Ultrasonic Cavitation Transforms Organic Matter to Achieve Reduction of Excess Sludge and Recycling of Carbon Sources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sludge Samples
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.2.1. Batch Treatment of Excess Sludge via Ultrasonic Cavitation
2.2.2. Batch Experiment for Denitrification
2.2.3. Functional Bacteria Separated by MMI
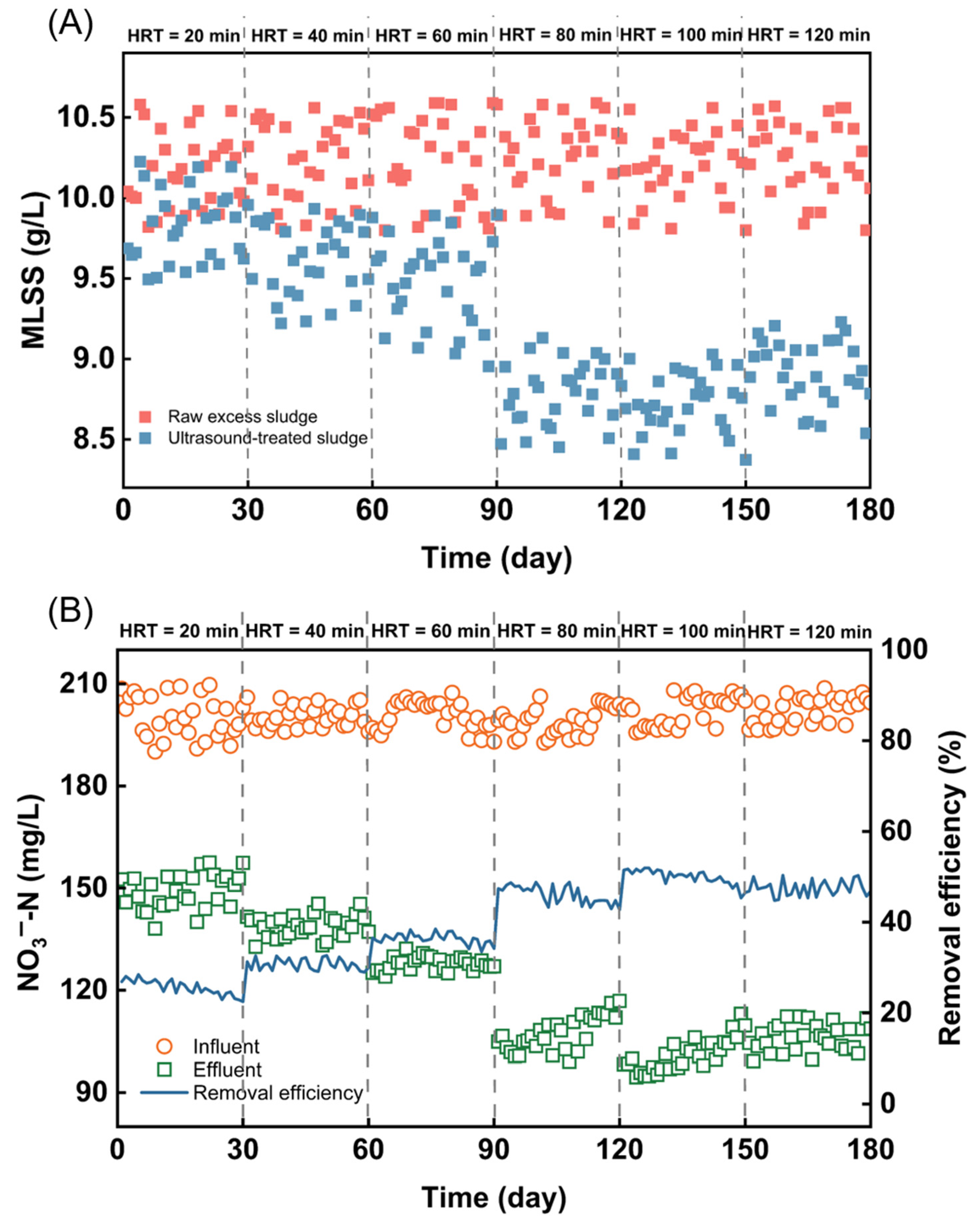
2.2.4. Pilot-Scale Long-Term Operation
2.3. Analytical and Data Methods
2.3.1. Analytical Methods
2.3.2. DNA Extraction
2.3.3. Metagenomic Sequencing
2.3.4. Sequencing Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
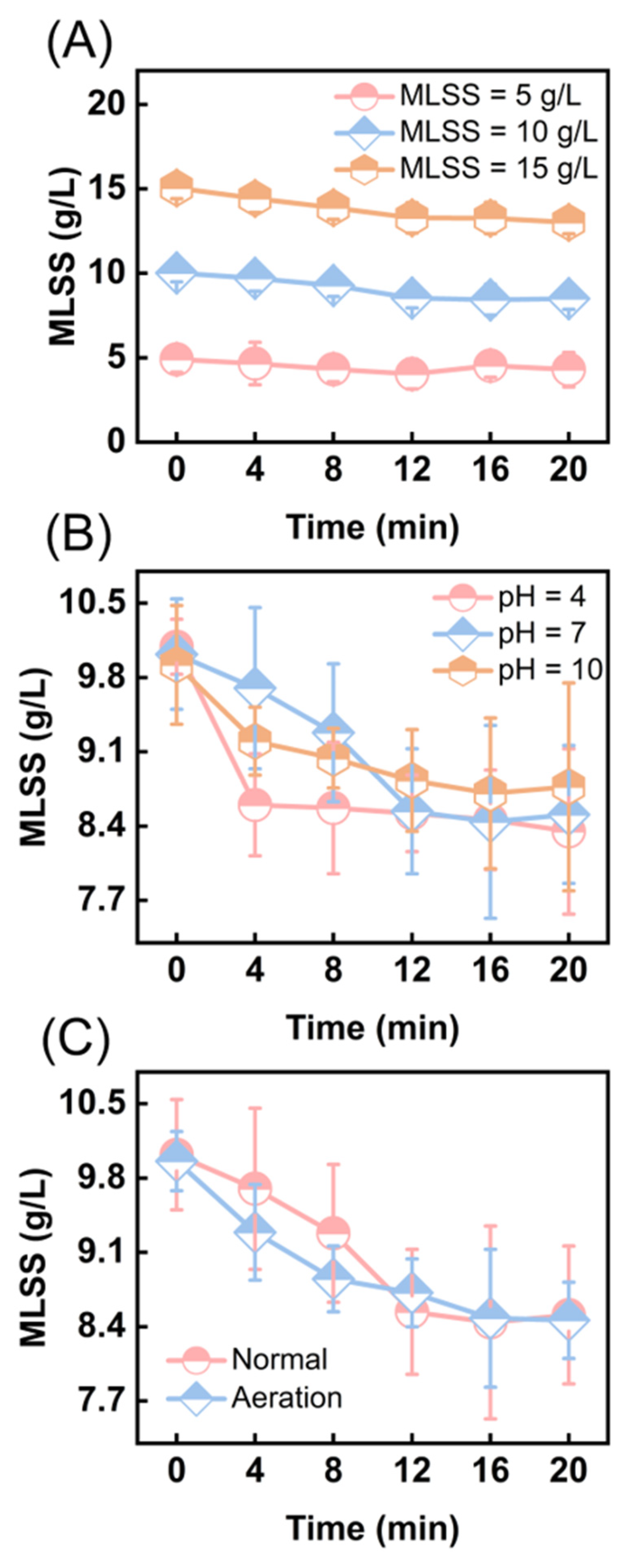
3.1. Effectiveness of Ultrasonic Cavitation Treatment in Reducing Excess Sludge
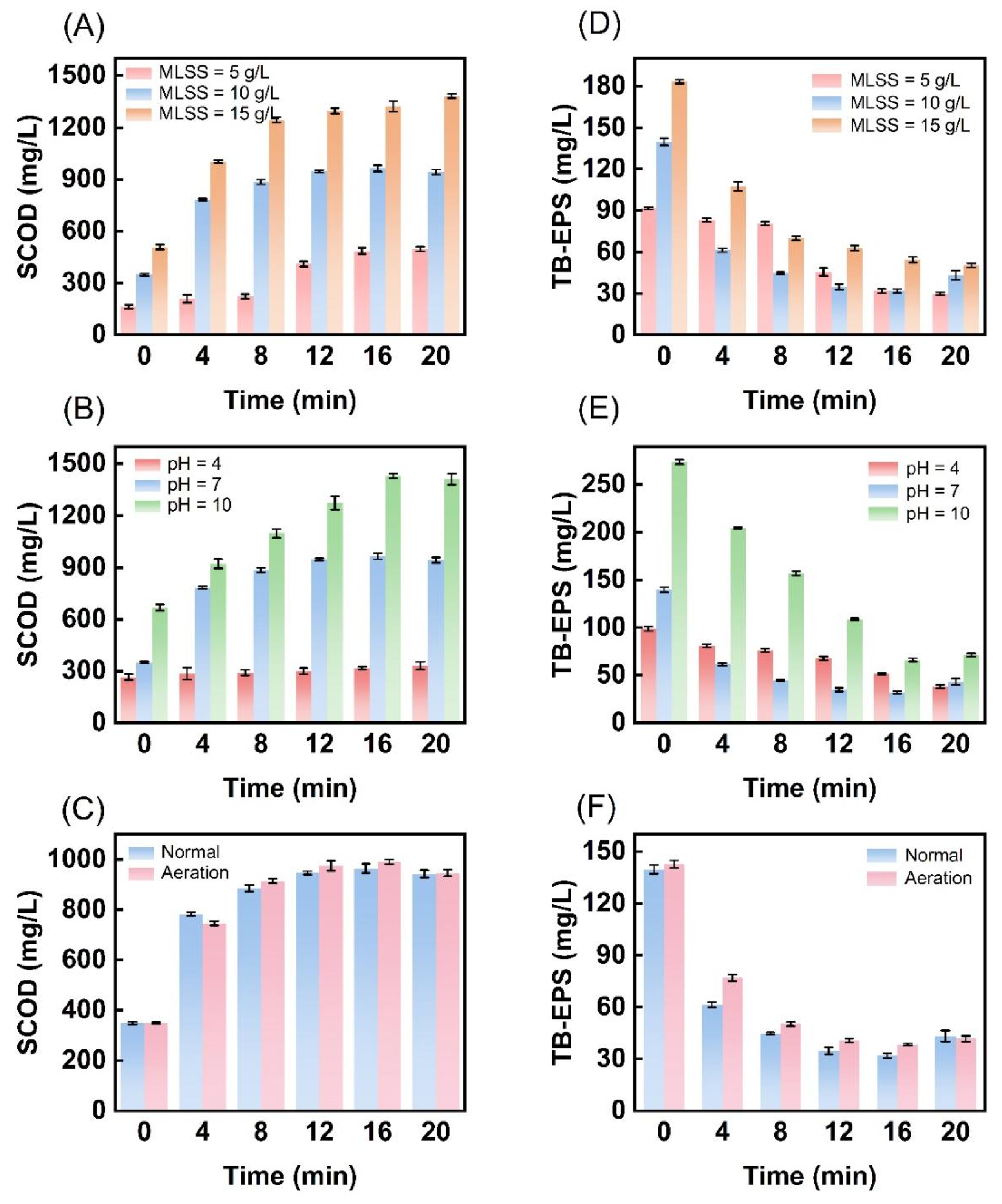
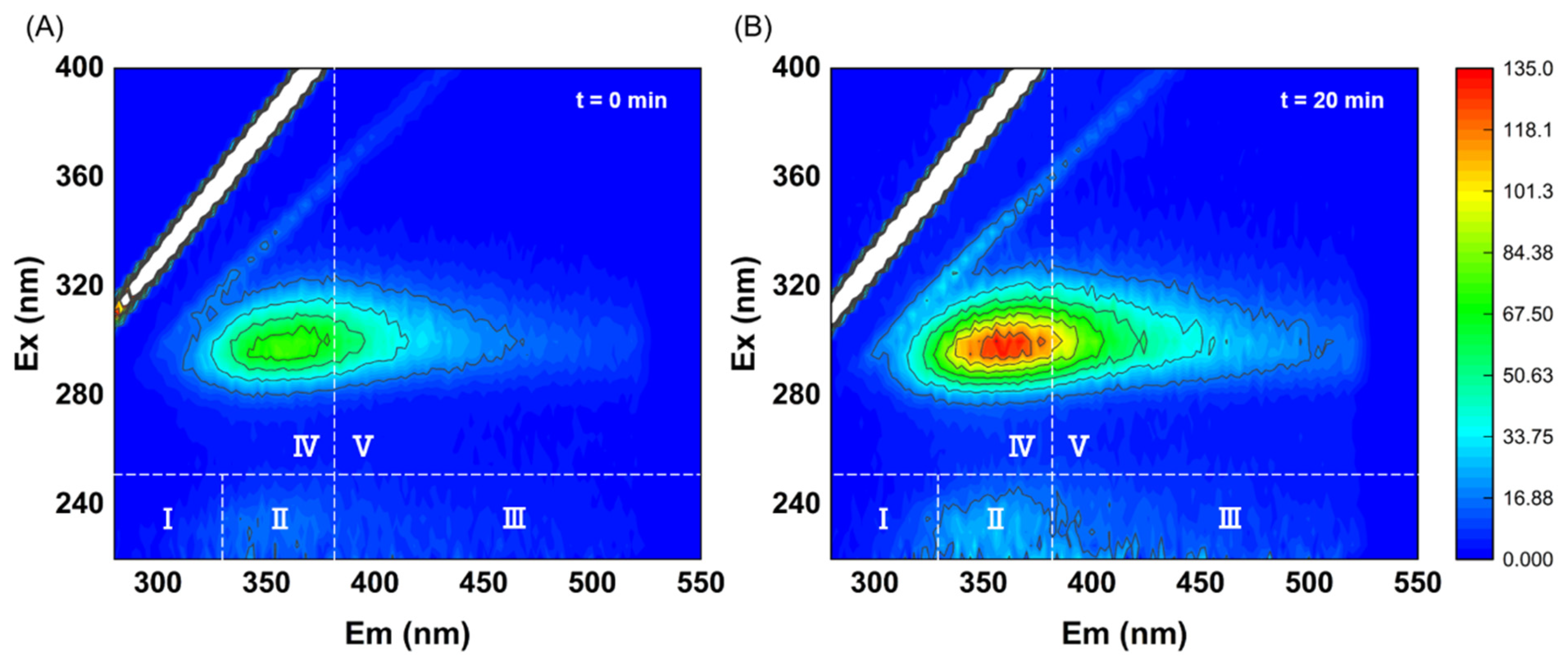
3.2. Conversion of Organic Matter in Excess Sludge Through Ultrasonic Cavitation Treatment
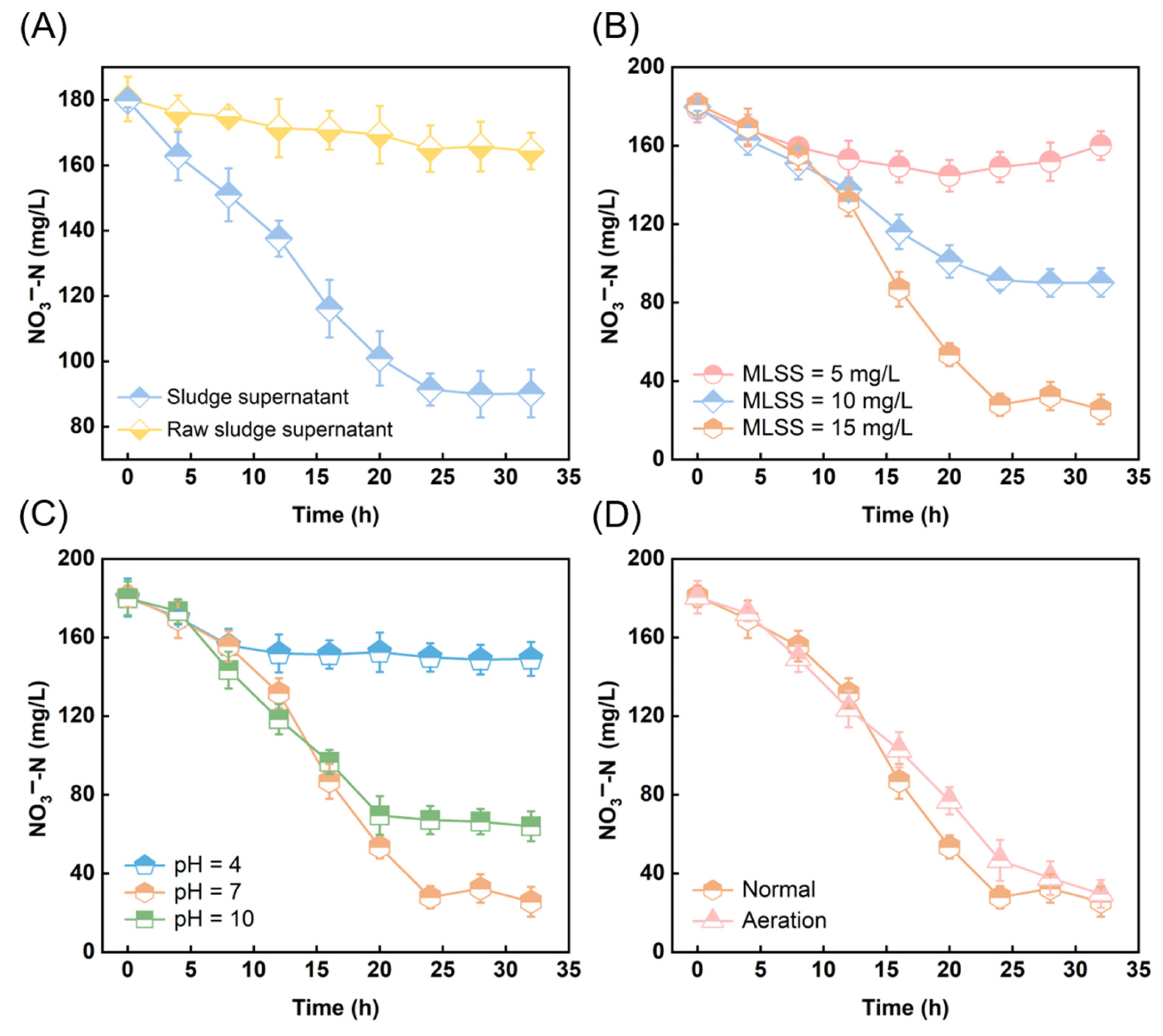
3.3. Organic Matter in the Sludge Supernatant After Ultrasonic Cavitation as a Carbon Source for Denitrification
3.4. Functional Bacteria and Genes Utilizing Organic Matter in Sludge Supernatant After Ultrasonic Cavitation Treatment
3.5. Long-Term Pilot-Scale Treatment of Excess Sludge by Ultrasonic Cavitation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.H.; Yang, W.N.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Jin, P.K.; Dzakpasu, M.; Yang, S.J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.C.; Ao, D. Current Status of Urban Wastewater Treatment Plants in China. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Damgaard, A.; Christensen, T.H. Review of Inventory Data for the Biological Treatment of Sewage Sludge. Waste Manag. 2022, 156, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, J.; Liao, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, L.; Sun, S. Ultrasonic Coupled Bioleaching Pretreatment for Enhancing Sewage Sludge Dewatering: Simultaneously Mitigating Antibiotic Resistant Genes and Changing Microbial Communities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Tian, K.; Xie, P.; Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Kou, Y.; Chon, K.; Hwang, M.-H.; Ko, M.-H. Insights into the Minimization of Excess Sludge Production in Micro-Aerobic Reactors Coupled with a Membrane Bioreactor: Characteristics of Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Mao, Y.; Meng, L. Excess Sludge Cell Lysis by Ultrasound Combined with Ozone. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, S.A.; Bolan, N.; Madhubashani, A.M.P.; Vithanage, M.; Perera, V.; Wijesekara, H.; Wang, H.; Srivastava, P.; Kirkham, M.B.; Mickan, B.S.; et al. Treatment Processes to Eliminate Potential Environmental Hazards and Restore Agronomic Value of Sewage Sludg: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fida, Z.; Price, W.E.; Pramanik, B.K.; Dhar, B.R.; Kumar, M.; Jiang, G.; Hai, F.I. Reduction of Excess Sludge Production by Membrane Bioreactor Coupled with Anoxic Side-Stream Reactors. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, N.; Van Aken, P.; Smets, I.; Appels, L.; Dewil, R. Performance Assessment of Ultrasonic Sludge Disintegration in Activated Sludge Wastewater Treatment Plants under Nutrient-Deficient Conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Niu, T.; An, Y.; Shen, X.; Pan, W.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J. Effects of Side-Stream Ratio on Sludge Reduction and Microbial Structures of Anaerobic Side-Stream Reactor Coupled Membrane Bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, W.; Du, Y.; Tan, Z.; Liu, R.; Xiao, R.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L. Electron Beam Irradiation Effect on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Municipal Excess Sludge. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 180, 109246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xin, X.; Ai, X.; Hong, J.; Wen, Z.; Li, W.; Lv, S. Synergic Role of Ferrate and Nitrite for Triggering Waste Activated Sludge Solubilisation and Acidogenic Fermentation: Effectiveness Evaluation and Mechanism Elucidation. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Fan, J.; Peng, Y. A Review of Enhanced Municipal Wastewater Treatment through Energy Savings and Carbon Recovery to Reduce Discharge and CO2 Footprint. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 364, 128135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, J.R.; Kumar, G.; Tyagi, V.K.; Bajhaiya, A.K.; Gugulothu, P.; Gunasekaran, M. Biohydrogen Production from Waste Activated Sludge through Thermochemical Mechanical Pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 358, 127301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco Mofatto, P.M.; Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; Mannina, G. Investigation of Intermittent Aeration and Oxic Settling Anaerobic Process Combination for Nitrogen Removal and Sewage Sludge Reduction. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannina, G.; Barbara, L.; Cosenza, A.; Wang, Z. Treatment and disposal of sewage sludge from wastewater in a circular economy perspective. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Niu, J.; Du, Z.; Federica, C.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Pedersen, T.H.; et al. Systematic Analysis of Sludge Treatment and Disposal Technologies for Carbon Footprint Reduction. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 128, 224–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Li, S.; Liu, C. Effect of Lysozyme Combined with Hydrothermal Pretreatment on Excess Sludge and Anaerobic Digestion. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayeri, D.; Mohammadi, P.; Bashardoust, P.; Eshtiaghi, N. A Comprehensive Review on the Recent Development of Anaerobic Sludge Digestions: Performance, Mechanism, Operational Factors, and Future Challenges. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Liang, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T.; Lu, X.; Li, L.; Wu, X.; Zan, F. In-Situ Sulfite Treatment Promotes Solid Reduction during Aerobic Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge: Feasibility for Small-scale Wastewater Treatment Plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 394, 130224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; He, J.; Zhang, P.; Pan, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Li, B.; Tang, X.; Xiao, X.; et al. Insights into Carbon Recovery from Excess Sludge through Enzyme-catalyzing Hydrolysis Strategy: Environmental benefits and carbon-emission reduction. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Ding, J.; Guo, H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, T.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y. Ultrasonic Radiation Enhances Percarbonate Oxidation for Improving Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Review on Research Achievements of Biogas from Anaerobic Digestion. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawoof, S.A.A.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Subramanian, S.J.E.C.L. Sequential Production of Hydrogen and Methane by Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Wastes: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 19, 1043–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Eskicioglu, C.; Marin, J. Microwave, Ultrasonic and Chemo-Mechanical Pretreatments for Enhancing Methane Potential of Pulp Mill Wastewater Treatment Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7815–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yu, N.; Fang, A.; Liu, B.; Ren, N.; Xing, D. Co-Treatment of Potassium Ferrate and Ultrasonication Enhances Degradability and Dewaterability of Waste Activated Sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolny, L.; Wolski, P. Ultrasounds Energy as an Agent of Polyelectrolyte Modification Prior to Sewage Sludge Conditioning. Energies 2021, 14, 6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, B. Waste Activated Sludge Disintegration in an Ultrasonic Batch Reactor. Clean-Soil Air Water 2008, 36, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, T.; Bandelin, J.; Schlederer, F.; Drewes, J.E.; Koch, K. Impact of Ultrasound-Induced Cavitation on the Fluid Dynamics of Water and Sewage Sludge in Ultrasonic Flatbed Reactors. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 55, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.T.; Zhou, J.T.; Jin, R.F.; Li, X. Treatment of Sulfate Wastewater by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria with Residual Sludge Thermal Alkaline Hydrolysate as Carbon Source. Environ. Eng. 2024, 42, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricasole, P.; Provenzano, M.R.; Hatcher, P.G.; Senesi, N. Chemical Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter during Composting of Different Organic Wastes Assessed by 13C CPMAS NMR Spectroscopy. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8232–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrdadi, N.; Kootenaei, F.G. An Investigation on Effect of Ultrasound Waves on Sludge Treatment. Energy Procedia 2018, 153, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Kang, G.; Xu, Z. Ultrasound Activated Peroxymonosulfate Oxidation for Advanced Water Treatment: Cavitation Mechanism, Free Radical Generation and Process Simulation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2025, 122, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Berry, J.P.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, B.; Huang, S.; Langford, H.; Li, G.H.; Davison, P.A.; et al. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Mediated Isolation of Functional Bacteria in a Complex Microbial Community. ISME J. 2015, 9, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, D. Coupling Magnetic-Nanoparticle Mediated Isolation (MMI) and Stable Isotope Probing (SIP) for Identifying and Isolating the Active Microbes Involved in Phenanthrene Degradation in Wastewater with Higher Resolution and Accuracy. Water Res. 2018, 144, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhen, Z.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Luo, C.; Ding, A.; Zhang, D. Application and Reactivation of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Microcystis aeruginosa Harvesting. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Fakhrullin, R.F.; Özmen, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Paunov, V.N.; Li, G.H.; Huang, W.E. Functionalization of Whole-Cell Bacterial Reporters with Magnetic Nanoparticles. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 4, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Chuang, S.-H. The Characteristics of Stepwise Ultrasonic Hydrolysates of Sludge for Enhancing Denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ling, Z.; Zhao, M.; Sha, L.; Li, C.; Lu, X. Investigation of the Properties and Mechanism of Activated Sludge in Acid-Magnetic Powder Conditioning and Vertical Pressurized Electro-Dewatering (AMPED) Process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 328, 124973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L.; American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Bin, L.; Li, P.; Fu, F.; Huang, S.; Tang, B. Rapid Granulation of Aerobic Granular Sludge in an Integrated Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor-membrane Bioreactor: Effects and Mechanism of Streptomyces cellulosus Microspheres. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 22, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. Relevance of Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPSs)—Part I: Structural and Ecological Aspects. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, G.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. How does zero valent iron activating peroxydisulfate improve the dewatering of anaerobically digested sludge? Water Res. 2019, 163, 114912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, N. New Advances in Fluorescence Excitation–Emission Matrix Spectroscopy for the Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter in Drinking Water Treatment: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandoush, S.; Mokhtarani, N. Reducing Excess Sludge Volume in Sequencing Batch Reactor by Integrating Ultrasonic Waves and Ozonation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wan, J.; Liu, F. Promotion of Sludge Process Reduction Using Low-Intensity Ultrasonic Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, K.; Chatzitakis, A.; Norby, T. Photocatalytic Generation of Gas Phase Reactive Oxygen Species from Adsorbed Water: Remote Action and Electrochemical Detection. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. Enhanced Technology Based for Sewage Sludge Deep Dewatering: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.R.; Dai, X.H.; Chai, X.L. Critical Review on Dewatering of Sewage Sludge: Influential Mechanism, Conditioning Technologies and Implications to Sludge Re-Utilizations. Water Res. 2020, 180, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Wu, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, A.; Hao, Y. Optimizing Sludge Dewatering Efficiency with Ultrasonic Treatment: Insights into Parameters, Effects, and Microstructural Changes. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2024, 102, 106736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W. Ultrasonic Treatment of Biological Sludge: Floc Disintegration, Cell Lysis and Inactivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, L.; Yiying, J.; Mahar, R.B.; Zhiyu, W.; Yongfeng, N. Effects of Ultrasonic Disintegration on Sludge Microbial Activity and Dewaterability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L. Exploiting Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) Controlling Strategies for Performance Enhancement of Biological Wastewater Treatments: An Overview. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.H.; Shon, H.K.; Kim, J.H. Minimization of Excess Sludge and Cryptic Growth of Microorganisms by Alkaline Treatment of Activated Sludge. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 28, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.K.; Baker, A.; Murphy, K.R.; Hambly, A.; Stuetz, R.M.; Khan, S.J. Fluorescence as a Potential Monitoring Tool for Recycled Water Systems: A Review. Water Res. 2009, 43, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Yang, B.; Bin, L.; Hu, Y.; Fan, D.; Chen, W.; Li, P.; Tang, B. Intensifying the Simultaneous Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus of an Integrated Aerobic Granular Sludge–Membrane Bioreactor by Acinetobacter junii. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 397, 130474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsabimana, E.; Belan, A.; Bohatier, J. Analysis at the Genomospecies Level of Microbial Populations Changes in Activated Sludge: The Case of Aeromonas. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1696–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, R.; Spring, S.; Amann, R.; Huber, I.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.-H.; Kämpfer, P. Genotypic Diversity of Acidovorax Strains Isolated from Activated Sludge and Description of Acidovorax defluvii sp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 22, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Pan, D.; Yang, G.; Zhong, R.; Niu, R.; Xia, B.; Cheng, K.; Liu, T.; Li, X. Cadmium Immobilization during Nitrate-Reducing Fe(II) Oxidation by Acidovorax sp. BoFeN1: Contribution of Bacterial Cells and Secondary Minerals. Chem. Geol. 2023, 639, 121729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Yue, X.; Wang, G. Simultaneous Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification at High Initial Phenol Concentration by Isolated Bacterium Diaphorobacter sp. PD-7. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, D.; Lyu, Y. Metabolic Mechanism of Cr(VI) Pollution Remediation by Alicycliphilus denitrificans Ylb10. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, D.; Lv, L.; Gao, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, G.; Ren, Z. Effects of Ultrasonic Lysis Frequency on Sludge Lysis–Cryptic Growth: Sludge Reduction, Microbial Community, and Metabolism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 469, 144000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, B.; Yan, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Z.; Han, L.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Y. Comamonas-Dominant Microbial Community in Carbon-Poor Aquitard Sediments Revealed by Metagenomic-Based Growth Rate Investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J.; Jiang, F.; Wang, X.; Kang, J. Isolation of Oxytetracycline-Degrading Bacteria and Its Application in Improving the Removal Performance of Aerobic Granular Sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Cao, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Sanchuan, M.; Wang, Z. Study on Ultrasonic Treatment for Municipal Sludge. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 57, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wu, Q.; Yu, P.; Zhang, L.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X.-X.; Ren, H. Denitrification Using Excess Activated Sludge as Carbon Source: Performance and Microbial Community Dynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Dai, X.; Chai, X. Effect of Different Carbon Sources on Denitrification Performance, Microbial Community Structure and Denitrification Genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, S.; Ji, G. Influences of Carbon Sources on N2O Production during Denitrification in Freshwaters: Activity, Isotopes and Functional Microbes. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhao, S.; Song, G.; Lu, C.; Liu, R.; Hu, C.; Qu, J. Ultrasonication-Enhanced Biogas Production in Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Active Sludge: A Pilot-Scale Investigation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 192, 106902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Chen, S.T.; Zheng, N.Y.; Wang, H.C. Green Sludge Dewatering and Recycling Technology for Generating Renewable Energy and Liquid Nutrients: Bench- and Pilot-Scale Studies. Energy 2023, 278, 128008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Li, J.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Ren, Y.; Xu, X.; He, J.; et al. Ultrasonic Cavitation Transforms Organic Matter to Achieve Reduction of Excess Sludge and Recycling of Carbon Sources. Toxics 2025, 13, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110941
Sun H, Li J, Zhuang L, Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Sun J, Wang D, Ren Y, Xu X, He J, et al. Ultrasonic Cavitation Transforms Organic Matter to Achieve Reduction of Excess Sludge and Recycling of Carbon Sources. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110941
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Haohao, Jie Li, Lu Zhuang, Yunian Zhang, Zhou Zhou, Jiayue Sun, Di Wang, Yanfang Ren, Xia Xu, Junyu He, and et al. 2025. "Ultrasonic Cavitation Transforms Organic Matter to Achieve Reduction of Excess Sludge and Recycling of Carbon Sources" Toxics 13, no. 11: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110941
APA StyleSun, H., Li, J., Zhuang, L., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Z., Sun, J., Wang, D., Ren, Y., Xu, X., He, J., & Xue, Y. (2025). Ultrasonic Cavitation Transforms Organic Matter to Achieve Reduction of Excess Sludge and Recycling of Carbon Sources. Toxics, 13(11), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110941






