Leachate from Weathered Face Masks Increases DNA Damage to Sperm of Sand Dollars Scaphechinus mirabilis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
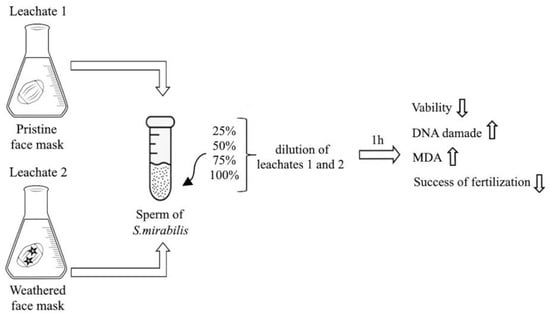
2.1. Preparation of Experimental Solutions from Masks
2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.3. Description of the Experiments
2.4. Determination of the DNA Damage
2.5. Determination of Malondialdehyde Content
2.6. Resazurin Cytotoxicity Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of FMs Using FTIR
3.2. Characterization of Sperm
3.2.1. Sperm Viability
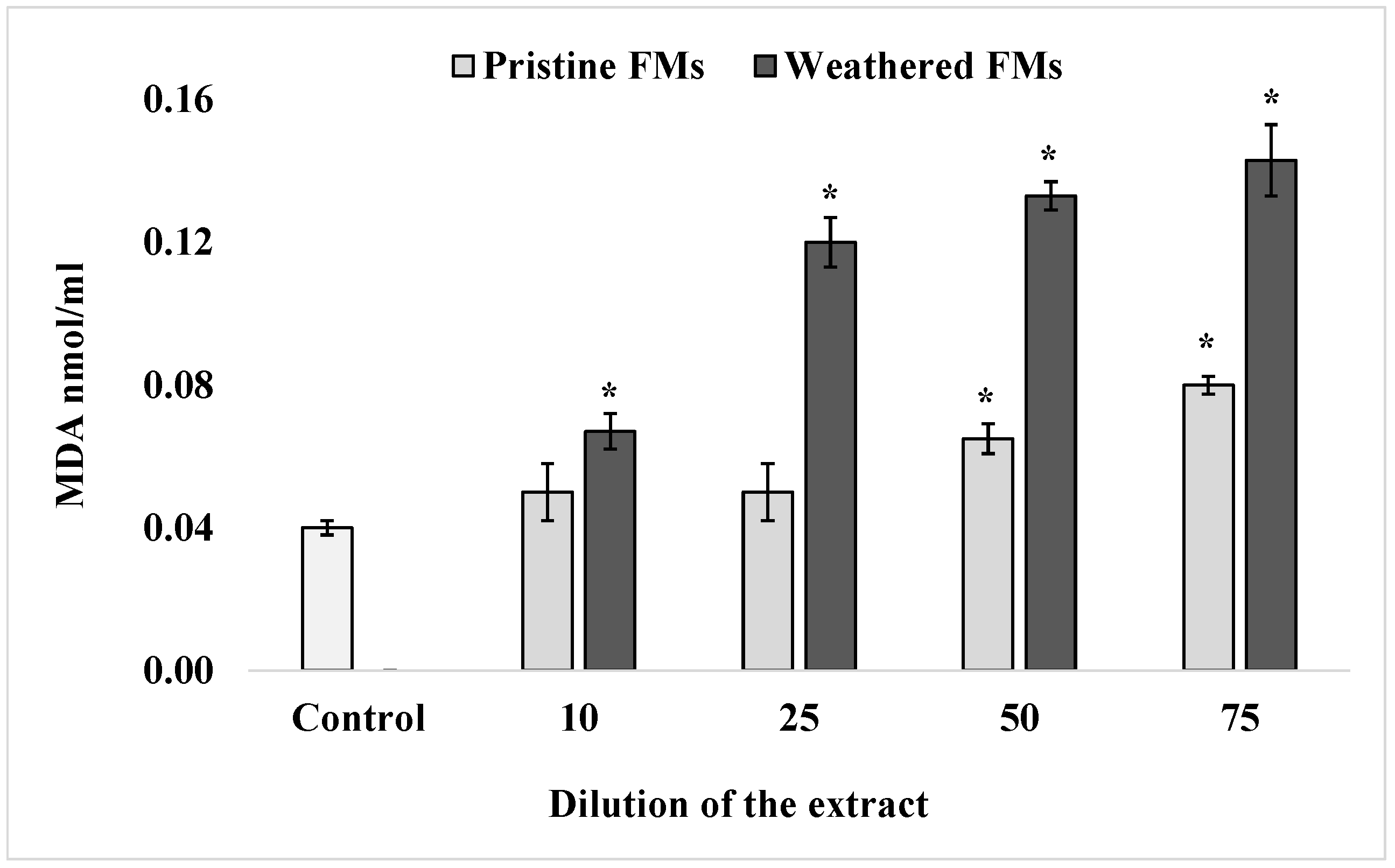
3.2.2. MDA Content in Sperm
3.2.3. Genotoxicity
3.2.4. Success of Fertilization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McHale, M.E.; Sheehan, K.L. Bioaccumulation, transfer, and impacts of microplastics in aquatic food chains. J. Environ. Expo. Assess. 2024, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, P.L.; Biesinger, M.C.; Grifi, M. Plastics and beaches: A degrading relationship. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgana, S.; Casentini, B.; Amalfitano, S. Uncovering the release of micro/nanoplastics from disposable face masks at times of COVID-19. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 419, 126507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mghili, B.; Analla, M.; Aksissou, M. Face masks related to COVID-19 in the beaches of the Moroccan Mediterranean: An emerging source of plastic pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Yang, S.; Zhou, G.J.; Zhang, K.; Lu, Y.; Jin, Q.; Lam, P.K.S.; Leung, K.M.Y.; He, Y. Release of microplastics from discarded surgical masks and their adverse impacts on the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelomin, V.P.; Dovzhenko, N.V.; Slobodskova, V.V.; Mazur, A.A.; Kukla, S.P.; Zhukovskaya, A.F. Expanded polystyrene-debris-induced genotoxic effect in littoral organisms. Toxics 2023, 11, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Shi, H. Insight into chemical features of migrated additives from plastics and associated risks to estuarine ecosystem. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 448, 130861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-la-Torre, G.E.; Dioses-Salinas, D.C.; Pizarro-Ortega, C.I.; Fernández-Severini, M.D.; Forero-López, A.D.; Dobaradaran, S.; Selvasembian, R. Face mask structure, degradation, and interaction with marine biota: A review. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 10, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioses-Salinas, D.C.; Pizarro-Ortega, C.I.; Fernández Severini, M.D.; Forero López, A.D.; Prieto, G.; Dobaradaran, S.; Kannan, G.; De-la-Torre, G.E. Face mask exposure to environmental conditions: In situ physical and chemical degradation and interaction with marine organisms. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 62, 102966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício Silva, A.L.; Prata, J.C.; Mouneyrac, C.; Barcelò, D.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Risks of Covid-19 face masks to wildlife: Present and future research needs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, K.; Sun, Y.; Van Hulle, S.; Jia, H. Generation of environmental persistent free radicals (EPFRs) enhances ecotoxicological effects of the disposable face mask waste with the COVID-19 pandemic. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 119019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrejos-Cardeña, U.; De-la-Torre, G.E.; Dobaradaran, S.; Rangabhashiyam, S. An ecotoxicological perspective of microplastics released by face masks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, I.D.G.; Macusi, E.D.; Jondonero, M.A.P.; Guihawan, J.Q.; Bacosa, H.P.; Amparado, R.F. Facemask: Protection or threat? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.M.; Patrício Silva, A.L.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Barceló, D.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Current knowledge on the presence, biodegradation, and toxicity of discarded face masks in the environment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; Silva, A.L.P.; Walker, T.R.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. COVID-19 pandemic repercussions on the use and management of plastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7760–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-la-Torre, G.E.; Dioses-Salinas, D.C.; Dobaradaran, S.; Spitz, J.; Nabipour, I.; Keshtkar, M.; Akhbarizadeh, R.; Tangestani, M.; Abedi, D.; Javanfekr, F. Release of phthalate esters (PAEs) and microplastics (MPs) from face masks and gloves during the COVID-19 pandemic. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Khan, R.; Saxena, A.; Sekar, S. Microplastics from face masks: A potential hazard post Covid-19 pandemic. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, J.; Shahriar, S.I.; Shahjahan, M. Release of microfibers from surgical face masks: An undesirable contributor to aquatic pollution. Water Emerg. Contam. Nanoplastics 2023, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, S.; Jiao, Y. Assessing disposable masks consumption and littering in the post COVID-19 pandemic in China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; An, C.; Chen, X.; Lee, K.; Zhang, B.; Feng, Q. Disposable masks release microplastics to the aqueous environment with exacerbation by natural weathering. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliu, F.; Veronelli, M.; Raguso, C.; Barana, D.; Galli, P.; Lasagni, M. The release process of microfibers: From surgical face masks into the marine environment. Environ. Adv. 2021, 4, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisafi, F.; Smedile, F.; Yakimov, M.M.; Aulenta, F.; Fazi, S.; La Cono, V.; Martinelli, A.; Di Lisio, V.; Denaro, R. Bacterial biofilms on medical masks disposed in the marine environment: A hotspot of biological and functional diversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pol, W.; Mierzynska, K.; Włodarczyka, T.; Hauschildb, T.; Zielinski, P. No trophy for the trophy?—How lake trophy impacts bacterial assemblages of biofilm on microplastic. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2023, 23, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, M.; Rodriguez-Romero, A.; Yeste, M.P.; Blasco, J.; Tovar-Sánchez, A. Products released from surgical face masks can provoke cytotoxicity in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Unmasking effects of masks: Microplastics released from disposable surgical face masks induce toxic effects in microalgae Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlorella sp. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 267, 109587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Lin, C.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Yang, H. Effect of chronic exposure to microplastic fibre ingestion in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 209, 111794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, T.; Edo, C.; Vilke, J.M.; Astudillo-Pascual, M.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Bebianno, M.J. Impact of face masks weathering on the mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Water Emerg. Contam. Nanoplastics 2024, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, M.; Pereiro, P.; Yeste, M.P.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A. Surgical face masks as a source of emergent pollutants in aquatic systems: Analysis of their degradation product effects in Danio rerio through RNA-Seq. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 15, 128186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualhato, G.; Cirqueira Dias, F.; Rocha, T.L. Hazardous effects of plastic microfibres from facial masks to aquatic animal health: Insights from zebrafish model. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, H.; Yin, J. The release of polypropylene plastic from disposable face masks in different water conditions and their potential toxicity in human cells. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeda, R.; Gunaalan, K.; Alonso-López, O.; Vilas, A.; Clérandeau, C.; Loisel, T.; Nielsen, T.G.; Cachot, J.; Beiras, R. A protocol for lixiviation of micronized plastics for aquatic toxicity testing. Chemosphere 2023, 333, 138894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouillon, C.; Bussiere, P.O.; Desnoux, E.; Collin, S.; Vial, C.; Therias, S.; Gardette, J.L. Is carbonyl index a quantitative probe to monitor polypropylene photodegradation? Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 128, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to assess the degree of alteration of artificially aged and environmentally weathered microplastics. Polymers 2023, 15, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N. Marine pollution bioassay by sea urcin eggs, an attempt to enhance accuracy. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1985, 30, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biological Test Method: Fertilization Assay Using Echinoids (Sea Urchins and Sand Dollars); EPS 1/RM/27; Environment Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2011; Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/wildlife-research-landscape-science/biological-test-method-publications/fertilization-assay-echinoids.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Dovzhenko, N.V.; Chelomin, V.P.; Mazur, A.A.; Kukla, S.P.; Slobodskova, V.V.; Istomina, A.A.; Zhukovskaya, A.F. Oxidative Stress in Far Eastern Mussel Mytilus trossulus (Gould, 1850) Exposed to Combined Polystyrene Microspheres (PSs) and CuO Nanoparticles (CuO-NPs). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buege, J.A.; Aust, S.D. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1978, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, J.L.A.; González-Pinzón, R.; Haggerty, R. The resazurin-resorufin system: Insights from a decade of “smart” tracer development for hydrologic applications. Water Res. 2018, 54, 6877–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, M.; Mohanty, J.; Dey, S.; Dutta, K.; Shah, M.P.; Das, A.P. The face mask: A tale from protection to pollution and demanding sustainable solution. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoironi, A.; Hadiyanto, H.; Hartini, E.; Dianratri, I.; Joelyna, F.A.; Pratiwi, W.Z. Impact of disposable mask microplastics pollution on the aquatic environment and microalgae growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 77453–77468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamaras, G.; Antonopoulou, M.; Beobide, A.S.; Triantafyllidis, V.; Dailianis, S. Disposable face masks into aquatic media: Chemical and biological testing of the released compounds during the leaching process. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, D.D.; Sharma, A.; Das, D.K.; Pramanik, A.; Kay, P.; Goycoolea, F.M. Toxicological impacts of plastic microfibers from face masks on Artemia salina: An environmental assessment using Box-Behnken design. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, A.D.F.; De-la-Torre, G.E.; Fernández Severini, M.D.; Prieto, G.; Brugnoni, L.I.; Colombo, C.V.; Dioses-Salinas, D.C.; Rimondino, G.N.; Spetter, C.V. Chemical-analytical characterization and leaching of heavy metals associated with nanoparticles and microplastics from commercial face masks and the abundance of personal protective equipment (PPE) waste in three metropolitan cities of South America. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogush, A.A.; Kourtchev, I. Disposable surgical/medical face masks and filtering face pieces: Source of microplastics and chemical additives in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 348, 123792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.; Galloway, T.S. Genotoxic damage in Polychaetes: A study of species and cell-type sensitivities. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2008, 654, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacaze, E.; Geffard, O.; Goyet, D.; Bony, S.; Devaux, A. Linking genotoxic responses in Gammarus fossarum germ cells with reproduction impairment, using the Comet assay. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Manfra, L.; Boni, R.; Rotini, A.; Migliore, L.; Tosti, E. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of CuO nanoparticles in sea urchin spermatozoa through oxidative stress. Environ. Int. 2018, 118, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero, M.; Schiavo, S.; Dumontet, S.; Manzo, S. DNA damages and offspring quality in sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus sperms exposed to ZnO nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, S.P.; Slobodskova, V.V.; Zhuravel, E.V.; Mazur, A.A.; Chelomin, V.P. Exposure of adult sand dollars (Scaphechinus mirabilis) (Agassiz, 1864) to copper oxide nanoparticles induces gamete DNA damage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 39451–39460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, S.P.; Chelomin, V.P.; Mazur, A.A.; Slobodskova, V.V. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce DNA Damage in Sand Dollar Scaphechinus mirabilis Sperm. Toxics 2022, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, A.A.; Chelomin, V.P.; Zhuravel, E.V.; Kukla, S.P.; Slobodskova, V.V.; Dovzhenko, N.V. Genotoxicity of Polystyrene (PS) Microspheres in Short-Term Exposure to Gametes of the Sand Dollar Scaphechinus mirabilis (Agassiz, 1864) (Echinodermata, Echinoidea). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Wu, R.S. Ultraviolet damages sperm mitochondrial function and membrane integrity in the sea urchin Anthocidaris crassispina. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Wu, R.S. UV induces reactive oxygen species, damages sperm, and impairs fertilisation in the sea urchin Anthocidaris crassispina. Mar. Biol. 2005, 148, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Naz, S.; Ma, Y.; Ullah, Q.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Luosang, D.-Z.; Tabassum, S.; Chatha, A.M.M.; et al. An Overview of Comet Assay Application for Detecting DNA Damage in Aquatic Animals. Agriculture 2023, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Fernandez-Triana, J.; Roughley, R.; Hebert, D.N. DNA barcode accumulation curves for understudied taxa and areas. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaye, N.; Thwala, M.; Cowan, D.A.; Musee, N. Genotoxicity of metal based engineered nanoparticles in aquatic organisms: A review. Mutat. Res. 2017, 773, 134–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christudoss, A.C.; Kundu, R.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Mukherjee, A. Time dependent release of microplastics from disposable face masks poses cyto-genotoxic risks in Allium cepa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 280, 116542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christudoss, A.C.; Kundu, R.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Mukherjee, A. Aging of disposable face masks in landfill leachate poses cyto-genotoxic risks to Allium cepa: Perils of uncontrolled disposal of medical waste. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 220, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappucci, U.; Proietti, M.; Casale, A.M.; Schiavo, S.; Chiavarini, S.; Accardo, S.; Manzo, S.; Piacentini, L. Assessing genotoxic effects of plastic leachates in Drosophila melanogaster. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, S.; Schiavo, S.; Oliviero, M.; Toscano, A.; Ciaravolo, M.; Cirino, P. Immune and reproductive system impairment in adult sea urchin exposed to nanosized ZnO via food. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcha, F.; Spagnol, C.; Rouxel, J. Genotoxicity of diuron and glyphosate in oyster spermatozoa and embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 106–107, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaux, A.; Fiat, L.; Gillet, C.; Bony, S. Reproduction impairment following paternal genotoxin exposure in brown trout (Salmo trutta) and Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cardiolinc Network. Long noncoding RNAs in cardiac development and ageing. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.; Palos-Ladeiro, M.; Besnard, A.; Porcher, J.M.; Bony, S.; Sanchez, W.; Devaux, A. Relationship between DNA damage in sperm after ex vivo exposure and abnormal embryo development in the progeny of the three-spined stickleback. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 36, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussan, D.D.; Snaychuk, L.; Bartzas, G.; Douvris, C. Quantification of trace elements in surgical and KN95 face masks widely used during the SARS-COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 151924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.S.H.; Sathishkumar, P.; Selahuddeen, M.L.W.; Mahmood, W.M.A.; Abidin, M.H.Z.; Wahab, R.A.; Huri, M.A.M.; Abdullah, F. Adverse environmental effects of disposable face masks due to the excess usage. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.L.; Delgado-Gallardo, J.; Watson, T.M.; Sarp, S. An investigation into the leaching of micro and nano particles and chemical pollutants from disposable face masks—Linked to the COVID-19 pandemic. Water Res. 2021, 196, 117033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Okoffo, E.D.; Banks, A.P.; Li, Y.; Thomas, K.V.; Rauert, C.; Aylward, L.L.; Mueller, J.F. Phthalate esters in face masks and associated inhalation exposure risk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423 Pt A, 127001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wang, W.X. Phthalate acid esters contribute to the cytotoxicity of mask leachate: Cell-based assay for toxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, C. Insight into the microplastics release from disposable face mask: Simulated environment and removal strategy. Chemosphere 2022, 309 Pt 1, 136748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelomin, V.P.; Mazur, A.A.; Slobodskova, V.V.; Kukla, S.P.; Dovzhenko, N.V. Genotoxic Properties of Polystyrene (PS) Microspheres in the Filter-Feeder Mollusk Mytilus trossulus (Gould, 1850). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagorti, G.; Kaya, B. Genotoxic effect of microplastics and COVID-19: The hidden threat. Chemosphere 2022, 286 Pt 3, 131898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Li, R.; Li, F.; Guo, X.; Xu, L.; Gan, L.; Yan, M.; Wang, J. Toxicity of nanoplastics to aquatic organisms: Genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, individual level and beyond individual level. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443 Pt B, 130266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, C.; Majorani, C.; Cresti, R.; Marcello, I.; Berardi, E.; Fava, L.; Attias, L.; D’Ilio, S. Determination and risk assessment of phthalates in face masks. An Italian study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443 Pt A, 130176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaalan, K.; Fabbri, E.; Capolupo, M. The hidden threat of plastic leachates: A critical review on their impacts on aquatic organisms. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, A.; Cuccaro, A.; Sole, M.; Freitas, R. Micro(nano)plastics and plastic additives effects in marine annelids: A literature review. Environ. Res. 2022, 214 Pt 1, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biale, G.; La Nasa, J.; Mattonai, M.; Corti, A.; Castelvetro, V.; Modugno, F. Seeping plastics: Potentially harmful molecular fragments leaching out from microplastics during accelerated ageing in seawater. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, E.G.; Braun, J.M.; Meeker, J.D.; Cooper, G.S. Phthalate exposure and male reproductive outcomes: A systematic review of the human epidemiological evidence. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 764–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, E.E.; Euling, S.Y.; Weaver, J.A.; Beverly, B.E.; Keshava, N.; Mudipalli, A.; Arzuaga, X.; Blessinger, T.; Dishaw, L.; Hotchkiss, A. Hazards of diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP) exposure: A systematic review of animal toxicology studies. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Han, W.; Xie, Q.; Xu, T.; Zhu, M.; Chen, J. Face mask-A potential source of phthalate exposure for human. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Fu, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, J. High sperm DNA stainability might not be an accurate predictive indicator of male fertility and assisted reproductive technology outcomes. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1510114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleysen, E.; Ledecq, M.; Siciliani, L.; Cheyns, K.; Vleminckx, C.; Blaude, M.N.; De Vos, S.; Brassinne, F.; Van Steen, F.; Nkenda, R.; et al. Titanium dioxide particles frequently present in face masks intended for general use require regulatory control. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodskova, V.V.; Chelomin, V.P.; Kukla, S.P.; Mazur, A.A. Copper Induced DNA Damage in the Gills of the Mussel Mytilus trossulus and Reversibility after Depuration. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsman, P.; Meijers, G.; Vitarelli, G. Comparison of the UV-degradation chemistry of polypropylene, polyethylene, polyamide 6 and polybutylene terephthalate. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1999, 65, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandow, N.; Will, V.; Wachtendorf, V.; Simon, F.G. Contaminant release from aged microplastic. Environ. Chem. 2017, 14, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Cao, R.; Shang, E.; Zhang, W. ROS-mediated photoaging pathways of nano- and micro-plastic particles under UV irradiation. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Kong, X.; Tao, S.; Xing, B. Sorption of four hydrophobic organic compounds by three chemically distinct polymers: Role of chemical and physical composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, P.; Huang, H.; Gao, S. Adsorption of triclosan onto different aged polypropylene microplastics: Critical effect of cations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, J. Environmental risks of polymer materials from disposable face masks linked to the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lu, K.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Qian, L.; Wang, M.; Gao, S. Effect of aging on adsorption behavior of polystyrene microplastics for pharmaceuticals: Adsorption mechanism and role of aging intermediates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, P.; Madhuvandhi, J.; Priya, K.K.; Thiagarajan, R.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Elumalai, S.; Thilagam, H. Weathered polyethylene microplastics exposure leads to modulations in glutathione-S-transferase activity in fish. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 990351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelomin, V.P.; Istomina, A.A.; Mazur, A.A.; Slobodskova, V.V.; Zhukovskaya, A.F.; Dovzhenko, N.V. New Insights into the Mechanisms of Toxicity of Aging Microplastics. Toxics 2024, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
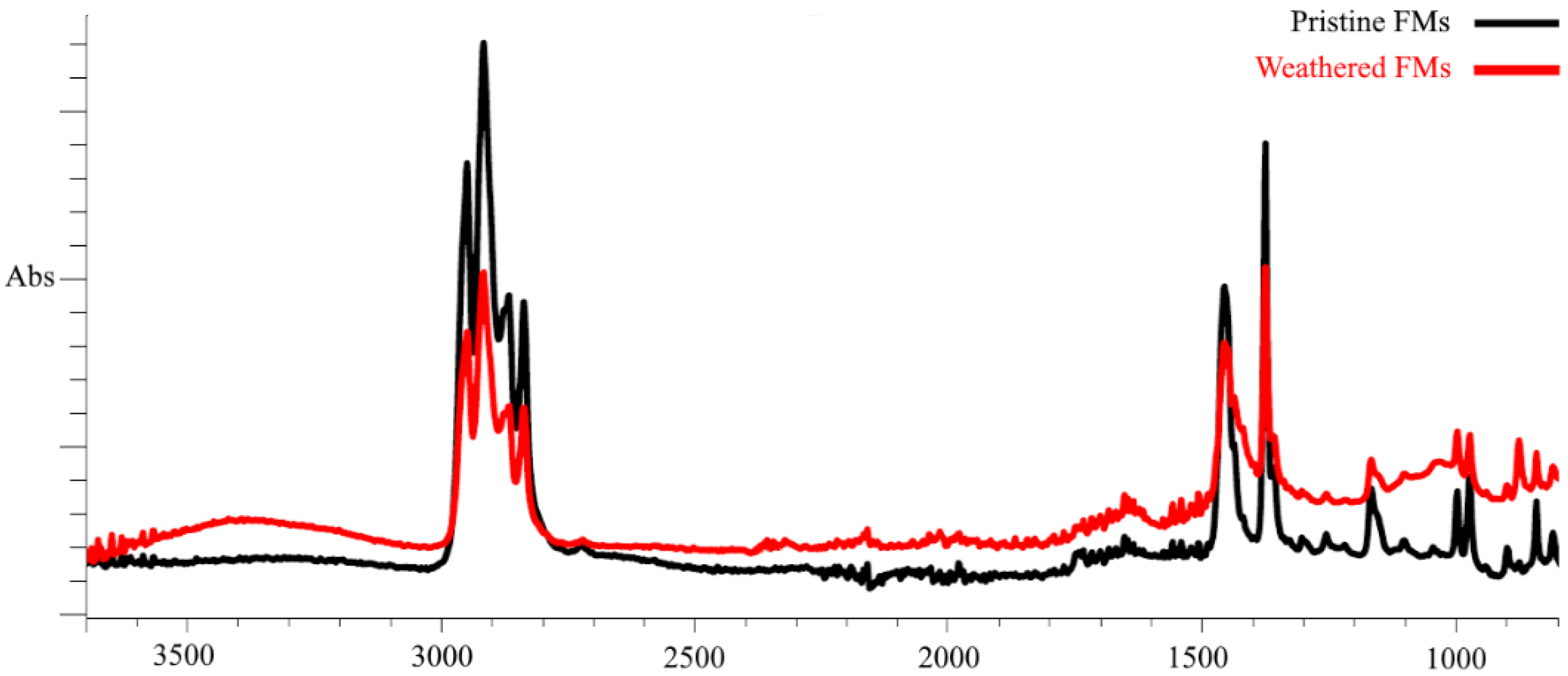



| Index | Formula | Pristine FMs | Weathered FMs |
|---|---|---|---|
| CI | 1850−1650/1500−1420 cm−1 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 1.11 ± 0.15 * |
| HI | 3400−3300/986−952 cm−1 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.11 * |
| COI | 1200−1100/2940−2885 cm−1 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.04 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chelomin, V.P.; Mazur, A.A.; Slobodskova, V.V.; Dovzhenko, N.V.; Kukla, S.P. Leachate from Weathered Face Masks Increases DNA Damage to Sperm of Sand Dollars Scaphechinus mirabilis. Toxics 2025, 13, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050372
Chelomin VP, Mazur AA, Slobodskova VV, Dovzhenko NV, Kukla SP. Leachate from Weathered Face Masks Increases DNA Damage to Sperm of Sand Dollars Scaphechinus mirabilis. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050372
Chicago/Turabian StyleChelomin, Victor Pavlovich, Andrey Alexandrovich Mazur, Valentina Vladimirovna Slobodskova, Nadezhda Vladimirovna Dovzhenko, and Sergey Petrovich Kukla. 2025. "Leachate from Weathered Face Masks Increases DNA Damage to Sperm of Sand Dollars Scaphechinus mirabilis" Toxics 13, no. 5: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050372
APA StyleChelomin, V. P., Mazur, A. A., Slobodskova, V. V., Dovzhenko, N. V., & Kukla, S. P. (2025). Leachate from Weathered Face Masks Increases DNA Damage to Sperm of Sand Dollars Scaphechinus mirabilis. Toxics, 13(5), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050372