Assessment of Potential Toxic Effects of Fungicide Fludioxonil on Human Cells and Aquatic Microorganisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Biological Testing
2.3.1. Ethics Statement
2.3.2. Whole Blood Collection
2.3.3. Cell Viability
2.3.4. CBMN Assay in Human Lymphocytes In Vitro
2.4. Algal Biotest
2.5. A. fischeri Bioluminescence Inhibition Test
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxic and Cyto-Genotoxic Effects of Fludioxonil in Human Lymphocytes
3.1.1. Determination of Cell Viability in Fludioxonil-Treated Human Lymphocytes
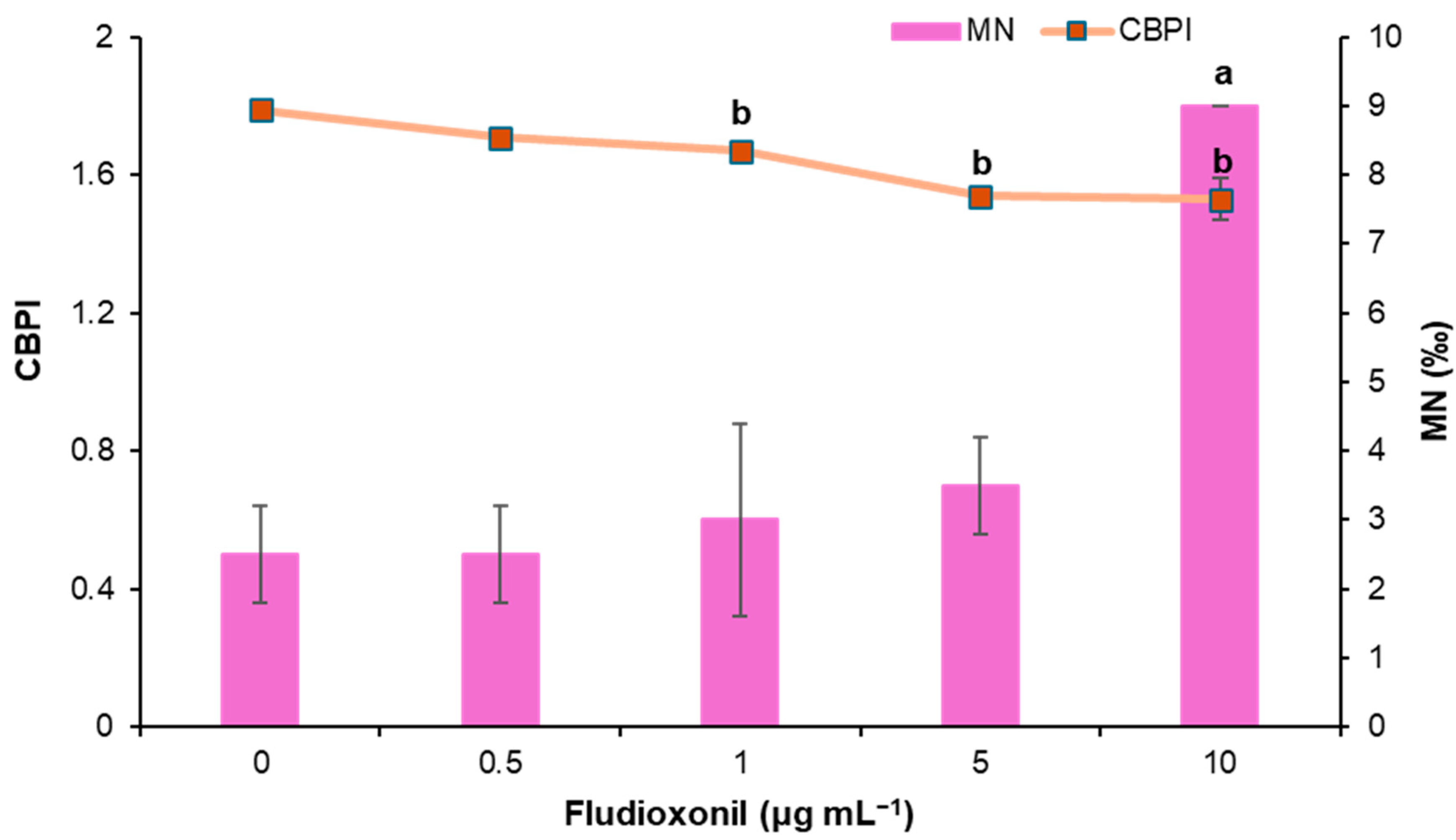
3.1.2. Study of Cyto-Genotoxic Effects of Fludioxonil Using CBMN Assay
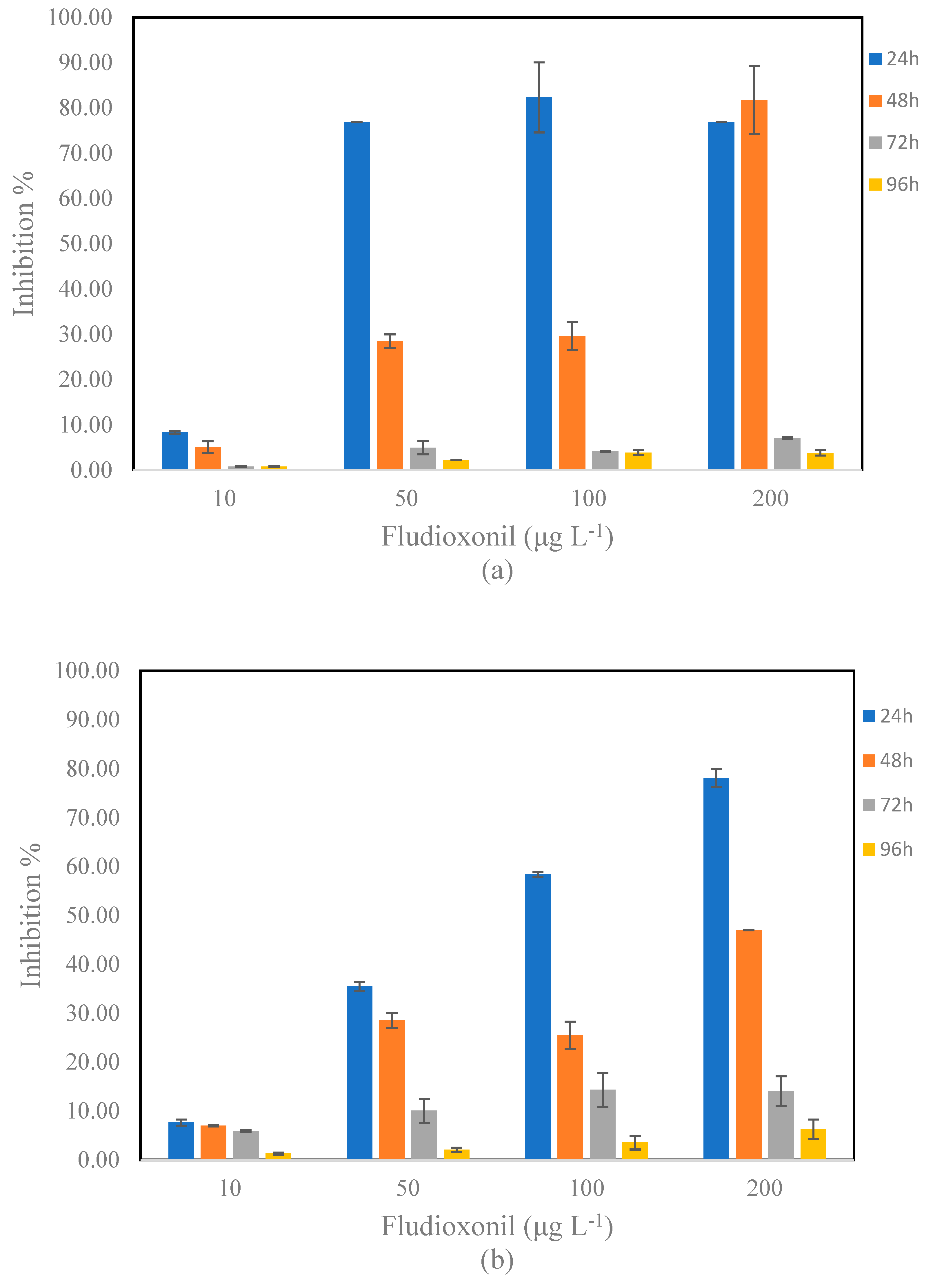
3.2. Toxic Effects of Fludioxonil on S. rubescens and D. tertiolecta
3.3. Toxic Effects of Fludioxonil on A. fischeri
4. Discussion
4.1. Toxic and Cyto-Genotoxic Effects of Fludioxonil on Human Lymphocytes
4.2. Toxic Effects of Fludioxonil on S. rubescens and D. tertiolecta
4.3. Toxic Effects of Fludioxonil on A. fischeri
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SD | Standard deviation |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CBMN | Cytokinesis Block MicroNucleus |
| MN | Micronuclei |
| CBPI | Cytokinesis block proliferation index |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| BN | Binucleated |
| BNMN | Micronucleated binucleated cells |
| MMC | Mitomycin-C |
| SMART | Somatic mutation and recombination test |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
References
- Gong, H.Q.; Ying, S.; Jin, H.Y.; Liao, C.X.; Chen, B.B. Earthworm tolerance to residual agricultural pesticide contamination: Field and experimental assessment of detoxification capabilities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Na, L.; Jin, X.W.; Mu, Y.S.; Feng, C.L.; Wu, F.C.; Wang, Y.Y. Review of environmental behavior, toxicity and ecological risk of triadimefon in the aquatic environment. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2017, 12, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.G.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Guo, B. The toxicity of three pesticides of mefenoxam, fludioxonil, azoxystrobin and their compounds to Brachydanio rerio. Asian J. Ecotoxicl. 2017, 12, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, P. Use of freshwater plants for phytotoxicity testing: A review. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 87, 319–336. [Google Scholar]
- Sewell, T.; Moloney, S.; Ashworth, M.; Ritchie, F.; Mashanova, A.; Huang, Y.J.; Stotz, H.U.; Fitt, B.D.L. Effects of a penthiopyrad and picoxystrobin fungicide mixture on phoma stem canker (Leptosphaeria spp.) on UK winter oilseed rape. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 145, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Lei, L.L.; Liu, M.T.; Song, Y.; Lu, S.B.; Li, D.; Shi, H.H.; Raley-Susman, K.M.; He, D.F. Single and mixture toxicity of strobilurin and SDHI fungicides to Xenopus tropicalis embryos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Code of Federal Regulations, Title 40, Part 180.516: Fludioxonil; Tolerances for Residues; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Kilani, J.; Fillinger, S. Phenylpyrroles: 30 Years, two molecules and (nearly) No resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.H.; Brock, T.-C.-M.; Barone, L.-E.; Belgers, J.-D.-M.; Boerwinkel, M.-C.; Buijse, L.; Van wijngaarden, P.-P.-A.; Hamer, M.; Roessink, I. Exposure and effects of sediment-spiked Fludioxonil on macroinvertebrates and zooplankton in outdoor aquatic microcosms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 1, 1222–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandhorst, T.-T.; Klein, B.-S. Uncertainty surrounding the mechanism and safety of the post-harvest fungicide fludioxonil. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 123, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Jun, E.; Lee, Y.; Kim, K.W. Exploring comprehensive toxic effects of fludioxonil on Caenorhabditis elegans. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 294, 117996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Couso, A.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.; López-Periago, E.; Soto-González, B.; Simal-Gándara, J. Seasonal distributions of fungicides in soils and sediments of a small river basin partially devoted to vineyards. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4515–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, A.-W.; Huang, M.; Yu, W.; Li, Z.; Wu, S.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, K.; Hu, D. Simultaneous determination of boscalid and fludioxonil in grape and soil under field conditions by gas chromatography/tandem triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, e4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, I.; de la Torre, A.; Sanz, P.; Baldi, I.; Harkes, P.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Nørgaard, T.; Glavan, M.; Pasković, I.; Pasković, M.P.; et al. Occurrence of pesticide residues in indoor dust of farmworker households across Europe and Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Manavalan, T.-T.; Hu, C.; Medjakovic, S.; Jungbauer, A.; Klinge, C.-M. Endocrine disruptors fludioxonil and fenhexamid stimulate miR-21 expression in breast cancer cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svartz, G.; Meijide, F.; Pérez Coll, C. Effects of a fungicide formulation on embryo-larval development, metamorphosis, and gonadogenesis of the south american toad Rhinella arenarum. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, S.M.; Go, R.E.; Lee, H.K.; Choi, K.C. Fludioxonil induces cardiotoxicity via mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in two cardiomyocyte models. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Weng, H.; Yang, G.; Guo, D.; Yu, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Combined toxic effects of fludioxonil and triadimefon on embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Chai, T.T.; Liu, X.X.; Wang, C.J. Toxicity of three strobilurins (kresoxim-methyl, pyraclostrobin, and trifloxystrobin) on Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassold, E.; Backhaus, T. The predictability of mixture toxicity of demethylase inhibiting fungicides to Daphnia magna depends on life-cycle parameters. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 152, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubrod, J.P.; Baudy, P.; Schulz, R.; Bundschuh, M. Effects of current-use fungicides and their mixtures on the feeding and survival of the key shredder Gammarus fossarum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 150, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yao, X.; Qiao, Z.; Deng, J.; Jiao, Q.; Gong, L.; Jiang, X. Toxic effects of fludioxonil on the growth, photosynthetic activity, oxidative stress, cell morphology, apoptosis, and metabolism of Chlorella vulgaris. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalampous, N.; Antonopoulou, M.; Chasapis, C.-T.; Vlastos, D.; Dormousoglou, M.; Dailianis, S. New insights into the oxidative and cytogenotoxic effects of Tetraglyme on human peripheral blood cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, I.; Vlastos, D.; Ioannidou, C.; Tsilimigka, F.; Drosopoulou, E.; Mavragani-Tsipidou, P.; Potsi, G.; Gournis, D.; Antonopoulou, M. Assessment of the genotoxic potential of three novel composite nanomaterials using human lymphocytes and the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster as model systems. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development). Test No. 487: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test; OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Vlastos, D.; Dormousoglou, M.; Bouras, S.; Varela-Athanasatou, M.; Bekakou, I.-E. Genotoxic and Toxic Effects of The Flame Retardant Tris(Chloropropyl) Phosphate (TCPP) in Human Lymphocytes, Microalgae and Bacteria. Toxics 2022, 10, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Dormousoglou, M.; Spyrou, A.; Dimitroulia, A.A.; Vlastos, D. An overall assessment of the effects of antidepressant paroxetine on aquatic organisms and human cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Adil, M.; Ehtisham-ul-Haque, S.; Munir, B.; Yameen, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Abbas Shar, G.; Tahir, M.A.; Iqbal, M. Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay for ecotoxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyum, A. Separation of white blood cells. Nature 1964, 204, 793–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surallès, J.; Xamena, N.; Creus, A.; Catalan, J.; Norppa, H.; Marcos, R. Induction of micronuclei by five pyrethroid insecticides in whole-blood and isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat. Res. 1995, 341, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Test No. 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test; OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graiet, I.; Hamdi, H.; Abid-Essefi, S.; Eyer, J. Fludioxonil, a phenylpyrrol pesticide, induces Cytoskeleton disruption, DNA damage and apoptosis via oxidative stress on rat glioma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 170, 113464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graillot, V.; Takakura, N.; Hegarat, L.-L.; Fessard, V.; Audebert, M.; Cravedi, J.-P. Genotoxicity of pesticide mixtures present in the diet of the French population. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2012, 53, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz Pekgöz, A.; Kaya, B.; Savas, B.; Topcuoglu, S. Effects of two fungicides, cyprodinil and fludioxonil, on genotoxicity in drosophila smart assay and on proliferation and viability of HEK293 cells from the perspective of carcinogenesis. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 1920–1925. [Google Scholar]
- Isidori, M.; Caterino, E.; Criscuolo, E.; Fatigati, V.; Liguori, G.; Parrella, A. Antimutagenic and antigenotoxic effects of vegetable matrices on the activity of pesticides. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess 2009, 26, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-H.; Hwang, K.-A.; Choi, K.-C. Effects of Fludioxonil on the Cell Growth and Apoptosis in T and B Lymphocytes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.-D.; O’Neil, J.-D.; Woehrling, E.-K.; Ndunge, O.-B.; Hill, E.-J.; Menache, A.; Reiss, C.-J. A preliminary investigation into the impact of a pesticide combination on human neuronal and glial cell lines in vitro. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 42768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholze, M.; Taxvig, C.; Kortenkamp, A.; Boberg, J.; Christiansen, S.; Svingen, T.; Lauschke, K.; Frandsen, H.; Ermler, S.; Hermann, S.S.; et al. Quantitative in vitro to in vivo extrapolation (QIVIVE) for predicting reduced anogenital distance produced by anti-androgenic pesticides in a rodent model for male reproductive disorders. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 117005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdisson, S.; Couderchet, M.; Vernet, G. Effects of procymidone, fludioxonil and pyrimethanil on two non-target aquatic plants. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, T.C.M.; Romão, J.; Yin, X.; Osman, R.; Roessink, I. Sediment toxicity of the fungicide fludioxonil to benthic macroinvertebrates-Evaluation of the tiered effect assessment procedure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Lv, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Gao, J. Indirect photodegradation of fludioxonil by hydroxyl radical and singlet oxygen in aquatic environment: Mechanism, photoproducts formation and eco-toxicity assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westlund, P.; Nasuhoglu, D.; Isazadeh, S.; Yargeau, V. Investigation of Acute and Chronic Toxicity Trends of Pesticides Using High-Throughput Bioluminescence Assay Based on the Test Organism Vibrio fischeri. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 74, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomba, L.; Lapeña, D.; Ros, N.; Aso, E.; Cannavò, M.; Errazquin, D.; Giner, B. Ecotoxicological study of six drugs in A. fischeri, Daphnia magna and Raphidocelis subcapitata. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 9891–9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Pérez, J.; Loureiro, S.; Menezes, S.; Palma, P.; Fernandes, R.M.; Barbosa, I.R.; Soares, A.M.V.M.A. Assessment of water quality in the Alqueva Reservoir (Portugal) using bioassays. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, F.T.; Oliveira, R.; Silva, A.; Catarino, A.L.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Nogueira, A.J.A.; Domingues, I. Lethal and sub lethal effects of the biocide chlorhexidine on aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fludioxonil (μg mL−1) | % Viability |
| 0 | 99.75 ± 0.07 |
| 0.5 | 99.45 ± 0.07 |
| 1 | 99.50 ± 0.14 |
| 5 | 98.45 ± 0.07 |
| Solvent | % Viability |
| 0 (Ethanol) | 99.80 ± 0.00 |
| Treatment (μg mL−1) | BNMN | MN | p | CBPI | p | Cytostasis (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.50 ± 0.70 | 2.50 ± 0.70 | - | 1.79 ± 0.00 | - | - |
| 0.5 | 2.50 ± 0.70 | 2.50 ± 0.70 | - | 1.71 ± 0.01 | 0.053 | 9.51 ± 0.72 |
| 1 | 3.00 ± 1.40 | 3.00 ± 1.40 | 1.00 | 1.67 ± 0.02 b | 8.47 × 10−5 | 14.83 ± 2.87 |
| 5 | 3.50 ± 0.70 | 3.50 ± 0.70 | 0.550 | 1.54 ± 0.01 b | 1.66 × 10−14 | 31.05 ± 0.72 |
| 10 | 9.00 ± 0.00 | 9.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.001 | 1.53 ± 0.06 b | 8.07 × 10−19 | 32.57 ± 7.17 |
| MMC (0.05) | 53.50 ± 6.40 | 54.00 ± 5.70 b | 2.7 × 10−52 | 1.65 ± 0.00 b | 5.42 × 10−7 | 18.00 ± 0.90 |
| Exposure Time (h) | S. rubescens | D. tertiolecta |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 0.08 (0.07–0.1) | 0.08 (0.06–0.09) |
| 48 | 0.08 (0.07–0.09) | 0.19 (0.15–0.27) |
| 72 | 22.51 (1.65–2.53 × 1017) | 2.42 (0.90–25.51) |
| 96 | 29.77 (2.57–5.28 × 1015) | 12.52 (2.11–23,067.66) |
| Exposure Time (min) | IC50 (mg L−1) |
|---|---|
| 5 | 260.24 (152.06–1026.50) |
| 15 | n.d. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antonopoulou, M.; Tzamaria, A.; Papas, S.; Efthimiou, I.; Vlastos, D. Assessment of Potential Toxic Effects of Fungicide Fludioxonil on Human Cells and Aquatic Microorganisms. Toxics 2025, 13, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050358
Antonopoulou M, Tzamaria A, Papas S, Efthimiou I, Vlastos D. Assessment of Potential Toxic Effects of Fungicide Fludioxonil on Human Cells and Aquatic Microorganisms. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050358
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntonopoulou, Maria, Anna Tzamaria, Sotiris Papas, Ioanna Efthimiou, and Dimitris Vlastos. 2025. "Assessment of Potential Toxic Effects of Fungicide Fludioxonil on Human Cells and Aquatic Microorganisms" Toxics 13, no. 5: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050358
APA StyleAntonopoulou, M., Tzamaria, A., Papas, S., Efthimiou, I., & Vlastos, D. (2025). Assessment of Potential Toxic Effects of Fungicide Fludioxonil on Human Cells and Aquatic Microorganisms. Toxics, 13(5), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050358











