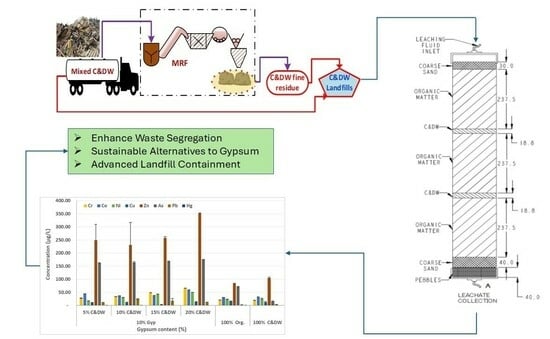
The Effects of Construction and Demolition Waste (C&DW) Fine Residues on Landfill Environments: A Column Leaching Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- i.
- Assess the levels and release potential of heavy metals from C&DW fine residues.
- ii.
- Investigate the impact of C&DW and gypsum content on the leaching and release behavior of heavy metals.
- iii.
- Determine environmentally friendly C&DW–gypsum content and identify combinations that pose environmental risks.
2. Materials and Methods
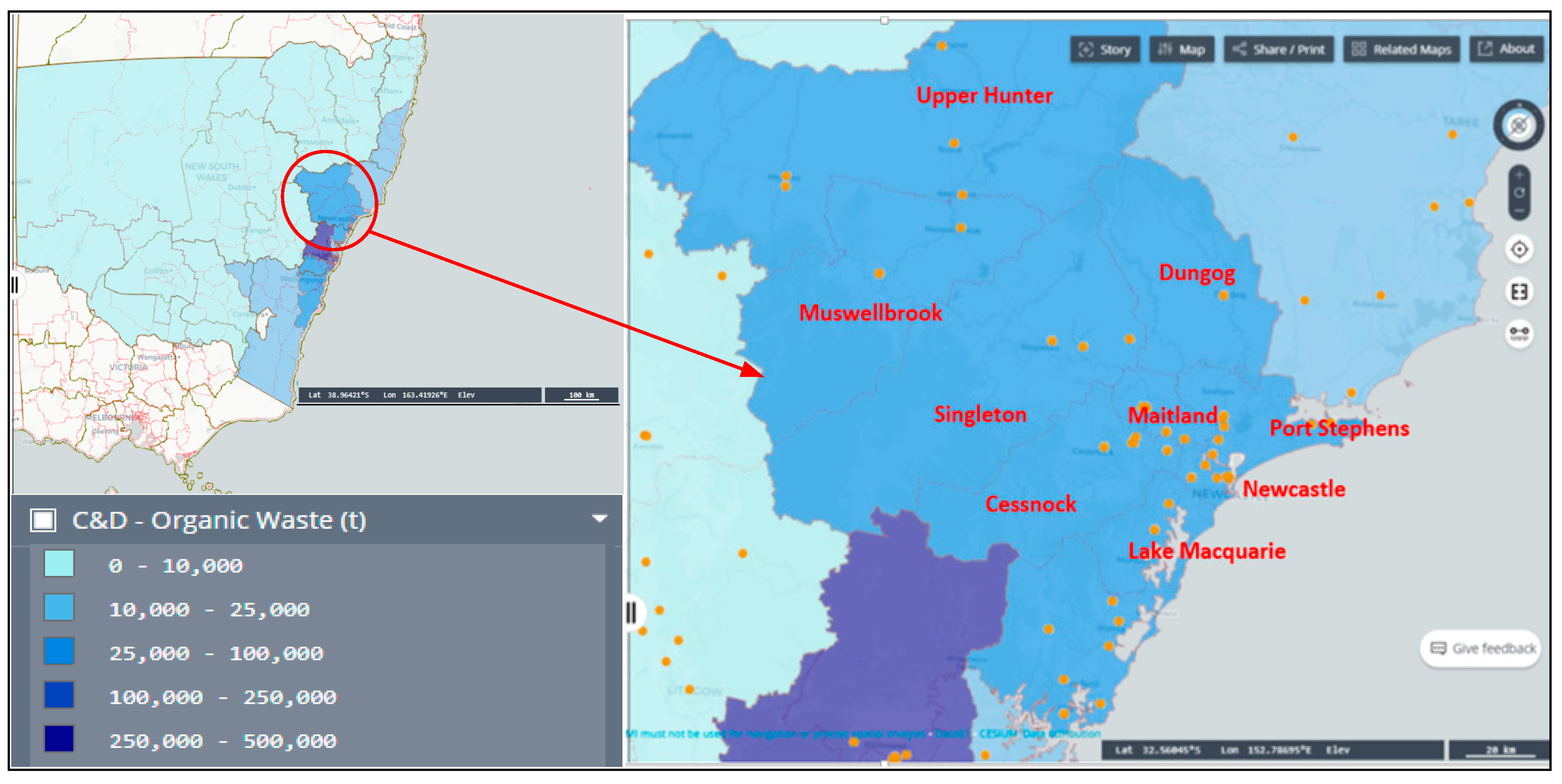
2.1. Study Area and Site Selection
2.2. Experimental Setting
2.3. Column Setup and Material of Construction
2.4. Leaching Column Composition and Packing
2.5. Leaching Fluid Preparation, Feeding, and Sampling
2.6. Determination of Heavy Metals and Major Cations
2.6.1. Sample Preparation
2.6.2. Apparatus
2.6.3. Reagents and Chemicals
2.6.4. Analysis of Heavy Metals and Cations (ICP-MS and ICP-OES)
2.6.5. Quality Control and Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
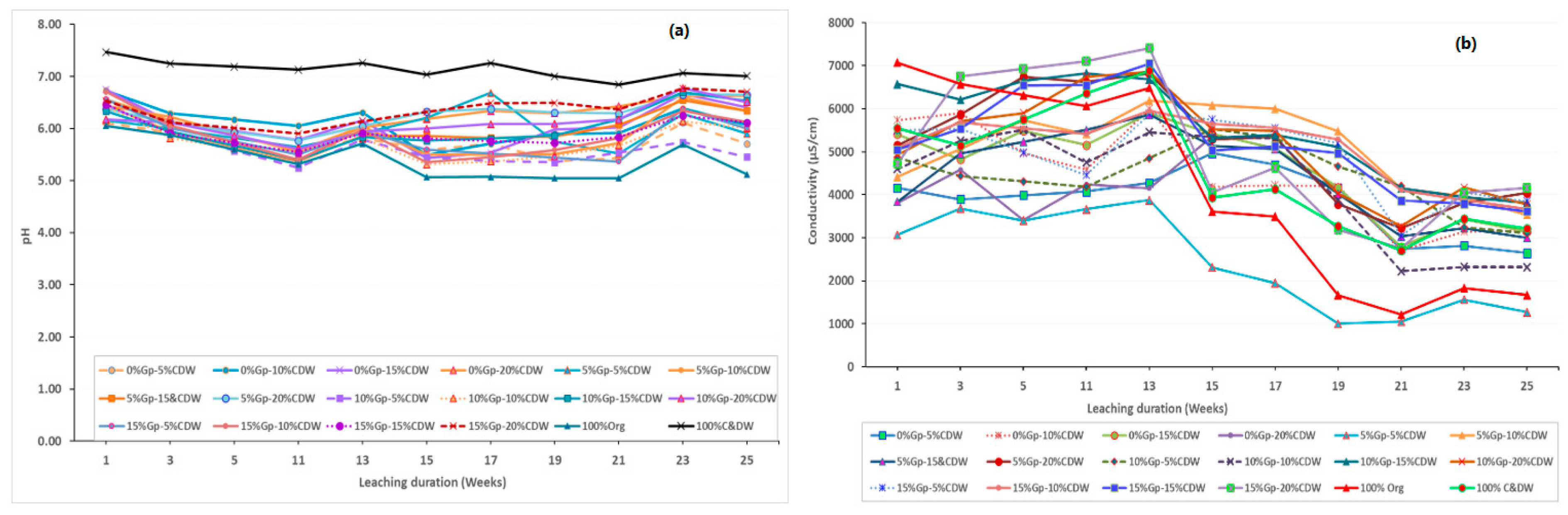
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Column Fill C&DW Fines
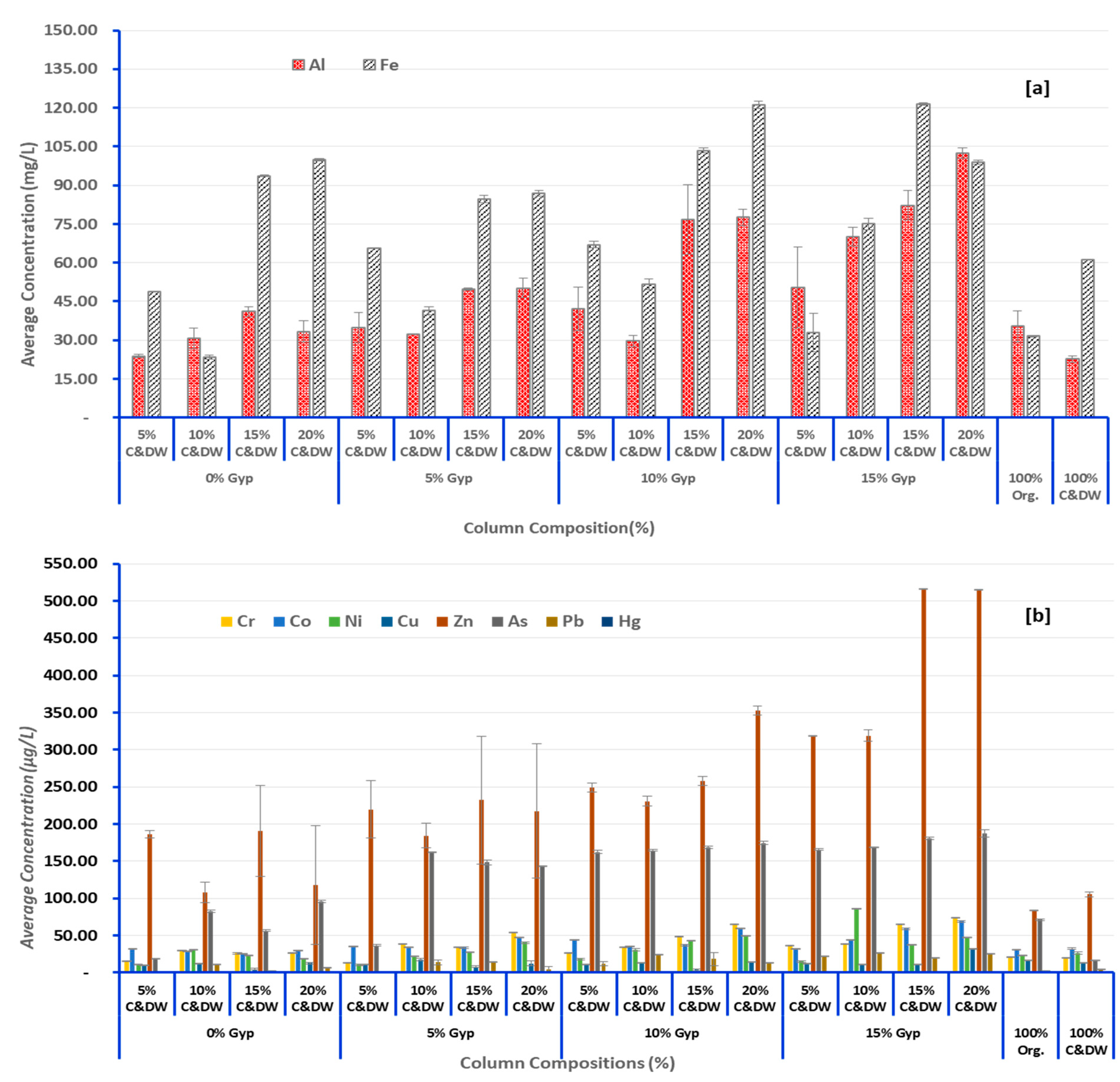
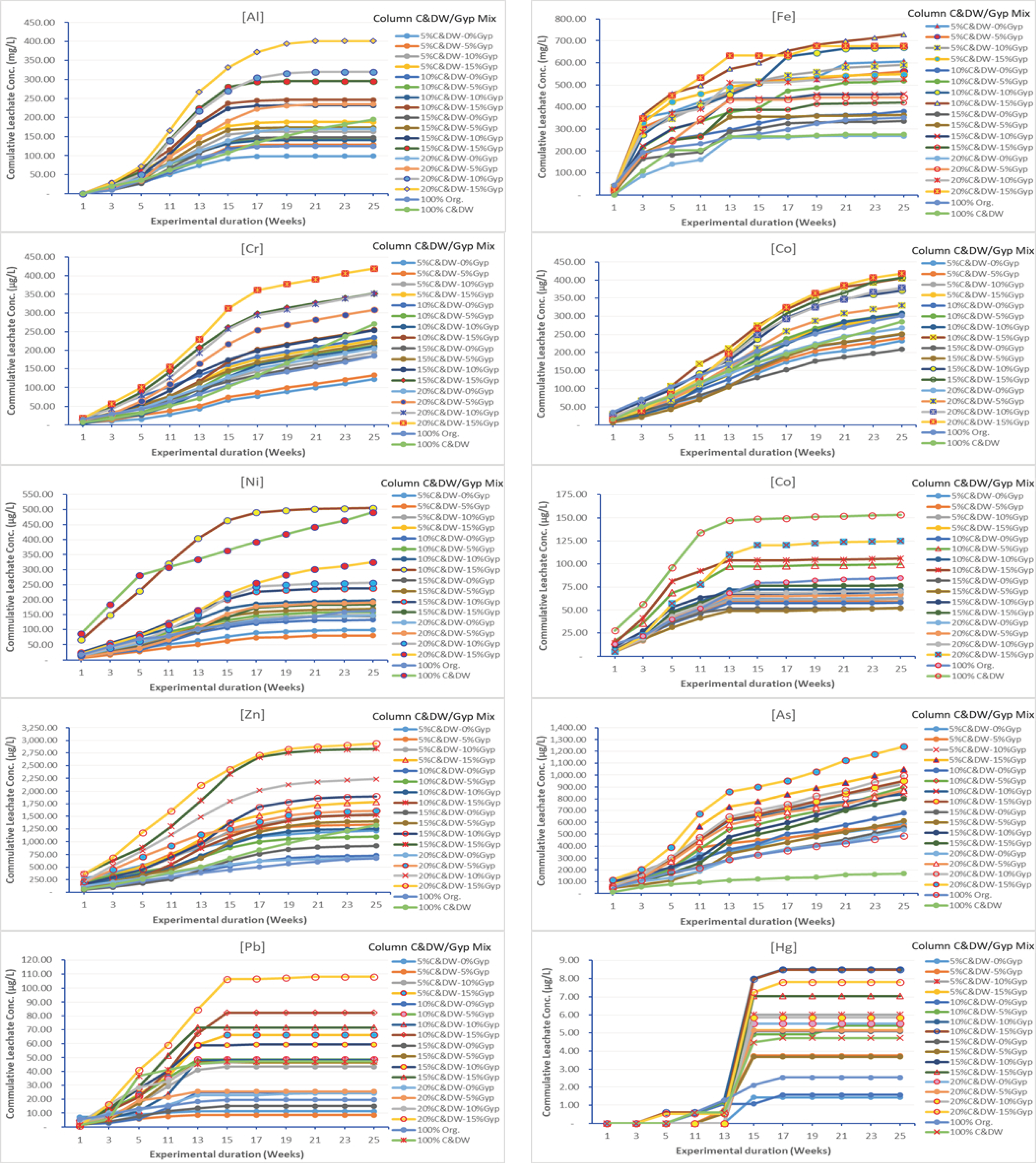
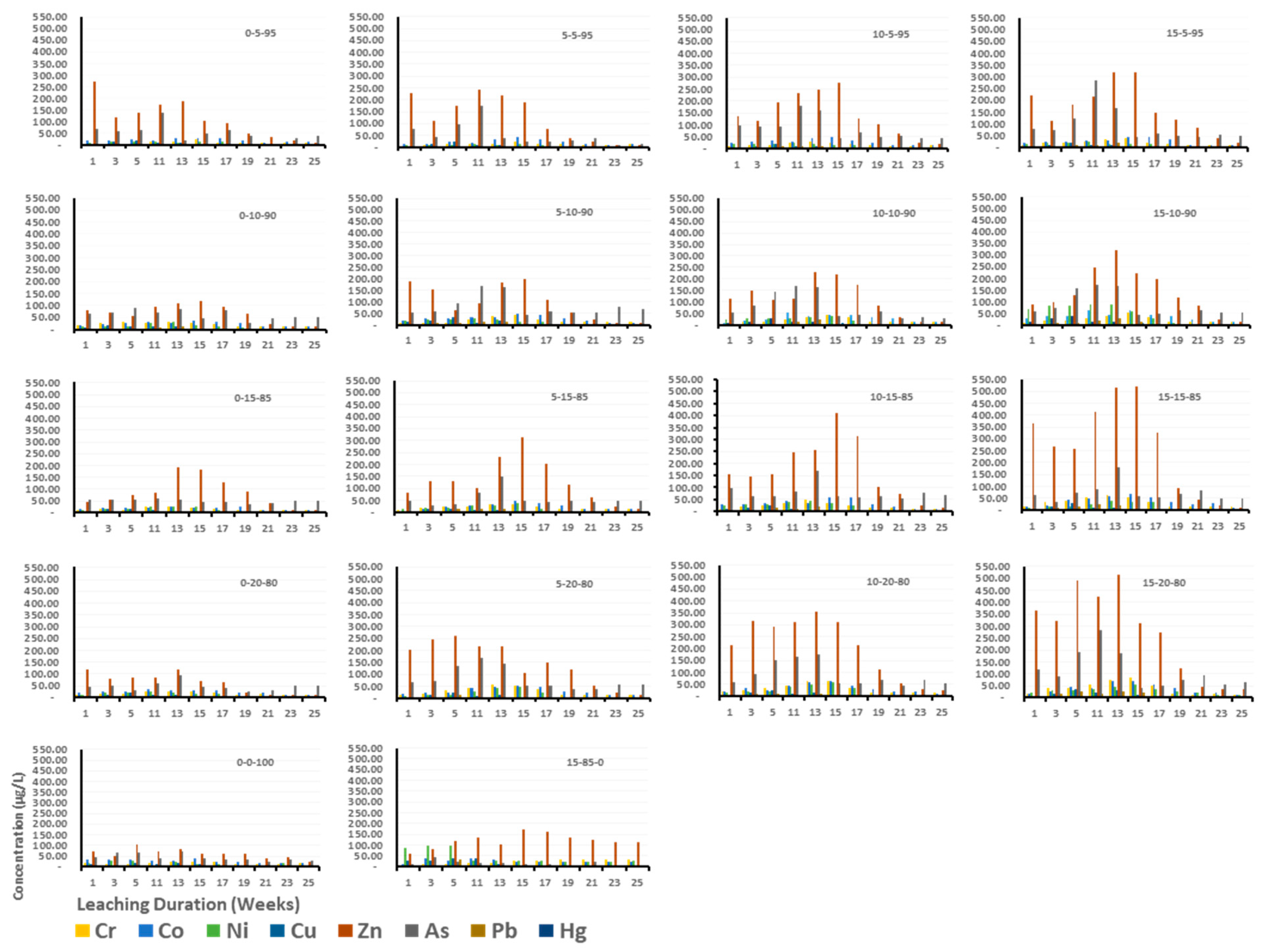
3.2. Heavy Metals of Concern Leached from C&DW
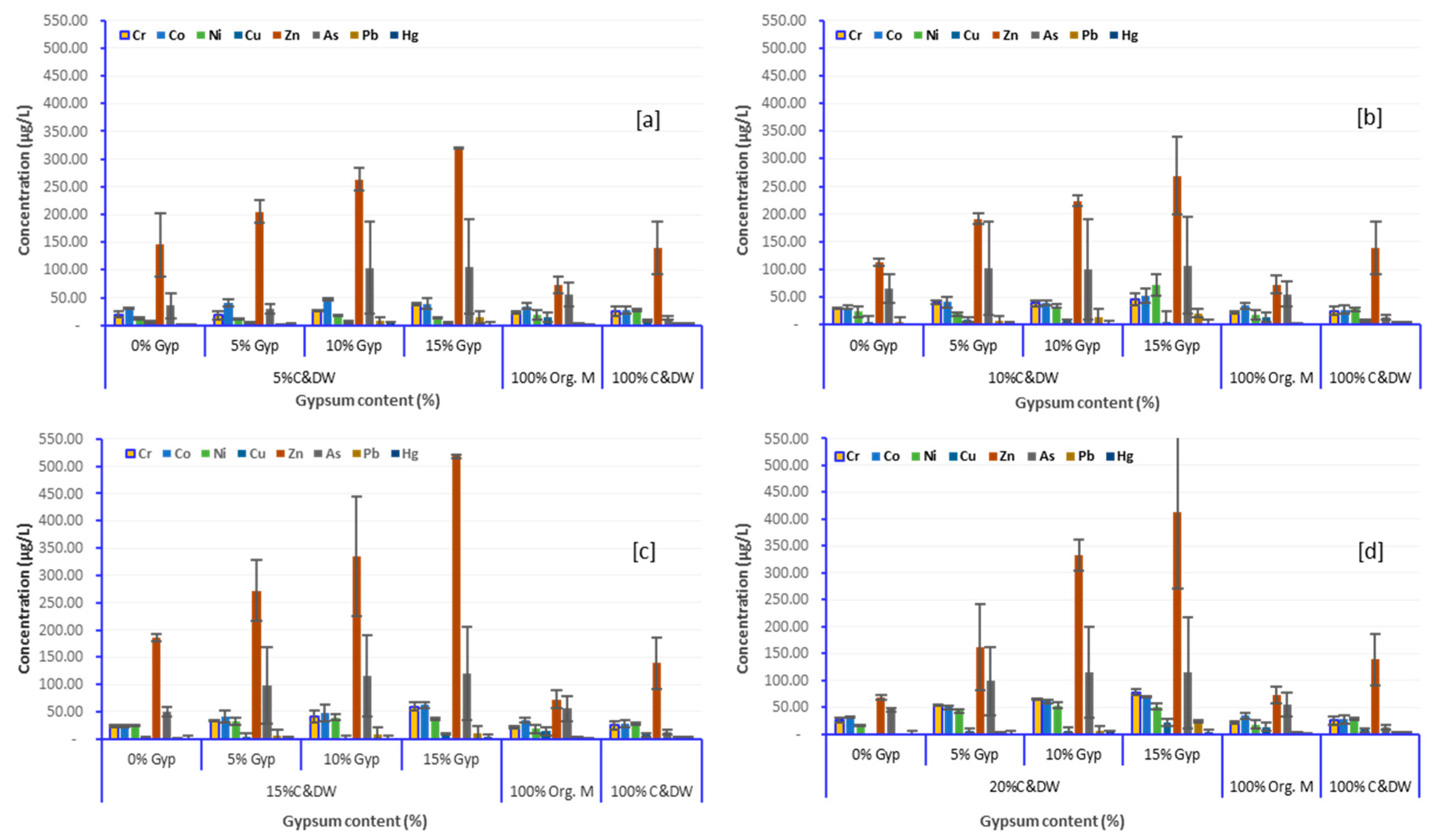
3.3. Effect of C&DW Content on the Concentration of Heavy Metals in the Leachate
3.4. Effect of Gypsum on Leaching Characteristics of Heavy Metals
4. Conclusions and Recommendation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABBA | Australian Biomass for Bioenergy Assessment |
| ARENA | Australian Renewable Energy Agency |
| C&DW | Construction and Demolition Waste |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Authority |
| GCER | Global Centre for Environmental Remediation |
| HPIC | High-Pressure Ion Chromatography |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectroscopy |
| MRF | Material Recovery Facility |
| MSW | Municipal Solid Waste |
| NIER | Newcastle Institute for Energy and Resources |
| NSW | New South Wales |
| ORS | Octapole Reaction System |
| ppt | Part per trillion |
| SCC | Specific Contaminant Concentration |
| SRB | Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria |
| TCLP | Toxicity Characteristics Leaching Procedure |
| UPVC | Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride |
References
- Ritchie, H.; Rodés-Guirao, L.; Mathieu, E.; Gerber, M.; Ortiz-Ospina, E.; Hasell, J.; Roser, M. Population Growth. 2024. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/population-growth?insight=the-unexpects-the-global-population-to-peak-by-the-end-of-the-century#article-citation (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Worldometers.info. World Population Clock: 8.12 Billion People (2024)—Worldometer. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/ (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Mo, K.H.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z. Structural performance of reinforced geopolymer concrete members: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, P.; Milić, V.; Brostrom, T. Balancing preservation and energy efficiency in building stocks. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 2019, 38, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehbaghi, K.; Rahmani, F.; Paterno, D. Sustainable concrete in transportation infrastructure: Australian case studies. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 829, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.H.; Poon, C.S. Properties of recycled aggregate concrete made with recycled aggregates with different amounts of old adhered mortars. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Chen, L.; Gharehbaghi, K. Sustainable utilization of recycled aggregates: Robust construction and demolition waste reduction strategies. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 2020, 39, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickin, J.; Wardle, C.; O’Farrell, K.; Nyunt, P.; Donovan, S. National Waste Report 2020; Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment, Ed.; Blue Environment Pty Ltd.: Docklands, VIC, Australia, 2020; p. 156. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Mohsen, K.; Abbas, R. Building information modeling (BIM) for construction and demolition waste management in Australia: A research agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Yu, D.F.; Zuo, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.K.; Niu, Y.N. Characterization of brominated flame retardants in construction and demolition waste components: HBCD and PBDEs. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingard, H.; Graham, P.; Smithers, G. Waste management in the Australian construction industry: A human factors approach. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual ARCOM Conference, Cambridge, UK, 15–17 September 1997; Volume 1, pp. 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Lingard, H.; Gilbert, G.; Graham, P. Improving solid waste reduction and recycling performance using goal setting and feedback. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2001, 19, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, T.; Yang, L. Evaluating the performance and intellectual structure of construction and demolition waste research during 2000–2016. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19259–19266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.; Fetherston, É.; Meyer, L.; Makled, T. Towards a Circular Plastics Economy: Policy Solutions for Closing the Loop on. Master’s Thesis, Center for Sustainabl e Systems, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.; Goto, H.; Matsuda, T. The impact of China’s tightening environmental regulations on international waste trade and logistics. Sustainability 2021, 13, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoostarain, S.; Maqsood, T.; Yang, R.; Khalfan, M.; Wong, P. The Impact of New International Waste Policies on the Australian Construction and Demolition Waste Stream. In Proceedings of the 44th AUBEA-Australasian Universities Building Education Association Conference, Geelong, VIC, Australia, 27–29 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, K. Impacts of China’s ‘Green Sword’ Policy on Australia’s Waste Disposal. HG Lawyers. Available online: https://www.hopgoodganim.com.au/page/knowledge-centre/blog/impacts-of-chinas-green-sword-policy-on-australias-waste-disposal (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Shooshtarian, S.; Maqsood, T.; Wong, P.S.P.; Malik, K.; Yang, R.J. Landfill levy imposition on construction and demolition waste: Australian stakeholders’ perceptions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahajwalla, V. Big challenges, micro solutions: Closing the loop in Australia’s waste crisis. AQ-Aust. Q. 2018, 89, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shooshtarian, S.; Maqsood, T.; Wong, P.S.P.; Malik, K.; Yang, R.J. Australian Construction and Demolition Waste Management System in Australia: Investigation of Challenges and Opportunities. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Miller, T.R.; Liu, G.; Tam, V.W.Y. Construction debris becomes growing concern of growing cities. Waste Manag. 2019, 83, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molla, A.S.; Tang, P.; Sher, W.; Bekele, D.N. Chemicals of concern in construction and demolition waste fine residues: A systematic literature review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delay, M.; Lager, T.; Schulz, H.D.; Frimmel, F.H. Comparison of leaching tests to determine and quantify the release of inorganic contaminants in demolition waste. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.-C.; Townsend, T. Sulfate leaching from recovered construction and demolition debris fines. Adv. Environ. Res. 2001, 5, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussat, N.; Méhu, J.; Abdelghafour, M.; Brula, P. Leaching behaviour of hazardous demolition waste. Nucl. Chem. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Townsend, T.G.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M. Landfill Disposal of CCA-Treated Wood with Construction and Demolition (C&D) Debris: Arsenic, Chromium, and Copper Concentrations in Leachate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5740–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, B.I.; Jambeck, J.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M.; Townsend, T.G.; Cai, Y. Release of Arsenic to the Environment from CCA-Treated Wood. 2. Leaching and Speciation during Disposal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Saraya, S.; Hwidong, K.; Brajesh, D.; Timothy, T. Mobilization of iron and arsenic from soil by construction and demolition debris landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, S.; Christensen, T.H.; Astrup, T.F. Composition and leaching of construction and demolition waste: Inorganic elements and organic compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.T.; Jain, P.; Smith, J.; Townsend, T.G.; Tolaymat, T.M. Does disposing of construction and demolition debris in unlined landfills impact groundwater quality? Evidence from 91 landfill sites in Florida. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9029–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New South Wales Government. Protection of the Environment Operations (Waste) Regulation 2014, Section 12(7)(c): Recovered Fines Alternative Daily Cover Specifications. 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.nsw.gov.au/sites/default/files/NSWGG.2019.5.24.G53.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- NSW-EPA. POEO Public Register, List of Licences. 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.nsw.gov.au/licensing-and-regulation/public-registers/about-prpoeo/list-of-licences (accessed on 17 August 2019).
- RENEW-NSW. Regional Networks for Effective Waste Management. Available online: https://www.riverinawaste.nsw.gov.au/renew-nsw/ (accessed on 17 August 2019).
- Cross, S. ‘Bridging the Gap’ to divert plasterboard from landfill and reduce project costs. In Waste Less, Recycle More Initiative; Cross Connections Consulting, Ed.; NSW EPA: Newcastle, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Renewable Energy Agency. Australian Renewable Energy Mapping Infrastructure. 13 August 2019. Available online: https://nationalmap.gov.au/renewables/ (accessed on 17 August 2019).
- ASTM D5231-92 (Reapproved 2016); Standard Test Methods for Determination of the Composition of Unprocessed Municipal Waste. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Lisa, D.; Anders, L. Methods for household waste composition studies. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AS 1141.5-2000; Methods for Sampling and Testing Aggregates. Australia Standard: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2000.
- EPA-Victoria. A Guide to the Sampling and Analysis of Waters, Wastewaters, Soils and Wastes; EPA-Victoria: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- AS 1289.1.1; Methods of Testing Soils for Engineering Purposes—Method 1.1: Sampling and Preparation of Soils—Preparation of Disturbed Soil Samples for Testing. Australia Standard: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2001.
- Chubaka, C.E.; Whiley, H.; Edwards, J.W.; Ross, K.E. A Review of Roof Harvested Rainwater in Australia. J. Environ. Public Health 2018, 2018, 6471324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulia, M.M.; Grace, M.V.; Richard, L.A.; Clare, D. Lead and other heavy metals: Common contaminants of rainwater tanks in Melbourne. In Water Down Under; Citeseer: University Park, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Government Bureau of Metereology. Climate Data Online. 2021. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/cdo/about/cdo-rainfall-feature.shtml#graphs (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Rayment, G.E.; Higginson, F.R. Australian Laboratory Handbook of Soil and Water Chemical Methods; Inkata Press Pty Ltd.: North Clayton, VIC, Australia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
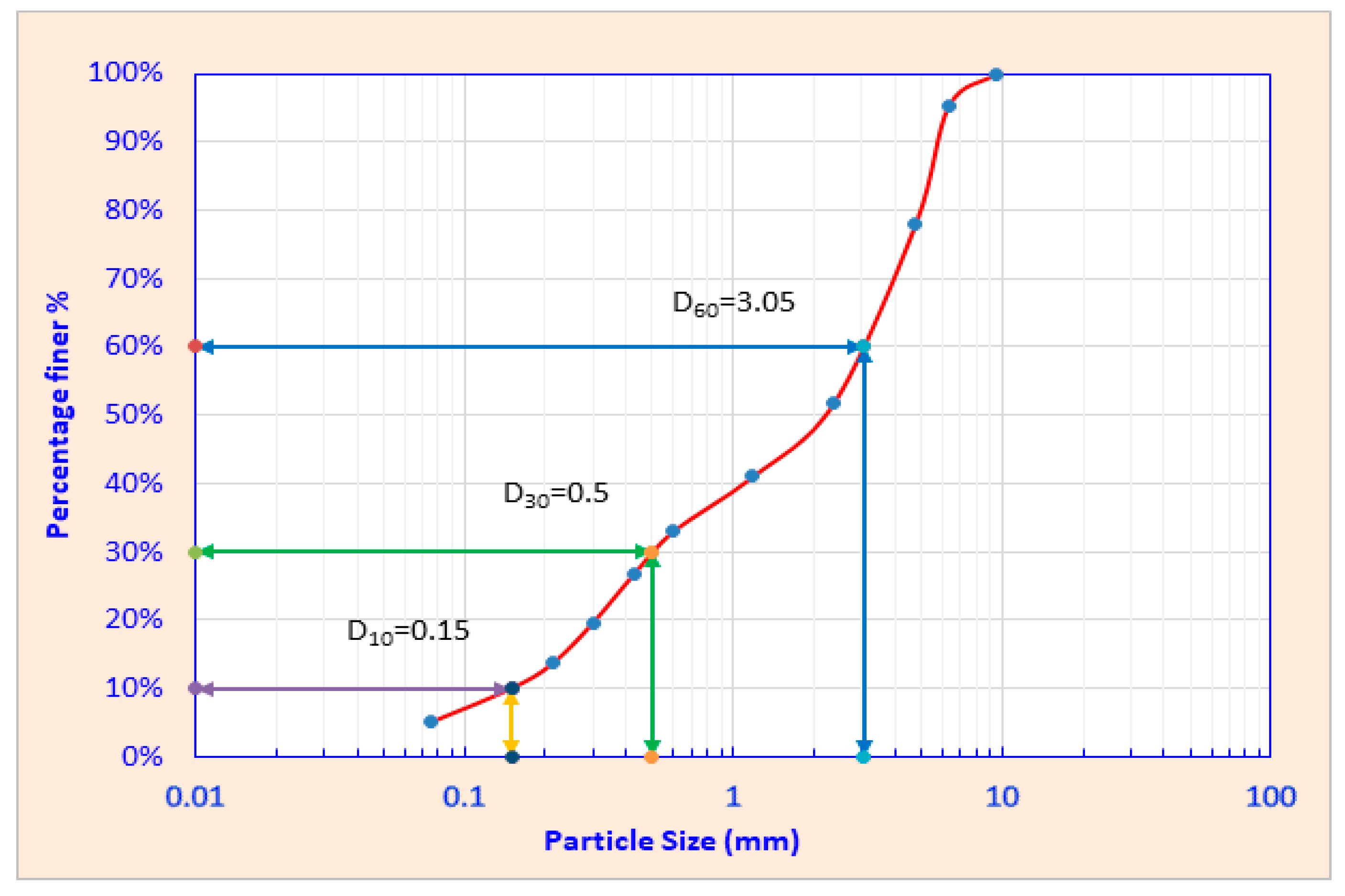
- AS 1289.3.6.1; Methods of Testing Soils for Engineering Purposes—Soil Classification Tests—Determination of the Particle Size Distribution of a Soil—Standard Method of Analysis by Sieving. Australia Standard: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2009.
- Dragomir, B.; Nicolae, C.M. Soil Characterization in Terms of Granularity and Uniformity. Ann. Univ. Craiova—Agric. Mont. Cadastre Ser. 2017, 47, 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Khater, S. Development of soil Particle size distribution model and determination of all related coefficients. Ann. Agric. Sci. Moshtohor 2023, 61, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Ono, Y.; Yamada, M.; Inoue, Y.; Alfaro, A.M. Characteristics of fine processed construction and demolition waste in Japan and method to obtain fines having low gypsum component and wood contents. Waste Manag. Res. 2010, 28, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lategano, E.; Costa, G.; Lombardi, F.; Baciocchi, R. Characterization of the bottom ash produced in a sanitary waste incineration facility and influence of the operating conditions aimed at material recovery or safe disposal. In Proceedings of the Sardinia 2007: Eleventh International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, Cagliari, Italy, 1–5 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, F.; Carvalho, M.T.; Evangelista, L.; De Brito, J. Physical–chemical and mineralogical characterization of fine aggregates from construction and demolition waste recycling plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 52, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AS 4439.3-1997; Wastes, Sediments and Contaminated Soils. Part 3. Preparation of Leachates—Bottle Leaching Procedure. Australia Standard: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1997.
- ASTM D4874-95; Standard Test Method for Leaching Solid Material in a Column Apparatus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Somasundaram, S.; Jeon, T.-W.; Kang, Y.-Y.; Kim, W.-I.; Jeong, S.-K.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yeon, J.-M.; Shin, S.K. Characterization of wastes from construction and demolition sector. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saca, N.; Dimache, A.; Radu, L.; Iancu, I. Leaching behavior of some demolition wastes. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2017, 19, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; O’Loughlin, E.J.; Kwon, M.J. Anaerobic microbial metabolism in soil columns affected by highly alkaline pH: Implication for biogeochemistry near construction and demolition waste disposal sites. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, B. Timber leachates prompt preservative review. Eng. Aust. 2003, 75, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Deborah, R. Report On Copper, Chromium and Arsenic (CCA) Treated Timber; ERMA New Zealand: Wellington, New Zealand, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pickin, J.; Randell, P.; Trinh, J.; Grant, B. National Waste Report 2018; Department of the Environment and Energy, Ed.; Blue Environment Pty Ltd.: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gallen, C.; Drage, D.; Kaserzon, S.; Baduel, C.; Gallen, M.; Banks, A.; Broomhall, S.; Mueller, J.F. Occurrence and distribution of brominated flame retardants and perfluoroalkyl substances in Australian landfill leachate and biosolids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 312, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Construction and demolition waste management in Korea: Recycled aggregate and its application. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kumara, G.; Matsuno, A.; Kawamoto, K. Neutralization of acid discharged water around the Kusatsu hot spring area in Japan using construction and demolition wastes. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pallewatta, S.; Weerasooriyagedara, M.; Bordoloi, S.; Sarmah, A.K.; Vithanage, M. Reprocessed construction and demolition waste as an adsorbent: An appraisal. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damrongsiri, S. Feasibility of using demolition waste as an alternative heavy metal immobilising agent. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.P.; Tubino, R. Potential evaluation of the use of construction and demolition waste (CDW) in the recovery of degraded soils by mining in Brazil. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2021, 12, 200060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyks, J.; Astrup, T.; Christensen, T.H. Leaching from MSWI bottom ash: Evaluation of non-equilibrium in column percolation experiments. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyks, J.; Astrup, T.; Christensen, T.H. Long-term leaching from MSWI air-pollution-control residues: Leaching characterization and modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.J. Development of a Consistent Geochemical Modelling Approach for Leaching and Reactive Transport Prosesses in Contaminated Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nakao, K.; Shakya, S.; Nozaki, T.; Inazumi, S. Neutralization Treatment for Recycling Construction-Generated Soils. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloot, H.A.v.d.; Zomeren, A.v. Characterisation Leaching Tests and Associated Geochemical Speciation Modelling to Assess Long Term Release Behaviour from Extractive Wastes. Mine Water Environ. 2012, 31, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quina, M.J.; Bordado, J.C.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M. The influence of pH on the leaching behaviour of inorganic components from municipal solid waste APC residues. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Cheng, Y.; He, D.; Yang, E.-H. Review of leaching behavior of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) ash. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NSW DECC. Waste Classification Guidelines–Part 1: Classifying Waste. 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.nsw.gov.au/sites/default/files/140796-classify-waste.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council; Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand. Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality; Volume 1, pp. 1–314. 2000. Available online: https://www.waterquality.gov.au/guidelines/anz-fresh-marine (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Gao, X.; Gu, Y.; Xie, T.; Zhen, G.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y. Characterization and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in construction and demolition wastes from five sources (chemical, metallurgical and light industries, and residential and recycled aggregates). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9332–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotti, A.; Perèz Galvin, A.; Piccinali, A.; Plizzari, G.; Sorlini, S. Chemical and Leaching Behavior of Construction and Demolition Wastes and Recycled Aggregates. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder Consulting; Encycle Consulting; Sustainable Resource Solutions. Hyder Consulting, Encycle Consulting, and Sustainable Resource Solutions, Management of Construction and Demolition Waste in Australia. In Construction and Demolition Waste Status Report; Department of Sustainablity, Environment, Water, Population and Communities: Canberra, Australia, 2011; p. 197. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.-C.; Townsend, T.G. Effect of Waste Depth on Leachate Quality from Laboratory Construction and Demolition Debris Landfills. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2003, 20, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Feng, Q.; Yue, R.; Chen, Z.; Moselhi, O.; Soliman, A.; Hammad, A.; An, C. Construction, renovation, and demolition waste in landfill: A review of waste characteristics, environmental impacts, and mitigation measures. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 46509–46526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryabeigi Zand, A. Assessing the influence of particle size and dissolved organic carbon on heavy metal leaching from construction and demolition waste modified with carbon-rich materials. Adv. Environ. Technol. 2024, 10, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotti, A.; Plizzari, G.; Sorlini, S. Leaching Behaviour of Construction and Demolition Wastes and Recycled Aggregates: Statistical Analysis Applied to the Release of Contaminants. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kim, H.; Dubey, B.; Townsend, T. Arsenic leaching and speciation in C&D debris landfills and the relationship with gypsum drywall content. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Praagh, M.; Modin, H. Leaching of chloride, sulphate, heavy metals, dissolved organic carbon and phenolic organic pesticides from contaminated concrete. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timothy, T.; Thabet, T.; Kevin, L.; Jenna, J. Heavy metals in recovered fines from construction and demolition debris recycling facilities in Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 332, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, T.; Choudhury, M.; Kundu, D.; Dutta, D.; Samanta, P. Landfill: An eclectic review on structure, reactions and remediation approach. Waste Manag. 2023, 164, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckbo, C.; Okkenhaug, G.; Hale, S.E. The effects of soil organic matter on leaching of hexavalent chromium from concrete waste: Batch and column experiments. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 309, 114708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinos, D.A.; Spagnoli, G. Utilization of waste products as alternative landfill liner and cover materials—A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 376–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, T.; Parry, D.L. Removal of sulfate and heavy metals by sulfate reducing bacteria in short-term bench scale upflow anaerobic packed bed reactor runs. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3379–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, F.; Xiang, X.; Hu, J.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Yin, H.; et al. Behavior and Mechanisms of Antimony Precipitation from Wastewater by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Toxics 2024, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Ma, Y.; Strong, P.J.; Clarke, W.P. Fluctuation of dissolved heavy metal concentrations in the leachate from anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste in commercial scale landfill bioreactors: The effect of pH and associated mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahedi, M.; Cetin, B.; Dayioglu, A.Y. Leaching behavior of aluminum, copper, iron and zinc from cement activated fly ash and slag stabilized soils. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 334–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukerche, I.; Djerad, S.; Benmansour, L.; Tifouti, L.; Saleh, K. Degradability of aluminum in acidic and alkaline solutions. Corros. Sci. 2014, 78, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-P.; Fu, C.-H.; Chen, P.-H.; Yu, R.-F. Dynamics of aluminum leaching from water purification sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217–218, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cho, D.-W.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Cao, X.; Hou, D.; Shen, Z.; Alessi, D.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Poon, C.S. Green remediation of As and Pb contaminated soil using cement-free clay-based stabilization/solidification. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Jordá, M.P.; Garrido, F.; García-González, M.T. Potential use of gypsum and lime rich industrial by-products for induced reduction of Pb, Zn and Ni leachability in an acid soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Lowry, G.V.; Hsu-Kim, H. Biogeochemical transformations of mercury in solid waste landfills and pathways for release. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2016, 18, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, A.; Lemouchi, C.; Enescu, M.; Gaillot, A.-C.; Lanson, M.; Magnin, V.; Glatzel, P.; Poulin, B.A.; Ryan, J.N.; Aiken, G.R.; et al. Formation of Mercury Sulfide from Hg(II)–Thiolate Complexes in Natural Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9787–9796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, P.; Banerjee, P.; Mondal, P.; Saha, N. Effect of heavy metals on fishes: Toxicity and bioaccumulation. J. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, D.; Maiti, S.K. Sources, bioaccumulation, health risks and remediation of potentially toxic metal(loid)s (As, Cd, Cr, Pb and Hg): An epitomised review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E. Bioaccumulation of non-essential hazardous heavy metals and metalloids in freshwater fish. Risk to human health. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaynab, M.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Ameen, A.; Sharif, Y.; Ali, L.; Fatima, M.; Khan, K.A.; Li, S. Health and environmental effects of heavy metals. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, L.Q.; Letcher, R.; Bradford, S.A.; Feng, X.; Rinklebe, J. Biogeochemical cycle of mercury and controlling technologies: Publications in critical reviews in environmental science & technology in the period of 2017–2021. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 4325–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Hongxia, D.; Wang, D. Mercury methylation by anaerobic microorganisms: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1893–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellal, J.; Guédron, S.; Huguet, L.; Schäfer, J.; Laperche, V.; Joulian, C.; Lanceleur, L.; Burnol, A.; Ghestem, J.-P.; Garrido, F.; et al. Mercury mobilization and speciation linked to bacterial iron oxide and sulfate reduction: A column study to mimic reactive transfer in an anoxic aquifer. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 180, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houlihan, M.; Bilgen, G.; Dayioglu, A.Y.; Aydilek, A.H. Geoenvironmental evaluation of RCA-stabilized dredged marine sediments as embankment material. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04020435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robey, N.M.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M.; Jones, A.S.; Marini, J.; Townsend, T.G. Metals content of recycled construction and demolition wood before and after implementation of best management practices. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafu, M.; Chohji, T. Leaching behaviour of impurities in waste gypsum board. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 102, 991–998. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, P.N.; Bousfield, S.; Summers, R.; Kirsch, E.J. Anaerobic digestion of organic matter. C R C Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 1974, 4, 131–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akfas, F.; Elghali, A.; Toubri, Y.; Samrane, K.; Munoz, M.; Bodinier, J.-L.; Benzaazoua, M. Environmental assessment of phosphogypsum: A comprehensive geochemical modeling and leaching behavior study. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 359, 120929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Molinari, S.; Dalconi, M.C.; Valentini, L.; Ricci, G.; Carrer, C.; Ferrari, G.; Artioli, G. The leaching behaviors of lead, zinc, and sulfate in pyrite ash contaminated soil: Mineralogical assessments and environmental implications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi; Prakash, N.B.; Dhumgond, P.; Goiba, P.K.; Laxmanarayanan, M. The benefits of gypsum for sustainable management and utilization of acid soils. Plant Soil 2024, 504, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Duan, Y.; Lu, J.; Gupta, R.; Pudasainee, D.; Liu, S.; Liu, M.; Lu, J. Thermal stability, chemical speciation and leaching characteristics of hazardous trace elements in FGD gypsum from coal-fired power plants. Fuel 2018, 231, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, R.; El Samrani, A.G.; Kazpard, V.; Bassil, J.; Lartiges, B.; Saad, Z.; Chou, L. Applying physicochemical approaches to control phosphogypsum heavy metal releases in aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 9014–9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaslioti, E.-M.; Pérez-López, R.; Parviainen, A.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Nieto, J.M.; Marchesi, C.; Delgado-Huertas, A.; Garrido, C.J. Effects of seawater mixing on the mobility of trace elements in acid phosphogypsum leachates. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Tian, C.; Li, L.; Liang, Y.; Yan, S.; Hu, M.; Xu, W.; Lin, Z.; Chai, L. Microinteraction Analysis between Heavy Metals and Coexisting Phases in Heavy Metal Containing Solid Wastes. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coudray, C.; Amant, V.; Cantegrit, L.; Le Bocq, A.; Thery, F.; Denot, A.; Eisenlohr, L. Influence of Crushing Conditions on Recycled Concrete Aggregates (RCA) Leaching Behaviour. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 2867–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurhanim, A.; Norli, I.; Morad, N.; Khalil, H. Leaching behavior of construction and demolition waste (concrete and gypsum). Iran. J. Energy Environ. 2016, 7, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Tayibi, H.; Choura, M.; López, F.A.; Alguacil, F.J.; López-Delgado, A. Environmental impact and management of phosphogypsum. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chang, H.; Lee, J. Construction and demolition waste management and its impacts on the environment and human health: Moving forward sustainability enhancement. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 115, 105855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
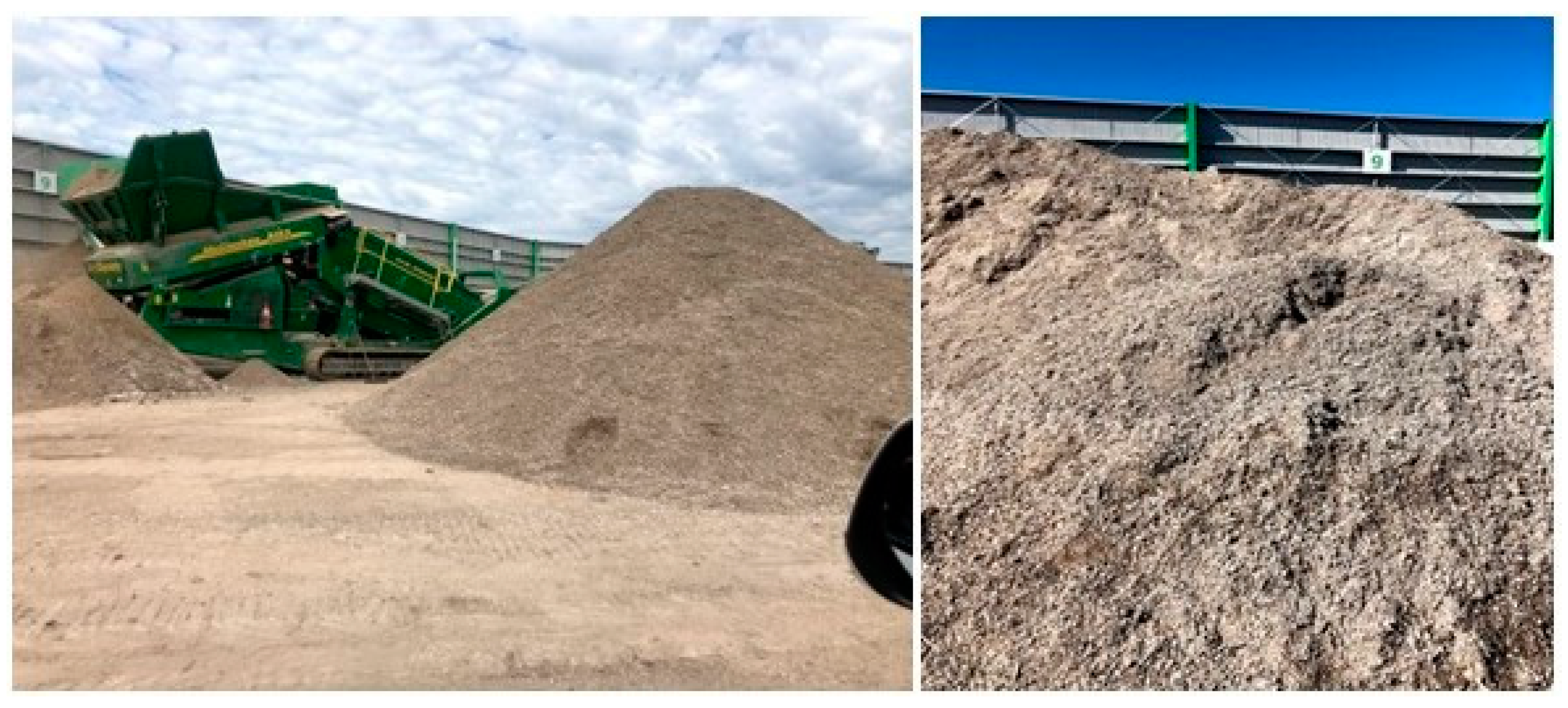
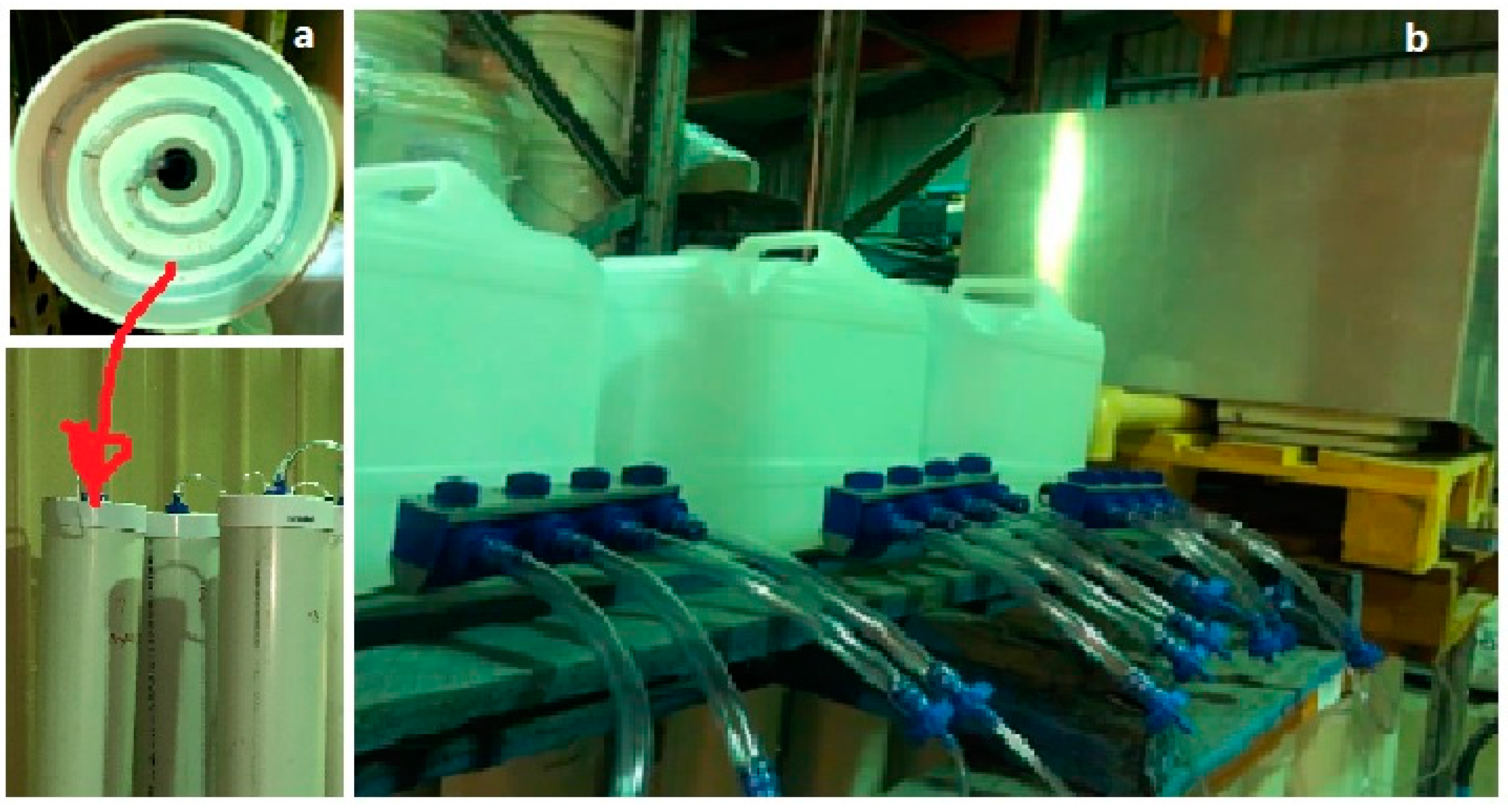
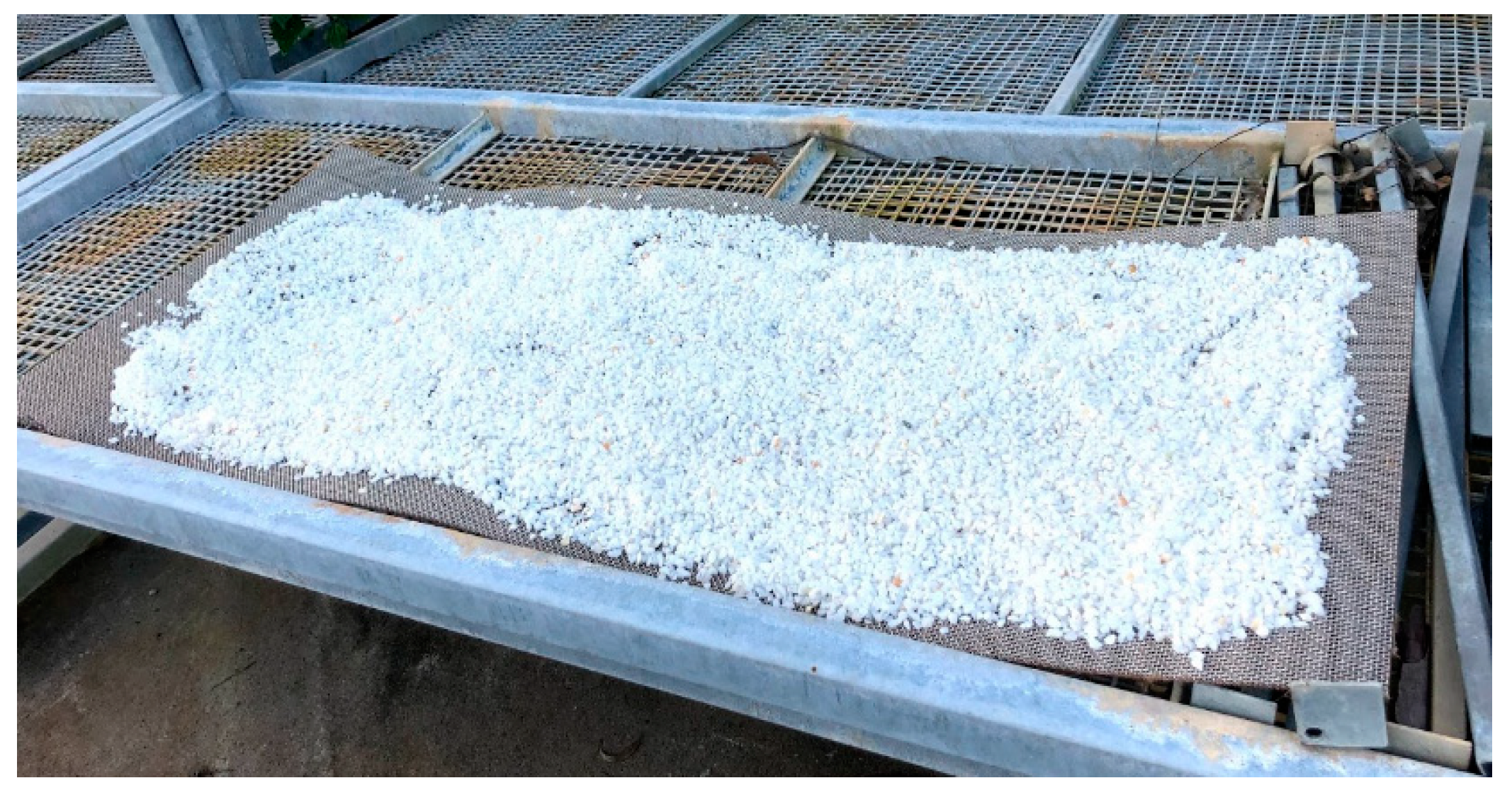
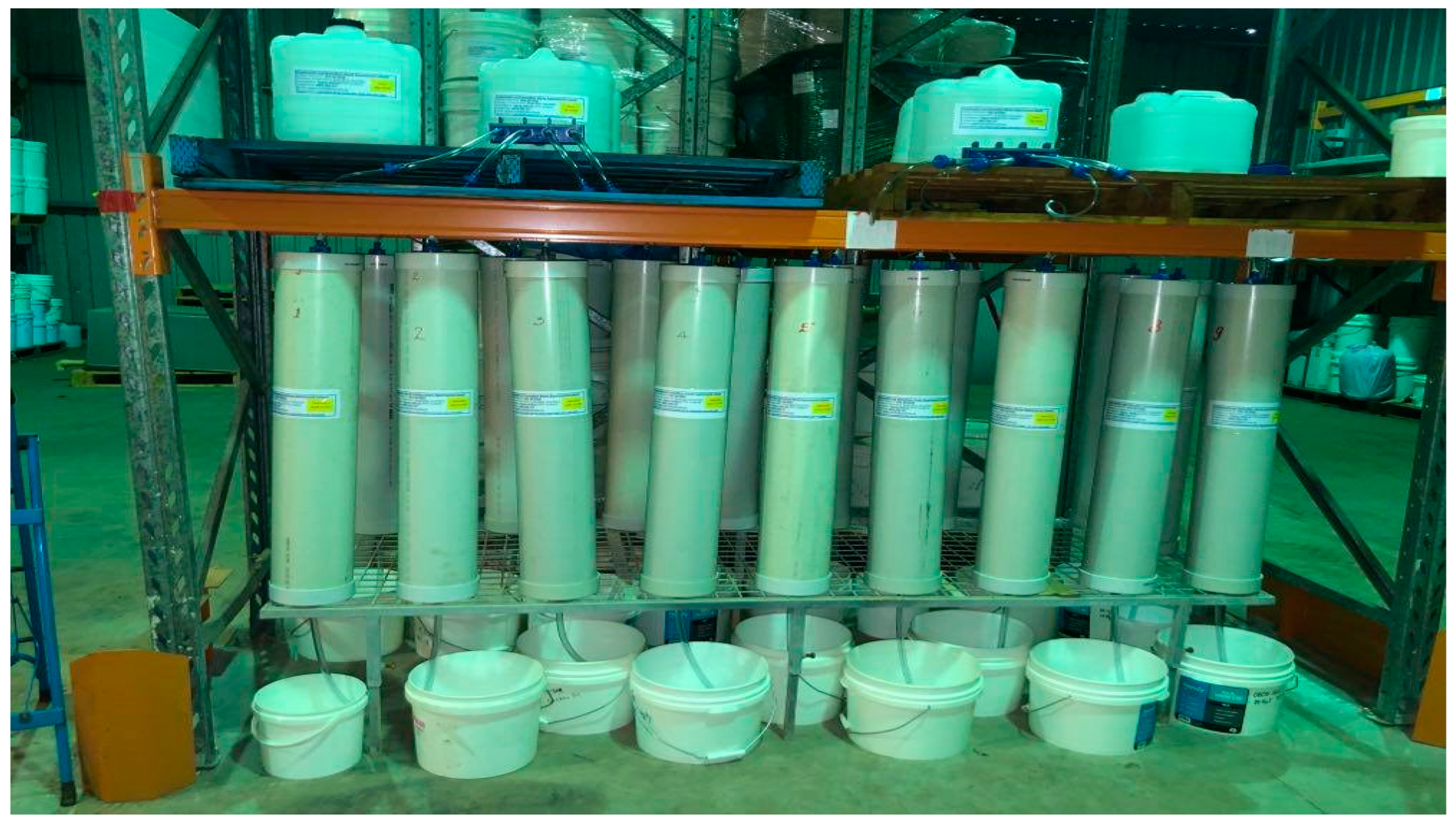



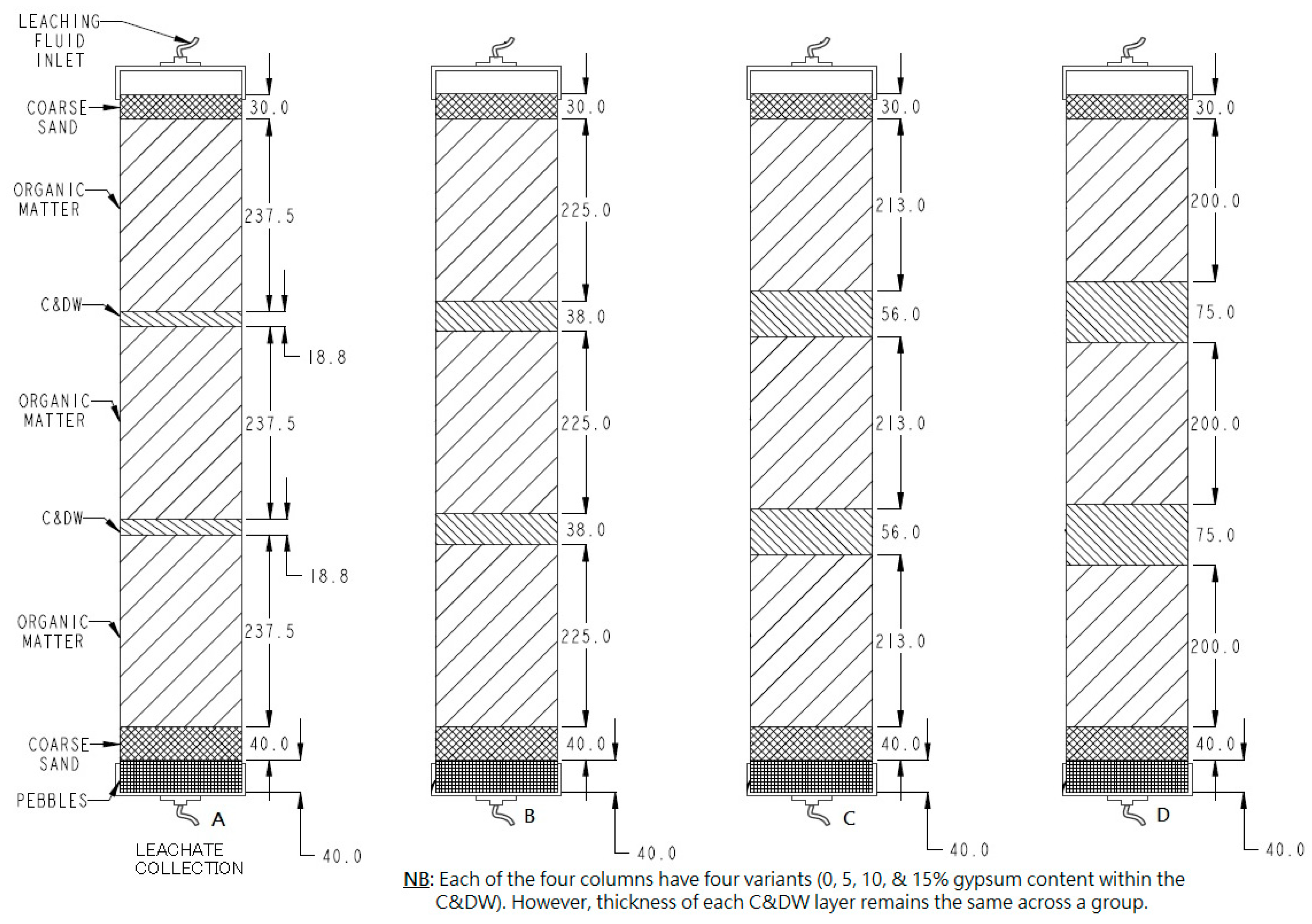

| Column ID No. | C&DW Content (%) | Gypsum Content (Gyp %) | Max. Organic Content (Org %) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–4 | 5 | 0, 5, 10 and 15 | 95% | Test columns |
| 5–8 | 10 | 90% | Test columns | |
| 9–12 | 15 | 85% | Test columns | |
| 13–16 | 20 | 80% | Test columns | |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 100 | Control-Org |
| 18 | 85 | 15 | 0 | Control-C&DW |
| Column Fill (%) | Metal Concentration, ±STDVE | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C&DW | Gypsum | Al * [20] | Fe * [20] | Cr * [100] | Co * [1000] | Ni * [2000] | Cu * [200] | Zn * [20,0] | As ** [5000] | Pb ** [5000] | Hg ** [200] |
| 5% C&DW | 0 | 23.9 ± 0.77 | 48.8 ± 0.04 | 15.2 ± 0.36 | 31.8 ± 0.42 | 11.2 ± 0.42 | 10.0 ± 0.45 | 186.4 ± 4.63 | 18.8 ± 0.29 | 0.9 ± 0.80 | <RL ± 0.03 |
| 5 | 34.9 ± 5.87 | 65.7 ± 0.00 | 13.2 ± 0.32 | 35.3 ± 0.35 | 10.4 ± 0.21 | 11.0 ± 0.41 | 219.5 ± 14.24 | 36.6 ± 1.66 | 1.1 ± 0.22 | 0.7 ± 0.00 | |
| 10 | 42.2 ± 8.28 | 67.0 ± 1.37 | 27.4 ± 0.86 | 44.8 ± 0.14 | 18.2 ± 0.09 | 11.8 ± 0.74 | 249.0 ± 61.00 | 162.2 ± 0.83 | 12.0 ± 0.04 | 0.6 ± 0.01 | |
| 15 | 50.4 ±15.64 | 32.9 ±7.52 | 36.7 ± 0.17 | 31.8 ± 0.48 | 15.1 ± 0.03 | 12.4 ± 0.85 | 319.3 ± 80.37 | 165.8 ± 1.80 | 22.7 ± 0.06 | <RL ± 0.00 | |
| 10% C&DW | 0 | 30.7 ± 4.03 | 23.5 ± 0.90 | 30.4 ± 0.23 | 28.9 ± 0.32 | 31.0 ± 0.83 | 12.1 ± 0.32 | 108.0 ± 38.54 | 83.0 ± 1.22 | 11.0 ± 0.13 | 0.5 ± 0.01 |
| 5 | 32.3 ± 0.10 | 41.4 ± 1.59 | 38.3 ± 0.40 | 34.3 ± 0.36 | 21.8 ± 0.86 | 17.7 ± 1.34 | 184.6 ± 16.81 | 162.4 ± 0.64 | 13.7 ± 3.12 | 0.6 ± 0.00 | |
| 10 | 29.7 ± 2.17 | 51.6 ± 2.06 | 34.2 ± 0.43 | 36.0 ± 1.04 | 31.0 ± 0.22 | 12.9 ± 0.97 | 230.6 ± 86.23 | 164.5 ± 3.20 | 24.6 ± 0.94 | 0.7 ± 0.01 | |
| 15 | 70.1 ± 3.75 | 75.1 ± 2.24 | 39.1 ± 0.01 | 44.0 ± 0.46 | 85.7 ± 1.07 | 11.5 ± 3.47 | 319.0 ± 90.43 | 168.7 ± 0.76 | 26.8 ± 4.36 | <RL ± 0.03 | |
| 15% C&DW | 0 | 41.1 ± 1.93 | 93.6 ± 0.28 | 25.9 ± 0.01 | 25.1 ± 0.29 | 24.0 ± 0.73 | 4.8 ± 0.05 | 190.6 ± 6.27 | 56.6 ± 2.14 | 2.2 ± 3.09 | <RL ± 0.01 |
| 5 | 49.8 ± 0.55 | 84.6 ± 1.52 | 33.8 ± 0.27 | 34.0 ± 0.28 | 27.3 ± 1.40 | 8.0 ± 0.46 | 232.2 ± 6.53 | 148.4 ± 1.32 | 14.1 ± 0.62 | 0.5 ± 0.00 | |
| 10 | 76. 8 ±13.39 | 103.4 ± 0.91 | 48.4 ± 0.54 | 37.2 ± 1.15 | 43.2 ± 0.26 | 4.0 ± 0.83 | 257.9 ± 5.76 | 168.6 ± 1.21 | 18.2 ± 8.63 | <RL ± 0.05 | |
| 15 | 82.2 ± 5.63 | 121.4 ± 0.37 | 64.7 ± 0.05 | 59.0 ± 0.39 | 37.8 ± 0.09 | 11. 6 ± 0.10 | 516.0 ± 6.53 | 181.0 ± 1.74 | 20.1 ± 0.56 | <RL ± 0.00 | |
| 20% C&DW | 0 | 33.4 ± 4.19 | 100.0 ± 0.46 | 26.9 ± 0.21 | 30.0 ± 0.52 | 19.5 ± 1.07 | 12.7 ± 0.15 | 117.9 ± 0.43 | 96.2 ± 1.00 | 7.3 ± 0.02 | <RL ± 0.02 |
| 5 | 50.2 ± 3.73 | 86.8 ± 1.14 | 54.8 ± 0.12 | 46.9 ± 0.43 | 40.4 ± 0.84 | 12.2 ± 0.13 | 217.6 ± 7.66 | 143.2 ± 0.41 | 4.1 ± 0.13 | <RL ± 0.01 | |
| 10 | 77.6 ± 3.14 | 121.1 ± 1.38 | 65.9 ± 0.31 | 59.3 ± 0.93 | 49.9 ± 0.19 | 14.2 ± 0.10 | 352.8 ± 0.61 | 174.7 ± 1.60 | 12.8 ± 0.05 | <RL ± 0.02 | |
| 15 | 102.4 ±2.03 | 98.9 ± 0.73 | 73.7 ± 0.37 | 69.1 ± 1.21 | 47.0 ± 0.38 | 31.9 ± 0.08 | 514.8 ± 0.31 | 187.2 ± 4.84 | 25.5 ± 0.33 | <RL ± 0.00 | |
| 100% Org. W | 26.4 ± 35.37 | 6.0 ± 31.57 | 0.0 ± 20.81 | 0.4 ± 20.81 | 0.2 ± 30.94 | 0.2 ± 24.06 | 0.0 ± 16.73 | 0.0 ± 83.79 | 0.6 ± 71.26 | 1.2 ± 2.95 | |
| 100% C&DW | 23.1 ± 22.73 | 1.3 ± 61.27 | 0.0 ± 19.61 | 0.1 ± 19.61 | 0.2 ± 32.39 | 0.7 ± 26.00 | 1.8 ± 13.15 | 0.3 ± 105.37 | 3.0 ± 16.21 | 0.4 ± 4.22 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molla, A.S.; Tang, W.; Sher, W.; Bahar, M.M.; Bekele, D.N. The Effects of Construction and Demolition Waste (C&DW) Fine Residues on Landfill Environments: A Column Leaching Experiment. Toxics 2025, 13, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050370
Molla AS, Tang W, Sher W, Bahar MM, Bekele DN. The Effects of Construction and Demolition Waste (C&DW) Fine Residues on Landfill Environments: A Column Leaching Experiment. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050370
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolla, Adane S., Waiching Tang, Willy Sher, Md Mezbaul Bahar, and Dawit Nega Bekele. 2025. "The Effects of Construction and Demolition Waste (C&DW) Fine Residues on Landfill Environments: A Column Leaching Experiment" Toxics 13, no. 5: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050370
APA StyleMolla, A. S., Tang, W., Sher, W., Bahar, M. M., & Bekele, D. N. (2025). The Effects of Construction and Demolition Waste (C&DW) Fine Residues on Landfill Environments: A Column Leaching Experiment. Toxics, 13(5), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050370