Microplastic Distribution and Transport Mechanisms in the South Sea and East China Sea of Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Method
2.2. Microplastic Pretreatment Method
2.2.1. Surface Seawater Microplastic Pretreatment Method
2.2.2. Sediment Microplastic Pretreatment
2.3. Polymer Identification
2.4. Shape Classification and Size Measurement of Microplastics
2.5. Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC)
2.6. Comparison with Other Studies
3. Results
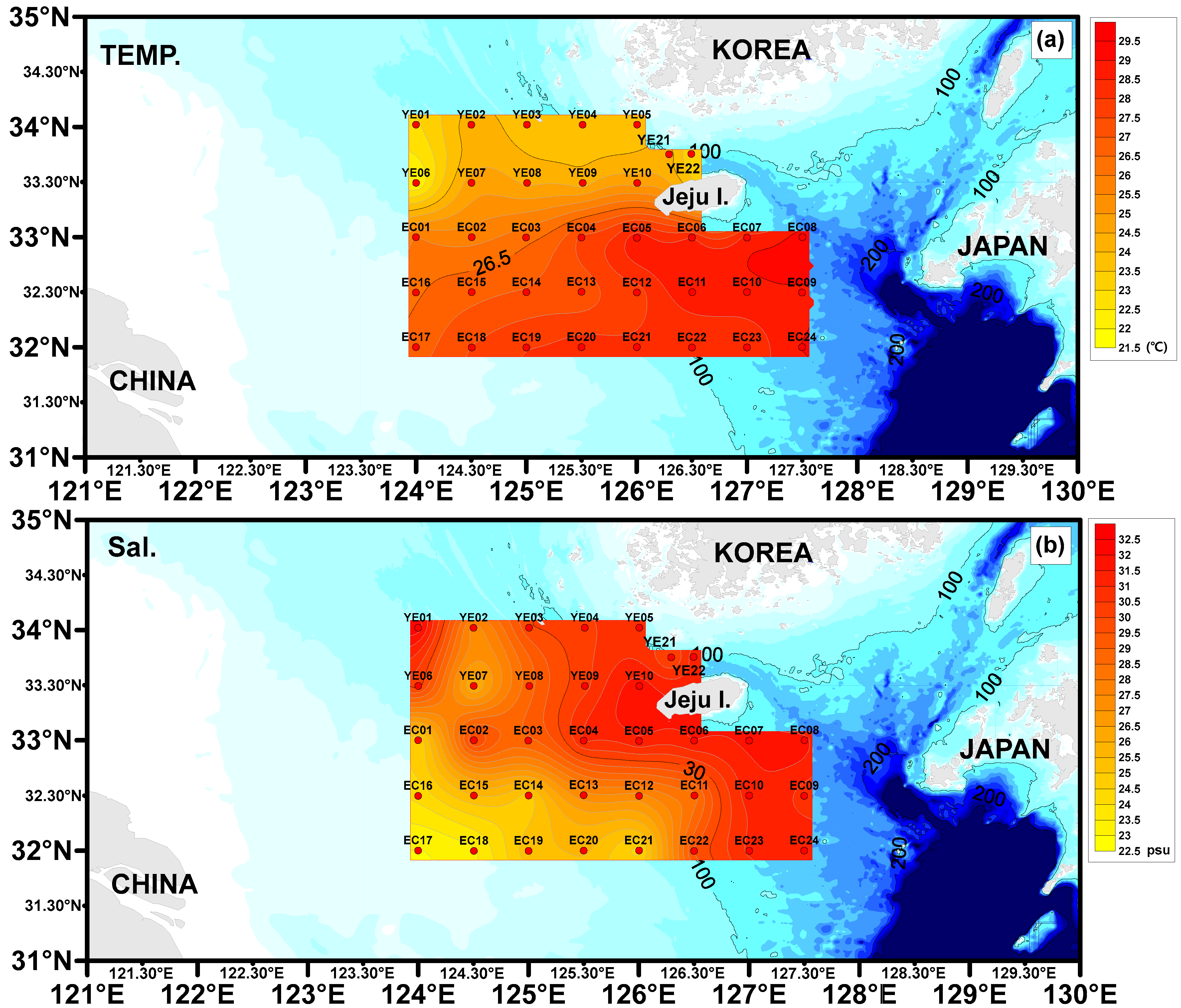
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Water Temperature and Salinity in the Surface Water
3.2. Microplastic Abundance
3.3. Microplastic Polymer Types
3.4. Microplastic Shapes
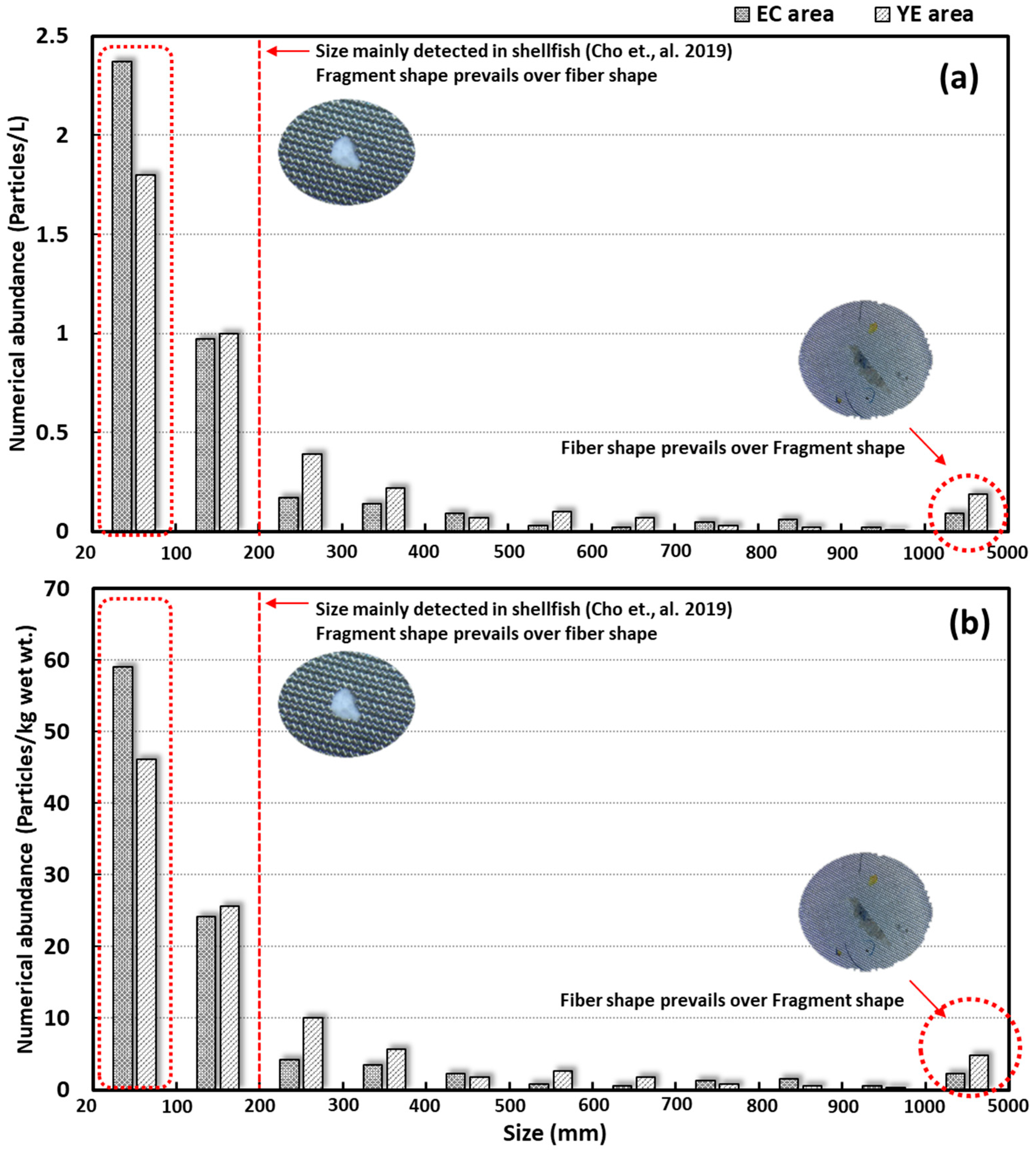
3.5. Microplastic Size
3.6. Comparison with Other Literature
| Nation | Area | Investigation | n | Collected Vol. | Abundance | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mesh Size) | (Mean/SD) | ||||||
| China | Jiaozhou | Bay | 2017 | 14 | 50 L (20 μm) | 1.602 ± 1.274 | [39] |
| Korea | Cheonsu | 2016/2017 | 5 | 100 L (20 μm) | 0.784 ± 0.272 | [11] | |
| Korea | Hampyeong | 2016/2017 | 5 | 100 L (20 μm) | 1.548 ± 0.211 | [11] | |
| Korea | Deukryang | 2016/2017 | 5 | 100 L (20 μm) | 1.146 ± 0.423 | [11] | |
| Korea | Youngil | 2016/2017 | 5 | 100 L (20 μm) | 1.688 ± 0.496 | [11] | |
| Korea | Gwangyang | 2016/2017 | 5 | 100 L (20 μm) | 2.362 ± 1.022 | [11] | |
| Korea | Gwangyang | 2020 | 5 | 100 L (20 μm) | 3.17 ± 1.123 | [30] | |
| Japen | Tokyo | 2021 | 4 | 1 L (20 μm) | 221.3 ± 189.5 | [10] | |
| Korea | Ulsan | Coastal | 2016/2017 | 5 | 100 L (20 μm) | 1.764 ± 1.006 | [11] |
| Korea | Incheon | 2016/2017 | 5 | 100 L (20 μm) | 4.064 ± 1.075 | [11] | |
| Korea | Busan | 2016/2017 | 6 | 100 L (20 μm) | 1.020 ± 0.279 | [11] | |
| Korea | Yellow Sea | 2018 | 9 | 200 L (20 μm) | 0.266 ± 0.459 | [43] | |
| Korea | South Sea | 2018 | 5 | ||||
| Korea | East Sea | 2018 | 8 | 200 L (20 μm) | 0.289 ± 0.280 | [43] | |
| Korea | Southwest Sea | 2020 | 23 | 30 L (20 μm) | 0.46 ± 0.27 | [27] | |
| Korea | SS area | 202 | 15 | 100 L (20 μm) | 0.01 ± 0.09 | [30] | |
| China | China | - | 16 | 100 L (50 μm) | 4.5 ± 1.8 | [12] | |
| China | North Yellow Sea | 2016 | 50 | 25 L (30 μm) | 0.545 ± 0.282 | [45] | |
| China | South China Sea | 2021 | 29 | 200 L (64 μm) | 0.103 ± 0.098 | [40] | |
| Chinese Taipei | Taiwan Strait (the northern area) | 2021 | 33 | 1000 L (44 μm) | 0.174 | [42] | |
| Chinese Taipei | Taiwan Strait (the southern area) | 2017 | 19 | 100 L (100 μm) | 0.035 ± 0.004 | [41] | |
| Malaysia | Malaysia | 2018 | - | 2.041 L/s (20 μm) | 0.211 ± 0.104 | [46] | |
| Atlantic Ocean | Open sea | 2014 | 23 | 2.6 m3 (10 μm) | 0.013–0.501 | [47] | |
| Greenland | Greenland Sea (GSG) | 2018 | 20 | 100 L (50 μm) | 2.43 ± 0.84 | [12] | |
| Greenland Sea (EGC) | 1.19 ± 0.28 | ||||||
| this study | YE area | 2022 | 12 | 100 L (20 μm) | 0.18 ± 0.10 | - | |
| EC area | 24 | 0.17 ± 0.13 | |||||
| Nation | Area | Investigation | n | Abundance | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mean/SD) | ||||||
| China | Qinzhou (mangrove side) | Bay | spoon | 7 | 1298 ± 2207 | [48] |
| China | Qinzhou (mangrove in) | spoon | 7 | 42.9 ± 26.8 | [48] | |
| China | Sanggou | Van Veen grab | 8 | 1674 ± 526 | [50] | |
| China | Laizhou | Van Veen grab | 58 | 461.6 ± 167 | [51] | |
| China | Lim Chu Kang | - | 7 | 36.8 ± 23.6 | [49] | |
| China | Belgian | Van Veen grab | 11 | 167 | [52] | |
| China | Perl River Estuary | grab | 20 | 4655 ± 1493 | [53] | |
| Japen | Tokyo | grab | 4 | 0.016 ± 0.0008 | [10] | |
| Korea | Gwangyang | Van Veen grab | 5 | 462.4 ± 143.9 | [30] | |
| Korea | West Coast tidal | Coastal | spoon | 7 | 2191 | [56] |
| Korea | SS area | grab | 12 | 50.5 ± 29.7 | [30] | |
| China | North Yellow Sea | Box sampler | 28 | 499.8 ± 370.1 | [57] | |
| China | Maowei Sea, | - | 10 | 520–2310 | [58] | |
| Chinese Taipei | Taiwan Strait | grab | 33 | 16–382 | [42] | |
| Belgian | Belgian coast | - | 6 | 97.2 | [52] | |
| French | Atlantic coastal | box-core | 3 | 67 ± 76 | [54] | |
| The Mediterranean | North African coasts | Corer/Visual | 4 | 182.7–649.3 | [59] | |
| The Spanish Mediterranean | Box-corer | 10 | 113.2 ± 88.9 | [55] | ||
| Pacific Ocean | The Western Pacific Ocean | Open sea | box corer | 15 | 240 | [61] |
| Baltic Sea | The Southern Baltic Sea | - | - | 15 ± 10 | [60] | |
| this study | YE area | grab | 15 | 124.4 ± 95.0 | - | |
| EC area | grab | 18 | 114.9 ± 62.6 | |||
4. Discussion
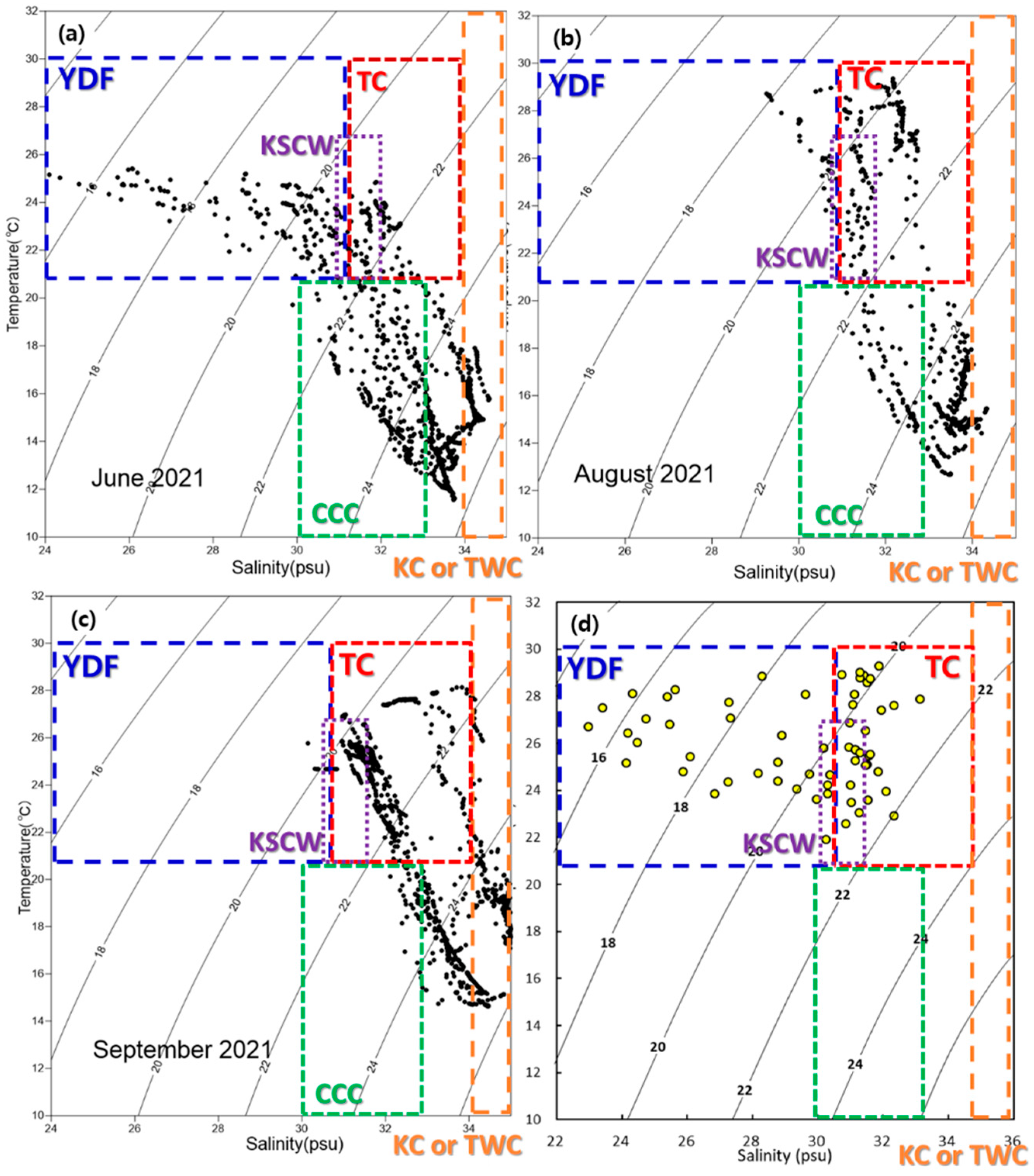
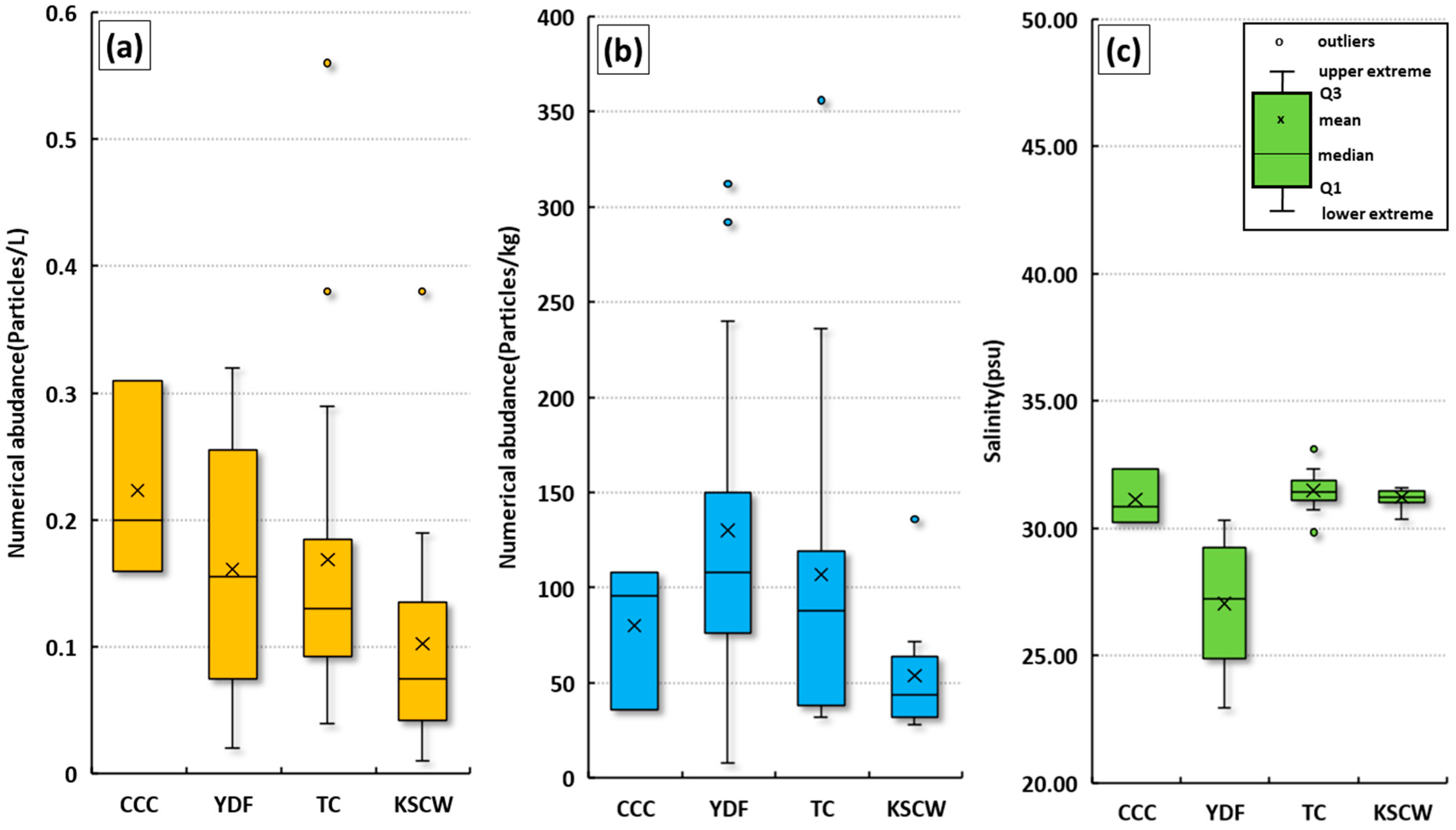
4.1. Taiwan Current Warm Water Group (TC) Group
4.2. Yangtze River Discharge Flow (YDF) Group
4.3. Korea Southern Coastal Water (KSCW) Group
4.4. Chinese Coastal Current (CCC) Group
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plastics Europe. An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data. Plastics Europe. In Plastics–The Facts; Plastics Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, F.; Fossi, C.; Weber, R.; Santillo, D.; Sousa, J.; Ingram, I.; Nadal, A.; Romano, D. Marine litter plastics and microplastics and their toxic chemicals components: The need for urgent preventive measures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, P.J.; Rochman, C.M. Sources, fate and effects of microplastics in the marine environment: Part 2 of a global assessment. In Reports and Studies—IMO/FAO/Unesco-IOC/WMO/IAEA/UN/UNEP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection (GESAMP); Eng No. 93; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Inter. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Wirzberger, V.; Krumpen, T.; Lorenz, C.; Primpke, S.; Tekman, M.B.; Gerdts, G. High quantities of microplastic in Arctic deep-sea sediments from the HAUSGARTEN observatory. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11000–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.D.; Sinclair, M.; Levi, C.J.; Reeves, S.E.; Edgar, G.J. Ubiquity of microplastics in coastal seafloor sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, S.M.; Alam, M.J.; Yang, Z.; Arakawa, H. Microplastic assessment in the benthic ecosystem of Tokyo Bay: Sediment, water, and macrobenthic perspectives. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 70, 103384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Isobe, A.; Shim, W.J. Horizontal and vertical distribution of microplastics in Korean coastal waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12188–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. Greenland Sea Gyre increases microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Nordic Seas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Turner, A.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Liu, K.; Zhu, L.; Song, Z.; Li, D. Atmospheric microplastic over the South China Sea and East Indian Ocean: Abundance, distribution and source. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sebille, E.; Aliani, S.; Law, K.L.; Maximenko, N.; Alsina, J.M.; Bagaev, A.; Wichmann, D. The physical oceanography of the transport of floating marine debris. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 023003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerger, C.M.; Lattin, G.L.; Moore, S.L.; Moore, C.J. Plastic ingestion by planktivorous fishes in the North Pacific Central Gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2275–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Galloway, T.S. Ingestion of nanoplastics and microplastics by Pacific oyster larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14625–14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Webb, H.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.S.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattin, G.L.; Moore, C.J.; Zellers, A.F.; Moore, S.L.; Weisberg, S.B. A comparison of neustonic plastic and zooplankton at different depths near the southern California shore. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Envrion. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, L.J.; Van Emmerik, T.; Van Der Ent, R.; Schmidt, C.; Lebreton, L. More than 1000 rivers account for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions into the ocean. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eaaz5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastics Europe. An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data. Plastics Europe. In Plastics–The Facts; Plastics Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; pp. 1–34.
- Lebreton, L.C.; Van Der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, J.; Kang, H.B.; Choi, Y.S. Microplastics in the marine environment and their impacts on human health. J. Life Sci. 2021, 31, 442–451. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.C.; Youn, S.H.; Whang, J.D.; Suh, Y.S.; Yoon, Y.Y. Long-term Variation in Ocean Environmental Conditions of the Northern East China Sea. J. Kor. Soc. Mar. Environ. Energy. 2015, 18, 189–206. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.A.; Park, J.E.; Choi, B.J.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, H.R.; Lee, S.R.; Lee, E.U.N.I.L. Schematic maps of ocean currents in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea for science textbooks based on scientific knowledge from oceanic measurements. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 2017, 22, 151–171. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.K.; Jeong, H.H.; Ju, M.J.; Ko, U.; Dae, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, H.S. Baseline study on microplastic distribution in the open surface waters of the Korean southwest sea. Water 2023, 15, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, S.; Isobe, A.; Kako, S.I.; Uchida, K.; Tokai, T. Fate of microplastics and mesoplastics carried by surface currents and wind waves: A numerical model approach in the Sea of Japan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, A.; Uchhda, K.; Tokai, T.; Iwasaki, S. East Asian seas: A hot spot of pelagic microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.K.; Cho, C.R.; Cheon, H.S.; Soh, H.Y.; Cho, H.S. A Study on the Distribution of Microplastics in the South Coast of Korea and Gwangyang Bay. Microplastics 2024, 3, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Fisheries Science (NFS). Guidelines for Qualitativeness and Quantification of Residual Microplastics in Seawater and Aquatic Life; National Institute of Fisheries Science (NFS): Busan, Republic of Korea, 2020; pp. 1–49. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- National institute of Fisheries Science (NFS). Guidelines for Qualitativeness and Quantification of Residual Microplastics in Sediment; NIPS: Busan, Republic of Korea, 2021; pp. 1–42. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Arthur, C. Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for Quantifying Synthetic Particles in Waters and Sediments. In NOAA Techical Memorandum; NOAA Marine Debris Division: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Marine Plastic Debris and Microplstics—Global Lessens and Research to Inspire Action and Guide Policy Change; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kershaw, P.; Turra, A.; Galgani, F. Guidelines for the Monitoring and Assessment of Plastic Litter in the Ocean-GESAMP Reports and Studies No. 99. GESAMP Reports and Studies; United Nations Office: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019; pp. 1–123. [Google Scholar]
- Michida, Y.; Chavanich, S.; Cozar, C.A.; Hagmann, P.; Hinata, H.; Isobe, A.; Kershaw, P.; Kozlovskii, N.; Li, D.; Lusher, A.L.; et al. Guidelines for Harmonizing Ocean Surface Microplastic Monitoring Methods; Ministry of the Environment Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Kusano, T.; Addai-Arhin, S.; Nugraha, W.C.; Novirsa, R.; Phan Dinh, Q.; Shirosaki, T.; Fujita, E.; Kameda, Y.; Cho, H.S.; et al. A Study on the Differences of Microplastics Distributions in the Surface Freshwater Collected by 100- and 355-μm Meshes. Environ. Monitor. Con. Res. 2022, 2, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.; Shim, W.J.; Jang, M.; Han, G.M.; Hong, S.H. Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in market bivalves from South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Cao, W.; Liu, X.; Jiang, F.; Ding, J.; Sun, C. Distribution characteristics of microplastics in the seawater and sediment: A case study in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gan, J.; Hu, J.; Wu, H.; Cai, Z.; Deng, Y. Progress on circulation dynamics in the East China Sea and southern Yellow Sea: Origination, pathways, and destinations of shelf currents. Prog. Oceanogr. 2021, 193, 102553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Fan, S.; Zheng, R.; Yu, X. Impacts of terrestrial input on the distribution characteristics of microplastics in the East China Sea characterized by chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Liu, M.; Ye, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, M. Microplastics in the Taiwan Strait and adjacent sea: Spatial variations and lateral transport. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 191, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, S.; Hong, S.H.; Song, Y.K.; Han, G.M.; Seo, S.; Shim, W.J. Prevalence of small high-density microplastics in the continental shelf and deep sea waters of East Asia. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. Characterization of microplastics in the surface seawater of the South Yellow Sea as affected by season. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Bai, H.; Chen, B.; Sun, X.; Qu, K.; Xia, B. Microplastic pollution in North Yellow Sea, China: Observations on occurrence, distribution and identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, Z.D.; Amin, R.M.; Anuar, S.T.; Nasser, A.A.A.; Sohaimi, E.S. MICROPLASTICS in seawater and zooplankton: A CASE study from Terengganu estuary and offshore waters, Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, K.; Lenz, R.; Stedmon, C.A.; Nielsen, T.G. Abundance, size and polymer composition of marine microplastics ≥ 10 μm in the Atlantic Ocean and their modelled vertical distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Yang, R.; Li, R.; Li, Y. Characterization, source, and retention of microplastic in sandy beaches and mangrove wetlands of the Qinzhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.H.M.; Obbard, J.P. Microplastics in Singapore’s coastal mangrove ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xia, B.; Chen, B.; Sun, X.; Zhu, L.; Qu, K. Spatiotemporal distribution, source identification and inventory of microplastics in surface sediments from Sanggou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, B.; Koelmans, A.A.; Wu, D.; Wang, Q. A systems analysis of microplastic pollution in Laizhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, M.; De Meester, S.; Van Landuyt, L.; De Clerck, K.; Janssen, C.R. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Shahab, A.; Rinklebe, J.; Xiao, H.; Li, J.; Ye, F.; Wei, G. Spatial distribution, morphology, and risk assessment of microplastics in sediments from the Pearl River Estuary, China. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.N.; Poirier, L.; Lagarde, F.; Kamari, A.; Zalouk-Vergnoux, A. Microplastic abundance and characteristics in French Atlantic coastal sediments using a new extraction method. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, A.V.; Gago, J.; Campillo, J.A.; León, V.M. Microplastic distribution in surface sediments along the Spanish Mediterranean continental shelf. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 21264–21273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Hong, S.; Shim, W.J.; Khim, J.S.; Park, J. Distribution, compositional characteristics, and historical pollution records of microplastics in tidal flats of South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 189, 114741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, D.; Yang, X.; Teng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q. Microplastic pollution in the surface sediments collected from Sishili Bay, North Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Xue, B.; Wang, Y. Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in the mangrove sediment of the semi-enclosed Maowei Sea of the south China sea: New implications for location, rhizosphere, and sediment compositions. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tata, T.; Belabed, B.E.; Bououdina, M.; Bellucci, S. Occurrence and characterization of surface sediment microplastics and litter from North African coasts of Mediterranean Sea: Preliminary research and first evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graca, B.; Szewc, K.; Zakrzewska, D.; Dołęga, A.; Szczerbowska-Boruchowska, M. Sources and fate of microplastics in marine and beach sediments of the Southern Baltic Sea—A preliminary study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7650–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments and organisms of the Western Pacific Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.; Lyons, B.P.; Galloway, T.S.; Lewis, C. Role of marine snows in microplastic fate and bioavailability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7111–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.C.; Chen, Y.L.L.; Liu, K.K. Chemical hydrography and chlorophyll a distribution in the East China Sea in summer: Implications in nutrient dynamics. Cont. Shelf Res. 1996, 16, 1561–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, H.B.; Jacobs, G.A.; Teague, W.J. Monthly variations of water masses in the Yellow and East China Seas, November 6, 1998. J. Oceanogr. 1999, 55, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.I. Analysis of the Generation Amount of Abandoned Marine Waste from Ships in the Northwest Sea of Jeju Island. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. 2021, 27, 81–87. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidli, S.; Antunes, J.C.; Ferreira, J.L.; Lahbib, Y.; Sobral, P.; El Menif, N.T. Microplastics in sediments from the littoral zone of the north Tunisian coast (Mediterranean Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 205, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, E.; Martin, C.; Galli, M.; Echevarría, F.; Duarte, C.M.; Cózar, A. The colors of the ocean plastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6594–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.N.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kaneko, A. Monitoring of Yangtze River Discharge at Datong Hydrometric Station Using Acoustic Tomography Technology. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 723123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wu, C.; Elser, J.J.; Mei, Z.; Hao, Y. Occurrence and fate of microplastic debris in middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River–from inland to the sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, D. Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary System, China: First observations on occurrence, distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jin, C.; Yu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C. Microplastic pollution in water, sediment, and fish from artificial reefs around the Ma’an Archipelago, Shengsi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H. Transport of microplastics in coastal seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 199, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Xu, X.M.; Yue, B.Y.; Xu, X.P.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, J.H. Multidecadal records of microplastic accumulation in the coastal sediments of the East China Sea. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, H.; Cui, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D. Microplastics in offshore sediment in the yellow Sea and east China Sea, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.O.; Choi, J.H. Distributions of water temperature and salinity in the Korea southern coastal water during Cochlodinium polykrikoides blooms. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Energy 2009, 12, 235–247. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zuo, T.; Wang, K.E. The Yellow Sea cold bottom water—An oversummering site for Calanus sinicus (Copepoda, Crustacea). J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, H.Y.; Choi, S.D. Species composition and occurrence patterns of zooplankton in Jinhae Bay. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2004, 22, 43–56. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Amin, R.M.; Sohaimi, E.S.; Anuar, S.T.; Bachok, Z. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton in Terengganu coastal waters, southern South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Seawater | Sediment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC Area | YE Area | EC Area | YE Area | |
| Temperature [unit: °C] | ||||
| 27.78 ± 1.02 (25.79–29.29) | 24.04 ± 0.87 (21.90–25.42) | - | - | |
| Salinity [unit: psu] | ||||
| 28.08 ± 3.07 (22.96–31.86) | 29.39 ± 2.16 (24.13–32.33) | - | - | |
| Abundance [unit: seawater-particles/L/sediment-particles/kg ww] | ||||
| 0.17 ± 0.13 | 0.19 ± 0.12 | 114.9 ± 62.6 | 153.3 ± 120.1 | |
| (0.02–0.56) | (0.04–0.38) | (32.0–292.0) | (8.0–356.0) | |
| Polymer composition * [unit: seawater-%(particles/L)/sediment-%(particles/kg ww)] | ||||
| PE (Polyethylene) | 49 | 66 | 63 | 84 |
| (0.08 ± 0.06) | (0.11 ± 0.07) | (74.4 ± 63.2) | (132.3 ± 109.1) | |
| PP (Polypropylene) | 39 | 26 | 33 | 11 |
| (0.06 ± 0.06) | (0.06 ± 0.05) | (36.8 ± 28.9) | (11.3 ± 11.3) | |
| PY (Polyester) | 12 | 8 | 4 | 5 |
| (0.03 ± 0.03) | (0.01 ± 0.02) | (3.7 ± 5.9) | (9.7 ± 14.6) | |
| Shape ** [unit: seawater-%(particles/L)/sediment-%(particles/kg ww)] | ||||
| Fragment | 91 | 87 | 96 | 97 |
| (0.15 ± 0.12) | (0.16 ± 0.10) | (110.9 ± 63.5) | (145.7 ± 112.10) | |
| Fiber | 9 | 8 | 3 | 3 |
| (0.02 ± 0.02) | (0.01 ± 0.02) | (3.7 ± 5.6) | (7.7 ± 13.7) | |
| Film | ND *** | 5 | 1 | ND *** |
| (0.01 ± 0.02) | (0.5 ± 2.0) | |||
| Size [unit: seawater-%(particles/L)/sediment-%(particles/kg ww)] | ||||
| 0.02–0.3 mm | 87 | 85 | 92 | 93 |
| (0.15 ± 0.11) | (0.15 ± 0.10) | (105.1 ± 59.3) | (113.5 ± 82.3) | |
| 0.3–0.6 mm | 6 | 10 | 5 | 4 |
| (0.01 ± 0.01) | (0.02 ± 0.02) | (5.9 ± 5.0) | (6.7 ± 9.2) | |
| 0.6–1.0 mm | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| (0.01 ± 0.01) | (0.01 ± 0.01) | (1.6 ± 2.4) | (0.9 ± 2.1) | |
| 1.0–5.0 mm | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| (0.00 ± 0.01) | (0.01 ± 0.01) | (2.4 ± 2.8) | (3.3± 8.2) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, B.; Jeong, H.; Cho, C.-R.; Cho, H.-S. Microplastic Distribution and Transport Mechanisms in the South Sea and East China Sea of Korea. Toxics 2025, 13, 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121070
Min B, Jeong H, Cho C-R, Cho H-S. Microplastic Distribution and Transport Mechanisms in the South Sea and East China Sea of Korea. Toxics. 2025; 13(12):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121070
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Byeongkyu, Huiho Jeong, Chon-Rae Cho, and Hyeon-Seo Cho. 2025. "Microplastic Distribution and Transport Mechanisms in the South Sea and East China Sea of Korea" Toxics 13, no. 12: 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121070
APA StyleMin, B., Jeong, H., Cho, C.-R., & Cho, H.-S. (2025). Microplastic Distribution and Transport Mechanisms in the South Sea and East China Sea of Korea. Toxics, 13(12), 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121070







