (SVR) Model
3. Results
3.1. Performance of Different Machine-Learning Models
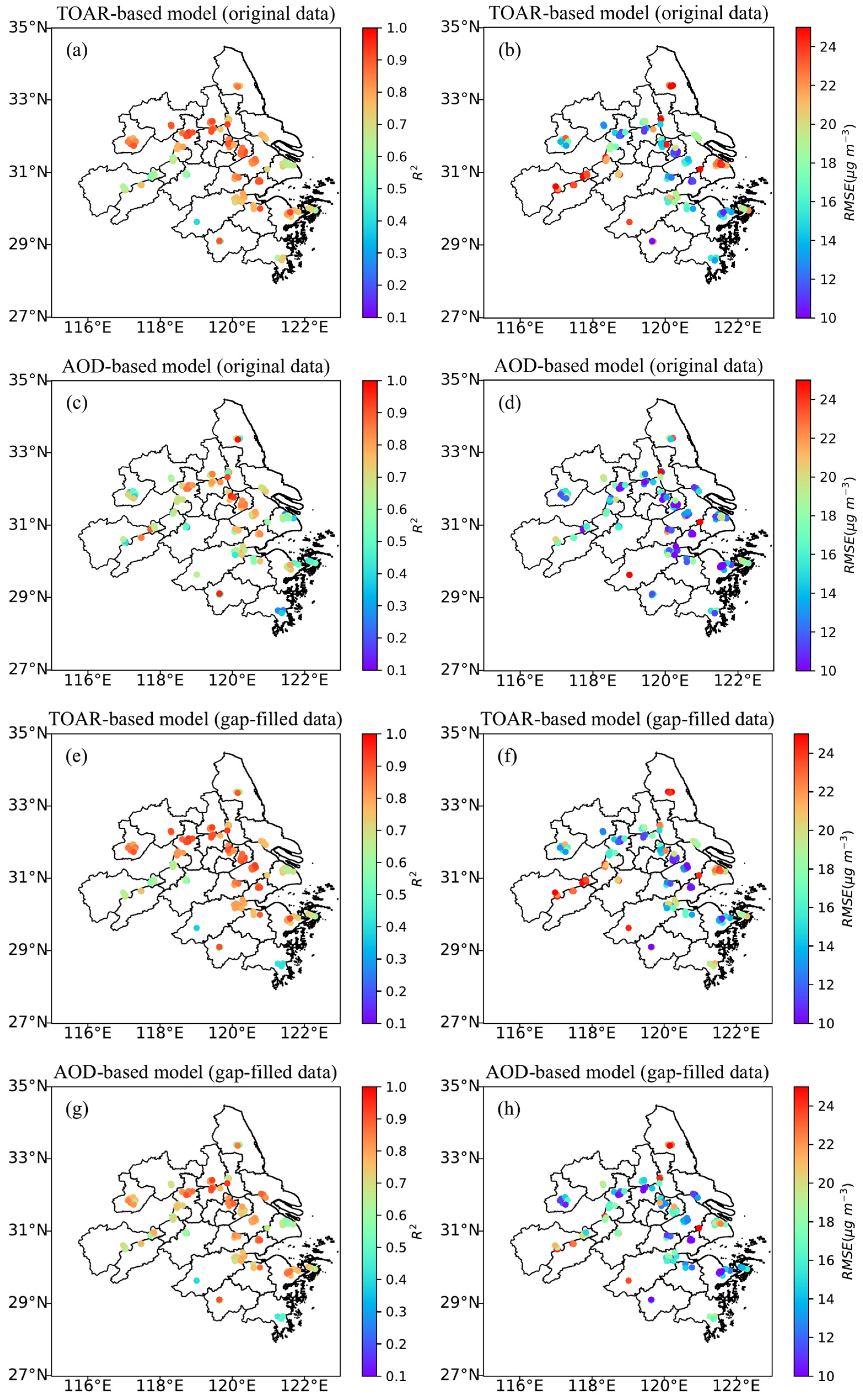
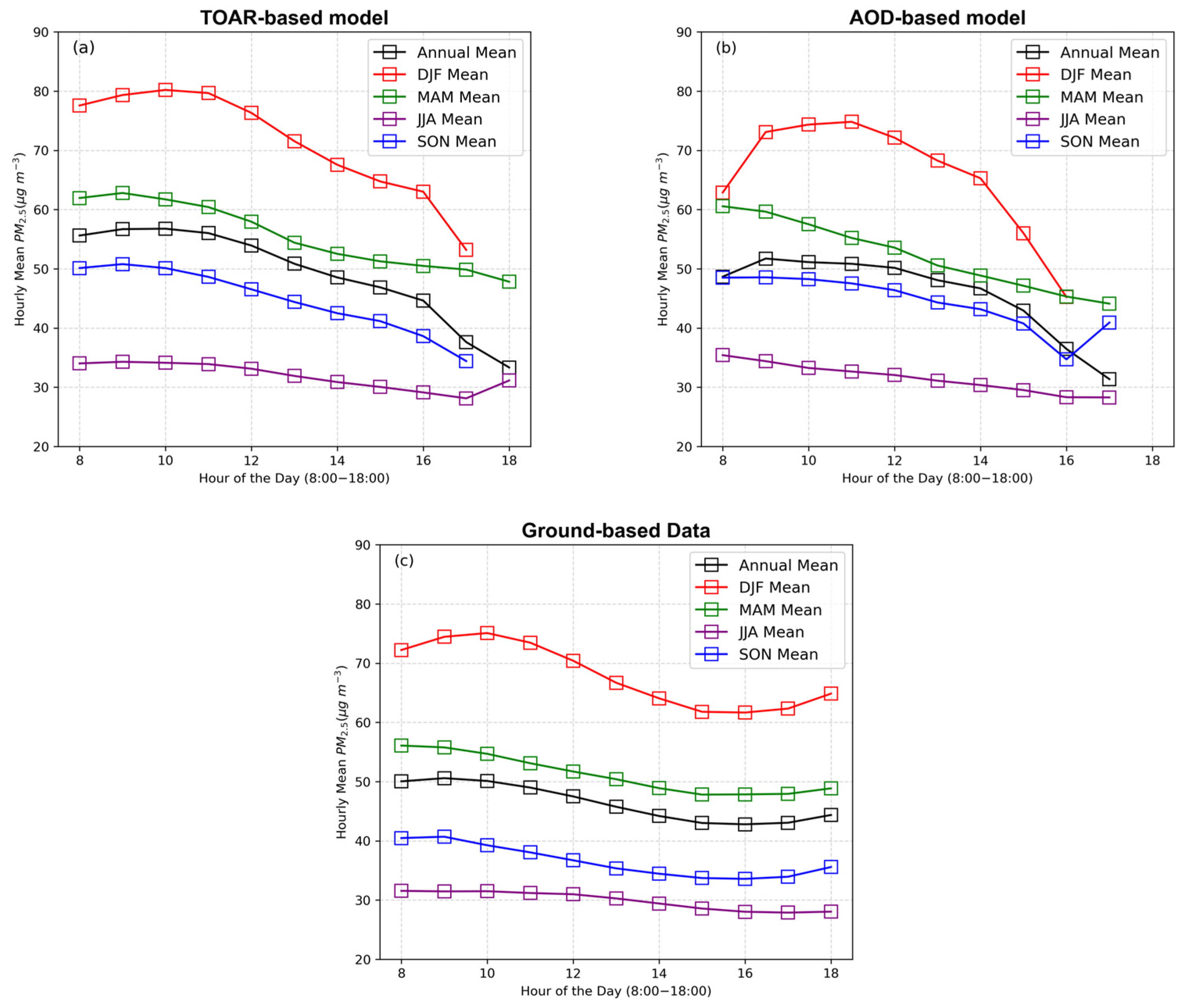
3.2. Site-Specific Performances of TOAR-Based and AOD-Based Models
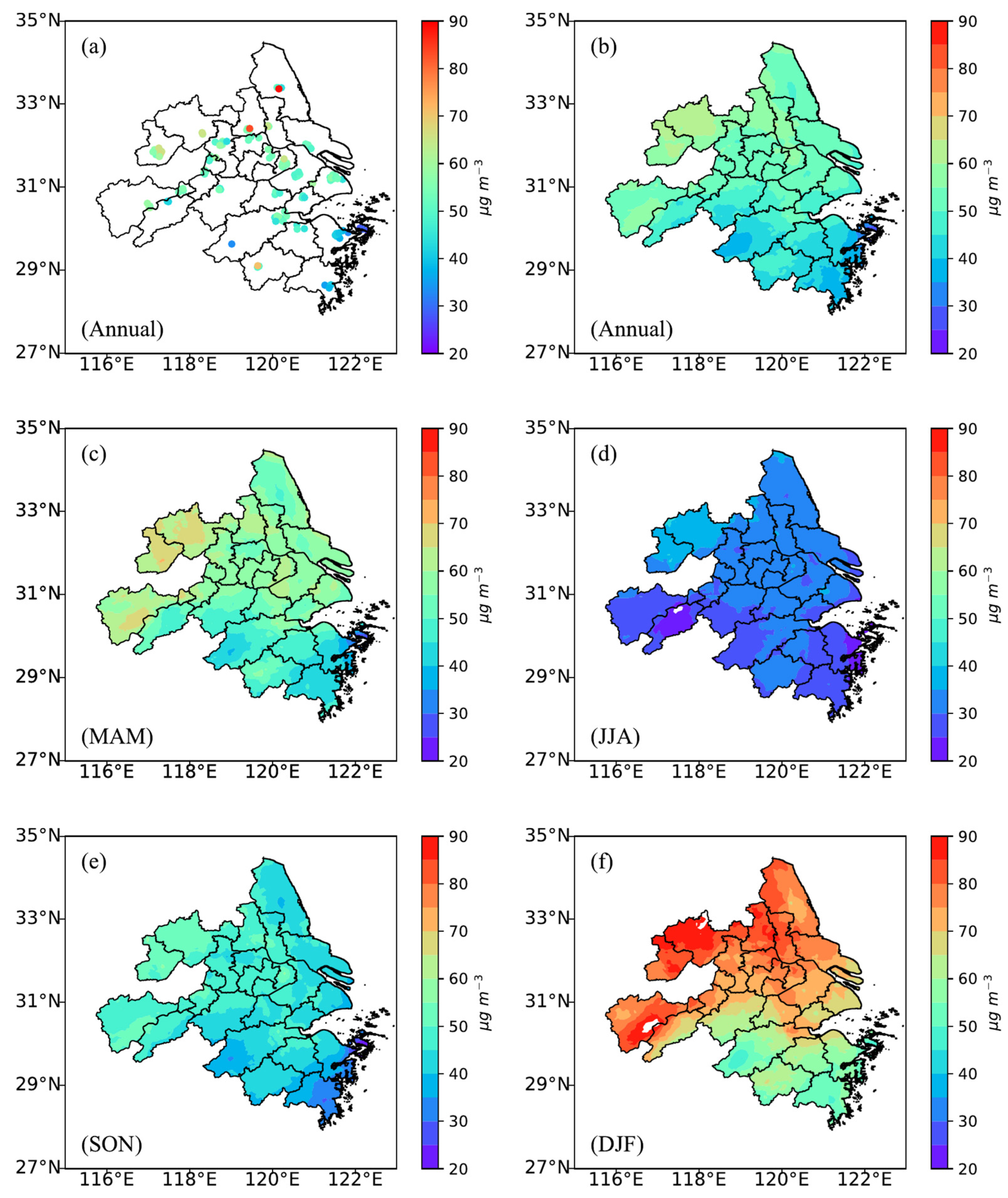
3.3. Spatiotemporal Distributions of PM2.5 Concentration
3.4. PM2.5 and Cardiovascular Disease
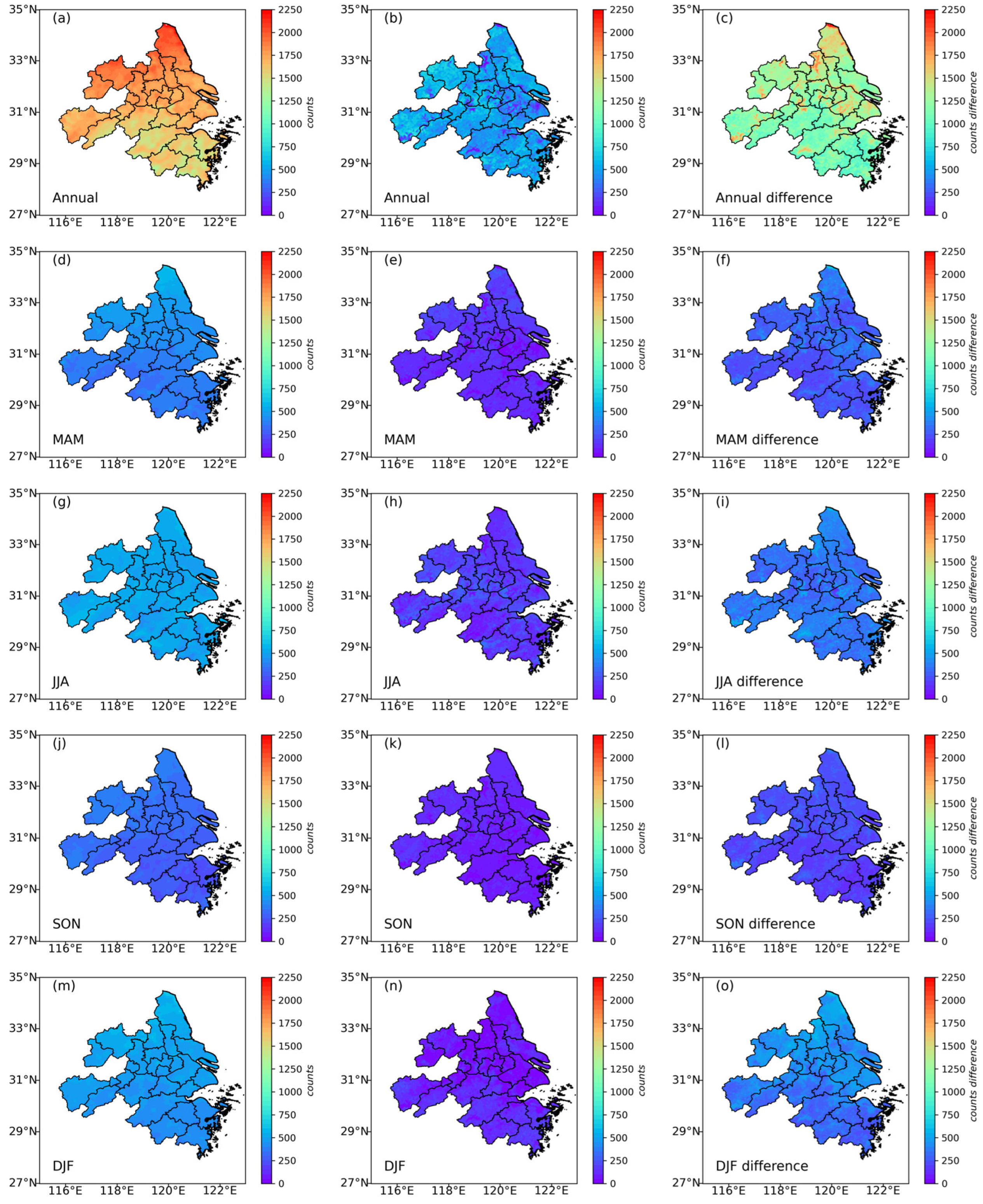
3.5. The Impact of Pixel-Count (Sampling) Differences on TOAR-Based and AOD-Based Models
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Cao, J. Atmospheric PM2.5 Exposure and Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Perfusion 2024, 39, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yazdi, M.D.; Yin, K.; Castro, E.; Shtein, A.; Qiu, X.; Peralta, A.A.; Coull, B.A.; Dominici, F.; et al. Exposure-Response Associations between Chronic Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter and Risks of Hospital Admission for Major Cardiovascular Diseases: Population Based Cohort Study. BMJ 2024, 384, e076939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henning, R.J. Particulate Matter Air Pollution Is a Significant Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, C.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Guo, H.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Shi, Z. Estimation of PM2.5 Concentration across China Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data and Machine Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, N.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, J.L.; Kephart, J.L.; Ortigoza, A.; Betancourt, R.M.; Sangrador, J.L.T.; Rodriguez, D.A.; Diez Roux, A.V.; Sanchez, B.; Yamada, G. Short-Term Associations between Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Cardiovascular and Respiratory Mortality in 337 Cities in Latin America. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 171073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhao, H.; An, L.; Li, L.; et al. Five-Year Observation of Aerosol Optical Properties and Its Radiative Effects to Planetary Boundary Layer during Air Pollution Episodes in North China: Intercomparison of a Plain Site and a Mountainous Site in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maftei, C.; Vaseashta, A.; Poinareanu, I. Toxicity Risk Assessment Due to Particulate Matter Pollution from Regional Health Data: Case Study from Central Romania. Toxics 2024, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yu, L.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Li, J.; Shen, P.; Lin, H.; Shui, L.; Tang, M.; Jin, M.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to PM2.5 and Mortality: A Cohort Study in China. Toxics 2023, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio, L.C.; Pachajoa, D.C.; Echeverri-Londoño, C.A.; Saiz, J.; Tobón, C. Air Pollution and Cardiac Diseases: A Review of Experimental Studies. Dose-Response 2023, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.I.; Jung, J.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.I.; Lee, C.M. A Comparison of Health Risks from PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Exposure in Industrial Complexes in Dangjin and Yeosu·Gwangyang. Toxics 2024, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, M.M.; Maddalon, A.; Iulini, M.; Galbiati, V. Air Pollution: Possible Interaction between the Immune and Nervous System? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 16037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Huang, J.; Ma, J.; Qin, W.; Li, R.; Mo, Z. Pollution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in PM2.5 during Winter in Nanning. China Trop. Med. 2024, 24, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolisnyk, A.; Chugai, A.; Mozgovyy, A.; Soloshych, I. Assessment of the Risks of Toxic Effects of Atmospheric Air Pollution for Humans (on the Example of Cities in Southern Ukraine). Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2023, 24, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory-Slechta, D.A.; Merrill, A.; Sobolewski, M. Air Pollution-Related Neurotoxicity Across the Life Span. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, G. Mendelian Randomization Study Supports the Causal Effects of Air Pollution on Longevity via Multiple Age-Related Diseases. npj Aging 2023, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussaini, A.R.; Aljabri, M.R.; Al-Harbi, Z.T.; Almohammadi, G.A.; Al-Harbi, T.M.; Bashir, S. Air Pollution and Its Adverse Effects on the Central Nervous System. Cureus 2023, 15, e38927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Qian, Z.; Li, D.; Cai, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Vaughn, M.G.; Keith, A.E.; Li, H.; et al. Associations between Air Pollution and the Risk of First Admission and Multiple Readmissions for Cardiovascular Diseases. Heart 2024, 110, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathieh, S.; Grieve, S.M.; Negishi, K.; Figtree, G.A. Potential Biological Mediators of Myocardial and Vascular Complications of Air Pollution—A State-of-the-Art Review. Heart Lung Circ. 2023, 32, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Ge, P.; Lu, Z.; Liu, X.; Cao, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, M. The Cytotoxic Effects of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) from Different Sources at the Air–Liquid Interface Exposure on A549 Cells. Toxics 2024, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abdollahpour, I.; Abegaz, K.H.; Abolhassani, H.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Global Burden of 87 Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krittanawong, C.; Qadeer, Y.K.; Hayes, R.B.; Wang, Z.; Virani, S.; Thurston, G.D.; Lavie, C.J. PM2.5 and Cardiovascular Health Risks. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Routledge, M.N. The Contribution of PM2.5 to Cardiovascular Disease in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 37502–37513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yang, X.; Chu, A.; Xie, X.; Bai, M.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Acute Effects of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) on Hospital Admissions for Cardiovascular Diseases in Lanzhou, China: A Time-Series Study. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, D.; Jiao, K.; Wang, X.; Suo, J.; Yang, H.; Liao, J.; Ma, L. Effect of Ambient Fine Particulates (PM2.5) on Hospital Admissions for Respiratory and Cardiovascular Diseases in Wuhan, China. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.C.; Lv, Z.; Ma, W.; Xiao, J.; Lin, H.; He, G.; Li, X.; Zeng, W.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Contribution of Heavy Metals in PM2.5 to Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Risk, a Case Study in Guangzhou, China. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, Y.; Kan, H.; Chen, R. Fine Particulate Matter and Cardiorespiratory Health in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiological Studies. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Guan, Y.; Shao, C.; Niu, R. Assessing the Health Impacts of PM2.5 and Ozone Pollution and Their Comprehensive Correlation in Chinese Cities Based on Extended Correlation Coefficient. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, B.; Shan, H.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; et al. Associations between Short-Term Exposure to Ambient PM2.5 and Incident Cases of Cardiovascular Disease in Yantai, China. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2024, 34, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, L.; Feng, Z.; Zhu, J.; Gu, Y.; Li, K.; Liao, H. Historical and Future Health Burden Attributable to PM2.5 Exposure in China. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 322, 120363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lu, X.; Yuan, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Fung, T.; Sun, H.; Fung, J.C.H. Global PM2.5 Prediction and Associated Mortality to 2100 under Different Climate Change Scenarios. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10039–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Liao, H. Radiative Forcing and Health Impact of Aerosols and Ozone in China as the Consequence of Clean Air Actions over 2012–2017. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 12511–12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. A Robust Deep Learning Approach for Spatiotemporal Estimation of Satellite AOD and PM2.5. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Shi, Y.; Seong, M.; Gao, W.; Li, Y. Influence of Spatial Resolution on Satellite-Based PM2.5 Estimation: Implications for Health Assessment. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, M.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Tao, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Himawari-8/AHI Aerosol Optical Depth Detection Based on Machine Learning Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Deng, R.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cao, B.; Liu, Y.; Hua, Z.; Yu, J. Estimating High-Spatial-Resolution Daily PM2.5 Mass Concentration from Satellite Top-of-Atmosphere Reflectance Based on an Improved Random Forest Model. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 302, 119724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falah, S.; Mhawish, A.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Kloog, I.; Banerjee, T.; Kizel, F.; Broday, D.M. Impact of Environmental Attributes on the Uncertainty in MAIAC/MODIS AOD Retrievals: A Comparative Analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Han, M.; Zhang, C. Long Short-Term Memory Network Model to Estimate PM2.5 Concentrations with Missing-Filled Satellite Data in Beijing. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 4175–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Guo, Y.; Carmichael, G.R.; Gao, M. A Deep Learning Approach to Increase the Value of Satellite Data for PM2.5 Monitoring in China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Jia, S.; Zhang, C. Estimation of High-Resolution PM2.5 Concentrations Based on Gap-Filling Aerosol Optical Depth Using Gradient Boosting Model. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Belle, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Wildani, A.; Liu, Y. Impacts of Snow and Cloud Covers on Satellite-Derived PM2.5 Levels. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ban, J.; Chen, N.X.; Li, T. High-Resolution Daily AOD Estimated to Full Coverage Using the Random Forest Model Approach in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 203, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Ding, Y.; Li, S.; Teng, M.; Yang, J. Estimation of Daily Seamless PM2.5 Concentrations with Climate Feature in Hubei Province, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liao, K.; Ren, Y. Handling Missing Data in Large-Scale Modis Aod Products Using a Two-Step Model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, Z.; Asrar, G.R.; Zhao, X. Gap-Filling MODIS Daily Aerosol Optical Depth Products by Developing a Spatiotemporal Fitting Algorithm. GISci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 762–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T. Ultrahigh-Resolution PM2.5 Estimation from Top-of-Atmosphere Reflectance with Machine Learning: Theories, Methods, and Applications. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gao, K.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, P. PM2.5 Estimation in Day/Night-Time from Himawari-8 Infrared Bands via a Deep Learning Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Fan, S.; Xia, K.; Wang, L. Estimation of Regional Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentrations Directly from Satellite Top-of-Atmosphere Reflectance Using A Hybrid Learning Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Yu, S. Estimating PM2.5 Concentrations in Yangtze River Delta Region of China Using Random Forest Model and the Top-of-Atmosphere Reflectance. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, L. Comparison of Satellite-Based Pm2.5 Estimation from Aerosol Optical Depth and Top-of-Atmosphere Reflectance. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Remer, L.A.; Vermote, E.F.; Chu, A.; Holben, B.N. Operational Remote Sensing of Tropospheric Aerosol over Land from EOS Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 17051–17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxsey-Whitfield, E.; MacManus, K.; Adamo, S.B.; Pistolesi, L.; Squires, J.; Borkovska, O.; Baptista, S.R. Taking Advantage of the Improved Availability of Census Data: A First Look at the Gridded Population of the World, Version 4. Pap. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 1, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Drucker, H.; Burges, C.J.C.; Kaufman, L.; Smola, A.; Vapnik, V. Support Vector Regression Machines. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 2–5 December 1996; pp. 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Harari, O.; Bingham, D.; Dean, A.; Higdon, D. Computer Experiments: Prediction Accuracy, Sample Size and Model Complexity Revisited. Stat. Sin. 2018, 28, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, Y.; Yin, D.; He, J.; Liu, N.; Qu, J.; Xiao, J. Annual and Diurnal Variations of Gaseous and Particulate Pollutants in 31 Provincial Capital Cities Based on in Situ Air Quality Monitoring Data from China National Environmental Monitoring Center. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.P.; Hansen, M.C.; Stehman, S.V.; Potapov, P.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Vermote, E.F.; Townshend, J.R. Global Land Change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 2018, 560, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Weng, F.; Li, Z. Ultrahigh-Resolution (250 m) Regional Surface PM2.5 Concentrations Derived First from MODIS Measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, T.D.; Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S.; Vaughan, M.A. A Bulk-Mass-Modeling-Based Method for Retrieving Particulate Matter Pollution Using CALIOP Observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 1739–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, X.; Rupakheti, D.; Dong, J.; Tang, L.; Kang, S. Evaluation and Comparison of Spatio-Temporal Relationship between Multiple Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and Near-Surface PM2.5 Concentration over China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
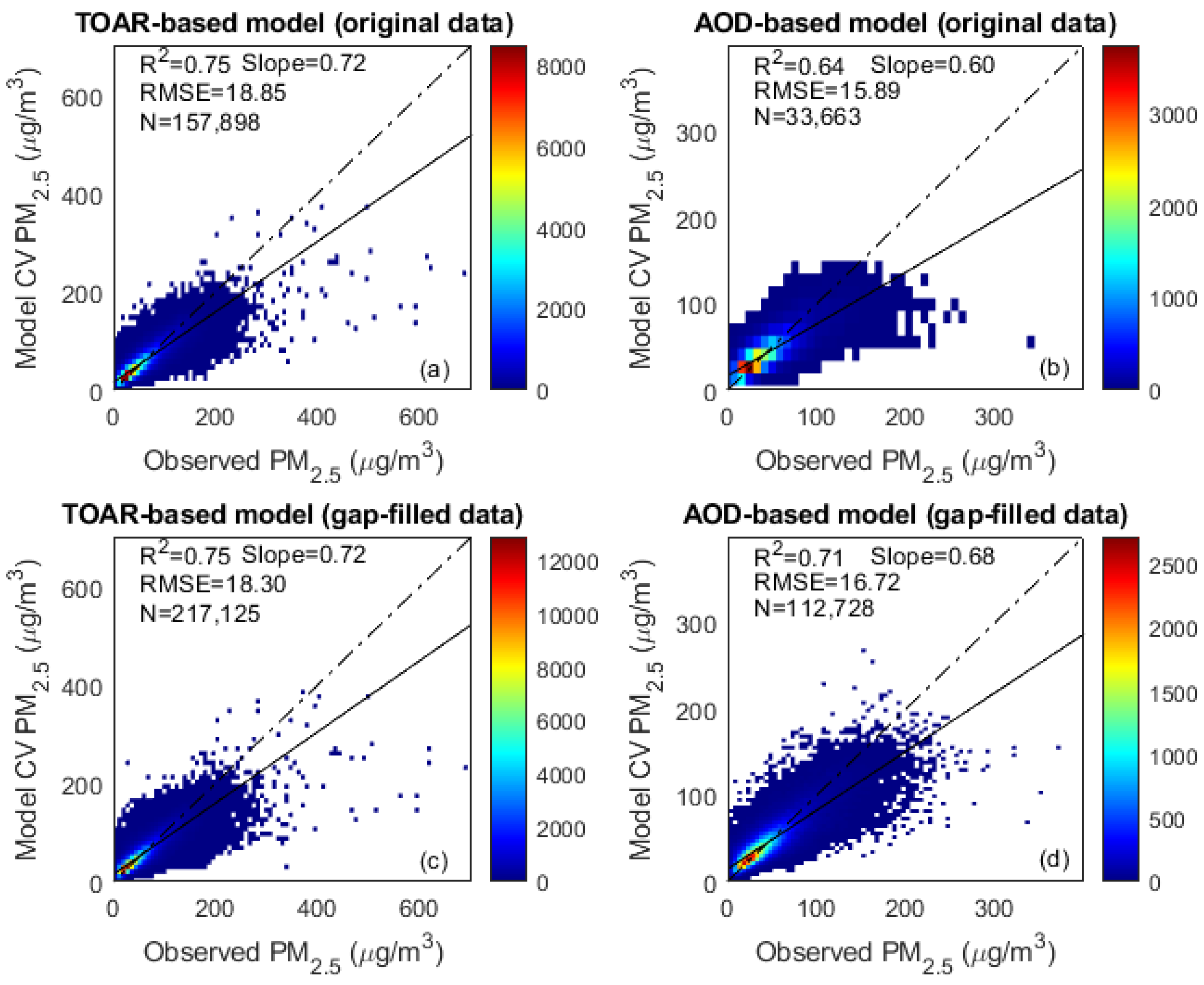


| Machine-Learning Algorithms | TOAR-Based Model | AOD-Based Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE (μg m−3) | Slope | R2 | RMSE (μg m−3) | Slope | |
| RF (gap-filled data) | 0.75 | 18.30 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 16.72 | 0.68 |
| RF (original data) | 0.75 | 18.85 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 15.89 | 0.60 |
| GBR (gap-filled data) | 0.71 | 20.42 | 0.73 | 0.67 | 17.79 | 0.68 |
| XGBoost (gap-filled data) | 0.73 | 19.44 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 17.45 | 0.66 |
| SVR (gap-filled data) | 0.69 | 20.95 | 0.68 | 0.65 | 18.85 | 0.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, M.J.; Seong, M.; Shahid, B.; Bai, H. Estimating PM2.5 Exposures and Cardiovascular Disease Risks in the Yangtze River Delta Region Using a Spatiotemporal Convolutional Approach to Fill Gaps in Satellite Data. Toxics 2025, 13, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050392
Hussain MJ, Seong M, Shahid B, Bai H. Estimating PM2.5 Exposures and Cardiovascular Disease Risks in the Yangtze River Delta Region Using a Spatiotemporal Convolutional Approach to Fill Gaps in Satellite Data. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050392
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Muhammad Jawad, Myeongsu Seong, Behjat Shahid, and Heming Bai. 2025. "Estimating PM2.5 Exposures and Cardiovascular Disease Risks in the Yangtze River Delta Region Using a Spatiotemporal Convolutional Approach to Fill Gaps in Satellite Data" Toxics 13, no. 5: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050392
APA StyleHussain, M. J., Seong, M., Shahid, B., & Bai, H. (2025). Estimating PM2.5 Exposures and Cardiovascular Disease Risks in the Yangtze River Delta Region Using a Spatiotemporal Convolutional Approach to Fill Gaps in Satellite Data. Toxics, 13(5), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050392