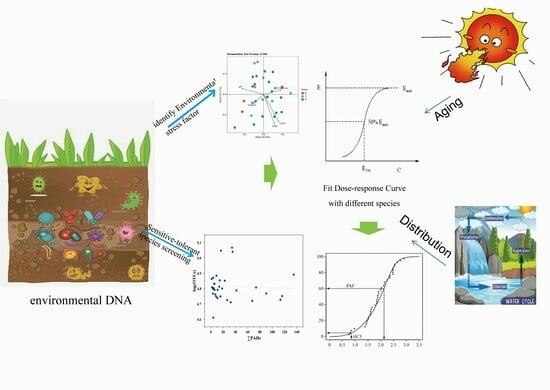
Environmental DNA-Based Ecological Risk Assessment of PAHs in Aged Petroleum-Contaminated Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
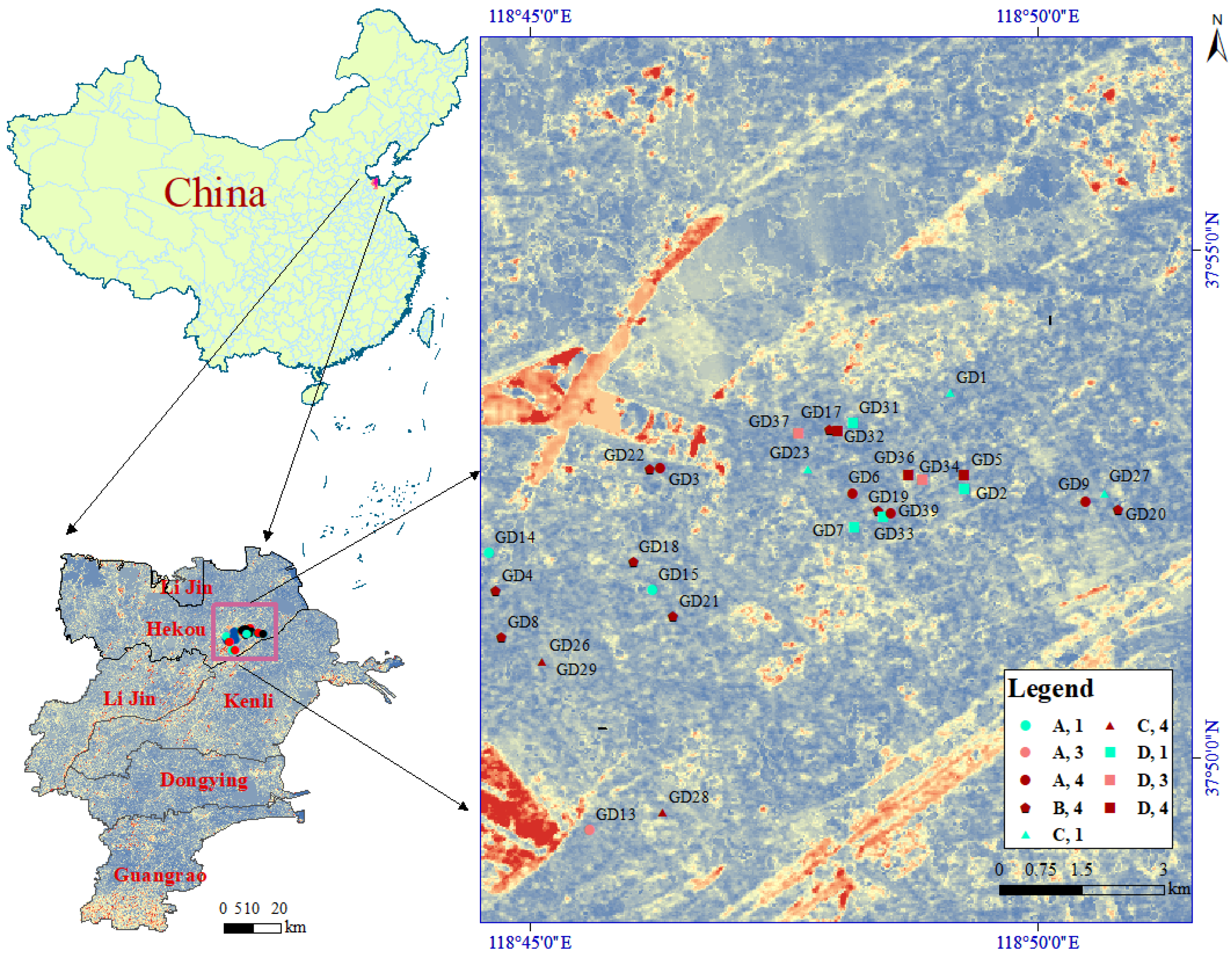
2.1. Soil Samples
2.2. Quantitative Analysis of PAHs and TPHs
2.3. Soil Microbial Community Analysis
2.4. Data Calibration
2.5. Data Analysis and Statistics
2.5.1. Screening of Sensitive and Tolerant Species
2.5.2. Construction of SSD Curves and Calculation of Ecological Risk Thresholds
2.5.3. Risk Level Evaluation
2.5.4. Biological Data Processing and Plotting
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Biological Distribution
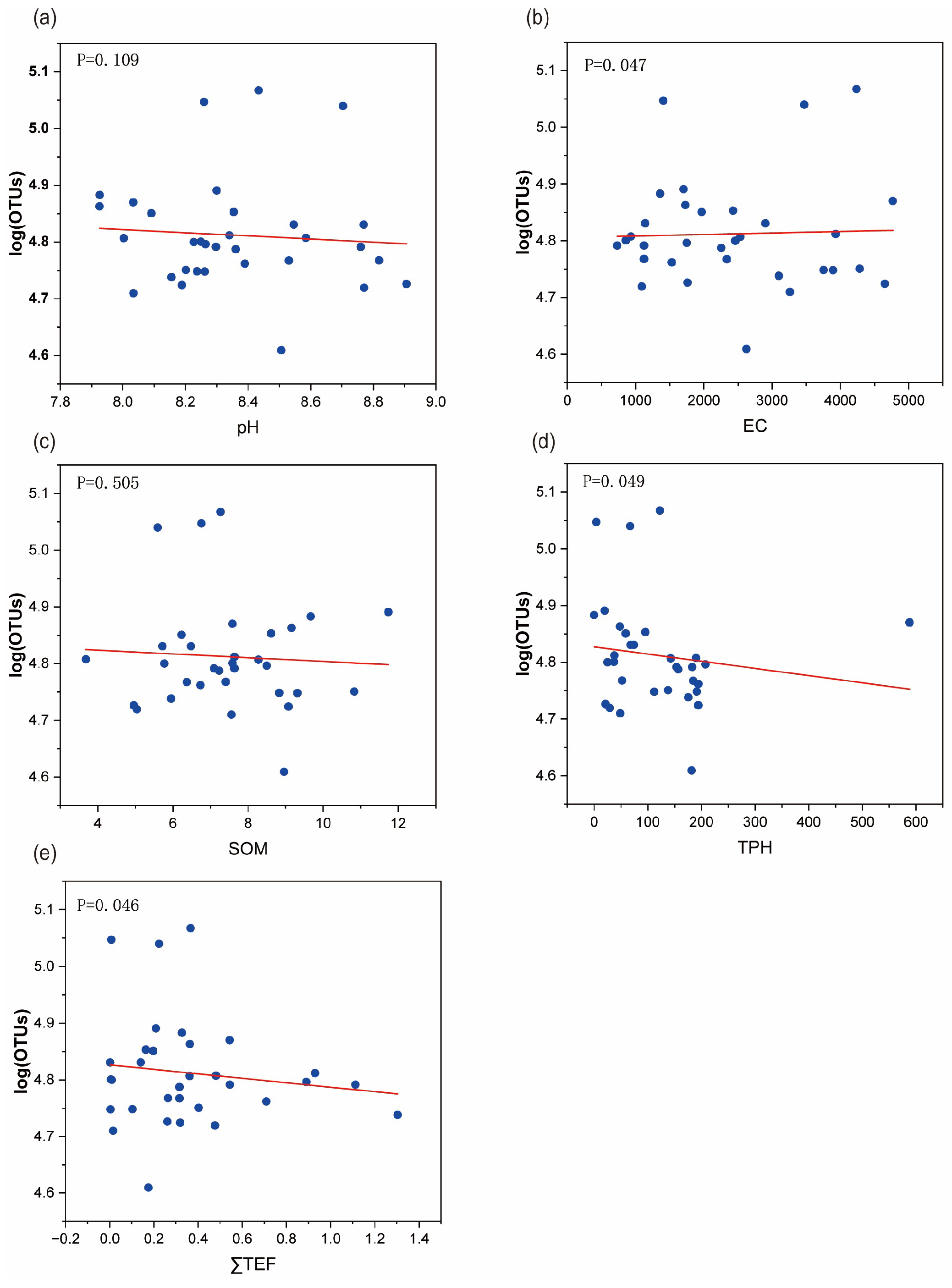
3.1.1. Analysis of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
3.1.2. Analysis of Relative Abundance and Biodiversity
3.2. Identification of Key Stress Factors and Screening of Sensitive/Tolerant Species
3.2.1. Identification of Key Stress Factors
3.2.2. Identification of Sensitive and Tolerant Species
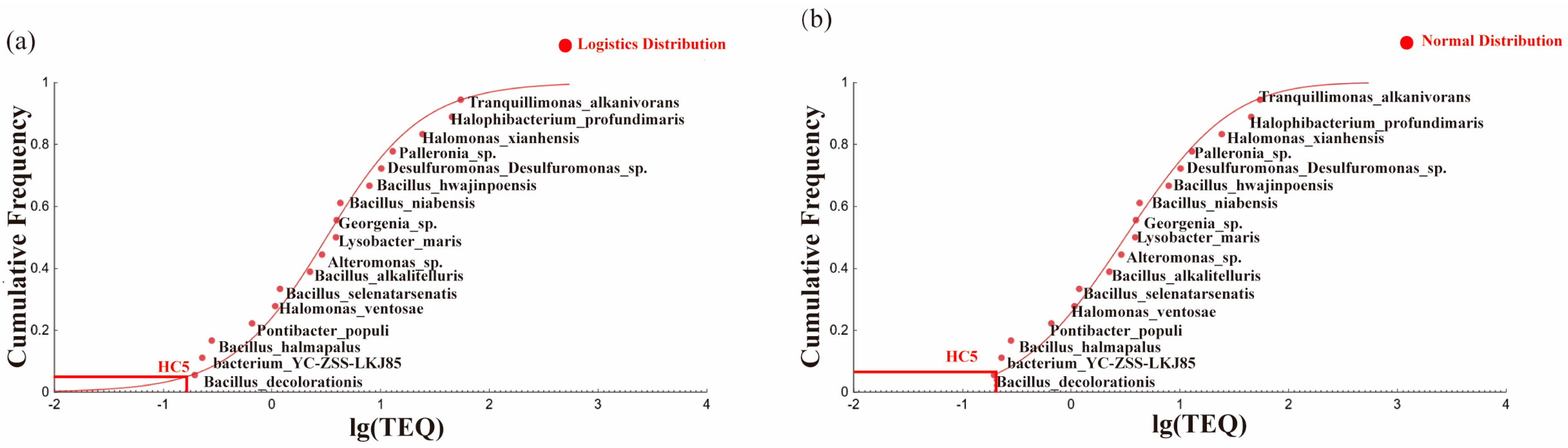
3.3. Calculation of Ecological Risk Thresholds
3.3.1. Ecological Risk Thresholds of Key Stress Factors
3.3.2. Data Modification
3.3.3. Determination of the Ecological Risk Threshold
3.4. Soil Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z. Statistical Analysis of the Structure of Total Petroleum Consumption in China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 300, 042089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.J.; Ni, J.S.; Dong, J. Research on the resilience of petroleum industry chain and supply chain network from the perspective of China. Energy Strategy Rev. 2025, 59, 101685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amossé, J.; Souki, R. Exploration of microRNAs from blood extracellular vesicles as biomarkers of exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lv, X.; Xie, R.; Chen, B.H.; Lai, Y.W.; Chen, L.; Teng, H.; Cao, H. A systematic study on the chemical model of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons formation from nutrients (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids) in food. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, S. Assessing the ecological impacts of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons petroleum pollutants using a network toxicity model. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 117901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, S.; Khoshakhlagh, A.H.; Alwan, N.; Carlsen, L. Health Risk Assessment of Exposure to BTEX and PAH Compounds in Workers of Burnt Oil Recycling Factory: Simulation Using Monte Carlo Method. Environ. Process 2024, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Wu, Q.H.; Luo, H. Ecological risk assessment for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in river sediments. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 33, 544–556. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Tan, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, K. Spatial distribution, environmental behavior, and health risk assessment of PAHs in soils at prototype coking plants in Shanxi, China: Stable carbon isotope and molecular composition analyses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Chao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Lin, D.; Yang, K. Drivers distinguishing of PAHs heterogeneity in surface soil of China using deep learning coupled with geo-statistical approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Yanagihara, M. Comparison of Model-averaging and single-distribution approaches to estimating species sensitivity distributions and hazardous concentrations for 5% of Species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2025, 44, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhond, A.K.; Barron, M.G. Advancing Fifth Percentile Hazard Concentration Estimation Using Toxicity-Normalized Species Sensitivity Distributions. Environ. Sci. Amp. Technol. 2022, 56, 17188–17196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garay, V.; Roman, G. Evaluation of PNEC values: Extrapolation from microtox, algae, daphnid, and fish data to HC5. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.F.; Xie, Z.H. Ecological risk assessment methods for oxidative by–products in the oxidation degradation process of emerging pollutants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 950, 175401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, C.; Mosa, A.; Ling, W. Determination of soil environment criteria for ecological safety of benzo[a]pyrene in soil based on the species sensitivity distribution approach. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 195, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.I.; Moon, J.; Kim, D.; Cui, R.; An, Y.J. Determination of the soil hazardous concentrations of bisphenol A using the species sensitivity approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Teng, Y.; Sun, R.; Tang, J.; Ji, C.; Wu, H.; Pan, Y.; Dai, J. Predictive Framework for Species Sensitivity Distribution Curves of Emerging Contaminants: A Comparative Study in Marine and Freshwater Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, F.N.; Raimondo, S.; Barron, M.G. Assessment of a New Approach Method for Grouped Chemical Hazard Estimation: The Toxicity-Normalized Species Sensitivity Distribution (SSD). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 8278–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishan, S.T.; Kline, R.J.; Rahman, M.S. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) to detect subterranean and aquatic invasive species: A critical review on the challenges and limitations of eDNA metabarcoding. Environ. Adv. 2023, 12, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chariton, A.A. Book review: Environmental DNA: For biodiversity research and monitoring by Pierre Taberlet, Aurélie Bonin, Lucie Zinger and Eric Coissac. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 4549–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Kuemmerlen, M. Combining environmental DNA and species distribution modeling to evaluate reintroduction success of a freshwater fish. Ecol. Appl. A Publ. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2020, 30, e02034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Zhong, W.J.; Liu, X.J.; Bi, W.J.; Qian, L.H.; Zhang, W.X. Biological Evaluation and Key Stress Factor Diagnosis of Compound Contaminated Soil Based on Environmental DNA. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 4130–4141. [Google Scholar]
- Gregorio, V.; Chèvre, N.; Junghans, M. Critical issues in using the common mixture toxicity models concentration addition or response addition on species sensitivity distributions: A theoretical approach. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebykina, E.; Abakumov, E.; Shamilishvilly, G. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons accumulation and toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) in postpyrogenic soils. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 862, 012094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoaneta, E.; Oleg, B. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry in soils from Southeastern Romania. Microchem. J. 2012, 100, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, J. Determination of 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil by Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. Sichuan Environ. 2020, 39, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.J. Study on the Promotion and Mechanism of Microbial Degradation of PAHs by Suaeda Glauca in Saline Soils. Master’s Thesis, Qilu University of Technology, Jinan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- HJ 1021-2019; Determination of Petroleum hydrocarbons (C10–C40) in Soils and Sediments by Gas Chromatography. Ministry of Ecology and Environment, PRC, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- EPA/600/R-96/001; Methods for Measuring the Distribution of Nonionic Organic Chemicals Between Soil Organic Matter and Water. US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Karickhoff, S.W. Adsorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments. CRC Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 1981, 11, 207–231. [Google Scholar]
- EPA/540/R-99/004; Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume III, Part A. US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Shiang, T.L.; Stanley, I.S. Prediction of Octanol−Water Partition Coefficients Using a Group Contribution Solvation Model. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 4081–4091. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, D.C.; Pankaj, R.D. Building a Quantitative Structure-Property Relationship (QSPR) Model. In Bioinformatics and Drug Discovery, 2nd ed.; Richard, S.L., Tudor, I.O., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1939, pp. 139–159. [Google Scholar]
- Brattin, W.J.; Barry, T.M. Montecarlo modeling with uncertain probability density functions. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 1996, 2, 820–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, I.C.T.; LaGoy, P.K. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 36600-2018; Soil Environmental Quality—Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land (Trial). Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Si, J.Y.; Hong, Y.J. Water Quality Criteria/Standards and Ecological Risk Assessment of Oxytetracycline for Freshwater Organisms in China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2023, 36, 403–413. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.D.; Hu, C.Y. On characterizations of the logistic distribution. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2008, 138, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoben, R.A.E.; Beek, M.A. Application of species sensitivity distributions as ecological risk assessment tool for water management. J. Hazard. Mater. 1998, 61, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lang, Y. Source contributions of PAHs and toxicity in reed wetland soils of liaohe estuary using a CMB–TEQ method. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalf, D.F.; Crommentuijn, T. Environmental quality objectives for 10 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1997, 36, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Xue, Y.F. Influences of microbial community structures and diversity changes by nutrients injection in Shengli oilfield, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 133, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.L.; Lang, Y.H. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of PAHs in soil from Liaohe estruarine wetland. Environ. Chem. 2011, 30, 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.; Li, F. Status of POPs accumulation in the Yellow River Delta: From distribution to risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Hu, N.J. Characterization and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Sediments from the Bohai Sea, China. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2015, 17, 8202. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yao, Y. Increasing contamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Chinese soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Xing, Y.; Liu, G.; Hu, C.; Wang, X.; Yan, G.; Wang, Q. Changes in soil bacterial and fungal community composition and functional groups during the succession of boreal forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerulker, G.; Patel, P.; Chafale, A.; Rathod, V.; Das, S.; Pandey, P.; Khan, N.A.; Devi, A.; Munshi, N.S.; Dhodapkar, R.; et al. Comparative assessment of soil microbial community in crude oil contaminated sites. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 328, 121578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.R.; Sarmadian, F.; Angelini, M.E.; Bogaert, P.; Omid, M. Cause-effect relationships using structural equation modeling for soil properties in arid and semi-arid regions. CATENA 2023, 232, 107392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Ou, Y.; Duan, X.; Wu, M. Sensitive indicator microorganisms and C, N-cycle processes in soil with different petroleum hydrocarbon pollution levels. Biochem. Eng. J. 2025, 220, 109752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Ecological Toxicity Risk of Alkanes and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons with Threshold. Master’s Thesis, Xian University of Architecture and Technology, Xian, China, June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Geng, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Hou, H. A New Method for Ecological Risk Assessment of Combined Contaminated Soil. Toxics 2023, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kwak, J.I.; Cui, R.; Kim, L.; Lee, T.Y.; Kim, H.; An, Y.-J. A comparative Study of Ecological Risk Index for Site-specific Soil Ecological Risk Assessment. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2022, 44, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, P.; Chowdhury, D.; Deka, H. Ecological risk assessment of priority PAHs pollutants in crude oil contaminated soil and its impacts on soil biological properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R.; Adhikari, K.; Sinha, R.; Bharti, S.; Mal, U. Arsenic contamination in groundwater of moribund delta of Bengal basin: Quantitative assessment through adsorption kinetics and contaminant transport modelling. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 133, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Cao, Y.Z.; Li, X.J. Deriving of soil guideline values and risk assessment of polyaromatic hydrocarbons at a typical petrochemical contaminated site. Res. Environ. Sci. 2007, 20, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Zi, F.; Huang, Y.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, J.; Li, J. Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystem Health in the Irtysh River Basin Using eDNA Metabarcoding. Water 2025, 17, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Deng, Z.; Hao, X.; Li, F. Linear models for describing relations between sensitive bacterial taxa and ecological risk from heavy metals in soils of coal mines in semi-arid region. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 193, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Liu, C.G.; Chen, X.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Wu, S.S.; Yang, W.C.; Huang, D.J. Pollution Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Soils Around a Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator. J. South China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 52, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bianca, S.M.K.; José, L.F.A. Critical evaluation of different methods to calculate the Geoaccumulation Index for environmental studies: A new approach for Baixada Santista—Southeastern Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 548–552. [Google Scholar]
- Ryszard, M.; Joanna, K. Assessment of heavy metals contamination in surface layers of Roztocze National Park forest soils (SE Poland) by indices of pollution. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 839–850. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, W.; Yang, M.; Wang, X. Environmental Health and Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Coastal Cities of Estuarine Bay—A Case Study of Hangzhou Bay, China. Toxics 2020, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Risk Levels | ∑16PAHs | |
|---|---|---|
| RQ∑16PAHs(NCs) | RQ∑16PAHs(MPCs) | |
| 1 | ≥1, <800 | >0, <1 |
| 2 | ≥800 | >0, <1 |
| 3 | <800 | ≥1 |
| 4 | ≥800 | ≥1 |
| Sample | pH | EC µs/cm | SOM % | TPH (mg/g) | ∑PAHs (mg·kg−1) | ∑TEQBaP (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GD1 | 8.51 | 2625.53 | 8.96 | 182.15 | 2.34 | 0.07 |
| GD2 | 8.03 | 3261.60 | 7.56 | 48.75 | 16.24 | 0.01 |
| GD3 | 8.34 | 3932.00 | 7.64 | 37.75 | 8.72 | 0.37 |
| GD4 | 8.19 | 4653.40 | 9.08 | 194.25 | 14.03 | 0.13 |
| GD5 | 8.39 | 1532.60 | 6.74 | 194.10 | 4.95 | 0.28 |
| GD6 | 8.76 | 733.38 | 7.10 | 183.15 | 4.39 | 0.22 |
| GD7 | 8.26 | 3891.83 | 9.32 | 112.15 | 4.28 | 0.00 |
| GD8 | 8.91 | 1760.58 | 4.96 | 21.30 | 56.83 | 0.10 |
| GD9 | 8.30 | 1125.65 | 7.64 | 153.60 | 7.47 | 0.45 |
| GD13 | 8.53 | 2338.15 | 6.37 | 184.90 | 11.56 | 0.08 |
| GD14 | 8.16 | 3097.15 | 5.96 | 175.45 | 2.75 | 0.00 |
| GD15 | 8.77 | 2903.55 | 6.49 | 67.85 | 7.98 | 0.04 |
| GD16 | 7.93 | 1359.40 | 9.67 | 0.00 | 1.93 | 0.15 |
| GD17 | 8.35 | 2427.18 | 8.62 | 95.60 | 34.50 | 0.19 |
| GD18 | 8.36 | 2254.73 | 7.24 | 156.85 | 58.66 | 0.16 |
| GD19 | 8.26 | 1749.78 | 8.50 | 207.70 | 3.58 | 0.36 |
| GD20 | 7.93 | 1728.93 | 9.16 | 48.25 | 2.29 | 0.13 |
| GD21 | 8.25 | 859.30 | 7.59 | 37.10 | 8.09 | 0.52 |
| GD22 | 8.59 | 933.58 | 3.69 | 189.85 | 1.37 | 0.15 |
| GD23 | 8.09 | 1969.58 | 6.23 | 59.05 | 2.42 | 0.00 |
| GD26 | 8.82 | 1123.65 | 7.41 | 52.05 | 7.54 | 0.07 |
| GD27 | 8.26 | 1703.70 | 11.74 | 19.70 | 9.27 | 0.00 |
| GD28 | 8.03 | 4767.38 | 7.59 | 588.10 | 37.25 | 0.19 |
| GD29 | 8.55 | 1142.48 | 5.73 | 74.00 | 45.49 | 0.11 |
| GD31 | 8.24 | 3752.65 | 8.83 | 191.20 | 3.15 | 0.06 |
| GD32 | 8.20 | 4281.85 | 10.83 | 137.90 | 21.43 | 0.13 |
| GD33 | 8.23 | 2460.83 | 5.78 | 25.15 | 8.27 | 0.00 |
| GD34 | 8.43 | 4236.90 | 7.27 | 122.60 | 17.86 | 0.15 |
| GD36 | 8.70 | 3471.23 | 5.60 | 67.10 | 18.05 | 0.09 |
| GD37 | 8.77 | 1090.30 | 5.05 | 29.35 | 67.77 | 0.08 |
| GD38 | 8.26 | 1406.73 | 6.76 | 4.05 | 2.92 | 0.22 |
| GD39 | 8.00 | 2534.75 | 8.28 | 142.75 | 5.00 | 0.13 |
| Tolerant Species | Sensitive Species | |
|---|---|---|
| ∑TEQBaP | Desulfuromonas_Desulfuromonas_sp. | Nitrospira_bacterium |
| bacterium_YC-ZSS-LKJ56 | ||
| Halomonas_xianhensis | ||
| Rhodovibrio_sp. | ||
| TPH | Rhodovulum_sp. | |
| bacterium_YC-LK-LKJ13 | ||
| Bacillus_hwajinpoensis | ||
| Halomonas_ventosae | ||
| bacterium_YC-ZSS-LKJ56 | ||
| Halomonas_xianhensis | ||
| Candidatus_Tectomicrobia | ||
| EC | Rhodovulum_sp. | Palleronia_sp. |
| Thalassobacillus_Thalassobacillus_sp. | Actinophytocola_sp. | |
| Candidatus_Tectomicrobia | Pontibacter_populi |
| Factors | ΣTEQ | TPH | EC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | RMSE | HC5 | RMSE | HC5 | RMSE | HC5 |
| Normal | 0.0741 | 0.0639 | 0.1081 | 111.30 | 0.0520 | 892.072 |
| Logistics | 0.0663 | 0.0223 | 0.0816 | 150.00 | 0.0525 | 864.422 |
| Species | EC50 (Before) | EC50 (After) |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterium_YC-LK-LKJ36 | 0.06367 | 0.2005 |
| Anaerobic_bacterium | 0.06390 | 0.2329 |
| Bacterium_YC-LK-LKJ25 | 0.07284 | 0.3298 |
| Bacillus_alkalitelluris | 0.1163 | 0.3532 |
| Bacillus_selenatarsenatis | 0.1194 | 0.4292 |
| Halomonas_ventosae | 0.1361 | 0.4586 |
| Blastococcus_sp. | 0.1588 | 0.7750 |
| Halophibacterium_profundimaris | 0.2108 | 1.580 |
| Bacterium_YC-ZSS-LKJ56 | 0.2907 | 1.651 |
| Pseudomonas_borbori | 0.3904 | 2.798 |
| Gemmatimonadetes_bacterium | 0.5322 | 3.126 |
| Rhodovulum_sp. | 0.8769 | 3.785 |
| Tistlia_consotensis | 1.366 | 7.191 |
| Halomonas_xianhensis | 3.678 | 9.918 |
| Lysobacter_maris | 4.853 | 10.52 |
| Palleronia_sp. | 11.02 | 25.41 |
| Photobacterium_halotolerans | 17.17 | 39.47 |
| Regression Equations | R2 | |
|---|---|---|
| n = 32 | DF = −1.073 SOM + 10.511 | 0.218 |
| DF = −1.132 SOM + 0.033 PAHs + 9.968 | 0.438 | |
| Species | EC50 (Before) | EC50 (After) |
|---|---|---|
| bacterium_YC-LK-LKJ36 | 0.2005 | 0.1956 |
| anaerobic_bacterium | 0.2329 | 0.2287 |
| bacterium_YC-LK-LKJ25 | 0.3298 | 0.2801 |
| Bacillus_alkalitelluris | 0.3532 | 0.6575 |
| Bacillus_selenatarsenatis | 0.4292 | 1.074 |
| Halomonas_ventosae | 0.4586 | 1.188 |
| Blastococcus_sp. | 0.7750 | 2.246 |
| Halophibacterium_profundimaris | 1.580 | 2.892 |
| bacterium_YC-ZSS-LKJ56 | 1.651 | 3.883 |
| Pseudomonas_borbori | 2.798 | 3.946 |
| Gemmatimonadetes_bacterium | 3.126 | 4.262 |
| Rhodovulum_sp. | 3.785 | 7.898 |
| Tistlia_consotensis | 7.191 | 10.16 |
| Halomonas_xianhensis | 9.918 | 12.95 |
| Lysobacter_maris | 10.52 | 24.31 |
| Palleronia_sp. | 25.41 | 45.36 |
| Photobacterium_halotolerans | 39.47 | 54.60 |
| Regression Models | R2 | |
|---|---|---|
| n = 32 | AF = 11.743 SOM + 42.867pH + 0.017EC | 0.991 |
| AF = 242.518SOM +1256.029lgpH + 0.024EC − 1415.447 | 0.995 | |
| Sample | Aged Years | ΣTEF mg·kg−1 | Risk Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RQ | Pi | Igeo | NIPI | |||||
| GD1 | 21 | 0.18 | 626.82 | 0.13 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| GD2 | 33 | 0.02 | 58.01 | 0.01 | 1 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD3 | 5 | 0.93 | 3319.46 | 0.71 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| GD4 | 20 | 0.32 | 1142.69 | 0.25 | 4 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD5 | 31 | 0.71 | 2532.71 | 0.54 | 4 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD6 | 7 | 0.54 | 1944.23 | 0.42 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| GD7 | 32 | 0.00 | 15.27 | 0.00 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |
| GD8 | 20 | 0.26 | 933.64 | 0.20 | 4 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD9 | 5 | 1.11 | 3974.25 | 0.85 | 4 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD13 | 7 | 0.32 | 706.76 | 0.15 | 3 | 3 | 1 | |
| GD14 | 7 | 1.30 | 9.82 | 0.00 | 1 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD15 | 7 | 0.14 | 367.12 | 0.08 | 1 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD16 | 7 | 0.33 | 1294.88 | 0.28 | 4 | 4 | 3 | |
| GD17 | 11 | 0.16 | 1703.45 | 0.37 | 4 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD18 | 11 | 0.32 | 1440.42 | 0.31 | 4 | 5 | 2 | |
| GD19 | 15 | 0.89 | 3180.53 | 0.68 | 4 | 5 | 2 | |
| GD20 | 15 | 0.36 | 1130.71 | 0.24 | 4 | 5 | 2 | |
| GD21 | 15 | 0.01 | 4655.08 | 1.00 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| GD22 | 20 | 0.48 | 1297.23 | 0.28 | 4 | 4 | 1 | |
| GD23 | 21 | 0.20 | 22.54 | 0.00 | 1 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD26 | 21 | 0.26 | 588.29 | 0.13 | 1 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD27 | 21 | 0.21 | 33.12 | 0.01 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| GD28 | 21 | 0.54 | 1719.15 | 0.37 | 4 | 5 | 2 | |
| GD29 | 29 | 0.00 | 941.62 | 0.20 | 4 | 5 | 2 | |
| GD31 | 30 | 0.10 | 502.79 | 0.11 | 1 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD32 | 31 | 0.40 | 1129.17 | 0.24 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| GD33 | 31 | 0.01 | 29.54 | 0.01 | 1 | 5 | 4 | |
| GD34 | 31 | 0.37 | 1311.43 | 0.28 | 4 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD36 | 31 | 0.22 | 799.30 | 0.17 | 3 | 5 | 3 | |
| GD37 | 36 | 0.48 | 749.48 | 0.16 | 3 | 2 | 2 | |
| GD38 | 39 | 0.01 | 1941.85 | 0.42 | 4 | 5 | 4 | |
| GD39 | 41 | 0.36 | 1169.98 | 0.25 | 4 | 5 | 3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Zhou, C.; Song, F.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Fu, X. Environmental DNA-Based Ecological Risk Assessment of PAHs in Aged Petroleum-Contaminated Soils. Toxics 2025, 13, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050357
Huang J, Zhou C, Song F, Li T, Wang J, Fu X. Environmental DNA-Based Ecological Risk Assessment of PAHs in Aged Petroleum-Contaminated Soils. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050357
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jinrong, Chang Zhou, Fanyong Song, Tianyuan Li, Jianing Wang, and Xiaowen Fu. 2025. "Environmental DNA-Based Ecological Risk Assessment of PAHs in Aged Petroleum-Contaminated Soils" Toxics 13, no. 5: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050357
APA StyleHuang, J., Zhou, C., Song, F., Li, T., Wang, J., & Fu, X. (2025). Environmental DNA-Based Ecological Risk Assessment of PAHs in Aged Petroleum-Contaminated Soils. Toxics, 13(5), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050357