Acrolein-Triggered Ferroptosis and Protection by Intermittent Fasting via the AMPK/NRF2-CLOCK/BMAL1 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. Western Blot Analysis
2.3. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.4. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Assay
2.5. siRNA and Plasmid Transfection
2.6. In Vivo Studies
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
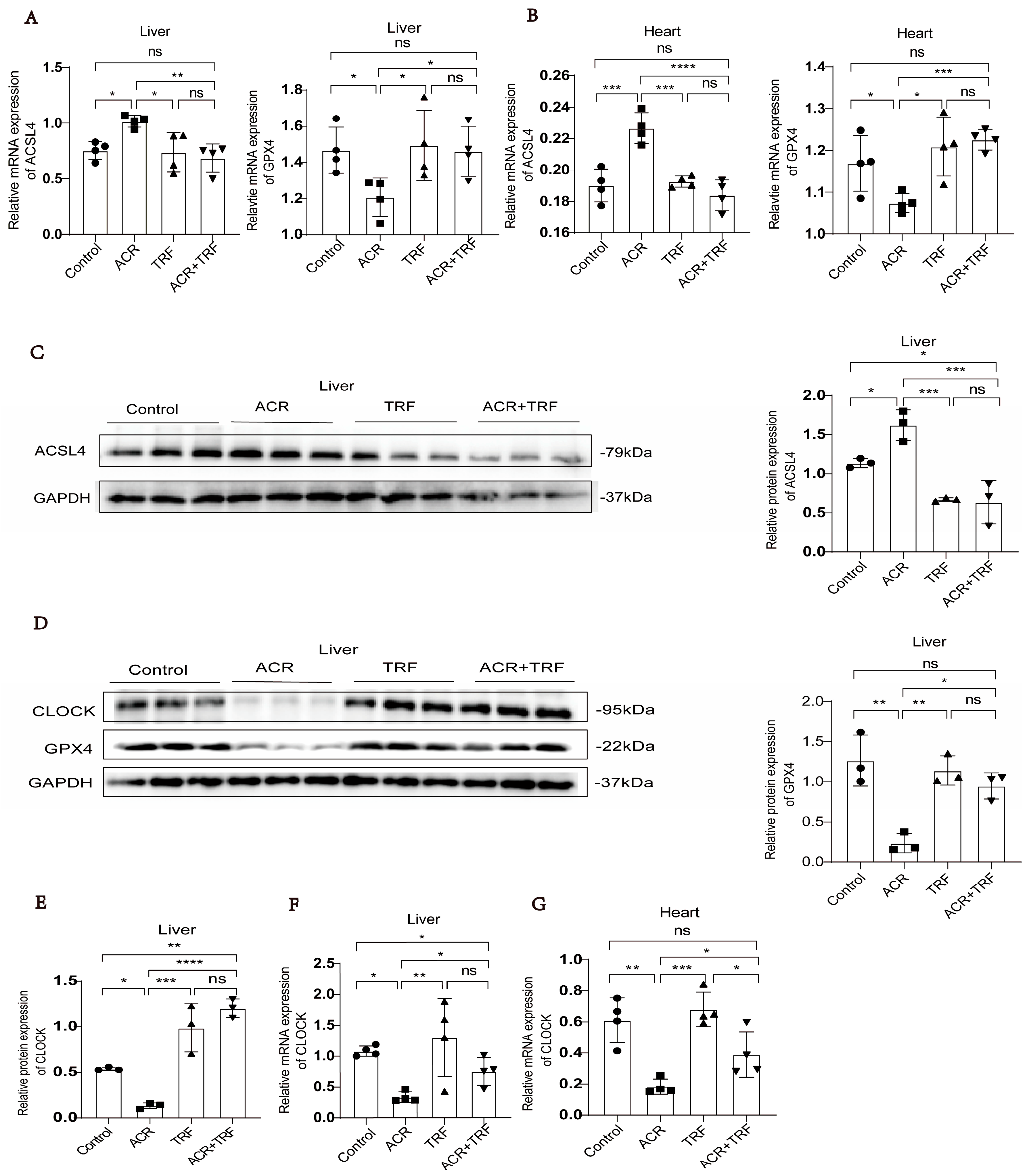
3.1. IF Attenuates Acrolein-Induced Ferroptosis and Low Expression of CLOCK In Vivo
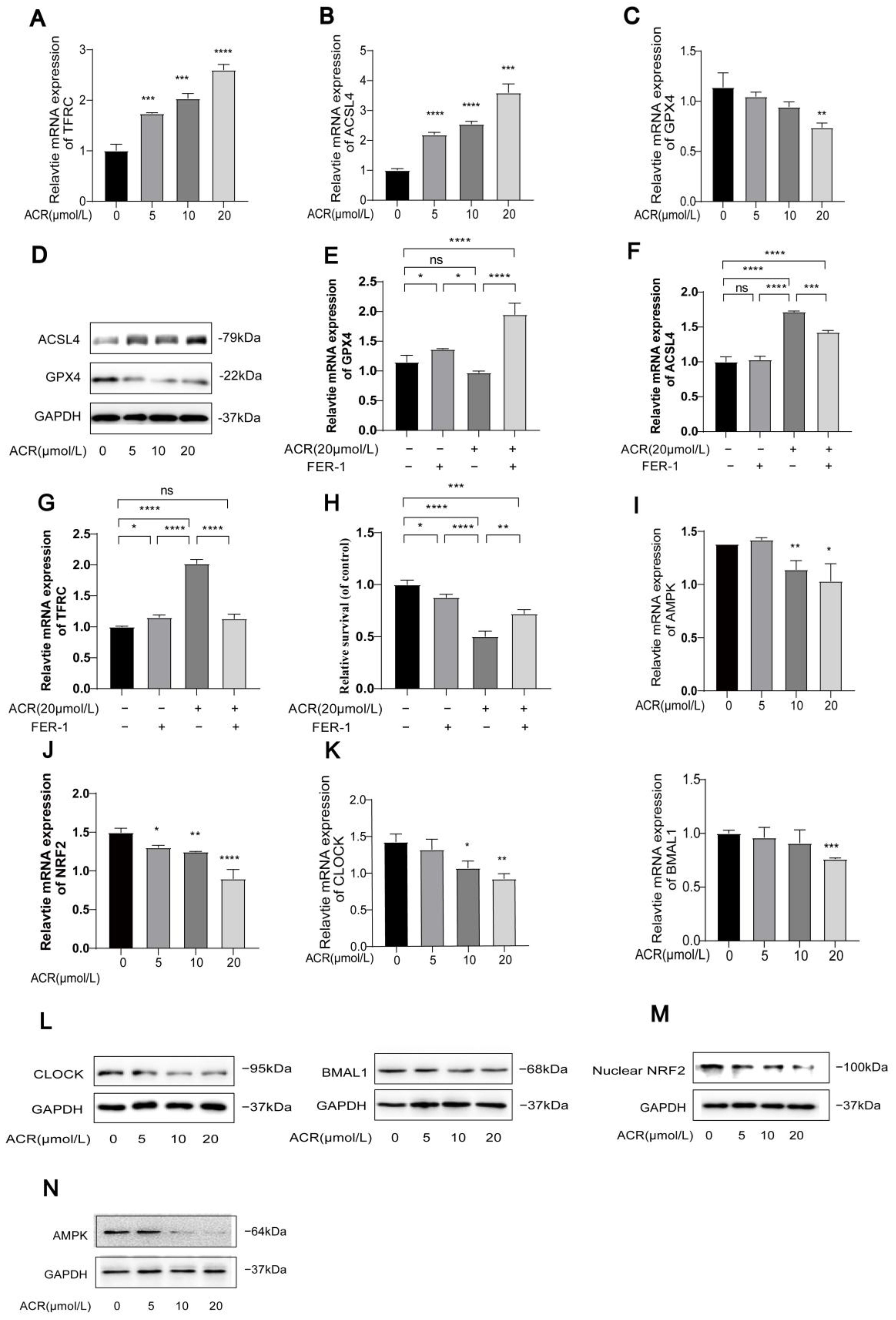
3.2. Acrolein Induces Ferroptosis and Inhibits the Expression of AMPK/NRF2 and CLOCK/BMAL1 in HUVECs
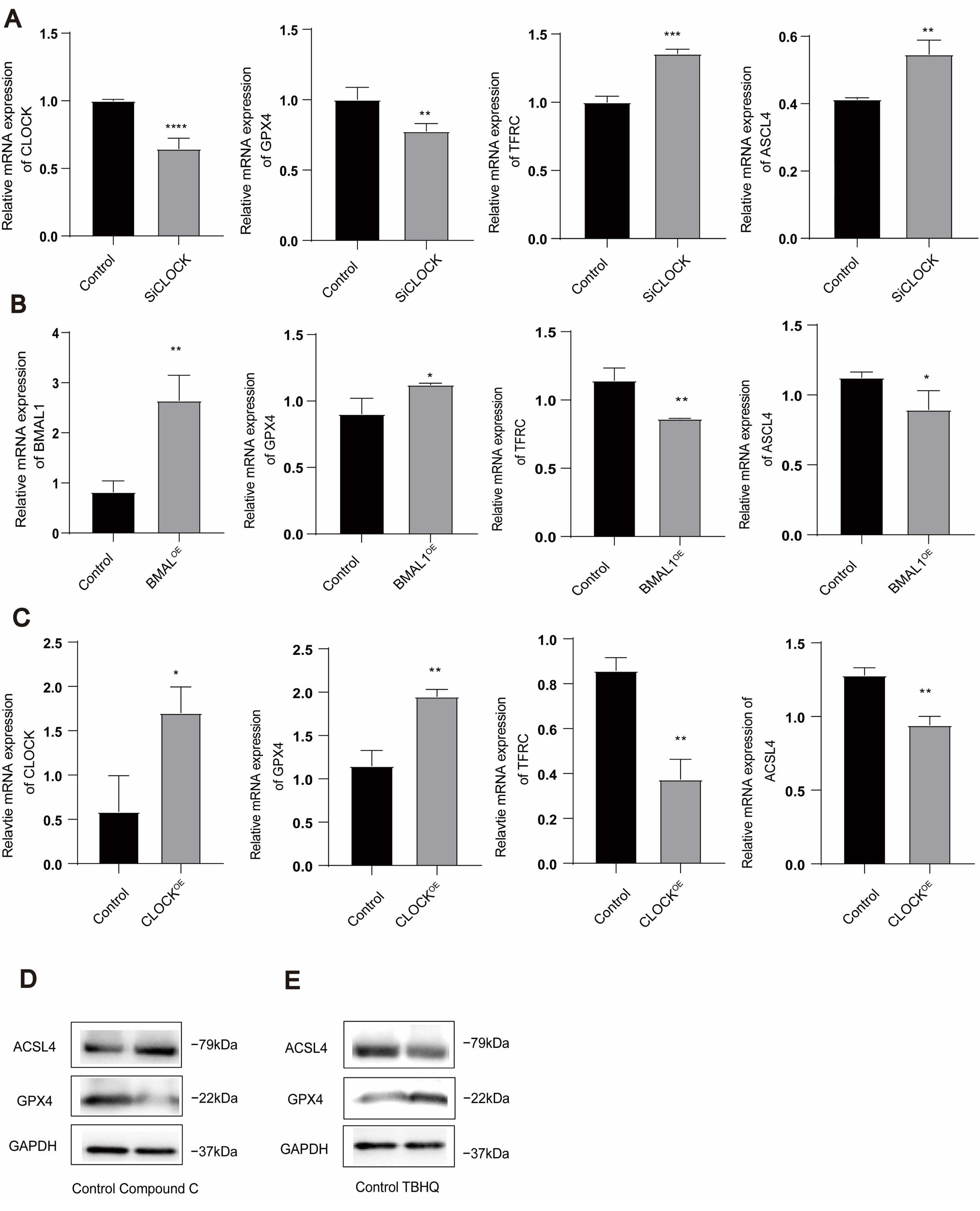
3.3. AMPK/NRF2 and CLOCK/BMAL1 Genes Are Involved in the Regulation of Ferroptosis in HUVECs
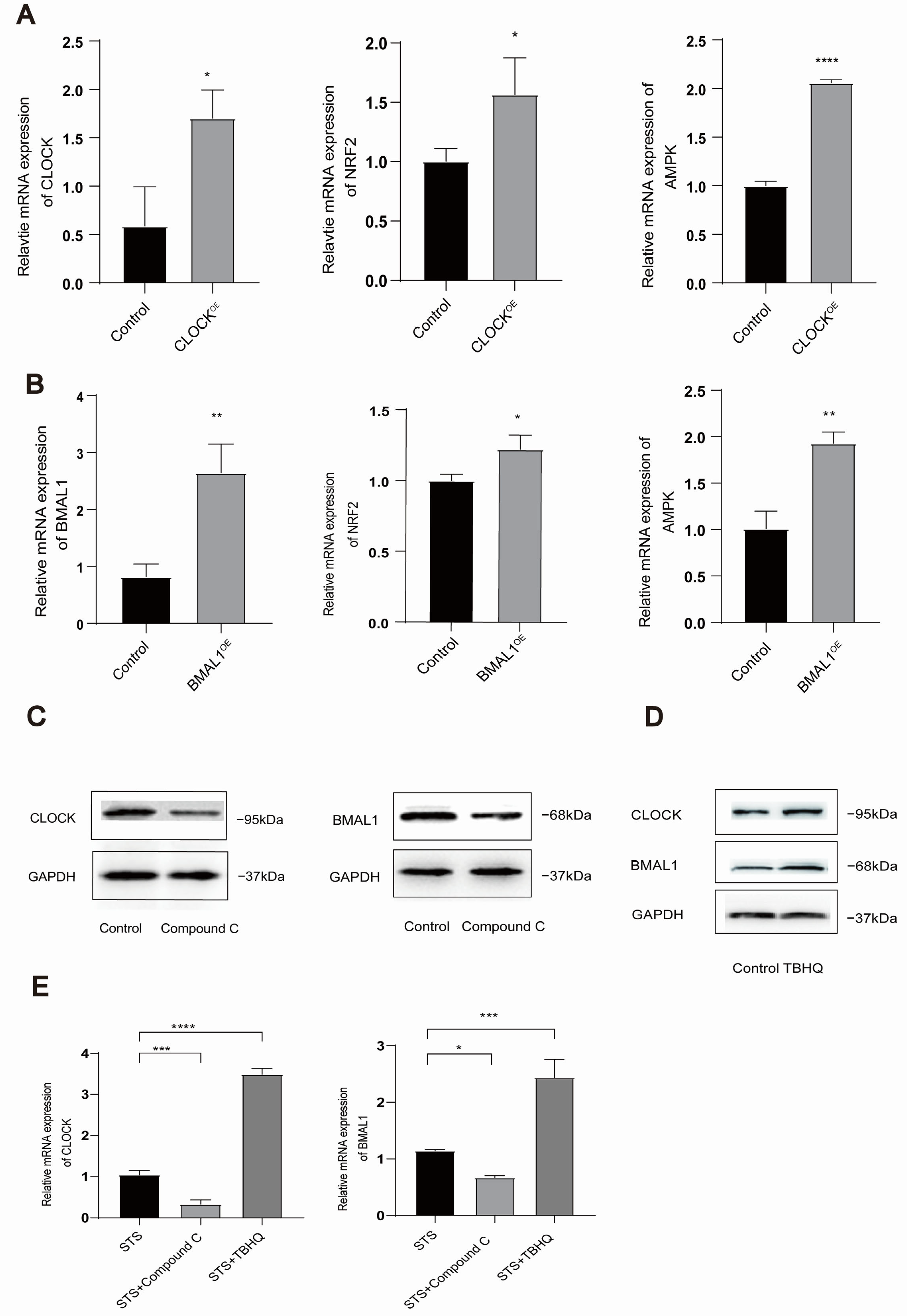
3.4. Mutual Regulation Exists Between AMPK/NRF2 and CLOCK/BMAL1 in HUVECs
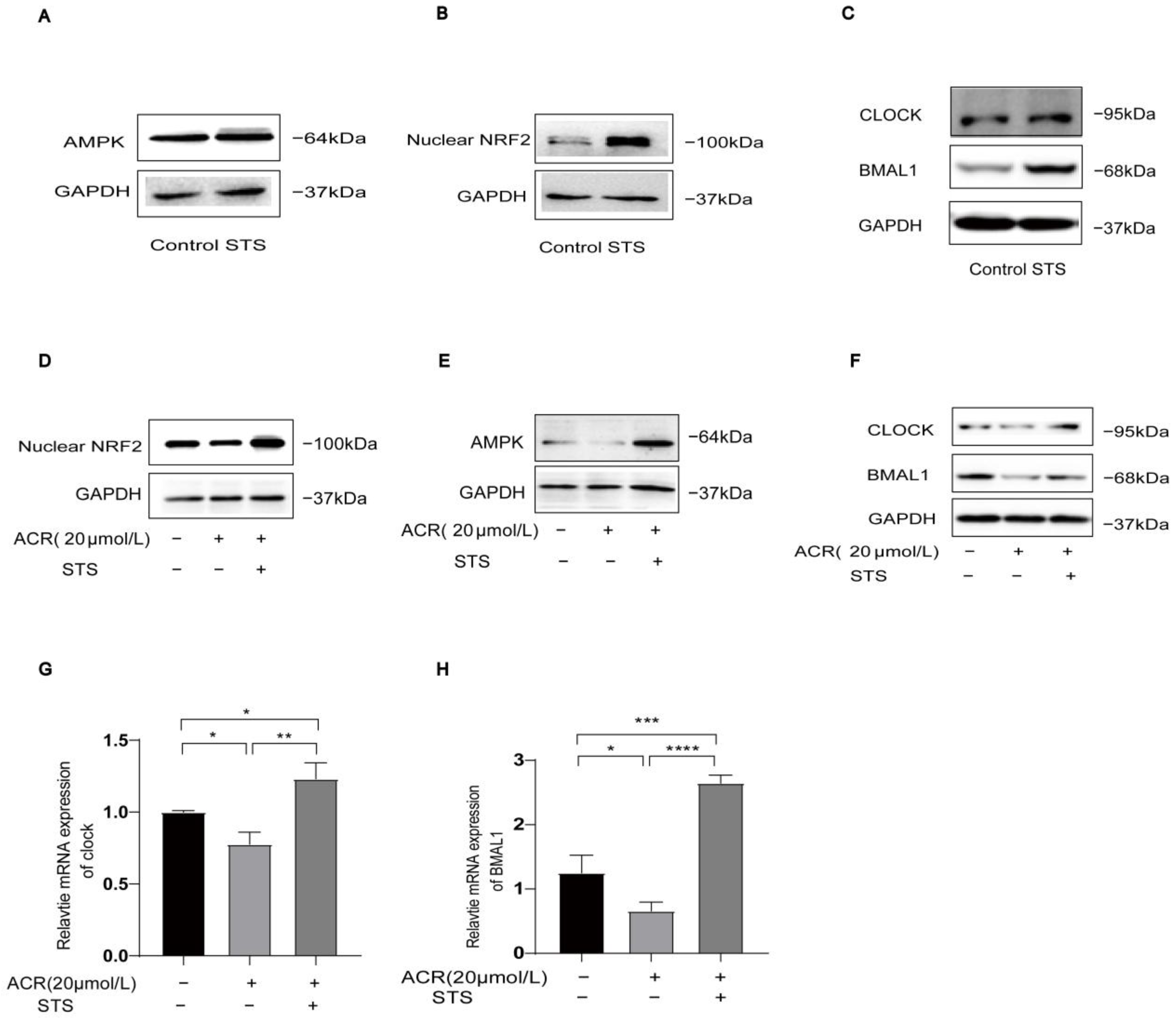
3.5. STS Activates Ferroptosis-Triggered Low Expression of AMPK/NRF2 and CLOCK/BMAL1 in HUVECs
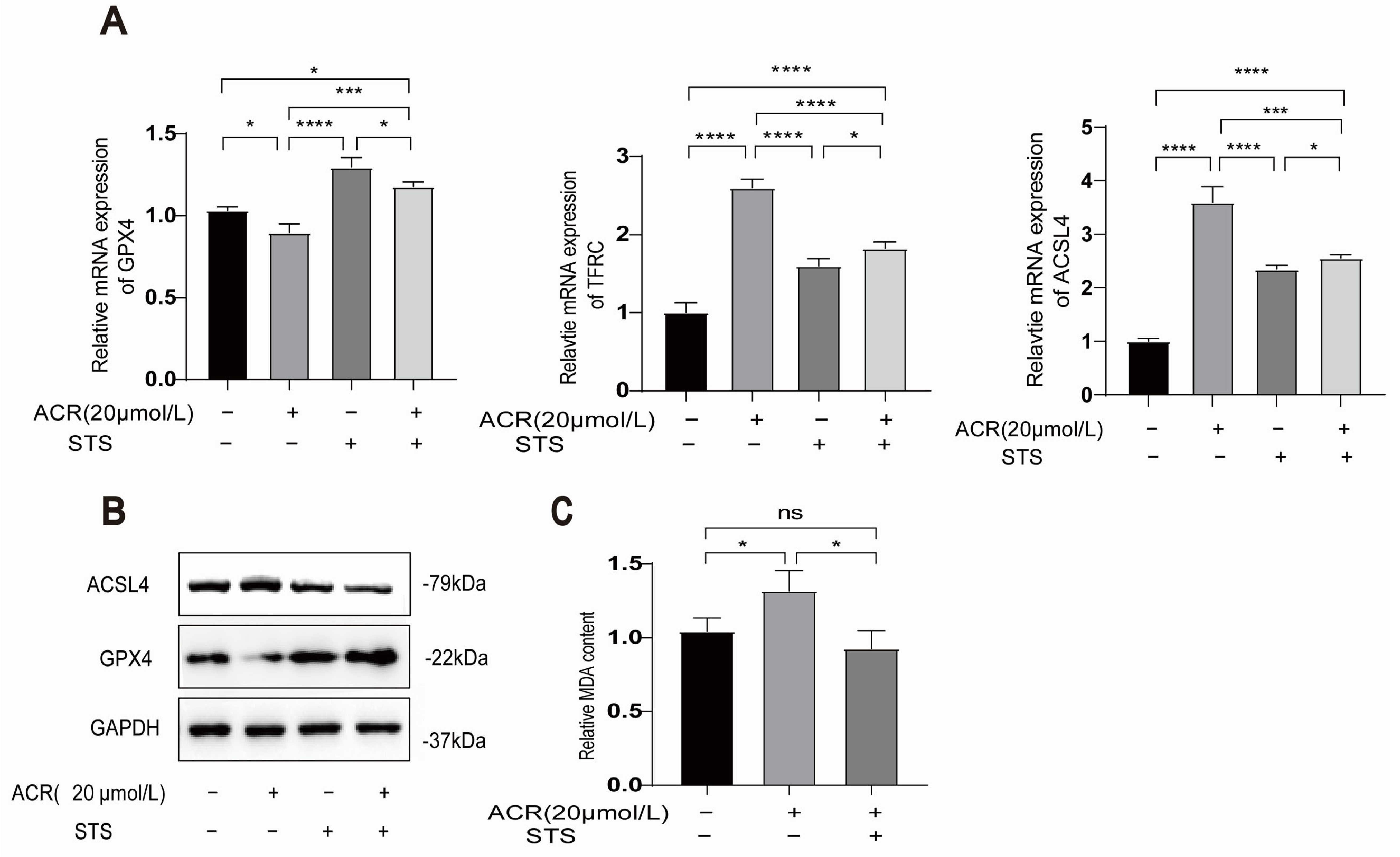
3.6. STS Reverses the Occurrence of Acrolein-Induced Ferroptosis and Lipid Peroxidation in HUVECs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vilcassim, R.; Thurston, G.D. Gaps and future directions in research on health effects of air pollution. EBioMedicine 2023, 93, 104668. [Google Scholar]
- Aizenbud, D.; Aizenbud, I.; Reznick, A.Z.; Avezov, K. Acrolein—An α, β-unsaturated aldehyde: A review of oral cavity exposure and oral pathology effects. Rambam Maimonides Med. J. 2016, 7, e0024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qian, B.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Pan, Y. Online Exploring the Gaseous Oil Fumes from Oleic Acid Thermal Oxidation by Synchrotron Radiation Photoionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 34, 2680–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikisz, P.; Jacenik, D. The tobacco smoke component, acrolein, as a major culprit in lung diseases and respiratory cancers: Molecular mechanisms of acrolein cytotoxic activity. Cells 2023, 12, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroon, O.; Roney, N.; Taylor, J.; Ashizawa, A.; Lumpkin, M.; Plewak, D. Acrolein health effects. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2008, 24, 447–490. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, M.M.; Beland, F.A.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Phillips, D.H.; Chung, F.-L.; Dorman, D.C.; Elmore, S.E.; Hammond, S.K.; Krstev, S.; Linhart, I. Carcinogenicity of acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and arecoline. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hou, X.; Ye, Z.; Wang, C. Quantitative and site-specific chemoproteomic profiling of targets of acrolein. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, L.; Chen, A.; Xu, C.; Feng, Q. Protective effects of olive leaf extract on acrolein-exacerbated myocardial infarction via an endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, X.; Zeb, F.; Huang, Y.; An, J.; Jiang, P.; Chen, A.; Xu, C.; Feng, Q. Acrolein-induced apoptosis of smooth muscle cells through NEAT1-Bmal1/Clock pathway and a protection from asparagus extract. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113735. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Zeb, F.; Li, C.; Jiang, P.; Chen, A.; Xu, C.; ul Haq, I.; Feng, Q. Clock-Bmal1 mediates MMP9 induction in acrolein-promoted atherosclerosis associated with gut microbiota regulation. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Li, B.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, T.; Zaitoun, M.; Rong, S.; Wan, H.; Feng, Q. Acrolein-triggered atherosclerosis via AMPK/SIRT1-CLOCK/BMAL1 pathway and a protection from intermittent fasting. J. Biomed. Res. 2024, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Haupt, S.; Eckstein, M.L.; Wolf, A.; Zimmer, R.T.; Wachsmuth, N.B.; Moser, O. Eat, train, sleep—Retreat? Hormonal interactions of intermittent fasting, exercise and circadian rhythm. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasim, I.; Majeed, C.N.; DeBoer, M.D. Intermittent fasting and metabolic health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Zandkarimi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Meena, J.K.; Kim, J.; Zhuang, L.; Tyagi, S.; Ma, L.; Westbrook, T.F.; Steinberg, G.R. Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varady, K.A. Intermittent versus daily calorie restriction: Which diet regimen is more effective for weight loss? Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e593–e601. [Google Scholar]
- Malinowski, B.; Zalewska, K.; Węsierska, A.; Sokołowska, M.M.; Socha, M.; Liczner, G.; Pawlak-Osińska, K.; Wiciński, M. Intermittent fasting in cardiovascular disorders—An overview. Nutrients 2019, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cabo, R.; Mattson, M.P. Effects of intermittent fasting on health, aging, and disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, K.H.; Takahashi, J.S. Circadian clock genes and the transcriptional architecture of the clock mechanism. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 63, R93–R102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Dai, M.; Wang, X.; Jiang, S.-H.; Hu, L.-P.; Zhang, X.-L.; Zhang, Z.-G. Signalling entrains the peripheral circadian clock. Cell. Signal. 2020, 69, 109433. [Google Scholar]
- Roenneberg, T.; Merrow, M. The circadian clock and human health. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R432–R443. [Google Scholar]
- Lamia, K.A.; Sachdeva, U.M.; DiTacchio, L.; Williams, E.C.; Alvarez, J.G.; Egan, D.F.; Vasquez, D.S.; Juguilon, H.; Panda, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK regulates the circadian clock by cryptochrome phosphorylation and degradation. Science 2009, 326, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crnko, S.; Du Pré, B.C.; Sluijter, J.P.; Van Laake, L.W. Circadian rhythms and the molecular clock in cardiovascular biology and disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilperoort, M.; van den Berg, R.; Bosmans, L.A.; van Os, B.W.; Dollé, M.E.; Smits, N.A.; Guichelaar, T.; van Baarle, D.; Koemans, L.; Berbée, J.F. Disruption of circadian rhythm by alternating light-dark cycles aggravates atherosclerosis development in APOE* 3-Leiden. CETP mice. J. Pineal Res. 2020, 68, e12614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervezee, L.; Shechter, A.; Boivin, D.B. Impact of shift work on the circadian timing system and health in women. Sleep Med. Clin. 2018, 13, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portaluppi, F.; Tiseo, R.; Smolensky, M.H.; Hermida, R.C.; Ayala, D.E.; Fabbian, F. Circadian rhythms and cardiovascular health. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, R.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Cao, S.; Dai, H.; Liao, M. Intermittent fasting ameliorates neuronal ferroptosis and cognitive impairment in mice after traumatic brain injury. Nutrition 2023, 109, 111992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, T.; Yang, L.; Shen, Y.; Li, H. Ferroptosis signaling and regulators in atherosclerosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 809457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Su, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, X.; Xu, L.; Lu, Z.; Dong, J.; Wu, Y. MYCN mediates TFRC-dependent ferroptosis and reveals vulnerabilities in neuroblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yan, X.; Xiao, C.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, J.; Sui, X.; et al. FTO deficiency in older livers exacerbates ferroptosis during ischaemia/reperfusion injury by upregulating ACSL4 and TFRC. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Jin, S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, R. Ferroptosis in cancer therapy: A novel approach to reversing drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, C.O.; de Freitas, F.A.; Sampaio-Silva, J.; Rokita-Rosa, L.; Barros, P.d.L.; Levy, D.; Bydlowski, S.P. Ferroptosis mechanisms involved in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, R.; Xiong, Z.; Bao, X.; Liang, S.; Zeng, H.; Jin, W.; Gong, Q.; Liu, L.; Guo, J. Ferroptosis: A potential target for the treatment of atherosclerosis: Ferroptosis and atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2024, 56, 331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, H.; Wei, S.; Yao, K.; Sun, X.; Yang, G.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N. Resveratrol protected acrolein-induced ferroptosis and insulin secretion dysfunction via ER-stress-related PERK pathway in MIN6 cells. Toxicology 2022, 465, 153048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmirczak, F.; Hartweck, L.M.; Vogel, N.T.; Mendelson, J.B.; Park, A.K.; Raveendran, R.M.; O-Uchi, J.; Jhun, B.S.; Prisco, S.Z.; Prins, K.W. Intermittent fasting activates AMP-kinase to restructure right ventricular lipid metabolism and microtubules. Basic Transl. Sci. 2023, 8, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhou, M.; Chen, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, X. Role of AMPK mediated pathways in autophagy and aging. Biochimie 2022, 195, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a transcription factor for stress response and beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsouki, E.; Cabrera, S.N.S.; Heiss, E.H. AMPK and NRF2: Interactive players in the same team for cellular homeostasis? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 190, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; Men, H.; Bao, T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Keller, B.B.; Tong, Q. Ferroptosis is essential for diabetic cardiomyopathy and is prevented by sulforaphane via AMPK/NRF2 pathways. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yang, L.; Xiao, J.-J.; Liu, Q.; Ni, L.; Hu, J.-W.; Yu, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, B.-F. Empagliflozin attenuates the renal tubular ferroptosis in diabetic kidney disease through AMPK/NRF2 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 195, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, W. The impact of environmental pollution and economic growth on public health: Evidence from China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 861157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Zhong, K.; Liu, X.; Zeng, X. Ferroptosis contributes to cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. Chem. Interactions 2023, 384, 110701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfarhan, M.; Jafari, E.; Narayanan, S.P. Acrolein: A potential mediator of oxidative damage in diabetic retinopathy. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Kan, K.; Sticht, C.; Bennewitz, K.; Li, S.; Qian, X.; Poschet, G.; Kroll, J. Acrolein-inducing ferroptosis contributes to impaired peripheral neurogenesis in zebrafish. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1044213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, Z. Inhibition of ferroptosis alleviates atherosclerosis through attenuating lipid peroxidation and endothelial dysfunction in mouse aortic endothelial cell. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Dogon, G.; Rigal, E.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism: Two corner stones in the homeostasis control of ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Peng, D.; Cai, Z.; Lin, H.-K. AMPK signaling and its targeting in cancer progression and treatment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Ding, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Q. Apoptotic extracellular vesicles alleviate Pg-LPS induced inflammatory responses of macrophages via AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway and inhibit osteoclast formation. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 1738–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, M.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qian, X.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, J. Dexmedetomidine attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced ferroptosis via AMPK/GSK-3β/Nrf2 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-h.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Q. Suppressive effect erythropoietin on oxidative stress by targeting AMPK/Nox4/ROS pathway in renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Transpl. Immunol. 2022, 72, 101537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, H. The emerging roles of MAPK-AMPK in ferroptosis regulatory network. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Jiang, L.; Gu, X.; Huang, S.; Pang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yin, J.; Wang, J. SIRT3 deficiency is resistant to autophagy-dependent ferroptosis by inhibiting the AMPK/mTOR pathway and promoting GPX4 levels. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 8839–8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.M.; Maltagliati, A.J. Nrf2 at the heart of oxidative stress and cardiac protection. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Li, Z.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Jia, B.; Gong, A.; Xu, M. Vitamin C Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis by Activating the AMPK/Nrf2/HMOX1 Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5361241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Horany, H.E.-S.; Atef, M.M.; Abdel Ghafar, M.T.; Fouda, M.H.; Nasef, N.A.; Hegab, I.I.; Helal, D.S.; Elseady, W.; Hafez, Y.M.; Hagag, R.Y. Empagliflozin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats by modulating Sesn2/AMPK/Nrf2 signaling and targeting ferroptosis and autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Sun, N. Intermittent fasting, fatty acid metabolism reprogramming, and neuroimmuno microenvironment: Mechanisms and application prospects. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1485632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.; Zhang, Q.; Sung, H.-K. From fasting to fat reshaping: Exploring the molecular pathways of intermittent fasting-induced adipose tissue remodeling. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 27, 13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifaai, R.A.; El-Tahawy, N.F.G.; Abozaid, S.M.M.; Abdelwahab, A. Intermittent fasting ameliorates age-induced morphological changes in aged albino rat kidney via autophagy activation and reduction of apoptosis and inflammation. Microsc. Microanal. 2024, 31, ozae102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GPX4 | ACAAGAACGGCTGCGTGGTGAA | GAGCTAGAAATAGTGGGGCAGGT |
| ACSL4 | TGGCAAAGGAGCAGATTAGTAGG | TCACTTAGGATTTCCCTGGTCC |
| TFRC | ACCATTGTCATATACCCGGTTCA | CAATAGCCCAAGTAGCCAATCAT |
| AMPK | GTAGTAAAAACAGGCTCCACGAA | CACCAGAAAGGATCTGTTGGA |
| NRF2 | ACAAGAACGGCTGCGTGGTGAA | GAGCTAGAAATAGTGGGGCAGGT |
| CLOCK | ATGGTTTTTACCGTAAGCTGTAG | CTCGCGTTACCAGGAAGCAT |
| BMAL1 | AGGCCCACAGTCAGATTGAAA | CCAAAGAAGCCAATTCATCAATG |
| GAPDH | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
| Primer | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CLOCK | CCTATCCTACCTTGGCCACACA | TCCCGTGGAGCAACCTAGAT |
| GPX4 | GCAACCAGTTTGGGAGGCAGGAG | CCTCCATGGGACCATAGCGCTTC |
| ACSL4 | TGAACGTATCCCTGGACTAGG | TCAGACAGTGTAAGGGGTGAA |
| TFRC | GTGGAGTATCACTTCCTGTCGC | CCCCAGATATGTCGGAAAGG |
| GAPDH | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTA | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
| Gene | Sequence |
|---|---|
| siCLOCK-01 | CAAAGAAGGTCATCATTTA |
| siCLOCK-02 | GGAGCCATCTACCTATGAA |
| siCLOCK-03 | GCTTCCTGGTAATGCTAGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Q.; Zaitoun, M.; Cheng, Y.; Ge, J.; Feng, Q. Acrolein-Triggered Ferroptosis and Protection by Intermittent Fasting via the AMPK/NRF2-CLOCK/BMAL1 Pathway. Toxics 2025, 13, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050369
Zhang Y, Chen H, Chen Q, Zaitoun M, Cheng Y, Ge J, Feng Q. Acrolein-Triggered Ferroptosis and Protection by Intermittent Fasting via the AMPK/NRF2-CLOCK/BMAL1 Pathway. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050369
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuandie, Hong Chen, Qianfeng Chen, Margaret Zaitoun, Ying Cheng, Jierong Ge, and Qing Feng. 2025. "Acrolein-Triggered Ferroptosis and Protection by Intermittent Fasting via the AMPK/NRF2-CLOCK/BMAL1 Pathway" Toxics 13, no. 5: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050369
APA StyleZhang, Y., Chen, H., Chen, Q., Zaitoun, M., Cheng, Y., Ge, J., & Feng, Q. (2025). Acrolein-Triggered Ferroptosis and Protection by Intermittent Fasting via the AMPK/NRF2-CLOCK/BMAL1 Pathway. Toxics, 13(5), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050369





