Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals from Long-Term Mining Activities: A Case Study of the Fengfeng Mining Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
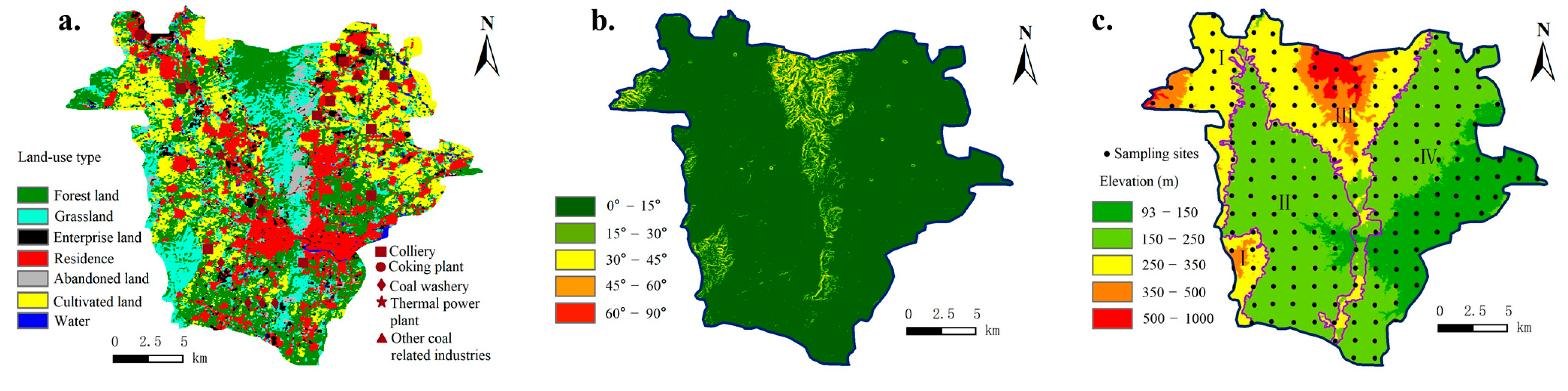
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Measurement
2.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analyzes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Distribution Patterns of HMs in Soil
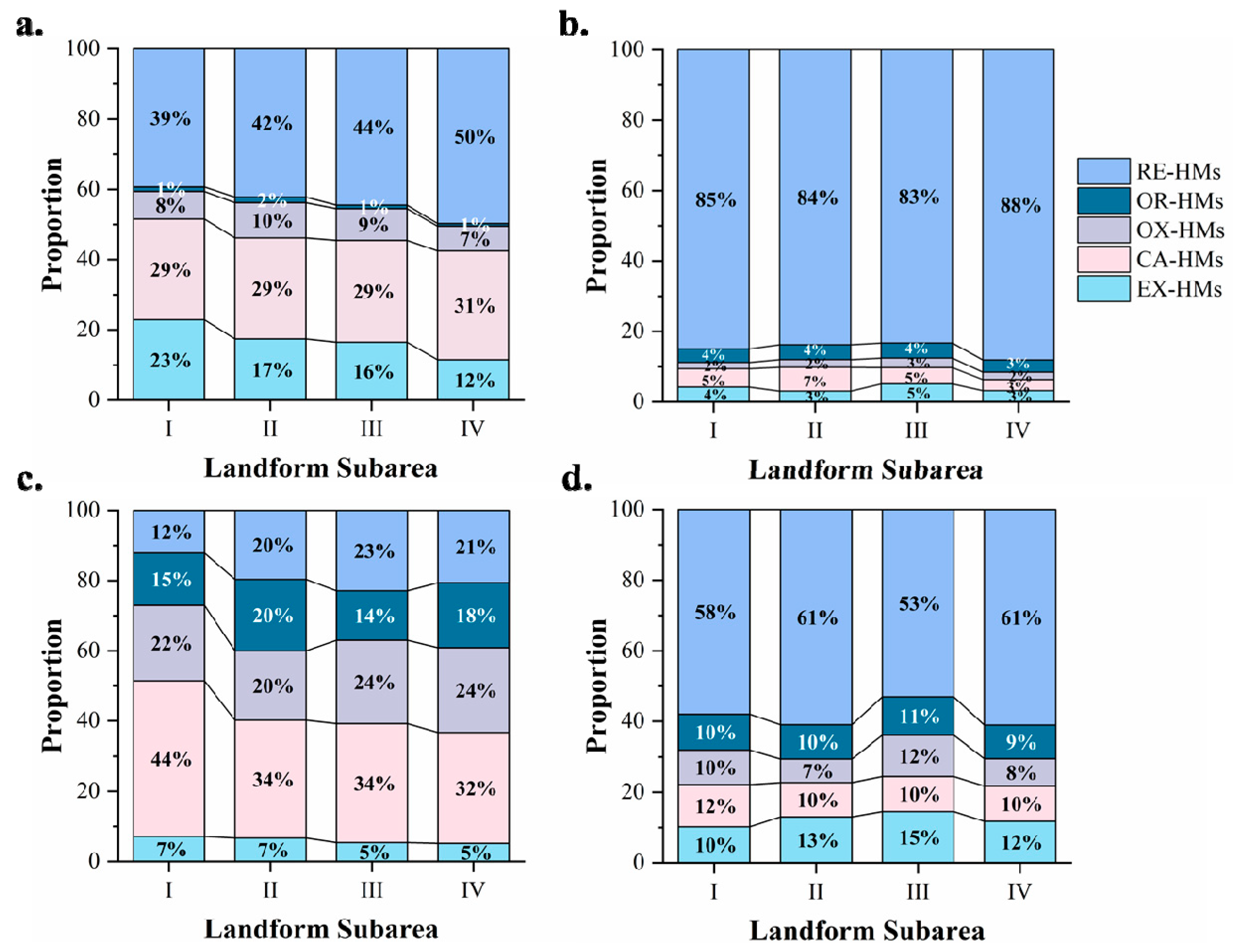
3.2. Distribution Characteristics of HM Speciation Based on Landform
3.3. Risk Assessment Based on Soil HM Speciation
3.4. Spatial Risk Assessment Based on the Kriging Model
3.5. Perspectives and Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMs | Heavy metals |
| Cd | Cadmium |
| Cu | Copper |
| Pb | Lead |
| Zn | Zinc |
| RSP | Secondary phase to primary phase ratio |
| RAC | Risk assessment code |
| EX | Exchangeable |
| CA | Carbonate-bound |
| OX | Fe-Mn oxide-bound |
| OR | Organic matter-bound |
| RE | Residual |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
References
- Xiong, H.; Yin, Y.; Cui, X.; Dai, W.; Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Duan, G. The Effects of Coal Mining on Heavy Metal Concentration and Microbial Composition in Surrounding Soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boente, C.; Baragaño, D.; Gallego, J.R. Benzo[a]Pyrene Sourcing and Abundance in a Coal Region in Transition Reveals Historical Pollution, Rendering Soil Screening Levels Impractical. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- All Azad, M.A.; Chiddiq, A.B.; Miah, M.R.; Rahman Sabbir, M.H. Temporal Assessment of Water and Soil Quality near Barapukuria Coal Mine, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, K.; He, X.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Z.; He, S. Research Status of Comprehensive Utilization of Coal-Based Solid Waste (CSW) and Key Technologies of Filling Mining in China: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, A.; Walentek, A. Mining Exploitation of Hard Coal Seams by Galleries and Surface Deformations. Acta. Montan. Slovaca. 2022, 27, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, A.; Do Amaral Filho, J.R.; Harrison, S.T.L.; Broadhurst, J.L. Acid Mine Drainage and Metal(Loid) Risk Potential of South African Coal Processing Wastes. Miner. Eng. 2024, 215, 108825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Su, P.; Tang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ma, T. A Review of Acid Mine Drainage: Formation Mechanism, Treatment Technology, Typical Engineering Cases and Resource Utilization. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 1240–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokubung, K.E.; Madzivha, N.N.; Lau, W.J.; Nxumalo, E.N. Polyethersulfone/Biochar-Fe3O4/GO Mixed Matrix Membranes with Enhanced Antifouling Properties for Heavy Metals Removal from Acid Mine Drainage. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 176, 114190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, E.C.; Gulser, C. Morphological, Physiological, and Anatomical Effects of Heavy Metals on Soil and Plant Health and Possible Remediation Technologies. Soil Secur. 2025, 18, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, D.; Ma, H.; Wu, Y.; Yu, C.; Pu, S. Spatial Distribution and Migration Characteristics of Heavy Metals at an Abandoned Industrial Site in the Southwest of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Zhao, P.; Xiao, B.; Ali, M.U.; Xiao, P. Heavy Metal Pollution and Source Analysis of Soils around Abandoned Pb/Zn Smelting Sites: Environmental Risks and Fractionation Analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 38, 104084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; An, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, L.; Lv, S. Geochemical Characteristics and Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils and Crops from a Coal Mining Area in Anhui Province, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Kazi, T.G.; Baig, J.A.; Arain, M.B.; Afridi, H.I. Exposure of Heavy Metals in Coal Gangue Soil, in and Outside the Mining Area Using BCR Conventional and Vortex Assisted and Single Step Extraction Methods. Impact on Orchard Grass. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Xiao, B.; Ali, M.U.; Xiao, P.; Zhao, P.; Wang, H.; Bibi, S. Heavy Metals Pollution from Smelting Activities: A Threat to Soil and Groundwater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 274, 116189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejman, A.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.; Ardestani, M.; Saeedi, M.; Baghvand, A. Fractionation of Heavy Metals in Sediments and Assessment of Their Availability Risk: A Case Study in the Northwestern of Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; You, M.; Liu, G.; Dong, Z. Characteristics and Potential Ecological Risks of Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Soil around Coal-Fired Power Plant. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtaz, H.R.; Jafarzadeh, A.A.; Torabi, H.; Oustan, S.; Samadi, A.; Davatgar, N.; Gilkes, R.J. An Assessment of the Variation in Soil Properties within and between Landform in the Amol Region, Iran. Geoderma 2009, 149, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lu, H.; Lin, H. Comprehensive Study on the Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals and Their Environmental Risks in High-Sulfur Coal Gangue Dumps in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 136, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liao, F.; Wang, G.; Qu, S.; Mao, H.; Bai, Y. Hydrogeochemical Evolution Induced by Long-Term Mining Activities in a Multi-Aquifer System in the Mining Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Huang, Y.; Ma, D.; Fan, X.; He, P.; Sun, W. Environmental Behaviors of PAHs in Ordovician Limestone Water of Fengfeng Coal Mining Area in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.; Bisson, M. Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Speciation of Particulate Trace-Metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokhbar, M.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Zafarani, G.G. Miankaleh International Wetland: Toxic Element Hazards and Possibility of Botulinum Poisoning. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 180, 114318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.F.; Fahmy, M.A.; Abdelkhaleq, M.A.; Nasr, S.M. Mapping Fluoride Footprints: Fractionation, Bioaccumulation, Sources, and Sophisticated Risk Assessment in El-Bardawil Lake, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 1002, 180581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Tian, B.; Li, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Ai, S.; Wang, X. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in Provinces of China Based on Different Soil Types: From Normalization to Soil Quality Criteria and Ecological Risk Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Di, Y.; Wu, X. Spatial Distribution Characteristic, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Soil of an Urban Riparian Zone. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 298, 118271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, N.; Haydar, C.; Koubaissy, B.; Fakih, M.; Awad, S.; Toufaily, J.; Villieras, F.; Hamieh, T. The Distribution of Heavy Metals in the Lower River Basin, Lebano. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Material Sciences, Csm8-Ism5, Beirut, Lebanon, 28–30 May 2012; Hamieh, T., Ed.; Elsevier Science Bv: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 55, pp. 456–463. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, N.; Kang, C.; Feng, B.Z.; Zhang, B. Insight of Heavy Metal Contamination of Soil in High Background Area: Field Investigation and Laboratory Test. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 22, 2833–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, P.; Tang, S.; Chen, X. Concentration and Distribution of Cadmium in Coals of China. Minerals 2018, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yang, C.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z. Cadmium Contamination in Tianjin Agricultural Soils and Sediments: Relative Importance of Atmospheric Deposition from Coal Combustion. Environ. Geochem Health 2013, 35, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, W.; Wu, Y. Source-Oriented Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Dust at Coal Resource-Based Urban Parks in Northern China Based on Bioaccessibilities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 297, 118252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Cheng, X.; Niu, R.; Ruan, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Study on Remediation Capacity of Typical Forage Grasses for Cu, Pb, and Cd Contamination in Coal Gangue-Accumulated Soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 299, 118404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Ali, S.; Kumar, R.; Shekhar, S. Global Lead Contamination in Soils, Sediments, and Aqueous Environments: Exposure, Toxicity, and Remediation. J. Trace Elem. Miner. 2025, 14, 100259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Li, L.; Shang, X.; Duan, X.; Cao, S. Estimation of Atmospheric Lead Emissions from Coal in China: From Past to the Future under China’s Dual-Carbon Policy. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2025, 16, 102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bai, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X. Heavy Metal Pollution of Soils from Coal Mines in China. Nat. Hazards 2019, 99, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Gu, H.; Van Le, Q.; Peng, W.; Lam, S.S.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Sonne, C. Perspectives on Phytoremediation of Zinc Pollution in Air, Water and Soil. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 24, 100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmer, N.; Wright, I.A. The Regulation and Impact of Eight Australian Coal Mine Waste Water Discharges on Downstream River Water Quality: A Regional Comparison of Active versus Closed Mines. Water Environ. J. 2020, 34, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Kharel, G. Acid Mine Drainage from Coal Mining in the United States—An Overview. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, B. Integrating Machine Learning for Enhanced Spatial Prediction and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal(Loid)s. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 383, 126919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkinahamira, F.; Suanon, F.; Chi, Q.; Li, Y.; Feng, M.; Huang, X.; Yu, C.-P.; Sun, Q. Occurrence, Geochemical Fractionation, and Environmental Risk Assessment of Major and Trace Elements in Sewage Sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gankhurel, B.; Fukushi, K.; Akehi, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Zhao, X.; Kawasaki, K. Comparison of Chemical Speciation of Lead, Arsenic, and Cadmium in Contaminated Soils from a Historical Mining Site: Implications for Different Mobilities of Heavy Metals. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2020, 4, 1064–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Jalali, M.; Antoniadis, V. The Release of Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn from Clay Loam and Sandy Loam Soils under the Influence of Various Organic Amendments and Low-Molecular-Weight Organic Acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Y.; Garland, G.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Competitive Transport of Heavy Metals in Soil: Cadmium Dynamics with Numerical Modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, X.; Wei, M.; Zeng, G.; Hou, S.; Li, D.; Xu, H. Elucidation of the Mechanisms into Effects of Organic Acids on Soil Fertility, Cadmium Speciation and Ecotoxicity in Contaminated Soil. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shylla, L.; Barik, S.K.; Behera, M.D.; Singh, H.; Adhikari, D.; Upadhyay, A.; Thapa, N.; Sarma, K.; Joshi, S.R. Impact of Heavy Metals on Water Quality and Indigenous Bacillus Spp. Prevalent in Rat-Hole Coal Mines. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Tang, C.; Qin, W.; Pan, H.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of Surface Water Quality after Mine Closure in the Coal-Mining Region of Guizhou, China. Env. Earth Sci 2020, 79, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Liu, H.; Tai, X.; Zheng, F.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Speciation and Migration of Heavy Metals in Sediment Cores of Urban Wetland: Bioavailability and Risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23914–23925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Tian, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhong, M.; Deng, X.; Liu, Y. Ecological Risk of Cd and Cr in the Black Rock Series Should Be Noticed: Based on the Study of Enrichment Mechanism, Occurrence Form in the Lower Cambrian Lujiaping Formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Guo, P.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, R.; Knorr, K.-H. Investigating Speciation and Toxicity of Heavy Metals in Anoxic Marine Sediments-a Case Study from a Mariculture Bay in Southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jing, M.; Bai, Z. Heavy Metal Concentrations of Soil, Rock, and Coal Gangue in the Geological Profile of a Large Open-Pit Coal Mine in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Schreck, E.; Xiong, T.; Niazi, N.K. Foliar Heavy Metal Uptake, Toxicity and Detoxification in Plants: A Comparison of Foliar and Root Metal Uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, T.; Dong, P.; Chen, X. Assessment of Heavy Metals in Water and Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) from Subsidence Pools in the Huaibei Coal Mining Region, China, with Evaluation of the Human Health Risk. Anal. Lett. 2023, 56, 2182–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Heavy Metals in Soil Layer | Cd (0–20 cm) | Cu (0–20 cm) | Pb (0–20 cm) | Zn (0–20 cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum content (mg/kg) | 0.10 | 7.03 | 52.17 | 91.18 |
| Maximum content (mg/kg) | 1.46 | 113.87 | 229.33 | 312.75 |
| Mean content (mg/kg) | 0.39 | 33.79 | 98.23 | 183.26 |
| Standard deviation | 0.224 | 15.09 | 28.51 | 46.84 |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 56.41 | 44.66 | 29.02 | 25.56 |
| Background values of soil in China (mg/kg) | 0.074 | 20.0 | 23.6 | 67.7 |
| Percentage of sampling points exceeding the background values (%) | 100 | 86.45 | 100 | 100 |
| Background values of soil in Hebei Province (mg/kg) | 0.06 | 21.00 | 20.50 | 71.90 |
| Percentage of sampling points exceeding the background values (%) | 100 | 86.92 | 100 | 100 |
| Technical requirements of planting soil for greening | 0.8 | 300 | 300 | 350 |
| Percentage of sampling points exceeding the technical requirements (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Method | Landform Type | Cd | Cu | ||
| RSP | I | 33.93 ± 124.28 a | HP (9-8-2-7) | 0.26 ± 0.18 a | NP (26-0-0-0) |
| II | 2.74 ± 3.60 b | MP (15-16-12-15) | 0.23 ± 0.17 ab | NP (57-1-0-0) | |
| III | 6.87 ± 14.86 b | HP (12-12-6-17) | 0.27 ± 0.22 a | NP (47-0-0-0) | |
| IV | 2.84 ± 5.33 b | MP (24-20-20-18) | 0.18 ± 0.16 b | NP (82-0-0-0) | |
| Total | 7.50 ± 44.54 | HP (60-56-40-57) | 0.22 ± 0.18 | NP (212-1-0-0) | |
| RAC | I | 53.54 ± 18.45% a | EHR (0-0-0-13-13) | 11.16 ± 7.81% a | MR (0-13-12-1-0) |
| II | 50.44 ± 16.33% a | EHR (0-0-5-21-32) | 10.52 ± 7.15% a | MR (2-31-22-3-0) | |
| III | 52.72 ± 22.22% a | EHR (0-1-9-11-26) | 10.80 ± 9.16% a | MR (0-30-14-3-0) | |
| IV | 49.86 ± 19.30% a | HR (0-1-15-16-50) | 7.76 ± 8.33% a | LR (8-56-15-3-0) | |
| Total | 51.10 ± 19.06% | EHR (0-2-29-61-121) | 9.59 ± 8.24% | LR (10-130-63-10-0) | |
| Method | Landform Type | Pb | Zn | ||
| RSP | I | 20.57 ± 32.94 a | HP (0-0-1-25) | 0.79 ± 0.31 a | NP (21-5-0-0) |
| II | 5.99 ± 6.35 b | HP (1-2-15-40) | 0.93 ± 1.15 a | NP (48-6-2-2) | |
| III | 5.48 ± 5.94 b | HP (1-0-18-28) | 1.10 ± 0.65 a | SP (29-12-5-1) | |
| IV | 4.72 ± 3.17 b | HP (0-6-20-56) | 0.81 ± 0.62 a | NP (67-11-2-2) | |
| Total | 7.17 ± 13.25 | HP (2-8-54-149) | 0.90 ± 0.49 a | NP (165-34-9-5) | |
| RAC | I | 50.51 ± 7.81% a | EHR (0-0-0-12-14) | 22.60 ± 7.24% a | MR (0-0-24-2-0) |
| II | 40.77 ± 10.97% b | HR (0-1-6-41-10) | 24.39 ± 9.66% a | MR (0-0-49-7-2) | |
| III | 41.04 ± 14.02% b | HR (0-0-12-23-12) | 25.29 ± 7.83% a | MR (0-0-33-14-0) | |
| IV | 37.57 ± 9.66% b | HR (0-0-11-63-8) | 22.81 ± 8.53% a | MR (0-3-66-13-0) | |
| Total | 40.79 ± 11.55% | HR (0-1-29-139-44) | 23.76 ± 8.57% | MR (0-3-172-36-2) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, L.; Qi, W.; Ye, H. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals from Long-Term Mining Activities: A Case Study of the Fengfeng Mining Area. Toxics 2025, 13, 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110969
Ren L, Qi W, Ye H. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals from Long-Term Mining Activities: A Case Study of the Fengfeng Mining Area. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):969. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110969
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Le, Wenyu Qi, and Hongling Ye. 2025. "Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals from Long-Term Mining Activities: A Case Study of the Fengfeng Mining Area" Toxics 13, no. 11: 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110969
APA StyleRen, L., Qi, W., & Ye, H. (2025). Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals from Long-Term Mining Activities: A Case Study of the Fengfeng Mining Area. Toxics, 13(11), 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110969






