The Production of Biochar and Its Impact on the Removal of Various Emerging Pollutants from Wastewater: A Review
Abstract
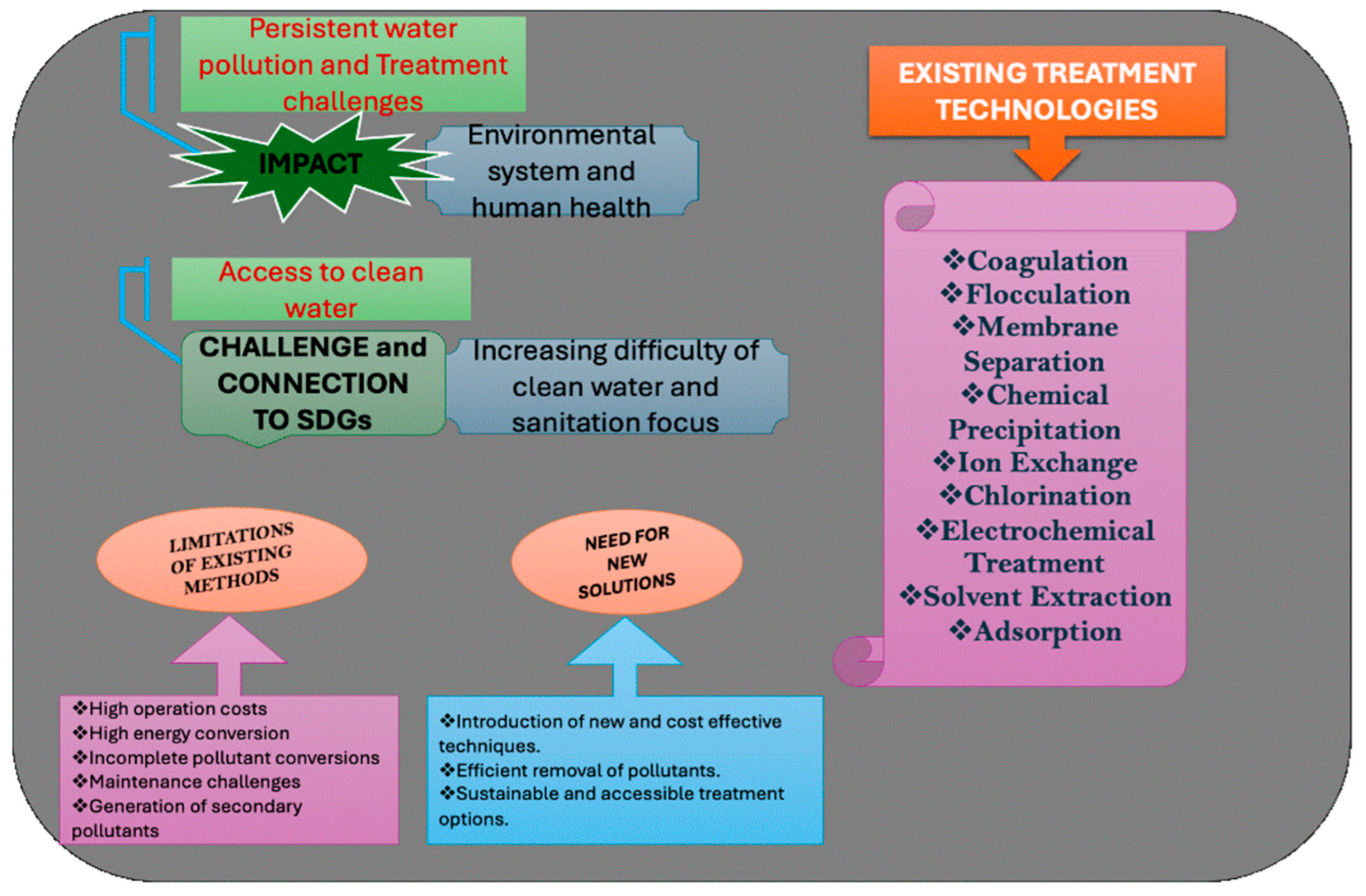
1. Introduction
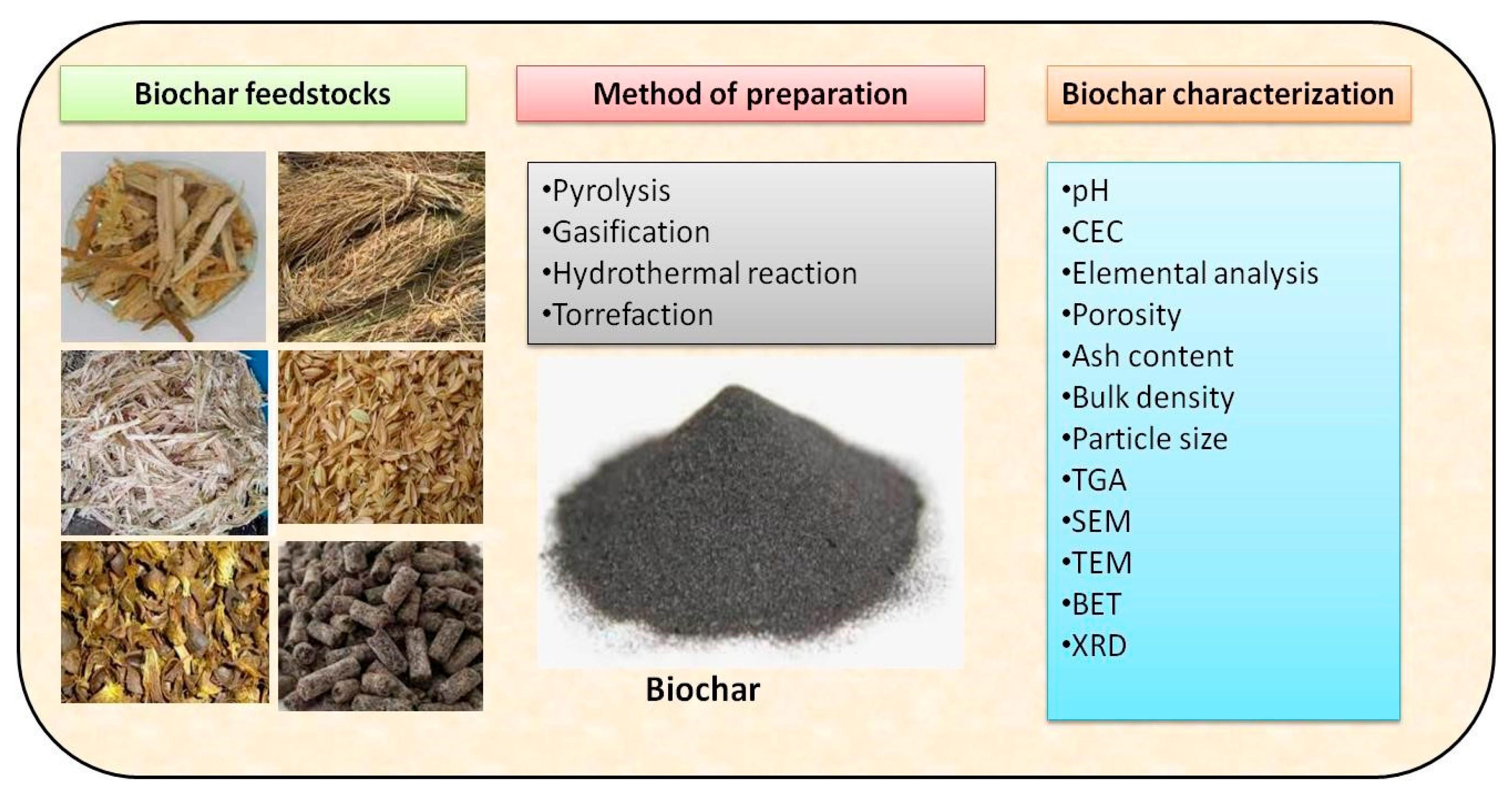
2. Characteristics of Biochar for Adsorption
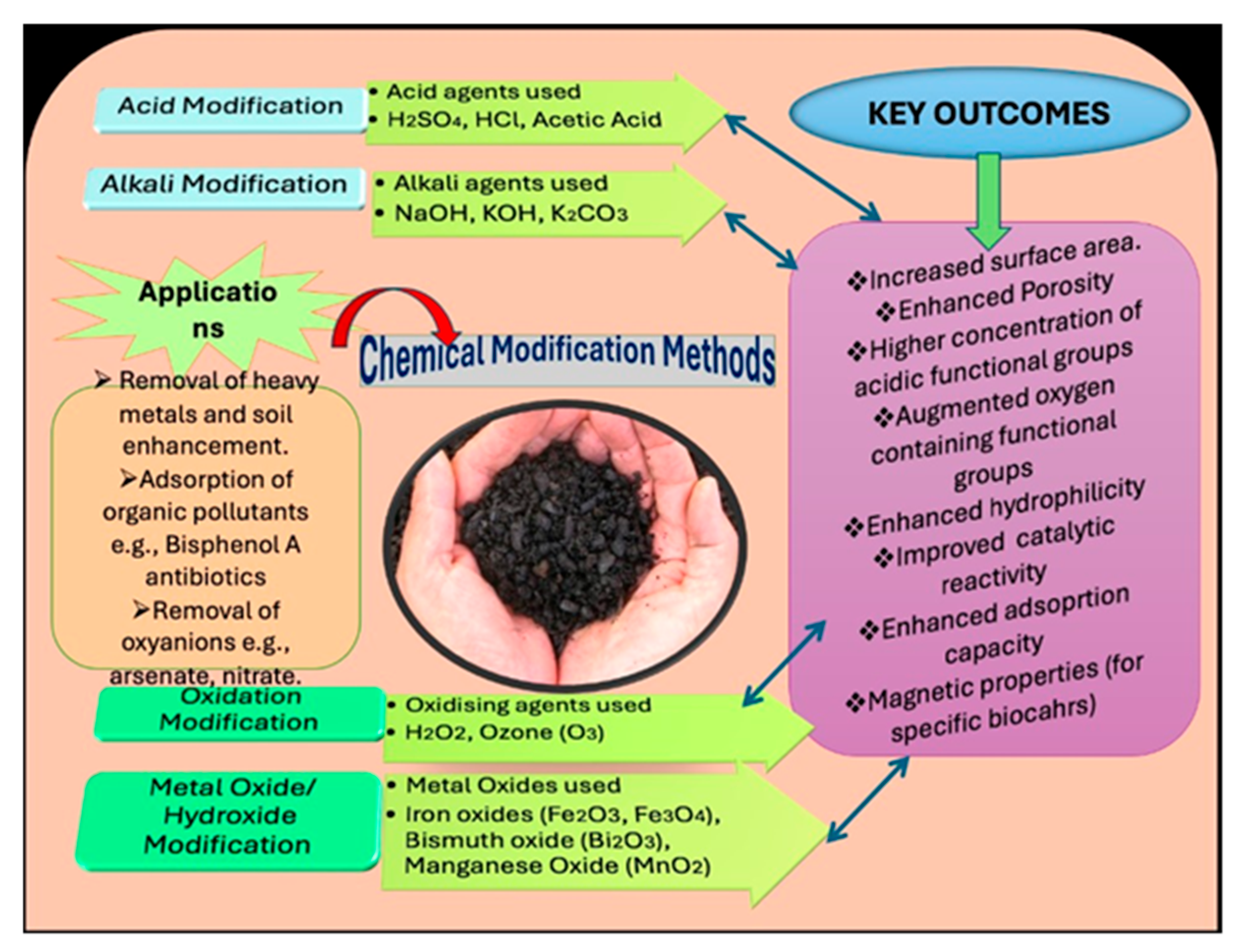
3. Synthesis, Production, and Modification of Biochar
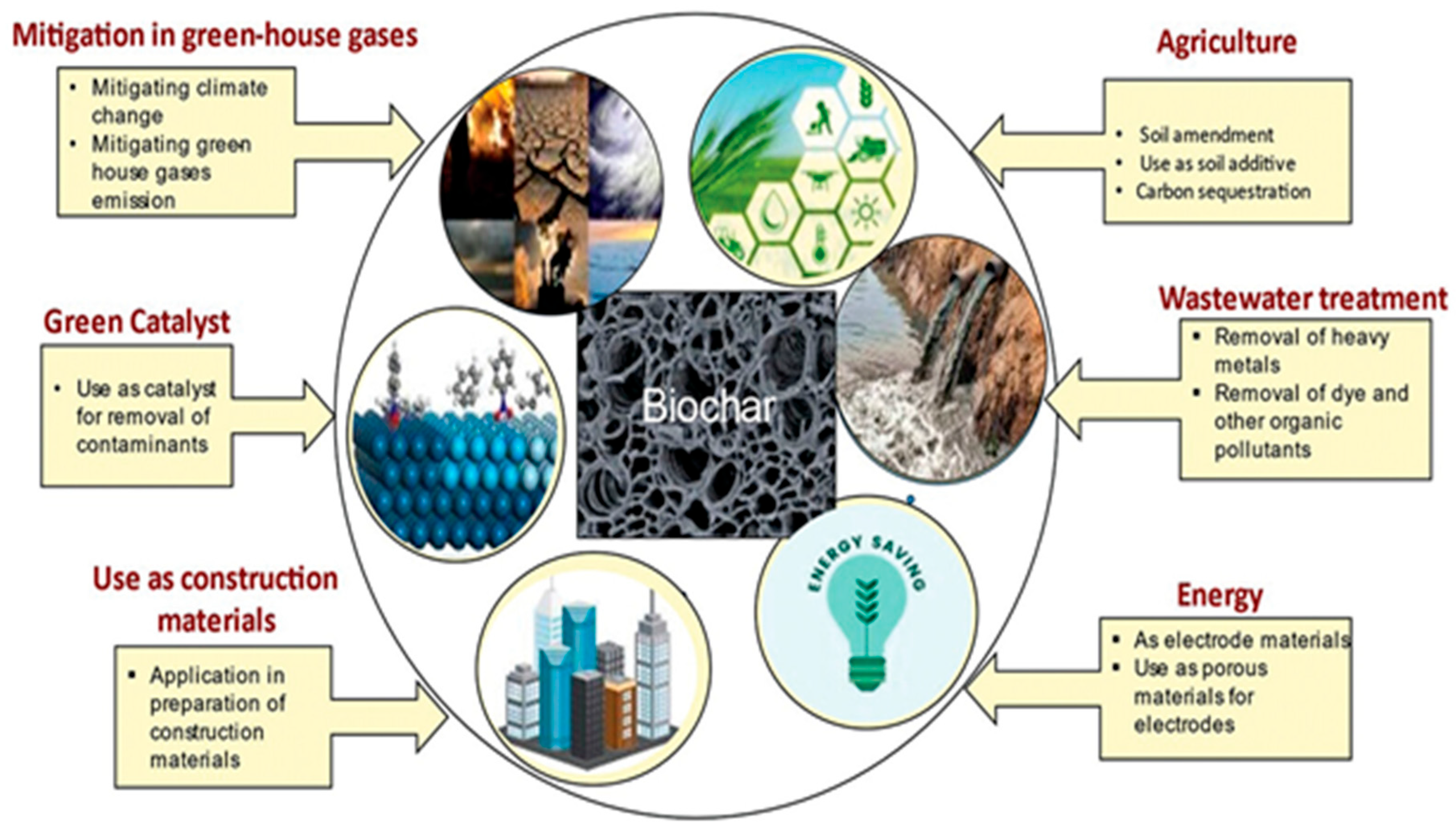
4. Biochar Applications and Performance
| Biomass for Biochar | Pre/Post-Treatment | Pyrolysis Temperature (°C) | Contaminants | Initial Concentration (mg/L) | Biochar Dose (g/L) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inorganic Contaminants | ||||||||
| Banana straw | MgCl2 | 430 | Cr(VI) | 50 | 0.02 | 125 | Complexation, electrostatic attraction, functional group bonding | [108] |
| Eucalyptus leaves | KOH | 200 | Pb2+ | 10 | 50 | - | Co-precipitation, complexation | [109] |
| Cornstalk | Fe2+/ZnCl2 | 700 | Pb2+ | 10 | 10 | 99.82 | ||
| Coconut shell | MgCl2 | 400 | Cd | 300 | 0.5 | 81.7 | Ion-exchange, metal-π electron coordination, mineral precipitation, and interaction with oxygenated functional groups | [110] |
| Coconut shell | Straw | Alkali treatment | Pb2+ | 300 | 0.5 | 214.4 | ||
| Date palm | NA | 800 | Pb2+ | 50–250 | 1 | 98.9 | NA | [111] |
| Hickory Chips | Ball-milling, H2O2 treatment | Cu2+ | 50–250 | 1 | 41 | |||
| Corncob | NA | 550 | Pb2+ | 1.95 mg/mL | 4 | NA | Ion diffusion | [22] |
| Cd2+ | 0.95 mg/mL | 4 | NA | |||||
| Brown algae | 300 | Zn2+ | 1–180 | 0.2 | 1.78 | NA | [112] | |
| Organic Contaminants | ||||||||
| Rice husk | Peroxymonosulfate | 450 | Tetracycline | 20–100 | 0.05–0.5 | NA | NA | [72] |
| Bisphenol A | 20–100 | 0.05–0.5 | NA | NA | ||||
| Date palm petiole | NA | 700 | Crystal violet | 5–500 | 0.05 | 209 | Pore filling, π–π interaction and H-bonding | [113] |
| Corncob | NA | 500 | Brilliant green dye | 50–200 | 2 | 39.4 | NA | [114] |
| Egg shell | HCl | 800 | Rhodamine B | NA | 1 | NA | NA | [40] |
| Cow dung | KOH/NaOH | 700 | Rhodamine B | 100–300 | 1 | 1241 | π–π interaction, electrostatic attraction, H-bonding | [115] |
5. Future Prospective and Directions
- ➢
- Biochar’s ability to adsorb various contaminants from polluted water enhances water quality and makes it a desirable option for wastewater treatment. As awareness of environmental sustainability grows, biochar can serve as an innovative solution that aligns with the principles of a circular economy by conserving resources and minimizing waste.
- ➢
- Beyond its role in wastewater treatment, biochar contributes to climate change mitigation by reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Its production from organic waste and subsequent use in soil can sequester carbon, helping to combat climate change while improving soil health.
- ➢
- Biochar is a renewable resource that fits well within the framework of a circular economy. By recycling organic waste into valuable biochar, it not only provides an alternative to waste disposal but also enhances resource efficiency. This approach can lead to significant improvements in resource conservation over extended periods.
- ➢
- Continued research is essential to maximize the potential of biochar in wastewater treatment. Specifically, the following areas require further exploration. Feedstock selection: Different types of biomass yield biochar with varying properties. Investigating the best feedstock for specific wastewater applications can optimize performance. Synthesis conditions: The techniques and parameters used in biochar production such as temperature, time, and chemical treatments can significantly affect its adsorption capacity. Researching these variables will help produce biochar tailored for specific contaminants. Adsorption mechanisms: While chemically treated biochar has shown improved contaminant adsorption compared to unmodified biochar, more in-depth studies are needed to understand the underlying adsorption mechanisms better.
- ➢
- Modification techniques: Various modification strategies, including chemical, physical, and biological methods, have been discussed, showcasing how these enhancements can improve biochar porosity, surface area, and functional groups. Such modifications lead to increased adsorptive performance, making biochar a more viable option for wastewater treatment.
- ➢
- Adsorption mechanisms: The review emphasizes the critical processes involved in biochar adsorption capabilities, elucidating how its structure and surface properties contribute to its efficiency in capturing contaminants.
- ➢
- Diverse applications: The properties of biochar and its production methods, alongside innovative modifications, position it as a multifunctional material that can address both organic and hazardous inorganic pollutants effectively.
- ➢
- Research on the interactions between processing variables, feedstock choices, and the regeneration and disposal of biochar is crucial to mitigate any environmental risks. Understanding how to safely manage biochar waste and its potential effects on soil and water systems will be critical as its use becomes more widespread.
- ➢
- Biochar holds significant promise for transforming wastewater treatment into a more sustainable and effective process. By focusing on the critical areas of research and development outlined above, stakeholders can ensure that biochar is used efficiently and effectively, contributing to environmental sustainability and improved water quality.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Bolan, N.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Wang, H.; Balasubramanian, P.; Zhang, P.; Nguyen, X.C.; Li, F. Critical review of biochar for the removal of emerging inorganic pollutants from wastewater. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 36, 109960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, M.I.; Hussain, D.; Ahmad, N.; Xiao, H.-M.; Musharraf, S.G. Improved visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of an industrial dye Acid Orange 7 using metal-free sulfur-doped graphitic carbon nitride. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 2810–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, M.I.; Gulzar, T.; Kiran, S.; Ahmad, N.; Raza, S.A.; Batool, U.; Rehan, Z.A. Tailoring Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4) for Multifunctional Applications: Strategies for Overcoming Challenges in Catalysis and Energy Conversion. Int. J. Energy Res. 2025, 2025, 5599894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, S.; Rasheed, S.; Nabeel, M.I.; Ahmad, W.; Riaz, M.T.; Musharraf, S.G.; Hussain, D. Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Sulfur–Nitrogen Co-Doped TiO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized using Dactylorhiza hatagirea Root Extract. ChemistrySelect 2025, 10, e01568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasooriya, R.R.; Liyanage, L.P.K.; Rathnappriya, R.H.K.; Bandara, W.B.M.A.C.; Perera, T.A.N.T.; Gunarathna, M.H.J.P.; Jayasinghe, G.Y. Industrial water conservation by water footprint and sustainable development goals: A review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 12661–12709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, M.I.; Hussain, D.; Ahmad, N.; Xiao, H.-M.; Ahmad, W.; Musharraf, S.G. Facile one-pot synthesis of metal and non-metal doped g-C3N4 photocatalyst for rapid acetaminophen remediation. Carbon 2025, 243, 120472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Manzoor, S.; Nabeel, M.I.; Waqas, R.; Hussain, S.; Joseph, C.G.; Suazo-Hernández, J. Harnessing High-Valent Metals for Catalytic Oxidation: Next-Gen Strategies in Water Remediation and Circular Chemistry. Catalysts 2025, 15, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Ali, T.; Nabeel, M.I.; Ahmed, K.; Baggash, H.; Hasnain, M.; Hussain, D. Facile modification of nylon filter via vacuum coating with chitosan@ MCM-41/GO for efficient oily wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 21993–22008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Kumar, U.; Kumar, I.; Dwivedi, A.; Singh, P.; Mishra, S.; Seth, C.S.; Sharma, R.K. Critical review on toxic contaminants in surface water ecosystem: Sources, monitoring, and its impact on human health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 56428–56462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, M.I.; Hussain, D.; Ahmad, N.; Najam-Ul-Haq, M.; Musharraf, S.G. Recent advancements in the fabrication and photocatalytic applications of graphitic carbon nitride-tungsten oxide nanocomposites. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 5214–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Nabeel, M.I.; Ali, S.J.; Fatima, B.; Rashid, H.N.; Najam-Ul-Haq, M.; Musharraf, S.G.; Hussain, D. Hierarchically grown CeO2/GO on nylon filter with enhanced hydrophilicity and permeation flux for oil-water separation. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 37, e00698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Rasheed, S.; Mohyuddin, A.; Fatima, B.; Nabeel, M.I.; Riaz, M.T.; Najam-Ul-Haq, M.; Hussain, D. 2D MXenes and their composites; design, synthesis, and environmental sensing applications. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Nabeel, M.I.; Bokhari, T.H.; Arif, S.; Haq, M.H.; Ajmal, Z.; A Awwad, F.; Ismail, E.A.; Mustafa, A.; Rasool, R.T.; et al. Radiation-Induced Degradation of PVA-26 by UV Radiation in the Presence of Zno Nanocatalyst. J. Biomed. Res. Environ. Sci. 2023, 4, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, N.; Rasheed, S.; Nabeel, M.I.; Mohyuddin, A.; Riaz, M.T.; Hussain, D. Silica-Based superhydrophobic and superoleophilic cotton fabric with enhanced self-cleaning properties for oil–water separation and methylene blue degradation. Langmuir 2024, 40, 5639–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Moeid, A.; Kiran, S.; Gulzar, T.; Pervez, I.; Shahid, R.; Nabeel, M.I.; Ali, A. Prunus armeniaca assisted green synthesis of Fe2O3/NiO nanohybrids using unripened fruit extract for remediation of acid orange 7 dye: A sustainable environmental cleaner approach. Waste Biomass Valorization 2025, 16, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.N.A.; Joseph, C.G.; Surugau, N.; Nabeel, M.I.; Ismail, S.S. From Waste to Water Cleanup: Preliminary Study on Sargassum-Derived Activated Carbon (AC) for Pollutant Adsorption. Mater. Emerg. Technol. Sustain. 2025, 1, 2550015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, M.I.; Ahmad, N.; Arif, S.; Hussain, D.; Musharraf, S.G. Facile Two-Step Synthesis of Yttrium-Doped g-C3N4 for Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue with Self-Cleaning Properties. Nanoscale Adv. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, M.W.; Kim, S.; Roddick, F.; Xie, Z.; Fan, L. A review of the recent advancements in adsorption technology for removing antibiotics from hospital wastewater. J. Water Process. Eng. 2025, 70, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmani, A.; Magdouli, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Kapoor, A.; Chellam, P.V.; Gökkuş, Ö. Agricultural waste materials for adsorptive removal of phenols, chromium(VI) and cadmium(II) from wastewater: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Maurya, V.K.; Kumar, D. Biochar: A Sustainable solution for agriculture and environment. In Biochar: A Precious Resource from Biological Waste: Applications for Soil, Plant and Environmental Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 21–46. [Google Scholar]
- Amen, R.; Bashir, H.; Bibi, I.; Shaheen, S.M.; Niazi, N.K.; Shahid, M.; Hussain, M.M.; Antoniadis, V.; Shakoor, M.B.; Al-Solaimani, S.G.; et al. A critical review on arsenic removal from water using biochar-based sorbents: The significance of modification and redox reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, L.; Bruggemann, R. The 17 United Nations’ sustainable development goals: A status by 2020. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2022, 29, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, H.; Huang, X.; MacFeely, S.; Entezarian, M.R. Big data and the united nations sustainable development goals (UN SDGs) at a glance. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2021, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindiran, G.; Rajamanickam, S.; Janardhan, G.; Hayder, G.; Alagumalai, A.; Mahian, O.; Lam, S.S.; Sonne, C. Production and modifications of biochar to engineered materials and its application for environmental sustainability: A review. Biochar 2024, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kwon, E.E.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Lee, J. Recently developed methods to enhance stability of heterogeneous catalysts for conversion of biomass-derived feedstocks. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, H. Improved Pb(II) removal in aqueous solution by sulfide@ biochar and polysaccharose-FeS@ biochar composites: Efficiencies and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Meng, Y.; Aihemaiti, A.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, H.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X. Preparation, environmental application and prospect of biochar-supported metal nanoparticles: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
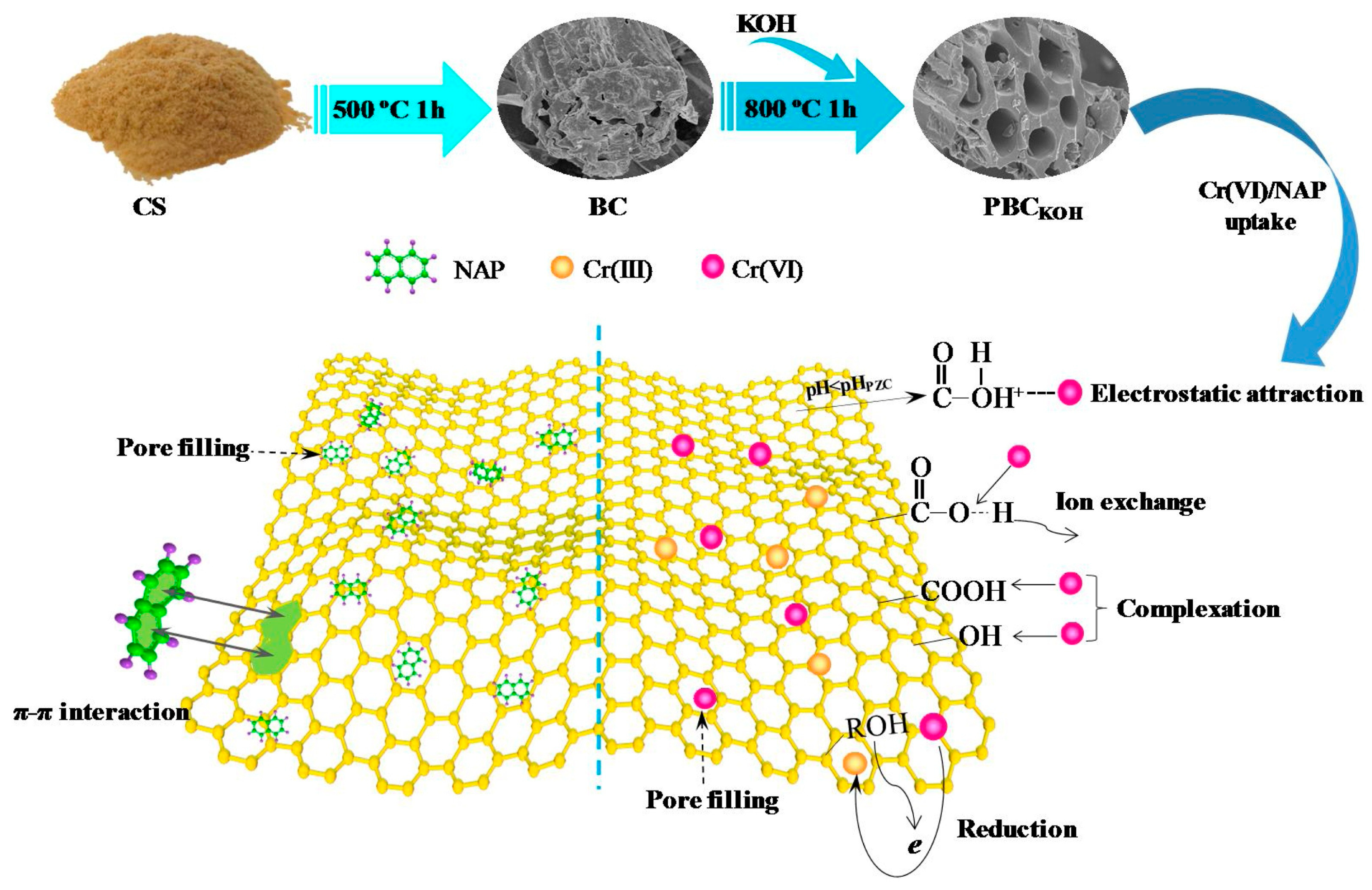
- Qu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Jiang, Z.; Deng, F.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. KOH-activated porous biochar with high specific surface area for adsorptive removal of chromium(VI) and naphthalene from water: Affecting factors, mechanisms and reusability exploration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
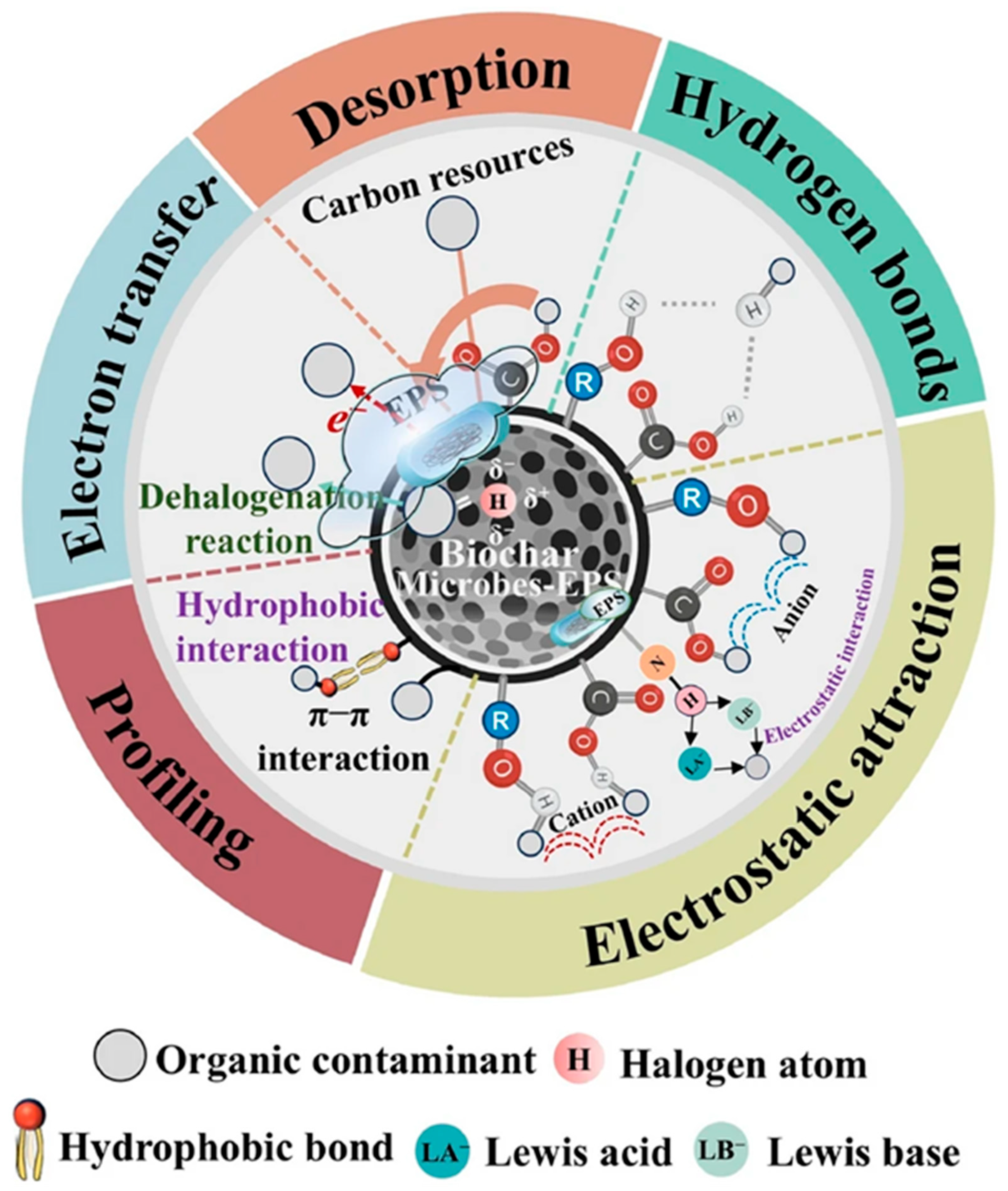
- Dong, W.; Xing, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wu, M.; Yi, P.; Pan, B.; Xing, B. Hydrogen bonds between the oxygen-containing functional groups of biochar and organic contaminants significantly enhance sorption affinity. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, A.; Layne, C.A.; Perez, F.; Hassan, E.B.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Mlsna, T.E. KOH-activated high surface area Douglas Fir biochar for adsorbing aqueous Cr(VI), Pb(II) and Cd(II). Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, L.; Xu, S.; Liu, R.; Yu, T.; Zhuo, X.; Leng, S.; Xiong, Q.; Huang, H. Nitrogen containing functional groups of biochar: An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
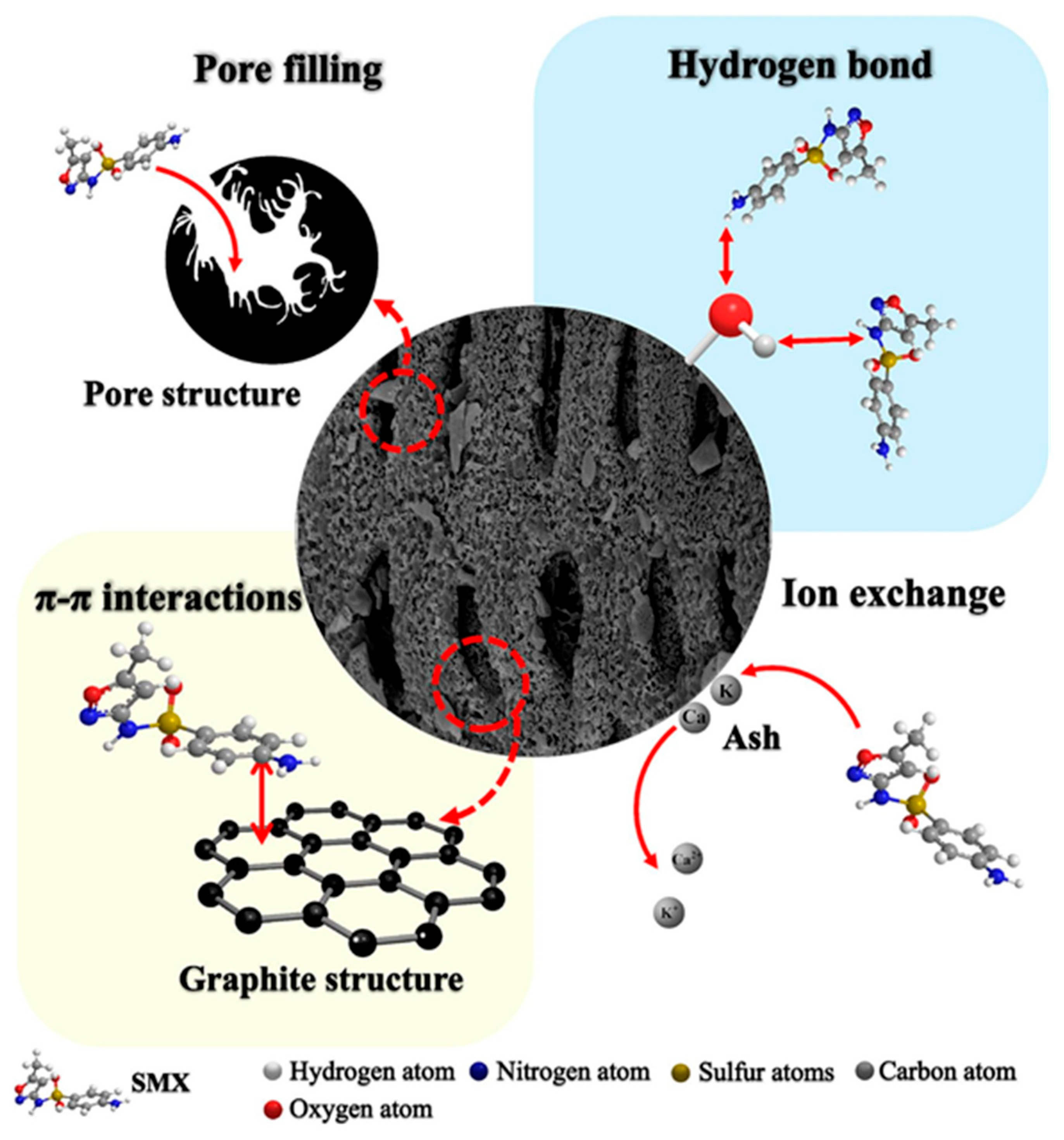
- Li, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Shang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wei, X.; Wang, T.; Zhou, W.; Yu, Y. Design of functional groups on biochar for sulfamethoxazole adsorption from adsorption efficiency and adsorption mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munera-Echeverri, J.; Martinsen, V.; Strand, L.; Zivanovic, V.; Cornelissen, G.; Mulder, J. Cation exchange capacity of biochar: An urgent method modification. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.M.; Han, J.; Chu, K.H.; Al-Hamadani, Y.A.J.; Her, N.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Influence of solution pH, ionic strength, and humic acid on cadmium adsorption onto activated biochar: Experiment and modeling. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 48, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, M.; Man, Y.B.; Christie, P.; Liang, P.; Shan, S.; Wong, M.H. The role of sewage sludge biochar in methylmercury formation and accumulation in rice. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
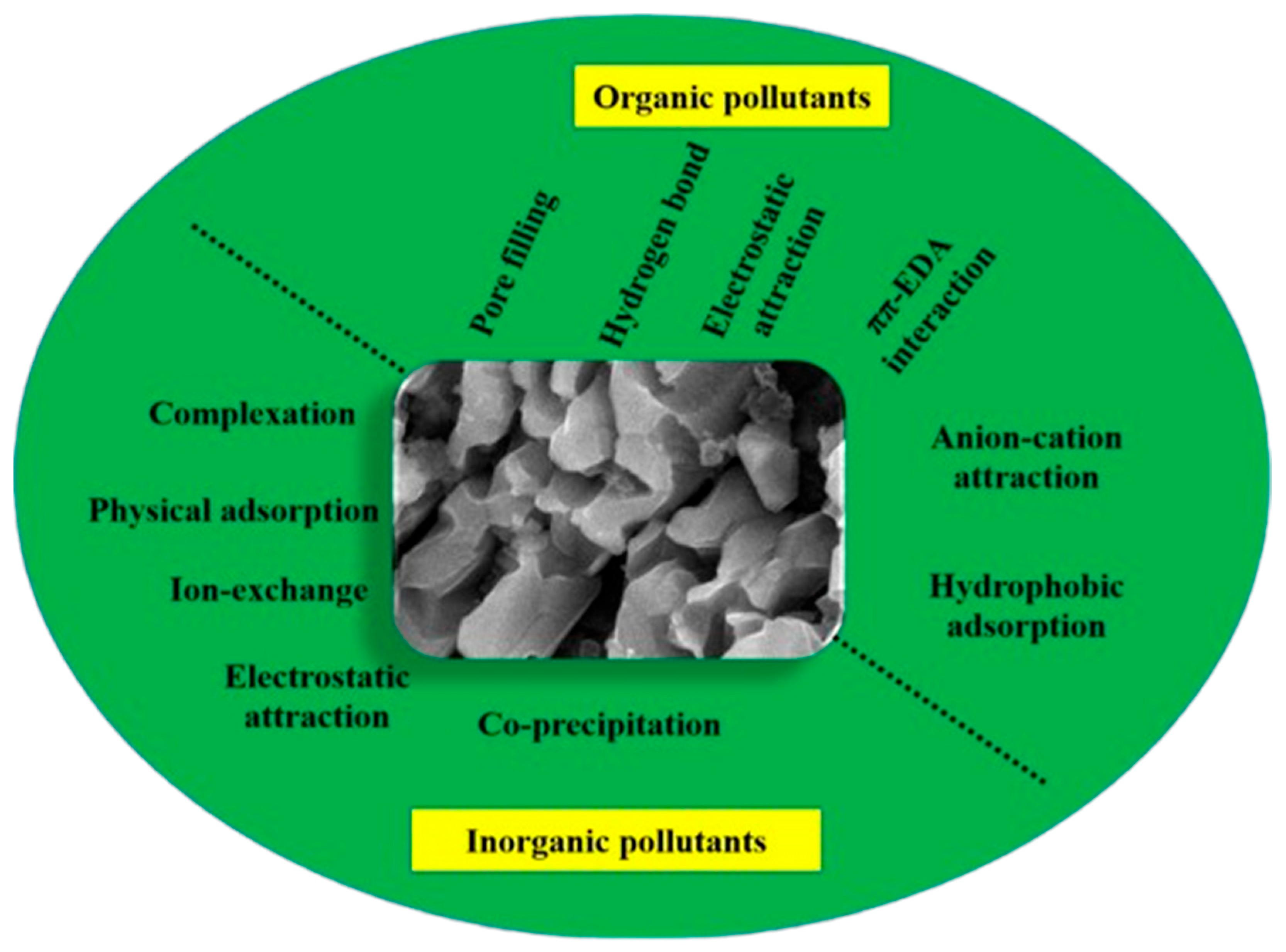
- Liang, L.; Xi, F.; Tan, W.; Meng, X.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Review of organic and inorganic pollutants removal by biochar and biochar-based composites. Biochar 2021, 3, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, M.M.; Liu, G. Recent progress in biochar-supported photocatalysts: Synthesis, role of biochar, and applications. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 14237–14248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; An, Y.; Gao, G.; Xue, J.; Algadi, H.; Huang, Z.; Guo, Z. Insights into selective glucose photoreforming for coproduction of hydrogen and organic acid over biochar-based heterojunction photocatalyst cadmium sulfide/titania/biochar. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 2538–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, M.; Zou, J.; Xie, Q. Egg shell biochar-based green catalysts for the removal of organic pollutants by activating persulfate. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, T.; Huang, Q.; Zhan, M.; Li, X.; Yan, J. Activation of persulfate by CO2-activated biochar for improved phenolic pollutant degradation: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukowska, S.; Szewczuk-Karpisz, K. Biochar and zeolite uses in improving immobilization of nutrients and pollutants in soils. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2025, 54, 354–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maged, A.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Hlawitschka, M.W.; Haneklaus, N.H.; Gupta, A.K.; Bhatnagar, A. Synergistic mechanisms for the superior sorptive removal of aquatic pollutants via functionalized biochar-clay composite. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.-F.; Zhu, S.-S.; Wang, R.-P.; Chen, Y.-D.; Show, P.-L.; Zhang, F.-F.; Ho, S.-H. Role of biochar surface characteristics in the adsorption of aromatic compounds: Pore structure and functional groups. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clurman, A.M.; Rodríguez-Narvaez, O.M.; Jayarathne, A.; De Silva, G.; Ranasinghe, M.I.; Goonetilleke, A.; Bandala, E.R. Influence of surface hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity of biochar on the removal of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, T.; Yoo, J.; Ryu, C.; Park, Y.-K.; Jung, J. Effect of steam activation of biochar produced from a giant Miscanthus on copper sorption and toxicity. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawzy, S.; Osman, A.I.; Yang, H.; Doran, J.; Rooney, D.W. Industrial biochar systems for atmospheric carbon removal: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3023–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, L.; Kushwaha, A.; Kafle, S.R.; Kim, B.-S. Surface modification of biochar for dye removal from wastewater. Catalysts 2022, 12, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, N.L.; Pawar, A. Influence of activation conditions on the physicochemical properties of activated biochar: A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.-H.; Islam, S.; Wang, S.; Messele, S.A.; Naeth, M.A.; El-Din, M.G.; Chang, S.X. Biochar properties and lead(II) adsorption capacity depend on feedstock type, pyrolysis temperature, and steam activation. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amusat, S.O.; Kebede, T.G.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. Ball-milling synthesis of biochar and biochar–based nanocomposites and prospects for removal of emerging contaminants: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 101993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Westholm, L.J.; Carvalho, L.; Thorin, E.; Yu, Z.; Yu, X.; Skreiberg, Ø. A critical review on production, modification and utilization of biochar. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 161, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; He, Y.; Ni, L.; Gao, Q.; Feng, X.; Liu, S.; Zhong, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Steam-activated biochar for efficient removal of sulfamethoxazole from water: Activation temperature-mediated differences. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 72, 107462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, G.; Peng, C.; Tan, J.; Wan, J.; Sun, P.; Li, Q.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; et al. Recent advances of carbon-based nano zero valent iron for heavy metals remediation in soil and water: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, I.; Baranov, O.; Riccardi, C.; Roman, H.E.; Cvelbar, U.; Ivanova, E.P.; Mohandas, M.; Ščajev, P.; Malinauskas, T.; Xu, S.; et al. Nanoengineered Carbon-Based Interfaces for Advanced Energy and Photonics Applications: A Recent Progress and Innovations. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2201739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, D.; Zhao, Z.; Li, P.; Su, H.; Feng, W.; Zhang, Z. Enhancing norfloxacin removal from water using nitrogen-doped biochar synthesized via solvent-free ball milling. J. Water Process. Eng. 2025, 71, 107256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.J.; Shaheen, S.M.; Xiao, R.; Rinklebe, J.; Xi, B.; He, X.; et al. Removing tetracycline and Hg (II) with ball-milled magnetic nanobiochar and its potential on polluted irrigation water reclamation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Chen, H.; Hu, X.; Gao, B. Mechanisms and adsorption capacities of hydrogen peroxide modified ball milled biochar for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Pan, J.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.; Ma, J. Adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions by modified biochar: A review. Environ. Chem. 2022, 19, 53–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Shaikh, W.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Sarkar, D.; Biswas, J.K. Biochar modification methods for augmenting sorption of contaminants. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2022, 8, 519–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapaksha, A.U.; Ahmad, M.; Vithanage, M.; Kim, K.-R.; Chang, J.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. The role of biochar, natural iron oxides, and nanomaterials as soil amendments for immobilizing metals in shooting range soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senadheera, S.S.; Yuan, X.; Yi, B.; Im, S.K.; Ok, Y.S. Plasma-modified biochar for energy and environmental sustainability. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2025, 49, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lv, J.; Pan, F.; Fu, Q.; Jia, H.; Li, Y.-F.; Hough, R.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, S.; Liu, G. Unveiling the role of nitrogen-related functional groups in Imidacloprid adsorption by chitosan-modified graphitic biochar: A mechanistic insight into N-containing pollutant removal. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2025, 7, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Singh, T.P.; Mandal, S.; Azad, D.; Kumar, S. Chemical treatments for biochar modification: Opportunities, limitations and advantages. In Engineered Biochar: Fundamentals, Preparation, Characterization and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjadi, B.; Zubatiuk, T.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J.; Chen, W.Y. Chemical activation of biochar for energy and environmental applications: A comprehensive review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 35, 777–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, E.; Karbassiyazdi, E.; Altaee, A.; Jesionowski, T.; Ciesielczyk, F. Hybrid metal oxide/biochar materials for wastewater treatment technology: A review. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 27062–27078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1002–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Rottler, E.; Herklotz, L.; Wirth, B. Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of wheat straw: Influence of feedwater pH prepared by acetic acid and potassium hydroxide. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Hong, Z.-N.; Jiang, J.; Dong, G.; Liu, H.; Xu, R.-K. Enhancement of Cd(II) adsorption by rice straw biochar through oxidant and acid modifications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 42787–42797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, D.N.G.; Chuang, X.-Y.; Huang, C.-P.; Hua, L.-C.; Huang, C. Compositional characterization of nine agricultural waste biochars: The relations between alkaline metals and cation exchange capacity with ammonium adsorption capability. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enaime, G.; Baçaoui, A.; Yaacoubi, A.; Lübken, M. Biochar for wastewater treatment—Conversion technologies and applications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhan, L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, S.; Pang, R.; Xie, B. Removal of emerging contaminants (bisphenol A and antibiotics) from kitchen wastewater by alkali-modified biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, L.; Azad, A.; Singh, J. Performance of a novel iron infused biochar developed from Raphanus sativus and Artocarpus heterophyllus refuse for trivalent and pentavalent arsenic adsorption from an aqueous solution: Mechanism, isotherm and kinetics study. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2022, 24, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, L.; Singh, J. Synthesis of novel biochar from waste plant litter biomass for the removal of Arsenic (III and V) from aqueous solution: A mechanism characterization, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, L.; Singh, J. As(III) removal using engineered biochar synthesized from waste biomass of a Timber plant refuse. J. Appl. Sci. Innov. Technol. 2022, 1, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, L.; Singh, J. Removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solution using engineered biochar: Batch and fixed-bed column study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 1961–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, H.; Sarkar, B.; Mitra, S.; Bhaladhare, S. Biochar from biomass: A review on biochar preparation its modification and impact on soil including soil microbiology. Geomicrobiol. J. 2022, 39, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Su, M.; Tian, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, S. Enhanced Pb immobilization via the combination of biochar and phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayoumu, M.; Wang, H.; Duan, G. Interactions between microbial extracellular polymeric substances and biochar, and their potential applications: A review. Biochar 2025, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xu, L.; Buyong, F.; Chay, T.C.; Li, Z.; Cai, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Modified biochar: Synthesis and mechanism for removal of environmental heavy metals. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, D.; Pateriya, R.N.; Arya, R.; Sharma, R.K. Biological treatment for biochar modification: Opportunities, limitations, and advantages. In Engineered Biochar: Fundamentals, Preparation, Characterization and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 85–104. [Google Scholar]
- García-Prats, M.; Olivera-Begué, E.; González, D.; Sánchez, A. Biochar: An emerging material for the improvement of biological treatment of organic waste. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 2, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, J.E.; Rillig, M.C. Characteristics of biochar: Biological properties. In Biochar for Environmental Management; Routledge: England, UK, 2012; pp. 117–138. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, A.; Moezzi, A.; Chorom, M.; Enayatizamir, N. Application of biochar changed the status of nutrients and biological activity in a calcareous soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Xie, J.; Jin, Q.; Lu, Y.; Lin, H. Advances in selective heavy metal removal from water using biochar: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and modifications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Tao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ding, X.; Chu, H. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Hu, B.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, X. Challenges of organic pollutant photocatalysis by biochar-based catalysts. Biochar 2021, 3, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Sarkar, B.; Aralappanavar, V.K.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Basak, B.; Srivastava, P.; Marchut-Mikołajczyk, O.; Bhatnagar, A.; Semple, K.T.; Bolan, N. Biochar-microorganism interactions for organic pollutant remediation: Challenges and perspectives. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 30, 119609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; He, L.; Lu, K.; Sarmah, A.; Li, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Pei, J.; Huang, H. Using biochar for remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals and organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8472–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Gul, J.; Naqvi, S.R.; Ali, I.; Farooq, W.; Liaqat, R.; AlMohamadi, H.; Štěpanec, L.; Juchelková, D. Recent progress in microalgae-derived biochar for the treatment of textile industry wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Song, W.; Tian, J. Biochar-facilitated soil remediation: Mechanisms and efficacy variations. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 521512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Selvamani, V.; Yoo, I.-K.; Kim, T.W.; Hong, S.H. A novel strategy for the microbial removal of heavy metals: Cell-surface display of peptides. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2021, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.T.; Ahmad, P.; Rafatullah, M. Insights into biochar applications: A sustainable strategy toward carbon neutrality and circular economy. In Catalytic Applications of Biochar for Environmental Remediation: Sustainable Strategies Towards a Circular Economy; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; Volume 2, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, X.J.; Ong, H.C.; Ooi, J.; Yu, K.L.; Tham, T.C.; Chen, W.H.; Ok, Y.S. Engineered macroalgal and microalgal adsorbents: Synthesis routes and adsorptive performance on hazardous water contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Deng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ye, C. High-efficiency removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by Mg-loaded biochars: Adsorption process and removal mechanism. Materials 2020, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neolaka, Y.A.; Lawa, Y.; Naat, J.; Riwu, A.A.; Lindu, Y.E.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Widyaningrum, B.A.; Iqbal, M.; Kusuma, H.S. Evaluation of magnetic material IIP@ GO-Fe3O4 based on Kesambi wood (Schleichera oleosa) as a potential adsorbent for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 166, 105000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H. Mechanistic insights of removing pollutant in adsorption and advanced oxidation processes by sludge biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wei, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ho, S.-H. Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole via biochar: The key role of characteristic components derived from different growth stage of microalgae. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, A.L.; Pham, T.D.; Izah, S.C.; Singh, N.; Singh, P.K. Biochar adsorbents for arsenic removal from water environment: A review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, X.; da Silva, E.B.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.Q. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Y.; Deng, H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ye, C.H.; Yu, B.G.; Zhou, X.L.; Ma, A.Y. Superefficient removal of heavy metals from wastewater by Mg-loaded biochars: Adsorption characteristics and removal mechanisms. Langmuir 2020, 36, 9160–9174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Abbas, F.; Bibi, I.; Riaz, M.; Khalil, U.; Niazi, N.K.; Rinklebe, J. A review of biochar-based sorbents for separation of heavy metals from water. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2020, 22, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, L.; Siddique, M.A.; Singh, J.; Bharagava, R.N. As(III) and As(V) removal by using iron impregnated biosorbents derived from waste biomass of Citrus limmeta (peel and pulp) from the aqueous solution and ground water. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, B.; Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Yaashikaa, P.; Thamarai, P.; Shaji, A.; Rangasamy, G. A review on algae biosorption for the removal of hazardous pollutants from wastewater: Limiting factors, prospects and recommendations. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: Mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Shan, R.; Lu, L.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. High-efficiency removal of Cr(VI) by modified biochar derived from glue residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 119935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, R.; Gopinath, K.; Kumar, P.S. Adsorptive separation of toxic metals from aquatic environment using agro waste biochar: Application in electroplating industrial wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonu, K.; Sogani, M.; Syed, Z.; Dongre, A.; Sharma, G. Enhanced decolorization and treatment of textile dye wastewater through adsorption on acid modified corncob derived biochar. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 12287–12297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhang, S.; Song, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, F. Activation of porous magnetized biochar by artificial humic acid for effective removal of lead ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, W.-P. A novel modified method for the efficient removal of Pb and Cd from wastewater by biochar: Enhanced the ion exchange and precipitation capacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.; Alazba, A.; Shafiq, M. Application of biochar derived from date palm biomass for removal of lead and copper ions in a batch reactor: Kinetics and isotherm scrutiny. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 722, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, R.; Saravanakumar, K.; Prasad, D.M.R.; Prasad, B.S.N.; Shaik, F. Effective batch and column remediation of zinc(II) from synthetic and electroplating effluents using biochar from brown alga. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 10317–10324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahinez, H.-O.; Abdelkader, O.; Leila, Y.; Tran, H.N. One-stage preparation of palm petiole-derived biochar: Characterization and application for adsorption of crystal violet dye in water. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.S.; Gun, S.; Pandey, S.; Trivedi, A.; Kapoor, R.T.; Singh, R.P.; Abdeldayem, O.M.; Rene, E.R.; Yadav, S.; Chaturvedi, P.; et al. Reusability of brilliant green dye contaminated wastewater using corncob biochar and Brevibacillus parabrevis: Hybrid treatment and kinetic studies. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, G.; Chen, Y.; Tang, S.; Su, Y. Cow dung-based biochar materials prepared via mixed base and its application in the removal of organic pollutants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjati-Najafabadi, A.; Mansoorianfar, M.; Liang, T.; Shahin, K.; Karimi-Maleh, H. A review on magnetic sensors for monitoring of hazardous pollutants in water resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasseghian, Y.; Arunkumar, P.; Joo, S.-W.; Gnanasekaran, L.; Kamyab, H.; Rajendran, S.; Balakrishnan, D.; Chelliapan, S.; Klemeš, J.J. Metal-organic framework-enabled pesticides are an emerging tool for sustainable cleaner production and environmental hazard reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owodunni, A.A.; Ismail, S.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Ahmad, A.; Imron, M.F.; Abdullah, S.R.S. A review on revolutionary technique for phosphate removal in wastewater using green coagulant. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 52, 103573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ma, S.; Jiang, H.; Yang, F. Start-up of the anaerobic hydrolysis acidification (ANHA)-simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD)/enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) process for simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal for domestic sewage treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130094. [Google Scholar]
- Lage, S.; Toffolo, A.; Gentili, F.G. Microalgal growth, nitrogen uptake and storage, and dissolved oxygen production in a polyculture based-open pond fed with municipal wastewater in northern Sweden. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.L.; Wang, B.; Elise, W.A.; Chen, J.J.; He, F.; Chen, H.; Gao, B. Reclaiming phosphorus from secondary treated municipal wastewater with engineered biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y. Necessity of direct energy and ammonium recovery for carbon neutral municipal wastewater reclamation in an innovative anaerobic MBR-biochar adsorption-reverse osmosis process. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Contaminant | Biochar Source | Modification | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead (Pb) | Sewage Sludge (SS), Rice Husk (RH) | Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) | 24.11–60.85 | [78] |
| Arsenic (As) | Rice Husk | Bismuth-induced modification | 16 | [22] |
| Mercury (Hg) | Municipal Solid Waste | KOH treatment | 101 | [71] |
| Tetracycline (TC) | Wheat straw | Ball milling | 99% removal | [57] |
| Bisphenol-A (BPA) | Straw | Alkali treatment | 95–100% removal | [72] |
| Indigo Carmine | Olive Mill Waste | KOH treatment | 599 | [71] |
| Methylene Blue | Hickory Chips | Ball-milling, H2O2 treatment | High efficiency | [73,74,75,103] |
| Nitrate, Phosphate, Arsenic | Municipal Solid Waste | Alkaline and metal oxide modification | High removal efficiency | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, Z.; Joseph, C.G.; Tian, Z.-Y.; Yasin, M.; Khan, M.N.; Ali, S.; Khan, A.; Suazo-Hernández, J.; Poblete-Grant, P.; Nabeel, M.I. The Production of Biochar and Its Impact on the Removal of Various Emerging Pollutants from Wastewater: A Review. Toxics 2025, 13, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121079
Ullah Z, Joseph CG, Tian Z-Y, Yasin M, Khan MN, Ali S, Khan A, Suazo-Hernández J, Poblete-Grant P, Nabeel MI. The Production of Biochar and Its Impact on the Removal of Various Emerging Pollutants from Wastewater: A Review. Toxics. 2025; 13(12):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121079
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Zafran, Collin G. Joseph, Zhen-Yu Tian, Muhammad Yasin, Muhammad Naeem Khan, Sajid Ali, Aqsa Khan, Jonathan Suazo-Hernández, Patricia Poblete-Grant, and Muhammad Ikram Nabeel. 2025. "The Production of Biochar and Its Impact on the Removal of Various Emerging Pollutants from Wastewater: A Review" Toxics 13, no. 12: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121079
APA StyleUllah, Z., Joseph, C. G., Tian, Z.-Y., Yasin, M., Khan, M. N., Ali, S., Khan, A., Suazo-Hernández, J., Poblete-Grant, P., & Nabeel, M. I. (2025). The Production of Biochar and Its Impact on the Removal of Various Emerging Pollutants from Wastewater: A Review. Toxics, 13(12), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121079












