Assessing Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Toxicity and Carcinogenicity Through Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Xenograft Assays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish
2.2. Toxicology Assays
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Zebrafish Xenografts
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicology Experiments
3.2. Xenograft Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PFOS | Perfluorooctane sulfonate |
| PFAS | Per- and Poly-fluoroalkyl substances |
| LC50 | Lethal Concentration causing 50% death |
| MTC | Maximum Tolerated Concentration |
| ACHN | Renal cell carcinoma |
| Caki-1 | Clear renal cell carcinoma cells |
| NAM | New Approach Methodology |
| hpf | Hours post-fertilization |
| dpf | Days post-fertilization |
| dpt | Days post-treatment |
| PTU | Phenylthiourea |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| NOAEL | No Observed Adverse Effect Level |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| DCEG | Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics |
References
- Zeng, Z.; Song, B.; Xiao, R.; Zeng, G.; Gong, J.; Chen, M.; Xu, P.; Zhang, P.; Shen, M.; Yi, H. Assessing the Human Health Risks of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate by in Vivo and in Vitro Studies. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; De Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; Van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Environment: Terminology, Classification, and Origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.G.; Jones, K.C.; Sweetman, A.J. A First Global Production, Emission, and Environmental Inventory for Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.J.; Gaines, L.G.T.; Grulke, C.M.; Lowe, C.N.; Sinclair, G.F.B.; Samano, V.; Thillainadarajah, I.; Meyer, B.; Patlewicz, G.; Richard, A.M. Assembly and Curation of Lists of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (Pfas) to Support Environmental Science Research. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 850019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, M.; Karrman, A.; Kukucka, P.; Scherbak, N.; Keiter, S. Mixture-Specific Gene Expression in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos Exposed to Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (Pfos), Perfluorohexanoic Acid (Pfhxa) and 3,3′,4,4′,5-Pentachlorobiphenyl (Pcb126). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Xiong, D.; Sun, Y. Combined Effects of Pfos and Pfoa on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fey, M.E.; Goodrum, P.E.; Razavi, N.R.; Whipps, C.M.; Fernando, S.; Anderson, J.K. Is Mixtures’ Additivity Supported by Empirical Data? A Case Study of Developmental Toxicity of Pfos and 6:2 Fts in Wildtype Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics 2022, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, A.; Fraser, T.W.K.; Nourizadeh-Lillabadi, R.; Kamstra, J.H.; Berg, V.; Zimmer, K.E.; Ropstad, E. A Mixture of Persistent Organic Pollutants and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid Induces Similar Behavioural Responses, but Different Gene Expression Profiles in Zebrafish Larvae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta-Cortes, R.; Farias, P.; Hoyo-Vadillo, C.; Kleiche-Dray, M. Carcinogenic Risk of Emerging Persistent Organic Pollutant Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (Pfos): A Proposal of Classification. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Winquist, A. Pfas and Cancer, a Scoping Review of the Epidemiologic Evidence. Environ. Res. 2020, 194, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingley, K. “Forever Chemicals” Are Everywhere. What Are They Doing to Us? The New York Times, 16 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Fletcher, T.; Mucs, D.; Scott, K.; Lindh, C.; Tallving, P.; Jakobsson, K. Half-Lives of Pfos, Pfhxs and Pfoa after End of Exposure to Contaminated Drinking Water. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 75, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Cao, Y.; Chen, R.; Bedi, M.; Sanders, A.P.; Ducatman, A.; Ng, C. A State-of-the-Science Review of Interactions of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (Pfas) with Renal Transporters in Health and Disease: Implications for Population Variability in Pfas Toxicokinetics. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 76002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Rashid, F.; Fazal, Z.; Singh, R.; Spinella, M.J.; Irudayaraj, J. Nephrotoxicity of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (Pfos)-Effect on Transcription and Epigenetic Factors. Environ. Epigenetics 2022, 8, dvac010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, J.; Tessmann, J.W.; Deng, P.; Hennig, B.; Zaytseva, Y.Y. The Role of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (Pfos) Exposure in Inflammation of Intestinal Tissues and Intestinal Carcinogenesis. Front. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 1244457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, X.; Tan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ma, L.; Hou, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, R.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; et al. Linking Pfos Exposure to Chronic Kidney Disease: A Multimodal Study Integrating Epidemiology, Network Toxicology, and Experimental Validation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 302, 118770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Glasgow, E.; Agarwal, S. Zebrafish Xenografts for Drug Discovery and Personalized Medicine. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, M.F.; López-Gil, J.F. Small Fish, Big Answers: Zebrafish and the Molecular Drivers of Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.; Siddiqui, H.; Riguene, E.; Nomikos, M. Zebrafish: A Versatile and Powerful Model for Biomedical Research. BioEssays 2025, 47, e70080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Alternative Methods Subcommittee. Potential Approaches to Drive Future Integration of New Alternative Methods for Regulatory Decision-Making: A Report to the Science Board to the Food and Drug Administration from the New Alternative Methods Subcommittee; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024.
- Morris-Schaffer, K.; McCoy, M.J. A Review of the Ld50 and Its Current Role in Hazard Communication. ACS Chem. Health Saf. 2020, 28, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, T.H.; Bögi, C.; Winter, M.J.; Owens, J.W. Benefits of the Maximum Tolerated Dose (Mtd) and Maximum Tolerated Concentration (Mtc) Concept in Aquatic Toxicology. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 91, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidi, I.; Cassidy, H.; Gaspar, V.I.; McCaul, J.; Higgins, M.; Halász, M.; Reynolds, A.L.; Kennedy, B.N.; McMorrow, T. Curcumin Sensitizes Kidney Cancer Cells to Trail-Induced Apoptosis Via Ros Mediated Activation of Jnk-Chop Pathway and Upregulation of Dr4. Biology 2020, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of Embryonic-Development of the Zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancheva, V.; Stoyanova, S.; Georgieva, E.; Arnaudova, D.; Iliev, I.; Vasileva, T.; Bivolarski, V.; Uzochukwu, I.E.; Nagy, L.; Somogyi, D.; et al. Do Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers Cause Adverse Effects in the Freshwater Bioindicator Zebra Mussel (Dreissena Polymorpha Pallas, 1771)? An Acute and Subchronic Biomarker Assessment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 287, 107490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyeste, K.; Zulkipli, N.; Uzochukwu, I.E.; Somogyi, D.; Nagy, L.; Czeglédi, I.; Harangi, S.; Baranyai, E.; Simon, E.; Nagy, S.A.; et al. Assessment of Trace and Macroelement Accumulation in Cyprinid Juveniles as Bioindicators of Aquatic Pollution: Effects of Diets and Habitat Preferences. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, F.; Pohl, J.; Ahrens, L.; Carlsson, G.; Örn, S. Behavioural Effects and Bioconcentration of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (Pfass) in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenaars, A.; Vergauwen, L.; De Coen, W.; Knapen, D. Structure-Activity Relationship Assessment of Four Perfluorinated Chemicals Using a Prolonged Zebrafish Early Life Stage Test. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yeung, L.W.; Lam, P.K.; Wu, R.S.; Zhou, B. Protein Profiles in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos Exposed to Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 110, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhou, B. The Role of Nrf2 and Mapk Pathways in Pfos-Induced Oxidative Stress in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 115, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantzen, C.E.; Annunziato, K.A.; Bugel, S.M.; Cooper, K.R. Pfos, Pfna, and Pfoa Sub-Lethal Exposure to Embryonic Zebrafish Have Different Toxicity Profiles in Terms of Morphometrics, Behavior and Gene Expression. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 175, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, X.; Dong, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Ding, G. Developmental Toxicity and Cardiotoxicity Induced by Pfos and Its Novel Alternative Obs in Early Life Stage of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Luo, G.Y.; Mao, C.H. Acute Toxicity Effect of Pfos on Zebrafish Embryo. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 356–360, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-M.; Liu, H.-L.; Shi, W.; Wei, S.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H.-X. Effects of Perfluorinated Compounds on Development of Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Rericha, Y.; Powley, C.; Truong, L.; Tanguay, R.L.; Field, J.A. Background Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (Pfas) in Laboratory Fish Diet: Implications for Zebrafish Toxicological Studies. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 842, 156831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushing, R.; Schmokel, C.; Brooks, B.W.; Simcik, M.F. Occurrence of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Contamination of Food Sources and Aquaculture Organisms Used in Aquatic Laboratory Experiments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, G.; Fjellander, S.; Selvaraj, K.; Vildeval, M.; Ali, Z.; Almter, R.; Erkstam, A.; Rodriguez, G.V.; Abrahamsson, A.; Kersley, Å.R.; et al. Zebrafish Tumour Xenograft Models: A Prognostic Approach to Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, R.V.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Gouveia, H.; de Almeida, C.R.; Castillo-Martin, M.; Brito, M.J.; Canas-Marques, R.; Batista, E.; Alves, C.; Sousa, B.; et al. Zebrafish Avatar Testing Preclinical Study Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Breast Cancer. npj Precis. Oncol. 2025, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Yi, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhi, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, T.; et al. Zebrafish Patient-Derived Xenograft System for Predicting Carboplatin Resistance and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer. Drug Resist. Updat. 2025, 78, 101162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Estrada, M.F.; Gomes, A.; Fernandez, L.M.; Azevedo, J.M.; Póvoa, V.; Fontes, M.; Alves, A.; Galzerano, A.; Castillo-Martin, M.; et al. Zebrafish Avatar-Test Forecasts Clinical Response to Chemotherapy in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, K.; Zhan, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Lv, T.; Song, Y. Zebrafish Patient-Derived Xenografts Accurately and Quickly Reproduce Treatment Outcomes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 248, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, N.; Fletcher, J.I.; Melong, N.; Lau, L.M.S.; Dolman, E.M.; Mao, J.; Tax, G.; Cadiz, R.; Tuzi, L.; Kamili, A.; et al. Modeling High-Risk Pediatric Cancers in Zebrafish to Inform Precision Therapy. Cancer Res. Commun. 2025, 5, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauert, A.; Olk, N.; Pimentel-Gutiérrez, H.; Astrahantseff, K.; Jensen, L.D.; Cao, Y.; Eggert, A.; Eckert, C.; Hagemann, A.I. Fast, in Vivo Model for Drug-Response Prediction in Patients with B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2020, 12, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Póvoa, V.; de Almeida, C.R.; Maia-Gil, M.; Sobral, D.; Domingues, M.; Martinez-Lopez, M.; Fuzeta, M.d.A.; Silva, C.; Grosso, A.R.; Fior, R. Innate Immune Evasion Revealed in a Colorectal Zebrafish Xenograft Model. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierozan, P.; Karlsson, O. Pfos Induces Proliferation, Cell-Cycle Progression, and Malignant Phenotype in Human Breast Epithelial Cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 92, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Sun, B.; Berardi, D.; Lu, L.; Yan, H.; Zheng, S.; Aladelokun, O.; Xie, Y.; Cai, Y.; Pollitt, K.J.G.; et al. Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid and Perfluorooctanoic Acid Promote Migration of Three-Dimensional Colorectal Cancer Spheroids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 21016–21028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccacece, L.; Costa, F.; Pascali, J.P.; Giorgi, F.M. Cross-Species Transcriptomics Analysis Highlights Conserved Molecular Responses to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Toxics 2023, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbu, S.; Dakshanamurthy, S. Predicting Dose-Dependent Carcinogenicity of Chemical Mixtures Using a Novel Hybrid Neural Network Framework and Mathematical Approach. Toxics 2023, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbu, S.; Glasgow, E.; Block, T.; Dakshanamurthy, S. A Machine-Learning-Driven Pathophysiology-Based New Approach Method for the Dose-Dependent Assessment of Hazardous Chemical Mixtures and Experimental Validations. Toxics 2024, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
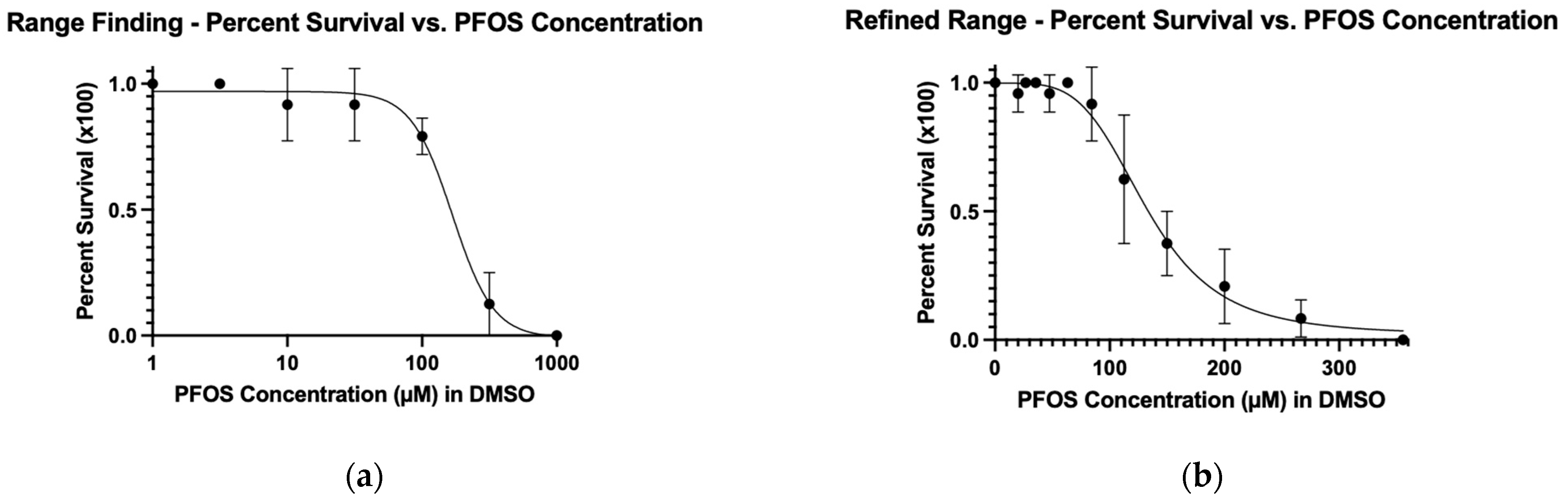


| Sample Set | LC50 (μM) | MTC (μM) | 5% of MTC (μM) | 10% of MTC (μM) | 20% of MTC (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range-Finding | 167 | 73 | - | - | - |
| Refined Range | 132 | 58 | 2.9 | 5.8 | 11.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Block, T.; DeMaio, J.R.; Skopec, L.; Ayers, M.; Glasgow, E. Assessing Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Toxicity and Carcinogenicity Through Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Xenograft Assays. Toxics 2025, 13, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121077
Block T, DeMaio JR, Skopec L, Ayers M, Glasgow E. Assessing Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Toxicity and Carcinogenicity Through Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Xenograft Assays. Toxics. 2025; 13(12):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121077
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlock, Tessa, Joan Renee DeMaio, Lela Skopec, Margaret Ayers, and Eric Glasgow. 2025. "Assessing Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Toxicity and Carcinogenicity Through Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Xenograft Assays" Toxics 13, no. 12: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121077
APA StyleBlock, T., DeMaio, J. R., Skopec, L., Ayers, M., & Glasgow, E. (2025). Assessing Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Toxicity and Carcinogenicity Through Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Xenograft Assays. Toxics, 13(12), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121077






